Fish Families
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Families we need to know for Fish Unit and their defining characteristics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Family Petromyzontidae
Superclass Agnatha— Jawless fishes (cyclostomes)
Includes hagfish and lamprey
They are anadromous, parasitic
They have no jaws and instead have gill arches made of cartilage to support the gills (cartilaginous skeleton).
Eel-like bodies
no paired fins (pectoral or pelvic)
muscular mouths
multiple gill openings (7 in lamprey, 12 in hagfish)

Class Chondrichthyes
Cartilaginous fishes and elasmobranchs
cartilaginous skeletons
5-6 gill openings
sharks, skates, rays, and chimeras
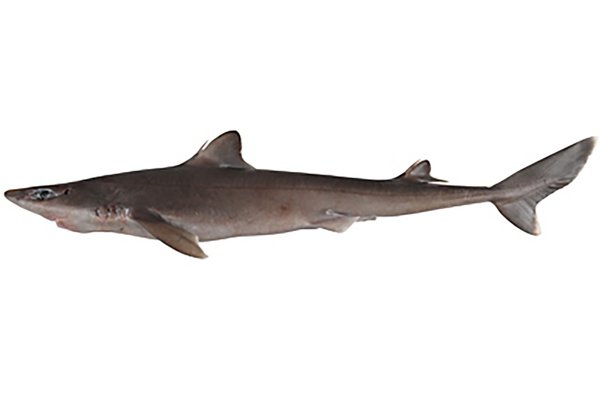
Family Squalidae
Dogfish Sharks (Spiny dogfish)
small bodied, shark shaped
no anal fin
1st dorsal fin in front of pelvic fins
spine at front of both dorsal fins
abdominal pelvic fins

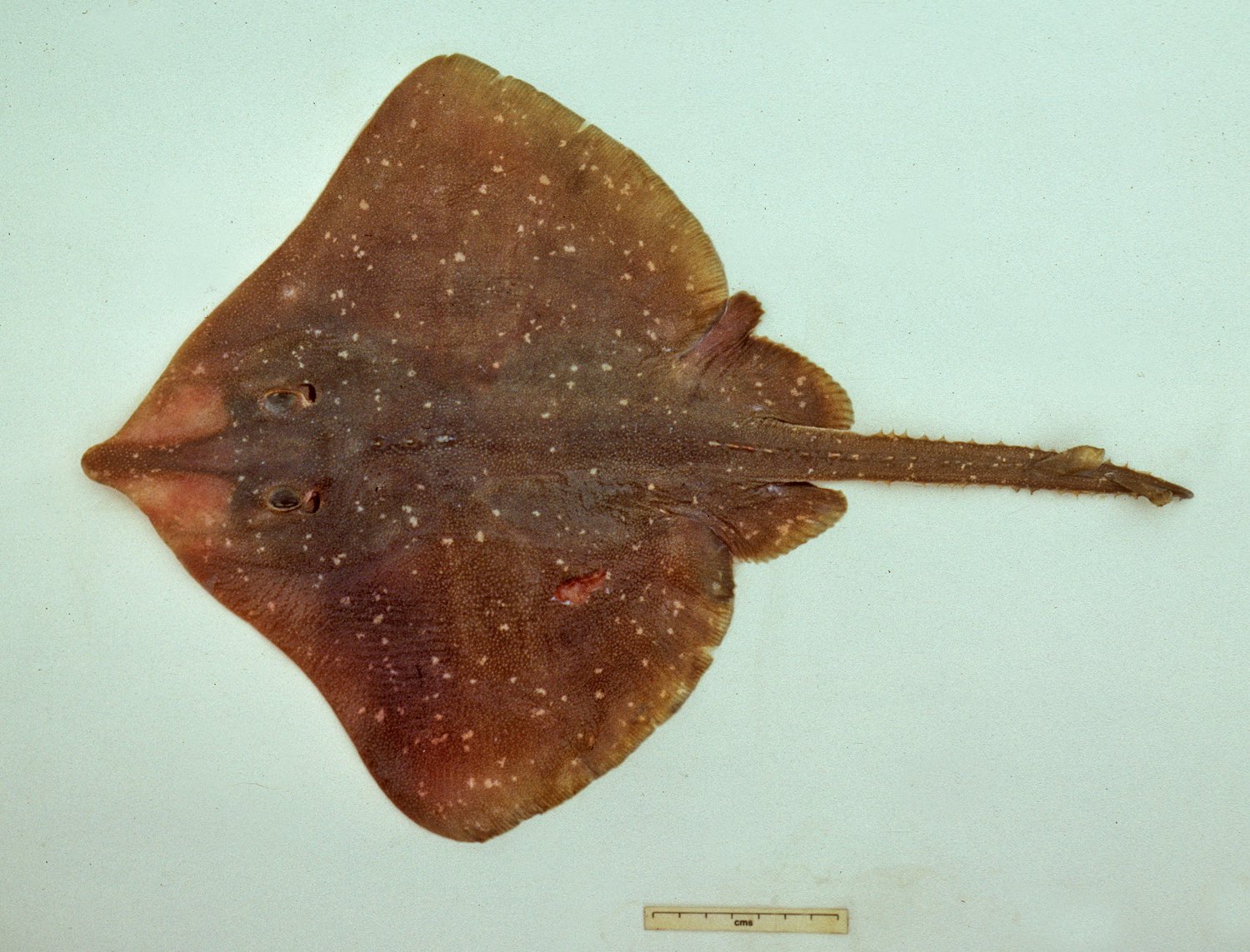
Family Rajidae
Skates (Big skate, longnose skate)
dorso-ventrally flattened
rhomboid to circular disk shape
spines on body and tail

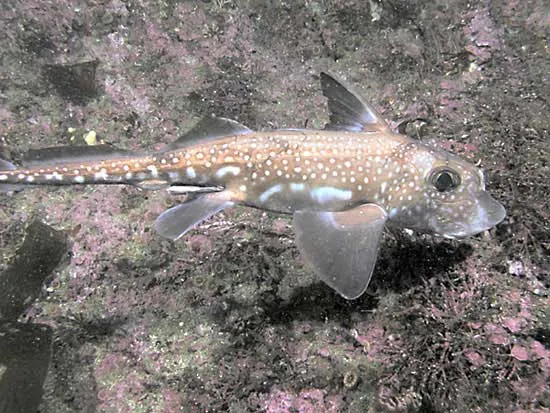
Family Chimaeridae
Ratfishes (spotted ratfish)
short blunt snout
rabbit shaped head
flat crushing teeth
prominent lateral line
slippery skin
large triangular pectoral fin
large green eyes
long tapering tail
white spots

Superclass Osteichthyes
The bony fishes
skeleton made of bones not cartilage
Family Acipenseridae
Sturgeons (White sturgeon, green sturgeon)
cartilaginous skeleton
heterocercal caudal fin
sub-terminal mouth
5 rows of dermal scutes
22-33 scutes on midside = green
38-48 scutes on midside = white

Division Teleostei
Teleosts
perfect bone
moveable jaw
homocercal caudal fins
spine ends at caudal peduncle
Family Clupeidae
Herrings and Shad (pacific herring, pacific sardine, american shad)
laterally compressed (less bullet shaped from front)
silver
countershaded
1 short dorsal fin
deeply forked caudal fin
no adipose fin
no spines
scutes on belly
schooling fish

Family Engraulidae
Anchovies (Northern anchovy)
small, silvery
long snout overhangs large mouth
inferior jaw
upper jaw extends well past eye
filter feeders

Family Salmonidae
Salmon, trout, charr (Chinook salmon, chum salmon, coho salmon)
adipose fin behind 1st dorsal
low pectoral fins
abdominal pelvic fins
no spines in fins
anadromous
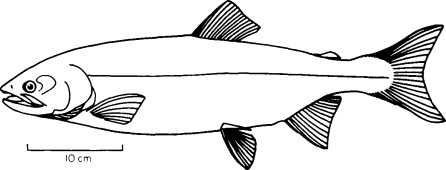
Family Osmeridae
Smelt (Whitebait smelt, surf smelt, eulachon)
small, frail
adipose fin
short dorsal fin at mid-body
pelvic fins abdominal
countershaded
anadromous
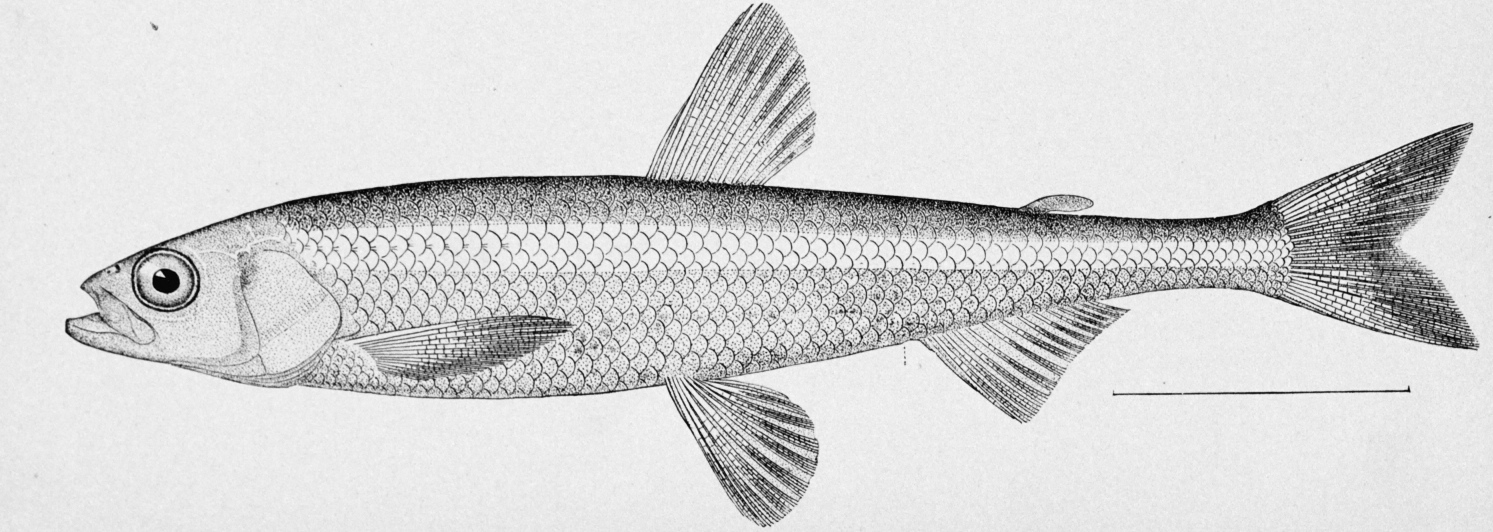
Family Gadidae
Cod (Pacific cod)
elongate
3 dorsal fins, 2 anal fins
thoracic pelvic fins
barbels on chin (chemosensory)
sub terminal mouth

Family Syngnathidae
Pipefish and Seahorses (bay pipefish)
encased in bony rings
body rigid, very long and slender
no pelvic fin
small, toothless mouth
tube snout
superior jaw
rounded caudal fin
highly modified fins
Family Gasterosteidae
Sticklebacks (threespine stickleback)
small mouth
armored with bony plates
no scales
3 isolated spines before soft dorsal (threespine stickleback)

Family Scorpaenidae
Rockfish (Black rockfish, copper rockfish, china rockfish, etc.)
very spiny
stout body
ovoviviparous
found in many habitats
very diverse in color, shape, size and pattern, often featuring venomous spines for defense.

Family Hexagrammidae
Greenlings (Kelp greenling, painted greenling, lingcod)
no spiny head
elongate body with long single dorsal fin
pelvic fins thoracic
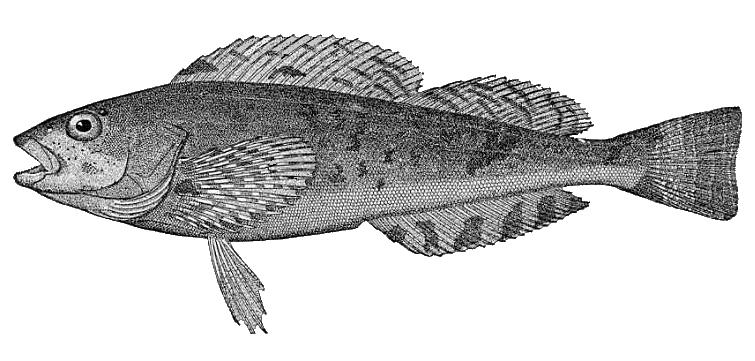
Family Cottidae
Sculpins
stout, round body
large (frog shaped) head with spines, knobs, or cirri
large fan like pectoral fins
dorsal, anal fins usually long
benthos fish

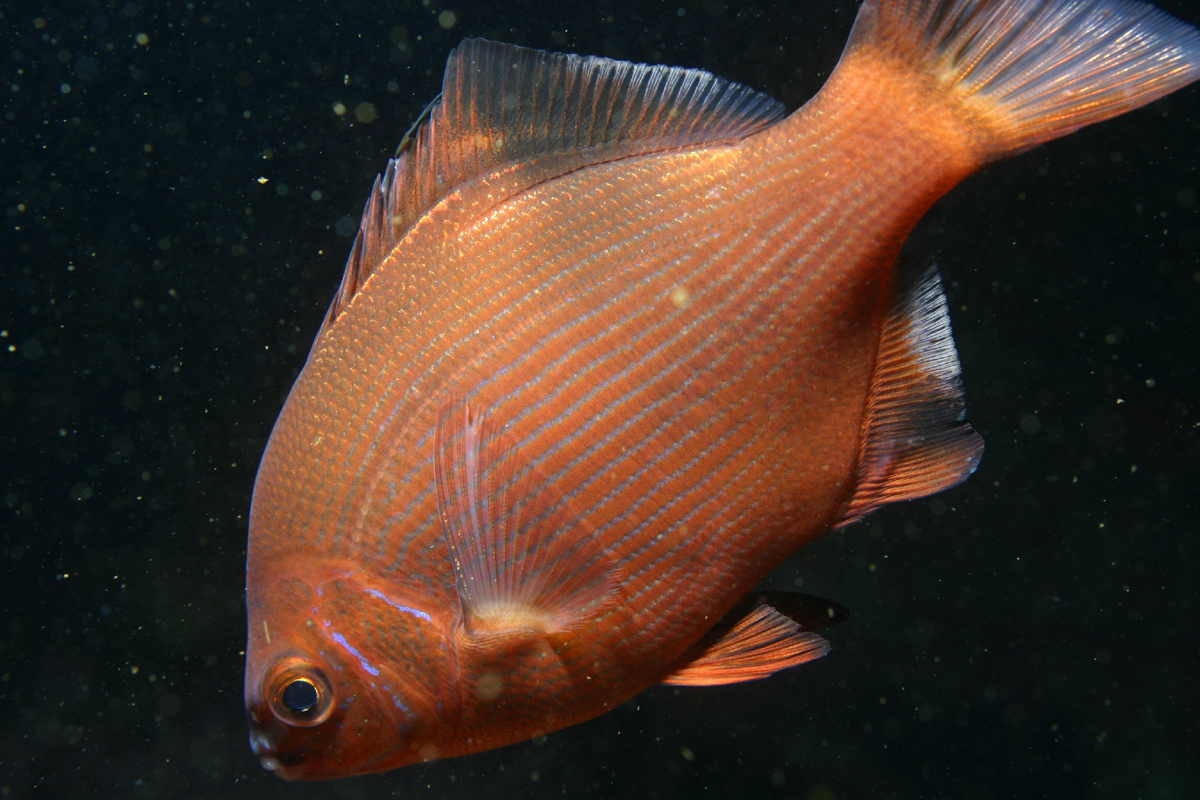
Family Embiotocidae
Surfperches
laterally compressed, elliptical
un-notches dorsal fin
viviparous

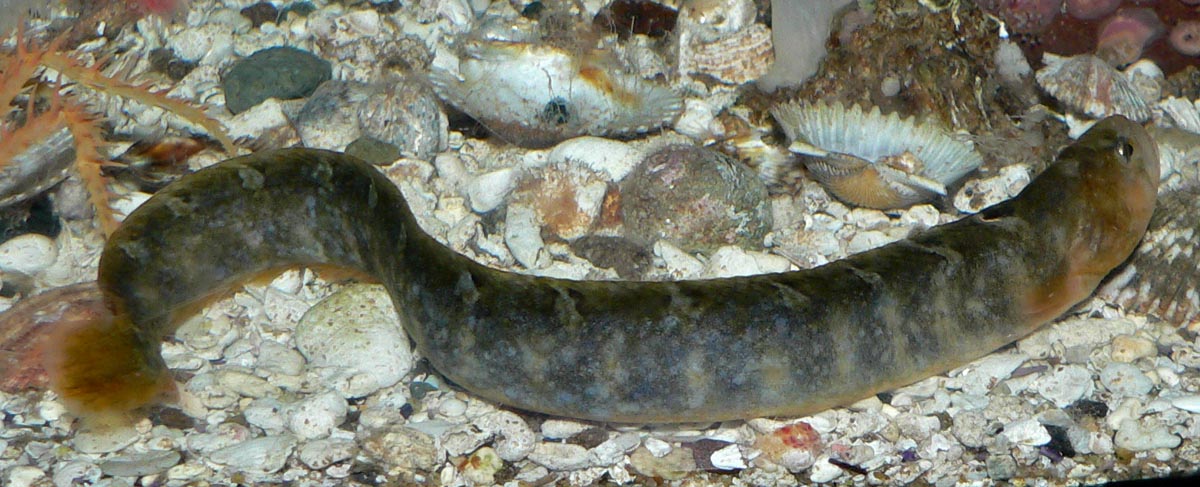
Family Pholidae
Gunnels (saddleback gunnel, rockweed gunnel, penpoint gunnel)
eel-like, long compressed bodies
dorsal fin long and flexible (soft spines)
dorsal and anal fins joined to caudal fin
anal fin less than 50% body length

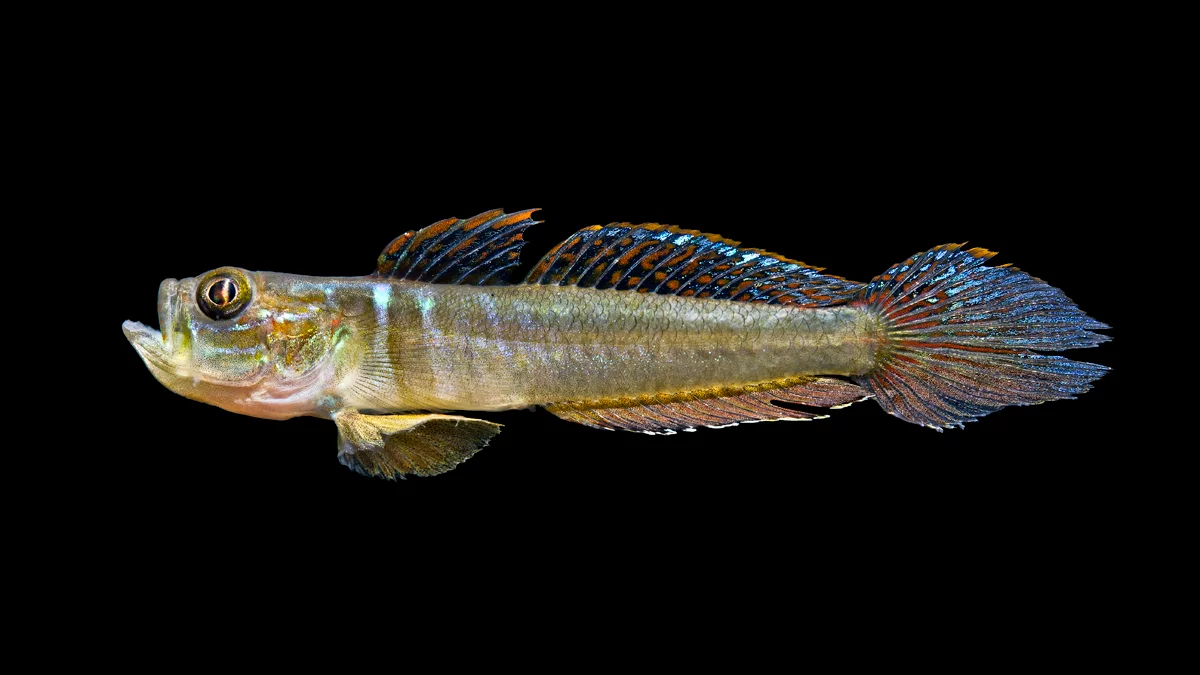
Family Gobiidae
Gobies
small fish
pelvic fins fused to form cone
1st dorsal fin w/ 7 spines
rounded caudal fin
smallish gill openings

Family Scombridae
Mackerels and Tuna
2 dorsal fins w/ 5-12 finlets behind 2nd dorsal fin and anal fin
pectoral fins high on body
slender caudal peduncle w/ 2 keels
specialized subcutaneous vascular system in some spp.
swim continuously
reduces drag
specialized heat keeping
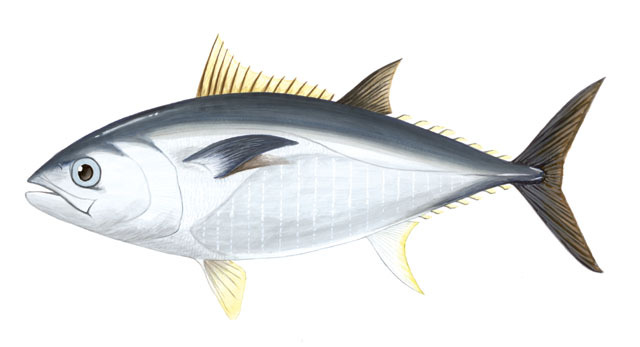
Family Paralichthyidae
Sand Flounders (pacific sanddab)
flat
both eyes on left side
lateral line arches over pectoral fin
eye rotates in metamorphosis
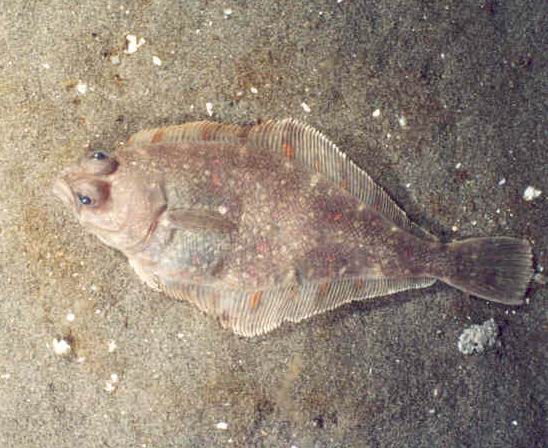

Family Pleuronectidae
Right eye flounders (starry flounder, english sole, pacific halibut)
flat
eyes on right side
triangle shaped dorsal and anal fins
