Higher Physics Particles and Waves
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
what is one order of magnitude difference?
is x10 by size (two orders is by x100)
fundamental particle
is a particle not composed of any other other particles
what are the 12 fundamental particles called?
fermions
two types of fermions
(6)quarks and (6)leptons
what are the 6 quarks?
-up
-down
-charm
-strange
-top
-bottom
what are the 6 leptons?
-electron
-electron neutrino
-muon
-muon neutrino
-tau
-tau neutrino
what are the 4 force carriers known as 'force mediators' called?
gauge-bosons
fundamental partciles table
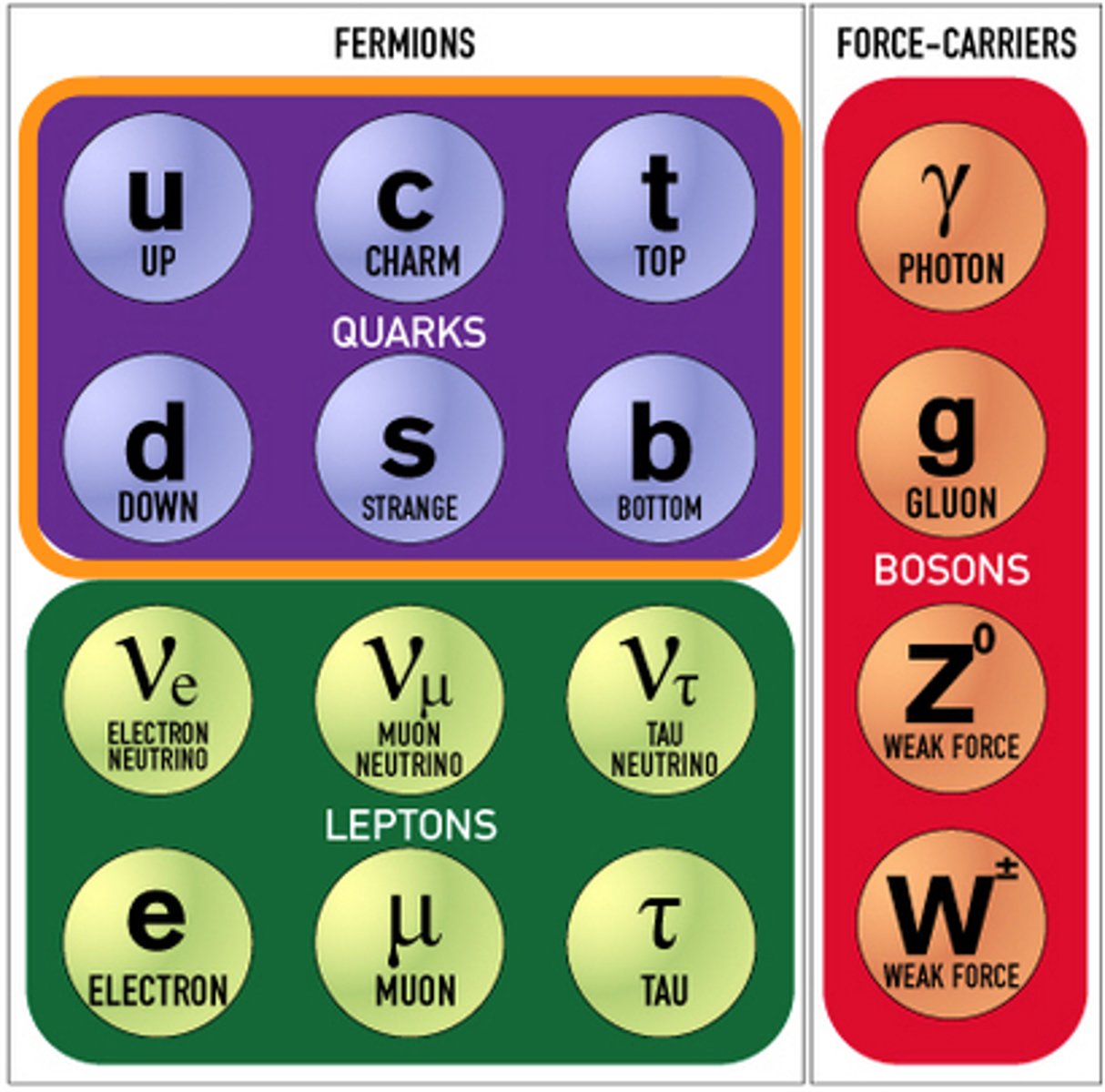
ALL the fundamental particles have corresponding ______________
antiparticles
antiparticles
have the same rest mass as the particles but the opposite charge
first antiparticle to be discovered?
the positron
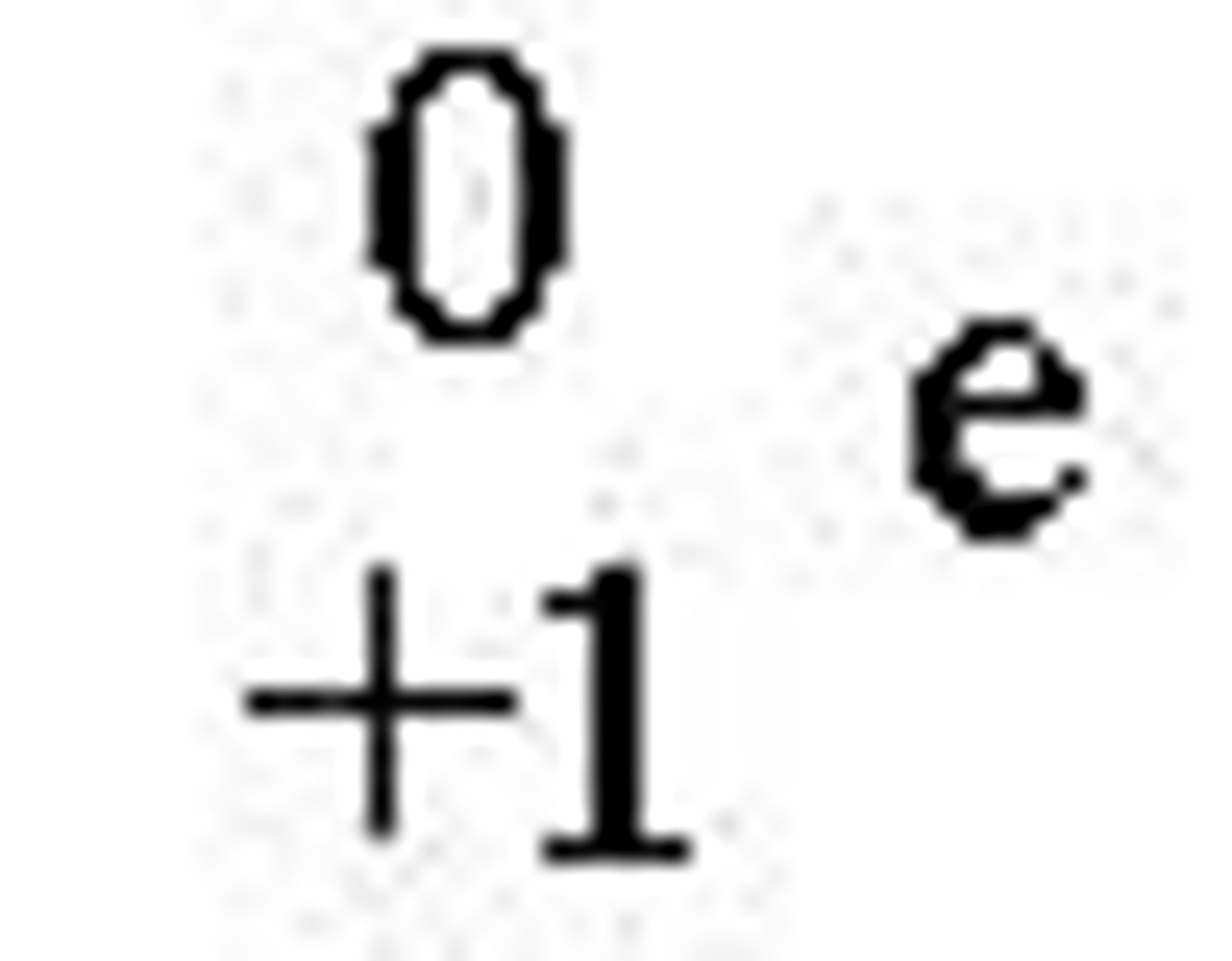
what happens when a particle and its antiparticle meet?
they will annihilate each other and their combined mass is converted into energy
hadrons
are particles made from quarks that are held together by the strong force
two types of hadron
baryon and meson
what are baryons?
made up of three quarks or three antiquarks (known as anti baryons)
what are mesons?
made up of a quark and an antiquark
baryons and mesons can only have whole _____________ charges
integer
leptons have no size and in most cases low or __ mass
no
there are __________ generations of leptons, only electrons occur in ordinary mass. muons occur in the upper atmosphere and tau only seen in lab experiments
three
what are the four forces particles may experience?
-strong (nuclear) force
-weak (nuclear) force
-gravitational force
-electromagnetic force
gauge boson for strong force
gluon
gauge boson for weak force
W and Z bosons
gauge boson for gravitational force
gravitation
gauge boson for electromagnetic force
photon
when can beta decay occur?
in an unstable nuclei where the nucleus emits an electron, leaving the nucleus with the same mass number but an increase in atomic number of 1
(beta decay) mass number is conserved the actual mass of the proton is less than the mass of the neutron, this decrease in mass results in a release of energy, available as _________ energy to the electron
kinetic
evidence for neutrino
momentum was not conserved, so concluded that another particle must be emitted, first evidence for neutrino was beta decay
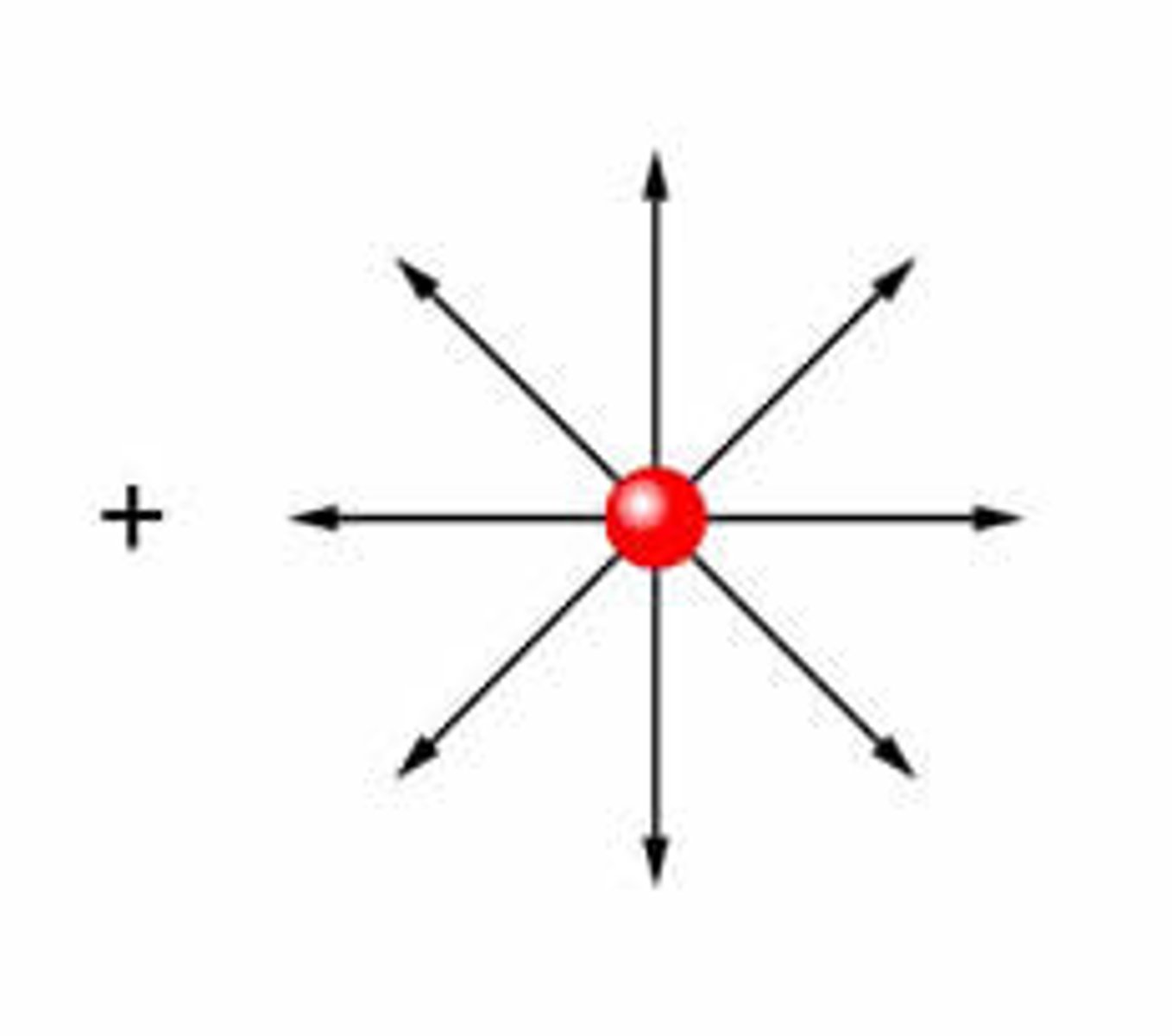
electric field
is a region where a charged particle (i.e. proton or electron) experiences a force. If the charged particle is free to move, it will accelerate in the direction of the unbalanced force
electric field of isolated positive charge
positive test charge would experience a repulsive force
electric field of isolated negative charge
negative test charge would experience a attractive force
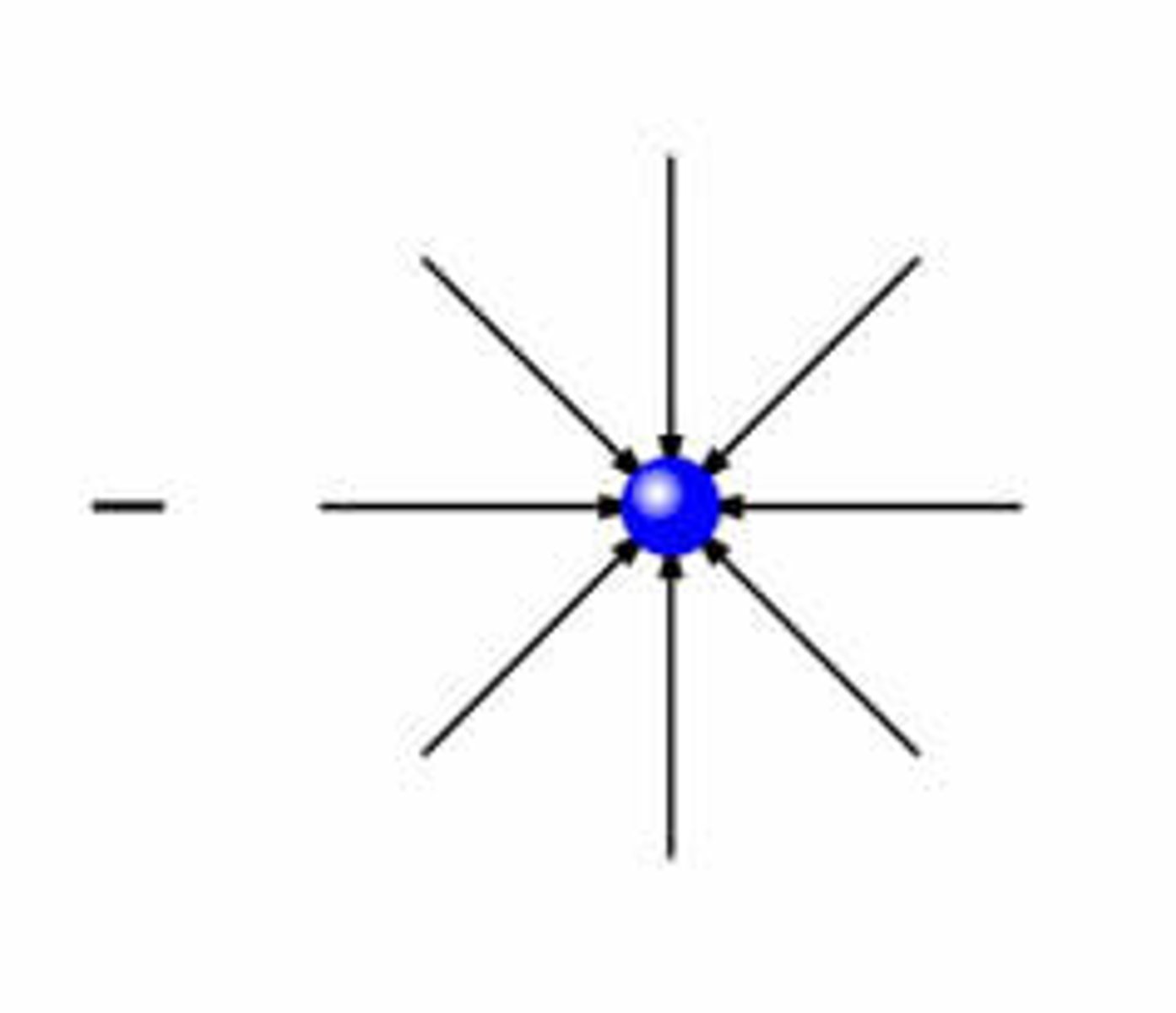
________ __ _____ when a charge is moved in an electric field
work is done
(for negative charge) to move an electron towards the negatively charged plate, energy is needed. the work done is gained by the electron as ____________ _____________ _________
electrical potential energy
(for negative charge) if electron is free to move back towards positively charged plate, electric field does work on the electron. electrons electrical potential energy is changed into _________ ________ as the electric field accelerates electron towards positive plate
kinetic energy
potential difference
the energy required to move one coulomb of charge between two points in the electric field
work done equation
Ew = Q x V
equation to work out speed of the charged particle after it has passed through the electric field
Ew by field = Ek gained by particle
Q x V = 1/2 x M x V2
v = √(2QV/m)
if the charged particles enters the field with an initial speed then its _________ _________ _________ must be added to kinetic energy gained in the field.
initial kinetic energy
magnetic fields are produced by _____________ __________
moving charges
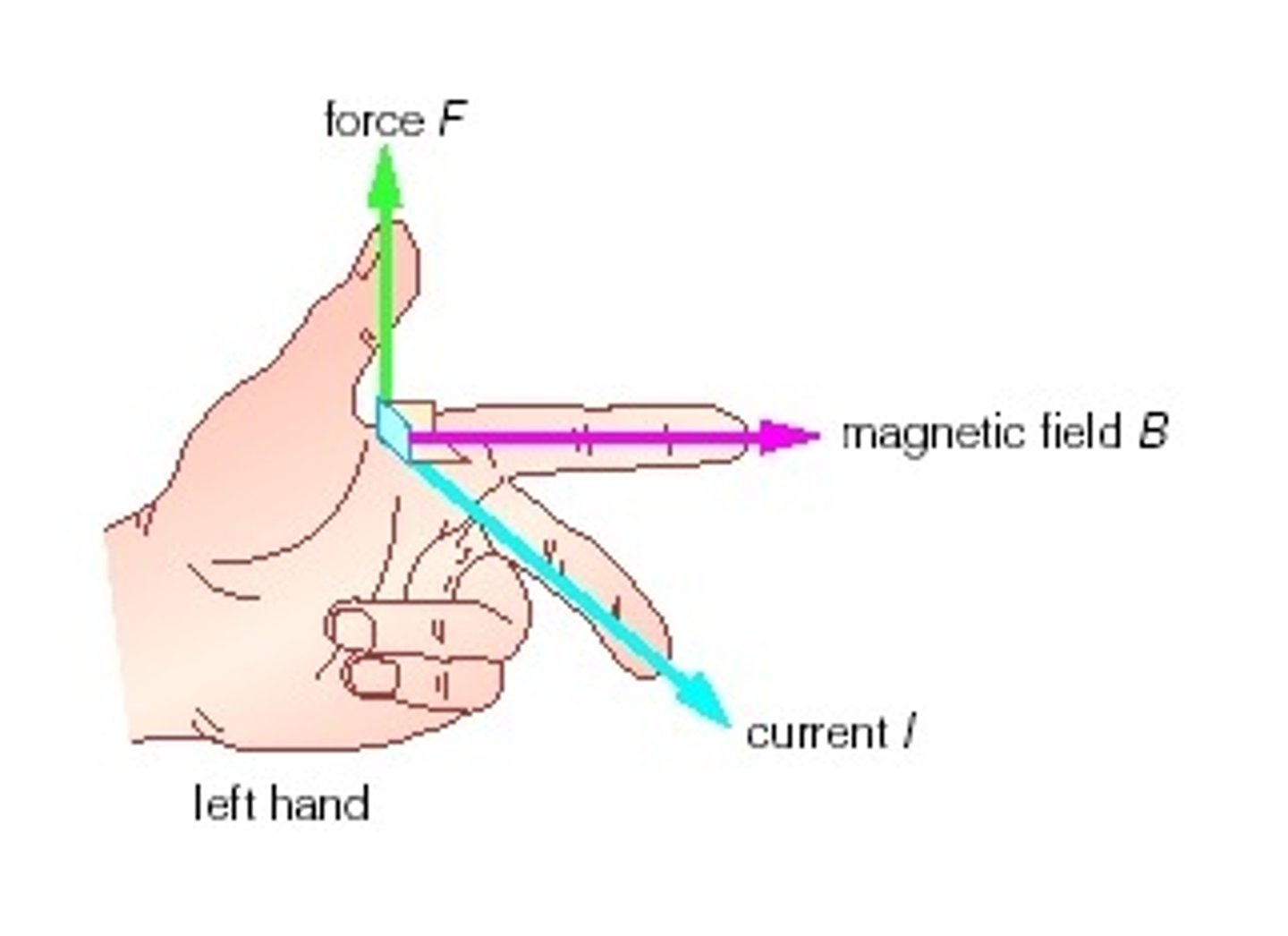
right hand rule physics
WITH RIGHT HAND (opposite for protons)
in particle accelerators ____________ _______ are used to accelerate the charged particles
electric fields
in particle accelerators _______________ _________ are used to deflect the charged particles
magnetic fields
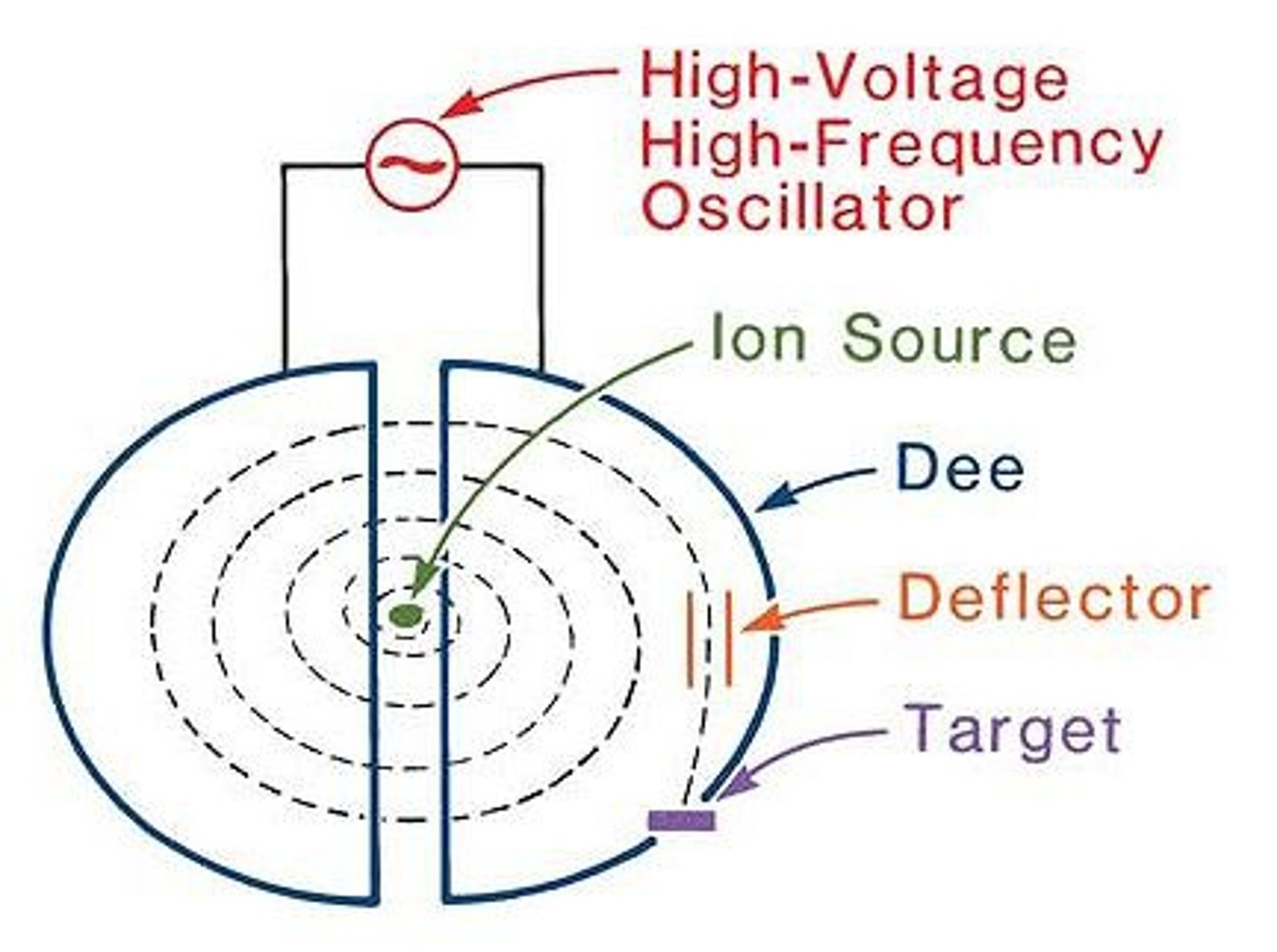
in cyclotron (particle accelerator) why is an AC supply used?
as it needs to be AC so you can always attract the particle to the opposite side
how does a cyclotron work?
ions are injected at point near the centre. AC potential difference between the 'dee' shaped electrodes accelerate the particles. a magnetic field causes the particles to move in a circular path. when particle crosses from one dee to another it accelerates. after each acceleration the particles moves to a slightly larger orbit. then extracted once it reaches the outer edge.
in a magnetic field, the mass of electron is smaller than proton so it _________ sooner
curves
what was Ernest Rutherford experiment?
alpha scattering experiment form gold foil, done in a vacuum as the alpha particle would be absorbed by air
internal structure of atoms (from Ernest exp)
-most of the atom is empty space (since most alpha particles passed straight through)
-most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in a very small central area
-the nucleus is positively charged (repels positive alpha particles)
nuclide notation
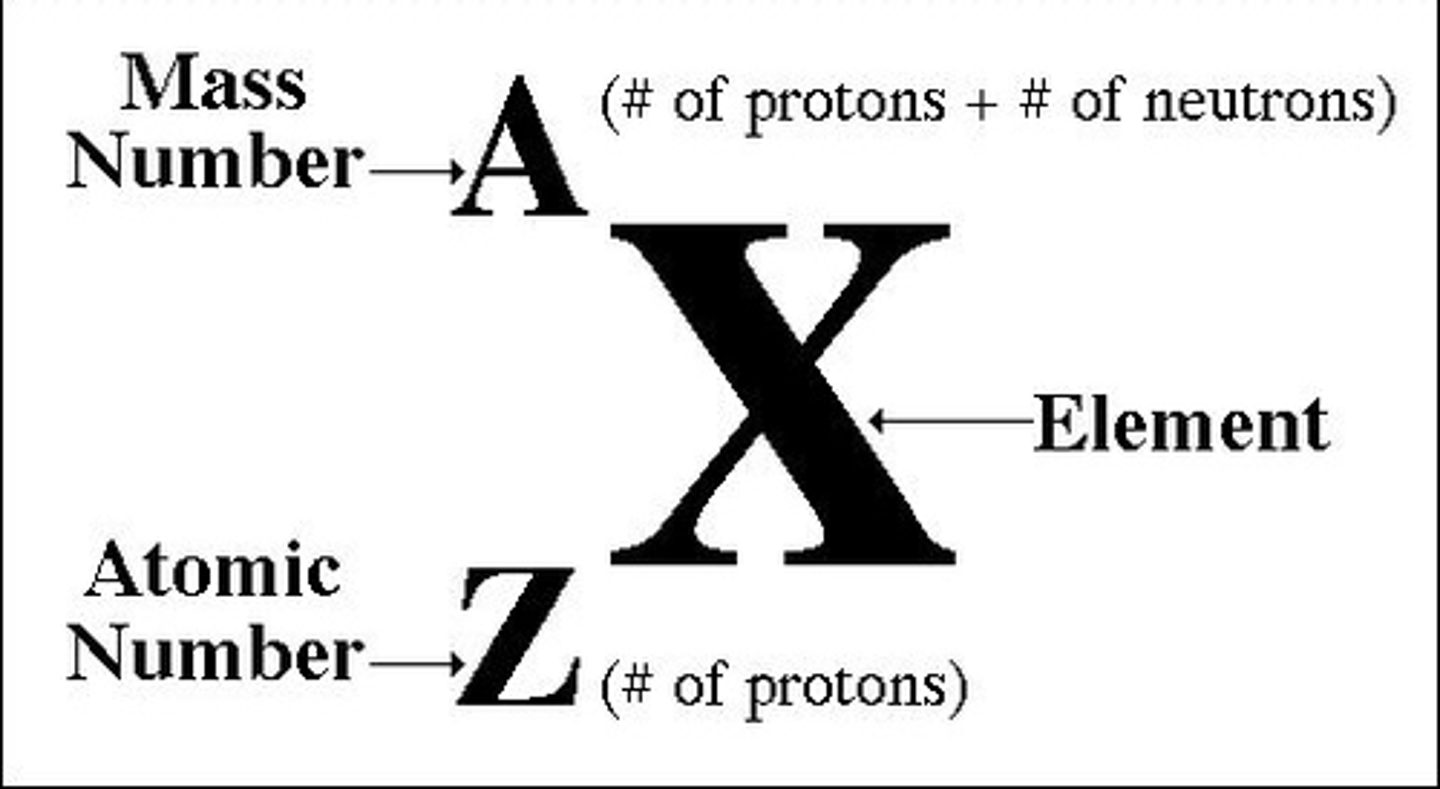
isotope
different mass numbers but same atomic number, same number of protons but different number of neutrons
alpha decay
the mass number of new atom is four less than the original. the atomic number is two less than the original
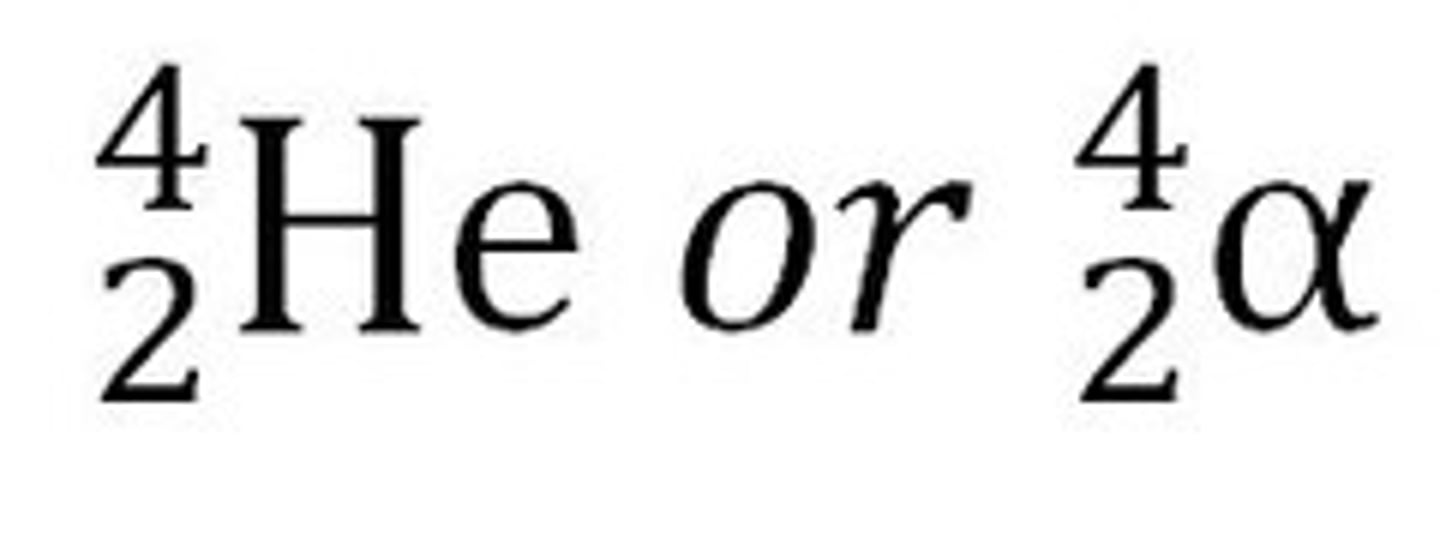
beta decay
the mass number of new atom is the same as the original. the atomic number increased by 1
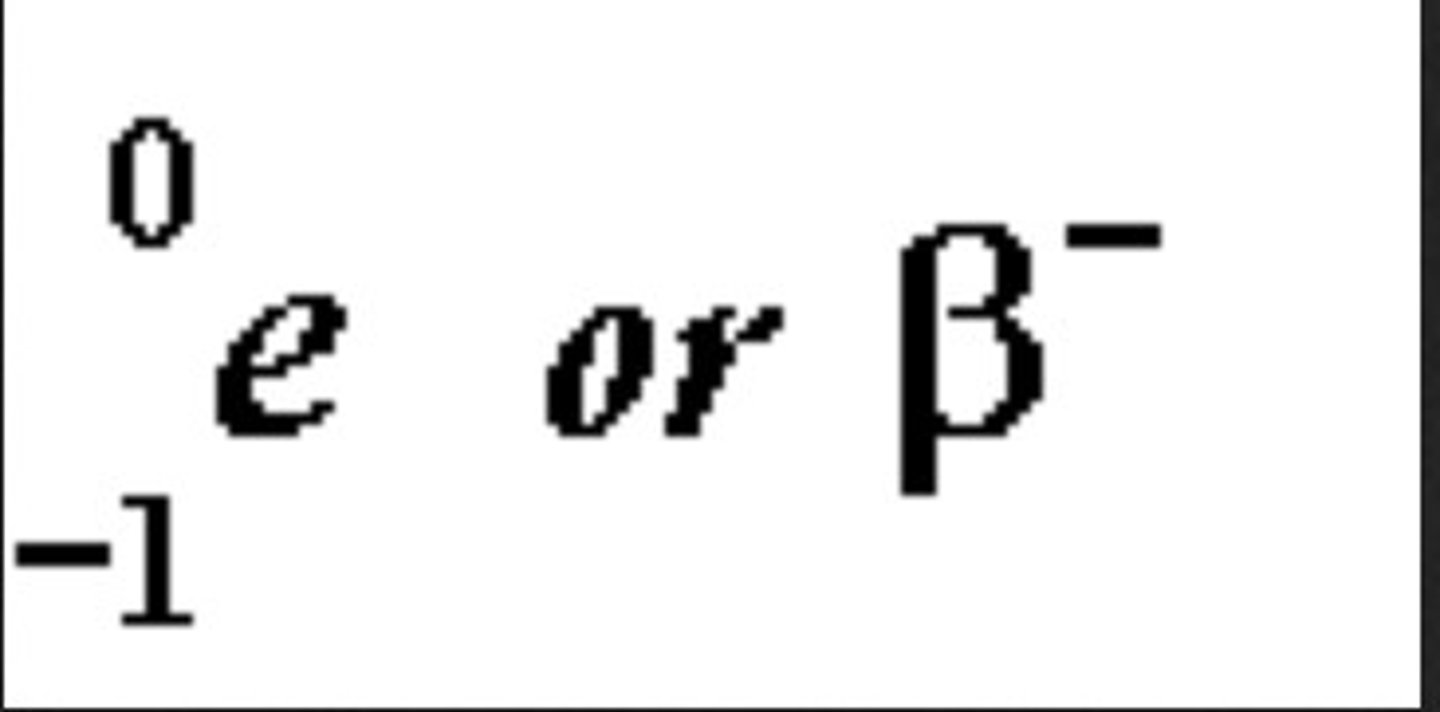
when does beta decay take place?
when a neutron in the nucleus splits into a proton and an electron. the proton stays in the nucleus while the electron is ejected from the atoms nucleus
gamma decay
when gamma rays are ejected form an atoms nucleus, this does not change the mass number or atomic number of the atom. it only changes the energy state of the nucleus
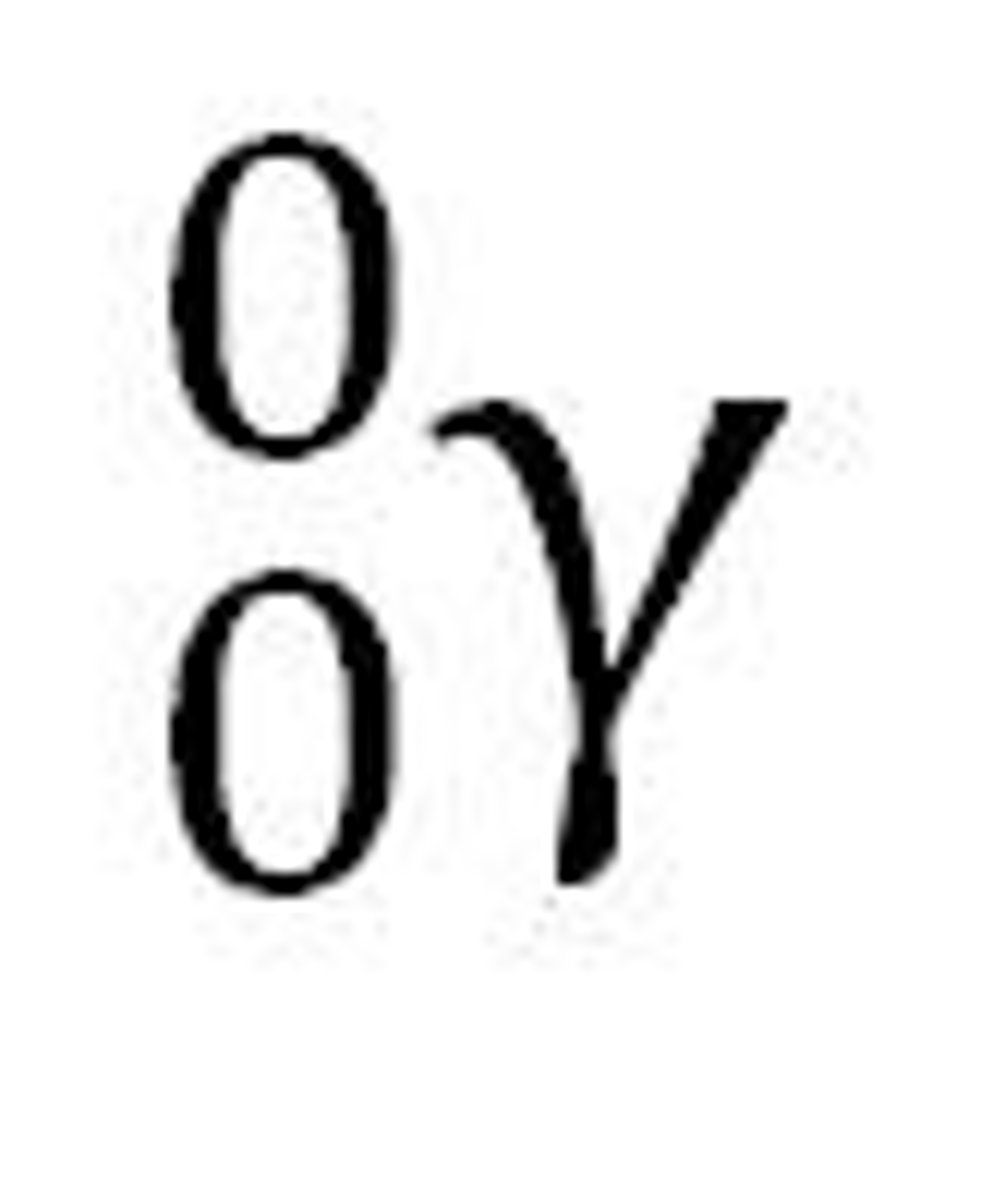
what are gamma rays?
are photons of electromagnetic energy- they are not particles
what happens during nuclear fission?
a large atomic nucleus splits into 2 small nuclei and sometimes several neutrons. the smaller nuclei and neutrons produced gain large amounts of kinetic energy.
two types of nuclear fission?
- spontaneous, large atomic nucleus splits up by itself at random
- induced by neutron bombardment, a neutron is fired at the nucleus, causing it to split
total mass before a nuclear fission reaction is __________ than total mass after (related to Einsteins equation)
greater
nuclear fission can be ____________ i.e. in a nuclear reactor or can be uncontrolled i.e. in nuclear weapons
controlled
what happens during nuclear fusion?
2 small atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nucleus. the larger nucleus and other particles produced (i.e. neutrons)gain large amounts of kinetic energy
in nuclear fusion, two small mass nuclei combine to larger mass, but the total mass before is ____________ than total mass after
greater
extremely high ______________ are required for this fusion reaction to occur
temperatures
what happens to the reactant molecules in these high temperatures for nuclear fusion?
they loose their electrons and become positively charged. refer to this as plasma
an example of where nuclear fusion takes place
in stars, like the sun
the lost mass in both nuclear fission and fusion reactions is converted into ____________ ________ of the products
kinetic energy
coolant for nuclear fission
cooling system involves the thermal energy produced by the fission reaction being transferred away from reactor into a conventional steam generator/ turbine combination to generate electricity.
coolant and containment issues for nuclear fusion
extremely high temperatures of the plasma required for fusion means a strong magnetic field is necessary to contain the plasma.
where is reactor for nuclear fission contained?
housed in a containment vessel consisting of concrete of lead to prevent escape of radioactive material and nuclear radiation
wave theory
electromagnetic energy (i.e. light) behaves as a continous wave. Meaning it can be reflected, refracted and diffracted. It can produce _______________
interference
light emits properties of both a wave (interference) and a __________ (photoelectric effect)
particle
quantum theory
electromagnetic energy is a stream of tiny, individual "wave packets" called quanta or photons.
however in quantum theory the energy of a photon does not depend on its amplitude. the energy is directly proportional to its _______________.
frequency
what is evidence for the theory of quantum physics?
the photoelectric effect
work function
is the minimum energy which must be supplied to enable an electron to escape from the metal surface.
photoelectric effect
one photon of eletromagnetic energy strikes a metal surface, it causes one electron to be ejected from the metal surface if the photons energy, hf, is greater or equal to the work function of the metal. part of photons energy is being used to enable the electron to escape, the rest is given to the emitted electron as kinetic energy.
threshold frequency
a photon must have a minimum energy equal to the work function of a metal and hence a minimum frequency to release an electron from the metal surface.
each metal has its own unique threshold _______________
frequency
what happens when hf is greater than the work function ?
electron is ejected
what happens when the hf is less than the work function?
no electron is ejected
____ photon transfers its energy to one electron. the ejected electrons can be reffered as 'photoelectrons'
one
photoelectric effect diagram
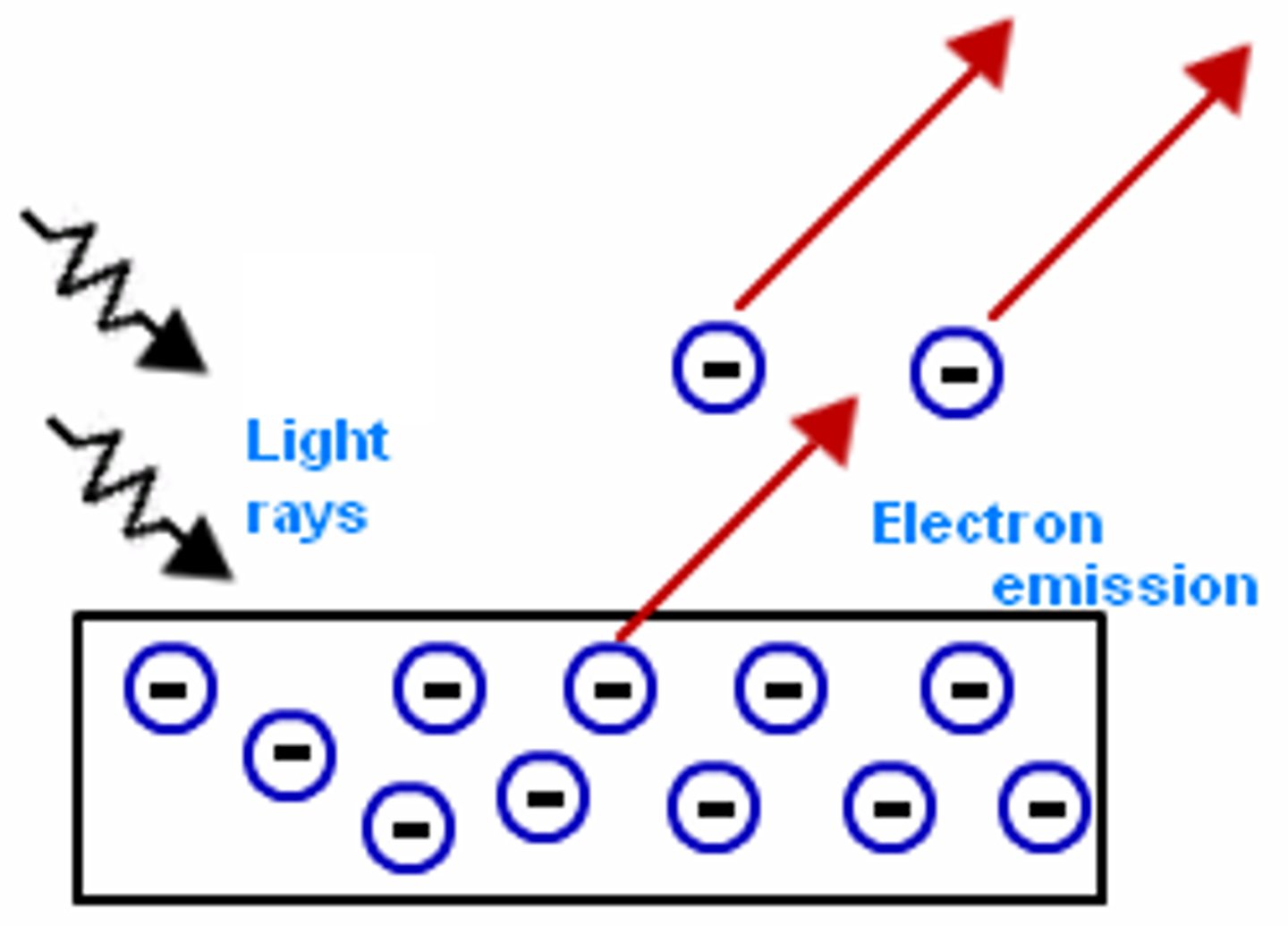
how is a photoelectric current produced?
the emmited electrons experince an unbalanced force and accelerates towards the postively charged plate. An electric current is thus created in the circuit.
photoelectric current and irradiance of the radiation are ____________ proportional
directly
electromagnetic waves consist of a _______________ that transmits energy in the form of varying electric and magnetic fields
disturbance
electromagnetic spectrum
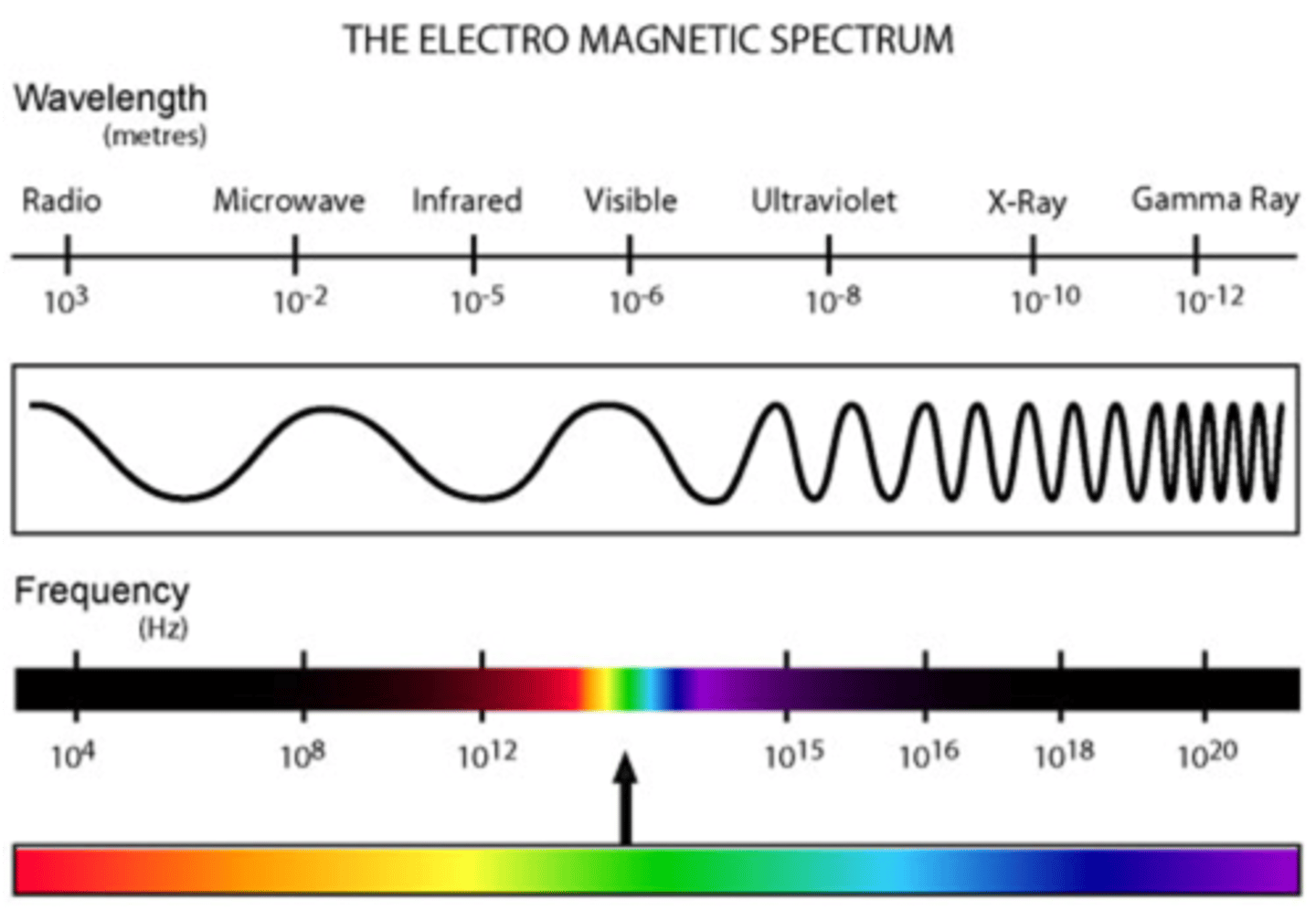
definition for interference:
is the test for a wave, in order to prove that any form of energy moves as a wave, an interference pattern must be shown
two types of interference?
constructive and destructive
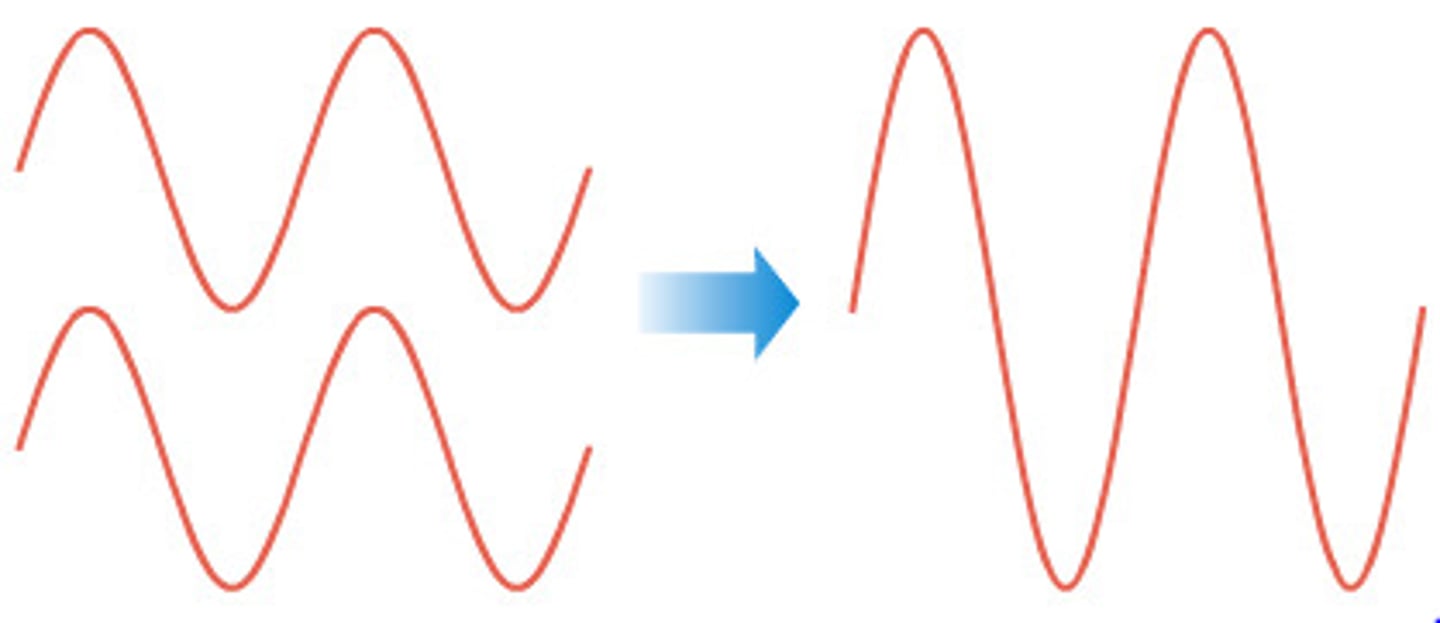
constructive interference
when 2 wave crests or 2 wave troughs arrive at the same point at the same time, they are in phase. the superposition of these two waves results in a stronger signal
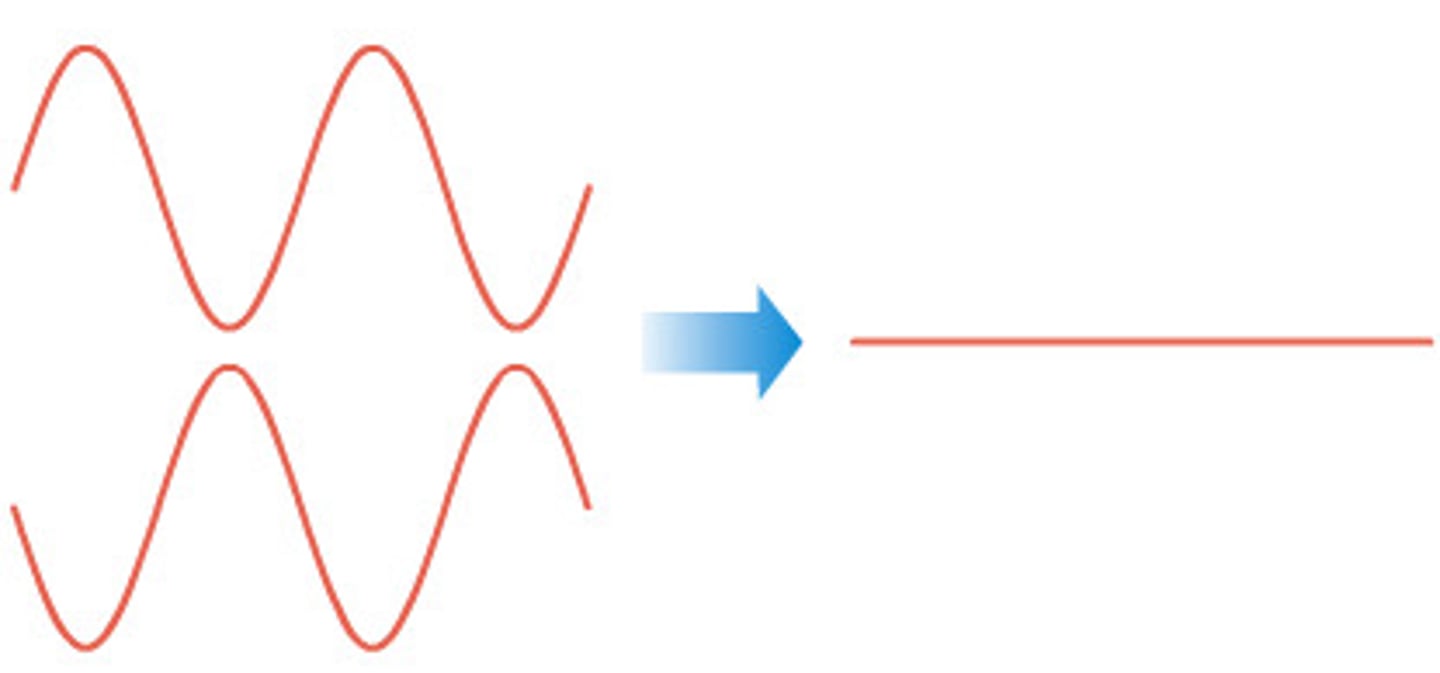
destructive interference
when a wave crest and a wave trough arrived at the same point at the same time, they are out of phase. the superposition of these two waves casues the signals to cancel each other out or reducing the amplitude of combined wave
constructive and destructive interference for water waves
at points of constructive the water wave has a maximum amplitude. at points of destructive interference the water appears calm.
constructive and destructive interference for sound waves
at points of constructive interference a loud sound can be detected. at points of destructive interference a quiet sound can be detected.
constructive and destructive interference for light waves
at points of constructive interference, bright fringes are observed. at points of destructive interference dark fringes are observed.
maxima
the points of maximum disturbance where the waves are completely in phases and constructive interference occurs
minima
the points of minimum disturbance where the waves are completely out of phase and destructive interference occurs
if 2 waves are coherent, they have the same frequency, wavelength and velocity and have a ___________ phase relationship
constant
what must be used in order to achieve coherent waves and interference patterns?
a single source must be used to produce the 2 waves
maxima number order
central maxima m=0
first order maxima m=1
second order maxima m=2
minima number order
first minima m=0
second minima m=1
third minima m=2
(No central maxima)
diffraction grating for the interference of light
light is diffracted through each slit, causing constructive and destructive interference. either monochromatic light or white light can be used.
a grating doesnt just result in diffracion of light, it results in more sources of light which create an _____________ _________
interference pattern
how to calculate the slit separation
d = 1 x 10-3 /number of lines per mm