LEC 9.2: Pulse | Vitals
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Pulse
Wave of blood created by contraction of Left Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Pulse is created by the contraction of what part of the heart?
Stroke Volume Output
What the pulse wave generally represents which is the amount of blood that enters the arteries with each ventricular contraction
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood that comes out into the arteries by the heart and equals the result of the Stroke Volume x Heart Rate per minute
Pulse Rate = Rate of Ventricular Contraction
In a healthy individual what is the relationship between pulse rate and the rate of ventricular contraction?
Apical Pulse
Peripheral Pulse
Clients heart produces very weak pulse waves that are not detectable in a pulse far from the heart, like peripheral pulse cells. So what should the nurse assess?
Apical Pulse
Central pulse that is located at the apex of the heart
Point of Maximal Impulse (PMI)
What is the apex of the heart referred to as?
Beats per minute (bpm)
What is rate of pulse expressed in?
Age
Sex
Exercise
Fever
Medicaitons
Hypovolemia or Dehydration
Stress
Position
Pathology
Factors Affecting the Pulse
Age
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Changes in pulse rate are usually associated with natural aging process, physical fitness, and overall health
As __ increases, average pulse rate gradually decreases
Sex
(Factor affecting the pulse)
After puberty, the average male’s pulse rate is lower than that of the females
Hormonal influences
Exercise
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Pulse rate normally increases with activity but rate of increase in professional athlete is often less than that of the average individual due to greater cardiac size, strength, efficiency
Fever
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Pulse rate increases in response to lowered BP that results from peripheral vasodilation related to elevated body temperature and due to increased metabolic rate
Medications
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Some decrease the pulse rate
Cardiotonics
Digitalis Preparations
Others increase it
Epinephrine
Hypovolemia/Dehydration
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Loss of fluid form vascular system increases pulse rate
Loss of circulating volume results in adjustment of heart rate to increase blood pressure as body compensates for the blood volume that is lost
Stress
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Sympathetic nervous stimulation increases the overall activity of the heart and rate, force of the heart
Fear and anxiety stimulate sympathetic system
Position
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Sometimes when clients sit up or stand up, blood usually pulls independent vessels in our venous system —> resulting in transient decrease in venous blood return to heart and increase heart rate because of reduction in BP
Pathology
(Factor affecting the pulse)
Certain diseases or heart conditions that could impair oxygenation that can alter the resting pulse rate of the patient
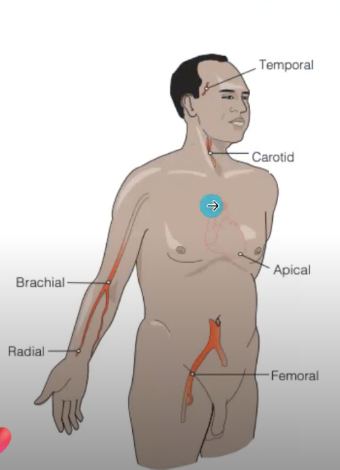
Temporal
Carotid
Apical
Brachial
Radial
Femoral
Popliteal
Posterior Tibial
Dorsalis Pedis
Locations to Assess Pulse
Temporal
(Location to Assess Pulse)
Where temporal artery passes over temporal bone of head
Superior and lateral from midline o
Carotid
(Location to Assess Pulse)
Side of the neck where ___ artery runs between trachea and sternocleidomastoid muscle
Do not press too hard or may stimulate Vagus nerve which can lead to drop in heart rate —> bradycardia —> dizziness, fainting
Should not be palpated at the same time
Apical
(Location to Assess Pulse)
At apex of the heart
In an adult, located at left side of chain about 3 inches to left of sternum at 5th intercostal space
In older adults, apex may be further in the left if conditions are present, like enlarged heart
Before 4 years of age, apex is on the left of the midclavicular line
Between 4-6 years, at midclavicular line
7-9 years, located at 4th or 5th intercostal space
3 inches to left of sternum at 5th intercostal space
In an adult, where is the apex of the heart located (apical pulse site)?
Further in the left of sternum if conditions are present, like enlarged heart
In an older adult, where is the apex of the heart located (apical pulse site)?
Left of the midclavicular line
In a child before 4 years old, where is the apex of the heart located (apical pulse site)?
At midclavicular line
In a child 4-6 years old, where is the apex of the heart located (apical pulse site)?
Located at 4th or 5th intercostal space
In a child before 7-9 years old, where is the apex of the heart located (apical pulse site)?
Brachial
(Location to Assess Pulse)
At the inner aspects of the biceps of the arm or medially in the antecubital space
Radial
(Location to Assess Pulse)
Thumb side of wrist
Femoral
(Location to Assess Pulse)
Alongside inguinal ligament
Popliteal
(Location to Assess Pulse)
__ artery passes behind the knee
Posterior Tibial
(Location to Assess Pulse)
On the medial surface of the ankle where the ___ artery passes behind the medial malleolus
Middle of the ankle
Dorsalis Pedis
(Location to Assess Pulse)
__ artery passes over the bones of the foot on an imaginary line drawn from the middle of the ankle to the space between the big and second toes
Palpation (feeling)
Auscultation (hearing)
How is pulse assessed?
Pads of the three middle fingers, moderate pressure
What is used for palpating all pulse sites, except for one?
Apical
What pulse site should NOT be palpated?
Auscultation via stethoscope
What is used to assess the apical pulse?

Doppler Ultrasound Stethoscope (DUS)
What stethoscope is used when there is a difficulty in pulse assessment?
Has a headset with ear pieces similar to standard stethoscopes’ ear pieces or speaker or ultrasound transducer
Detects movement of RBCs through a blood vessel
Eliminates environmental sounds, so very useful for noisy setting
Medications
Activities
Baseline Data
Position
What needs to be assessed prior to obtaining the pulse?
Medications
(One of the factors that needs to be assessed prior to obtaining the pulse)
There are certain ___ that can affect HR
Activities
(One of the factors that needs to be assessed prior to obtaining the pulse)
If patient/client has been physically ___, we have to wait 10-15 minutes until the client has rested and pulse has slowed to its usual rate
Baseline Data
(One of the factors that needs to be assessed prior to obtaining the pulse)
For example, those physically fit athletes may have low resting pulse rate
Position
(One of the factors that needs to be assessed prior to obtaining the pulse)
Sitting or change in certain __ due to change in blood flow or volume of autonomic nervous system activity
Rate
Rhythm
Volume
Arterial Wall Elasticity
Presence or Absence of Bilateral Equality
What also need to be taken note of when assessing pulse?
Tachycardia
Excessively fast heart rate over 100 bpm in adult px
Bradycardia
Heart rate less than 60 bpm in adult px
Pulse Rhythm
Pattern of the beats and the intervals between beats
Dysrhythmia/Arrhythmia
Pulse of an irregular rhythm
Apical pulse should be assessed and ECG/EKG should be necessary to define dysrhythmia further
What should be done if Dysrhythmia/Arrhythmia is noted?
Pulse Volume/Strength/Amplitude
Refers to force of blood with each beat
Peripheral Pulse Assessment
Refers to evaluating the pulses in the limbs to assess blood flow circulation and heart function
Typically checked to evaluate strength, rhythm, and rate of blood flow in the extremities
Can help identify problems like peripheral artery diseases, circulatory issues, or even heart conditions
To establish baseline data
To identify if it is normal
To determine the equality of corresponding peripheral pulses on each side of the body
What are the purposes of assessing Peripheral Pulse?
Apical Pulse Assessment
Indicated for clients whose peripheral pulse is irregular, unavailable
Also for those with known cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal diseases
Commonly assessed prior to administering medications that affect the heart rate of the client
Also used to assess pulse for newborns, infants, or children up to 2-3 years old
Indicated for clients whose peripheral pulse is irregular or unavailable
Prior to administering certain medications
Clients with known cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal diseases
To assess the pulse for newborns, infants, and children up to 2-3 years old
What are the purposes of assessing apical pulse?
False
True or False: Apical pulse assessment may be delegated to nursing aids.
Assess for clinical signs for cardiovascular alterations
Do not delegate apical pulse assessment to nursing aid
Need clock, timer, or watch; stethoscope, antiseptic wipes
Locate it: Position the client appropriately in a comfortable supine position or in a sitting position
Expose the area of the chest so the apex of the heart is exposed
Locate apical impulse, point over the apex of the heart where the apical pulse may be clearly heard
Palpate the angle of Bluey, angle between manubrium, top of sternum, and body of the sternum
Palpated below suprasternal notch and felt as a prominence
Slide index finger to left of sternum and palpate second intercostal space
Place middle or next finger into next spaces until 5th intercostal space is located
Move index finger laterally along 5th intercostal space toward midclavicular line (medial to midclavicular line)
Need to know how to document pulse rate, rhythm, nursing actions, related data (variations, discolorations, abnormal temperatures)
How do we assess Apical Pulse?
dyspnea
difficult respirations
fatigue
weakness
pallor
cyanosis
palpitations
syncope
dizziness
fainting
impaired peripheral tissue perfusion
skin discoloration
cold temperature
What signs of cardiovascular alteration does the nurse have to assess for prior to taking the apical pulse?
Diaphragm
Larger, flat circular side of stethoscope
High-pitched sounds like:
Normal Heart sounds
S1 & S2
Lung sounds (crackles, wheezes, breath sounds)
Bowel sounds
What sounds does the diaphragm pick up?
Bell
Smaller, concave bowl-shaped side of stethoscope
Low-pitched sounds like:
Heart murmurs
Abnormal heart sounds
S3 & S4 heart sounds
Gallops
Vascular sounds like bruits or venous hums
What sounds does the bell pick up?

Sample documentation of apical pulse assessment
Apical-Radial Pulse Assessment
May need to be assessed for clients with certain CV disorders
Either…
Thrust of blood from the heart is too weak for the waves to be left at the peripheral pulse site OR
Vascular disease is preventing impulses from being transmitted
What does an apical pulse greater than radial pulse?
Two-Nurse Technique
One-Nurse Technique
What are the techniques to conduct Apical-Radial Pulse Assessment?
Two-Nurse Technique
One nurse locates the apical impulse by palpation or with the stethoscope while the other nurse palpates the radial pulse site
If a clock or timer is not visible, nurse that is taking the radial pulse needs to have a watch, while the nurse taking the radial pulse decides when to begin and say and “start”
Ensures simultaneous counts are begun
Each nurse counts pulse for 60 seconds — nurse taking radial pulse says “stop”
One-Nurse Technique
Feel the radial pulse at the same time as listening to the apical pulse
Assess apical pulse for 60 seconds than radial pulse for 60 seconds - difference is the pulse deficit
Pulse Deficit
What is the difference between the 60 second-reading of the apical and radial pulses called?
Cardiac Glycoside/Digitalis Glycoside
Increase cardiac contractility which increases cardiac output, so as a result perfusion to the kidneys is increased, increasing the production of urine
Decrease heart rate by prolonging cardiac conduction
Digoxin
What is commonly used to used for clinical management of heart failure (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia)?
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
What conditions can Digoxin treat?
1 minute
How long should the apical pulse be taken before administering the dose?
60 bpm
What is the normal apical pulse?
Dose should not be administered and pulse should be retaken in 1 hour
If the apical pulse is less than 60 bpm or another specific parameter is set by the healthcare provider, what should be done?
Call the prescriber
If pulse remains less than 60 after an hour or patient reports dizziness initially, what should be done?