econ exam one
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
property
bundle of rights. These rights describe what people may and may not do with the resources they own: These rights may change.
rule of first possession
is that the first person to use previously unowned things to possession becomes their owner
incompatible uses`
May one property owner create a stench on his own property that offends his neighbors? In general, the law tries to prevent property owners from interfering with each other, but in this example, as in many other cases, there is a trade-off between competing activities.
Property Encroachment
whether a property owner can develop his land according to his own wishes or must conform to restrictions on development imposed by a local government. The general question concerns the extent to which government may constrain a private owner's use of her property.
enjoin
the court will issue an order that they must stop interfering on pain of punishment for contempt of court
Bargaining Theory
cooperative solution
list of strategies and payoffs that the participants would choose if they could commit themselves to a coordinated choice of strategies
non-cooperative solution
an equilibrium in a game in which players do not cooperate but pursue their own self-interest
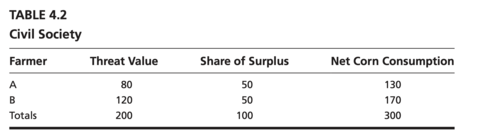
threat value
payoffs to the parties in the noncooperative solution
cooperative surplus
an equilibrium in a game created by moving the resource to a more valuable use
state of nature
corresponds to the threat values of the noncooperative solution, which prevails if the parties cannot agree.
rancher's rights
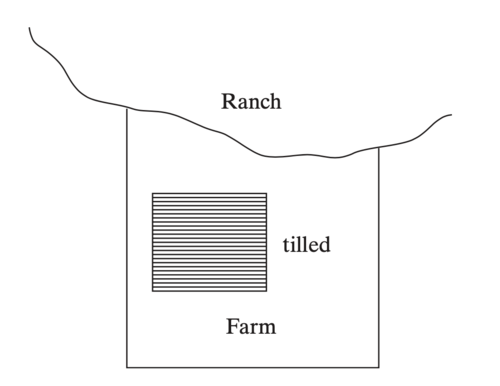
The farmer is responsible for keeping the cattle off his property, and he must pay for the damages when they get in
Farmers' Rights
The rancher is responsible for keeping the cattle on her property, and she must pay for the damage when they get out
Coase Theorem Corollary
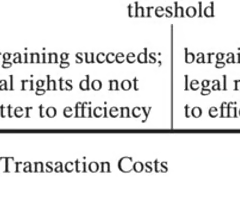
When transaction costs are high enough to prevent bargaining, efficient use of resources depends on legal rules assigning property rights from laws or courts.
Coase Theorem
When transaction costs are zero, private parties (people, households) will achieve an efficient use of resources (pareto optimal) regardless of the legal assignment of property rights by laws of courts
transaction costs
are the costs of exchange. An exchange has three steps. First, an exchange partner has to be located. Second, a bargain must be struck between the exchange partners. Third, after a bargain has been reached, it must be enforced.
legel remedy
the payment of compensatory money damages by the defendant to the plaintiff.
compensatory money damages
sum of money that compensates the plaintiff for the wrongs inflicted on her by the defendant. The court determines the appropriate amount of money that will, as the saying goes, "make the plaintiff whole."
equitable relief
consists of an order by the court directing the defen- dant to perform an act or to refrain from acting in a particular manner.
injunction
which is said to "enjoin" the defendant to do or to refrain from doing a specific act.
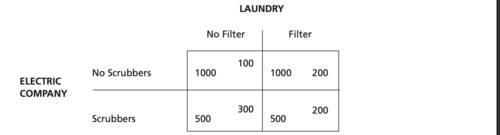
Polluter's Right
energy company is free to pollute, this is efficient already, no bargaining required
Pollutee's Right to Damages
laundry claims to have right to damages, this is inefficient, because surplus exists and parties bargain to efficiency
Pollutee's Right to Injunction
laundry claims to right to injunction agfainst energy company, most efficient remedy
efficient remedies
legal actions or measures that are effective in providing redress or resolving a legal dispute in a timely and cost-effective manner. For example, a court may seek efficient remedies to ensure that justice is served without undue delay or excessive expenses.
Calabresi and Melamed
Where there are few obstacles to cooperation (that is, low transaction costs), the more efficient remedy is to enjoin the defendant's interference with the plaintiff's property.
Where there are obstacles to cooperation (that is, high transaction costs), the more efficient remedy is to award compensatory money damages.
private goods
have the characteristic that one person's use precludes another's: For example, when one per- son eats an apple, others cannot eat it
free rider
Those people who do not pay for their consumption of a public good are called
purely public good
for which there is no rivalry in consumption
allocative efficiency
property rights are the legal basis of voluntary exchange, which achieves this by moving goods from people who value them less to people who value them more.
productive efficiency
Owners achieve this by balancing the social costs and benefits of what they do with what they own.
Normative Coase Theorem
Structure the law so as to remove the obstacles to private agreements.
Normative Hobbes Theorem
Structure the law so as to minimize the harm caused by failures in private agreements
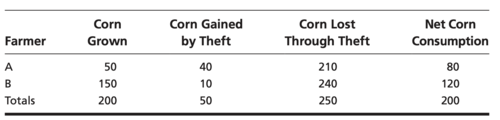
A cattle rancher lives beside a farmer. The farmer grows corn on some of his land and leaves some of it uncultivated. The rancher runs cattle over all of her land. The boundary between the ranch and the farm is clear, but there is no fence. Thus, from time to time the cattle wander onto the farmer's property and damage the corn. The damage could be reduced by building a fence, continually supervising the cattle, keeping fewer cattle, or growing less corn—each of which is costly. The rancher and the farmer could bargain with each other to decide who should bear the cost of the damage. Alternatively, the law could intervene and assign liability for the damages.
A threshold level of transaction costs that distinguishes the areas in which the Coase Theorem applies and does not apply.
The most efficient outcome is, by definition, a situation in which the total profits for the two parties, called the "joint profits," are greatest.
So, in civil society, each party receives half the cooperative surplus plus the individual net consumption in the state of nature, which is each party's threat value.
In a state of nature, each one grows some corn, steals corn from the other party, and defends against theft. Each of the parties has different levels of skill at farming, stealing, and defending.
maximization
Choosing the best alternative that the constraints allow
equilibrium
a pattern of in- teraction that persists unless disturbed by outside forces. Economists usually assume that interactions tend toward this, regardless of whether they occur in markets, elections, clubs, games, teams, corporations, or marriages.
productive efficiency
2 conditions must hold
It is not possible to produce the same amount of output using a lower-cost combination of inputs, or
It is not possible to produce more output using the same combination of inputs.
allocative efficiency
if it is impossible to change it so as to make at least one person better off (in his own estimation) without making another person worse off (again, in his own estimation)
Pareto Optimality
that point in free markets where the exchange of goods is so efficient that one more exchange would make someone feel worse off
completeness
means that the consumer be able to tell us how she ranks all the possible combinations of goods and services. The consumer is not allowed to say, "I can't compare them."
Reflexivity
It means that any bun- dle of goods, A, is at least as good as itself.
Transivity
means that the preference ordering obeys the following condition: If bundle A is preferred to bundle B and bundle B is preferred to bundle C, then it must be the case that A is preferred to C.
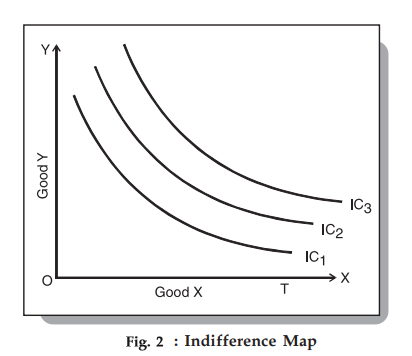
indifference curve
Each curve represents all the combinations of x and y that give the consumer the same amount of utility or well-being. Alternatively, we might say that the consumer's tastes are such that he is indifferent among all the combinations of x and y that lie along a given curve
price taking behavior
a price taker cannot control the price of the good it sells; it simply takes the market price as given, IMPOSSIBLE for a single firm to affect the market price by changing quantity supplied
market clearing price
the price at which the amount supplied is equal to the amount demanded
opportunity cost
refers to the economic cost of an alternative that has been foregon
comparative advantage
asserts that people should engage in those pursuits where their opportunity costs are lower than others
game theory
deals with any situation in which strategy is important. will, consequently, enhance our under- standing of some legal rules and institutions.
strategic form
Using a payoff matrix to represent strategy choices
extensive form
representation of a game by a game tree
present discounted value
Discount a multi-period flow of net receipts for each period
PDV equation
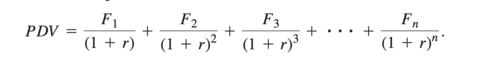
externalities
source market failure: economic side effects or by-products that affect an uninvolved third party; can be negative or positive
general equilibrium
will be achieved only when competitive forces have led to the equality of marginal benefit and marginal cost in the market for every single commodity and service.
public good
source market failure:
Nonrivalrous consumption: consumption of a public good by one person does not leave less for any other consumer.
Nonexcludability: the costs of excluding nonpaying beneficiaries who consume the good are so high that no private profit-maximizing firm is willing to supply the good.
asymmetric information
source market failure: a situation in which one party to an economic transaction has less information than the other party
Kaldor-Hicks efficiency
That criterion requires that gainers explicitly compensate losers in any change. If there is not explicit payment, losers can veto any change. That is, every change must be by unanimous consent.
Expected Monetary Value (EMV)
The monetary value of a risk exposure based on the risk's probability and impact in the risk matrix. This approach is typically used in quantitative risk analysis because it quantifies the risk exposure.
risk aversion
The tendency to prefer a sure gain of a moderate amount over a riskier outcome, even if the riskier outcome might have a higher expected payoff.
risk neutrality
a person has a constant marginal utility of income and is, therefore, indifferent between a certain prospect of income and an uncertain prospect of equal expected monetary value.
risk preferring
has an increasing marginal utility of income and, therefore, prefers an uncertain prospect of income to a certain prospect of equal expected monetary value -- willing to bet
Moral Hazard
major problem faced by insurance companies: arises when the behavior of the insured person or entity changes after the purchase of insurance so that the probability of loss or the size of the loss increases
Adverse Selection
major problem faced by insurance companies: A high-risk person benefits more from insurance, so is more likely to purchase it.
Behavioral economics
an approach to the study of consumer behavior that emphasizes psychological limitations and complications that potentially interfere with rational decision making
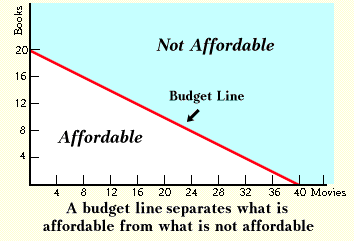
budget constraint equation
PxX + PyY = I
utility function
u = u(x, y)
indifference curve map
budget constraint map
Consumer Optimum
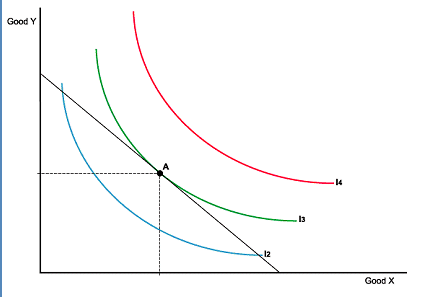
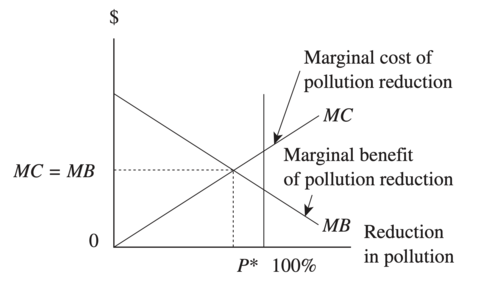
Economic Optimum
where marginal cost = marginal benefit
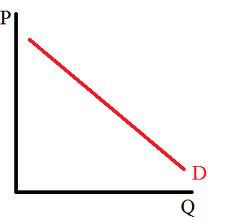
Individual demand curve
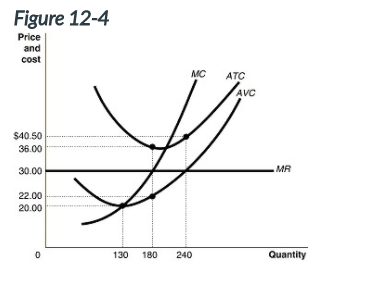
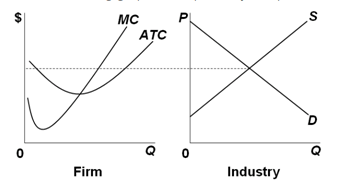
The profit-maximizing output for a firm.
Market equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market.
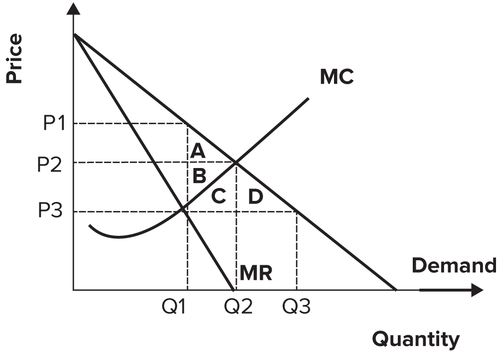
Profit-maximizing output and price for a monopolist.
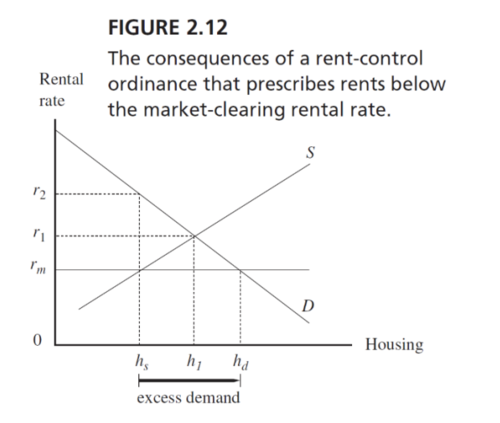
The consequences of a rent-control ordinance that prescribes rents below the market-clearing rental rate.
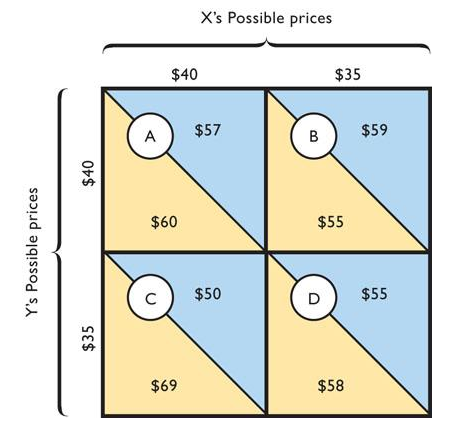
payoff matrix
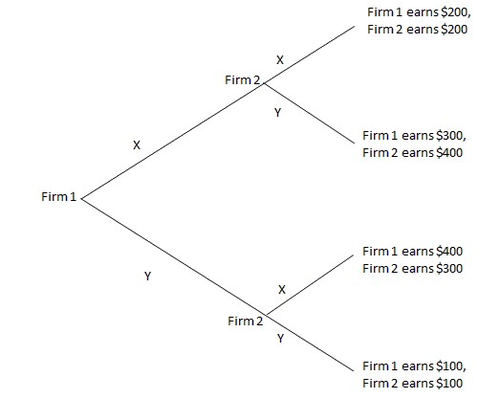
game tree
law and economics
Behavior theory to predict impacts of changes in law
antitrust laws
laws that prevent monopolies and promote competition and fairness
monetary fines
sums of money that offenders are required to pay as punishment for the commission of crimes
Litigants
people engaged in a lawsuit
Least cost risk bearer
The principle assumes that the entire loss from nonperformance must be allocated by the court to one of the parties.
redistributive approach
an action that is intended to share money more fairly between rich and poor people
tax and transfer system
progressive taxation and social welfare programs can accomplish redistributive goals in modern states
progressive taxation
a policy that raises tax rates as income increases
Oliver Wendell Holmes
one of the greatest justices in Supreme Court history. The study of law will require the use of economics and statistics. Opportunity cost relevant to law.
Richard Posner
Law and economics: law should aim to maximise wealth, prominent judge of law and economics
Civil Law
body of written rules which form the basis of law
Common Law
law which arises from better patterns and practices of individuals in society
Code Napoleon
The codification and condensation of laws assuring legal equality and uniformity in France. Modeled after Justinian Code and became the new Civil law.
adversarial process
the judge acts more or less as a neutral referee who makes the lawyers follow the rules of procedure and evidence.
setting aside lower level law
The power to review legislation for its constitutionality gives courts the power to set aside laws enacted by the legislature
trial courts of general jurisdiction
The main courts in the state court system and may be referred to as circuit courts, superior courts, or courts of common pleas. These are the "entry-level" courts that first hear a wide array of civil and criminal disputes.
appelate court
A court having juristriction to review cases and issues that were originally tried in lower courts. At the appellate level there will be no new evidence or facts introduced.
highest appellate court
US Supreme Court. That court has nine members, consisting of the Chief Justice of the United States and eight Associate Justices. They pick what cases they want to try.
US Appeals Court for DC
a federal appellate court with appellate jurisdiction. It hears appeals from the United States District Court for the District of Columbia and its rulings may be appealed to the Supreme Court of the United States.
federal questions
A question that pertains to the U.S. Constitution, an act of Congress, or a treaty and provides a basis for federal jurisdiction in a case.