Sensation and Perception
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Receptors
Specialized cells that convert physical energy in the environment to electrical energy that can be transmitted as nerve impulses to the brain
Transduction
Conversion of 1 form of energy to another (sensory receptors are biological transductors)
Sensory Adaptation
Repetitive/unchanged stimulation eventually disappears due to adaptation (ex.: perfume smell, cold water in a pool, food smells at a restaurant, noise of a projector, etc.)
Sensory Interaction
How senses influence one another (smell & taste have the most interaction between each other)
McGurk Effect
“Ba vs. Fa;” seeing mouth movements helps dictate what we hear (interaction between vision & hearing)
Synesthesia
Brain circuits of 2+ senses are jointly d& stimulation from 1 sense triggers an experience in another (ex.: auditory-tactile, Grapheme-color, sound-color, number-form); could be cause by genetics, faulty pruning, etc.
Light & the Visual Spectrum
The color something appears is the light that is reflected off of it
Light waves=energy from environment
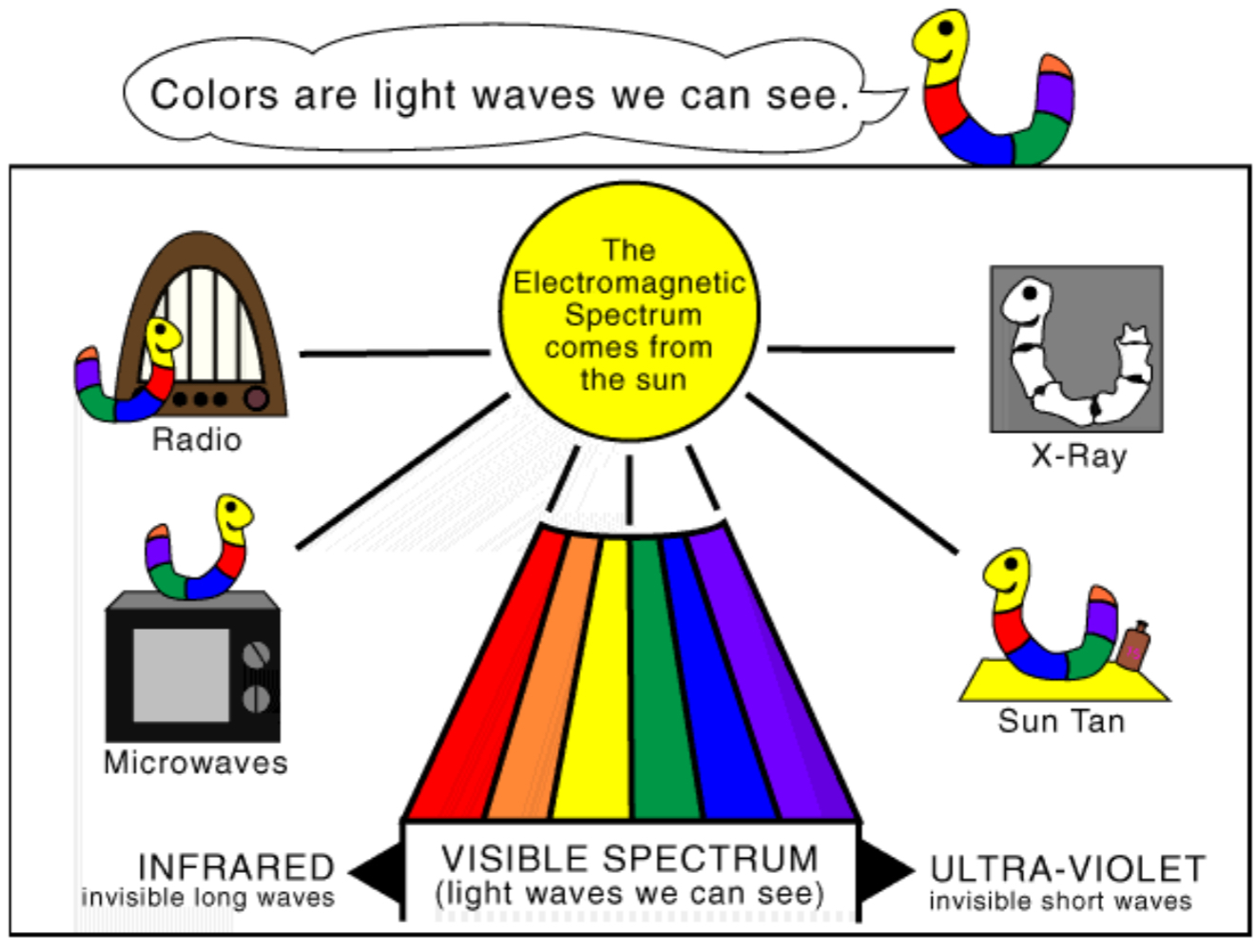
Cornea
Part of eye; transparent, protective outer coating; works w/ lens to collect and focus light rays
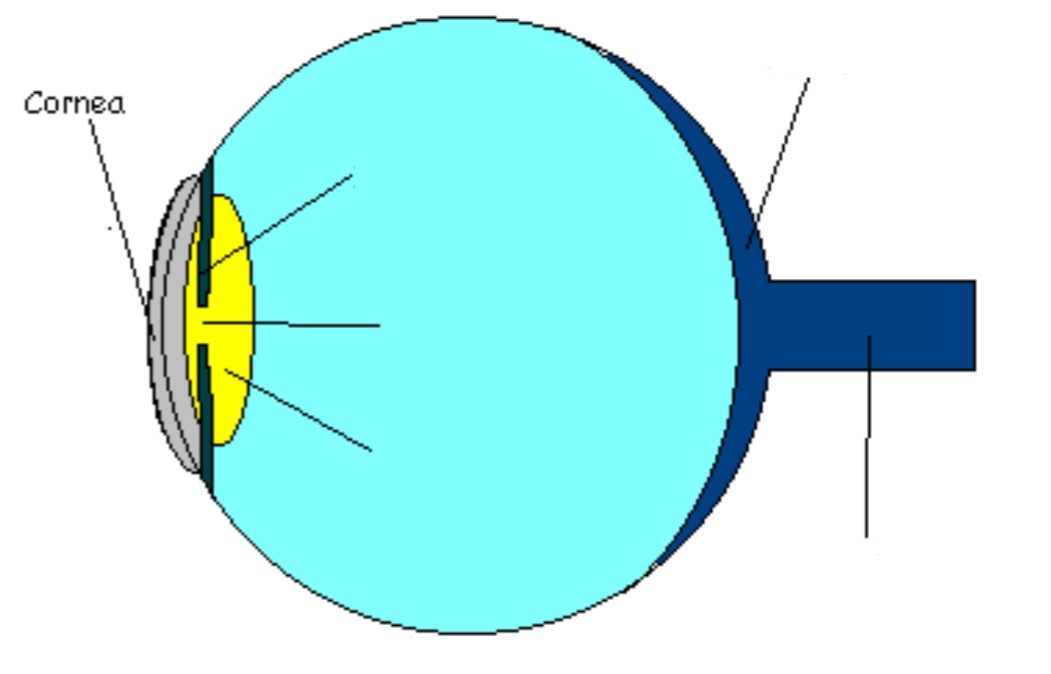
Pupil
Part of eye; opening in eye (lets light in)
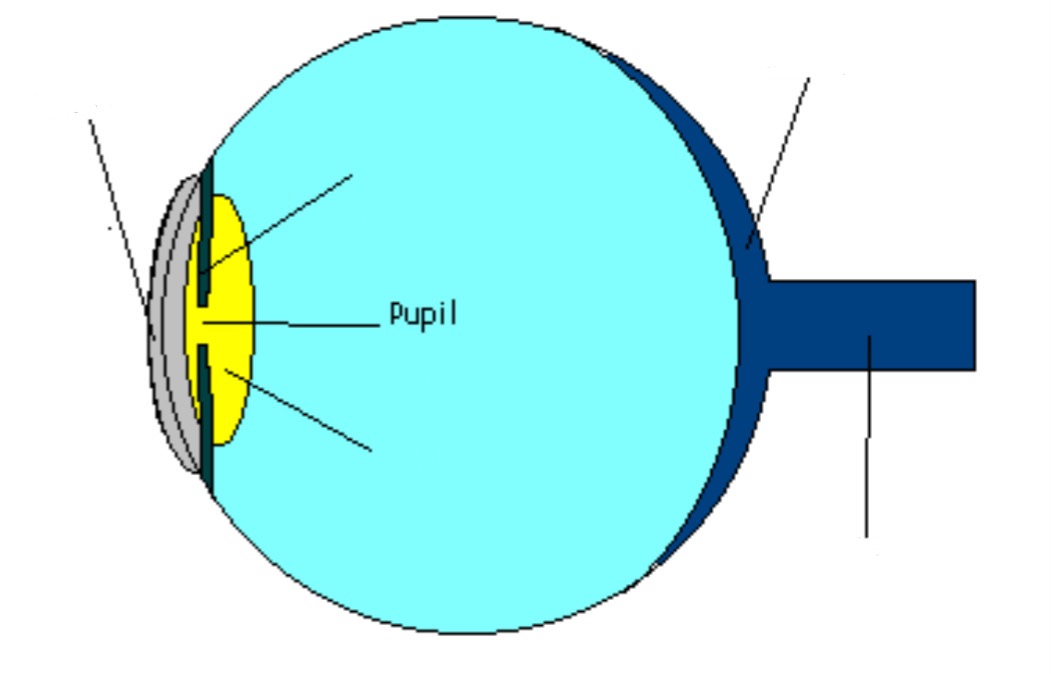
Iris
Part of eye; controls amnt. light that enters eye (like a camera shutter)
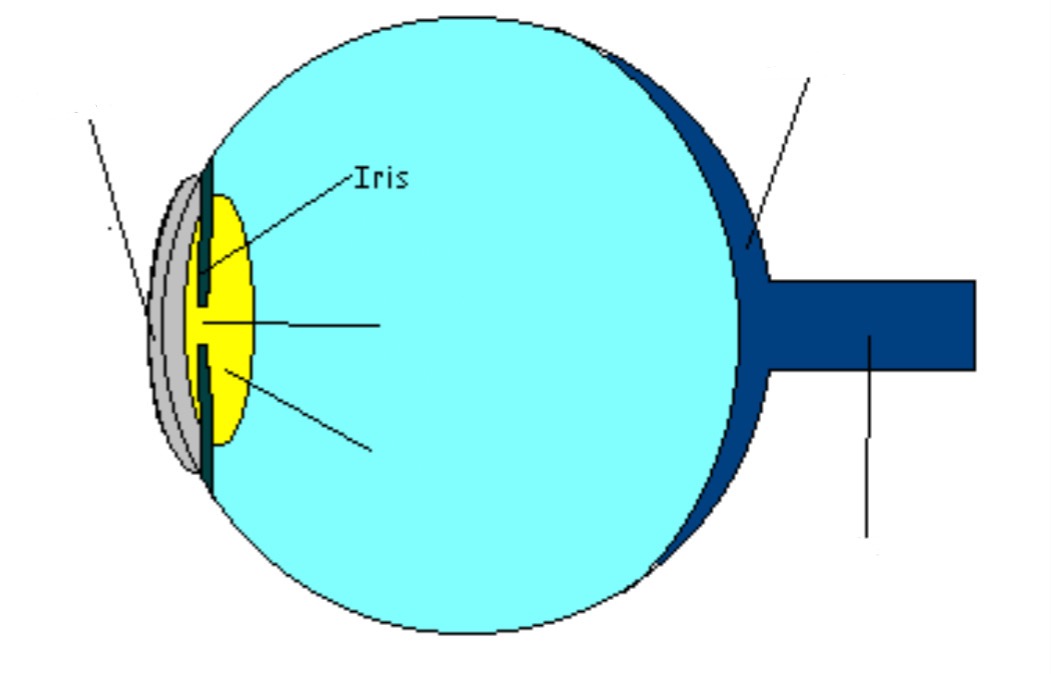
Lens
Part of eye; focuses incoming light on retina (contacts/glasses assist the lens)
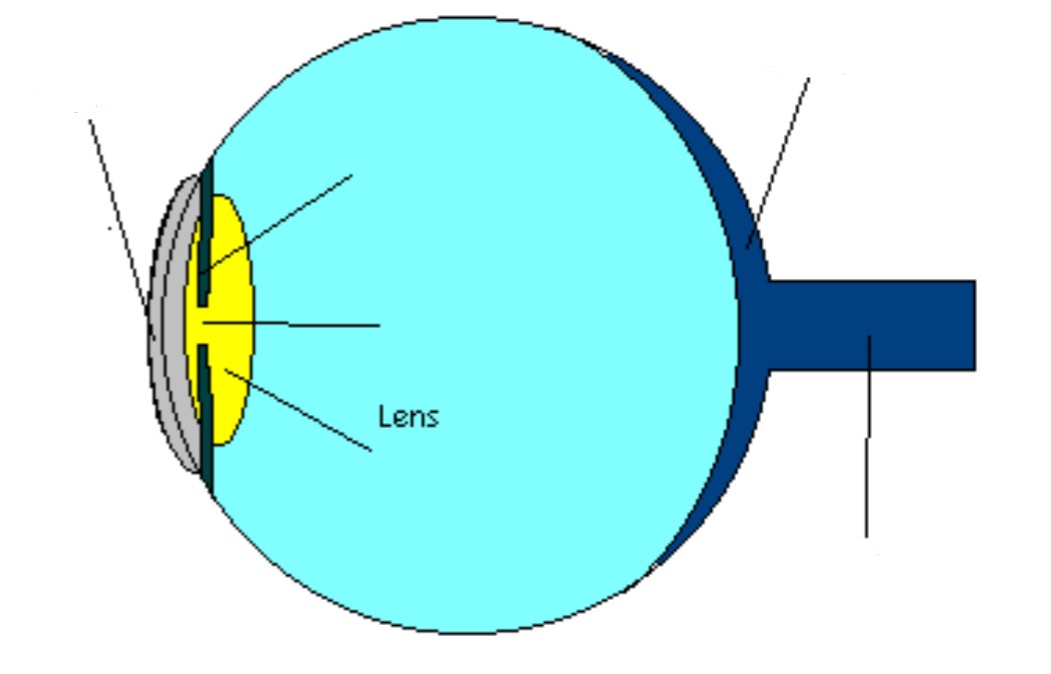
Accommodation
Process of curving lens to project images on retina; muscles behind iris change lens shape (flattens to focus on distant objects; thickens to focus on closer objects)
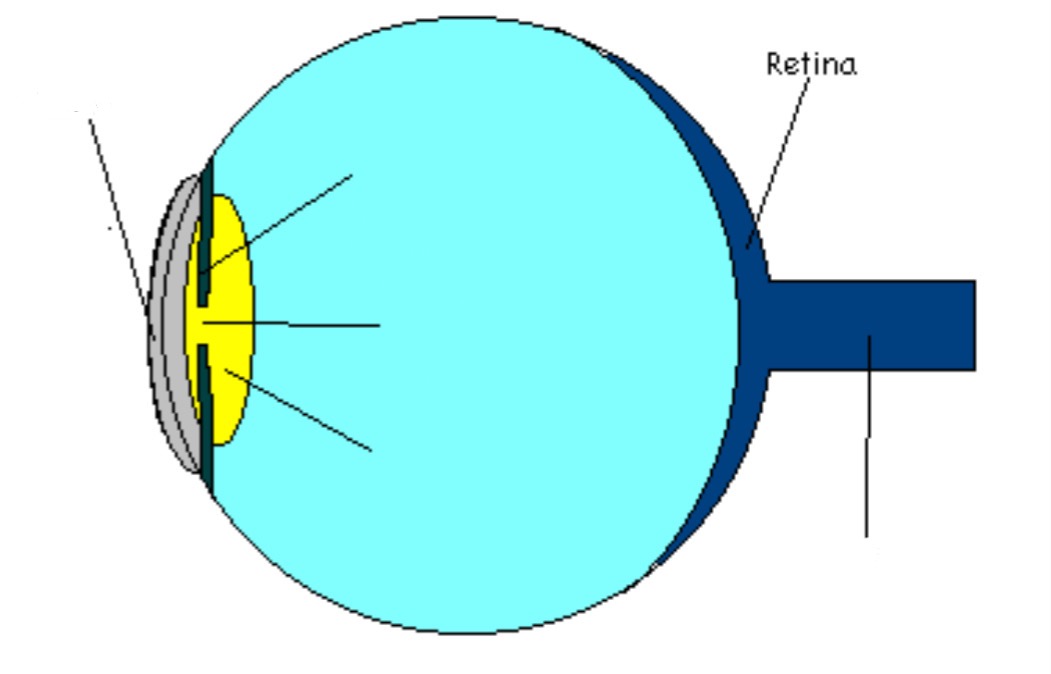
Retina
Photoreceptive portion of eye
Rods
Type of photoreceptor in retina; about 100 million/eye; VERY light sensitive; deals with night vision; deals with black & white info; concentrated at periphery of eye
Cones
Type of photoreceptor in retina; about 6.5 million/eye; good in bright light (NOT in dark); helps perceive color (150-200 diff. colors); good with discerning details; concentrated in fovea (center of eye)
Fovea
Center of macula (pt. of retina that provides sharp, central vision); only contain cones; sharpest pt. of vision in eye
Bipolar cells
Connect rods/cones to ganglion cells
Ganglion Cells
Neurons in retina that gather info from receptor cells; axons of ganglion cells make up optic nerve
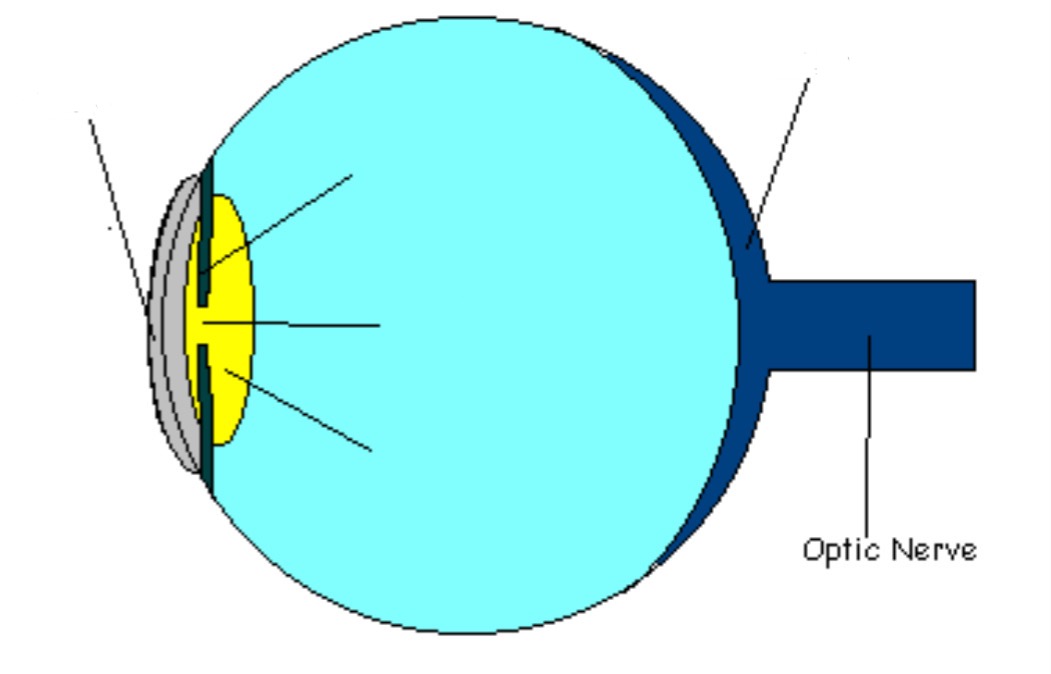
Optic Nerve
Part of eye; nerve tat leads to thalamus & then brain’s occipital lobe (occipital lobe is located @ back of head & intérprete optic nerve impulses)
Blindspot
Area on retina w/o receptors (place where optic nerve is in eye)
Feature Detectors
Cells in visual cortex that are sensitive to specific features (horizontal, vertical, angled lines); image that reaches brain is combination of lines/angles that somehow form a pattern that makes sense to brain
Normal Vision
Rays of light converge on retina of normal eye
Nearsightedness
Eyeball is longer than normal—>visual info focuses closer in front of retina—>faraway objects are blurry
Farsightedness
Eyeball is shorter than normal—>visual info focuses behind retina—>nearby objects are blurry
Trichromatic Theory
Color vision theory; all colors of light are made up of red, green, and blue; retina only has 3 cone types that correspond to these colors of light
Opponent Process Theory
Color vision theory; as the visual image leaves receptor cells, we analyze it in terms of 3 sets of opposing colors (red-green, blue-yellow, black-white); visual systems treat pairs of colors as opposing/antagonistic; when fatigued, the opposite color fills in
Afterimage Effect
Burst of neuron firing is produced when a color is removed; opposite color fills in
Monochromatism vs. Dichromatism (Color Blindness)
Monichromatism=type of color blindness in which one can only see 1 color (instead of “trichromatic”)
Dichromatism=type of color blindness in which one can only see 2 colors (instead of “trichromatic”)
Color blindness is a recessive trait carried on X chromosome; b/c males only have 1 X (females have 2), color blindness is much more common in men
Most common color blindness is red-green color blindness
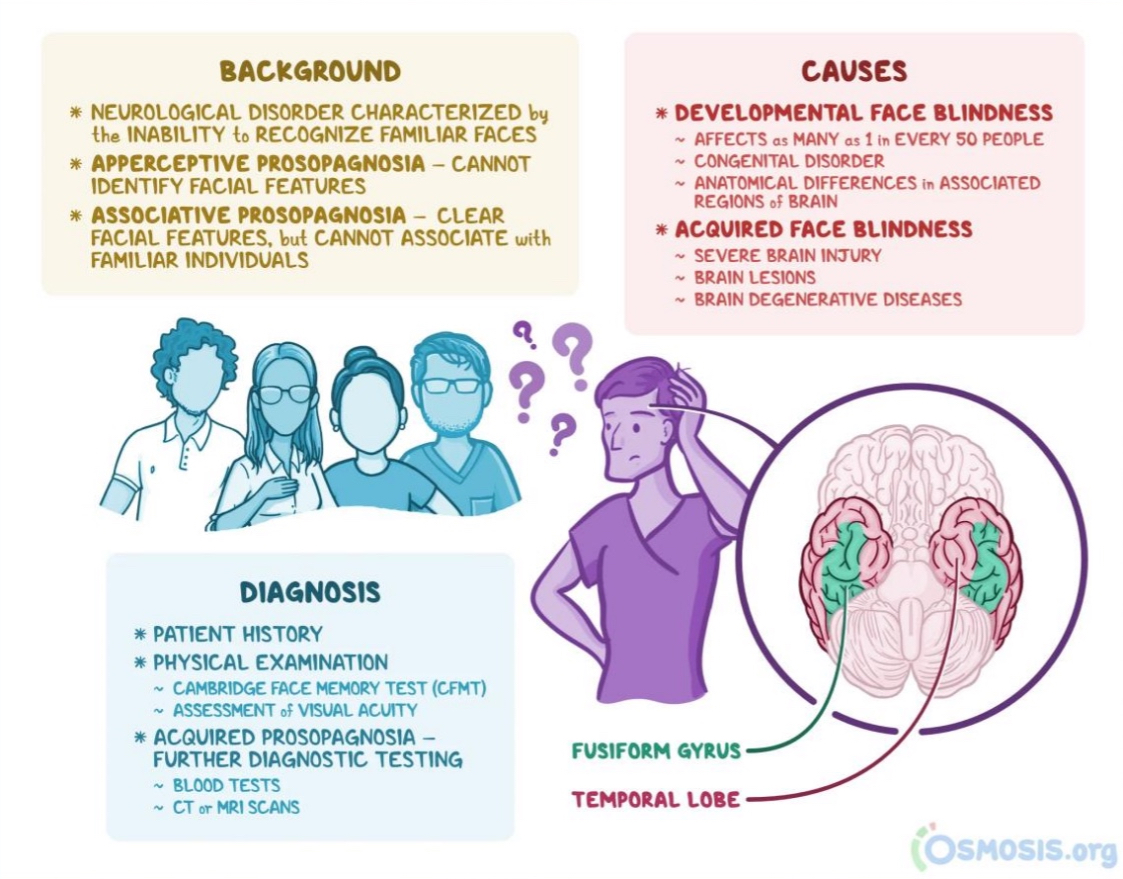
Prosopagnosia
“Face blindness;” inability to recognize any familiar face
Blindsight
Blind ppl. respond to items displayed in their blind area, where they can’t consciously see them; nerves send visual info to brain areas that don’t help with conscious vision, but may cause blindsight
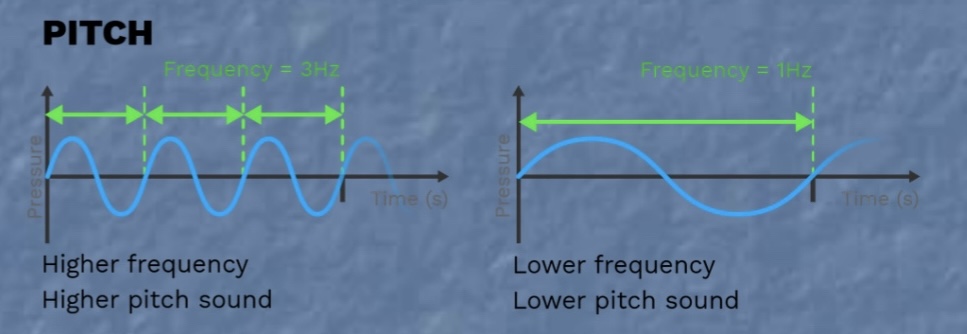
Pitch
Measure of frequency of a sound wave (Hz or “vibrations/sec”)
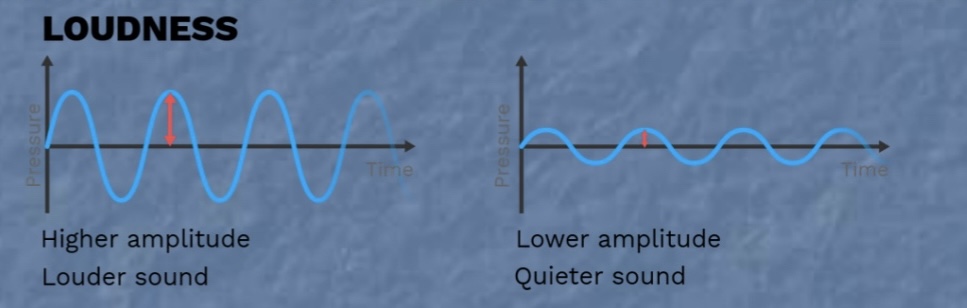
Loudness
Measure of amplitude of a sound wave
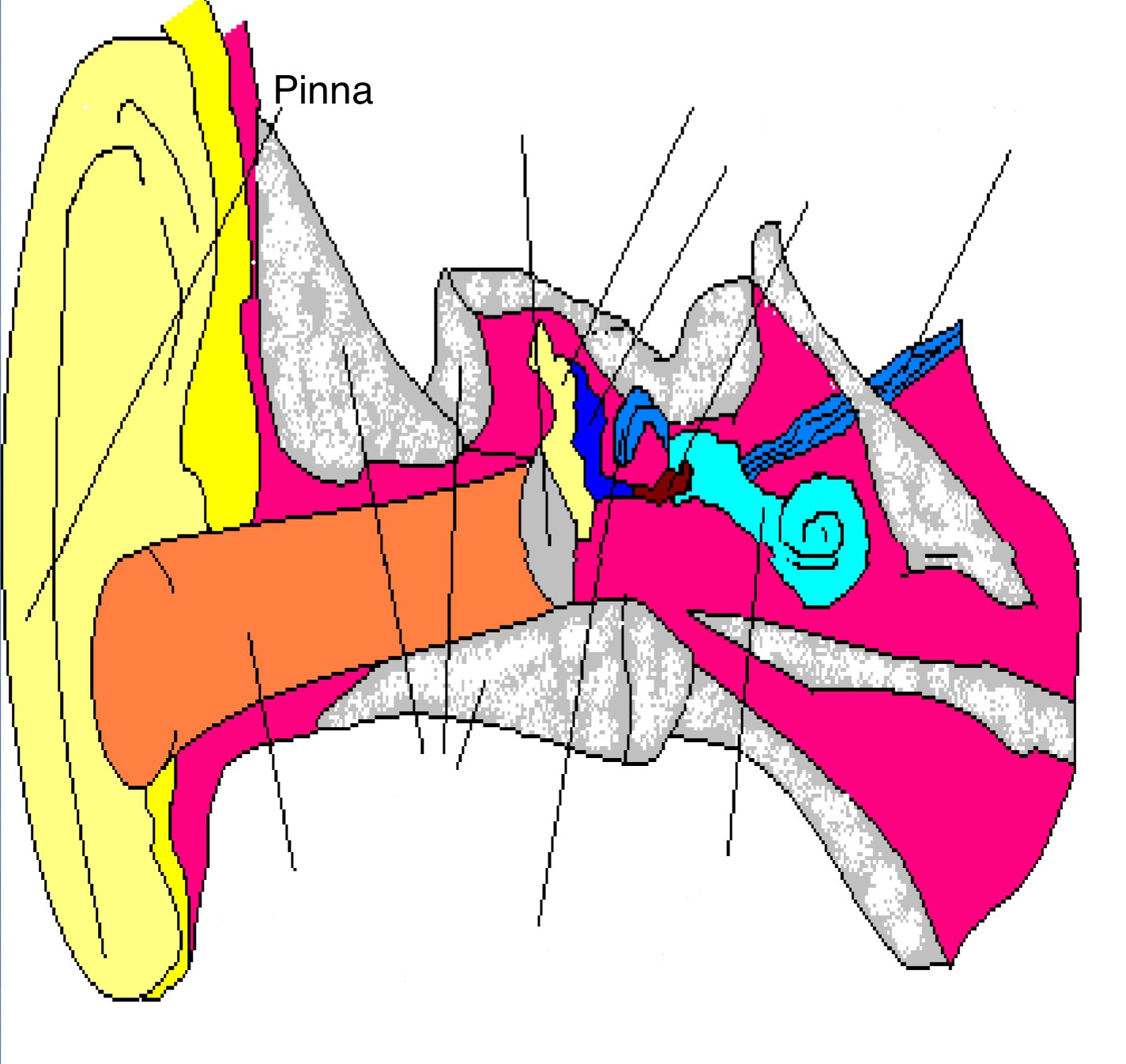
Function of Outer Ear
Collects sound waves
Pinna
Part of outer ear; outer flap & cartilage that receives sound waves
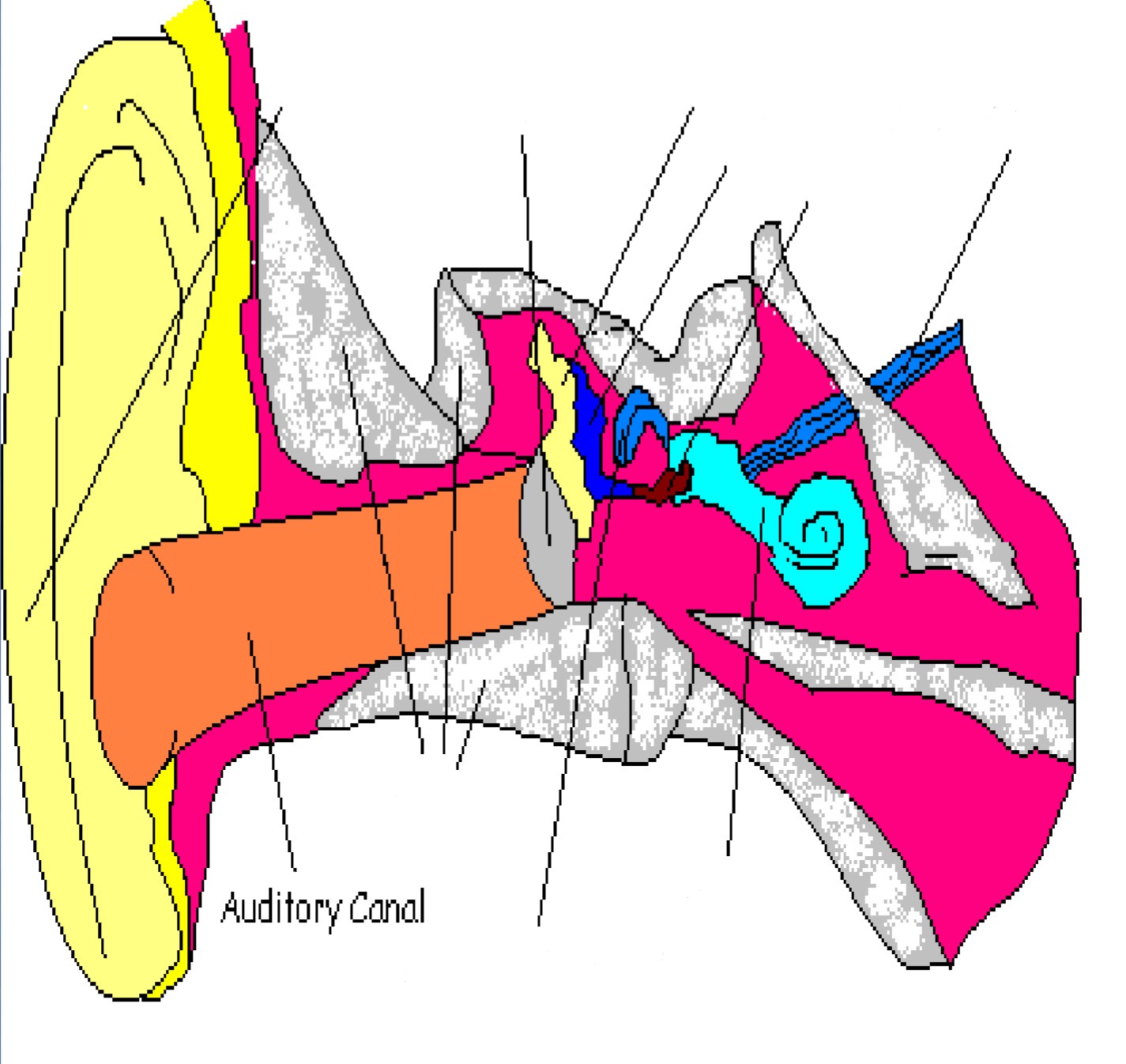
Auditory Canal
Part of outer ear; canal directly inside ear
Function of Middle Ear
Amplify sound waves
Tympanic Membrane (Eardrum)
Part of middle ear; piece of skin stretched over entrance to ear; vibrates to sound
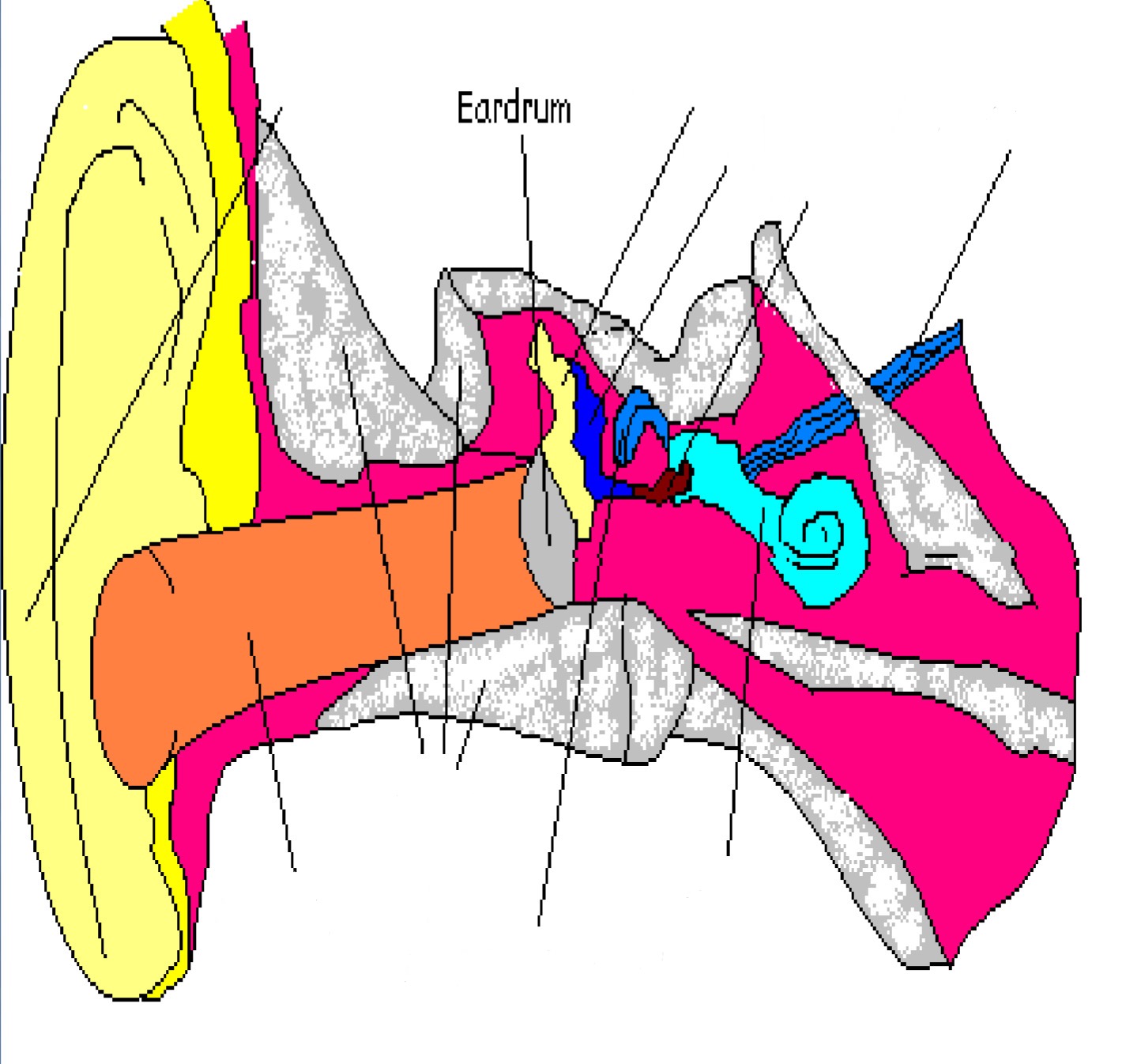
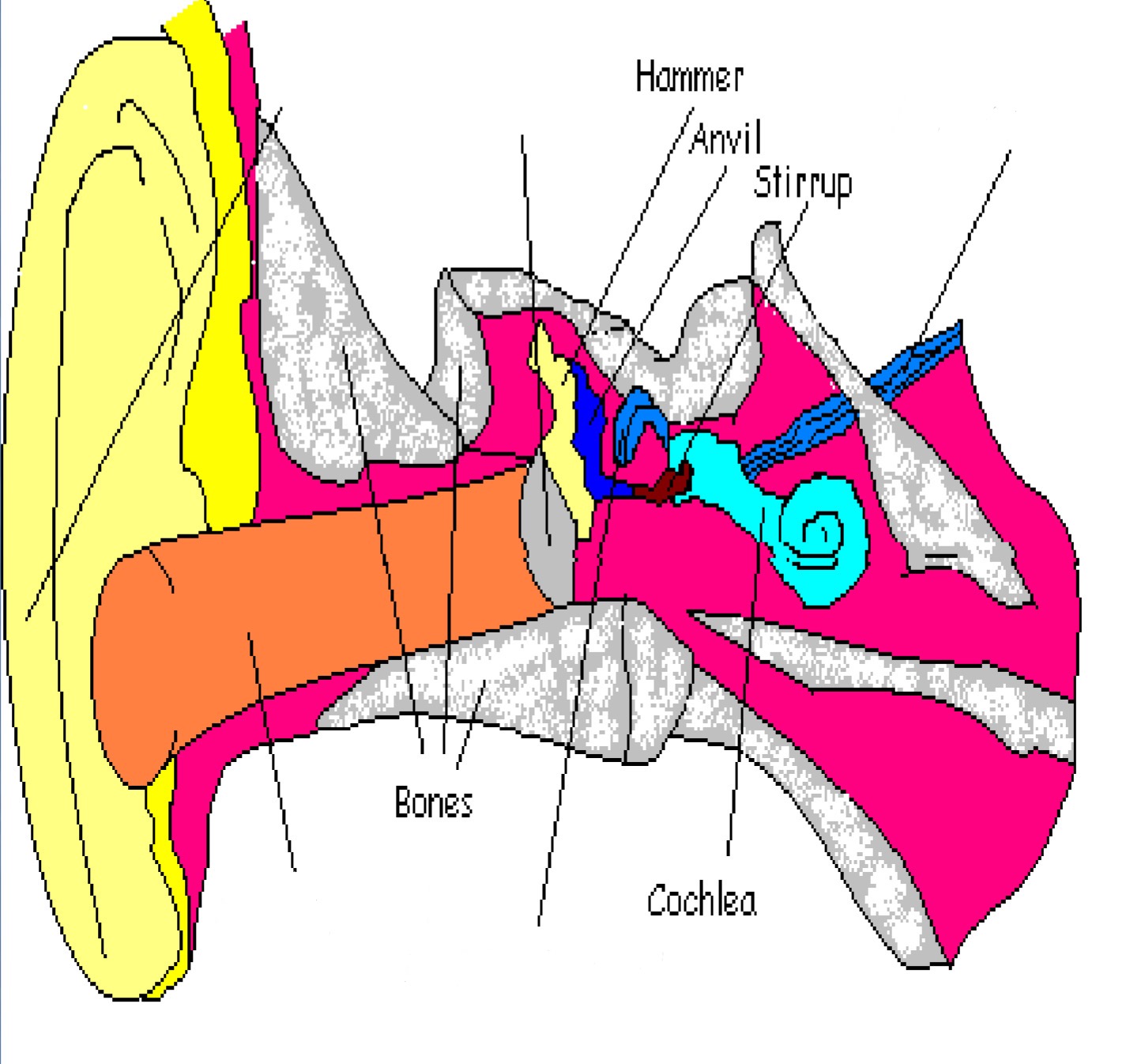
Ossicles (Hammer (Malleus), Anvil (Incus), Stirrup (Stapes))
Part of middle ear; 3 bones that transfer sound waves to cochlea (also called ossicles)
Eustachian Tubes
Part of middle ear; tube connecting throat & mouth to ear; helps maintain air pressure
Cochlea
Part of inner ear; filled w/ fluid & small hairs that vibrate to incoming sound
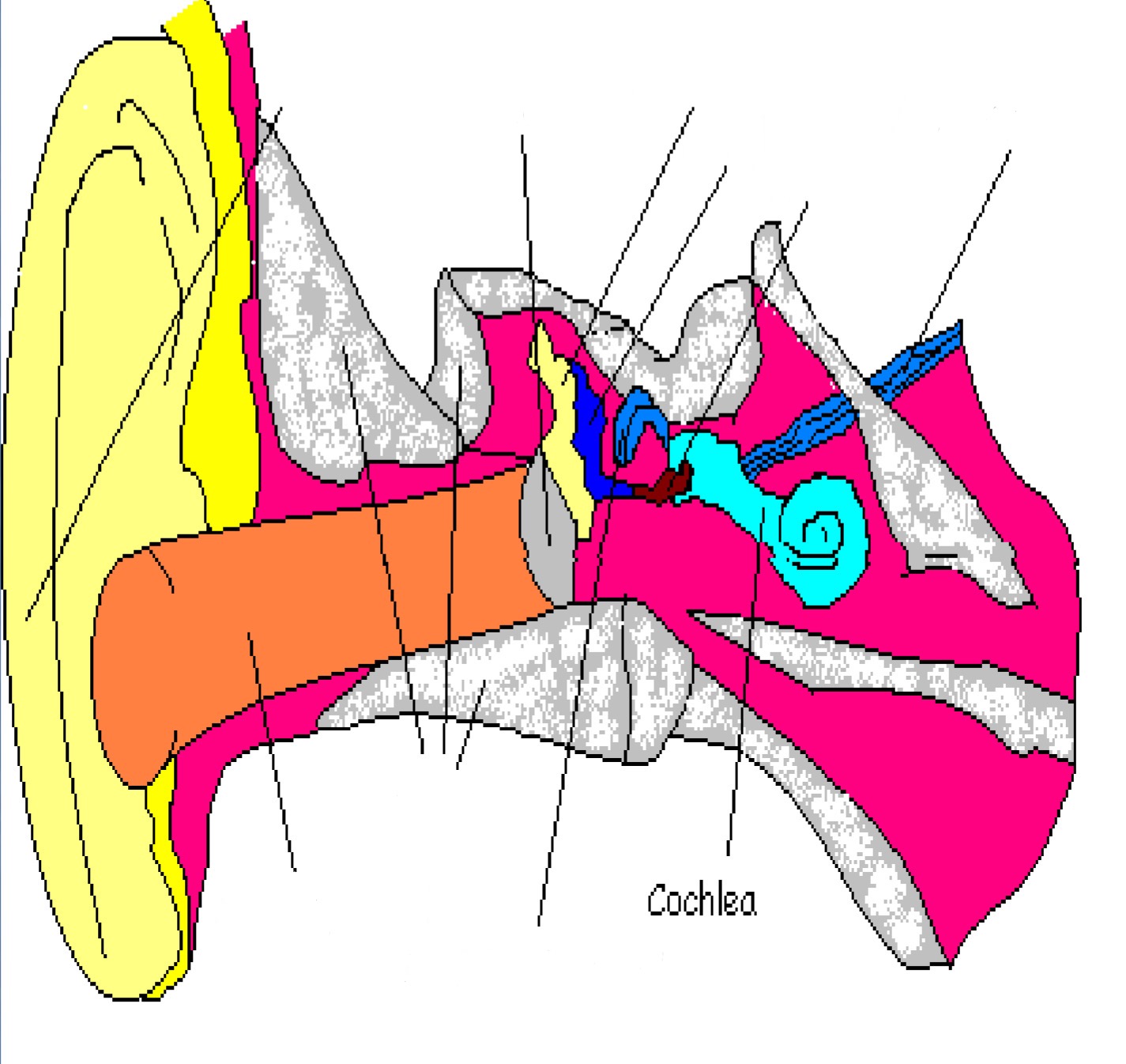
Basilar Membrane
Part of inner ear; runs through cochlea; hair cells are attached here
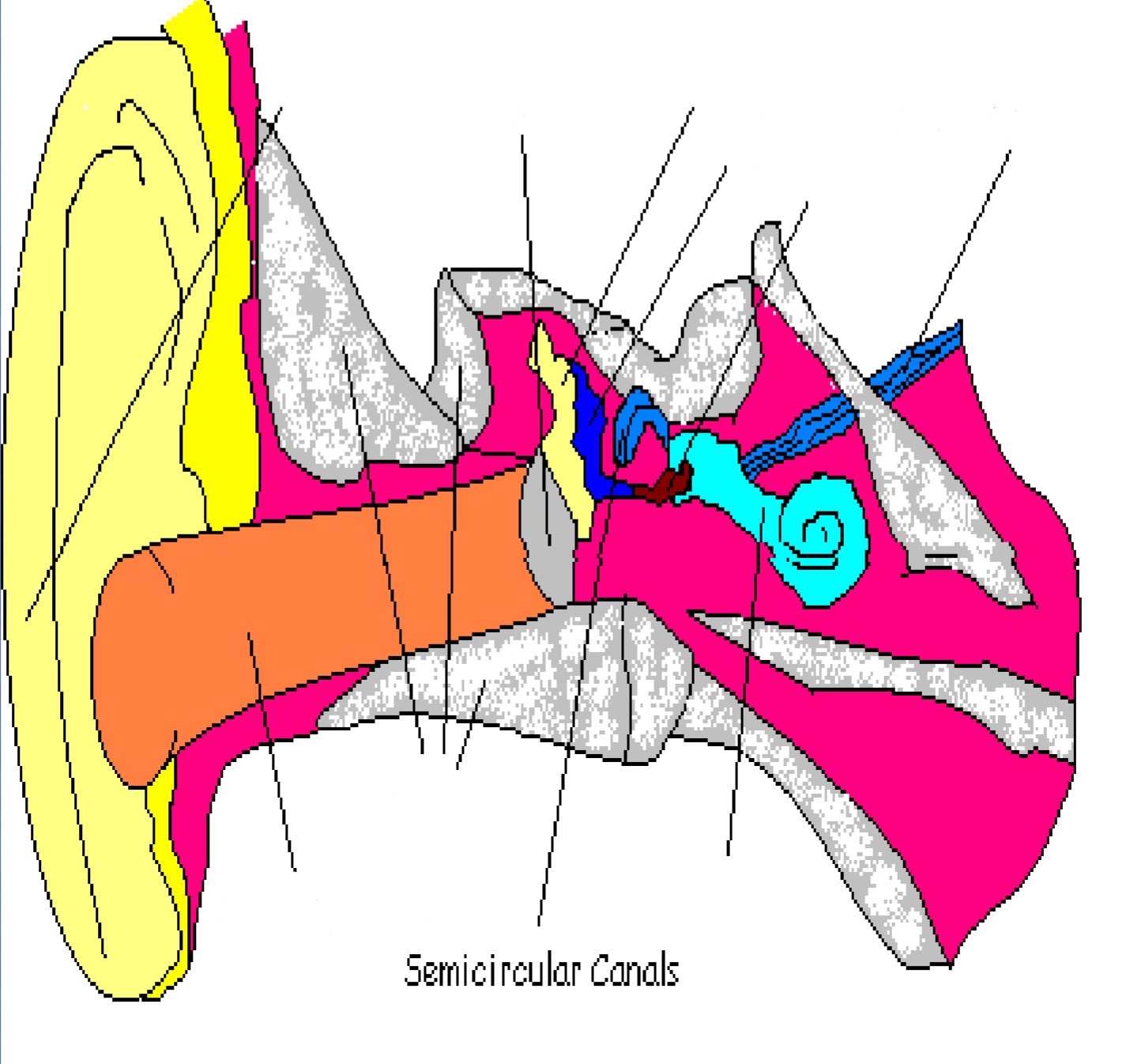
Semicircular Canals
Part of inner ear; help with balance
Conduction Deafness
Happens if hammer, anvil, or stirrup are damaged/become more brittle; often happens w/ age; can be helped w/ hearing aid (amplifies sound)
Sensorineural Deafness
Happens w/ damage to hair cells/auditory nerve; can’t be helped w/ hearing aid; can be caused by loud sounds
Place Theory
Hearing theory; diff. frequencies cause larger vibrations @ diff. locations along basilar membrane; explains that higher pitch sounds are interpreted based on where hair cells are more active
Frequency Theory
Hearing theory; basilar membrane vibrates @ same frequency as the sound wave; explains low frequency/pitch sounds BUT doesn’t explain high-pitch sounds, due to limit in neuron firing speed
Volley Theory
Hearing theory; neurons alternate firing to process highest pitch sounds
Interaction Between Place Theory, Frequency Theory, & Volley Theory
Place Theory explains high pitched
Frequency Theory (w/ help from Volley Theory) explains low pitches
Place Theory & Frequency Theory together help w/ medium pitches

Taste/Gustation Overview
Taste is a chemical sense
Taste exists for our pleasure
Bumps on the tongue=fungiform papille
Fungiform papille have taste buds that have taste receptors
Taste receptors reproduce in 1-2 weeks
We recognize 5 basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami, oleogustus
Taste cells respond to all tastes, but certain taste cells are somewhat specialized
Survival Function of Sweet Taste
Energy source
Survival Function of Salty Taste
Sodium; essential to physiological processes
Survival Function of Bitter Taste
Potential poisons
Survival Function of Sour Taste
Potential toxic acid
Survival Function of Umami Taste
Proteins to grow/repair tissue
Survival Function of Oleogustus Taste
Fats for energy, insulation, cell growth
Gustatiry Pathway
Gustation keeps poisons out of digestive system
Stimuli from taste are dissolved in saliva
Short hair-like structures (microvilli) come into direct contact w/ saliva & send electrical signal to brain stem—>thalamus—>gustatory cortex (in the insular cortex, which separates temporal lobe from frontal & parietal)
Testers (Non, Super, Medium)
Non-tasters=lessened sense of taste
Super tasters=have more taste buds & can taste more than the average person
Medium tasters=normal tasters
Smell/Olfaction
Most direct route to brain (bypasses thalamus)
Receptor cells (called olfactory cells) are stimulated by gassed dissolved in fluid of membrane
Olfactory cells regenerate every 30-60 days
For something to smell, it must be dissolvable in water
Odors trigger combos of receptors—>patterns interpreted by olfactory cortex
Nerve impulses—>sent to olfactory bulb (just below frontal lobe; by passes thalamus)—>impulse transfers to area in temporal lobe—>impulse transferred to limbic system
Large connection between certain smells, emotions, memories
Pressure
Pacinian corpuscle receptors help us perceive pressure
If pressure is constant, adaptation takes place & there’s a reduction/halt in signal
Temperature
ONLY have receptors for warm/cold
Feeling something cold←hot or cold stimulus
Feeling something warm←warm stimulus
Feeling something hot←warm/cold spots simultaneously stimulated
Pain Overview
Free nerve endings throughout body (called nociceptors) detect hurtful temp., pressure, chemicals, etc. (found in muscles, skin, membranes, around bones, joints, organs, etc.)
A-delta pain fibers=deal with sharp/immediate pain; myelinated, fast-conducting neurons; activated by strong physical pressure/temp. extremes; conducts info from spinal cord→thalamus→sensory cortex
C pain fibers=deal with chronic, steady, dull pain; un-myelinated, slow-conducting neurons; activated by chemical changes in tissue when skin is damaged; conducts info from spinal cord→thalamus→many brain areas (including frontal lobe)
Influences on Pain
Substance P=pain neurotransmitter
Endorphins can inhibit substance P
Psychological factors (distraction, expectation, learning, emotions (anxiety, fear, etc. can increase pain/signal gates to open))
Sociocultural (presence of others, empathy, cultural expectations, etc.)
Gate Control Theory
Pain perception theory; pain is controlled by “gates” in spinal cord (open=pain; closed=no pain)
Phantom Limb Syndrome
When normal sensory input is absent brain may misinterpret & amplify random nervous system stimulation (pain, movement experiences, sensation experiences, etc.); phantoms can impact other senses too
Kinesthetic Sense
Deals w/ location & position
Proprioceptors help w/ kinesthetic sense (located in muscles/joints)
Vestibular Sense
Deals w/ balance/equilibrium
Vestibular sense responds to changes in gravity, motion, body pos.
Fluid-filled semicircular canals & vestibular sacs in inner rear respond to changes
Vestibular sense works w/ eyes; problems arise when info between eyes conflict
Absolute Threshold
Minimum threshold of stimulus needed for the change to be detected (50% of the time)
Difference Threshold/Just Noticable Difference (JND)
Smallest possible difference between 2 stimuli that can be detected ½ the time
Weber’s Law
Size of JND varies depending on its relation to strength of original stimulus; size of JND is proportionate to original stimulus (bigger stimulus needs big change to be noticed; smaller stimulus needs small change to be noticed)
Selective Attention
Focusing of attention on selected aspects of environment & blocking out of others
Cocktail Party Phenomenon
In noisy places, auditory cortex boosts some sounds into help brain prioritize what’s important
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to see visible objects when attention is directed elsewhere
Change Effect/Change Blindness
Failing to notice changes in environment
Priming
Activation (often unconsciously) of certain associations, thus predisposing one’s perception, memory, response
Top Down Processing
Info @ high lvls. of processing can influence lower, earlier levels (expectations guide perception); related to perceptual set, culture, motivations emotions, prior knowledge, etc.
Bottom Up Processing
Lower to higher processing lvls.; NOT influenced by expectations/experiences
Motion Aftereffects
Look @ moving objects for a while→look @ something stationary→illusion of new scene moving in opp. dir. (waterfall effect, etc.)
Motion Parallax
Near objects seem to move more quickly in opp. dir. of our mvmnt., while far away objects seem to move more slowly
Induced Movement
Ex.: if you’re in a parked car & another car next to you moves, you feel like you’re moving (frame of reference is tricked)
Stroboscopic Movement
Movies, etc. that have one rapidly view a series of slightly varied still images
Phi Phenomenon
Illusion of mvmnt. that occurs when 2+ adjacent objects blink on/off in quick succession
Perceptual Constancy
Ppl. correctly perceive objects as constant in shape, size, color, lightness despite raw sensory data that could mislead; brain must compute ratios (size, shape, color, lightness despite raw/brightness, etc.)
Binocular Depth Cues
Depth cues involving both eyes
Binocular Disparity/Retinal Disparity
Type of binocular depth cue; brain has 2 diff., but overlapping retinal images; disparity is used to compute distances of nearby objects (ex.: camera 1/camera 2; looking at object while switching which eye you look through makes it appear to change location; etc.)
Convergence
Type of binocular depth cue; retinal images are combined by brain (ex.: floating sausage finger perception when putting fingers together & looking over top of them)
Monocular Depth Cues
Depth cues involving 1 eye (pictorial depth cues, etc.); often used by artists (da Vinci, etc.)
Interposition/Occlusion
Type of monocular depth cue; near objects block far objects
Relative Size
Type of monocular depth cue; far off objects are smaller than closer ones on retina
Relative Clarity
Type of monocular depth cue; more light passes through object that are farther away→objects are viewed as hazy, blurry, unclear; nearby objects are sharp/clear
Linear Persoective
Type of monocular depth cue; parallel lines appear to converge @ a distance
Texture Gradient
Type of monocular depth cue; there’s a continuous change in uniformly textured structures (as surface recedes, texture becomes denser/viewed almost as smooth)
Gestalt
“Organized whole”
Proximity
Gestalt; when elements are placed close together, they tend to be perceived as a group
Similarity
Gestalt; objects that look similar are perceived as group/pattern (“one of these things is not like the other”)
Continuity
Gestalt; eye is compelled to move through 1 object & continue to another
Closure
Gestalt; when an object is incomplete, we perceive the whole by filling the gaps
Figure/Ground
Gestalt; when identifying a figure, we assign the rest of the scene to background
Ames Boxes/Ames Rooms
Albert Ames created rooms that played w/ linear perspective & other distance cues; a diagonally cut room could appear rectangular due to crooked windows/floor tiles; room creates illusion that 2 objects placed on either side are equidistant from viewer & 1 object looks much bigger than the other