population
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
birth rate
number of live births per 1000 people per year
death rate
number of deaths per 1000 people per year
natural increase
difference between birth rate and death rate
(natural increase - birth rate is higher than death rate
natural decrease - death rate is higher than birth rate)
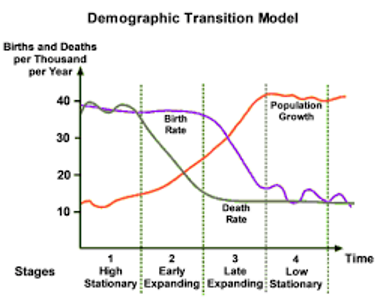
demographic transition model
explains population changes through five stages:
high fluctuating - high birth rates and death rates, stable population
early expanding - death rates fall, birth rates remain high, population grows rapidly
late expanding - birth rates decline, population growth slows down
low fluctuating - low birth and death rates, population stabilises
declining - birth rate falls below death rate, population declines
what do population pyramids shows?
they graphically display age and sex distribution within a country, showing trends such as youth bulges or ageing populations
what is china’s one child policy
a population control system implemented from 1979 to 2015, restricting most families to only have one child, with the goal to slow down rapid population growth and focus on economic development instead (exceptions made for ethnic minorities and rural families where the first child was a girl)
positive impacts of the one-child policy
successfully reduced population growth rate, easing pressure on resources and infrastructure
contributed to faster economic development
allowed women to focus on their education and careers
reduced family sizes contributed to better access to healthcare and improved living standards
negative impacts of one-child policy
the policy resulted in an imbalanced sex ratio, because the cultural preference for sons led to female infanticide, selective abortions and neglect - much more men than women
led to an ageing population - the workforce shrank and there were not enough people to take care of the elderly
only children faced issues of increased parental pressure and a lack of siblings
kerala’s non-birth policy - what is it?
kerala has managed to control its population growth by investing in social changes while still allowing people the freedom to choose their family size - based on empowerment rather than restriction
how did kerala control their population growth so successfully?
investing heavily in women’s eduction, leading to high literacy rates and increased access to healthcare
accessible and affordable healthcare, including family planning services
improvements in healthcare and education, resulting in a decline in infant mortality
non-coercive approach
impacts of the non-birth policy
one of the first Indian states to reach a “replacement level” fertility rate, meaning that parents are replacing themselves but the population growth is slowing
improved human development - its success has been linked to significant improvements in human development indicators, including poverty reduction and GDP
causes of an ageing population
declining fertility rates - lower birth rates mean that the proportion of the population that is older is increasing
increased life expectancy - improvements in healthcare and medical technology have led to people living longer, contributing to a larger elderly population
women’s education - more women are choosing to focus on their careers and education before getting married and having children
access to family planning - access to contraception and family planning services can contribute to lower rates
negative impacts of an ageing population
increased healthcare cost - as people age, they are likely to experience chronic conditions and need more frequent healthcare services
strain on social care systems - the elderly may require assistance with daily tasks, leading to increased demand for social care services
pension crises - with fewer working-age people, governments may struggle to fund pension schemes, potentially increasing retirement age
housing challenges - with old people still living in their homes, new houses must be built for young people to live in, potentially increasing cost of housing
positive impacts of an ageing population
increased knowledge and experience - older workers often possess valuable knowledge/experience which can help innovation and productivity
higher volunteer rates - elderly have more time available to volunteer, contributing to social services and community organisations
reduced demand for childcare services - with a declining birth rate, demand for schools, childcare etc. will decrease