UNIT 4: Cell Communication and Cell cycle
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
signal transduction pathway
The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response.
Hormone
A signaling molecule released into the bloodstream to trigger a cellular response to certain cells.
Ligand
A signaling molecule that has a specific shape to bind to the specific receptor molecule lying on or within the cell.
Protein Kinase
An enzyme that activates or inactivates proteins by adding a phosphate group!
secondary messengers
Molecules following the initial binding of a ligase to the receptor, relaying the signal to the cells interior mechanisms until the cell performs the function needed.
Cyclic AMP
Secondary messenger cAMP, which was made by being inactivated by phosphodiesterase from ATP
Apoptosis
Cell Death
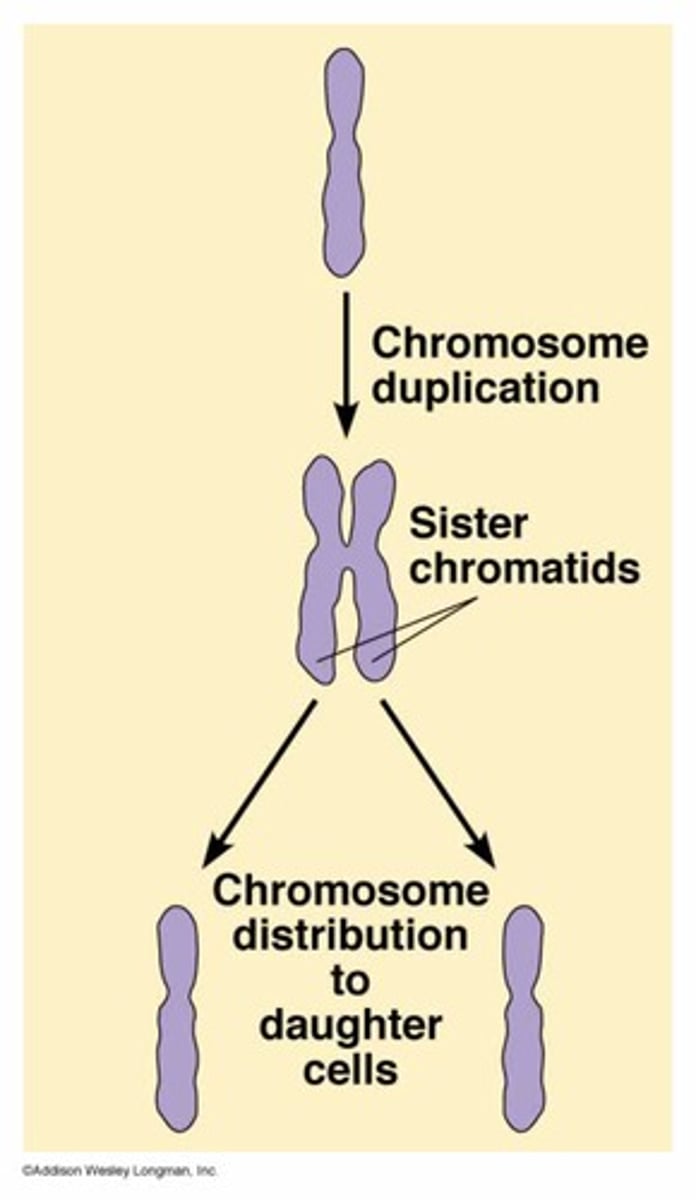
Chromosome
Condensed genetic material containing one set of genetic material
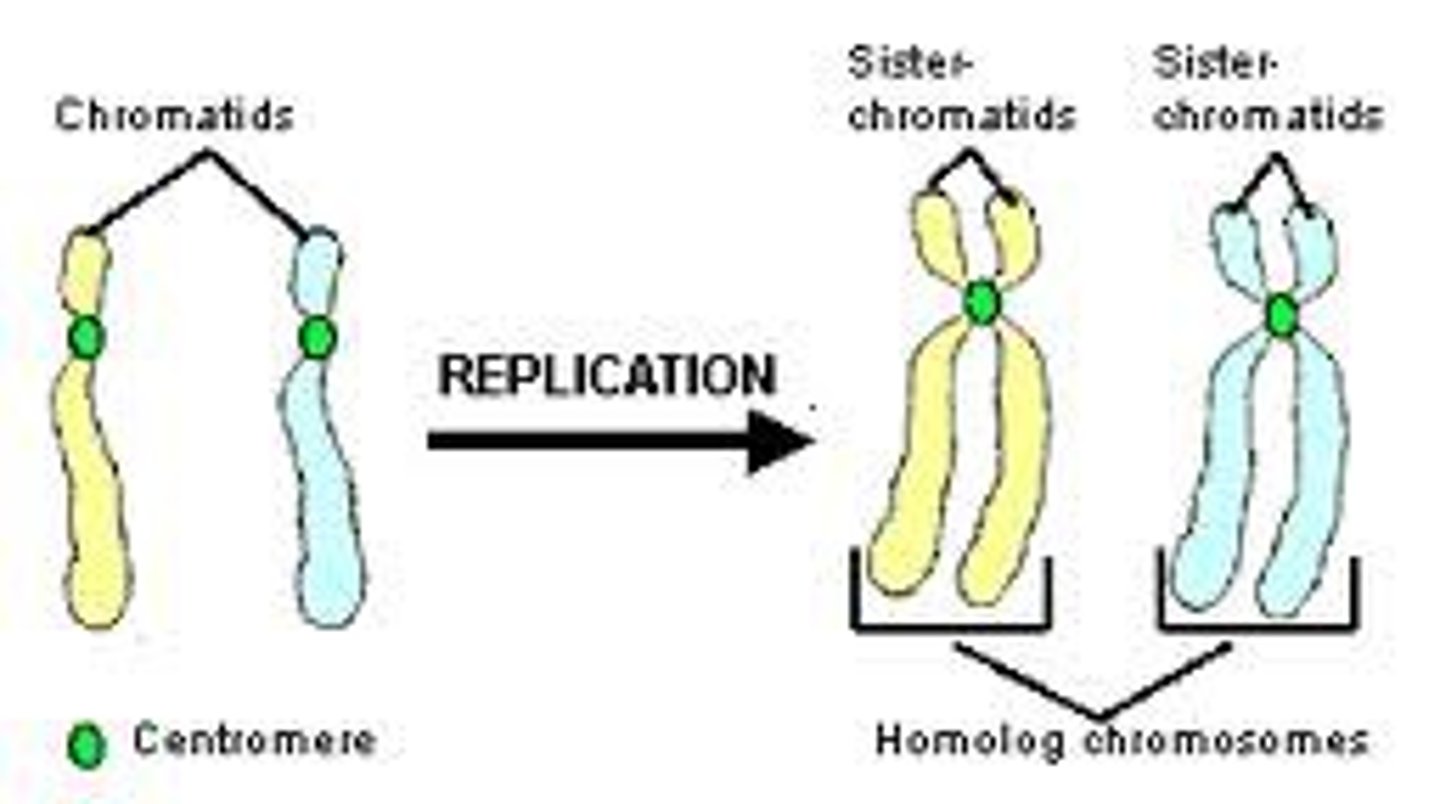
Chromatid
one of two identical "sister" parts of a duplicated chromosome
Chromatin
The uncondensed form of genetic material
Sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
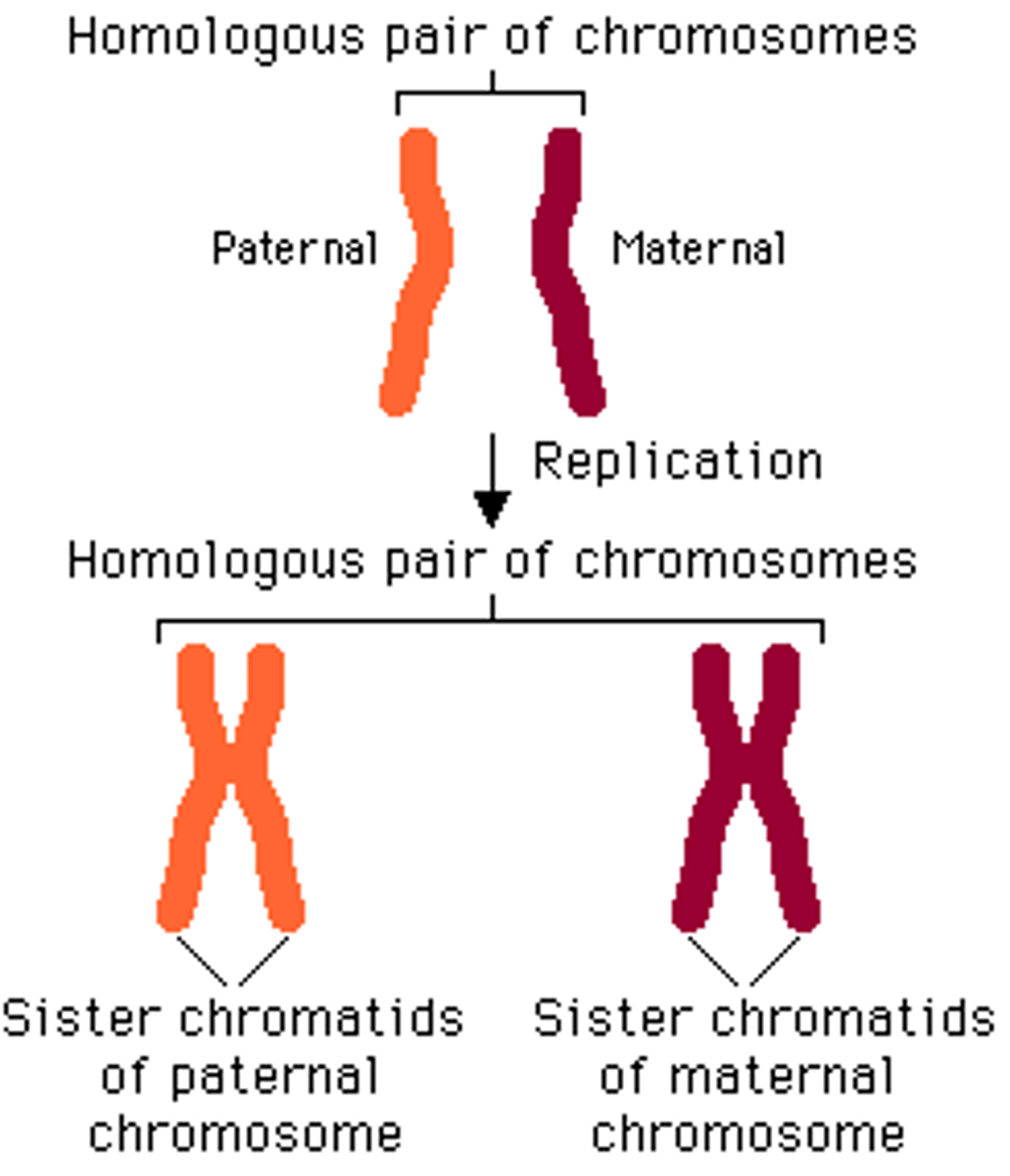
Homologous chromosomes
A pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes(meiosis)
Gamete
A haploid male or female cell containing genetic material from one parent, joining with another haploid to make a diploid cell.
Somatic Cell
A body cell/haploid cell
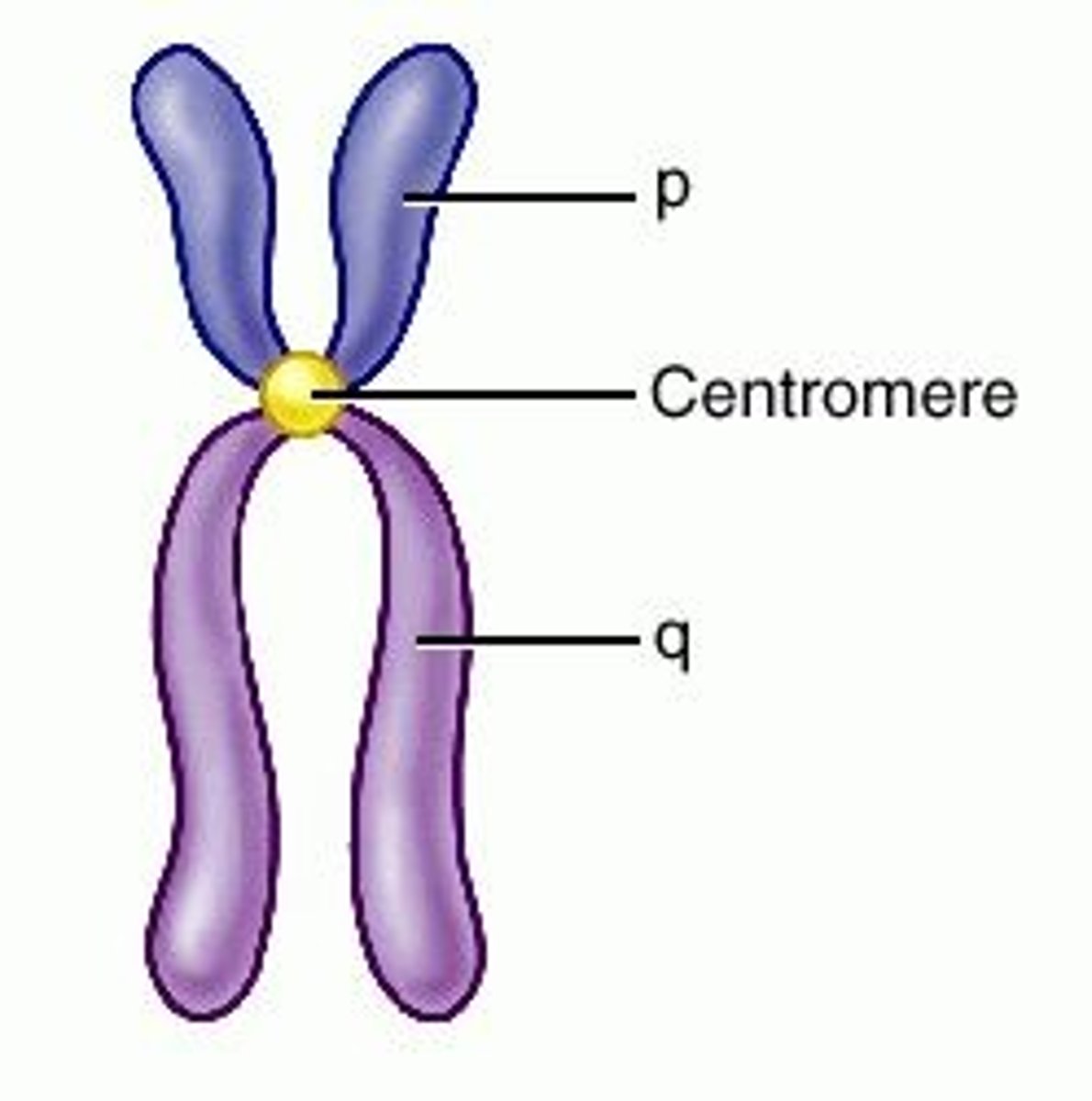
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
Mitosis
The process of a cell dividing into 2 identical diploid cells
Prophase in Mitosis
nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, spindle fibers start to form
Metaphase in Mitosis
The mitotic spindle fibers line up sister chromatids in the middle of the cell.
Anaphase in Mitosis
The equal separation of sister chromatids done by spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase in Mitosis
The cell membrane pinches in; in plant cells, the cell wall forms a line in between.
Chromatids decondense into chromosomes, nuclear membrane forms around each set of genetic material
Cytokinesis in Mitosis
The full division of the cytoplasm into daughter genetically identical daughter cells, normal cell functioning occurs.
Non-disjunction
Error in meiosis anaphase in which chromosomes fail to separate equally.
Mitotic Spindle
An assembly of microtubules attaching at the centromeres of chromosomes during cell division to equally line up and separate chromosomes.
Centrioles
a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
Cleavage
The region where the cell membrane pinches in during telophase
Binary Fission
The type of cell division, typically in prokaryotic cells resulting in 2 genetically identical daughter cells.
Cyclin dependent kinase
A positive regulator enzyme that attaches to cyclins(substrate) binding at certain parts of the cell cycle to regulate the cycle via phosphorylation.
Cyclins
Substrates that build up over time when needed during the cell cycle and binds with CDK's to regulate the cell cycle
desnity-dependent inhibition
Inhibition of cell division when cells have contact with each other.
Tumor
An uncontrollable mass of cells caused by unregulated cell division.
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome coding for a specific trait.
Karyotype
A picture of all chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
Meiosis
Cell division producing 4 genetically different haploid gametes
Meiosis 1
The process of mitosis with homologous chromosomes, and in prophase(crossing over and random assortment occurs)
Meiosis 2
The process of mitosis, but with genetically different cells, leading to the result of 4 genetically different haploid gametes(sex cells)
Crossing over/Recombination
The tips of homologous chromosomes trade arms, increasing genetic diversity
Independent assortment of chromosomes
The random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes into gametes during meiosis.
Random fertilization
source of genetic variation caused by the unlimited number of possible sperm & egg combinations
Difference between Meiosis and Mitosis
Meiosis is used for reproductive cells, Meiosis increases genetic diversity and has genetically different daughter cells.
Cell Cycle
Interphase-(G1, S Phase, G2, Gnot)
M phase-(Mitosis)
G1 processes
Normal cell growth, preparing for DNA replication
G2 processes
Continuous cell growth, preparing for cell division
S Phase processes
DNA replication
G_0 processes
Dormant cell, no growth or processes observed during this stage because the cells are not needed
M Phase Processes
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Check-Point locations + purpose
End of G1- Checks for enough cell size, nutrient growth, DNA damage, to enter replication
End of G2- Check for DNA replication and DNA damage before entering cell division
Metaphase- M checkpoint checks for fiber attachment to chromosomes
Reception
1st step of cell signaling, when the ligand binds to the receptor.
Transduction
2nd step of cell signaling, converts the signal to a form that can bring about a specific cellular response.
Response
3rd step of cell signaling, when the signal finally reaches what is needed for the cell to perform the response.
Contact inhibition
A process which cells do not divide because they are touching other cells.
Phosphorylation cascade
Signaling pathway where one enzyme phosphorylates another to reach a cellular response
G Protein
A eukaryotic coupled receptor protein
Bacterial Quorum sensing
Signal transduction pathway used with bacteria to communicate to other bacteria when responding to changes in population.
p53
negative regulatory molecule that can trigger apoptosis when events do not occur.
Negative feedback mechanism
A control mechanism designed to return cells back to homeostasis when something is disrupted.
Positive feedback mechanism
A control mechanism designed to push cells further away from homeostasis, typically starting the same mechanism to nearby cells.
Amplification
Occurs when the stimulus is further activated, initiating an additional response that produces the system change.
Positive regulators
proto-oncogenes which encourage cell growth and divsion
Negative regulators
tumor suppressor genes which suppress cell growth and division
Oncogenes
Mutated form of proto-oncogenes causing uncontrollable cell growth and division
Mutated tumor suppressor genes
Prevents cells from entering the next stage of division when they work completely normal.
Receptor tyrosine kinase receptors
Receptors that act as enzymes, used in cell growth, differentiation, and survival.