11. Crystal Field Stabilisation - Other Geometries
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Which orbitals are destabilised for a tetrahedral complex? How does this affect the orbital layouts for crystal stabilisation?
Orbital environments in a tetrahedral are called e and t2
They are in fact swapped around and the two e orbitals are now lower energy and the three t2 orbitals are now higher energy.
This is because with tetrahedral symmetry, the dxy, dyz and dxz orbitals are destabilised as they point towards the point charges
dx2-y2 and dz2 are stabilised this time and are the lower energy orbitals
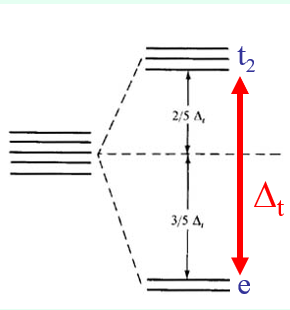
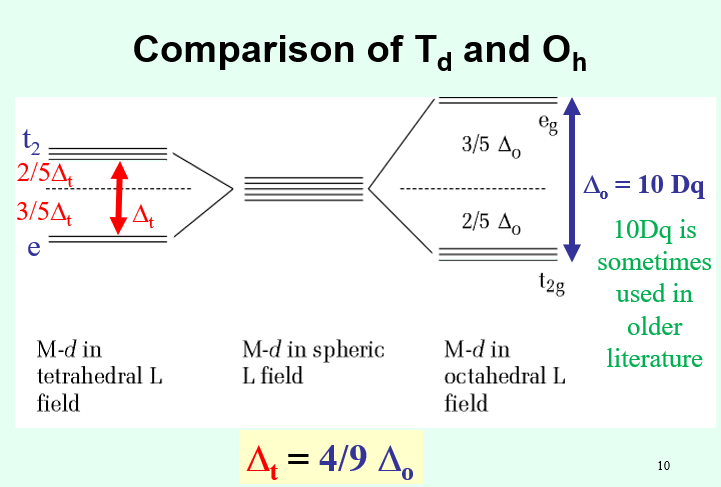
How does the field splitting in a Td system differ from Oh? What does this suggest about Td spin?
The field splitting symmetry is smaller in a Td system compared to Oh symmetry as there are only four ligands interacting with M.
Low spin configurations are rarely observed due tot his and if a strong field ligand is present, the square planar geometry will be favoured.
Δt = 4/9Δo
The smaller field splitting also implies that tetrahedral metal ions are always high spin
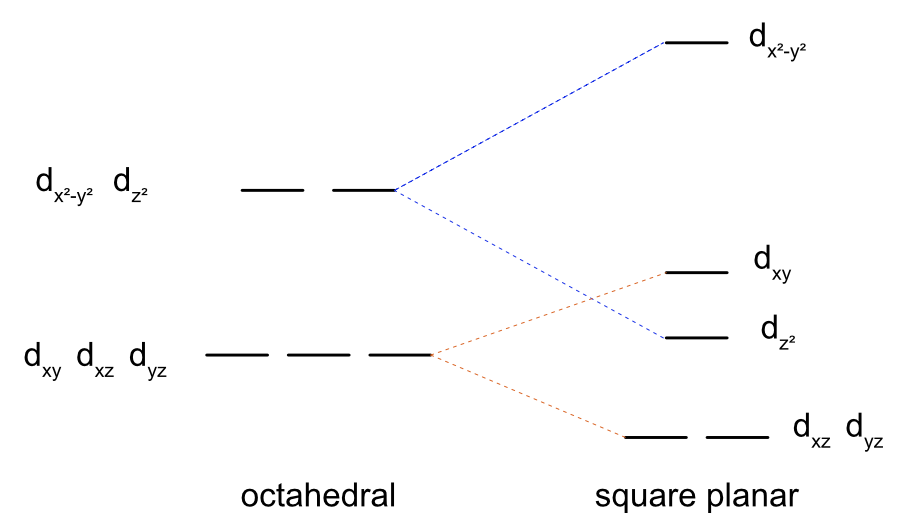
What is the crystal field splitting diagram for a square planar complex? Why does this occur? What electron orbital is this favoured for?
d8 ions favour square planar geometry with a strong field
square planar is like removing the axial ligands from an octahedral (distortion along z-axis)
so all orbitals with a z component has its energy lowered as the repulsions between electrons and the metal ion and ligand decrease .
So it makes a row of two orbitals, with two stacked on top, with the dx2-y2 orbital with a large energy gap
What magnetic property do d8 complexes have?
As all electrons spins are paired, the compound is diamagnetic
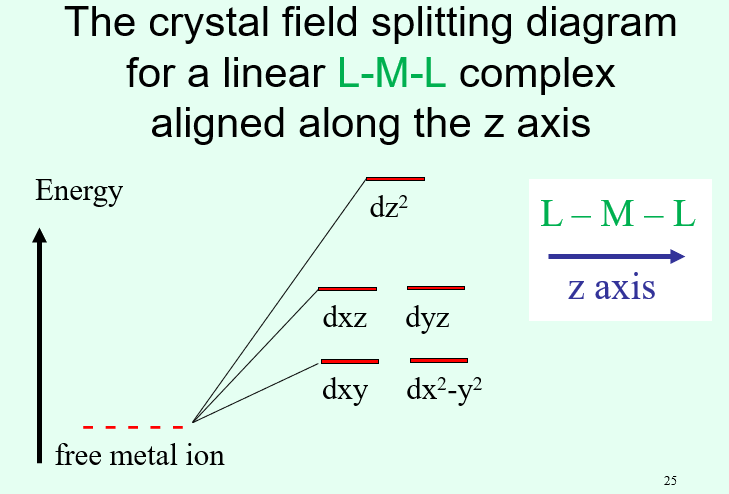
What does the crystal field splitting look like for a linear complex?