A&P II - Exam 6 (Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance and the Reproductive System)
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
electrolytes
substances that dissociate in water to form ions
nonelectrolytes
substances that do not dissociate in water
interstitial
spaces between cells
extracellular
the fluid compartments outside the cell (consists of the blood plasma + interstitial fluid)
intracellular
fluid compartments located IN the cell
edema
an atypical accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space
hypoproteinemia
a condition of unusually low levels of plasma proteins resulting in tissue edema
Addison's disease
a disorder which affected President Kennedy entailing deficient mineralocorticoid hormone production by the adrenal cortex
aldosterone
regulates sodium ion concentrations in the extracellular fluid
hyponatremia
a condition due to excessive water intake that results in net osmosis into tissue cells and leads to severe metabolic disturbances
sodium
ion whose levels are highest in the blood plasma
potassium, phosphate, protein
ions/substances whose levels are highest in the intracellular fluid
bicarbonate
ion whose levels are highest in the interstitial fluid
least
because fat is hydrophobic, adipose tissue is one of the (least/most) hydrated of all tissues in the human body
potassium
the most abundant cation in intracellular fluid
sodium
the most abundant cation in extracellular fluid
T
T/F Because they dissociate into ions, electrolytes have a greater impact on fluid osmolality than non-electrolytes.
F
T/F Solutes, regardless of size, are able to move freely between compartments because water carries them along osmotic gradients.
T
T/F Particle size limits solutes' ability to diffuse.
hypothalamus
where the thirst center in the brain is located
endocrine
dehydration can be caused by ________________ disturbances (such as diabetes mellitus or insipidus) because too little blood sugar or ADH can result in water loss
dehydration
water imbalance in which output exceeds intake, causing an imbalance in body fluids
low
hypoproteinemia reflects a condition of unusually (low/high) levels of plasma proteins and causes tissue edema
T
T/F As the sodium content of the body is altered, its concentration in the ECF over the short term remains stable because of immediate adjustments in water volume.
T
T/F Sodium is pivotal to fluid and electrolyte balance and to the homeostasis of all body systems.
loop of Henle
when aldosterone release in inhibited, sodium reabsorption cannot occur beyond the ________ ____ __________
sodium, potassium
aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of _____________ while enhancing _________________ secretion
high
aldosterone is secreted in response to (low/high) extracellular potassium
T
T/F To remain properly hydrated, water intake must equal water output.
excrete
the main way the kidneys regulate potassium ions is to (reabsorb/excrete) them
atrial natriuretic peptide
hormone that vasodilates and inhibits nearly all mechanisms that promote sodium and water retention in order to lower blood pressure and blood volume
sodium chloride
premenstrual edema may be due to enhanced reabsorption of _____________ ______________
T
T/F Heavy consumption of salt substitutes high in potassium can present a serious clinical problem when aldosterone release is not normal.
- (because aldosterone excretes K+ and high levels of K+ can stop organ function)
hypo
(hypo/hyper)calcemia causes muscle tetany, which is muscle cramps or spasms
hyper
(hypo/hyper)calcemia causes muscle weakness
parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
the two hormones responsible for the regulation of calcium
parathyroid hormone, calcitonin
___________________ ______________ targets the bones and causes the release of calcium from storage when serum levels are low, ______________ opposes this
7.35-7.45
normal pH range of blood
cellular metabolism
most acidic substances (hydrogen ions) originate as by-products of ______________ _________________
weak, strong
(weak/strong) acids are able to act as chemical buffering systems for the body because they weakly dissociate/bind H+ more tightly, whereas (weak/strong) acids dissociate almost completely
bicarbonate buffer system
the most important blood buffer system
T
T/F One of the most powerful and plentiful sources of buffers is the protein buffer system.
decreases, up
as ventilation increases and more carbon dioxide is removed from the blood, the H+ concentration of the blood (decreases/increases) and pH goes (down/up)
respiratory and renal
the two systems that regulate the acid-base system in the body
respiratory
acid-base regulation system that is short term
renal
acid-base regulation system that is long term
usually
severe damage to the respiratory system will (rarely/usually) result in acid-base imbalances
respiratory acidosis
the result of lung obstruction and gas exchange inefficiency (because the body cant get rid of CO2)
alkalosis
prolonged hyperventilation can cause (acidosis/alkalosis) because the body is getting rid of too much CO2
F
T/F Thirst is always a reliable indicator of body water need.
T
T/F Thirst is not always a reliable indicator of body water need because a little bit of water can calm oral and gastric stretch receptors and dampen thirst perception, but the body might still be dehydrated.
depression, overexcitement
blood acidity results in (depression/overexcitement) of the CNS, whereas blood alkalosis results in (depression/overexcitement) of the CNS
sodium
the body's water volume is closely tied to the level of ______________ ions
hypotonic hydration
a condition that may result from renal insufficiency or drinking extraordinary amounts of water
aldosterone
hormone important in the regulation of sodium ion concentrations in the extracellular fluid
atrial natriuretic peptide
hormone made in the atria of the heart that reduces blood pressure and blood volume by inhibiting sodium and water retention
acidosis
respiratory ______________ can occur when a person's breathing is shallow due to obstruction
lungs and kidneys
the two organs that function as the most important physiological buffer systems
T
T/F Essential roles of salts in the body include neuromuscular activity, membrane permeability, and secretory activity.
- do NOT include the anabolism of proteins
aldosterone
hormone that exerts primary control over sodium levels in the body
plasma
fluid link between the internal and external environments in the body
sodium
newborn infants have a relatively higher _____________ content in their ECF than do adults, causing them to retain more water which gives the appearance of "baby fat"
potassium
whereas sodium is found mainly in the extracellular fluid, most __________________ is found in the intracellular fluid
K, Na
(K/Na)+ mainly in the cells, (K/Na)+ mainly in the body fluids
kidneys
problems with fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance are particularly common in infants because of their inefficient ______________
blood plasma
the single most important factor influencing potassium ion secretion is potassium ion concentration in ___________ ___________
bicarbonate
the term "alkaline reserve" is used to describe the ___________________ buffer system
respiratory acidosis
a falling blood pH and rising partial pressure of carbon dioxide due to pneumonia or emphysema indicates __________________ _______________
osmotic and hydrostatic
the movement of fluids between cellular compartments is regulated by _____________ _____ ___________________ forces
vasoconstriction
ANP inhibits mechanisms that promote (vasodilation/vasoconstriction)
T
T/F Intrinsic methods for regulating the hydrogen ion concentration of the blood include chemical buffer systems, respiratory changes, and renal mechanisms.
- diet modification is NOT an intrinsic method
T
T/F Bicarbonate, phosphate, and protein are all chemical buffer systems.
- there is no nucleic acid buffer system
extracellular
lymph and interstitial fluid, blood plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid help compose the __________________ fluid of the human body
intracellular
the cytoplasm of blood cells is part of the ____________________ fluid in the human body
T
T/F Electrolytes have greater osmotic power than nonelectrolytes and therefore have the greatest ability to cause fluid shifts.
F
T/F Nonelectrolytes are insignificant factors in directing fluid shifts. Electrolytes are not as important as proteins in regulating fluid shifts. Ionic charge balance has no role in electrolyte movement and fluid shifts.
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
hormone that is important in stimulating water conservation in the medullary portion of the collecting duct
pH
the maintenance of the proper _____ of the body fluids may be the result of the control of respiratory ventilation
T
T/F Disorders of water balance include hypotonic hydration (where Na+ content is normal but water content is high), edema or tissue swelling (usually due to increased capillary hydrostatic pressure), and excess water in interstitial spaces (due to a low level of plasma proteins).
T
T/F Excessive hydration due to inadequate ADH secretion is NOT a disorder of water balance because inadequate ADH secretion would cause dehydration.
blood pressure
the regulation of sodium is linked to __________ _______________
metabolic acidosis
if blood analysis indicates a low pH, and the patient is breathing rapidly, the patient is most likely experiencing ________________ ______________
metabolic alkalosis
if a patient is breathing slowly and blood pH analysis indicates an abnormally high value, the most likely diagnosis is _________________ ______________
respiratory alkalosis
a high pH and a patient breathing rapidly would indicate ___________________ ______________
respiratory acidosis
a low pH and a patient breathing slowly would indicate __________________ ______________
osmolality
one of the major physiological factors that triggers thirst is a rise in plasma ________________
volume
consuming a large amount of salt results in a temporary increase in blood _____________ because the salt is absorbed into the blood, and water follows
hydrostatic
the dominant force causing net water flow across capillary walls is _________________ pressure of capillary blood
T
T/F Membrane polarity, neuromuscular excitability, and maintenance of osmotic relations between cells and ECF all depend on the presence of electrolytes.
- urea production does NOT depend on the presence of electrolytes
aldosterone
the regulation of potassium balance involves _________________-induced secretion of potassium
diploid
cell with 46 chromosomes (found near the basal lamina/outer surface of the seminiferous tubule)
haploid
cell with 23 chromosomes (found near the lumen of seminiferous tubule)
sustentacular (Sertoli) cell
supporting cells surrounding developing sperm cells
blood testes barrier
barrier of tight junctions that isolates sperm cells from the immune system
acrosome
starred portion of figure
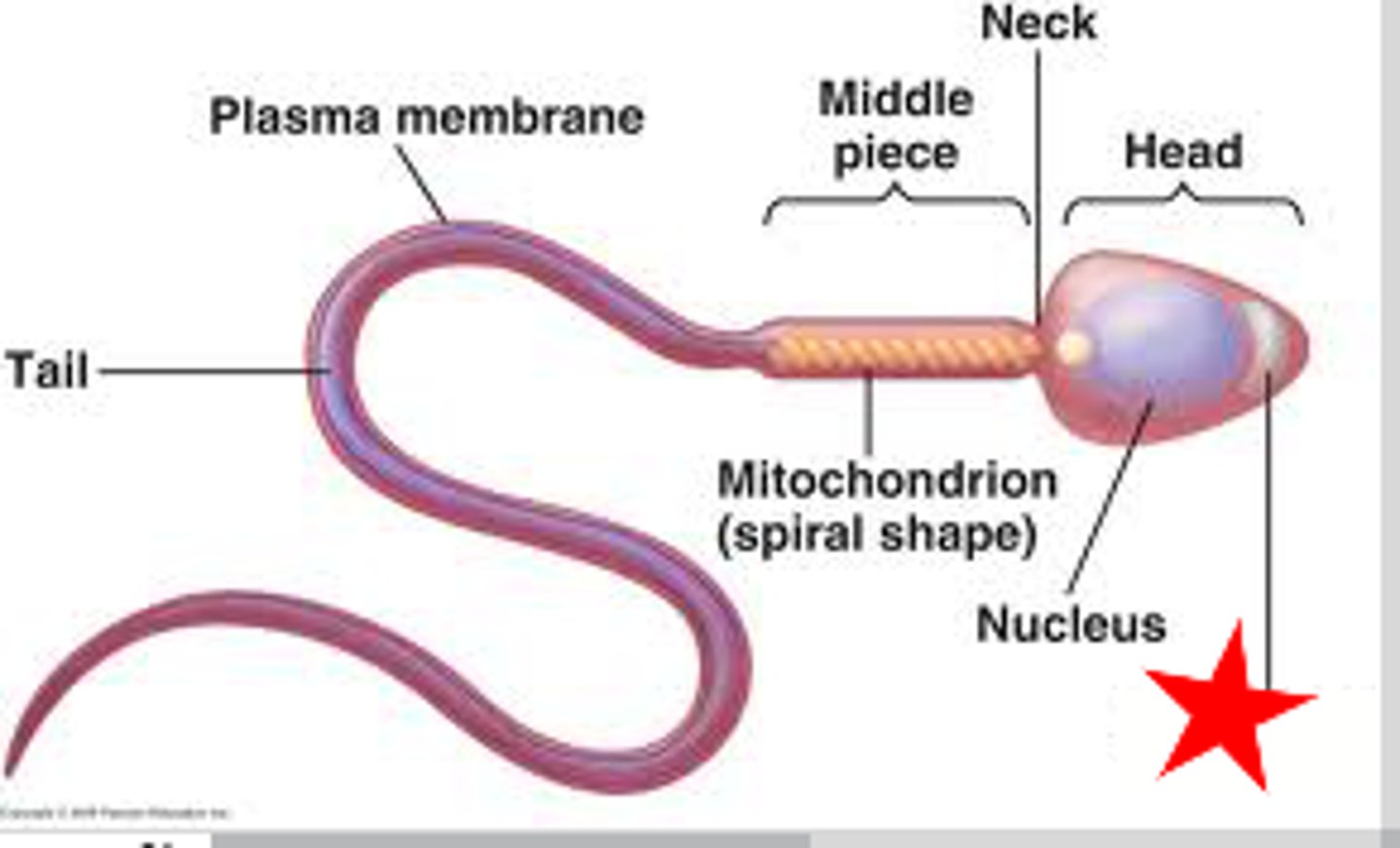
acrosome
region at the tip of a sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes that facilitate penetration of the egg
midpiece
part of sperm cell that contains mitochondria
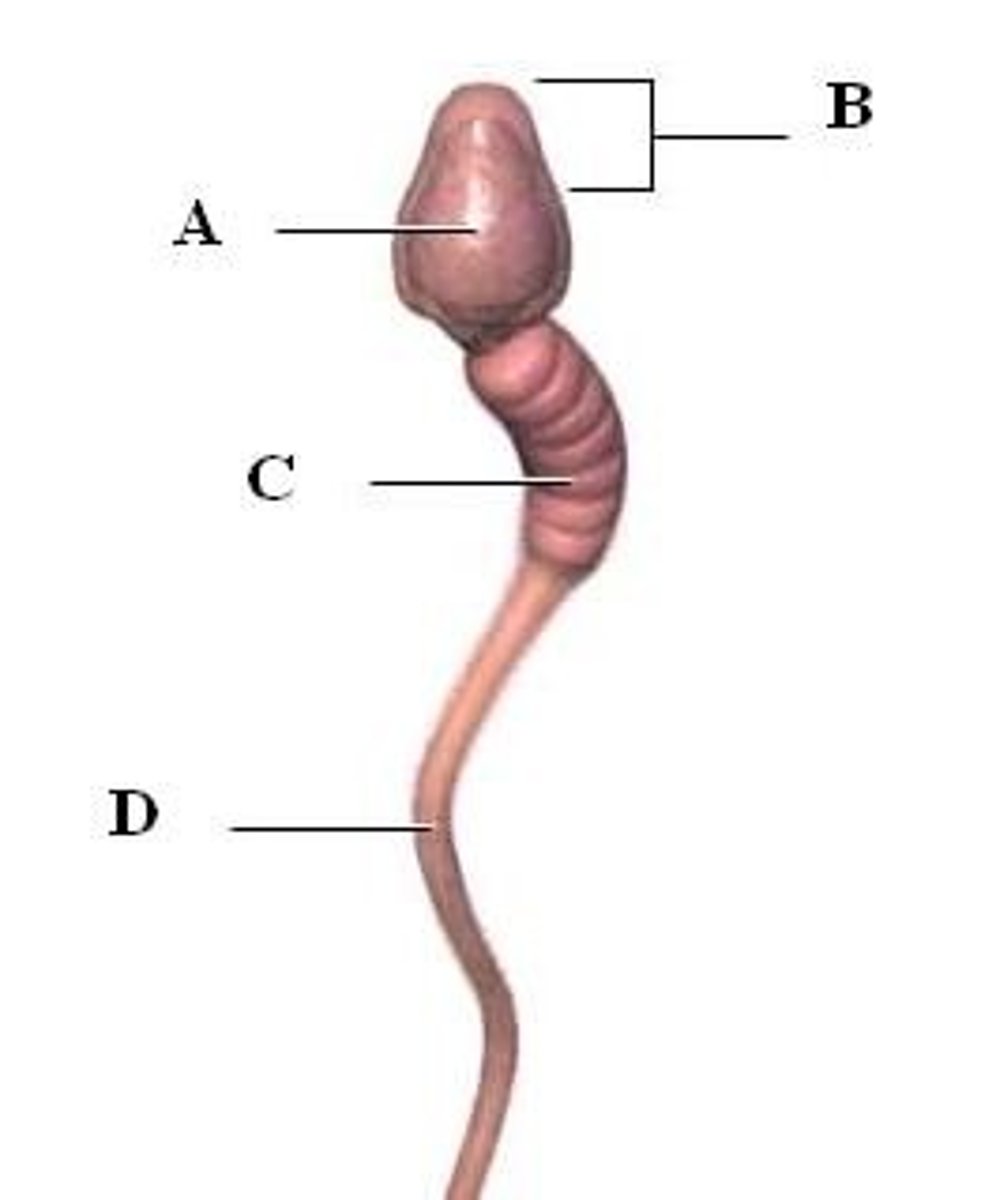
midpiece
C
nucleus
line labeled ?
the control center of the sperm cell, part of the head
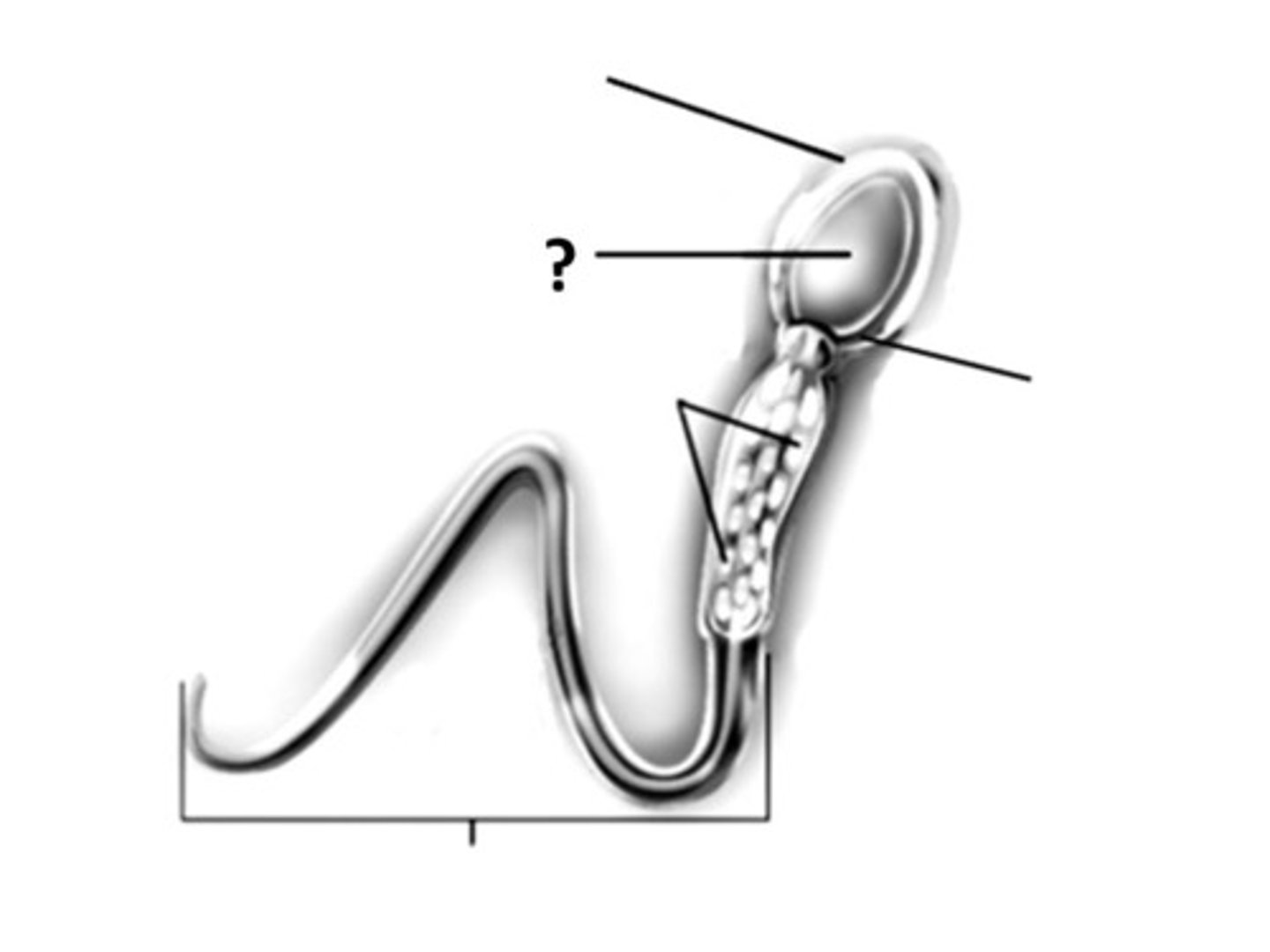
nucleus
area of compacted DNA in the sperm cell