Botany Exam 3 full set
1/339
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
340 Terms
Systematics
study of the diversity of life and the evolutionary relationships between organisms
Phylogenetic
pertaining to the development of a species
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
Biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Herbalists
Wrote Herbals- books of medicinal plants
(1400-1700's)
Herbals
Books of medicinal plants
Linnaeus
- mid 1700's
Wrote the first real flora-species Plantarum 1753
Introduced binomial system of nomenclature
Introduced a new rank-based taxonomic system
binomial system of nomenclature
System of naming a species by the combination of the genus name and a specific epithet.
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
taxonomic order
Linnaeus
Named: 7700 species of plants
4400 species of animals, including Homo sapiens
Philosophia Bontanica
Contains the rules of naming:
- "Every plant name must consist of a generic name and a specific one."
- Names should be sensible, only by botanist
- "Generic names one and a half feet long, those that are difficult to pronounce, or are disgusting, should be avoided"
Linnaeus
Father of taxonomy
Darwin
- mid 1800's
"On the Origin of Species" 1859
Birth of systematics
Natural taxonomy
From Darwin into the 1900's
Goal became ______ ______; reflects common ancestry; uses homologous characteristics
Replaced artificial taxonomy and analogous characteristics
Artificial
Natural or artificial? "Taxonomic group for all plants that produce tubers"
Natural
Natural or artificial? "Phylum for plants producing flowers and fruits (angiosperms)"
Natural
Natural or artificial? "Taxonomic class for plants with single cotyledon (monocots)"
Artificial
Natural or artificial?
"Taxonomic family for all carnivorous plants"
Artificial
Natural or artificial?
"Phylum or class for all woody plants"
Natural
Natural or artificial?
"Phylum for plants producing sieve tube members (angiosperms)"
Artificial
Natural or artificial?
"Group for all angiosperms with purple flowers"
Natural
Natural or artificial?
"Family for all plants with a composite flower (sunflower family)"
Classical
Current Taxonomy
- Opinions of professional taxonomists
Cladistics
Current Taxonomy
- Computerized, specific design to eliminate bias
Based entirely on common ancestry
Phylogenetically important characteristics only
Primitive traits
Current Taxonomy
ID ancestral =
advanced traits
Current Taxonomy
ID derived =
clades
Current Taxonomy
Organisms grouped into _____
Clade
Current Taxonomy
______ = common ancestor and all descendants
Displayed as a cladogram
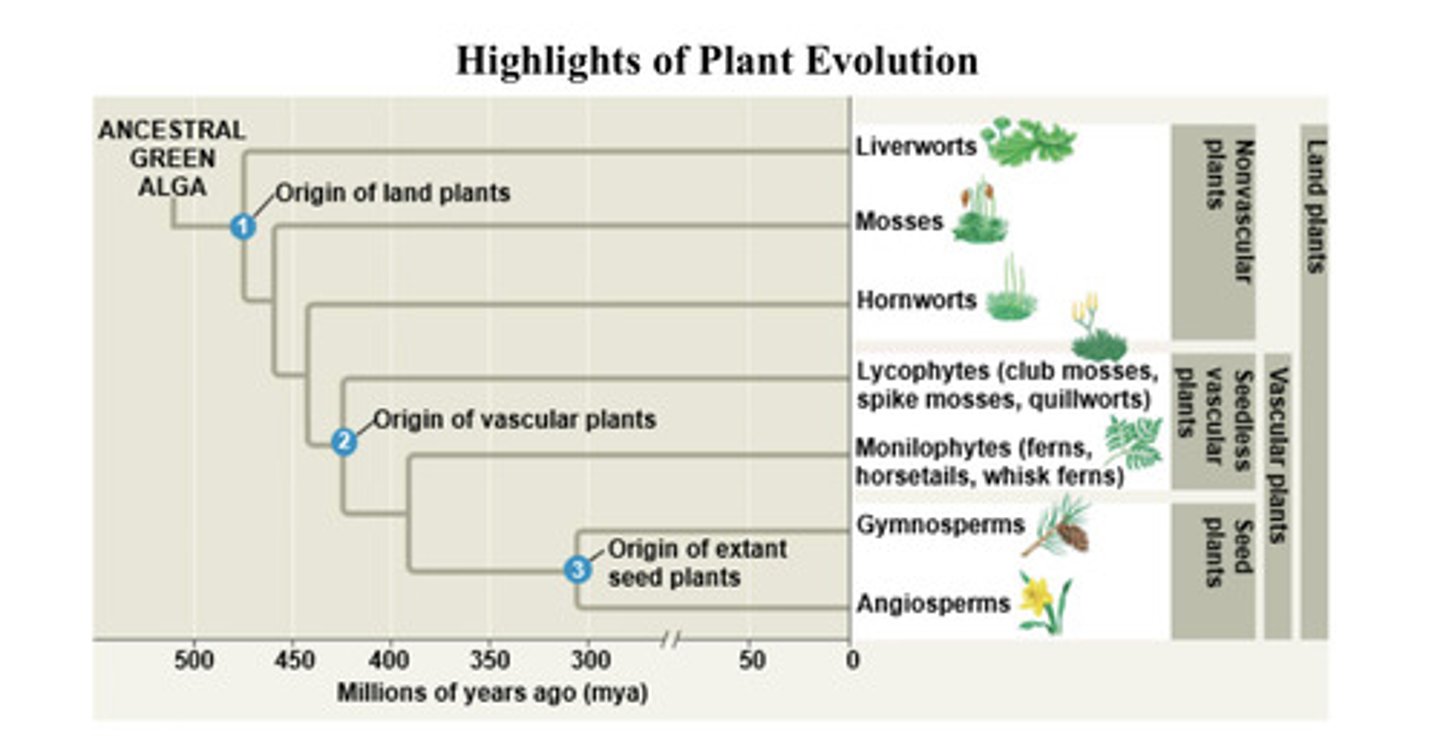
cladogram
Diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among a group of organisms
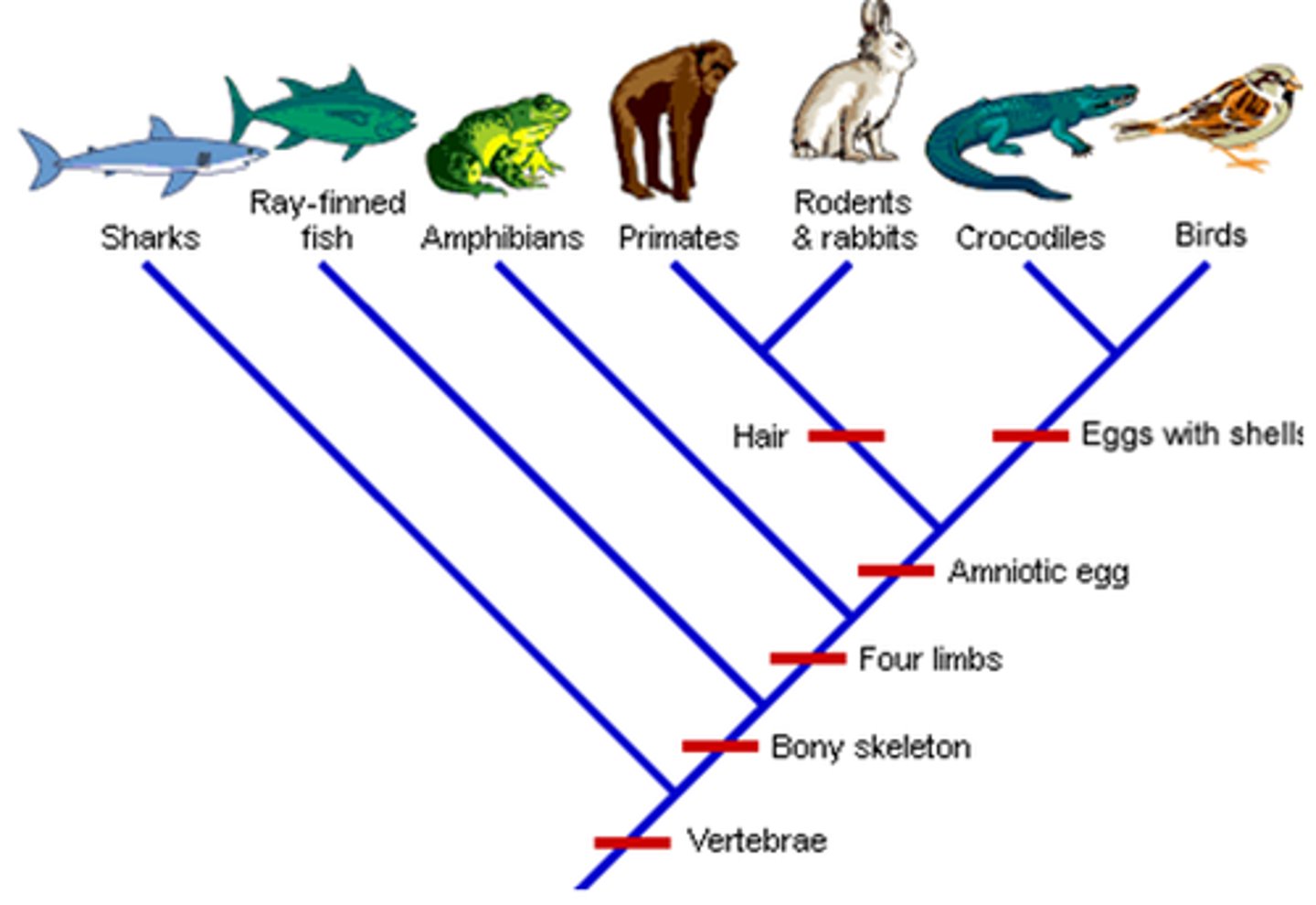
cladogram of plants
Node
_____ is a branch point and represents a common ancestral population
Sister groups
- share a common ancestor
Synapomorphy
- derived trait shared by a clade
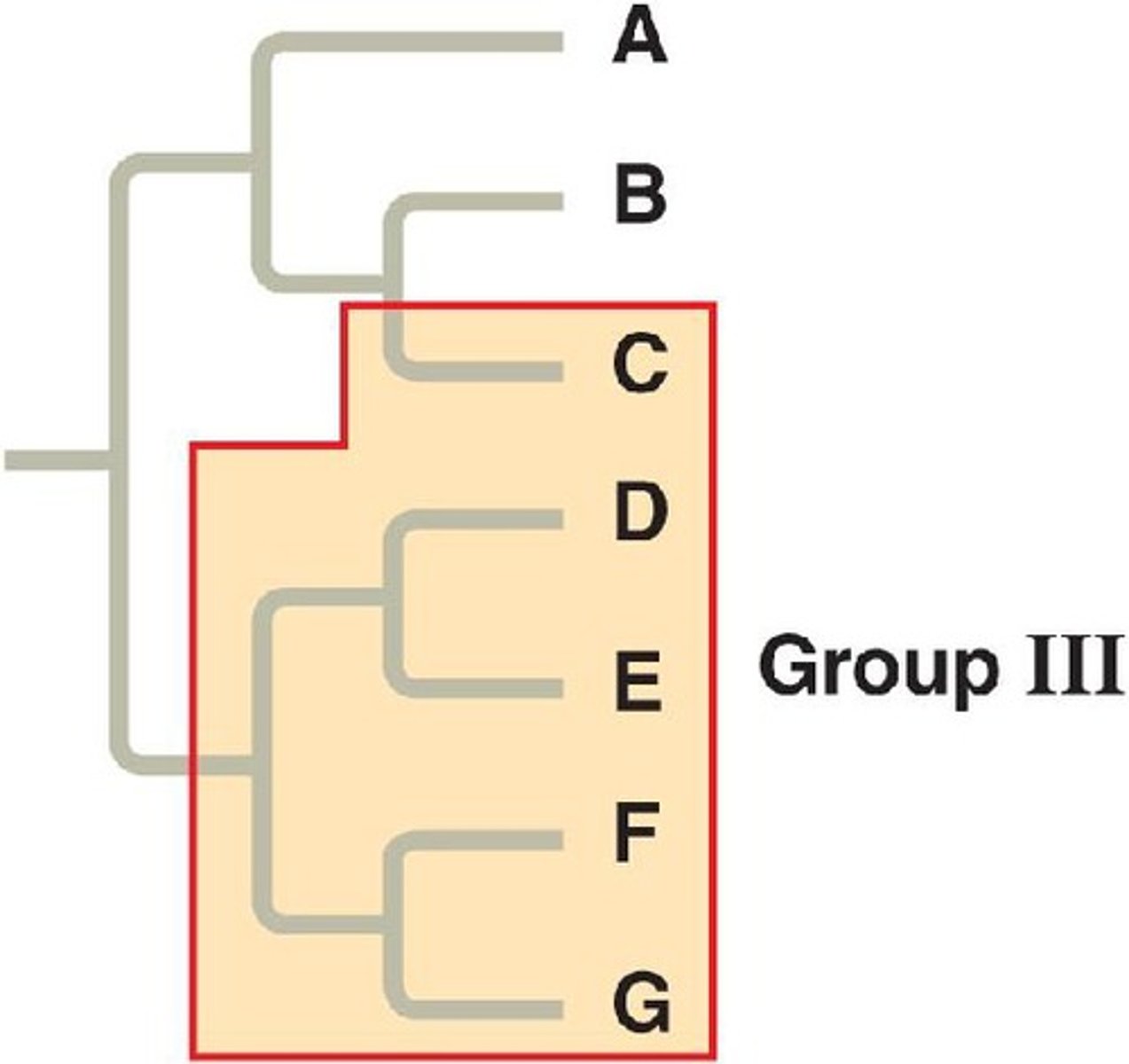
Monophyletic group
Common ancestor and all descendants
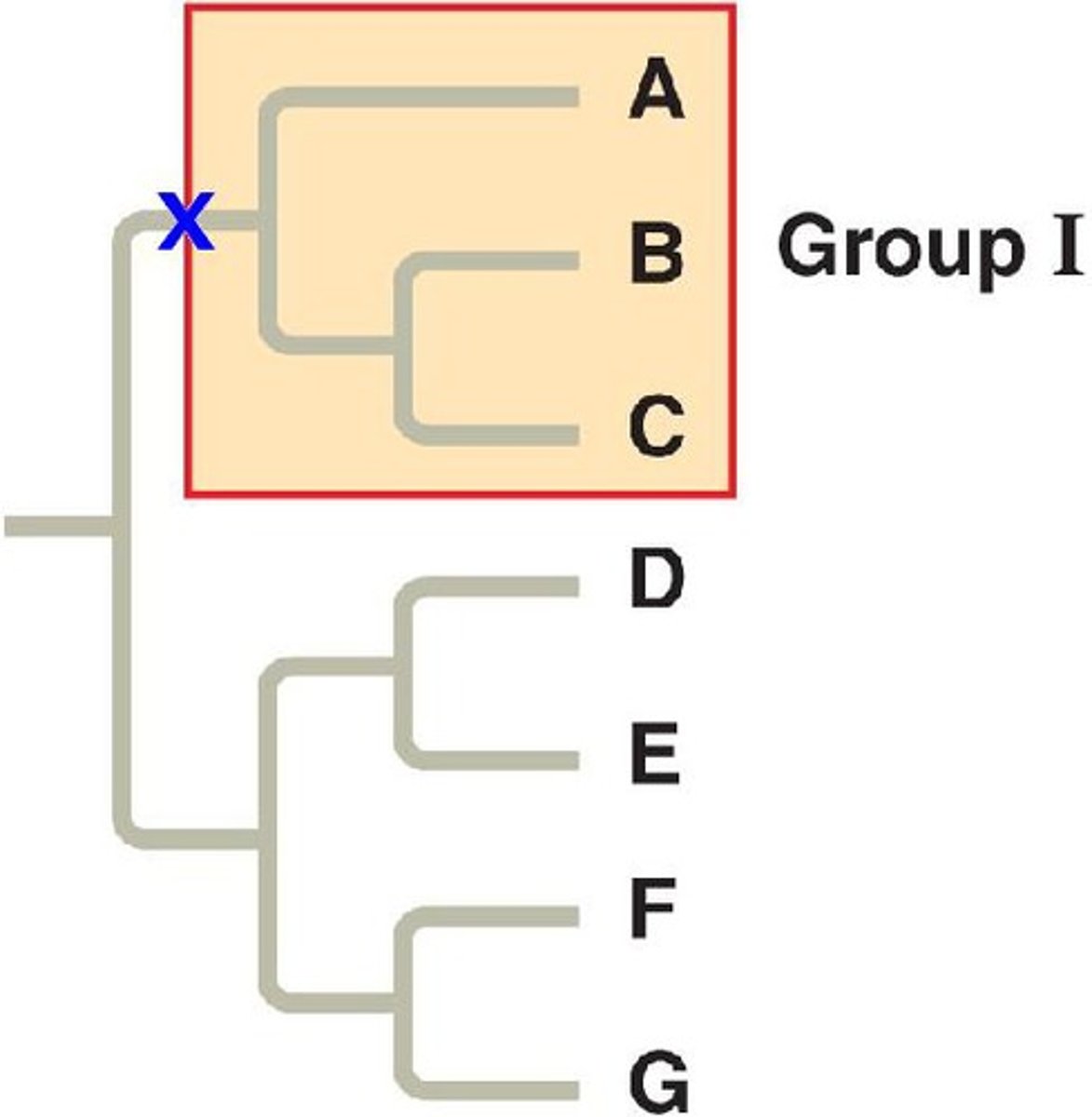
Paraphyletic group
All descendants not included
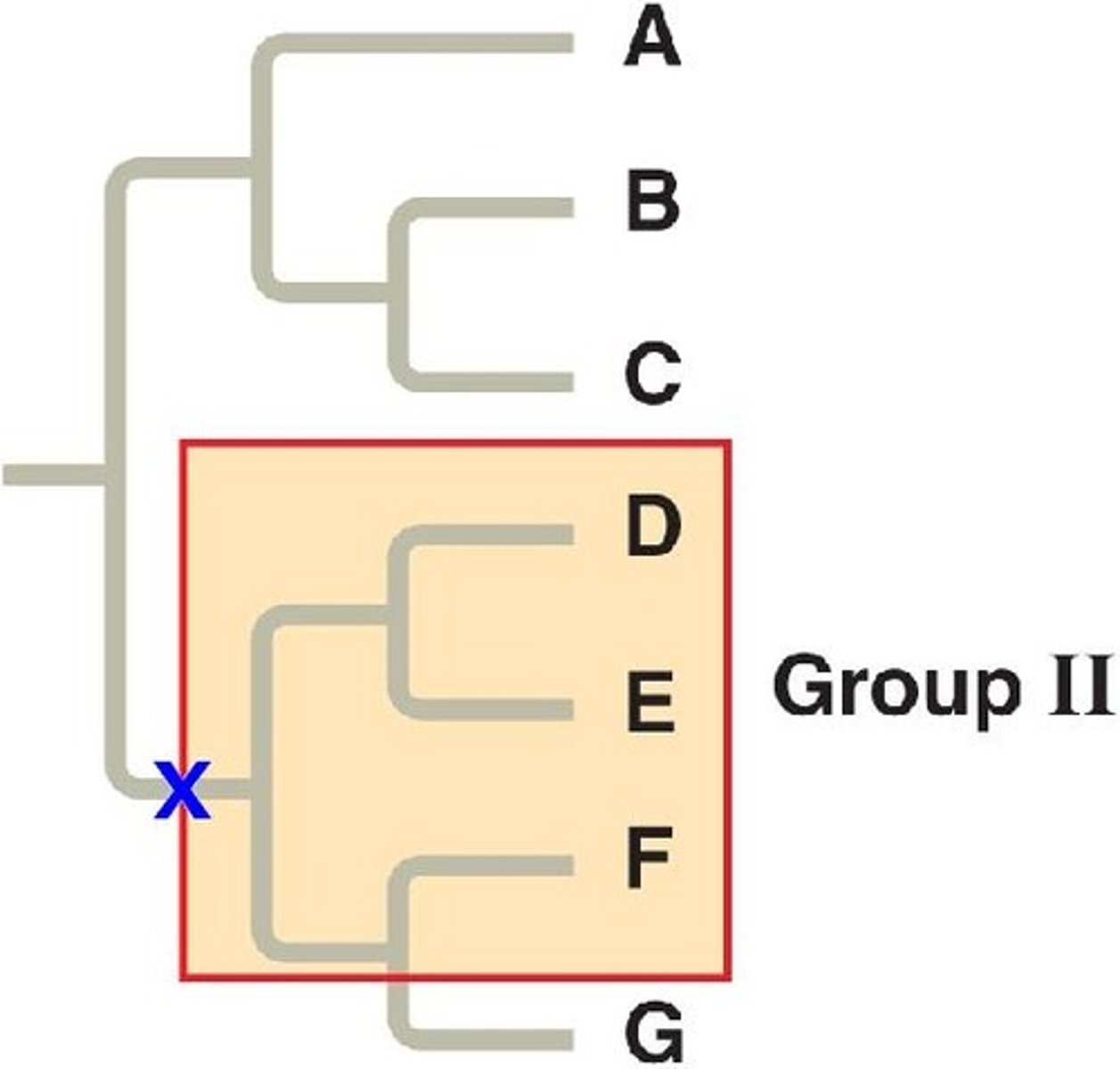
Polyphyletic group
More than one common ancestor
Kingdom Protista
Contain one celled eukaryotes such as algae and protozoa.
Eukaryote supergroups
- Alveolata
- Stramenopila
- Rhizaria
- Excavata
- Opisthokonta
- Amoebozoa
- Plants and algal relatives
PhyloCode
International Code of Phylogenic Nomenclature
Barcoding
- rapid ID of a plant Theory- plastid DNA may be unique for any species
- Nucleotide sequence produced (several possibilities exist)
- Database established for comparison
- Very successful for animals
Sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
Gametophyte
The stage in the life cycle of a plant in which the plant produces gametes, or sex cells.
Green and Purple Bacteria
Sulfur bacteria studied by Van Neil led to his generalized photosynthesis equation
Halobacterium
•Tolerates high salt

Bacteriorhodopsin
Pigmented protein found in abundance in the plasma membrane of the salt-loving archaeon Halobacterium halobium; pumps protons out of the cell in response to light.
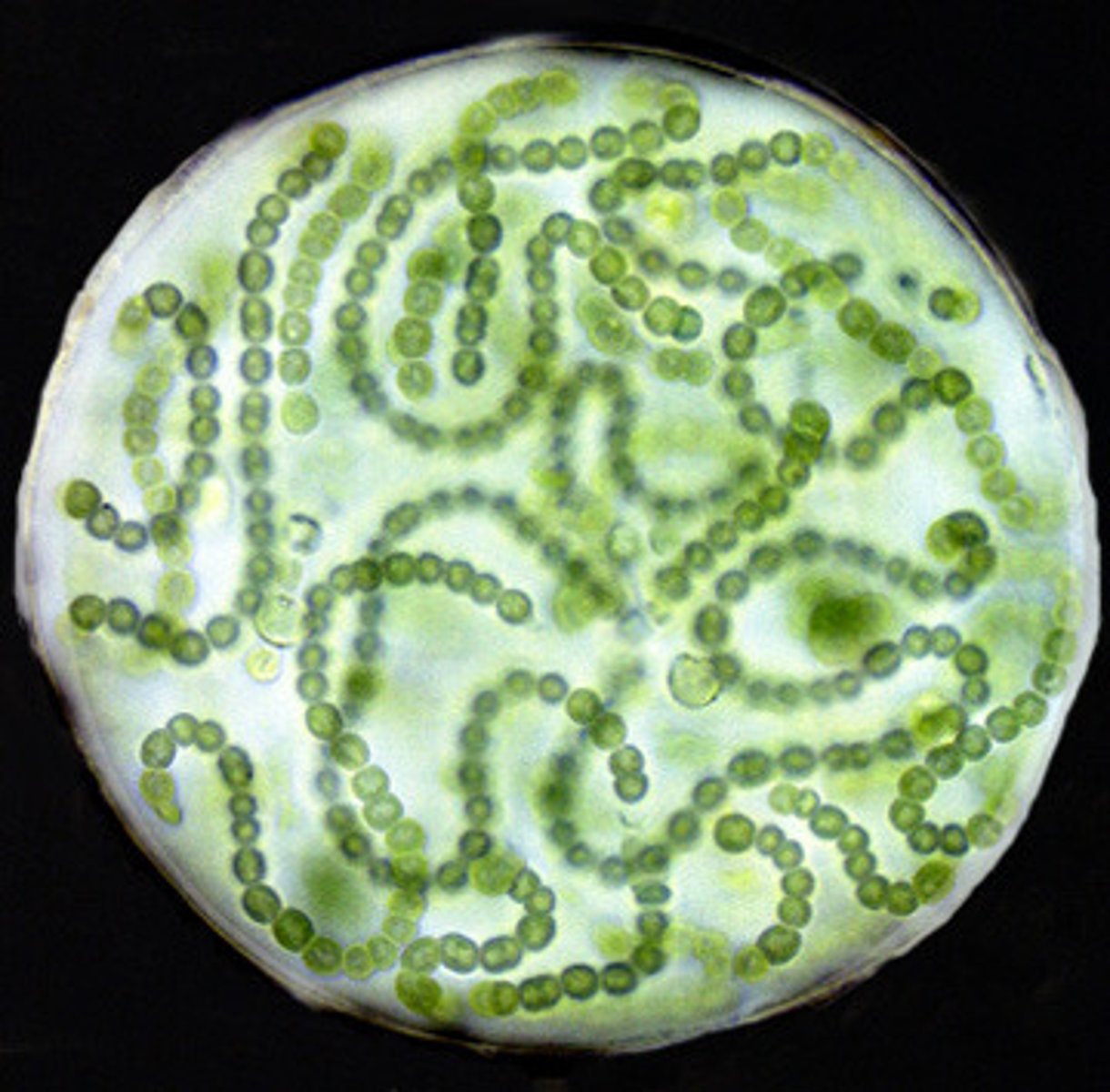
Cyanobacteria
"Blue-green algae"
Cyanobacteria
Characteristics
- Tiny prokaryotic cells often with slimy sheath
- Unicellular or filamentous
- Phycobilins- phycocyanin and phycoerythrin; Chl a
- Evolved oxygenic photosynthesis
- Dominant life form for ~ 85% of Earth's history
Eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria.
Nitrogen Fixation in Heterocysts
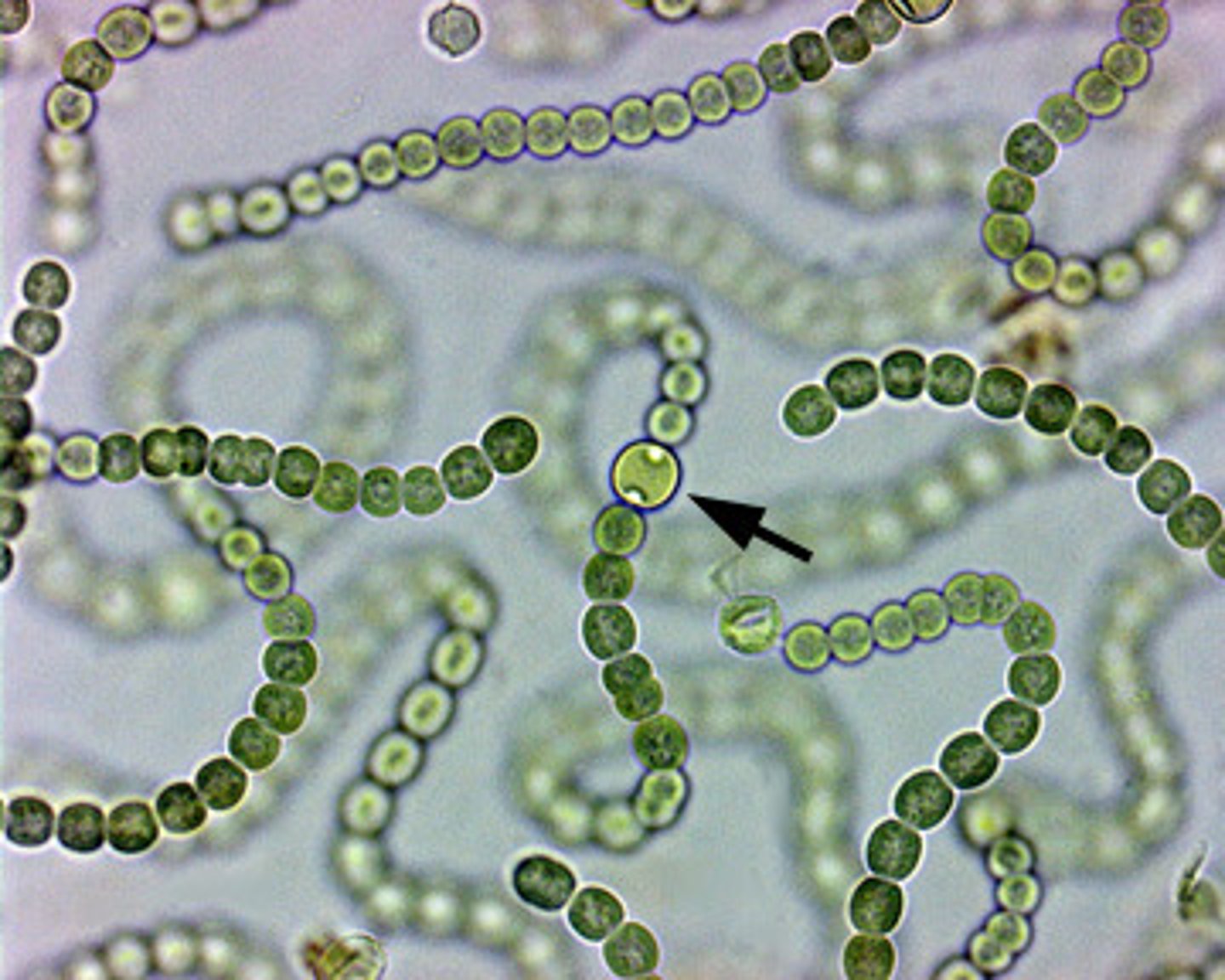
Prochlorophytes
Cyanobacteria? chlorophyll a, b; carotenoids; no phycobilins
Prochlorococcus
Most numerous photosynthetic organism
Tiny side and genome
40-50% of biomass of marine phytoplankton!
Extremely important global O2 producers
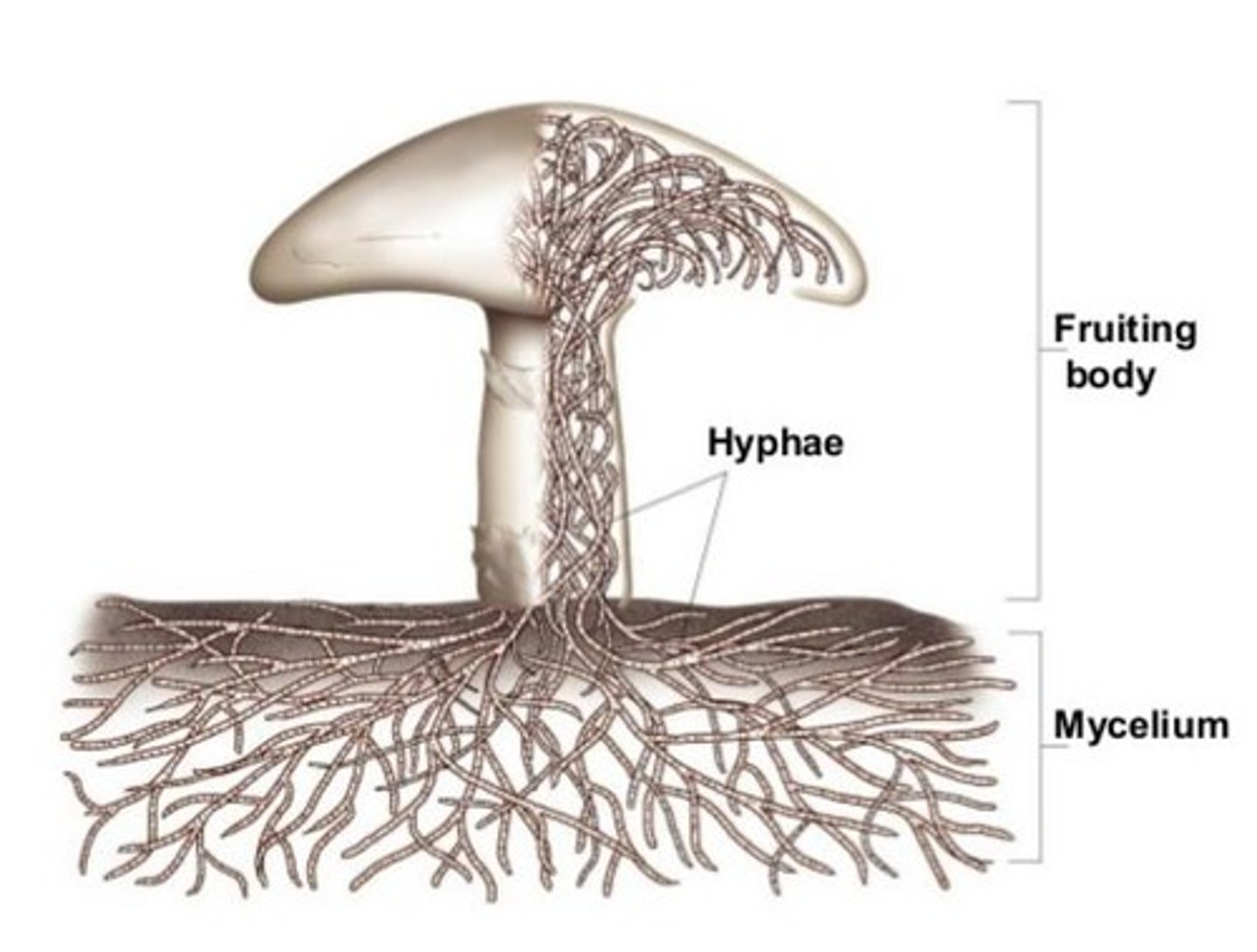
Mycology
study of fungi
Mycelium of hyphae
The vegetative body of most fungi is called a(n) ______, which consists of an interwoven mass of threadlike filaments called _____.
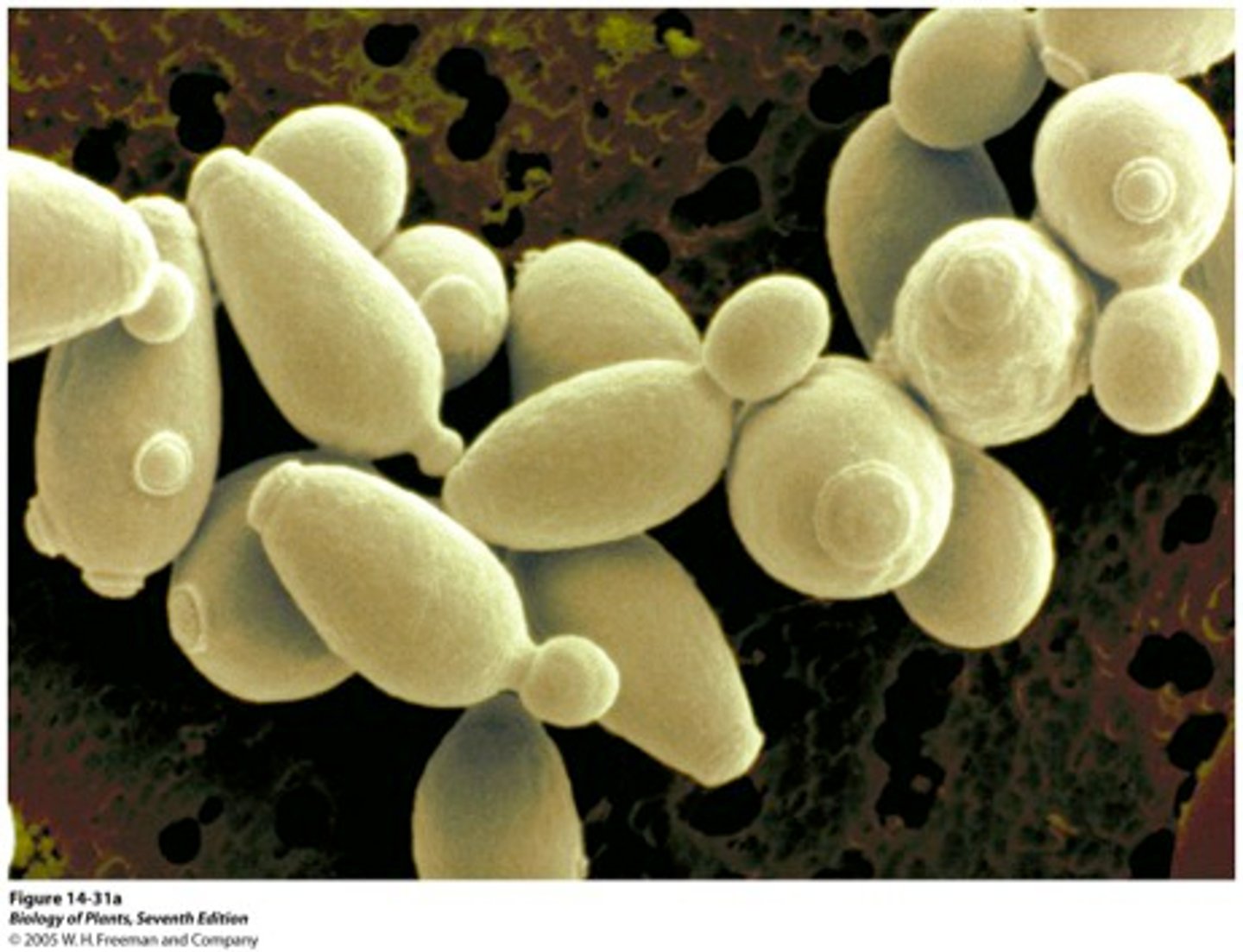
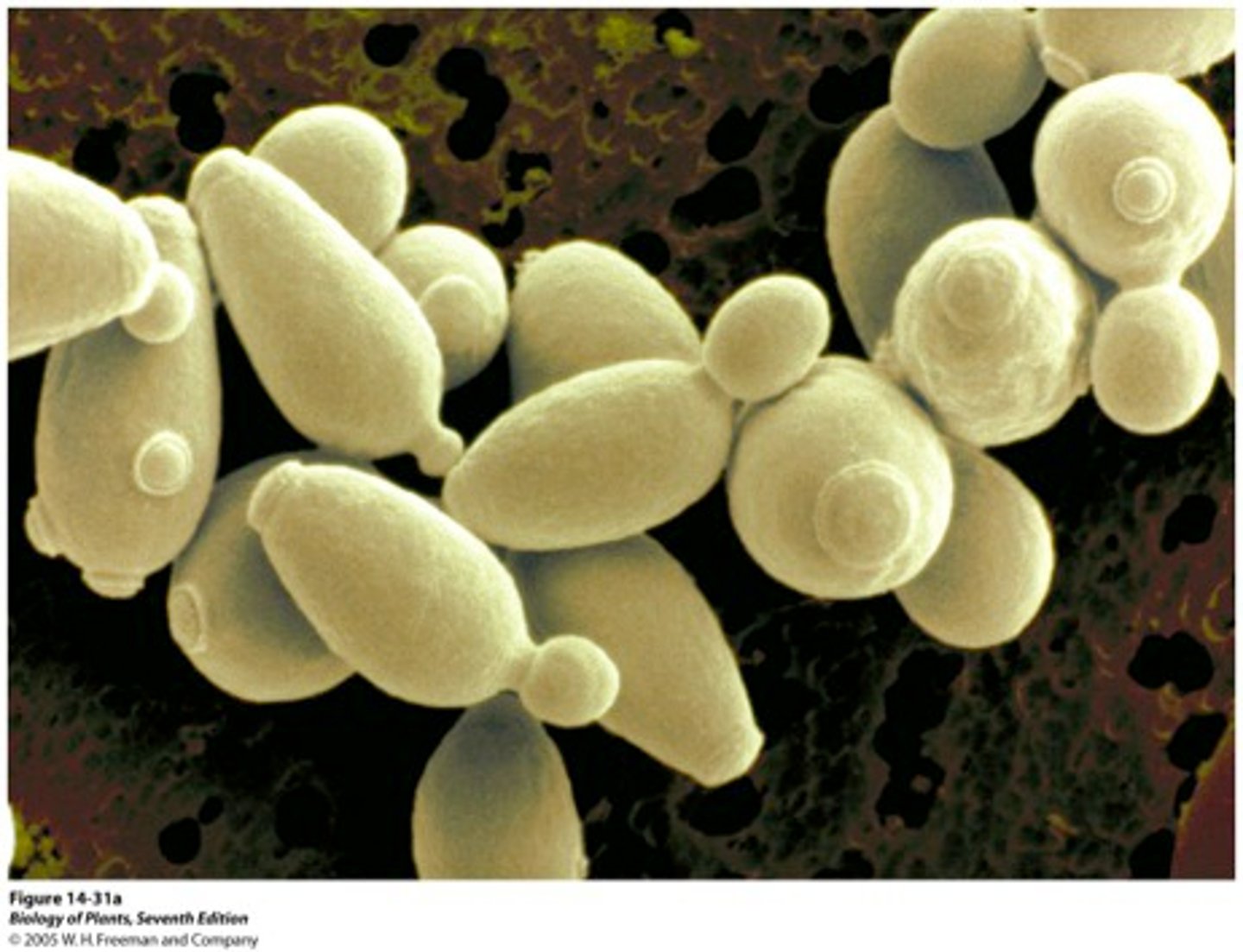
Yeasts
unicellular fungi
heterotrophic absorptive
what is the nutritional mode for fungi
parasites
corn smut, wheat rust, and many others
pathogens
Athlete's foot, ringworm, many others
symbionts
lichens, mycorrhizas
Chitin
Cell wall
aminopolysaccharide
structurally similar to cellulose
Chytrids and Zygomycetes
______ and ________ polyphyletic; others have phylum status
Zygomycetes
a fungal group that is not very pathogenic; complex life cycle consisted on sexual and asexual fungal groups...fungi spend most of their time as haploids; black bread mold;
Ascomycota
Form sexual spores in saclike asci
Basidomycota
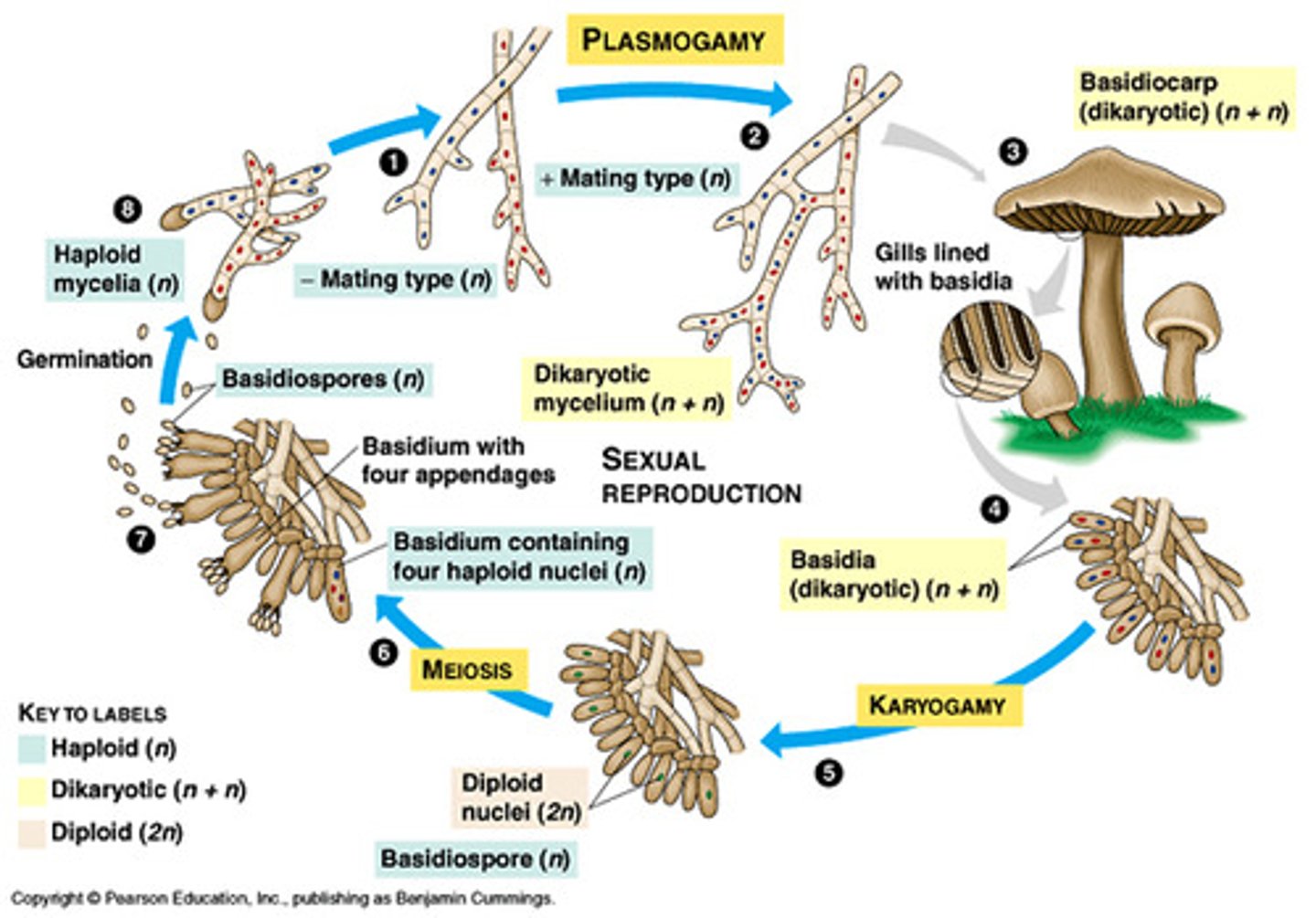
club fungi
Lichens
Fungus + Algae
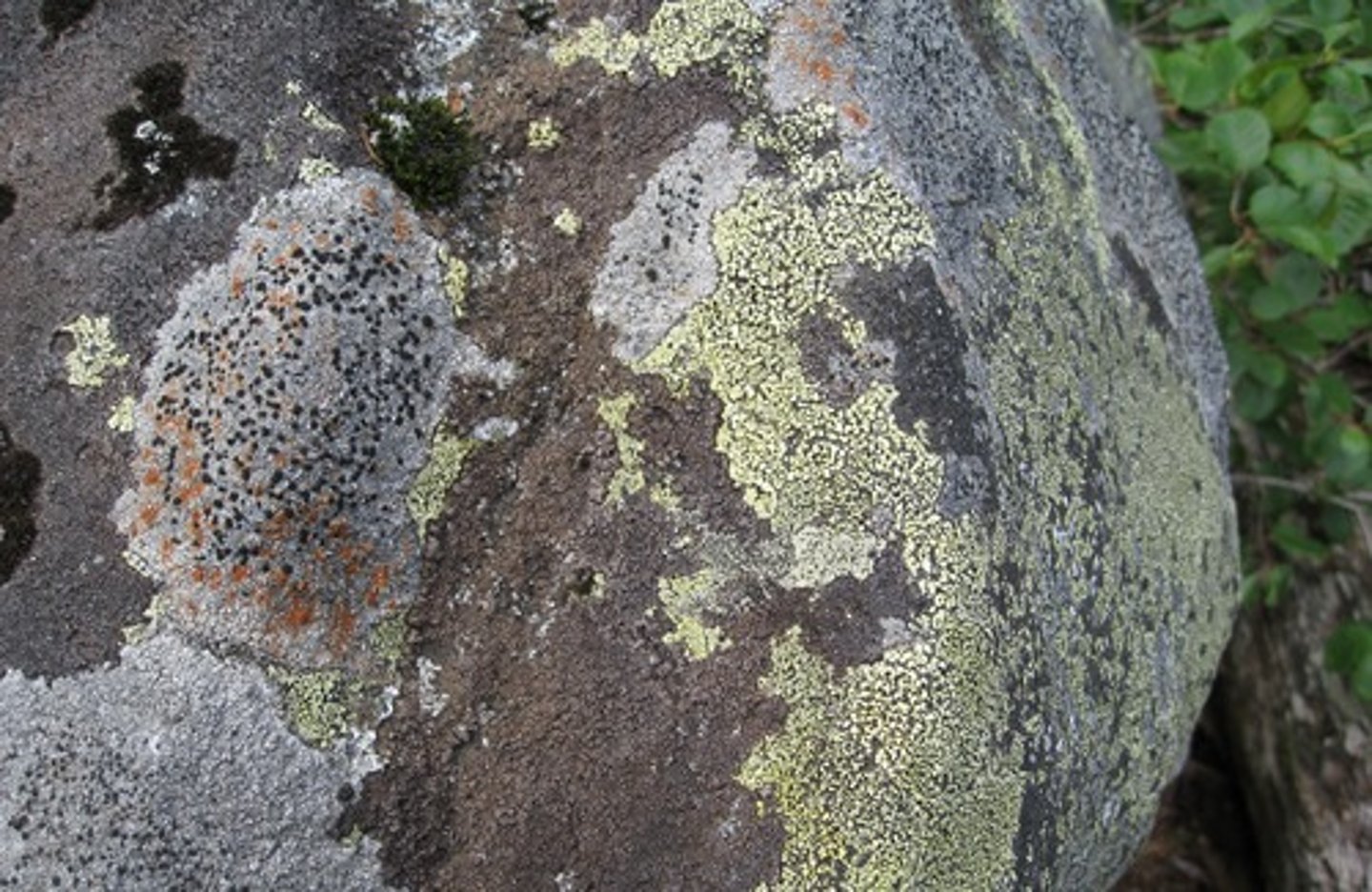
Crustose
(of lichens) having a thin crusty thallus that adheres closely to the surface on which it is growing

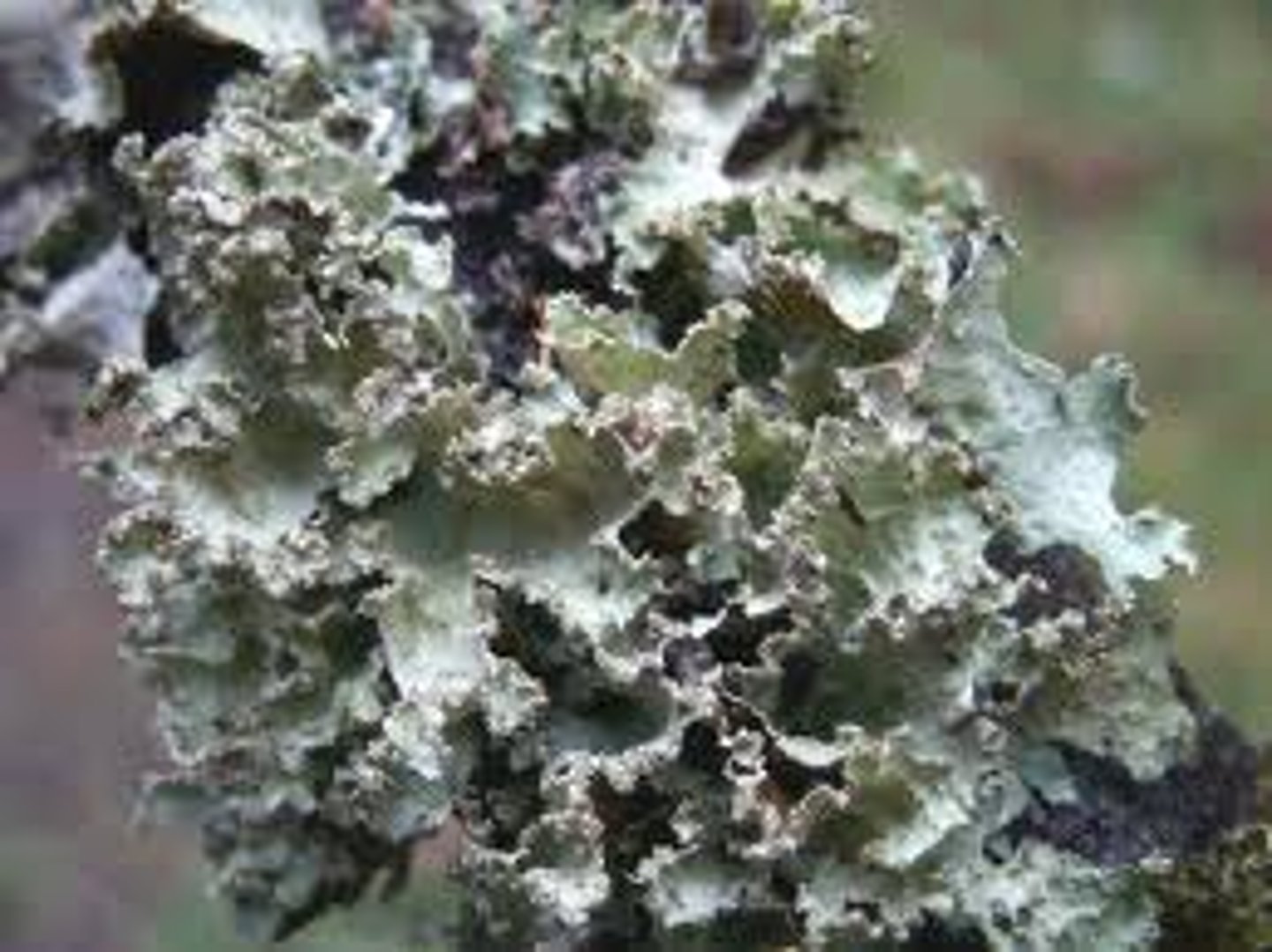
Foliose
leaf-like lichen

Fruticose
shrublike lichen
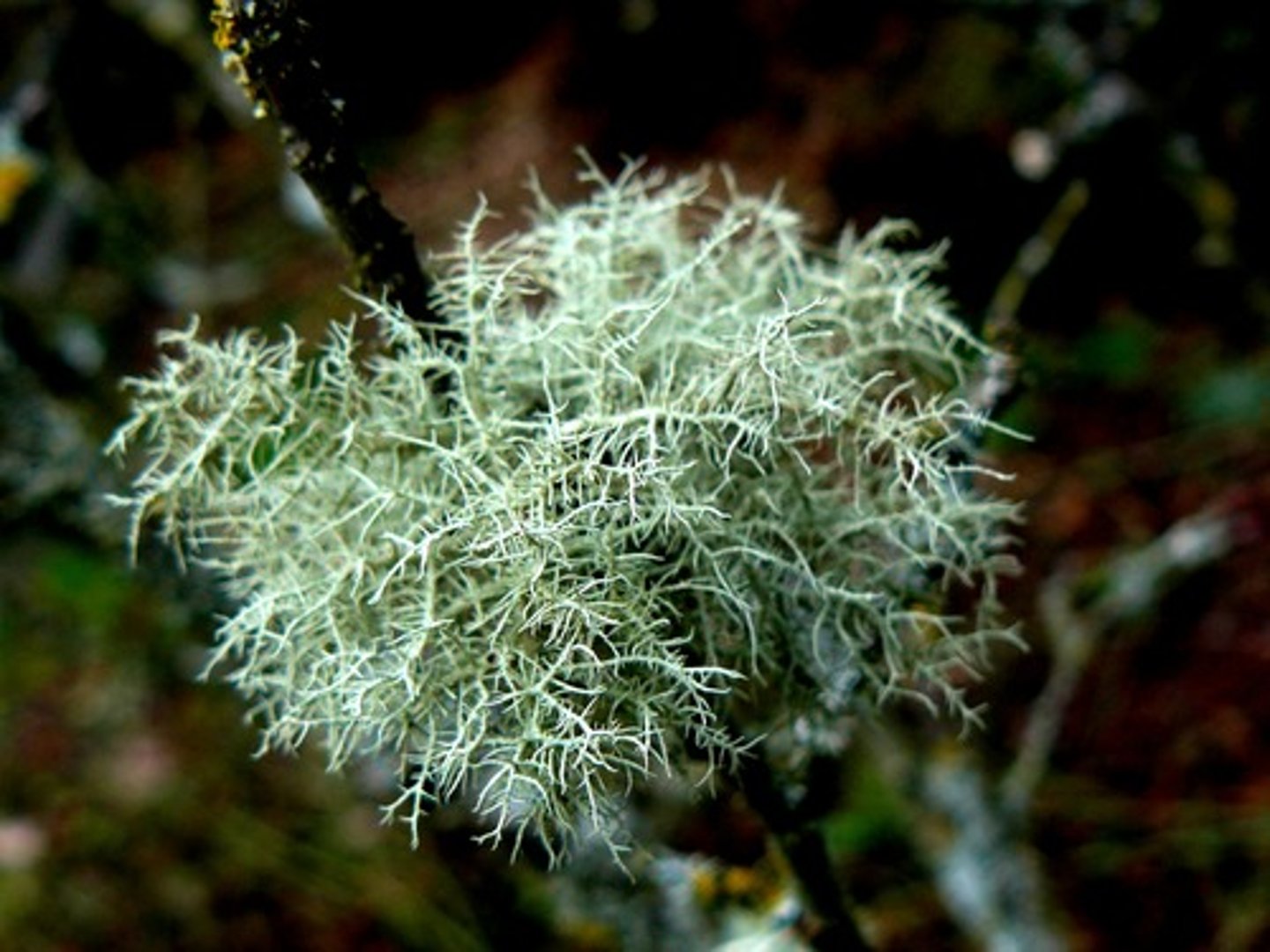

Mycorrhizas
Fungus + Plant roots
Ectomycorrhizas
fungi grow around plant cells, form sheath around root (mainly in conifers, beeches, oaks)
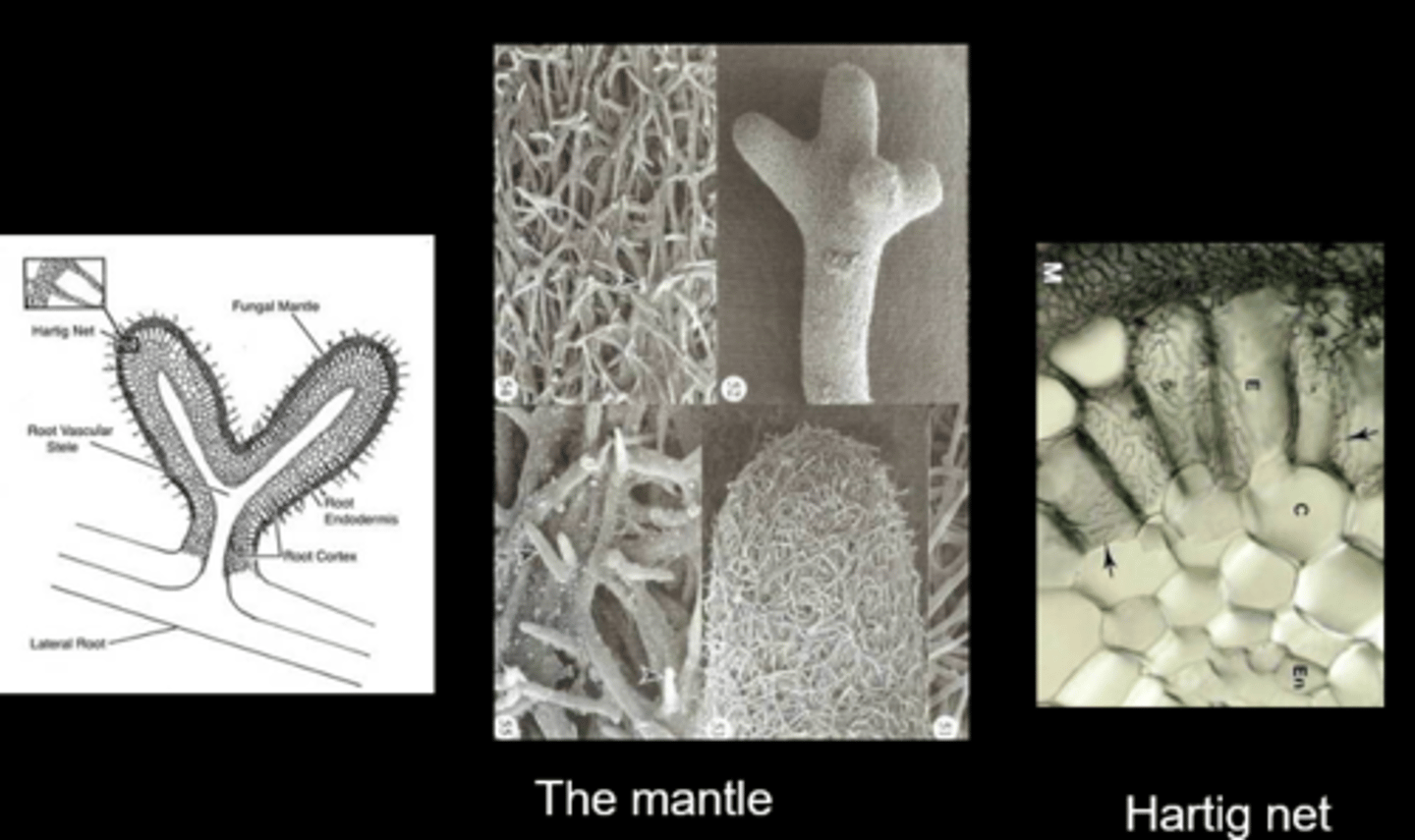
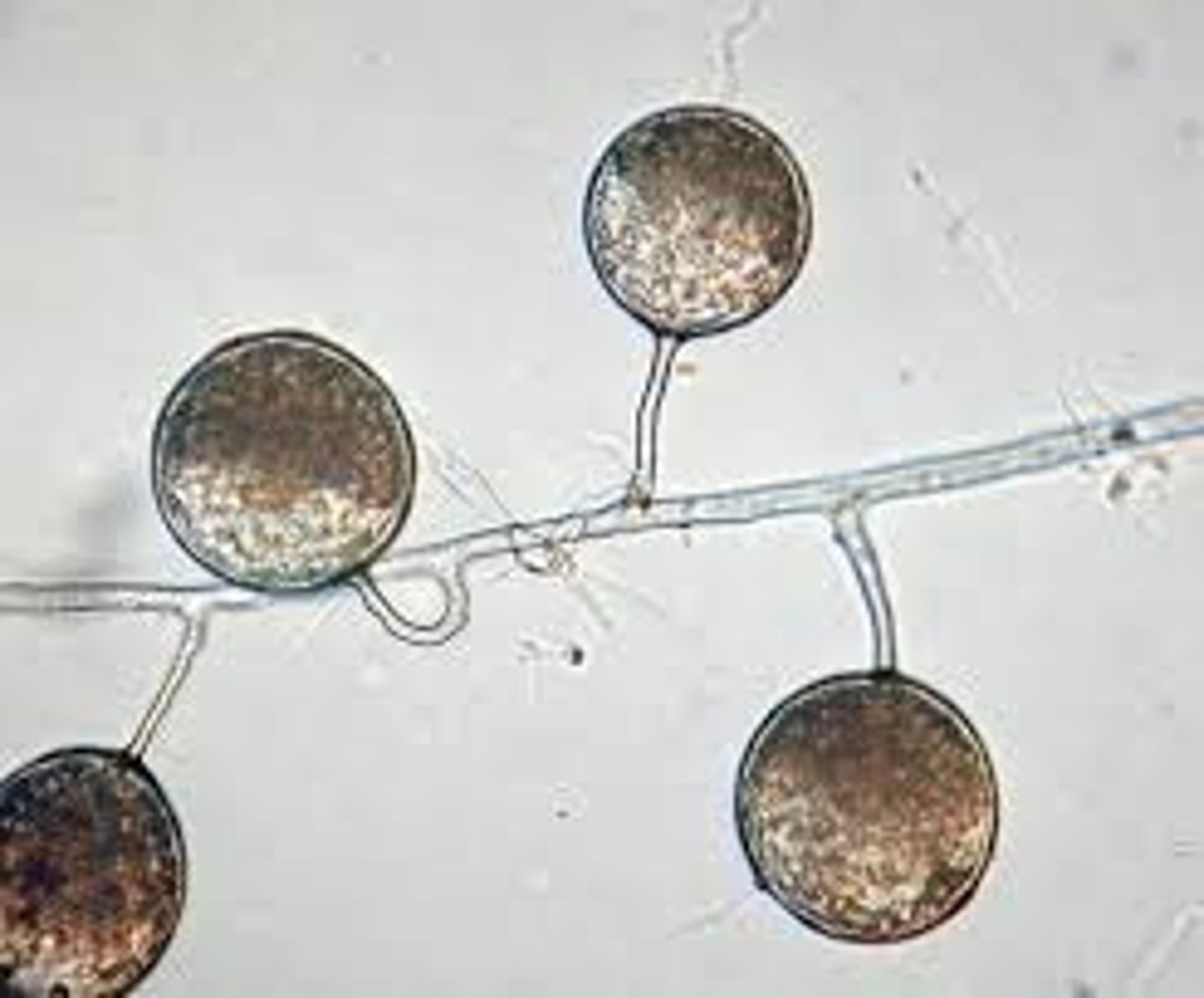
Glomeromycota
a group of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with the roots of trees
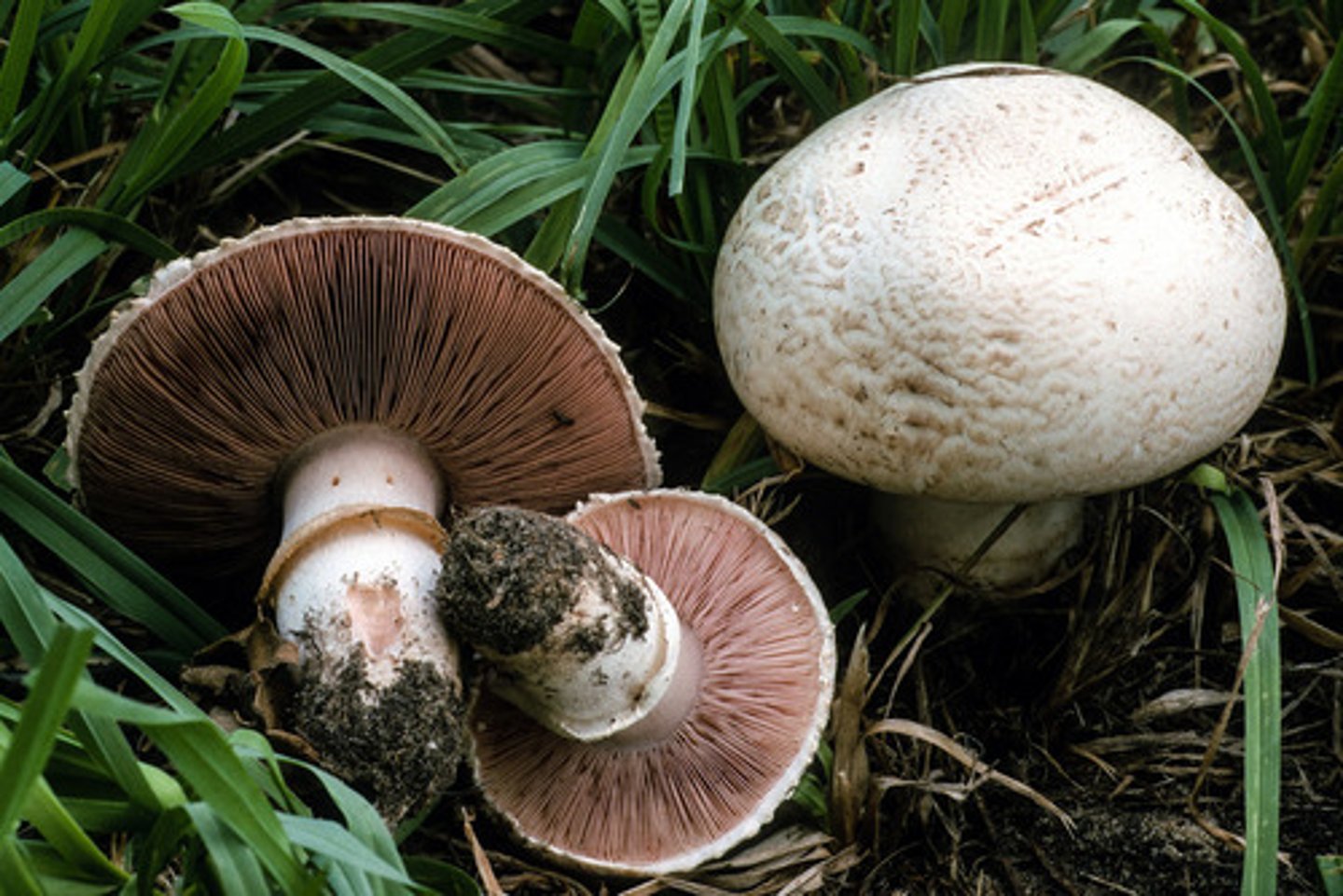
Agaricus bisporus
Common or button mushroom scientific name

Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Baker's and brewer's years scientific name
Penicillium
_______ for "moldy" cheeses
Aspergillus
ferments soy beans for soy sauce
Penicillin
antibiotic
Mevacor
The first statin drug
Cyclosporine
Immunosuppressant
Psilocybin
Psychoactive drugs
Mycotoxins
toxins produced by fungi (wild mushrooms)
Aflatoxins
contaminate stored grains and peanuts
Ergotism or St. Anthony's fire
stored grains, especially rye
Zygomycetes
a fungal group that is not very pathogenic; complex life cycle consisted on sexual and asexual fungal groups...fungi spend most of their time as haploids; black bread mold;
Phylum Ascomycota
sac fungi (yeasts, morels, truffles)
Phylum Basidiomycota
club fungi (mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi, rusts, smuts)
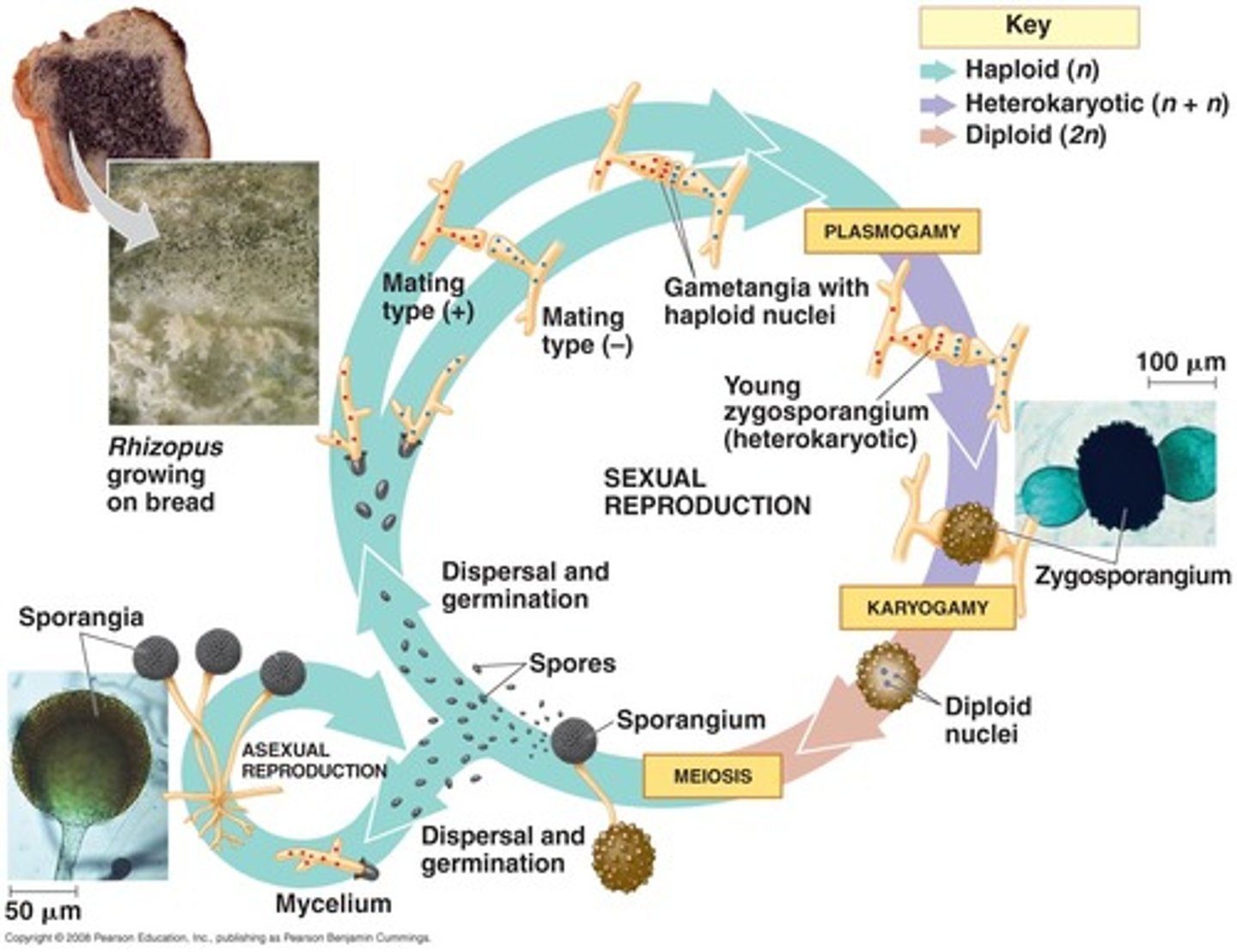
Zygomycetes life cycle
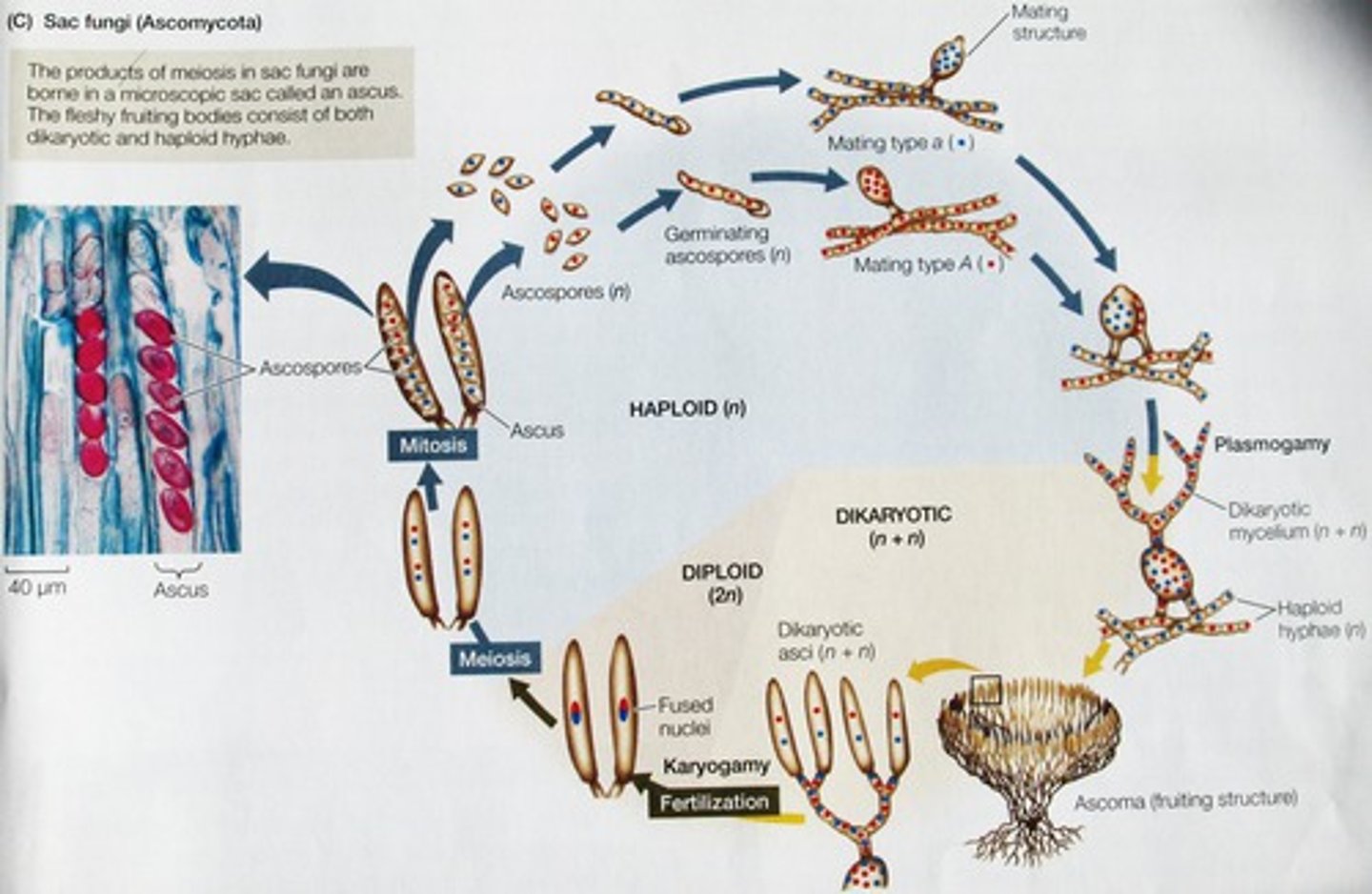
Ascomycota life cycle
Basidiomycota life cycle
Zygomycetes examples
Pin molds
Bread molds
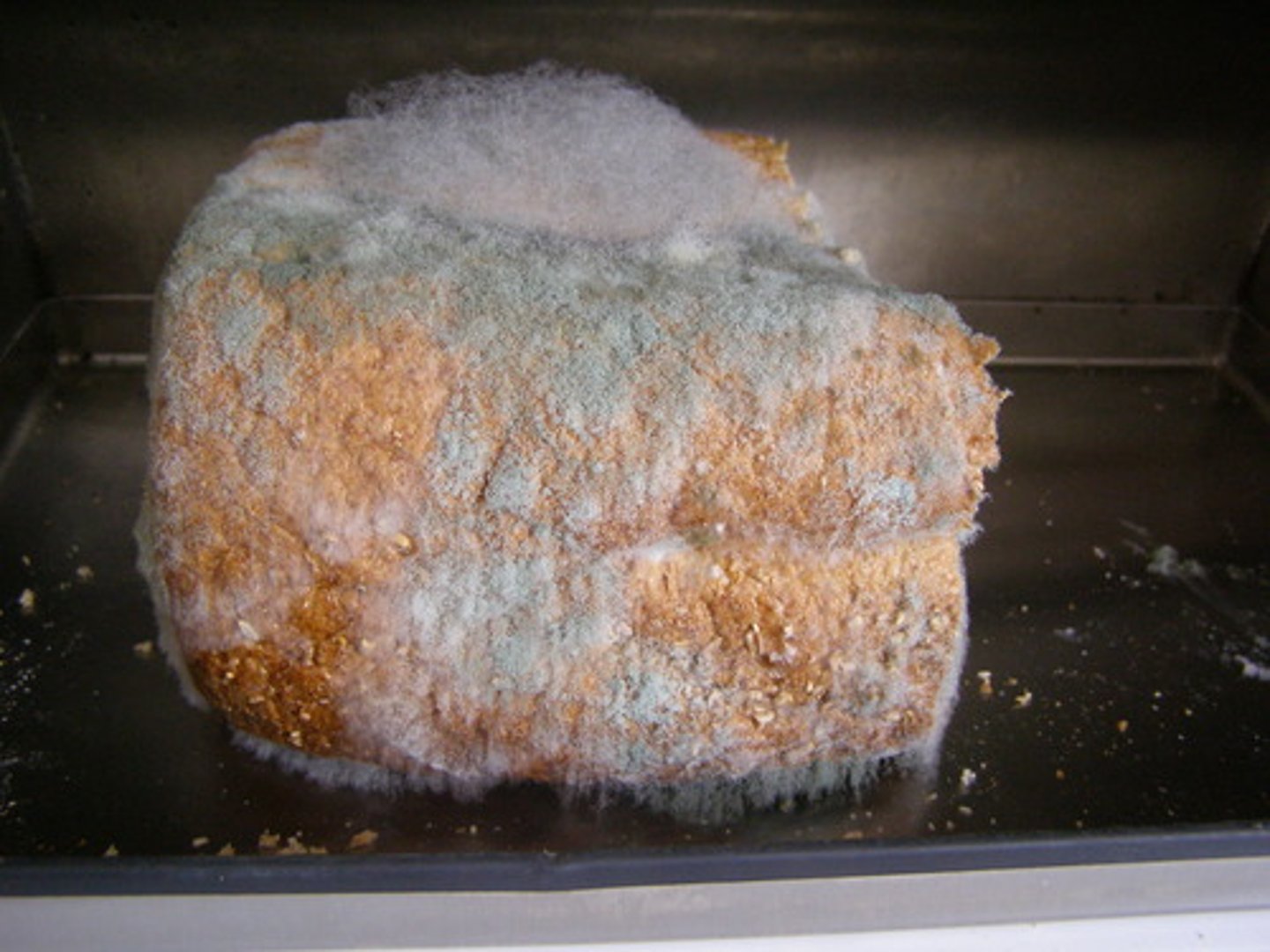
Pin molds
Zygomycota
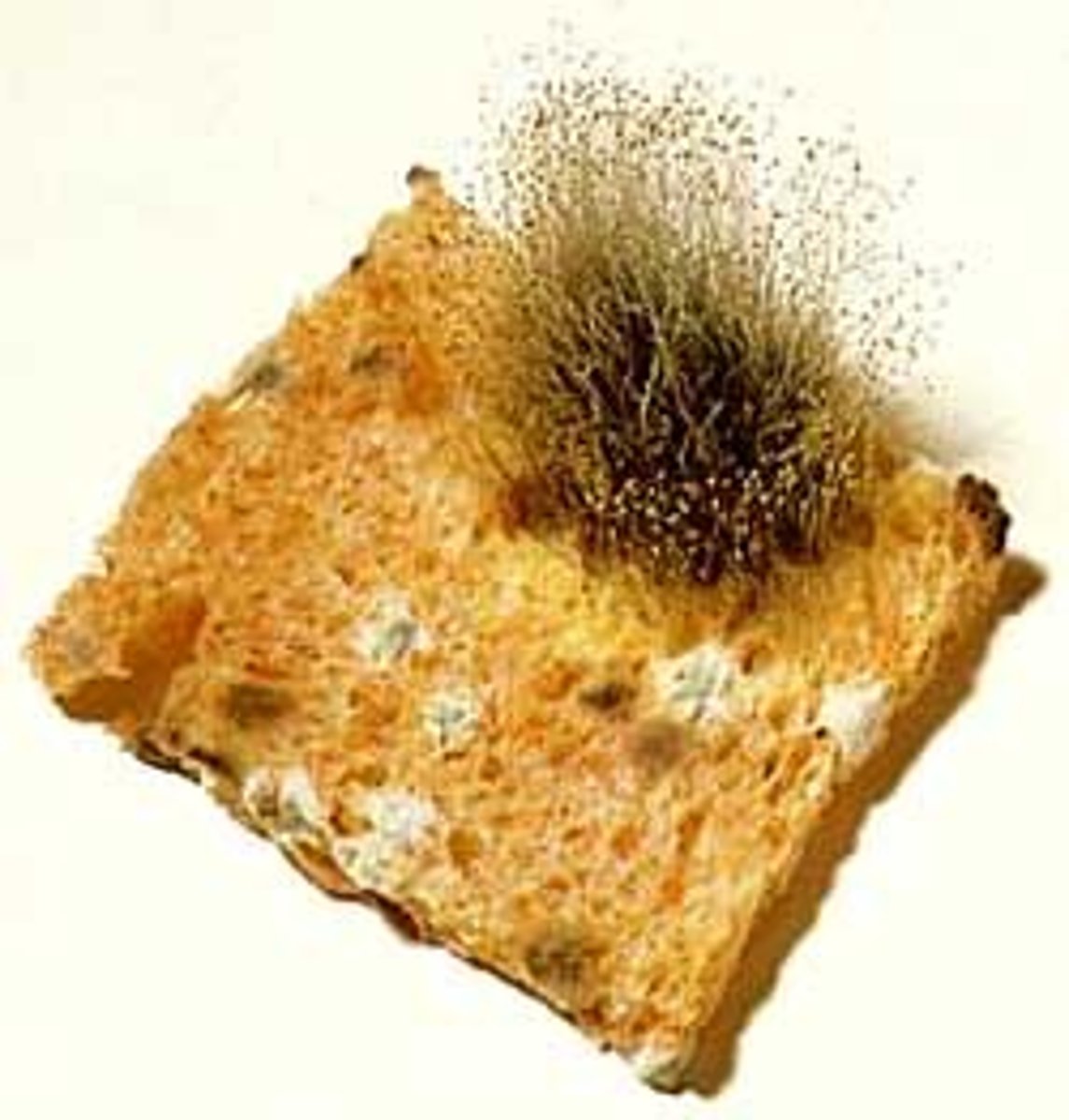

Bread molds
Zygomycota

Zygosporangium
Zygomycetes sexual structure
Zygosporangium
thick-walled reproductive structure formed from the fusion of the cytoplasm of the mycelia of two neighboring fungi
Zygosporangium
Zygomycetes meiosis site
Aseptate, coenocytic
Zygomycetes hyphae
Aseptate coenocytic
hyphae that have no cross-walls and are multinucleate
Pin-like sporangia
Zygomycetes asexual reproduction
Ascomycota examples
Molds, mildews, cup fungi, yeasts, morels, truffles, asexual fungi
Ascoma with dikaryotic hyphae
Ascomycota sexual structure
ascoma
a multicellular fruiting body of the cup fungi