Unit 1: Scientific Foundations of Psychology
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes major people, psychological approaches, subfields of psych, research methods, the scientific method, types of variables, cause/effect, types of bias, types of statistics, measures of central tendency, measures of variation, correlation, skews, and ethical guidelines.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Monism
The mind and body are the same; knowledge grows from experience and is stored in memories.
Believed by Aristotle, Francis Bacon, and John Locke
Dualism
The mind is separate from the body, therefore knowledge is born within you and the mind survives past the body.
Believed by Socrates, Plato, and Rene Descartes.
2 academic disciplines that shaped development of psych thought:
Physiology and Philosophy
Psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes.
Mary Whiton Calkins
first female pres of American Psychological Association (APA)
created self-psych (emphasized self-evaluation of ones personal experiences).
Charles Darwin
developed theories of evolution and natural selection
beliefs inspire evolutionary approach
Dorothea Dix
advocated for mentally ill by highlighting bad conditions of asylums
created 1st US mental hospitals
Sigmund Freud
father of psychoanalysis
G. Stanley Hall
founder of educational and child psych
shaped adolescent themes in psych.
William James
author of “the principles of psych”
Functionalism
mentored Mary Whiton Calkins
created james-lange theory
Ivan Pavlov
work in classical conditioning
Jean Piaget
created stages of development for kids including sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operation phases.
Carl Rogers
humanist psychologist
created client-centered therapy where therapist guides personal growth.
B.F. Skinner
behaviorist psychologist
created theory of operant conditioning (studied how consequences shape behavior)
Margaret Floy Washburn
1st female to get Ph.D. in pysch
John B. Watson
Behaviorism
Little albert experiment
Wilhelm Wundt
Father of Psych
Structuralism
created 1st psych lab
Structuralism
a theory of consciousness that seeks to analyze the elements of mental experiences, such as sensations, mental images and feelings, and how these elements combine to form more complex experiences.
Wilhelm Wundt
structure > function
mind must be broken down to understand brain and its functions
uses introspection (looking inward)
Failure: for structuralism to work, subject must be intelligent and verbal. Introspection provided unreliable results b/c results varied.
Functionalism
created to understand how the conscious mind is related to behavior. it emphasizes the practical function/purpose of behavior and mental processes.
William James
was heavily influenced by Darwin’s theory of evolution
marked departure from “structuralism”
was formalized in UoChicago by John Dewey, Harvey A. Carr, and James Rowland Angell.
Behaviorism
focuses on observable and measurable behaviors as the basis for understanding human/animal behavior.
John Watson
shifted psych: study of (un)conscious mind —> science-based studies on observable events.
Little Albert Experiment
Watson took infant boy (albert) and exposed it to a white rat, rabbit, monkey, masks, and burning newspaper to observe its reactions.
Next time albert was exposed to rat, Watson made a loud noise —> boy cries.
Rat and loud noise were then repeatedly paired —> albert was expecting loud noise —> albert cried simply after seeing rat.
Gestalt Psychology
says that the whole is dif than the sum of its parts.
looks at mind and behavior as whole.
suggests that human minds do not focus on small components, but instead humans see the greater whole. (more in U.3)
Psychoanalytic/psychodynamic approach:
focuses on study of the unconscious mind. It states that behavior is determined by past experiences.
Sigmund Freud
Humanistic approach
believes that humans have free will and the ability to grow. All individuals are striving to reach self-actualization and their greatest potential with this approach.
Evolutionary approach
uses evolutionary biology to explain human behavior.
looks at how natural selection due to variable traits promotes the survival of genes.
Ex: evolutionary psychologist may study how anger could be a gene inherited from our ancestors.
Biological approach
states that behavior is based on physical processes relating to the brain, hormones, and other chemicals.
Cognitive approach
states that thought processes impact the way ppl behave.
ex: a cognitive psychologist may study how an emotion affects one’s thinking.
Biopsychosocial approach
acknowledges the person as a whole and tries to look at all of the patient's circumstances. It looks at biological, psychological, and social factors to understand a person’s behavior.
Sociocultural approach
studies how thinking and behavior vary across cultures and situations.
ex: a sociocultural psychologist may study how expressions of sadness vary across cultures.
Biological psych
states that physical processes shape behavior.
ex: a biological psychologist might say that anger is due to a certain hormonal balance in the brain.
Clinical psych
a section of psychology focused on assessing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
Cognitive psych
studies the mental processes associated with thinking, knowing, and communicating.
Counseling psych
focuses on personal issues that are not classified as mental disorders. These types of therapists help people cope with challenges and crises in life.
ex: counseling psychologists can help a student with social or academic struggles. They could even help an individual with marital issues.
Developmental psych
studies social, physical, and cognitive changes throughout the lifespan.
study from “womb to tomb.”
Educational psych
the study of how psychological processes can impact and improve learning and teaching.
Experimental psych
uses the experimental method to examine relationships between behavior and the mind.
Industrial-organizational psych
studies the relationships between work and people in order to help companies increase productivity, boost morale, and select and train employees.
Personality psych
is the study of how personality affects the way people think and behave.
Psychometric psych
study of the measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits.
Social psych
studies how humans are influenced by one another and how we relate and think about each other.
Positive psych
focuses on making human existence more fulfilling, rather than focusing on the treatment of mental illness. It promotes strengths and virtues to improve the lives of people and communities.
Experiments
Manipulates one or more independent variables to determine the effects of certain behaviors.
Strengths and weaknesses of Experiments?
Strengths:
can determine cause/effect
can be retested and proven
Weaknesses:
cld have potential ethical issues
Hawthorne effect (ppl. know they are being researched —> cld impact what they say/do)
Correlational studies
Involves looking at the relationships between two or more variables and is used when performing an experiment is not possible.
Strengths and weaknesses of correlational studies?
Strengths:
easier to conduct than an experiment
can be used when an experiment is impossible.
ex: a researcher may want to examine the relationship between school grades and Adderall. It would not be ethical to force students to take high doses of Adderall. So, one can only rely on participants’ responses
Weaknesses:
cannot determine cause/effect
Survey research
The collection of information reported by people about a particular topic.
Strengths and weaknesses of survey research?
Strengths:
cost-effective
most reliable
weaknesses:
low response rates
can’t verify accuracy of responses
Naturalistic observations
A researcher observes a subject's behavior without intervention.
Strengths and weaknesses of naturalistic observations?
Strengths:
natural setting is more reliable than a lab setting
weaknesses:
Hawthorne effect
two researchers could see the same behavior but draw different conclusions
Case studies
an in-depth study of an individual or a small group. Usually, case studies are done on people with rare circumstances.
ex: a girl named was locked in her room, causing a delay in development. Researchers did a case study about her to understand more about language and human development stages.
Strengths and weaknesses of case studies?
strengths:
provides detailed info
weaknesses:
cannot generalize results to a wider population
difficult to replicate
time-consuming
Longitudinal studies
The same individuals are studied over a long period of time from years up to decades.
Strengths and weaknesses of longitudinal studies?
strengths:
can show the effects of changes over time
more powerful than cross-sectional studies
weaknesses:
require large amounts of time
expensive
Cross-sectional studies
a study examines people of different groups at the same time.
ex: studying people that are different ages at the same time to see what differences can be attributed to age.
Strengths and weaknesses of cross-sectional studies?
strengths:
quick and easy to conduct
generalizable results
weaknesses:
difficult to find a population that differs by only one factor
cannot measure changes over time
Phineas Gage case study:
Phineas Gage was a railroad construction foreman who survived a severe brain injury in 1848 (damaged his frontal lobes). Despite the severity of the injury, Gage was able to walk and talk immediately after the accident and appeared to be relatively uninjured. However, Gage's personality underwent a dramatic change following the injury. He became impulsive, irresponsible, and prone to outbursts of anger, which were completely out of character for him before the accident.
Gage's case is famous in the history of psych bc it was one of the first to suggest that damage to the frontal lobes of the brain can have significant effects on personality and behavior.
Basic research
Is curiosity-driven and used to expand upon knowledge. It doesn't have an immediate objective.
ex: a study assessing the impacts of caffeine consumption on the brain. (the goal is not to solve a problem it is only to increase knowledge about a particular topic).
Applied research
answers specific questions and is used to solve a problem or do something of practical use.
ex: trying to find a cure for obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Scientific method
observation
question
research
hypothesis
experiment
analysis
conclusion
Operational definition
statements of the exact procedures used in the study, which would eventually allow other researchers to replicate the research.
ex: how would you describe human intelligence?
You may have said how smart someone is, measured by their grades, but this is a biased definition. The operational definition would be what an intelligence test (such as an IQ test) measures.
Independent variable
the variable that changes in an experiment.
Dependent variable
the effect of the change in the experiment. This is what gets measured.
Confounding variable
an outside influence that changes the effect of the dependent and independent variables.
Control variable
the variable that's kept the same throughout an experiment.
Random assignment
when participants are assigned to each experimental group with an equal chance of being chosen
helps reduce possible confounding variables
Random sample
each individual in the population has an equal chance of participating in an experiment.
Sampling bias
a result of a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample.
Experimenter bias:
when researchers influence the results of an experiment to portray a certain outcome.
Double-blind procedure
neither the researcher or the participants know what groups the participants have been assigned to.
Hindsight bias
the tendency to believe that you knew what was going to happen,
"I knew it all along."
Overconfidence
we are often overconfident in what we find/believe, which misleads others about the truth.
Hawthorne effect
A psychological phenomenon where individuals modify their behavior when they are aware of being observed, leading to improved performance or productivity.
External Validity
refers to how generalizable the results of the experiment are.
ex: if the study on a drug is done on an Asian, middle-aged, average-weight man with high blood pressure, can the results be generalized to the population?
Internal Validity
when a study shows a truthful cause-and-effect relationship and the researcher is confident that the changes in the dependent variable were produced only by the independent variable. A confounding variable hurts the internal validity because it creates lower confidence in the research conclusion.
Descriptive research method
to observe and record behavior
Strengths and weaknesses of descriptive research method?
strengths:
only requires 1 participant
naturalistic observations may be done when it is not ethical to manipulate variables
surveys may be done quickly and inexpensively (compared with experiments)
weaknesses:
Uncontrolled variables mean cause and effect cannot be determined
single cases may be misleading
Descriptive statistics
involves the use of numerical data to measure and describe the characteristics of groups, and this includes measures of central tendency and variation. It does not involve making inferences about a population based on sample data.
Inferential statistics
involves using statistical methods to make inferences about a population based on data. It allows you to draw conclusions about a population based on the characteristics of a sample. Specifically, it provides a way to see validity drawn from the results of the experiment
Mean
average set of scores
Median
middle score of distribution
Mode
most frequently recurring score in a dataset.
Standard deviation
a measure of how much the values in a dataset deviate from the mean. It is basically used to assess how far the values are spread below and above the mean.
low standard deviation = values that are relatively close to the mean
high standard deviation = values that are more spread out.
Range
difference between highest and lowest values in dataset.
Correlation coefficient
a statistical measure that describes the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
It can range from -1 to 1.
-1 = strong negative relationship
1 = strong positive relationship
0 = no relationship.
Positive correlation
as one variable increases ⬆, the other variable increases ⬆.
Negative correlation
Negative correlation shows that as one variable increases ⬆, the other decreases ⬇
No correlation
there is no connection between the two variables.
Frequency distribution
a breakdown of how the scores fall into different categories or ranges.
Normal distribution
bell-shaped frequency distribution that is symmetrical about the mean.
Bimodal distribution
a frequency distribution with two peaks. This occurs when the dataset has two distinct groups of values that occur with different frequencies.
positively skewed
distribution has a tail extending to the right (towards larger values). This occurs when the dataset has a few unusually large values that pull the mean to the right.
negatively skewed
distribution has a tail extending to the left (towards smaller values). This occurs when the dataset has a few unusually small values that pull the mean to the left.
What are the 2 important values that you should memorize for normal distributions and why?
68% : 68% of the data falls within one standard deviation of the mean.
95% : 95% of the data falls within two standard deviations of the mean.
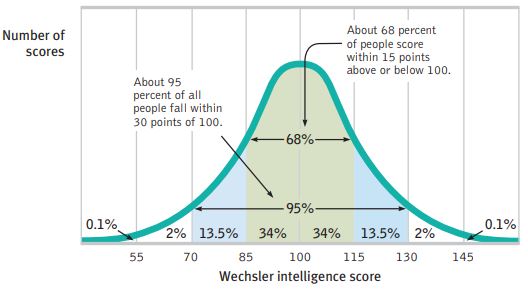
Statistical significance
the likelihood that something DOESNT occurs by chance.
What are the ethical guidlines?
No coercion
informed consent
anonymity/confidentiality
Risk
debriefing
protection from harm/discomfort
right to withdraw
Informed consent
participants must agree to participate
Deception
when a researcher gives false information to subject or intentionally misleads them about some key aspect of research.
Debriefing
a researcher explains the purpose of the study AFTER study is complete.
Anonymity
information about the participant will be held a secret.
Coercion
participants cannot be coerced to give consent to be in any study.