Unit M - Electrical Energy & Supply
1/12
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
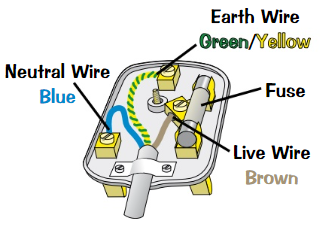
Plugs
Have three wires - live, neutral, earth
Only live and neutral wires usually needed, but earth wire stops you getting hurt if something goes wrong
LIVE WIRE alternates between HIGH +VE AND -VE VOLTAGE of 230V
NEUTRAL WIRE always at 0V
Electricity normally flows in through live and neutral wire
EARTH WIRE and fuse are just for safety
Double insulation
If appliance has plastic casing and no metal parts showing, it’s said to be double insulated
Plastic is insulator, so stops current flowing - meaning you can’t get a shock
Anything with double insulation doesn’t need earth wire
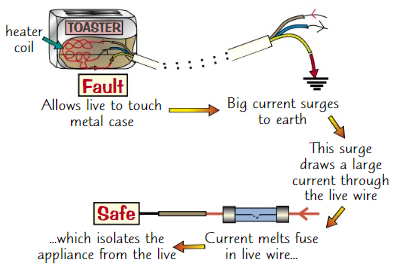
Earthing and fuses
If fault develops in which live touches metal case, then because case is earthed, big current flows through live wire, case and earth wire
Surge in current melts the fuse, cutting off the live supply
This isolates the whole appliance, making it impossible to get electric shock from case
Also prevents risk of fire caused by heating effect of large current
Circuit breakers
Protect circuit from damage if too much current flows
When circuit breakers detect surge in current, they break circuit by opening a switch
Circuit breaker can easily be reset by flicking a switch on the device
This makes them more convenient than fuses (have to be replaced once melted)
Heating effect in resistors
When there is electrical current in resistor, there is energy transfer which heats resistor
Because electrons collide with ions in lattice that make up resistor as they flow through it
This gives ions energy, causing them to vibrate and heat up
Heating effect increases resistor’s resistance - so less current flows
Heating effect can cause components in circuit to melt - so circuit stops working
Use of heating effect in resistors
Toasters contain coil of wire with very high resistance
When current passes through coil, temp increases so much that it glows and emits IR (heat) radiation which cooks bread
Equation: Power, Current and Voltage
P = IV
Power = Current x Voltage
[W] = [A] x [V]
Fuse ratings
Fuses have current ratings and should be rated as near as possible but just higher than the normal operating current
To work out the fuse needed, you need to work out the current that item normally uses

Equation: Energy, Current, Voltage and Time
E = IVt
Energy transferred = Current x Voltage x Time
[J] = [A] x [V] x [s]
Alternating current (a.c.)
Current is constantly changing direction
Used for mains supply, e.g. UK mains supply is approx. 230V
Direct current (d.c.)
Current keeps flowing in same direction
Used in cells and batteries
Voltage
Energy transferred per unit charge passed
One volt = one joule per coulomb
Equation: Energy, Charge and Voltage
E = QV
Energy transferred = Charge x Voltage
[J] = [C] x [V]