12- Genetic Diversity
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is biodiversity?
the variety of living organisms in a community/ habitat )includes species diversity and genetic diversity
What is a habitat?
the place where an organism lives e.g. pond or rocky shore
What is a community?
all the organisms (of different species in a habitat)
(population is members on 1 species)
What does species diversity include?
species richness
number of individuals of each species
more evenly distributed data= more species diversity
What does genetic diversity include?
mutation (only one on list that is also for a-sexually producing)
meiosis
random fusion of gametes
What is species richness?
the number of different species in a habitat
What is species diversity index?
A number used to describe species diversity. This diversity of a community reflects:
number of different species present
number of individuals in each species
Helps us to make an objective assessment of diversity.
How can you calculate diversity index?
D= N(N-1) /
sum of n(n-1)
This is always given you just need to remember:
N= total number of organisms in all species
n= total number of organisms of a particular species
D= diversity index
What is the correlation for diversity index?
the larger the value of D, the greater the diversity
the lowest possible value of D is 1
Explain why it is more useful to calculate the diversity index rather than just record the number of species present (species richness)
it measures the number of individuals in each species as well as the number of species and takes into account the fact that some species may be present in very low or high numbers
When would you use diversity index?
to compare diversity of different habitats or the same habitat over time
What does a low value of diversity index mean? In terms of Nature of environment, and explain
ENVIRONMENT:
Unfavourable/ harsh/ agricultural land/ polluted habitat (e.g. desert, Arctic tundra, upper seashore, wheat field, polluted river etc.)
EXPLANATION:
Few species present and populations are small
Generally abiotic factors determine which species present
Ecosystems unstable
Only few species are adapted to survive harsh conditions
What does a high value of diversity index mean? In terms of Nature of environment, and explain
ENVIRONMENT:
Favourable/ ancient/ stable (e.g. tropical rainforest, temperate woodland, lower seashore etc.)
EXPLANATION:
Many species present and large populations
Generally biotic factors (like competition and predation) determine which species present
Ecosystems usually stable
Complex food webs so a change in population of 1 species is less likely to affect other populations
How can we ensure sampling is representative?
large sample size
Why should sampling be random?
avoids bias
Describe a random sampling method using quadrats (5 marks)
A grid is laid out across sample area using tape measures.
A random number generator (from a random number table) provides coordinates on the grid. These are the sample points where to a frame quadrat is placed.
Within each quadrat the community is sampled, each organism in the quadrat is identified and the number of individuals of each species is counted.
As any 1 sample is unlikely to be representative of the area, a large number of randomly placed quadrats are used.
Mean number of each species can then be calculated.
How many quadrats are needed to give a representative sample?
at least 20 quadrats
What is monoculture?
modern intensive farming which involves the removal of existing vegetation and the growth of one crop species
aim to provide ideal conditions for crop to grow and supply a high yield
How does agriculture provide ideal conditions for crop photosynthesis, growth and harvesting maximum yield?
fertilisers added to provide minerals such as nitrates for growth
fields irrigated so there is enough water
the crop species themselves are specifically selected to grow well in the conditions provided and to provide high yields of the useful product
weeds, which are unwanted plants that would compete with the crop plants, are removed/ killed using herbicides
animal pests, such as insects that would eat the crop plants, are killed by insecticides
Why do farmers remove hedgerows/ field boundaries, unprofitable woodland, and drain marshy areas?
to make maximum use of land for crops
to remove sources of pests and disease
How and why does human activites, particularly agriculture, affect the species diversity of an area?
lowers species diversity
a lower variety of habitats/ niches
fewer plant species because just 1 crop species grown and most weeds removed or killed by herbicides
few species of herbivores as so little variety of plant food types
fewer types of carnivore species because so few herbivore species to feed on
use of pesticides will reduce diversity of insect species
How can you find a balance between observation and farming?
plant hedges as field boundaries not fences
maintain ponds and where possible create new ones
let wet corner of fields rather than drain them
plant native tree species on land with a low species diversity
reduce use of pesticides
use organic fertilisers
use crop rotations that includes a nitrogen-fixing crop to improve soil fertility
leave the cutting of verges and field edges until after flowering and when seeds have dispersed
introduce conservation headlands
What is genetic diversity?
refers to the number of different alleles of genes in a population (members of the same species)
Why does genetic diversity matter?
members of same species have the same genes yet are still different
there are differences within species due to different alleles
Define a gene
the sequence of DNA bases that codes for a polypeptide
Define an allele
a different version of a particular gene
What is a gene pool?
the set number of alleles a species can possess
the bigger the gene pool, the greater variation within that species
the greater the variation, the better chances of survival of that species as they can adapt to change in environment better
What are the causes of genetic diversity?
mutations
meiosis
random fusion of gametes
Which of these methods is the only way asexually reproducing organisms show variation?
mutation
Explain how a gene mutation could result in the production of a non-functioning protein (6 marks)
A gene is the sequence of bases in DNA that codes for production of specific polypeptide
If the sequence of DNA bases is altered in a gene then this will change the sequence of bases in the mRNA that is transcribed
This may change the sequence of amino acids in the protein
This change in primary structure of the protein causes a change in tertiary structure as hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds form in different places
This can lead to a loss or reduction in function of the protein
Why would this prevent an enzyme functioning? - carried on from mutations resulting in non-functioning protein (3 marks)
active site changes shape, substrate no longer complementary, so fewer/ no E-S complexes form
What do mutations include?
arise spontaneously
base deletion
base substitution
What can increase rate of gene mutation?
mutagenic agents
What are the key features of meiosis?
DNA replicates itself but there are 2 nuclear divisions, so 4 daughter cells are formed
The daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes (haploid)
When male and female gametes join during fertilisation, diploid number is restored, so meiosis ensures that the chromosome number is kept constant from 1 generation to the next
What is the haploid number in humans?
23
What is the name given to the number of chromosomes found in a body cell?
diploid
What happens during meiosis I?
homologous pairs separate and the cells become haploid
What happens during meiosis II?
centromere breaks and chromatids separate
What is chromosome non- disjunction?
sometime homologous chromosomes or chromatids don’t separate properly during meiosis and both chromosomes of a pair go into the same cell
as a consequence, after fertilisation zygotes can end up with an extra copy of a particular chromosome
What is down’s syndrome a result of?
chromosome non- disjunction
extra chromosome 21 (shortest chromosome)
can survive with extra 21 as it codes for shorter polypeptides?
How does meiosis lead to variation in gametes?
Provides opportunities for new combinations of alleles to occur in gametes
independent segregation
crossing over
What is independent segregation of homologous chromosomes?
when homologous chromosomes line up along the equator, their orientation is completely random
separation results in different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the gametes formed
a cell that has ‘n’ pairs of chromosomes has 2^n different numbers of combinations at the end of meiosis
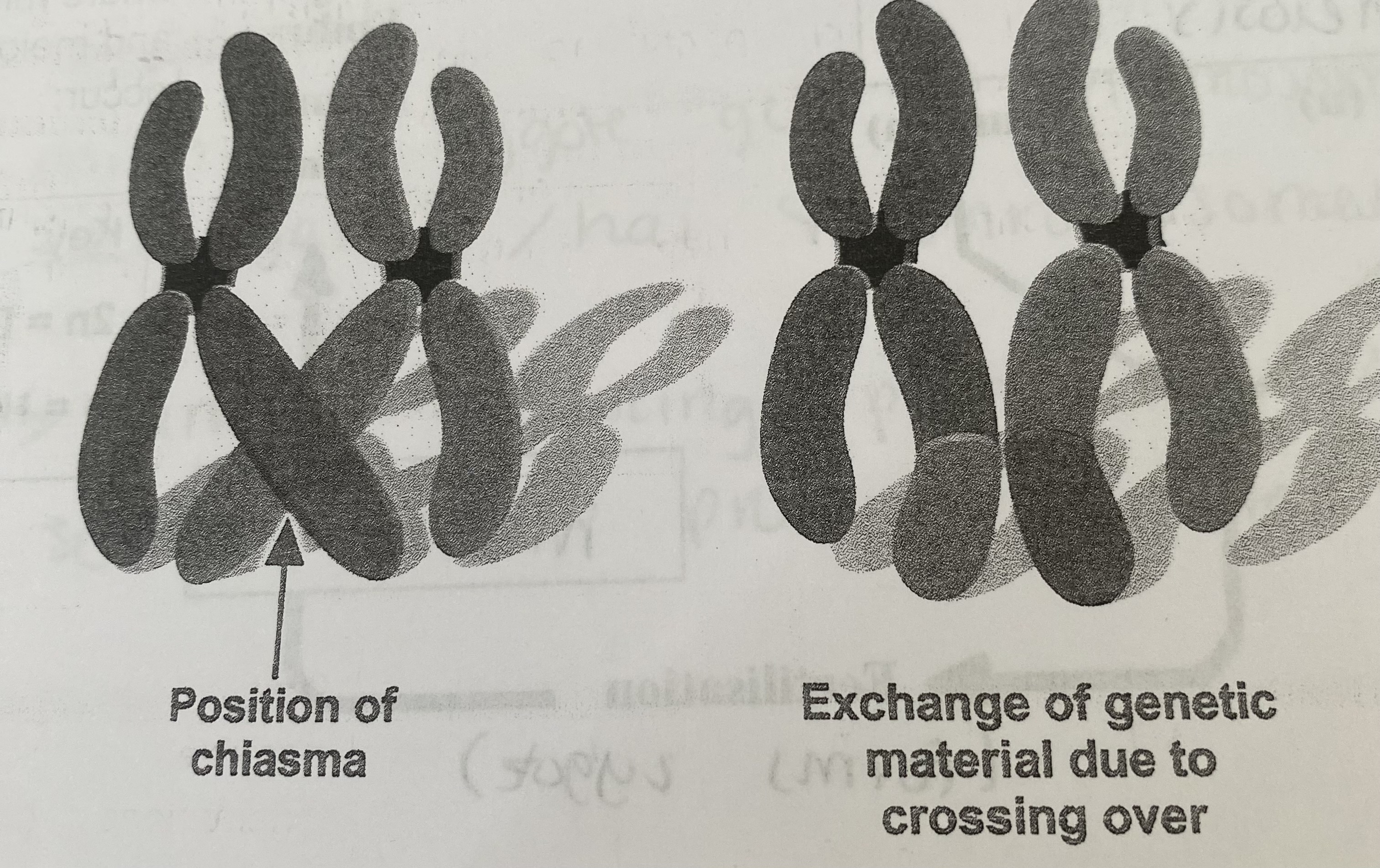
What is crossing over of homologous chromosomes?
when homologous pairs associate, in meiosis I, they form a bivalent and one chromatid of each chromosome becomes wrapped around each other at points called chiasmata
this causes sections of each chromatid to break off and rejoin the chromatid of the homologous partner (crossing over)
alleles are exchanged and genetic recombination occurs
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis? (6 marks)
MITOSIS:
1 division, forming 2 daughter cells
number of chromosomes remains the same (haploid to haploid) or (diploid to diploid)
no crossing over
no pairing of homologous chromosomes- no independent assortment
daughter cells have identical genes to parent cell
MEIOSIS:
2 divisions, forming 4 daughter cells
number of chromosomes halves (diploid to haploid)
crossing over occurs
homologous chromosomes pair up, allowing independent segregation
daughter cells are genetically different to parent cell