Applied Nutrition Exam 2
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What are the 4 stages of production beef cows?
1. post calving, early lactation
2. 1st trimester, late lactation
3. 2nd trimester, mid gestation/dry period
4. 3rd trimester, late gestation, dry period
Maintenance is about ____ of annual energy requirement
69%
Energy requiremets dip during
weaning
At what BCS do we weant to see mature cows at when calving?
5
What BSC do we want to see 2 yr old cows at when calving?
6
Nutrient excess or deficiency is equal to
nutrients from forage - nutrient requirements
Daily dry matter intake is about _____ of the cow's body weight
1.8-2%
How do you determine the appropriate amount of supplemental feed?
divide supplemental need by supplemental nutrient concentration
More energy is given when you give more of a _____ concentrate
low
In one 3-4 hr. grazing bout, cows consume ______ lbs of protein from forage
2-3
During the pre-weaned phase of dairy cows, the majority of nutrients come from the
milk
Water and starter grain are offered to dairy cows _____
day 1
Why should started be around 30% starch?
to have high butyrate
A dairy calf should be double their birth weight by
56-60 days of age
In the pre-weaned period a calf can get _____ lbs of gain for a lb of feed
0.5-0.8
Dairy calves drop to _______ of gain per lb of feed post-weaning
0.15-0.30
Six month or older dairy calves, feed conversion drops to ____ lb per lb of feed
less than 0.1
What are weaned calves expected to have?
a high function rumen
What phase do dairy calves get introduced to hay?
weaned
Dairy cattle are body conditioned on a scale of ______
1-5
Over ______ BCS in the dry off period can lead to metabolic diseases when calving in
3.75
What is the goal of the close up period for dairy cattle?
transition the rumen before entering lactation
What is usully fed during the close up period for dairy caltte?
DCAD diet
What are the 3 phase in dairy cattle lactation?
early lactation, mid lactation, late lactation
In what phase does nutritent uses shift to body reserves in dairy cattle?
late lactation
How do you estimate dry matter intake for dairy cows?
using the milk production and size of the cows
One pound of protein is required to produce _____ lbs of milk
10
excess rumen undegradable protein results in:
lower milk production, stiff dry manure, lower dry matter intake
excess rumen degradable protein results in:
low milk production, high early milk peaks with low milk persistency, high milk urea nitrogen levels (MUN), loose manure
excess fiber in diet can result in:
low milk production, dry matter intake lower, high milk fat percent, early lactation cows feed too high forage and low energy rations may be prone to ketosis and rapid body weight loss
deficiency in fiber can result in:
acidosis, low milk fat percent, cows not chewing their cud
total fat should not go above ____ for dairy cattle
7%
What is the goal BCS for dairy cattle at peak milk?
2.75
What is the second highest concentration of any nutrient?
protein
protein deficiency results in:
reduced appetite and feed intake, reduced birth weights and growth, reduced colostrum and milk production, decreased hormonal production, decreased fertility
Ruminants possess a _____ -stomach with ___ compartments and a _____ stomach
fore-stomach with 3 compartments and true stomach
microorganisms in the ruman convert feed ___ and ____ to ____
protein and urea to NH3
What is the difference between rumianlly degradable protein and undegradable protein?
degradable: protein degraded to produce ammonia (NH3)
undegradable: protein that passes intact from the rumen to the abomasum and small intestine
Rumen microorganims require a minimum of about _____ nitrogen
1.2%
Diet less than ____ crude protein results in decreased growht and reporduction of microorganisms
7.5%
the crude protein equivalent to non-protein nitrogen (NPA) =
288%
the rate of digestion of ____ by microbial urease is very rapid
non-protein nitrogen
What is the rumen NH3 requirement?
5mg/100mL
What correctly distinguishes between microbial crude protein (MCP) and microbial true protein (MTP)?
microbial crude protein consists of 80% true protein and 20% nucleic acids, with microbial true protein assumed to have 80% intestinal digestibiltiy
Concentrate feed RUP digestibility is ____ while forage is ____
80%, 60%
metabolizable protein MP is equal to
MPfeed (metabolizable protein from rumianlly degraded protein) + MPmtp (metabolizable protein from microbial true protein)
What is the range of BCS for beef cattle?
1-9
Beef cattle BCS has ____ of cow body weight between scores
7%
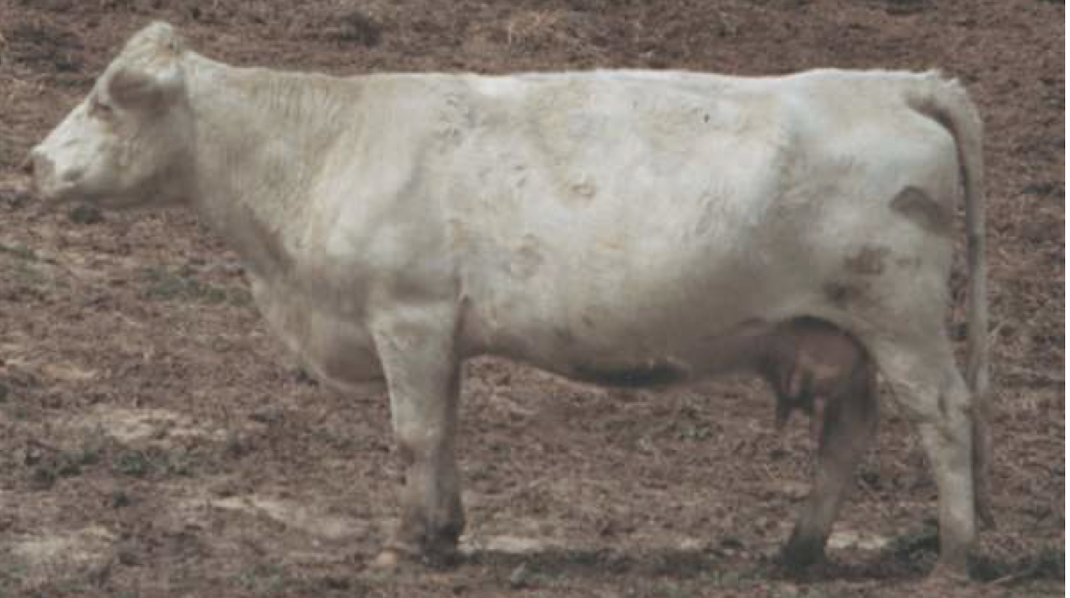

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
5
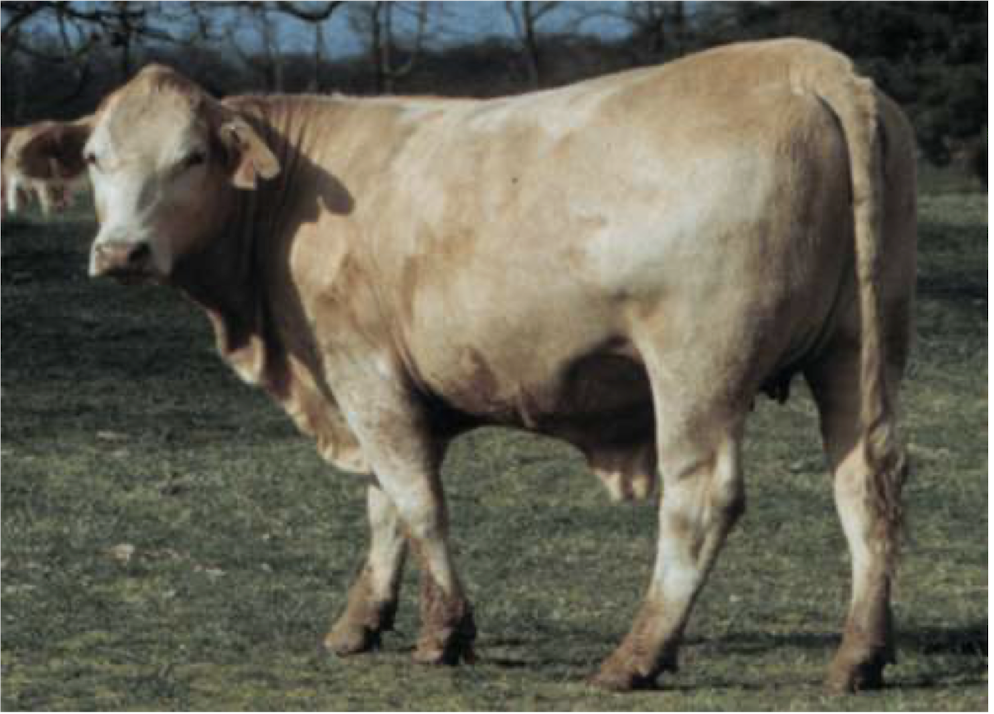

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
6
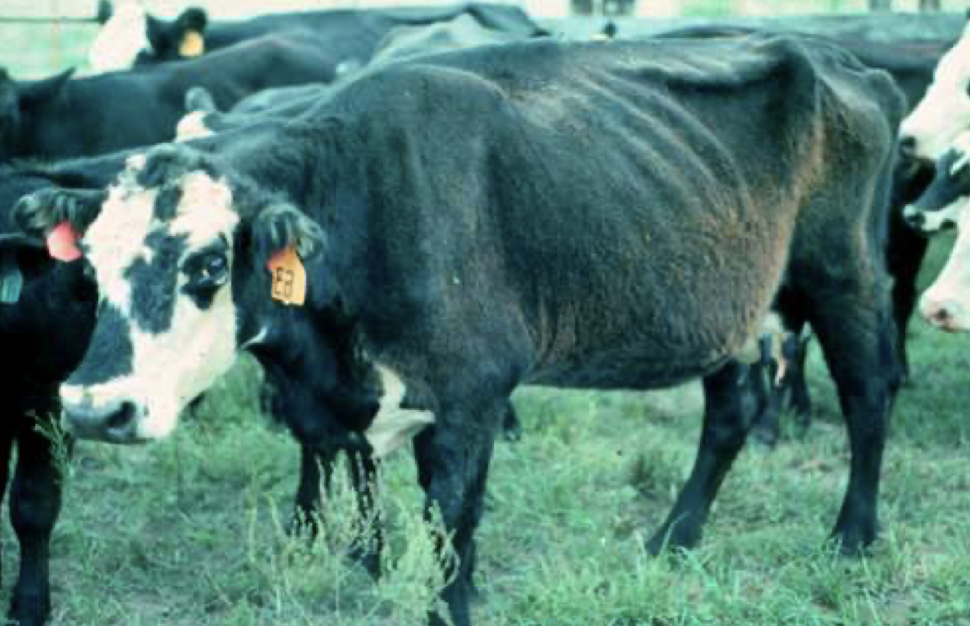

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
1
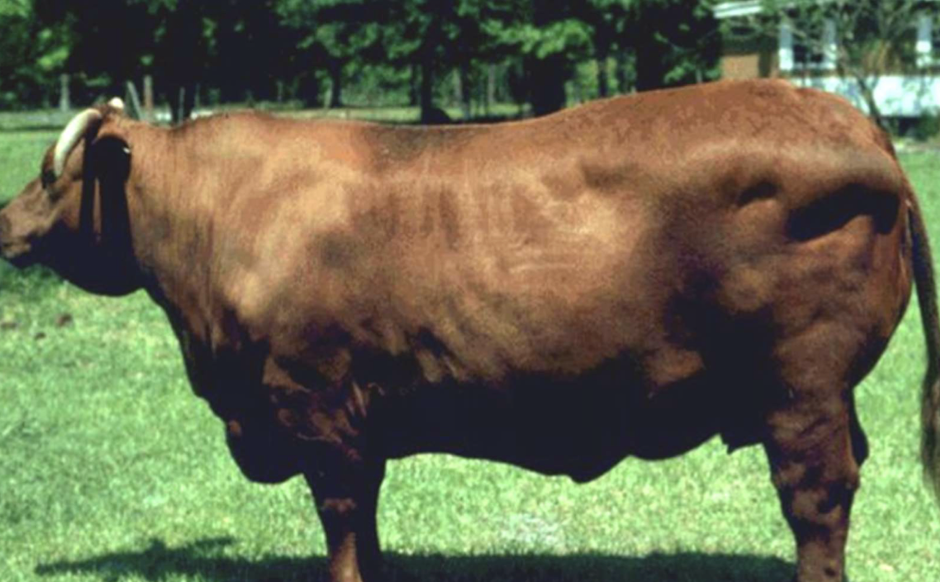

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
9
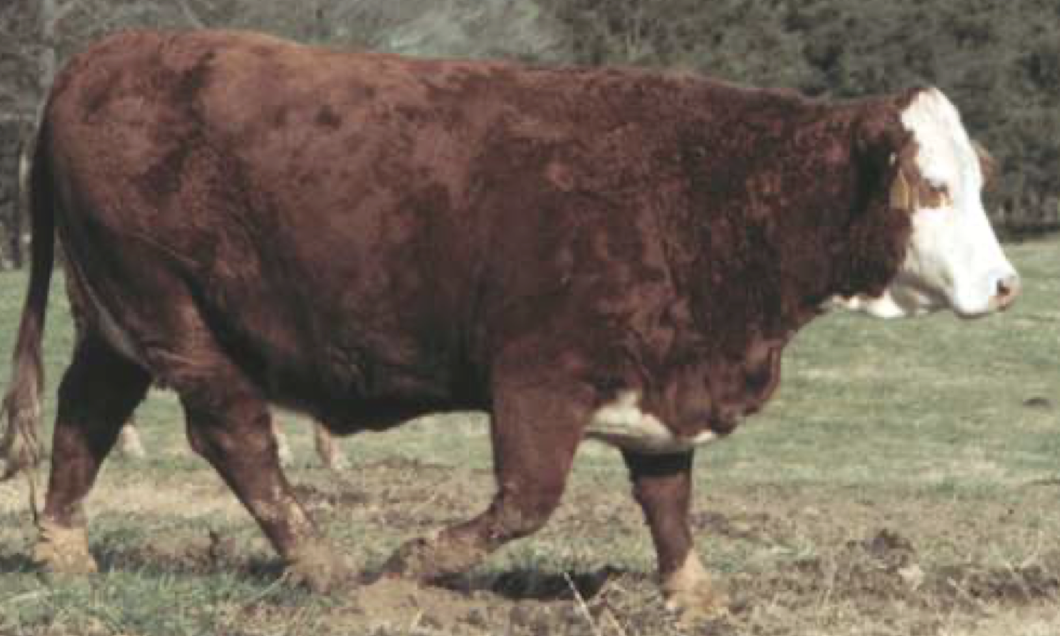

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
7
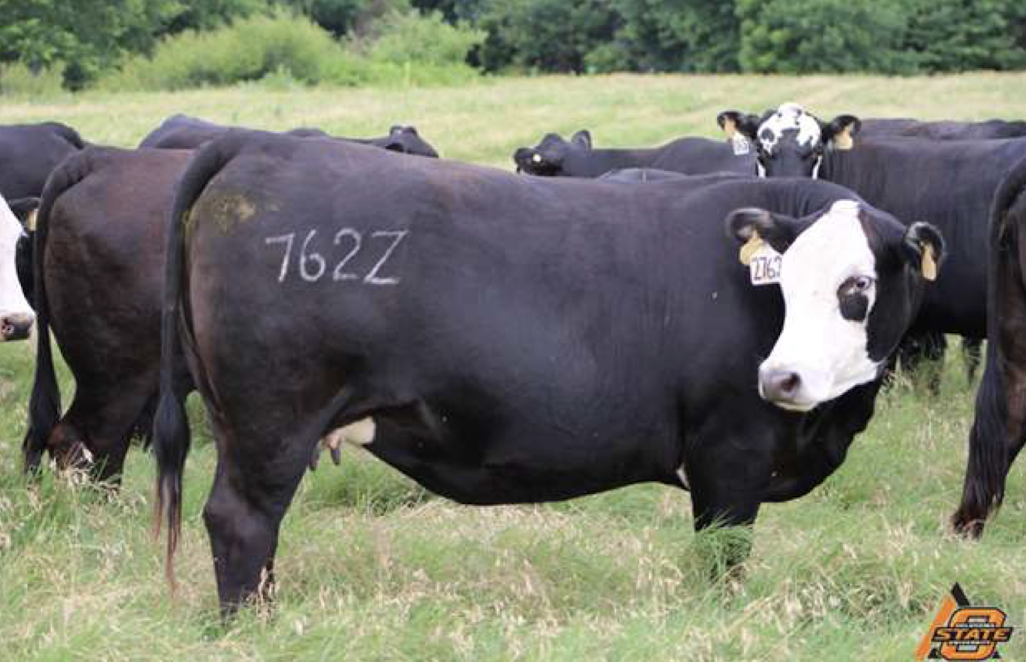

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
6
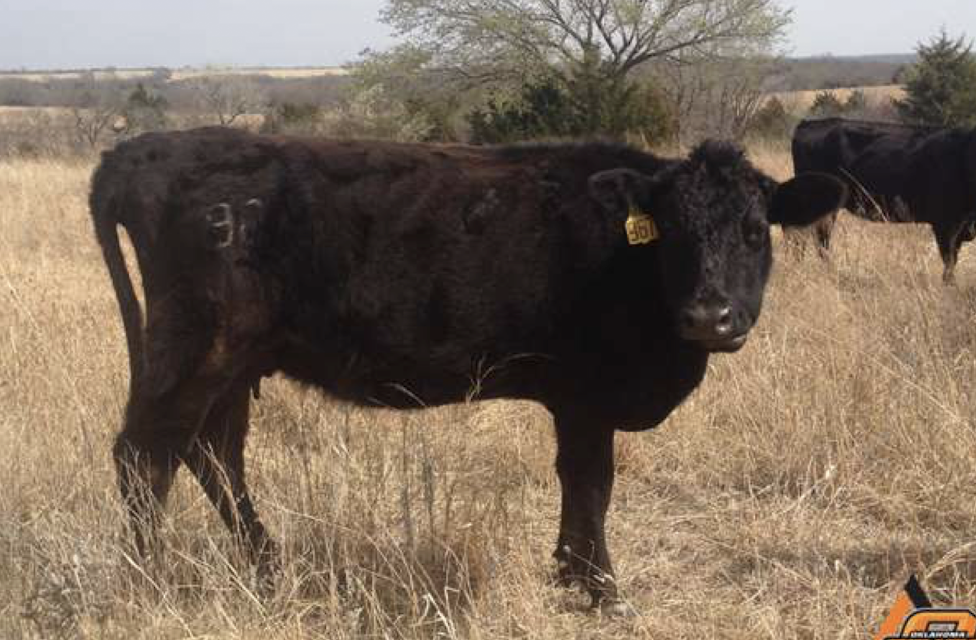

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
3
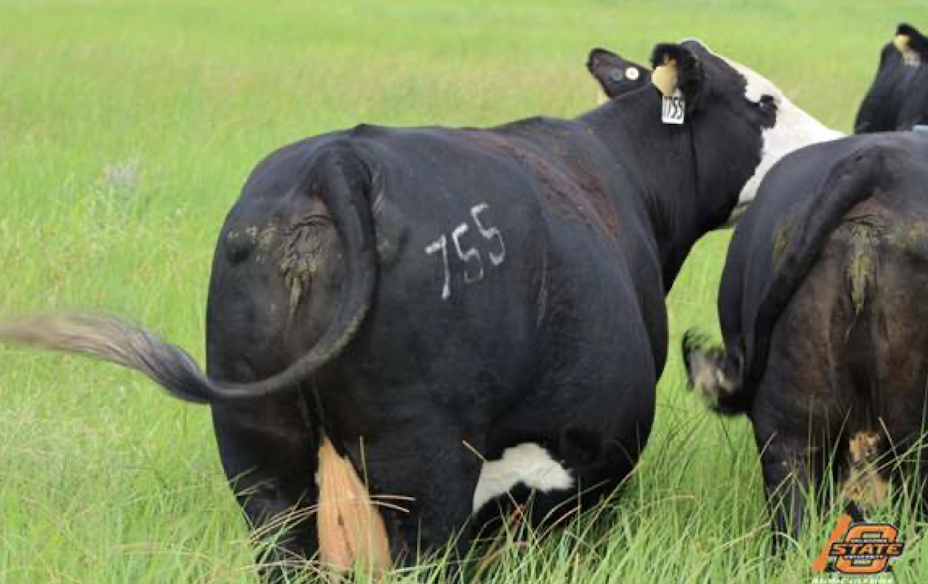

What is the BCS of this beef cow?
6
BCS is highly related to ______
energy sources
Body fat composition at ____ is a criticial factor in determing time to breed back
calving
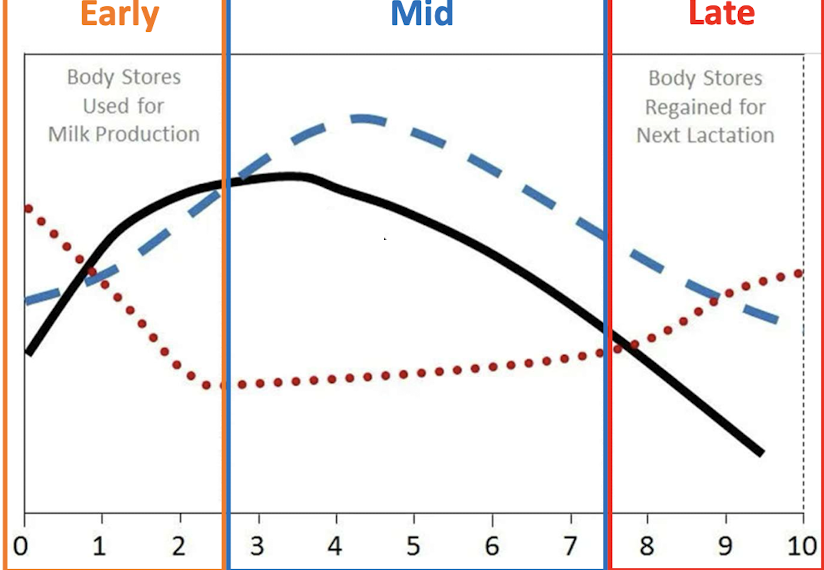
What does the blue, black, and red line show?
blue: dry matter intake
black: milk production
red: body weight
How do you calculate %CP?
N% x 6.25 = %CP
What are the functions of proteins?
structure of organs and soft tissues, enzyzmes, hormones, antibodies, hide/hair/wool, milk synthesis
What are the dietary essential amino acids?
threonine, trytophan, methionine, lysine, phenylalanine, valine, isoleucine, histidine, arginine, leucine
The essential amino acid that is present in the lowest quantity of the diet as a percentage of the aniaml’s requirement is the _____
first limiting amino acid
Where do swine and poultry diets get most of their protein?
“natural” and plant proteins
____ digestibility is more accurate for amino acid digestibility
illeal
What is the reference standard for protein quality in swine diets
soybeanmeal
Whole soybeans act as
trypsin inhibitors
Cottonseed meal causes
gossypol toxicity in livestock.
Blood meal contains an
unbalanced branch chain AA
Meat and bone meal are a source of
Ca and P
Fish meal has a ____ and is a source of ___-
good AA profile and source of Omega-3 fatty acids
What is trypsin?
a protease enzyme crucial to protein digestion
Where is trypsin produced/secreted?
trypsin is produced in the pancreas and secreted into the small intestine to break proteins down into peptides and AA
What is the role of the trypsin inhibitor?
acts as a defense mechanism against insects and pests in soybean plants by inhibiting their digestive enzymes (heat sensitive to above 176F and borken down by rumial MCO)
What is gossypol?
naturally occurring pigment in cottonseed that can be toxic to animals
What are the effects of gossypol?
cardiac failure, anemia, liver necrosis, reproductive issues
How can gossypol affect male bull fertility?
It binds with proteins in the rumen and makes them unavailable for absorption
What are the critical limits of gossypol in swine and other monogastrics, and preruminatn calves and lambs?
</= 100ppm free gossypol
What are the critical limits of gossypol in young growing calves?
</= 400 to 600 ppm
What are the critical limits of gossypol in mature cattle?
no more than 800 ppm
What are the most limiting AA at small intestine in beef cattle?
methionine and lysine are the most limiting amino acids.
Feather meal is a good source of ____
sulfur containing AA, primarily keratin (cheaper)
Poultry blood meal is a good source of _____
lysine, leucine, and histidine (although expensive)
Fish meal is
“rich in met,” very digestible, and expensive
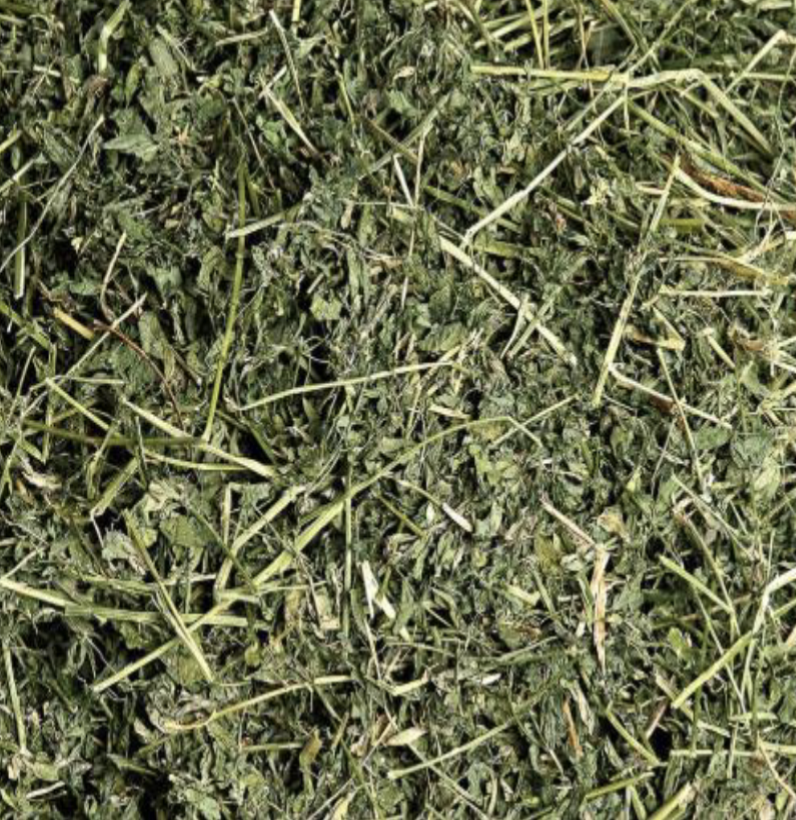

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Alfalfa Hay
19.8% CP
55.2% TDN
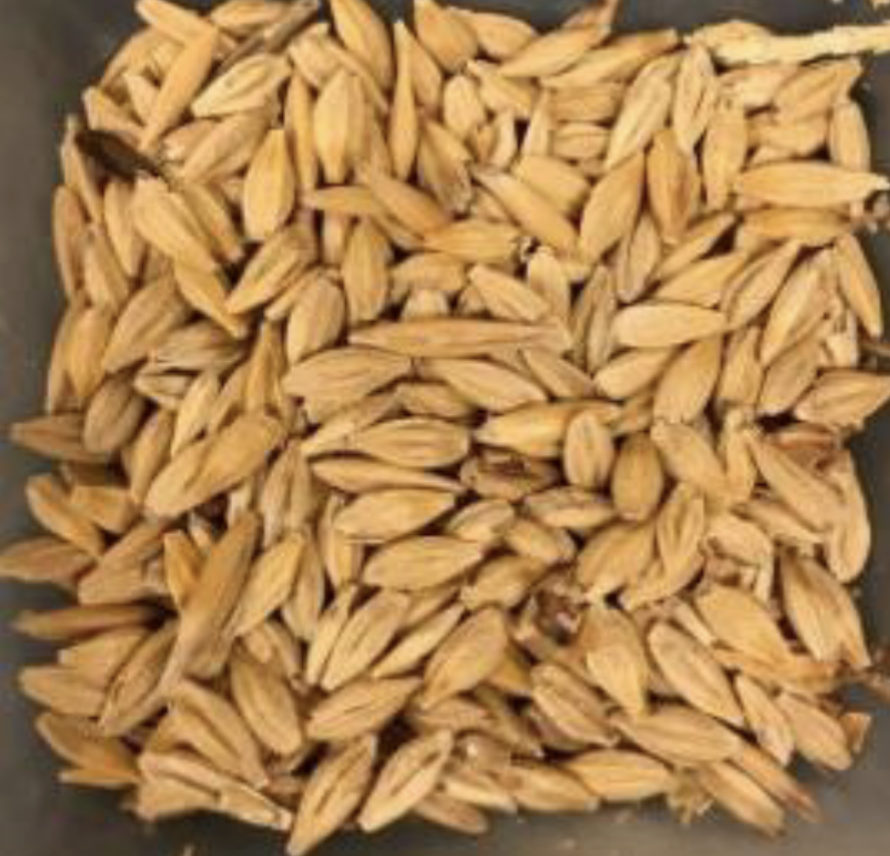

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Barley
12.7% CP
84.1% TDN
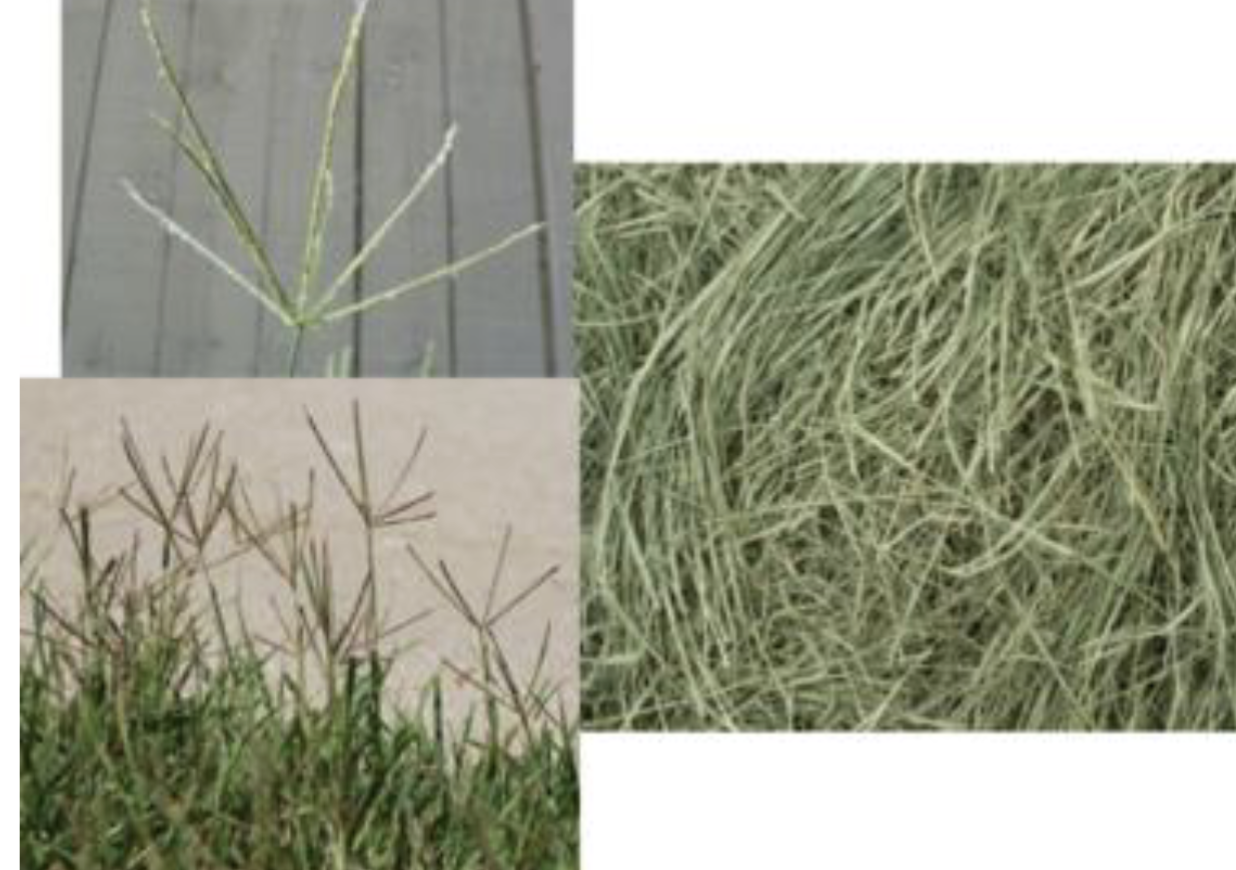

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Bermudagrass Hay
11.1% CP
56.3% TDN
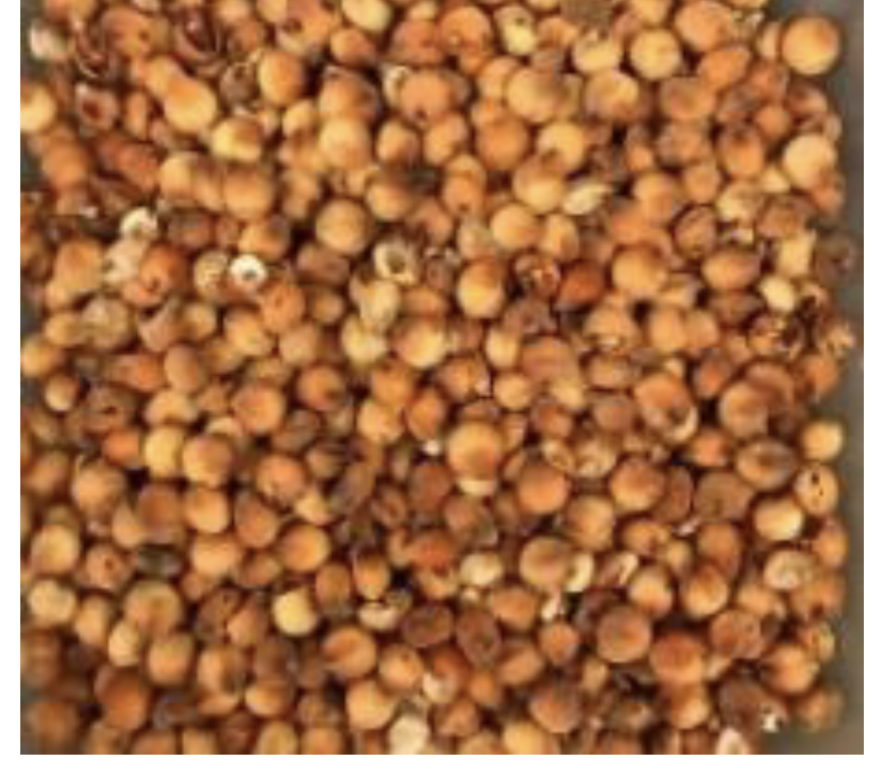

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Milo
11.2% CP
76.2% TDN

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
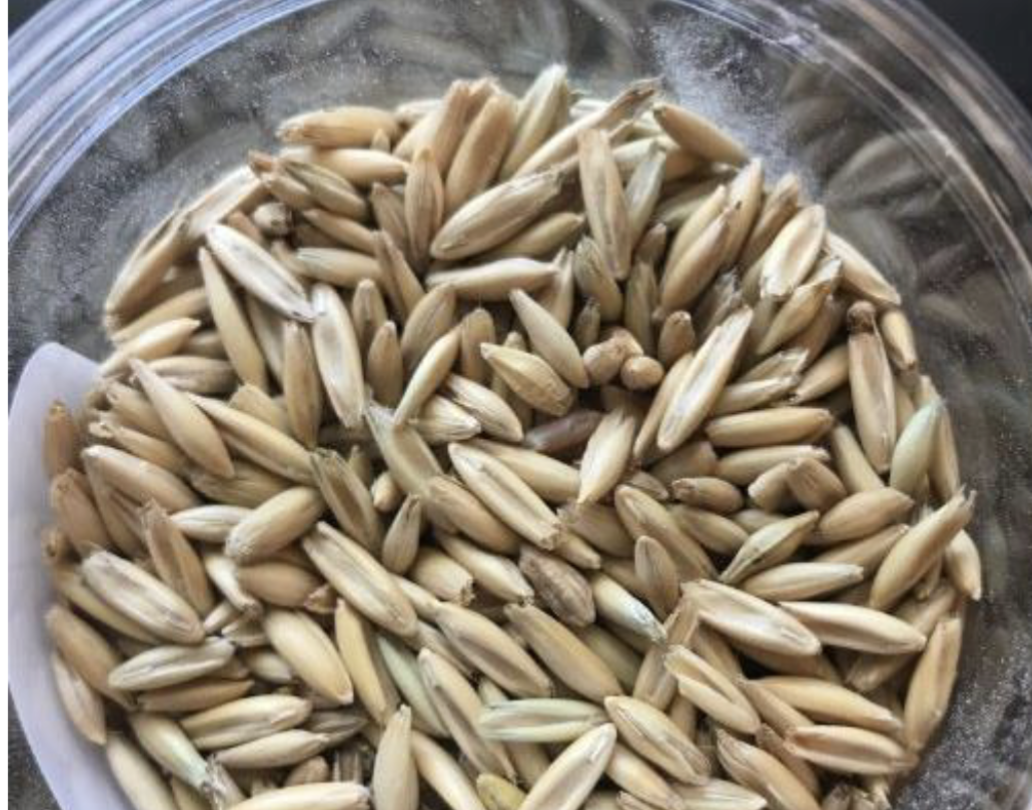
Oat
12.2% CP
83% TDN%

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
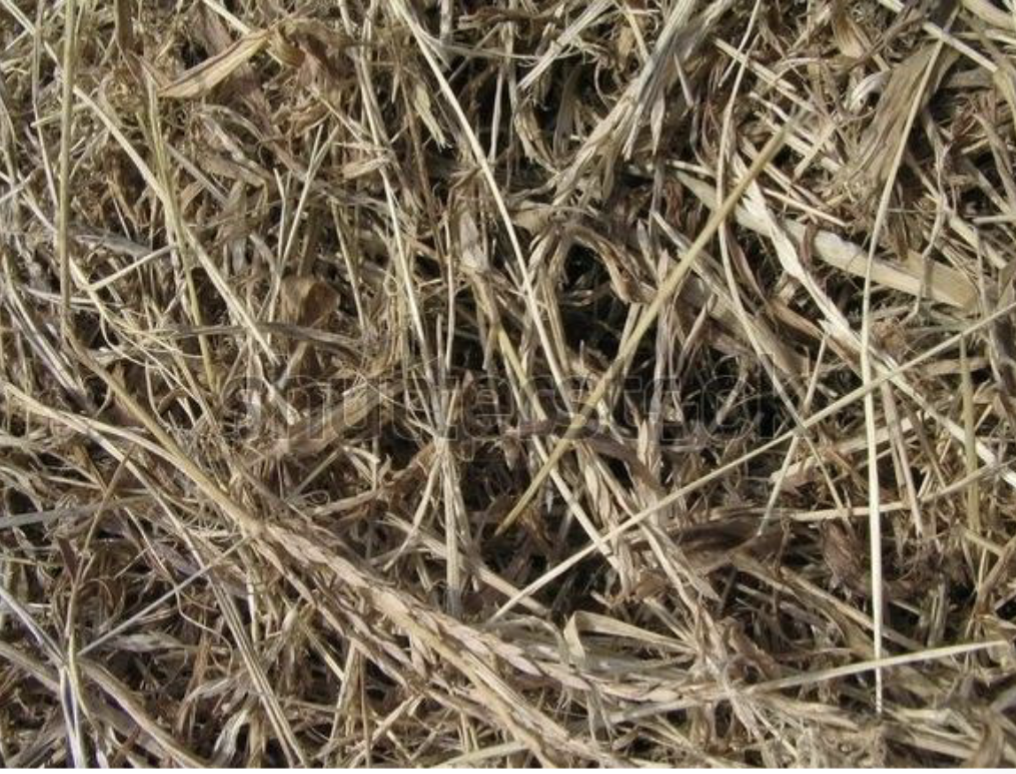
Prarie Hay
6.7% CP
48.4% TDN
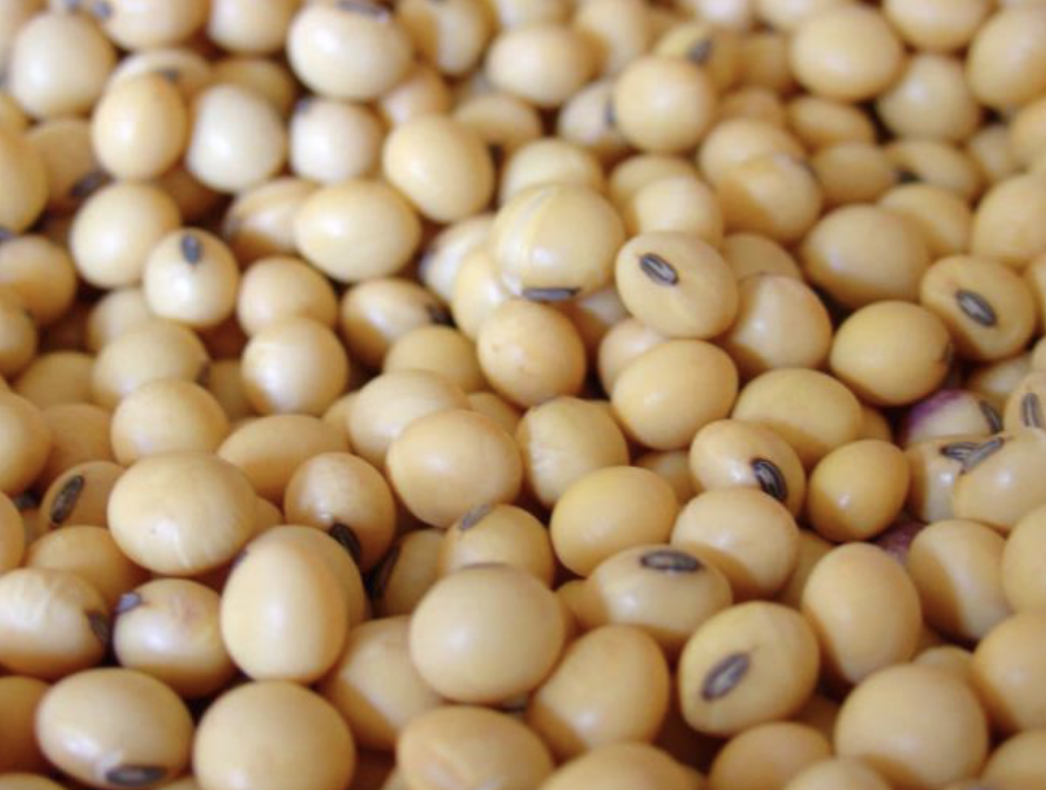

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Soybeans
39.9% CP
91% TDN
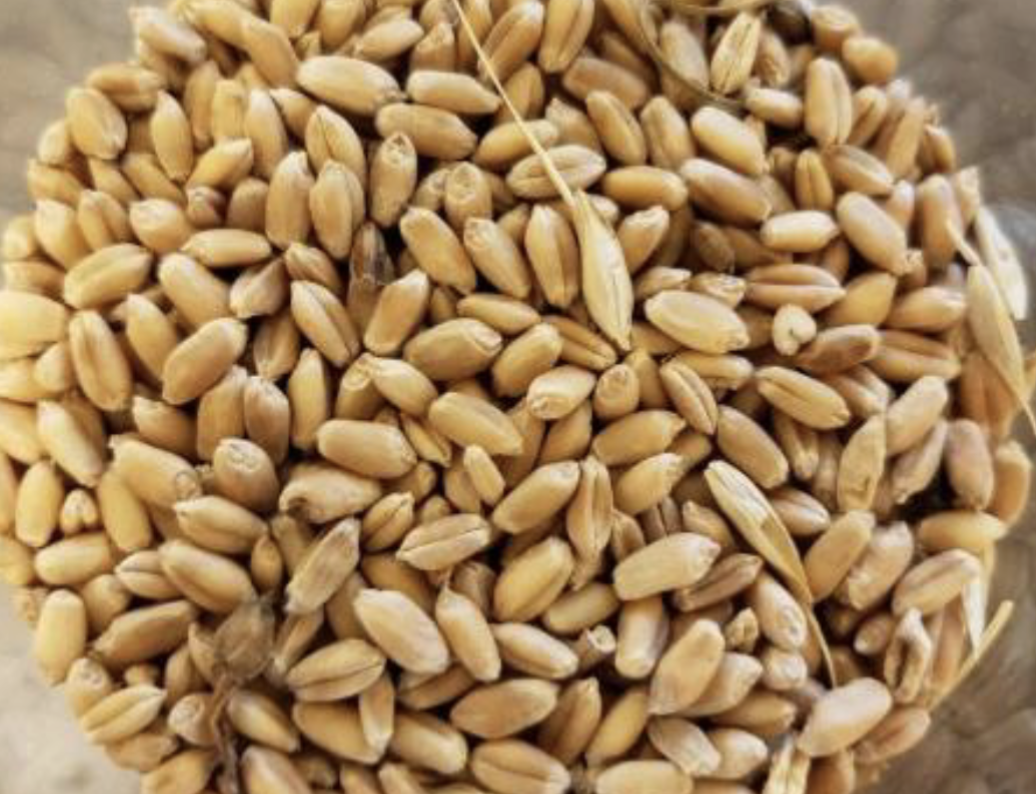

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Wheat
13.7% CP
86.8% TDN
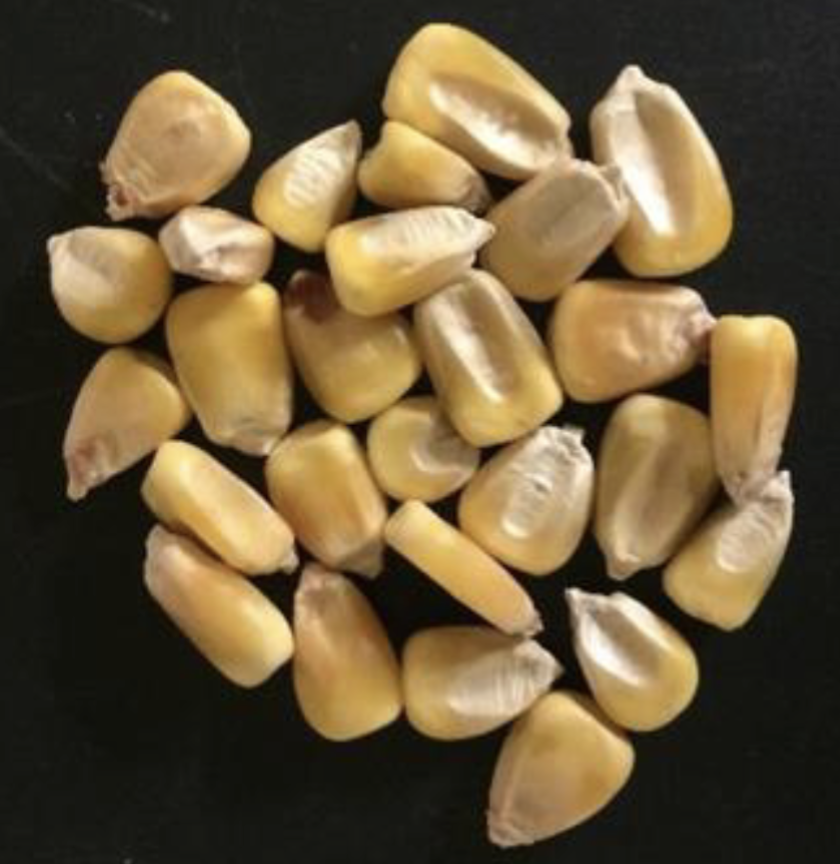

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Whole Corn
10.4% CP
92% TDN

Identify this whole feedstuff. What is the CP and TDN %?
Whole Cottonseed
22.8% CP
93% TDN
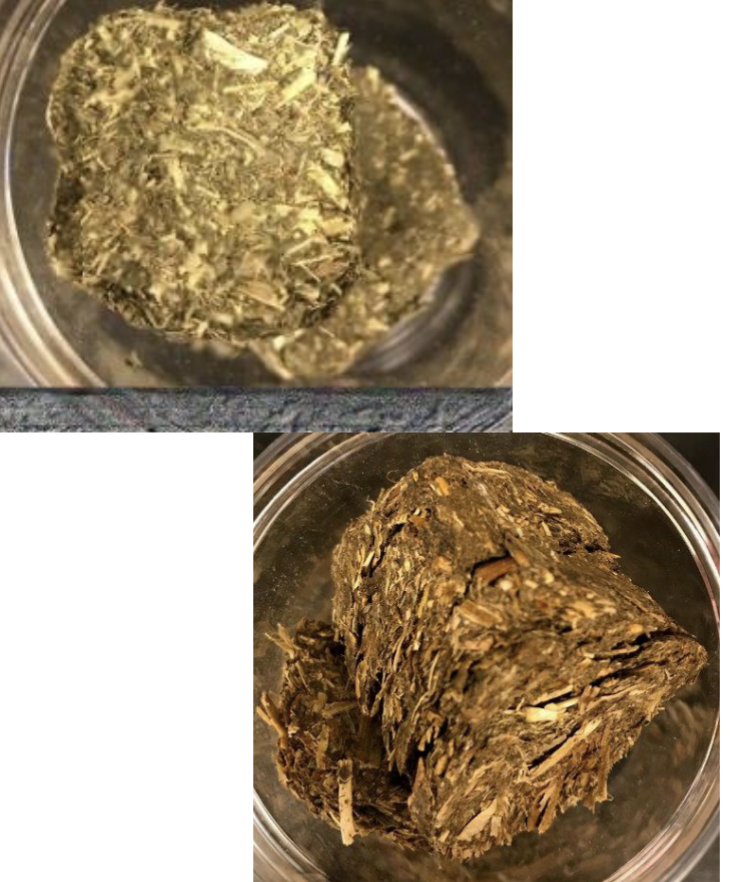

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Alfalfa Cubes
18% CP
56% TDN
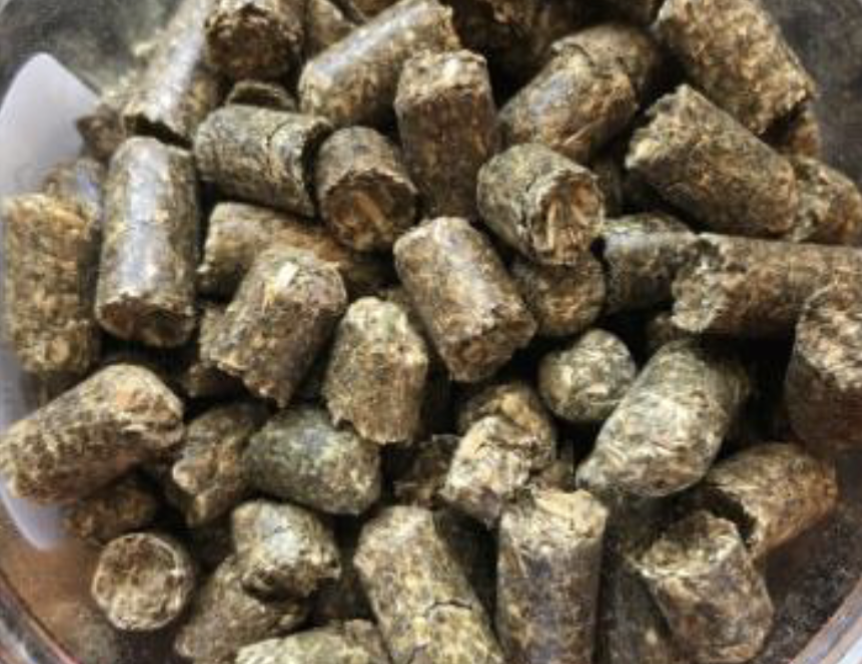

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Alfalfa Pellets
18% CP
56% TDN
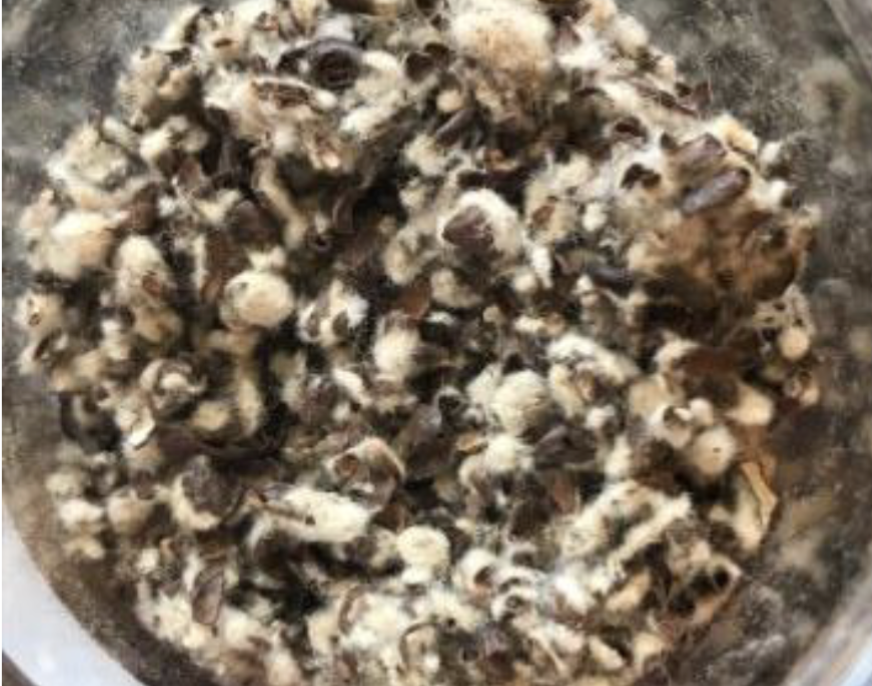

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Cottonseed Hulls
6.6% CP
42% TDN
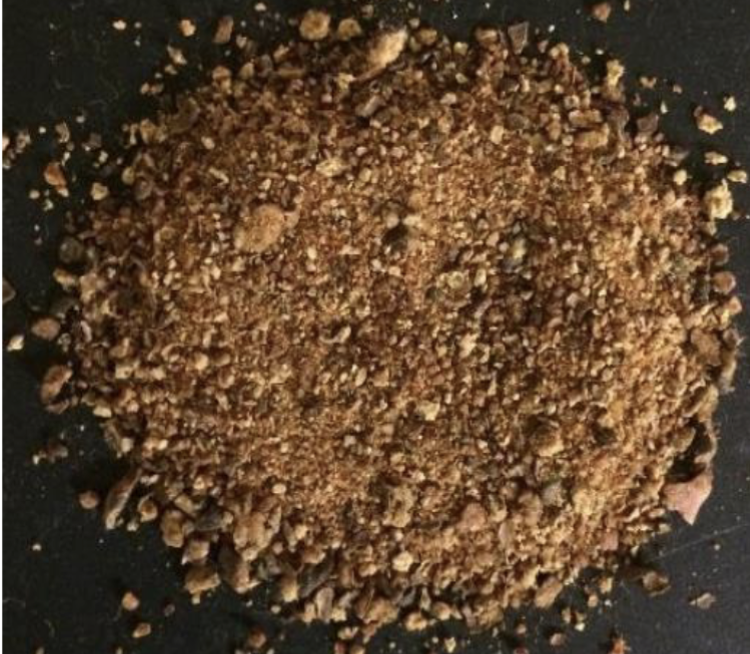

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Cottonseed Meal
44.9% CP
69.6% TDN
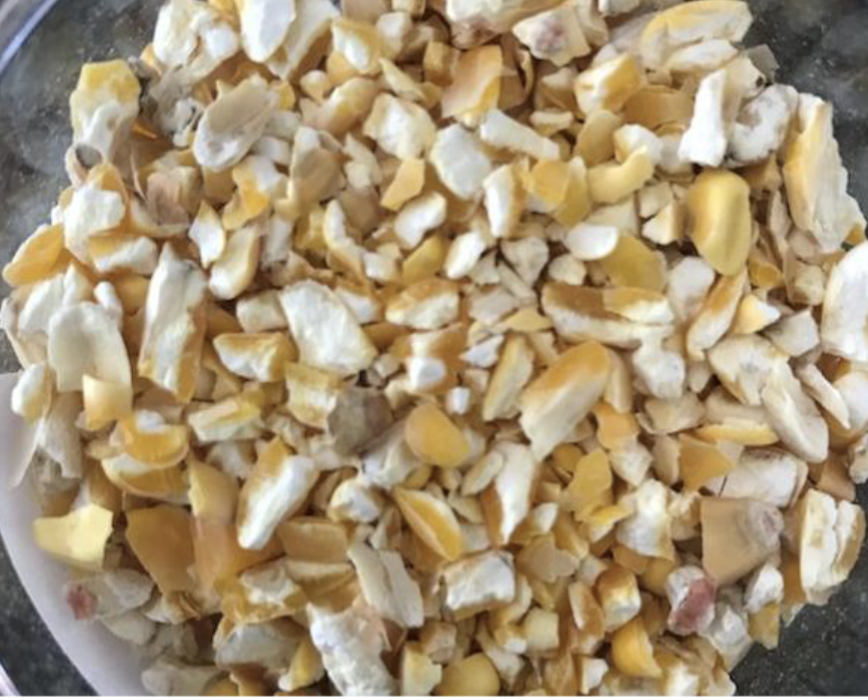

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Cracked (dry rolled) Corn
8.7% CP
87.6% TDN
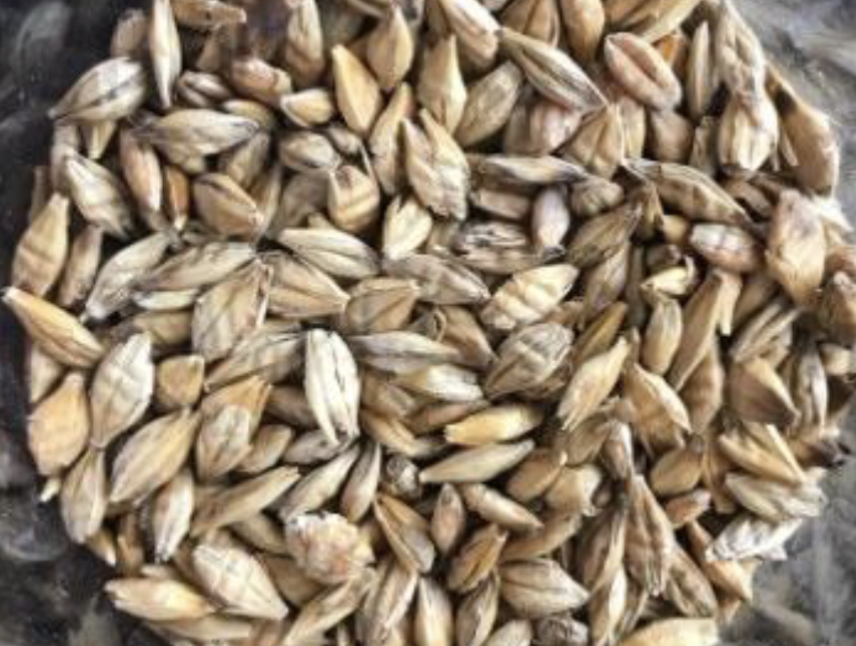

Identify this processed feed. What is the CP and TDN %?
Crimped (Steam Rolled) Barley
12% CP
84% TDN