1.3 Algorithms and Programs
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Algorithm
A sequence of steps to solve a problem
Pseudocode
Is a generic programming language that is not meant to be run directly or complied, but used to represent algorithmic ideas
Flowcharts? When are they used?
Flow charts are a diagrammatic visualisation of the inputs, outputs, and processes completed by an algorithm.
Less commonly used for representing algorithms but can be used to represent the exact same as pseudocode. They are more common for smaller algorithms
Variables
Is a named location in computer's memory that a programmer can use to store data whilst the program is running
Constants
is a special kind of variable that cannot be changed during program execution
Scope of Variables
Scope refers to the section of code in which the variable is available. Local variables have limited scope which means that they can only be accessed within the block of code in which they were defined. If a local variable is defined within a subroutine, it can only be accessed within that subroutine and that subroutine is its scope. Global variables, on the other hand, can be accessed from anywhere in the program, making their scope the whole program.
Global Variables
Exist throughout the run of a program
Local Variables
Declared in a subroutine and exist only for the time the subroutine is run
Identifiers
Names given to variables, constants, functions, parameters, or routines
Self-documenting identifiers Pros?
i) They allow code to be followed and understood more easily.
ii) They reduce the need for additional documentation to be produced, such as additional annotations or software manuals.
Example: int VAT = 20
Annotation
i) Annotation is important as it allows developers to record the development process and logic of the actual code.
ii) This is important as many developers could be working on the same project, and each developer needs to understand the logic between one and another's code.
iii) Example: 'X DIV 2 //calculate if X is even/odd' - Comments included in computer code that are ignored during execution
Program Layout
i) Program layout allows blocks of code and constructs to be followed and identified more easily.
ii) A consistent program layout helps improve the quality of the software and allows developers to maintain quality and standards.
ii) Using indentation to identify the start and end of constructs such as IF statements and Nested loop structures
Parameter/Argument
Variable/value that can be passed to/from a procedure
Passing by Value
This is where a value is passed via a parameter into a subroutine, and a copy of the value is created for the duration of the subroutine call.
This ensures that the original value passed to the subroutine cannot be changed.
Passing by Reference
Is where a value is passed via a parameter into a subroutine, and the original value is passed and used by that subroutine.
This is used if any changes made in the subroutine need to be stored in the original value or variable outside the subroutine.
uses the Ref or Out Keyword
Recursion Algorithm
Algorithm that calls itself using a parameter and has a terminating condition, e.g., quicksort
Advantages of Non-recursive algorithm
i) useful when a data structure is fixed in size, like an array.
ii) reduce time complexity in sorting algorithms if implemented efficiently.
iii) require less memory than recursive solutions reducing the demand on resources.
iv) are easier to write.
Mathematical Functions
DIV and MOD functions for divide operation
DIV
The DIV operator is used to perform integer division.
Integer division is used to find the integer quotient (left part of a decimal number) after division.
e.g. 9 DIV 2 = 4
MOD
The MOD (modulo) operator is used to find the modulus when one number is divided by another.
The modulus is the integer remainder (right part of a decimal number) after division.
e.g. 9 MOD 2 = 1 or 9 % 2 = 1
Sequence algorithm
Is where one line of code is executed one after the other.
Sequencing is used in both procedural programming and object-oriented programming.
Selection Algorithm
Selection uses a boolean expression (condition) to determine which line of code to execute next.
Selection is used in both procedural programming and object-oriented programming. Ex: IF Statement
Repition Algorithm
The purpose of repetition (also called loops) is to repeatedly execute code until a certain condition is satisfied.
Ex: Repeat
Input Num1
Until (Num1 is an Integer)
Validation
It is the process of checking if the data entered is sensible for the context in which it is being used. Validation reduces the possibility of entering invalid data into a system
Verification
It is a means of checking to see if the data being entered is consistent. Verification reduces the chance of incorrect data being entered into the system.
Validation Examples
Character Check, Length Check, Format Check, Presence Check (existence), Check Digit
Verification Examples
Double Entry, Proofreading
Sorting
allow an unordered set of data elemnts to be organised (numerical or alphabetic)
Bubble Sort
It works by comparing two consecutive items in a list and swapping them over if necessary
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Start Procedure BubbleSort
Declare myArray[] of integer
declare i is integer
declare temp is integer
set i = 0
set swap = TRUE
while (swap == TRUE)
swap = FALSE
i = 0
for i to len(myArray[]) - 1
if myArray[ i ] > myArray[ i + 1 ]
temp = myArray[ i ]
myArray[ i ] = myArray[ i + 1 ]
myArray[ i + 1 ] = temp
swap= true
end if
next i
endwhile
end procedure
Insertion Sort
- 2 Lists one is for input and one is for the sorted items. the input list is added to the sorted list one by one untill it is empty
- Good for small datasets
- Each item in the input list is looked at in turn.
- Item is compared with the (sorted) list to find the correct position.
- Items in the sorted list are moved up or down to enable new items to be added in the correct place.
Insertion Sort Algorithm
Declare myArray[0 999] of integer
i is integer
j is integer
currentItem is integer
for i = 0 to len (myArray) - 1
currentItem = myArray[i]
j = i
while ( j > 0 and myArray [j - 1] > currentItem)
myArray[j] = myArray (j - 1)
j = j - 1
endwhile
myArray[j] = currentItem
next i
Quick Sort
The fastest and most efficient sort algorithm
- An item or pivot selected (which item is unimportant)
- Produce two new list of smaller and larger numbers
- Repeat above points on new sub list (recursively) until sorted.
Quick Sort Algorithm
Declare subprocedure QuickSort (myArray is string, indexLow is integer, indexHi is integer)
Pivot is string
tmpSwap is string
tmpLow is integer
tmpHi is integer
tmpLow = indexLow
tmpHi =indexHi
pivot = myArray (int(indexLow + indexHi)/2))
while (tmpLow <= tmpHi)
while (myArray(tmpLow) < pivot and tmpLow < indexHi)
tmpLow = tmpLow + 1
wend
while (myArray(tmpHi) > pivot and tmpHi > indexLow)
tmpHi = tmpHi - 1
wend
if (tmpLow <= tmpHi) then
tmpSwap = myArray(tmpLow)
myArray(tmpLow) = myArray(tmpHi)
myArray(tmpHi) = tmpSwap
tmpLow = tmpLow + 1
tmpHi = tmpHi -1
end if
wend
if (indexLow < tmpHi) then
QuickSort (myArray , indexLow, tmpHi)
endif
If (indexHi > tmpLow) then
QuickSort (my Array, tmpLow, indexHi)
end if
end sub
Searching
Finding specific data in a list
Linear Search
Is when the first item in a list is looked at. If this is not the required data, the next one is looked at, and so on.
It is not very efficient way of searching, but if the data is not in sorted into order, it is the only way
Linear Search Algorithm
myArray[] of Integer
SearchValue Is Integer
Found Is Boolean
Set Found = False
set i = 0
Input SearchValue
For i to len(myArray)
If SearchValue = myArray(i) then
Set Found = True
Output "SearchValue found at position ", i
End If
End For
If Found = False
Output "SearchValue not found."
End if
Binary Search
This involves looking at the middle record. If the record is before this one, then discard the second half of the file; if it is after this one, then discard the first half of the file. Repeat the process, discarding half of the file each time, until the required record is found.
IF (and ONLY IF) the data is sorted into order, then a BINARY SEARCH can be used.
Binary Search Algorithm
myArray(0 to 10) Is Integer
Declare Start Is Integer
Declare End Is Integer
Declare Found Is Integer
Declare Mid Is Integer
Declare SearchValue is integer
Set Start = 0
Set End = 10
Set Found = False
Input SearchValue
Repeat
Set Mid = (Start + End) DIV 2
If SearchValue = myArray(Mid) Then
Set Found = True
Output "SearchValue found at position ", Mid
End If
If SearchValue > myArray(Mid) Then
Set Start = Mid + 1
End If
If SearchValue < myArray(Mid) Then
Set End = Mid - 1
End If
Until (Found = True) OR (End < Start)
If Found = False
Output "SearchValue not found."
endif
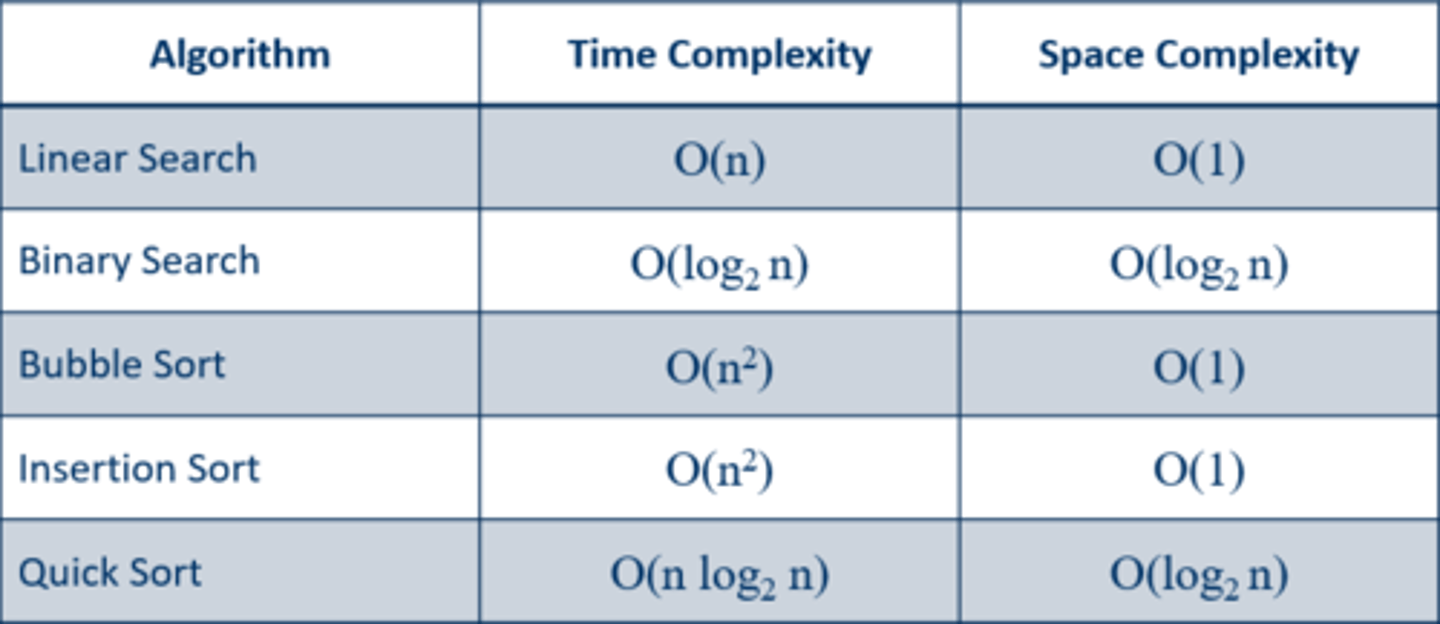
Big O Notation
A mathematical way to describe the efficiency of an algorithm (asseses runtime or space requirements as input size grows)
It provides the upper bound of complexity (worst case)
This is used to compare algorithms in terms of time and space complexity (how long it will take and how much storage/memory it will use up) as input grows
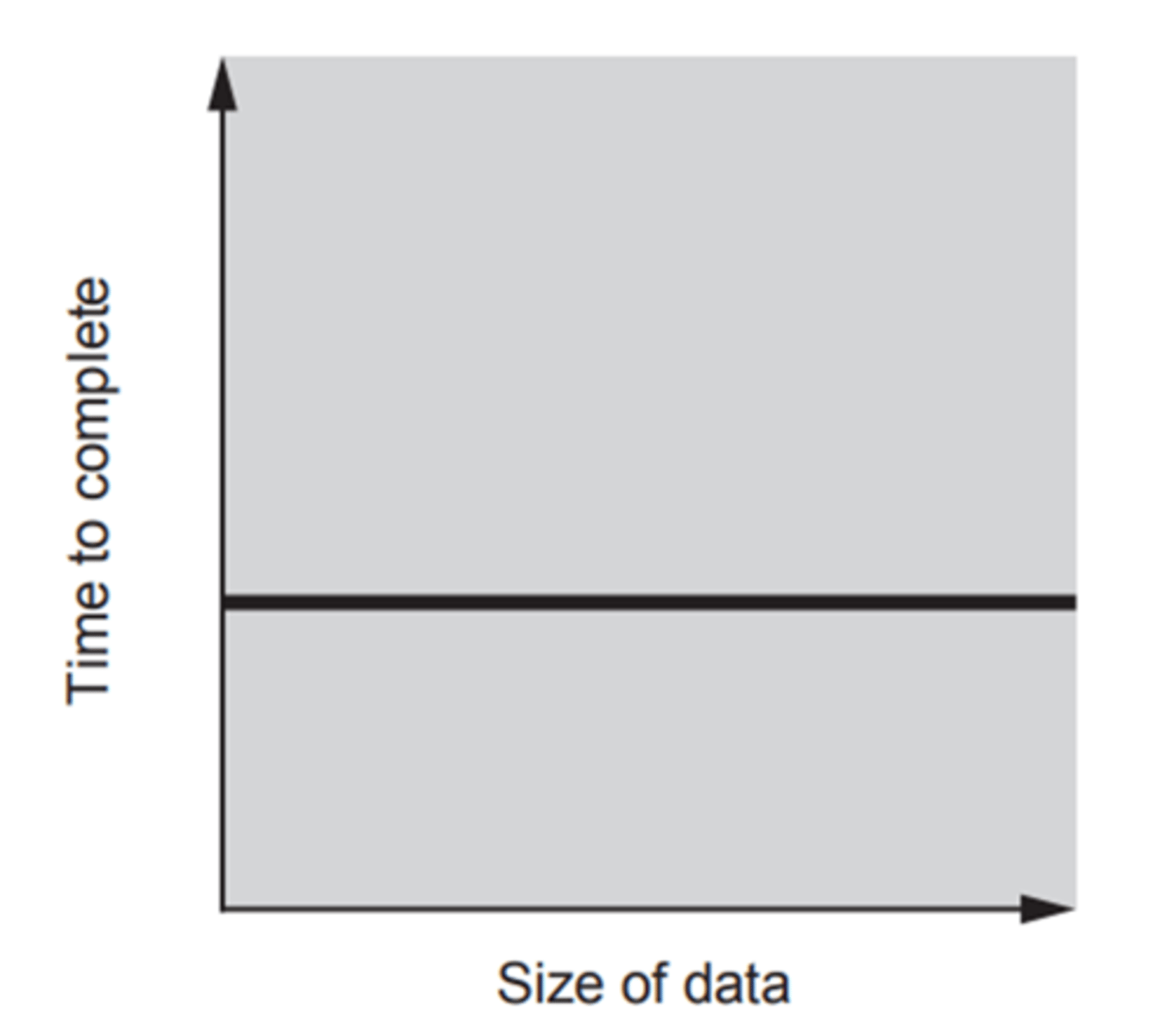
Constant complexity O(1)
Sizes doesnt matter with input (for example printing the first element of an array) Also for loops are also constant as they run a set number of times ulike for while loops
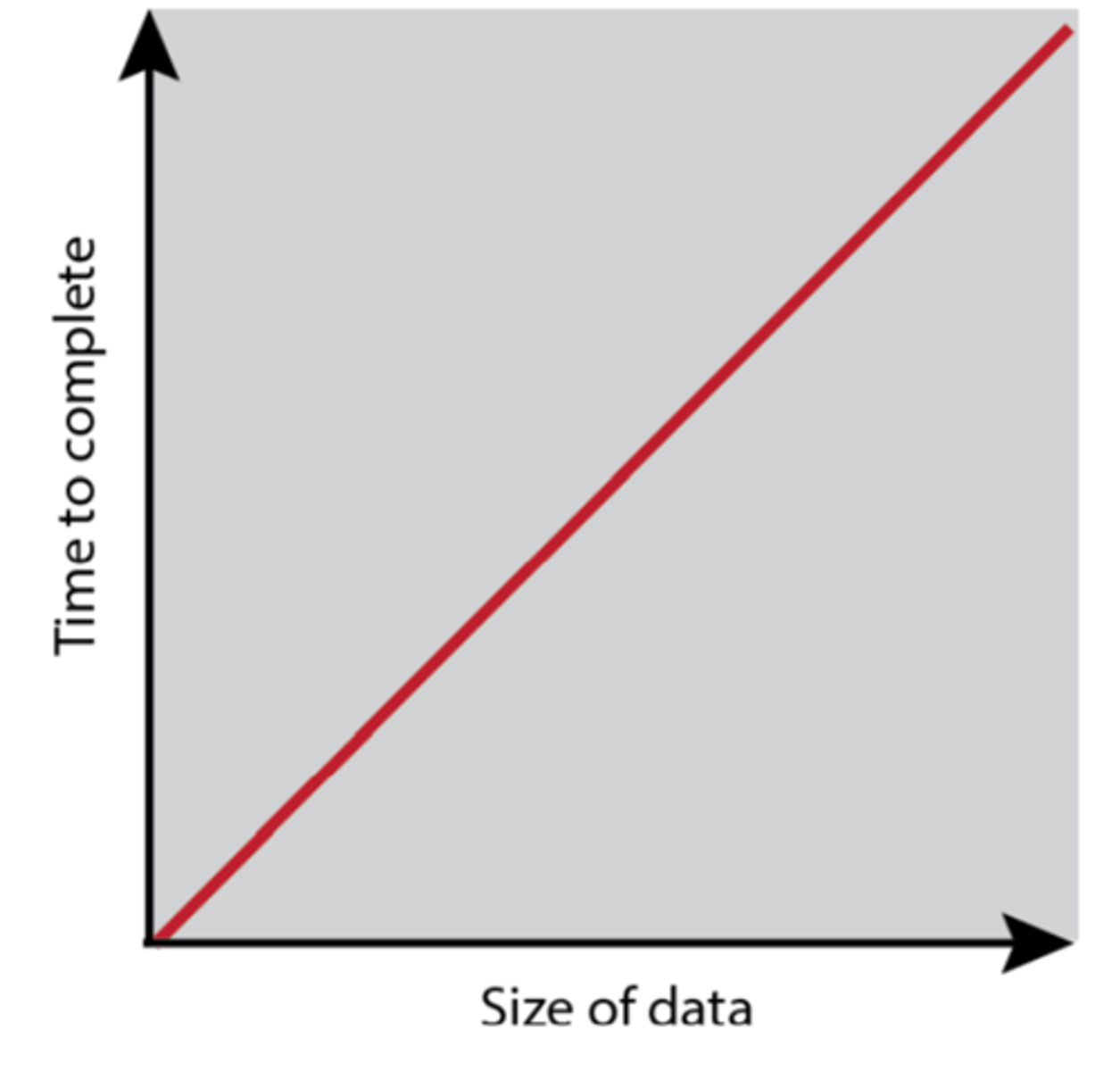
Linear Complexity O(n)
Rate of growth increases linearly with input (like a linear search)
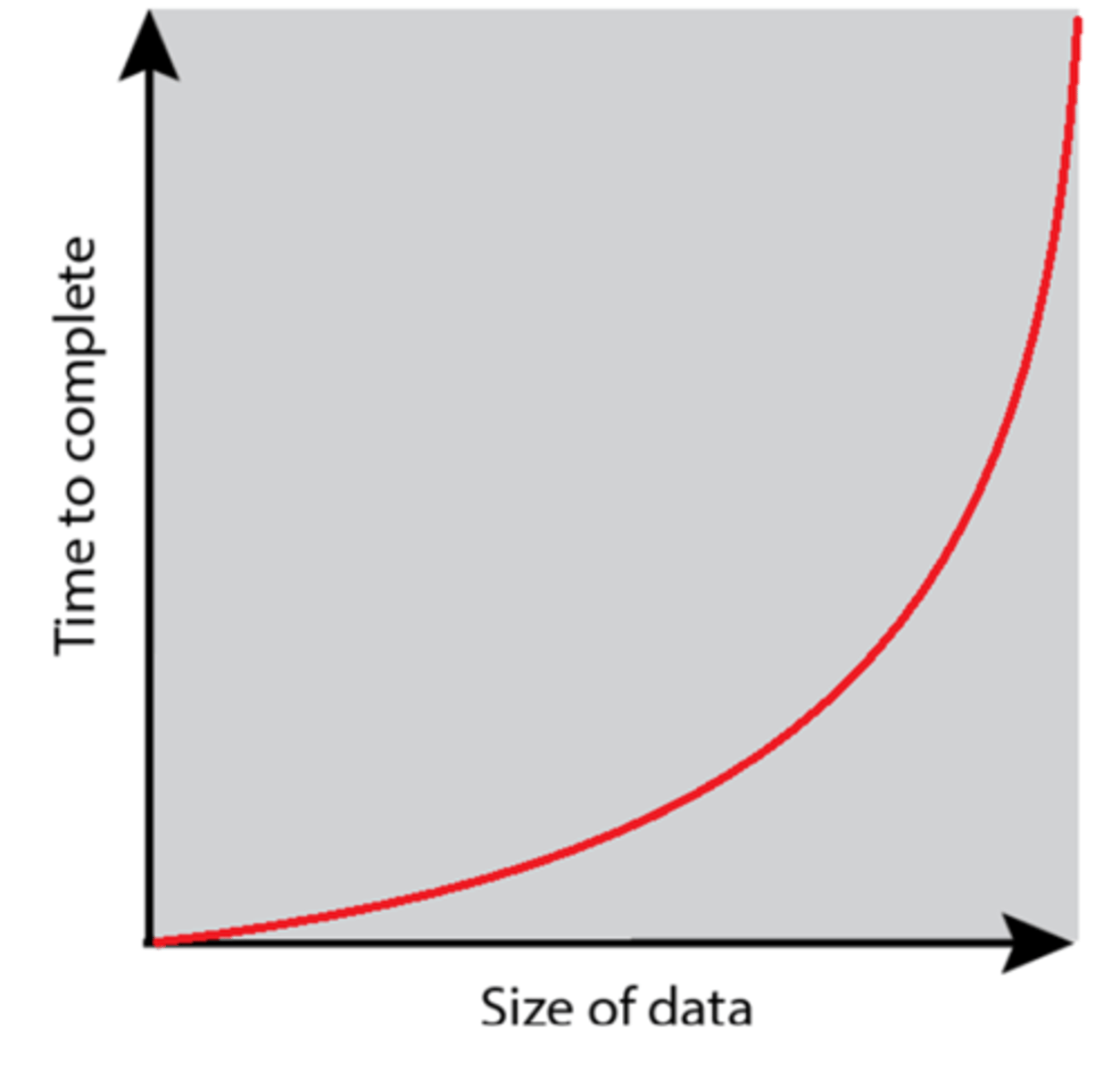
Polynomial complexity O(n^2)
Rate of growth increases polynomially (squared or cubed) with input due to something like a nested loop (like in a bubble sort going through the array of n and repeating it n times (n*n))
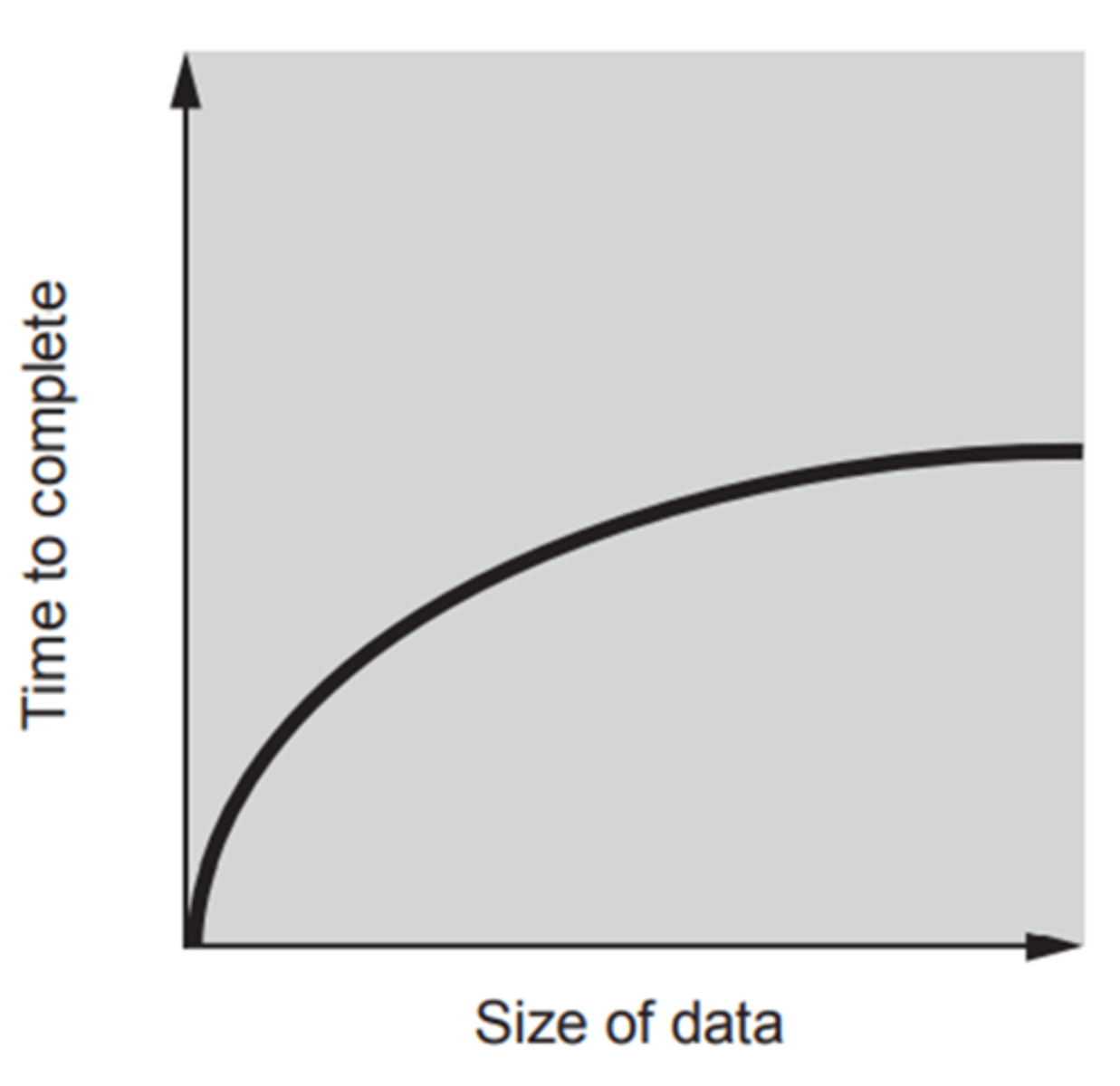
Logarithmic complexity O(log base 2 n)
The growth rate increases in proportion of log n (For example Binary Search is log2 because you are halving the data so it will increase less than proportionally) - input is cut by a constant factor and steps needed to reduce size is proportional to log2n
This is because each iteration will halve the dataset so doubling the data will only add one iteration onto the algorithm so it is log2
Most likley to be a binary search in an exam question
Big O Notation: common algorithms
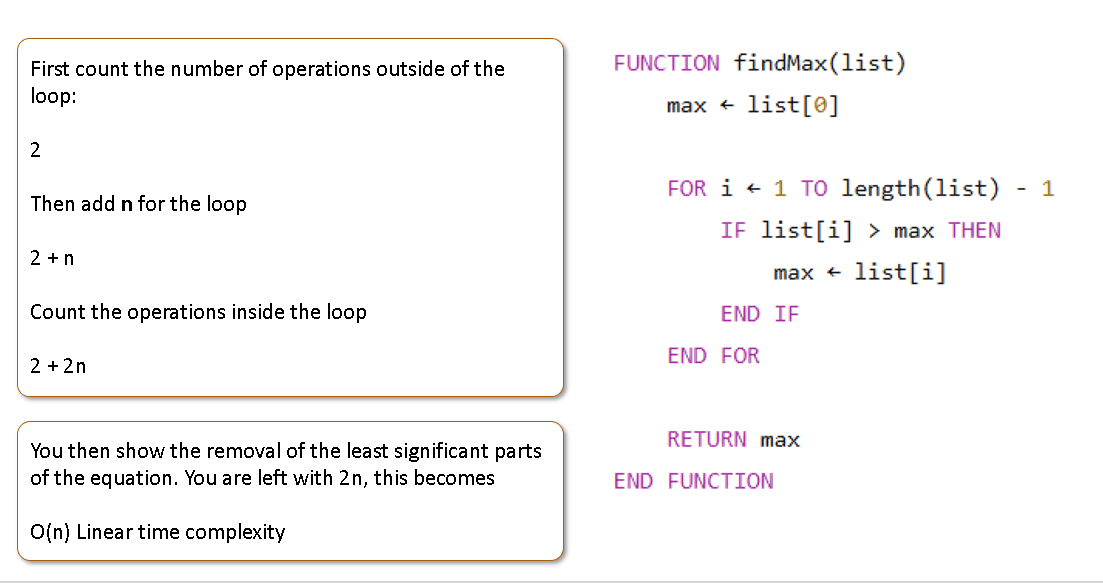
Exam style question for linear
You would count the data outside the loop (any operations) and then count inside the loop ( worst case) then you cancel it until its just the most significant part (…. is dominated by….)
Another question
Just count and cancel you count stuff inside loops and nested loops unless and use it for constant then linear then polynomial

Terms in solving Big O Notation
- __ loop will execute ___ times
- Number of operations ____
- Order will be dominated by ____
- The growth for time performance is ___
If the algorithm only use one data structure, the total storage requirements will be 1, and the growth rate of memory will be constant, O(1)
Then draw a fully lablled diagram (O(n) Linear time complexity with time and input on axis)
Some key things to look for in Big O Notation
Nested loops - indicate polynomial time O(n^k)
Recursive calls - often indicate at least O(n) time
Iterating over the entire input - indicates O(n) time
No loops or recursion - indicates O(1) time
Why is quicksort linearithmic?>
Linearithmic O(n log n) becase:
Paritioning Each loop goes through the list and compares element (o(n))
Recurvise splitting The list is split in half each recursion (making it log2(n))
Multiply both parts to get n log n

What is space complexity?
The amount of space an algorithm needs to execute as input size changes
Give examples of each space complexity
Constant - Simple algorithm no changes (like swapping variables)
Linear - If input double space required doubles (like having an array and creating a new one with a for loop)
Quadratic - Often seen in 2D arrays where creating a 2d matrix based on the input
Counts
A variable (integer) is used to count values that satisfy a certain condition.
Remember, counting always starts at 0, so the value of the variable must be initialised to 0.
Rogue Values
A sequence of inputs may continue until a specific value is entered. This value is called a rogue value and must be a value that would not normally arise.
Data Compression
A process for reducing the number of bits needed to represent a piece of information
Lossy Compression
Lossy compression means that the file is compressed to a smaller size but some information is lost during the process.
Lossless Compression
Lossless compression techniques are able to reduce a file's size without losing any information.
Run Length Encoding (RLE)
Run-length encoding (RLE) is a lossless compression, method widely used for reducing file sizes. It replaces sequences of repeated characters with a flag character, followed by the character itself and the number of times it is repeated. For example, "BBBBBBBBB" becomes "$B9", resulting in a compression ratio of 0.3. However, non-repeated characters are not compressed and are included as is. For instance, "AAAAAANNNBBBBBBBBUUBYE" becomes "$A6NNN$B8UUBYE", achieving a compression ratio of 0.69. Sequences of letters shorter than four are not compressed because the overhead of highlighting repeated characters outweighs the compression benefits.
Dictionary Coding (Lossless)
Dictionary encoding is a form of lossless compression where common sequences of characters in a text are replaced by pointers to a dictionary. These pointers are shorter than the words they replace, resulting in a reduction in file size. Creating the dictionary involves scanning the document to identify the most common words and assigning a reference to each. This method is effective for compressing text files by exploiting repetitive patterns and sequences.
Huffman encoding
Huffman encoding is a dictionary encoding method used for lossless compression. It leverages the frequency of occurrence of characters in a text to assign shorter codes to more common letters. This helps reduce the overall size of the encoded text by representing frequently occurring letters with shorter bit sequences. By using a Huffman dictionary to map each character to its corresponding code, the compression ratio is significantly improved compared to using a fixed-length representation for each character. This method efficiently utilizes storage space by assigning shorter codes to more commonly occurring letters, thereby achieving effective compression.
Compression ratio
A ratio between the original file and the new compressed file.
Compression Ratio = Original File Size / Compressed File Size
Examples: 20MB/4MB = 5:1
Compression/decompression time
The amount of time it takes to compress or decompress a file Sometimes size saving may be sacrificed for speed
Saving Percentage
A percentage measure of how much smaller the compressed file is compared to the original.
Shortest-Path Algorithm (Dijkstra)
It finds the shortest path between two vertices/nodes on a graph by analysing the associated cost (weight) to each path. The path with the smallest cost (distance/time) is the shortest
Applications of shortest path?
Navigation systems - like google maps with distance and time being cost, roads being paths, and places being nodes
Network routing - the best path for all data packets
Game development - for AI naviagtion
How to answer shortest path question?
find the path with the least cost then lay out all of the letters.
E.G.
a → c → e → d
OR
{a,c},{c,e},{e,d}
What is structured English
Breaks down complied algorithms into simple English words to show step by step solutions
What is hungarian notation and CamelCase
Hungarian notation is a naming convention that prefixes variable names with a type indicator (Str_Name)
CamelCase is a style of writing where the first letter of each word is capitalized except for the first word, improving readability.
Procedure vs function
Both are self contained blocks of code that perform specific tasks that take input parameter input them and process them
Procedures- Return no Value
Functions- Return a Value
Searching and sorting speeds Fastest to slowest
Sort:
Merge
Quick
Insertion (Equal)
Bubble
Search:
Binary
Linear