kin 365 exam 3 (hip and pelvic girdle)
5.0(1)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:20 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
posterior muscles of the hip
gluteus maximus
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
2
New cards
anterior mucles of the hip
iliopsoas
pectineus
rectus femoris
sartorius
pectineus
rectus femoris
sartorius
3
New cards
lateral muscles of the hip
gluteus medius
gluteus minimus
tensor fasciae latae
gluteus minimus
tensor fasciae latae
4
New cards
anterior muscles of the hip function primarily in ____
hip flexion
5
New cards
lateral muscles of the hip function primarily in ____
hip abduction
6
New cards
posterior muscles of the hip function primarily in ____
hip extension
7
New cards
medial muscles of the hip function primarily in ____
hip adduction
8
New cards
biarticulate hip and knee muscles
rectus femoris
sartorius
tensor fasciae latae
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
sartorius
tensor fasciae latae
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
9
New cards
iliopsoas origin (iliacus)
inner surface of the ilium
10
New cards
iliopsoas insertion (iliacus and psoas major)
lesser trochanter of the femur and the shaft just below
11
New cards
iliopsoas origin (psoas major and minor)
lower borders of the transverse processes of L1-L5
sides of bodies of last 3 thoracic, L1-L5, intervertebral fibrocartilage and base of sacrum
sides of bodies of last 3 thoracic, L1-L5, intervertebral fibrocartilage and base of sacrum
12
New cards
iliopsoas insertion (psoas minor)
pectineal line of pubis and iliopectineal eminence
13
New cards
iliopsoas muscle
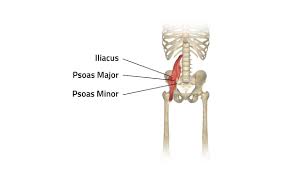
14
New cards
iliopsoas action
hip flex
anterior pelvic rot
hip external rot
contralateral transverse pelvic rot
contralateral lateral pelvic rot
anterior pelvic rot
hip external rot
contralateral transverse pelvic rot
contralateral lateral pelvic rot
15
New cards
true/false
the psoas minor works on the hip joint
the psoas minor works on the hip joint
false
16
New cards
iliopsoas strengthen
hip flexion against gravity
17
New cards
iliopsoas stretch
hip and knee extension
hip external rotation
hip external rotation
18
New cards
rectus femoris
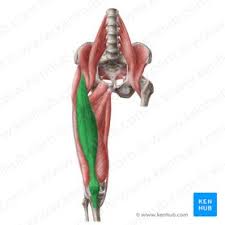
19
New cards
rectus femoris origin
anterior inferior iliac spine of ilium and posterior groove above acetabulum
20
New cards
rectus femoris insertion
superior aspect of patella and patellar tendon to the tibial tuberosity
21
New cards
rectus femoris action
hip flexion
knee extension
anterior pelvic rotation
knee extension
anterior pelvic rotation
22
New cards
true/false
the rectus femoris is biarticulate in hip and knee movement
the rectus femoris is biarticulate in hip and knee movement
true
23
New cards
the rectus femoris is a powerful ___ of the knee when the hip is ___
extender, extended
24
New cards
rectus femoris strengthen
running
jumping
hip flexion
knee extension
jumping
hip flexion
knee extension
25
New cards
the rectus femoris is the only biarticulate muscle of the ____ group
quadriceps
26
New cards
rectus femoris stretch
full flexion of knee with full extension of hip
27
New cards
sartorius
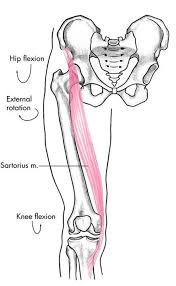
28
New cards
sartorius origin
anterior superior iliac spine and notch just below spine
29
New cards
sartorius insertion
anterior medial surface of tibia just below condyle
30
New cards
sartorius action
hip flex
knee flex
hip external rot in hip flex
hip abduction
anterior pelvic rot
knee internal rot
knee flex
hip external rot in hip flex
hip abduction
anterior pelvic rot
knee internal rot
31
New cards
the sartorius is biarticulate in ___ and ___ flexion
hip, knee
32
New cards
sartorius referred to as the ___ muscle because if it used when sitting down
tailors
33
New cards
true/false
the sartorius is the longest muscle in the body
the sartorius is the longest muscle in the body
true
34
New cards
sartorius stengthen
hip flexion
35
New cards
sartorius stretch
passive hip extension, adduction, internal rotation
knee extension
knee extension
36
New cards
pectineus
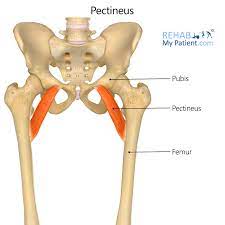
37
New cards
pectineus origin
space 1 inch wide on front of pubis just above crest
38
New cards
pectineus insertion
rough line leading from lesser trochanter down to linea aspera
39
New cards
pectineus action
hip flexion
hip adduction
hip external rot
anterior pelvic rot
hip adduction
hip external rot
anterior pelvic rot
40
New cards
the pectineus is exercised with the ___ in leg raising and lowering
iliopsoas
41
New cards
pectineus strengthen
hip flexion
hip adduction
hip adduction
42
New cards
pectineus stretch
hip abduction, extension, and internal rotation
knee in flexion
knee in flexion
43
New cards
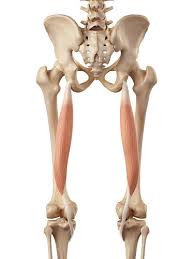
semitendinosus
44
New cards
semitendinosus origin
ischial tuberosity
45
New cards
semitendinosus insertion
anterior medial surface of tibia just below condyle
46
New cards
semitendinosus action
knee flexion
hip extension
hip internal rot
internal rot of flexed knee
posterior pelvic rotation
hip extension
hip internal rot
internal rot of flexed knee
posterior pelvic rotation
47
New cards
the semitendinosus provides ___ stability to the knee
dynamic
48
New cards
the semitendinosus is used in walking as a hip ___
extender
49
New cards
semitendinosus strengthen
hamstring curls
further emphasized with knee interal rotation
further emphasized with knee interal rotation
50
New cards
semitendinosus stretch
knee extension
hip flexion and external rotation
hip flexion and external rotation
51
New cards
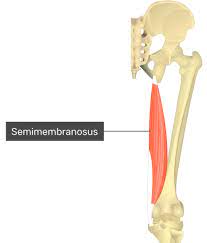
semimembranosus
52
New cards
semimembranosus origin
ischial tuberosity
53
New cards
semimembranosus insertion
posteromedial surface of the medial tibial condyle
54
New cards
semimembranosus action
knee flexion
hip extension
hip internal rot
flexed knee internal rot
posterior pelvic rot
hip extension
hip internal rot
flexed knee internal rot
posterior pelvic rot
55
New cards
semimembranosus provides dynamic ___ stability
posterior
56
New cards
semimembranosus strengthen
leg curls
57
New cards
semimembranosus stretch
knee extension
hip flexion and external rot
hip flexion and external rot
58
New cards
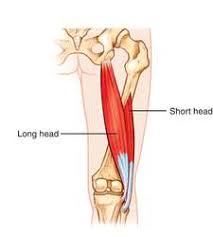
biceps femoris
59
New cards
biceps femoris origin (long head)
ischial tuberosity
60
New cards
biceps femoris origin (short head)
lower half of linea aspera and lateral condyloid ridge
61
New cards
biceps femoris insertion
lateral condyle of tibia and head of fibula
62
New cards
biceps femoris action
knee flexion
hip extension
hip external rotation
external rotation of flexed knee
posterior pelvic floor rotation
hip extension
hip external rotation
external rotation of flexed knee
posterior pelvic floor rotation
63
New cards
biceps femoris used with ___ to extend hip when knee is straight
gluteus maximius
64
New cards
the hamstring group is made up of the ___, ___, and ___
semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris
65
New cards
biceps femoris strengthen
hamstring curls
66
New cards
biceps femoris stretch
knee extension with hip flexion
67
New cards
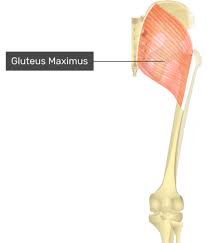
gluteus maximus
68
New cards
gluteus maximus origin
posterior 1/4 of crest of ilium, posterior surface of sacrum and coccyx near ilium, and fascia of lumbar area
69
New cards
gluteus maximus insertion
oblique ridge on the lateral surface of the greater trochanter and the iliotibialband of fasciae latae
70
New cards
gluteus maximus action
hip extension
hip external rotation
hip abduction (upper)
hip adduction (lower)
posterior pelvic rotation
hip external rotation
hip abduction (upper)
hip adduction (lower)
posterior pelvic rotation
71
New cards
gluteus maximus used after ___ of extension
15 degrees
72
New cards
true/false
the gluteus maximus is used in walking
the gluteus maximus is used in walking
false
73
New cards
gluteus maximus strengthen
hip extension from a prone position
74
New cards
gluteus maximus stretch
hip flexion
75
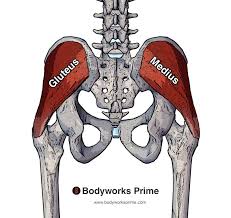
New cards
gluteus medius
76
New cards
gluteus medius origin
lateral surface of the ilium just below the crest
77
New cards
gluteus medius insertion
posterior and middle surface of the greater trochanter of femur
78
New cards
gluteus medius action
hip abduction
ipsilaterl pelvic rot
ipsilaterl pelvic rot
79
New cards
gluteus medius anterior action
hip internal rot
hip flexion
anterior pelvic rot
hip flexion
anterior pelvic rot
80
New cards
gluteus medius posterior action
hip external rot
hip extension
posterior pelvic rot
hip extension
posterior pelvic rot
81
New cards
gluteus medius strengthen
side lying hip abduction
82
New cards
gluteus medius stretch
adduction in front and behind
83
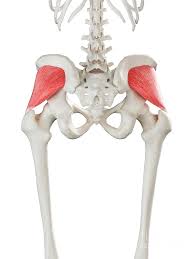
New cards
gluteus minimus
84
New cards
gluteus minimus origin
lateral surface of the ilium just below the origin of the gluteus medius
85
New cards
gluteus minimus insertion
anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur
86
New cards
gluteus minimus action
hip abduction
ipsilateral pelvic rot
internal rotation as femur abducts
hip flexion
anterior pelvic rotation
ipsilateral pelvic rot
internal rotation as femur abducts
hip flexion
anterior pelvic rotation
87
New cards
the gluteus minimus works to maintain proper hip ___ when ___
abduction, running
88
New cards
gluteus minimus strengthen
hip abduction
hip internal rot
hip internal rot
89
New cards
gluteus minimus stretch
hip adduction and external rot
90
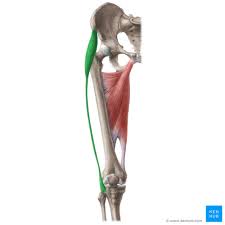
New cards
tensor fasciae latae
91
New cards
tensor fasciae latae origin
anterior iliac crest and surface of ilium just below crest
92
New cards
tensor fasciae latae insertion
1/4 way down thigh into iliotibial tract, gerdys tubercle of anterolateral tibial condyle
93
New cards
tensor fasciae latae action
hip abduction
hip flexion
ipsilateral pelvic rot
hip internal rot as hip flexes
knee external rot
anterior pelvic rotation
hip flexion
ipsilateral pelvic rot
hip internal rot as hip flexes
knee external rot
anterior pelvic rotation
94
New cards
tensor fasciae latae prevents ___ ____ of hip as it is flexed
external rot
95
New cards
tensor fasciae latae strengthen
side lying hip abduction
96
New cards
tensor fasciae latae stretch
passive hip extension