Gas Transport System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Family history & culture that affect gas transport system
History of mouth, throat, sinus, lung, or nose cancer
History of lung disease or pulmonary disorders (asthma)
Did family members smoke in your home
History of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, or elevated cholesterol
Physical assessment
Head to toe sequence
cardiac
Vascular
Pulmonary
Techniques
inspect
Palpate
Percuss
Auscultate
Head inspection includes…
Face, mouth, lips, oral cavity nose, nostril air flow, internal, nasal flaring, jugular veins (neck)
Cyanosis =
Hypoxia
Ruddy to purple =
COPD or CHF due to polycythemia (excess RBC)
Circumoral pallor =
Anemia & shock
Cyanotic in mouth
Cold or hypoxic
Reddish in mouth
Carbon monoxide poisoning and COPD
Pursed lip breathing
Asthma, emphysema, COPD
Physiological response to slow expiration that attempts to keep the alveoli open longer
Tonsil enlargement
Indication of infection
Foul odor
Respiratory infection
Nose - external color & shape
Nostril airflow, impeding one side and asking pt to breathe may indicate infection or foreign object
Nasal flaring
Outward movement of nostrils with inspiration, labored breathing, hypoxia
Jugular venous pulse
Elevate HOB 45°, Pulse should not be visible visible indicates RT ventricular failure, pulmonary HTN, pulmonary emboli, or cardiac tamponade
jugular Venus pressure
Pt supine, Turn head to Left and shine light on jugular vein then @ 30, 45, 60 & 90°
Any bulging, distention or protruding may indicate RT, side heart failure, COPD, or Pericarditis
Tender sinuses =
Bacterial infection
Symmetrical inequality
Arterial constriction or occlusion
Weak pulse
Hypovolemia, shock, decreased cardiac output
Bounding pulse
Hypervolemia, increased cardiac output
Loss of elasticity
Artherosclerosis
Posterior thorax inspection, configuration
Observe the position of the scapula, shape, configuration, and appearance of the chest wall.
Scapula should be symmetric, Non-protruding, and equal horizontally.
Spinous process should appear straight, thorax is symmetrical with ribs sloping downward.
Posterior thorax expression, accessory muscle use
Observed the trapezius muscle or shoulders to see if they are being used to assist in breathing.
Pt Should primarily use the diaphragm
Posterior thorax Inspection, Positioning
Observe their posture and ability to support their weight
Pts Should be sitting up, relaxed and breathing easily with arms at their sides
Posterior thorax palpation, Tenderness and sensation
Use one or two hands to check for tenderness, warmth, pain, or other sensations
Start at midline level of left scapula, and move left to right, Compare findings
Posterior thorax palpation, crepitus
SC Emphysema, is a crackling sensation (Like hairs rubbing together), Occurs one air escapes from the lungs into the SC tissue, use fingers and follow the same sequence as when palpating for tenderness
Masses and lesions
Palpate any lesions noted during the inspection
Fremitus
Vibrations of air in the bronchial tubes transmitted to the chest wall
Chest expansion
Chest expansion, Posterior chest wall with thumbs @ T9 or T10 level, Press together a small skin fold
When the client deep breaths, observed thumb symmetry and 5-10 cm apart
Posterior thorax auscultation
Auscultation sequence
Breath sounds
Bronchial
Bronchovesicular
Vesicular
Posterior thorax auscultation; abnormal sounds
Crackles
Wheeze
Plural friction rub
Rhonchi
Stridor
Anterior thorax Inspection
Shape and configuration
Sternum position
Slope of ribs
Respiratory pattern
Intercostal spaces
Accessory muscle use
Pulsations
Apical pulse
Anterior thorax palpation
Tenderness and sensation
Masses and lesions
Crepitus and fremitus
Chest expansion
Apical impulse
Abnormal pulsations
Arm and hand inspection
Size
Edema
Lesions
Venous pattern
Color
Arm and hand palpation
Temperature
Capillary refill
Radial pulse
Shape of nails
Leg and foot inspection
Hair distribution
Lesions
varicosities
Thrombophlebitis
Edema
Color
Measure circumference
Leg and foot palpation
edema
Temperature
Superficial
Inguinal lymph
Nodules
Pulses
Femoral
Popliteal
Dorsalis pedis
Posterior tibal
Leg and foot auscultation
Pulses
Posterior tibal
Dorsalis pedis
Popliteal
Femoral
Validation and documentation
Discrepancies of data
Subjective
Objective
Validate
Verifies reliability, and accuracy
Document
AACC Nursing program policy
Healthcare facility policy
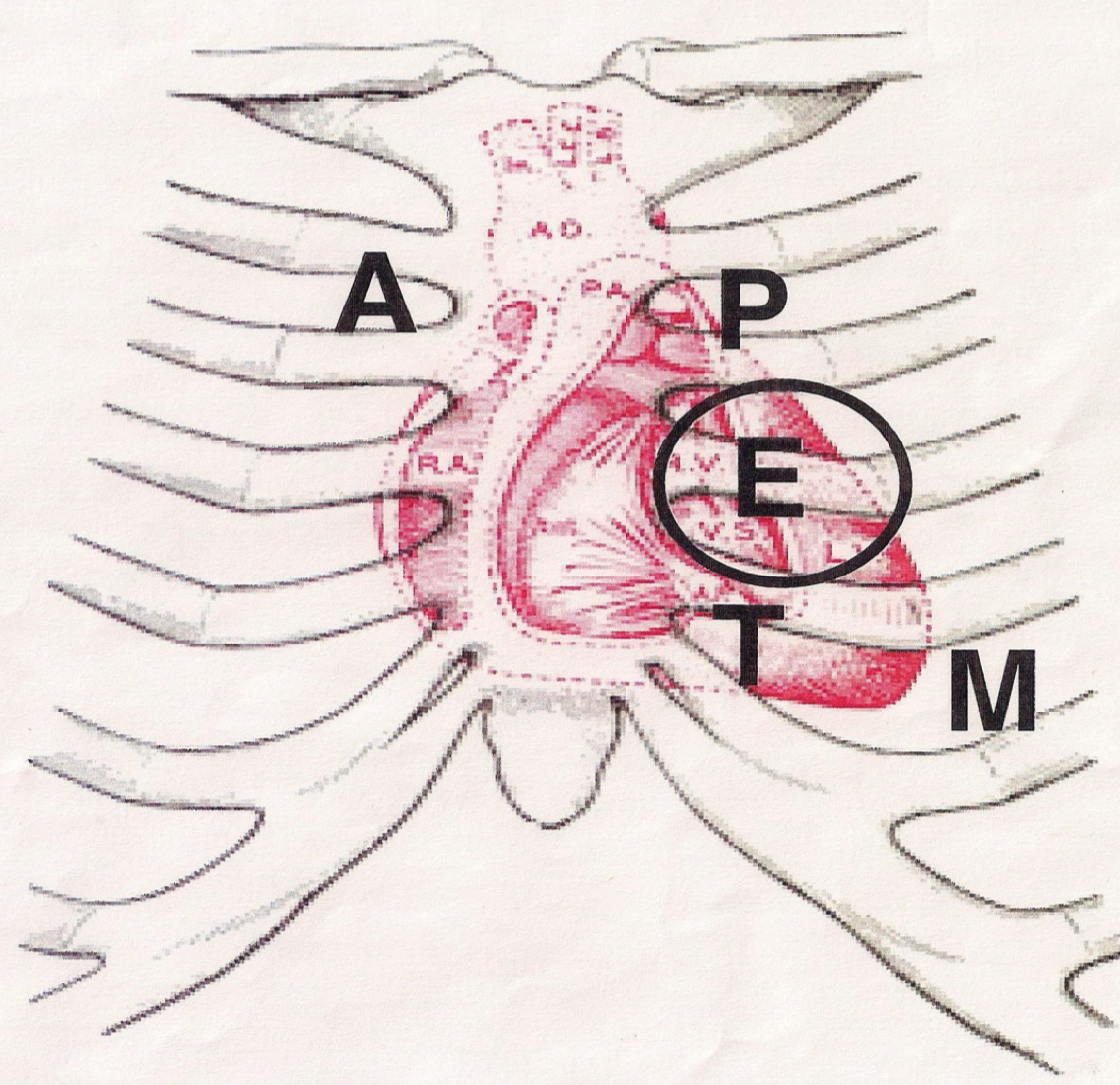
Heart sound landmarks, aortic
2nd ICS, R sternal border, S2
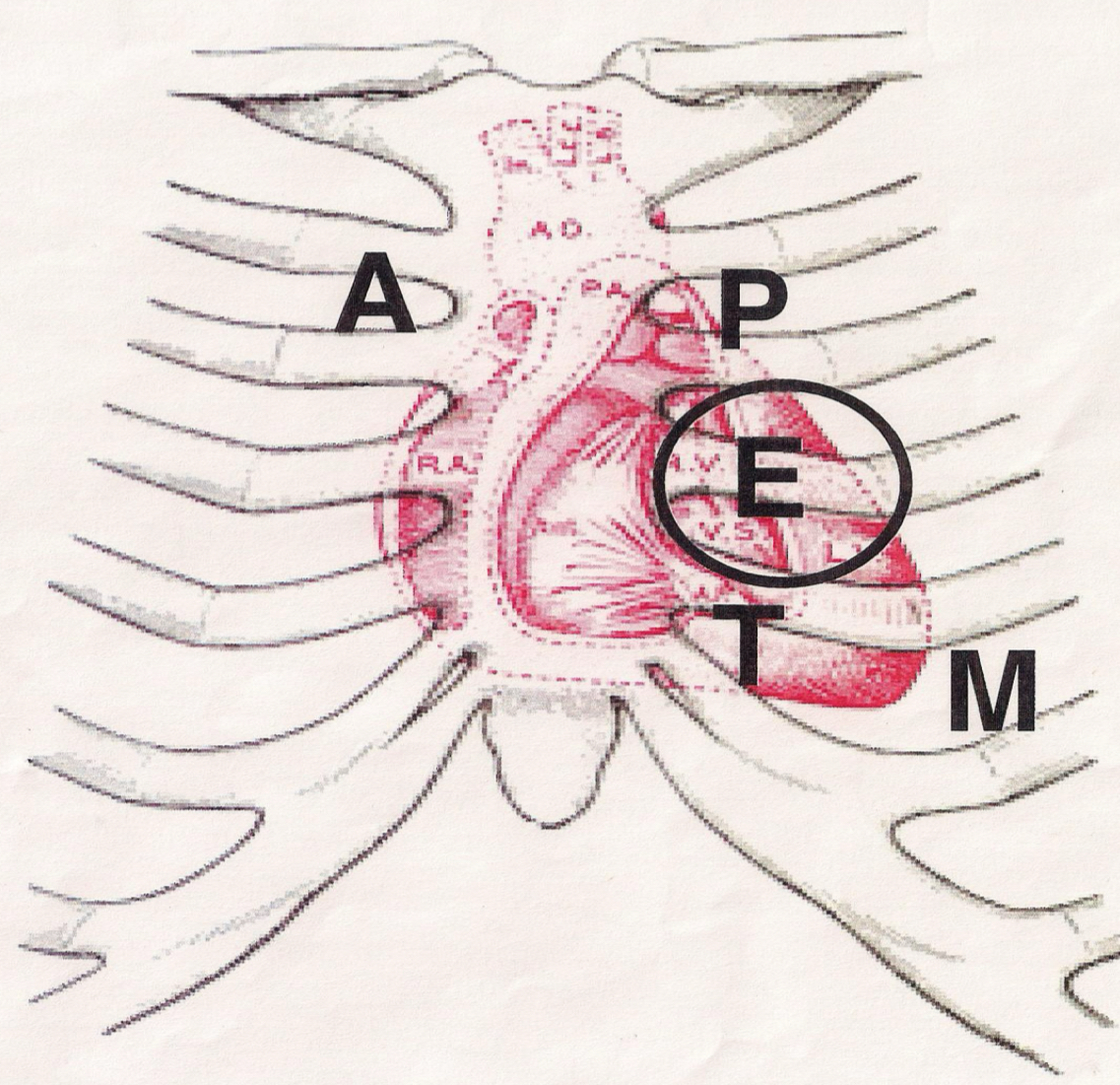
Heart sound landmarks, pulmonic
2nd ICS, L sternal border, S2
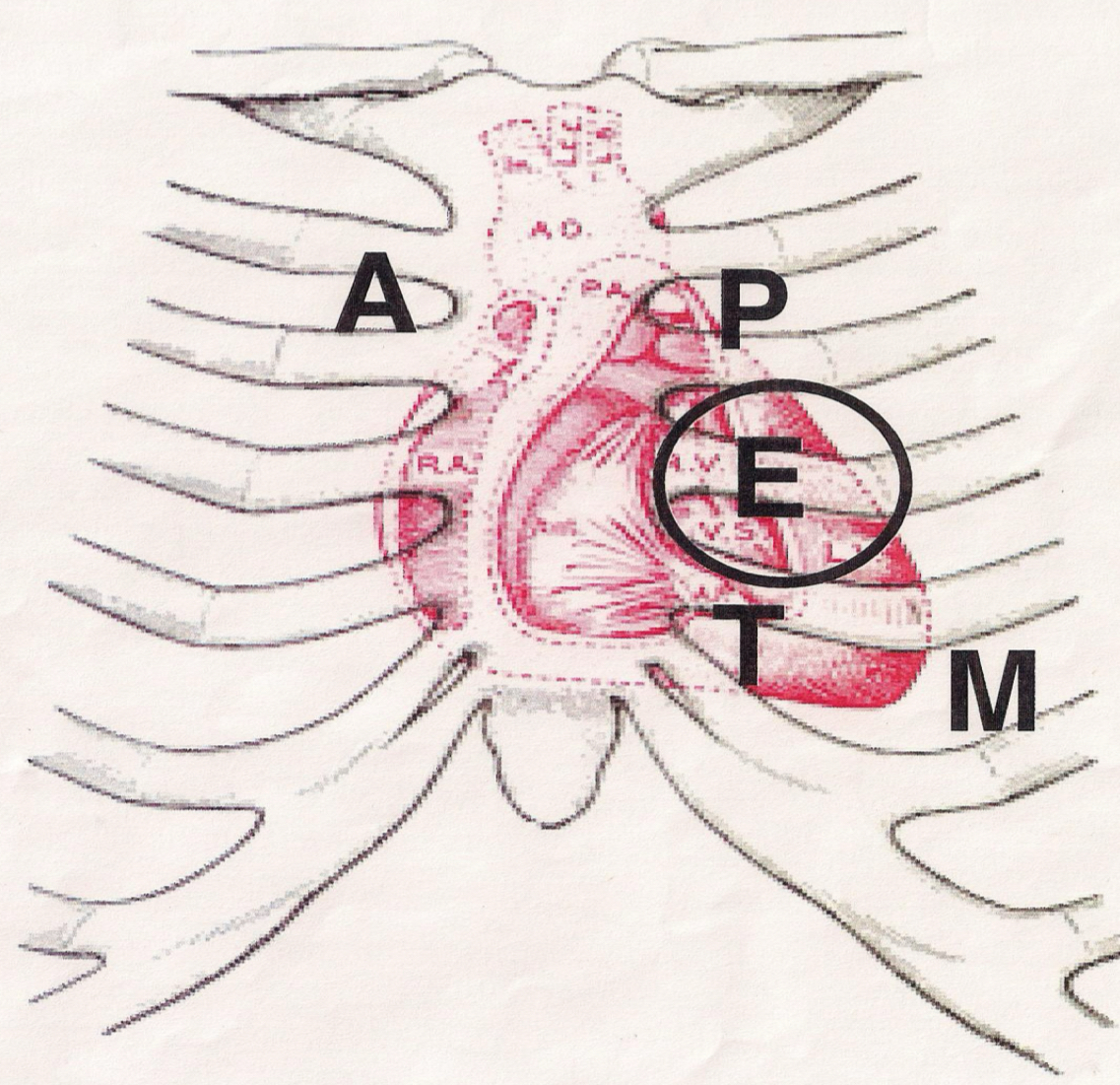
Heart sound landmarks, tricuspid
4th ICS, L sternal border, S1
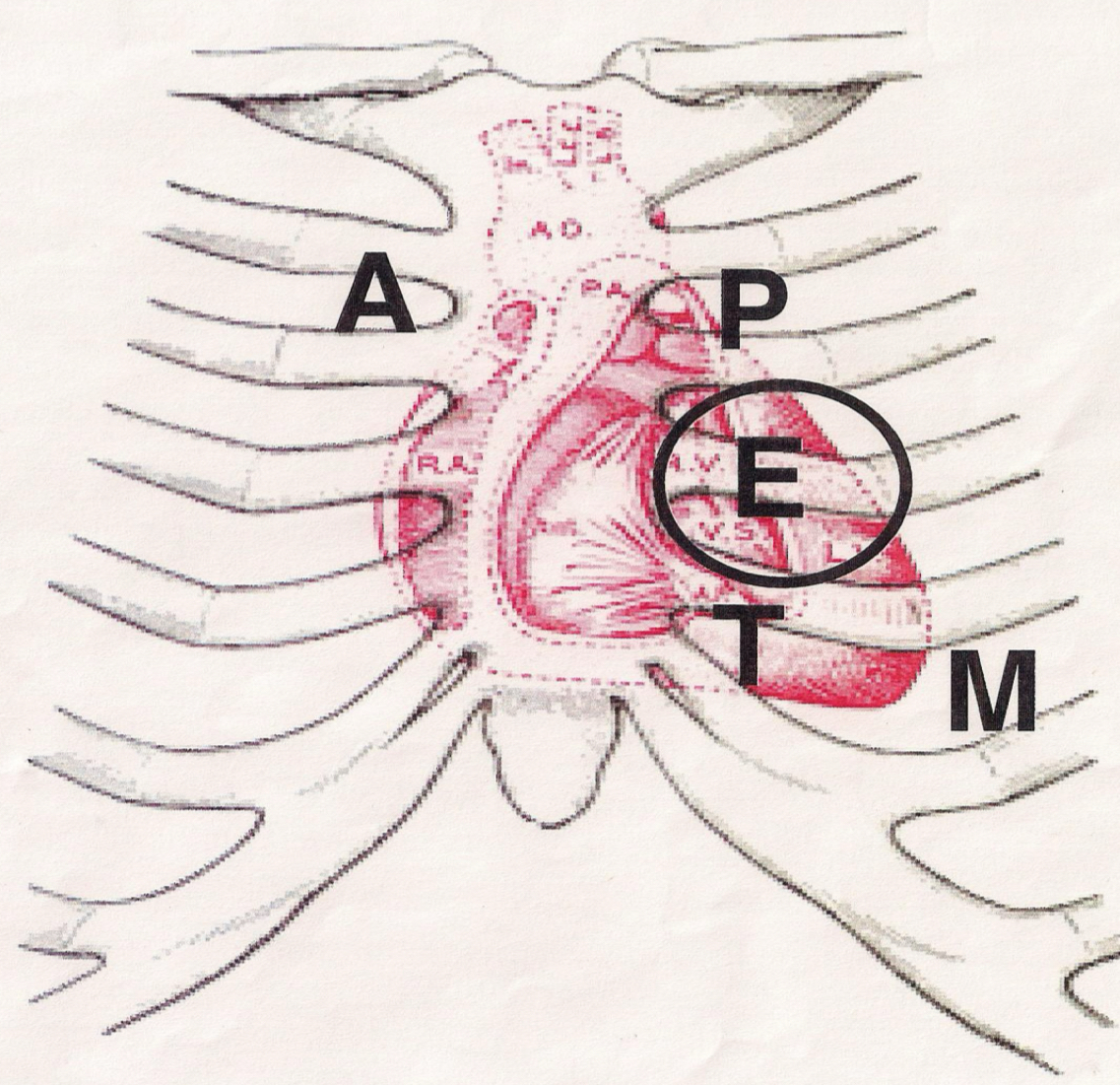
Heart sounds landmark, mitral
5th ICS, midclavicular line, S1