2B LIPIDS AND RELATED SYSTEMS: CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF TRIACYLGLYCEROLS
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Fatty acids
• Most contain an even number of carbon atoms.
• Carbon chain length is up to 24 carbon atoms.
SATURATED
No double bonds are present in the carbon chain
SATURATED
Dietary effect is an increase in heart disease risk
Monounsaturated
One double bond is present in the carbon chain
Monounsaturated
Dietary effect is a decrease in heart disease risk
Polyunsaturated
Two or more double bonds are present in the carbon chain.
Polyunsaturated
Dietary effect is "mixed"; there have been several conflicting studies relative to heart disease risk.
Saturated
Monounsaturated
Polyunsaturated
Classification based on degree of unsaturation
Cis
Trans
Classification Based on Configuration of Double Bond
Cis
Naturally occurring fatty acids generally contain cis double bonds.
Trans
Hydrogenation converts trans dis double bonds to _ double bonds
Trans
fatty acids have effects on blood chemistry similar to those of saturated fatty acids
Omega-3
Omega-6
Classification Based on Location of Double Bond
Omega-3
First double bond is three carbons away from the CH, end of the carbon chain.
Omega-3
Linolenic acid (18:3) is the primary member of this family.
Omega-6
First double bond is six carbons away from the CH end of the carbon chain.
Omega-6
Linoleic acid (18:2) is the primary member of this family.
esters and alkenes
The chemical properties of triacylglycerols (fats and oils) are typical of _because these are the two functional groups present in triacylglycerols.
Hydrolysis
Saponification
Hydrogenation
Oxidation
Four important Triacylglycerols reactions
Hydrolysis
of a triacylglycerol is the reverse of the esterification reaction by which it was formed.
trimester of glycerols
three water molecules
glycerol
three fatty acids
Triacylglycerol hydrolysis
when carried out in a laboratory setting, requires the presence of an acid or a base
acidic conditions
the hydrolysis products are glycerol and fatty acids.
basic conditions
the hydrolysis products are glycerols and fatty acid salts.
digestion
Within the human body, triacylglycerol hydrolysis occurs during the process of
enzymes
Such hydrolysis requires the help of _ produced by the pancreas..
These _ cause the triacylglycerol to be hydrolyzed in a stepwise fashion.
monoacylglycerol
First, one of the outer fatty acids is removed, then the other outer one, leaving a
monoacylglycerol
most cases, this is the end product of the initial digestion (hydrolysis) of the triacylglycerol.
glycerol
enzymes remove all three fatty acids, leaving a free molecule of
enzymes
remove all three fatty acids, leaving a free molecule of glycerol
mono- and diacylglycerols
Naturally occurring _ are seldom encountermed
Synthetic mono- and diacylglycerols
are used as emulsifiers in many food products
Emulsifiers
prevent suspended particles in colloidal solutions from colloidal solutions from coaslescing and settling
Emulsifiers
are usually present in so-called fat-free cakes and other fat-free products.
complete hydrolysis
In situations where all three fatty acids are removed, the hydrolysis process is referred to as
complete hydrolysis of Triacylglycerols
produces glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
partial hydrolysis
If one or more of the fatty acid residues remains attached to the glycerol, the hydrolysis process is called
partial hydrolysis of Triacylglycerols
produced monoacylglycerol and two fatty acids
three water molecules
are required for the hydrolysis, one to interact with each of the ester linkages present in the triacylglycerol
glycerol and three fatty acids
breaking of the three ester linkages produces four product molecules
Saponification
is a reaction carried out in an alkaline (basic) solution.
glycerol and fatty acid salts
For fats and oils, the products of saponification are
First step: hydrolysis of the ester linkages to produce glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
Second step: involves a reaction between the fatty acid molecules and the base (usually NaOH) in the alkaline solution. This is an acid–base reaction that produces water plus salts:
The overall reaction of triacylglycerol saponification can be thought of as occurring in two steps
Saponification of animal fat
is the process by which soap was made in pioneer times.
Soap making
involved heating lard (fat) with lye (ashes of wood, an impure form of KOH).
lard
fat
lye
ashes of wood, an impure form of KOH
soap
Today most _ is prepared by hydrolyzing fats and oils (animal fat and coconut oil) under high pressure and high temperature.
Sodium carbonate
is used as the base
carboxylate ions
The cleansing action of soap is related to the structure of the _ present in the fatty acid salts of soap and the fact that these ions readily participate in micelle formation.
micelle formation
The cleansing action of soap is related to the structure of the carboxylate ions present in the fatty acid salts of soap and the fact that these ions readily participate in
micelle
is a spherical cluster of molecules in which the polar portions of the molecules are on the surface, and the nonpolar portions are located in the interior
surface
micelle polar portions of the molecules are on the
interior
micelle nonpolar portion of the molecules are located in the
Soaps
are carboxylic acid salts. They are thus ionic compounds, as are all salts.
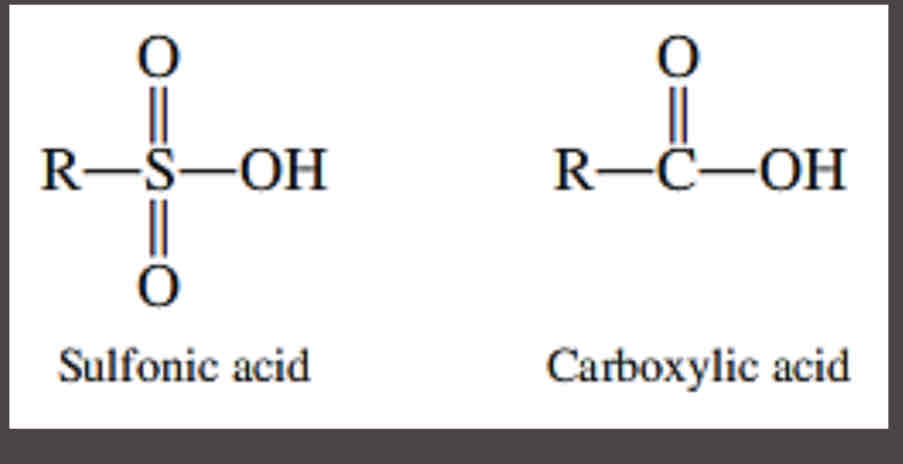
Detergents
are also acid salts. They are, however, salts of sulfonic acids rather than carboxylic acids.
Sulfonic acids
were used as substitutes for carboxylic acids
general structures for a sulfonic acids and a carboxylic acid
1) small positive ion usually Na+ or K+
2) negative ion that connotations a very long carbon chain
Structurally, both soaps and detergents contain a very small positive ion (_) and a negative ion that contains a very long carbon chain.
“active ingredient”
– The negative ion is the _ in both soaps and detergents.
salt dissociation
In aqueous solution, _occurs, which releases the salt’s constituent ions.
Salt dissociation
This allows the carboxylate ions (soaps) and sulfonate ions (detergents) present to exert their effects.
“dual polarity”
The cleansing action of soaps and detergents relates to the_ that carboxylate and sulfonate ions possess.
tail
The long carbon chain present, which is called the _ of the ion, is nonpolar,
head
the small oxygen-containing group present, which is called the “_” of the ion, is polar.
nonpolar tail
long carbon chain
polar head
oxygen- containing group
Nonpolar substances
, such as fats, oils, and greases, are insoluble in water.
Soap or detergent
affects the solubility of such substances in water.
nonpolar “tail”
The _of the soap or detergent molecule interacts with (dissolves in) the insoluble nonpolar substance
polar “head”
of the soap or detergent molecule interacts with polar water molecules.
nonpolar -polar solubility
The soap or detergent thus overcomes the _ barrier
nonpolar portion of the carboxylate or sulfonate ion
dissolves in the nonpolar oil or grease
polar portion
maintains its solubility in the polar water.
formation of micelles
The penetration of the oil or grease by the nonpolar end of the carboxylate or sulfonate ion is followed by the
carboxyl sulfonyl groups (the micelle exterior) and water molecules
are attracted to each other, causing the solubilizing of the micelle.
carboxyl sulfonyl groups
the micelle exterior
micelles
do not combine into larger drops because their surfaces are all negatively charged, and like charges repel each other.
water-soluble micelles
are subsequently rinsed away, leaving a material devoid of oil and grease
Hydrogenation
is a chemical reaction that involves hydrogen addition across carbon–carbon multiple bonds, which increases the degree of saturation as some double bonds are converted to single bonds.
melting point
Hydrogenation
• With this change, there is a corresponding increase in the _of the substance
Hydrogenation
involving just one carbon–carbon bond within a fatty acid residue of a triacylglycerol
oleic acid 18:1
The structural equation for the complete hydrogenation of a triacylglycerol in which all three fatty acid residues are
partial hydrogenation
Many food products are produced via
partial hydrogenation
some, but not all, of the double bonds present are converted into single bonds.
partial hydrogenation
In this manner, liquids (usually plant oils) are converted into semi-solid materials.
partial hydrogenation
Peanut butter is produced from peanut oil through
partial hydrogenation
Solid cooking shortenings and stick margarine are produced from liquid plant oils through
partial hydrogenation
Soft-spread margarines are also _products.
refrigerator temperatures (48C)
Here, the extent of hydrogenation is carefully controlled to make the margarine soft at
Concern
has arisen about food products obtained from hydrogenation processes because the hydrogenation process itself converts some cis double bonds within fatty acid residues into trans double bonds, producing trans unsaturated fatty acids.
hydrogenation process
converts some cis double bonds within fatty acid residues into trans double bonds, producing trans unsaturated fatty acids
trans unsaturated fatty acids
hydrogenation process itself converts some cis double bonds within fatty acid residues into trans double bonds, producing
partially hydrogenated vegetable oils
play a role in raising blood cholesterol
(1) some of the cis double bonds present are converted to single bonds (the objective of the process) and
(2) some of the remaining cis double bonds are converted to trans double bonds (an unanticipated result of the process).
When the triacylglycerols in vegetable oils are subjected to partial hydrogenation, two types of changes, rather than just one, occur in the fatty acid residues present:
some of the cis double bonds present are converted to single bonds
the objective of the process
some of the remaining cis double bonds are converted to trans double bonds
an unticipated result of the process
cis–trans conversions
These latter_ affect the general shape of the fatty acid residues present in triacylglycerols, which in turn affects the biochemical behavior of the triacylglycerols
trans double bonds
Studies show that farty acids with_affect blood cholesterol levels in a manner similar to saturated fatty acids