Lecture 19: Hearing and Balance
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
Organs for hearing and balance are both innervated by the ______ nerve.
Inner Ear
Where are the organs of hearing and balance located?
Hearing: Cochlea
- the organ that transduces sound into nerve impulses
- part of the labyrinth.
Labyrinth: Inner Ear
- the structure comprised of the cochlea, the vestibule (utricle & saccule) and semicircular canals
Balance: Semicircular Canals
- organs that transduce angular acceleration (i.e. rotation) into nerve impulses
- three per side
- three are oriented perpendicularly to each other; sense rotation in x, y and z axes
Balance: Vestibule
- these organs sense linear acceleration, including gravity
Utricle
any acceleration in the horizontal plane; part of vestibule
Saccule
acceleration in the sagittal plane; part of vestibule
Bony Labyrinth
passageways in temporal bone
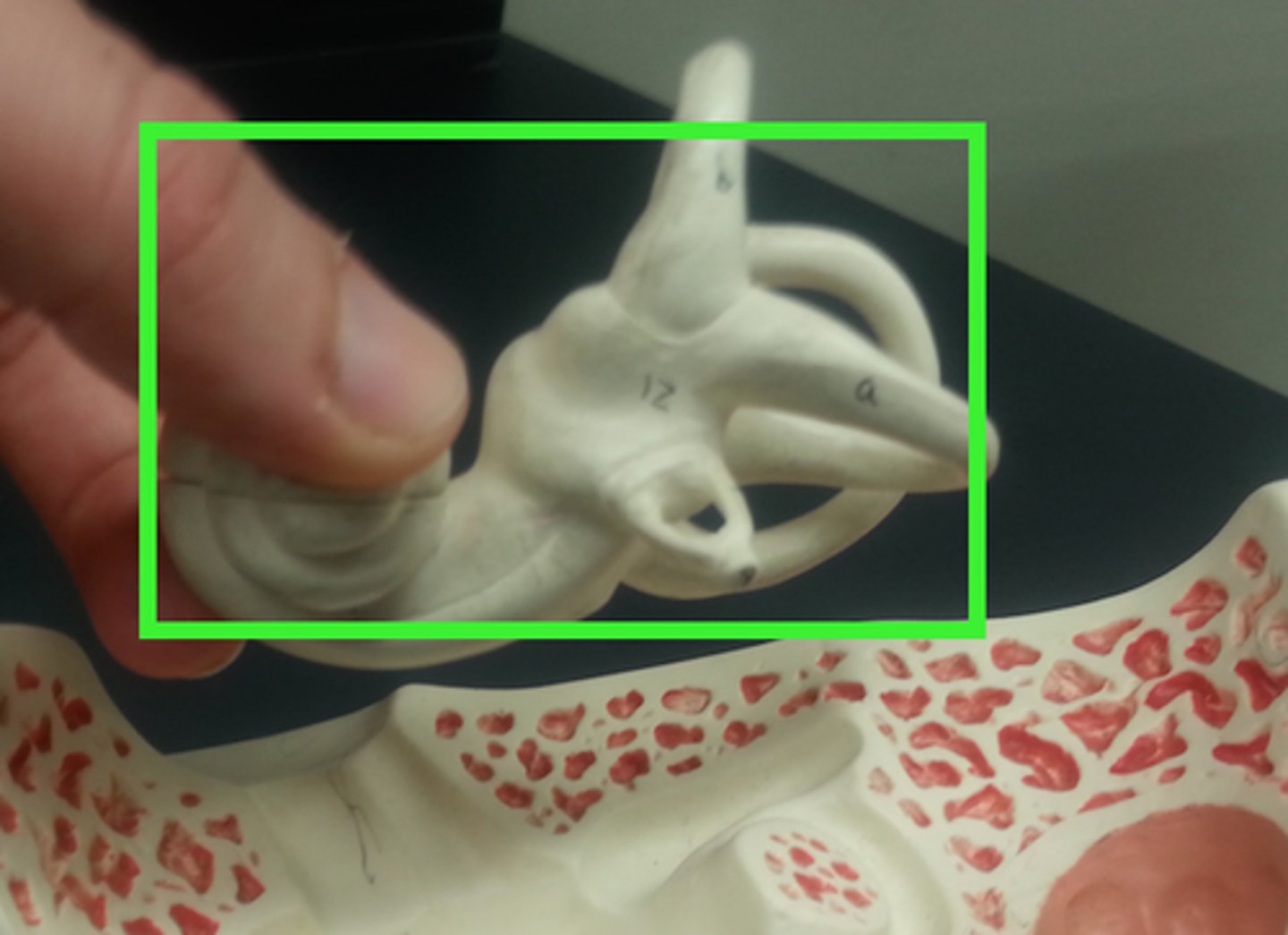

Membranous Labyrinth
membrane-covered tubes inside the bony labyrinth
External Ear Function
collects sound
Tympanic Membrane Function
vibrates in response to sound waves
Ossicles Function
maleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup), which translate motion of tympanic membrane to oval window of cochlea
Cochlea Function
transduction of sound
External Ear
- air-filled; open chamber
- pressure from sound moves the ear drum
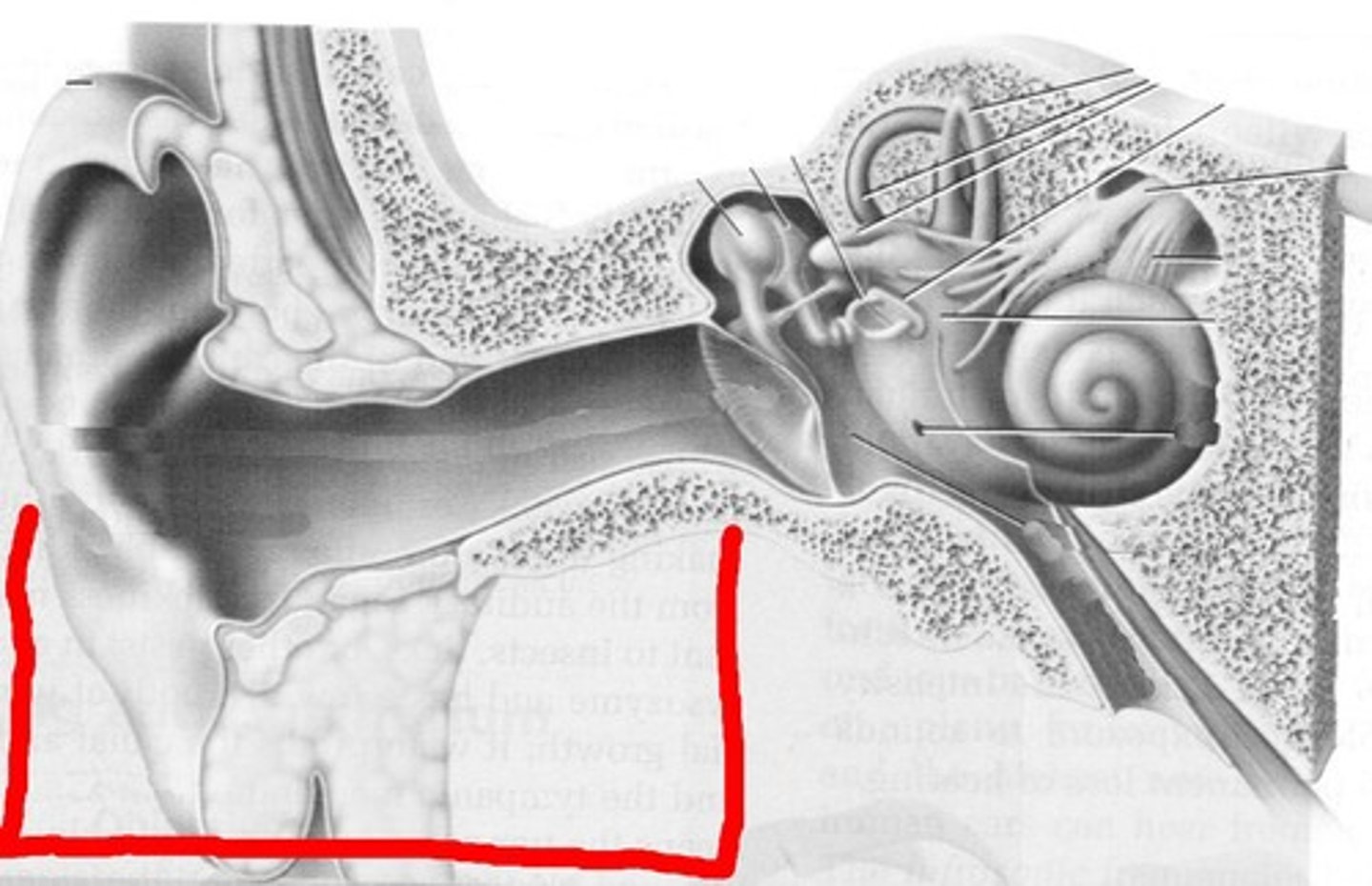
Middle Ear
- ossicles transmit pressure exerted by sound to the cochlea
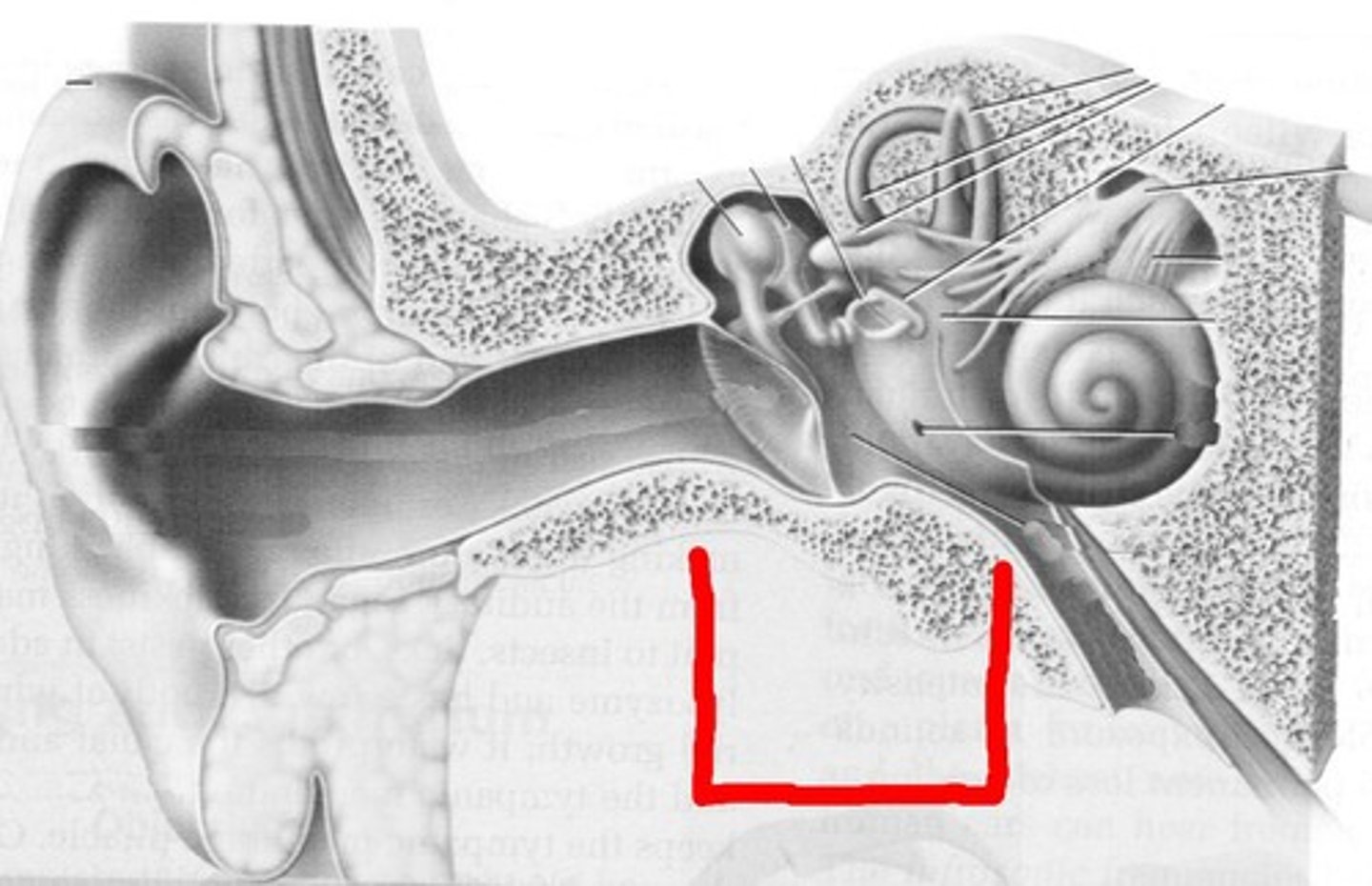
Inner Ear (Cochlea)
- sound vibrations are transmitted to liquid-filled, closed chamber
- floor of chamber ("basilar membrane") vibrates in response to sound
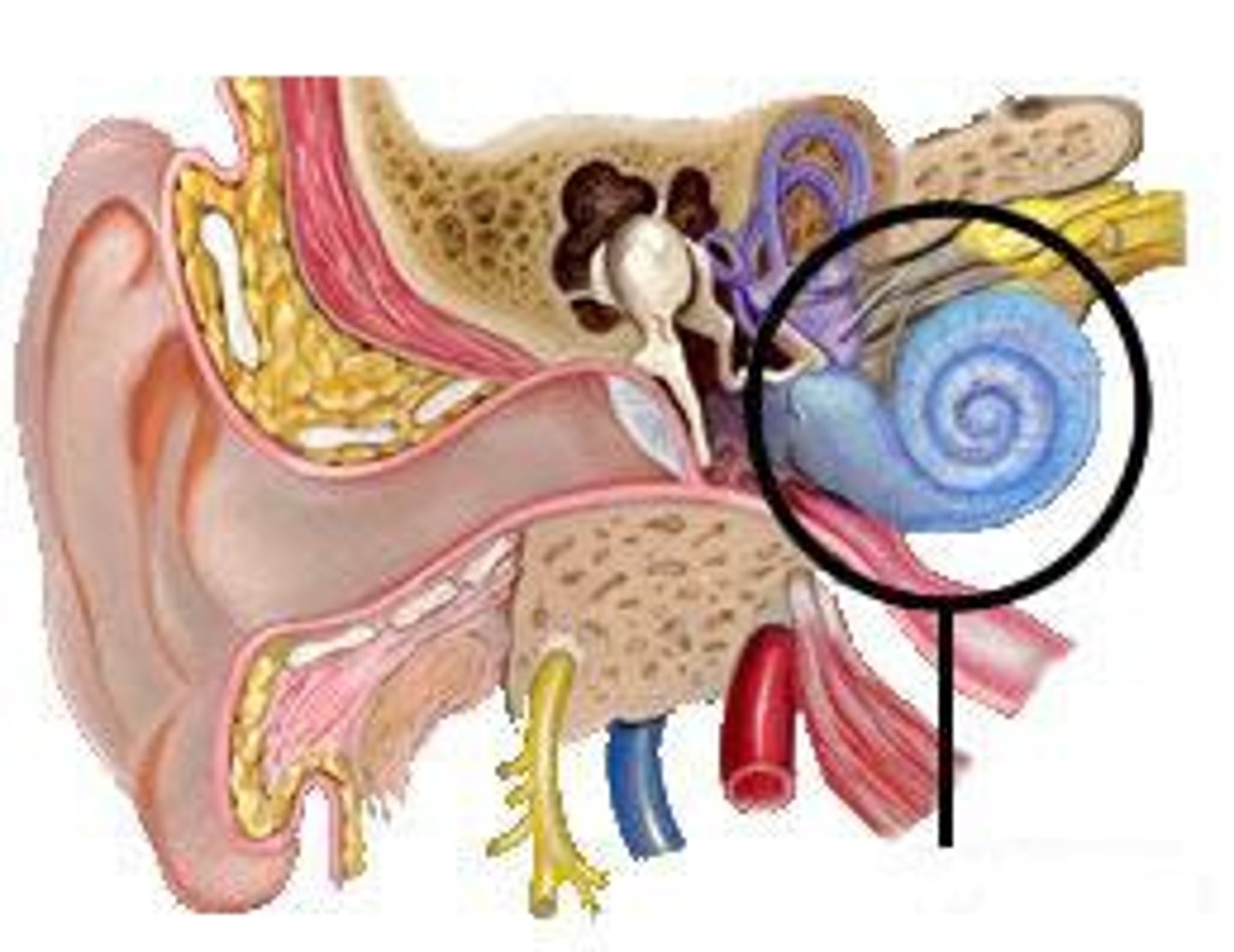
Cochlea
on the anterior-medial side of the labyrinth
Middle Ear and Ossicles
What is structure #1?
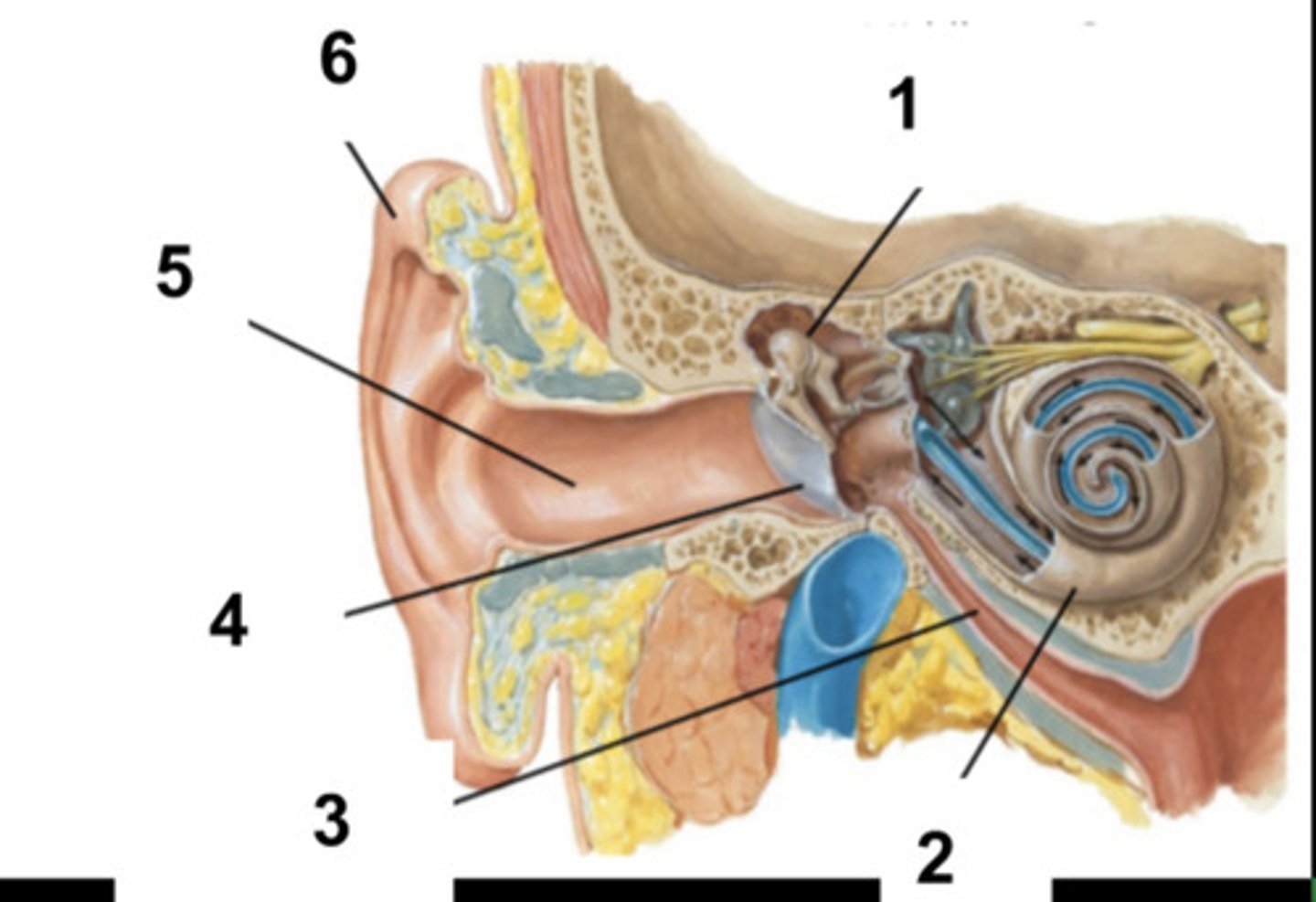
Cochlea
What is structure #2?
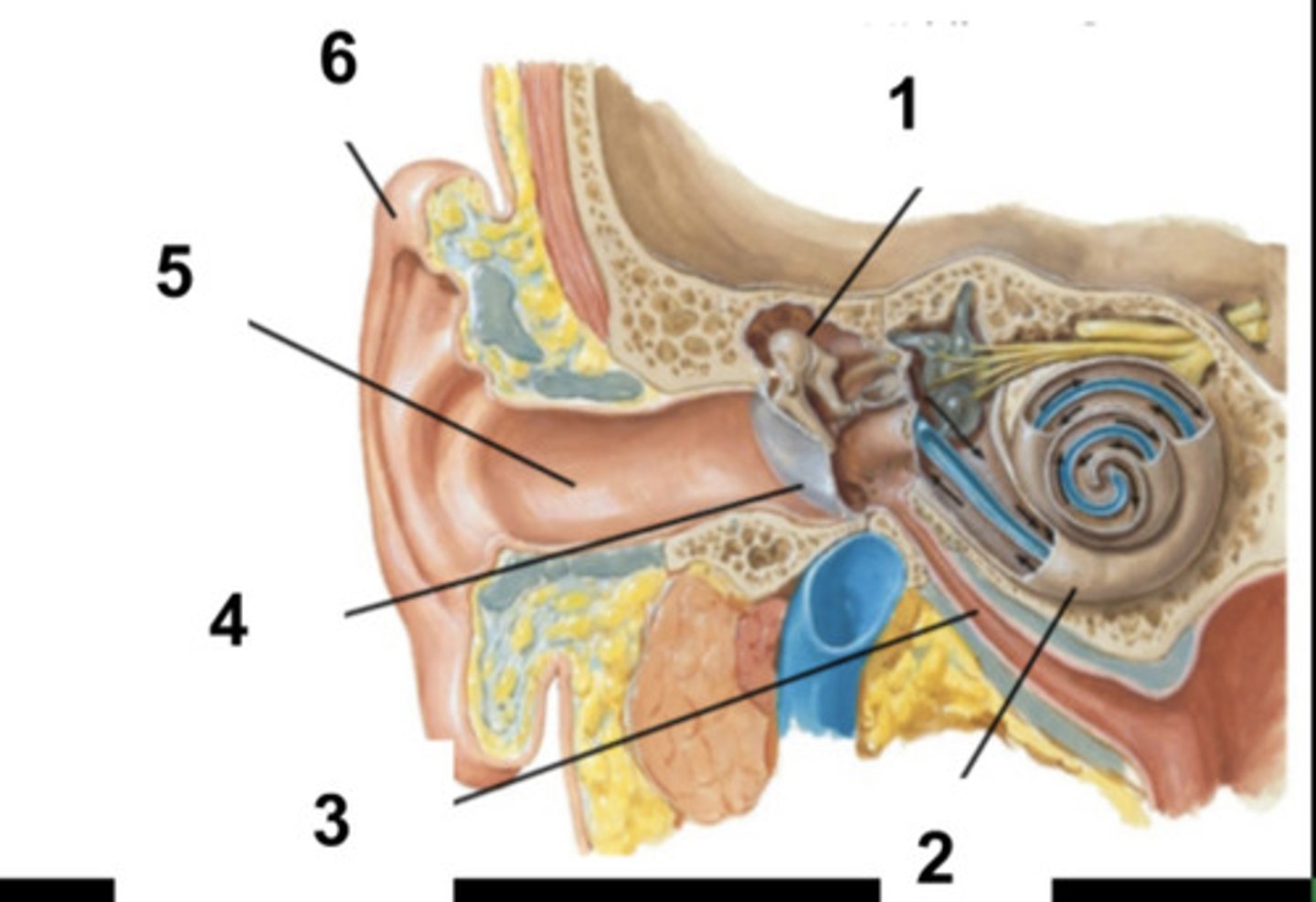
Auditory Tube
What is structure #3?
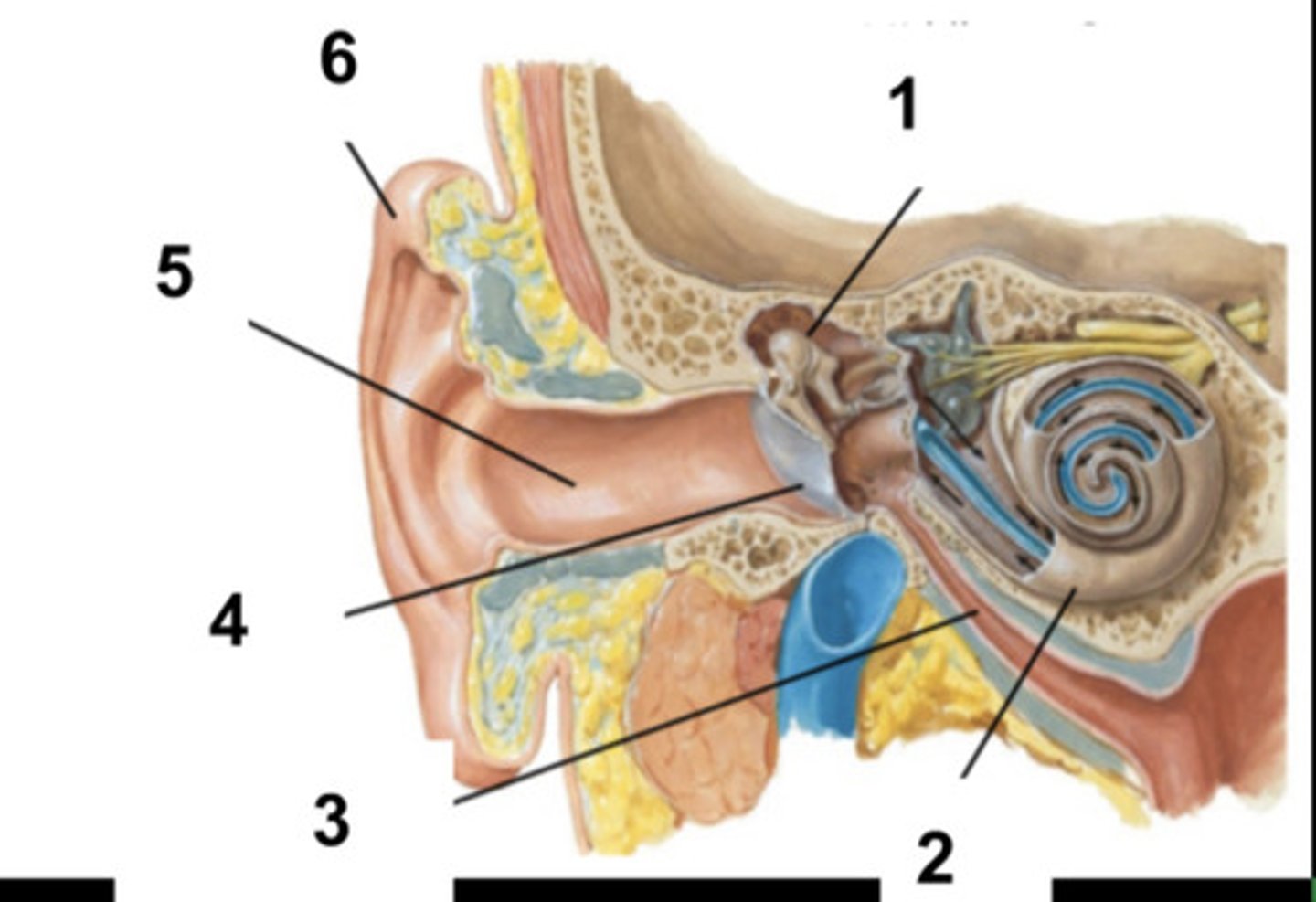
Tympanic Membrane
What is structure #4?
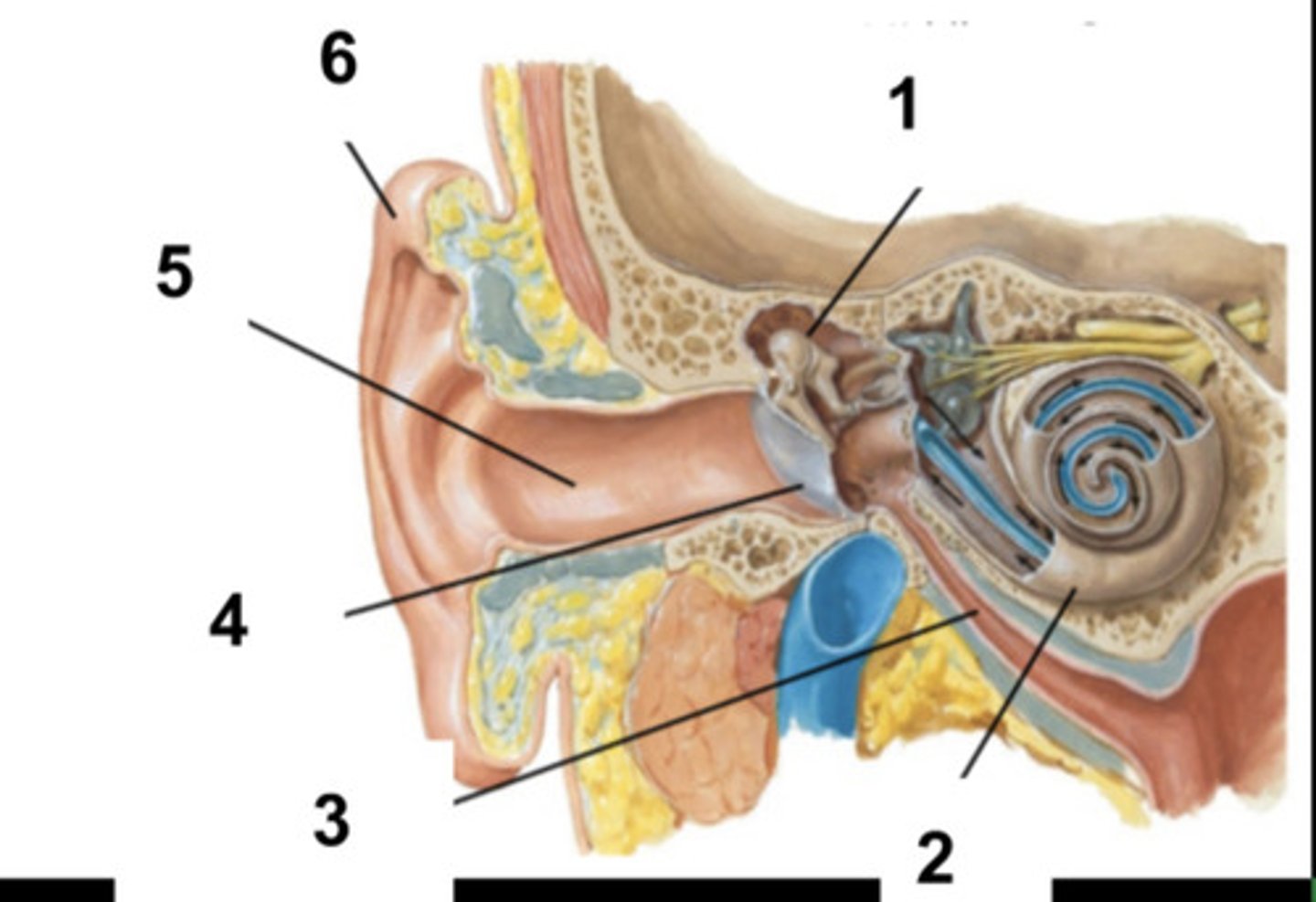
External Ear Canal
What is structure #5?
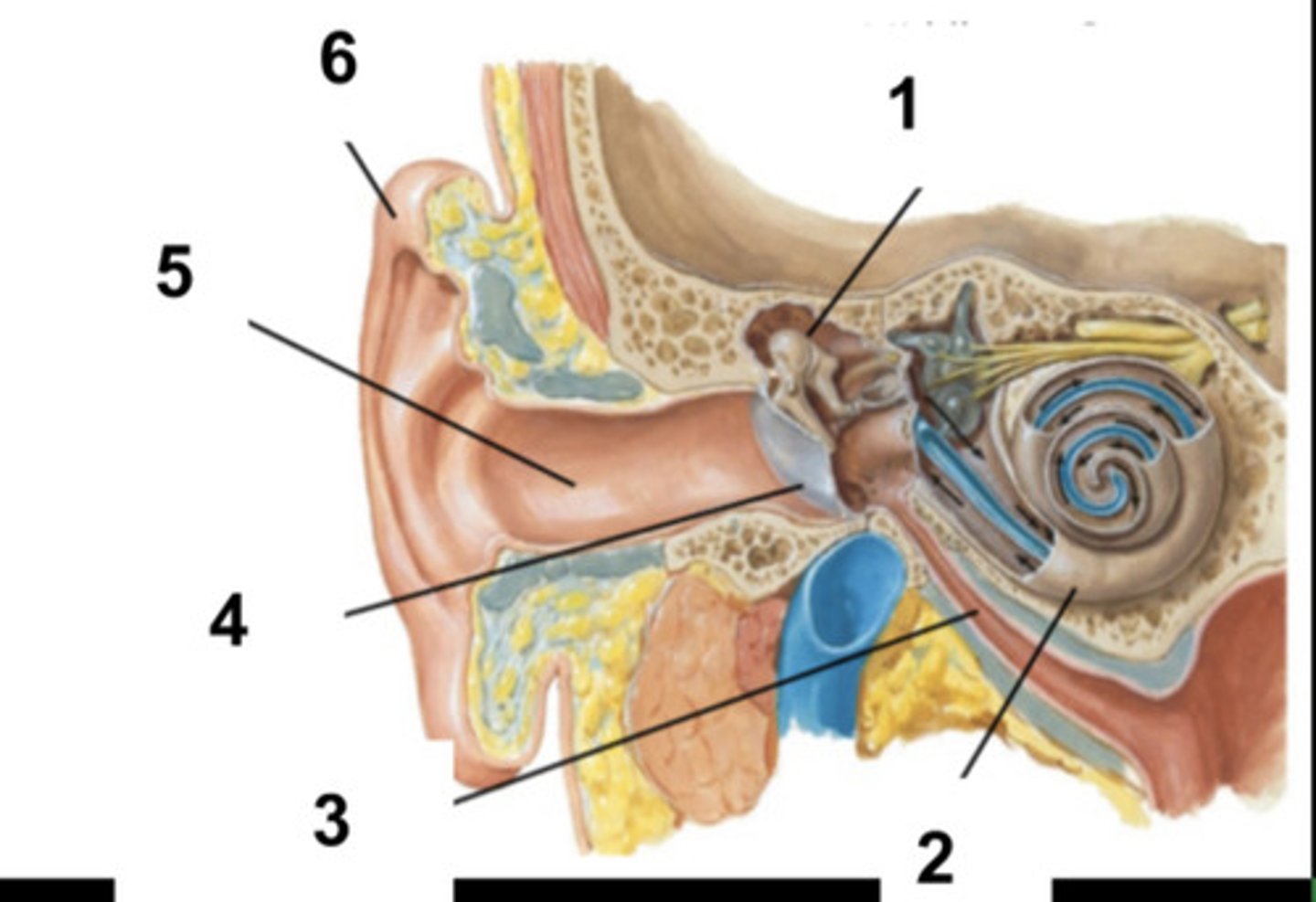
External Ear
What is structure #6?
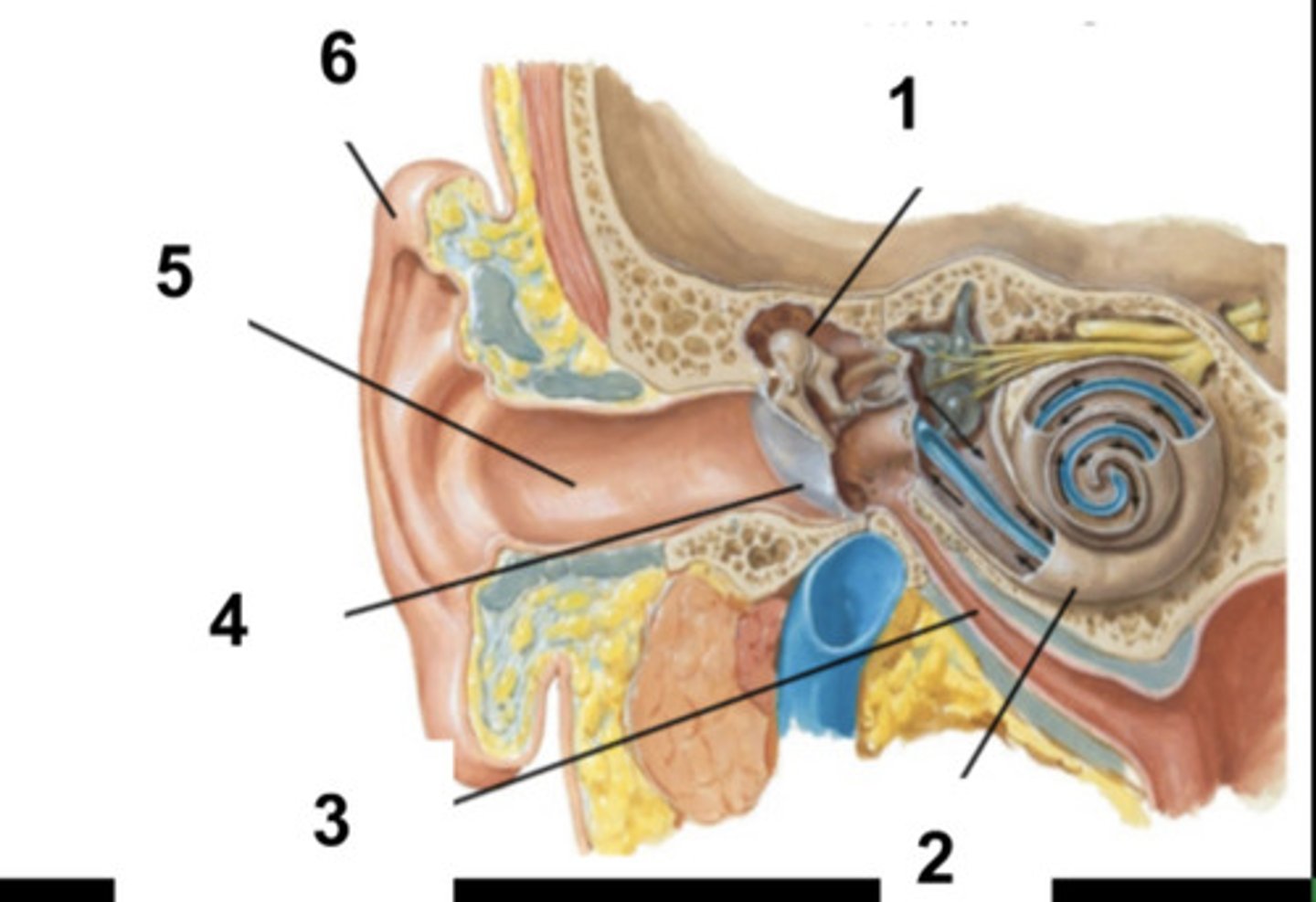
Cochlear Nerve
What is structure #1?
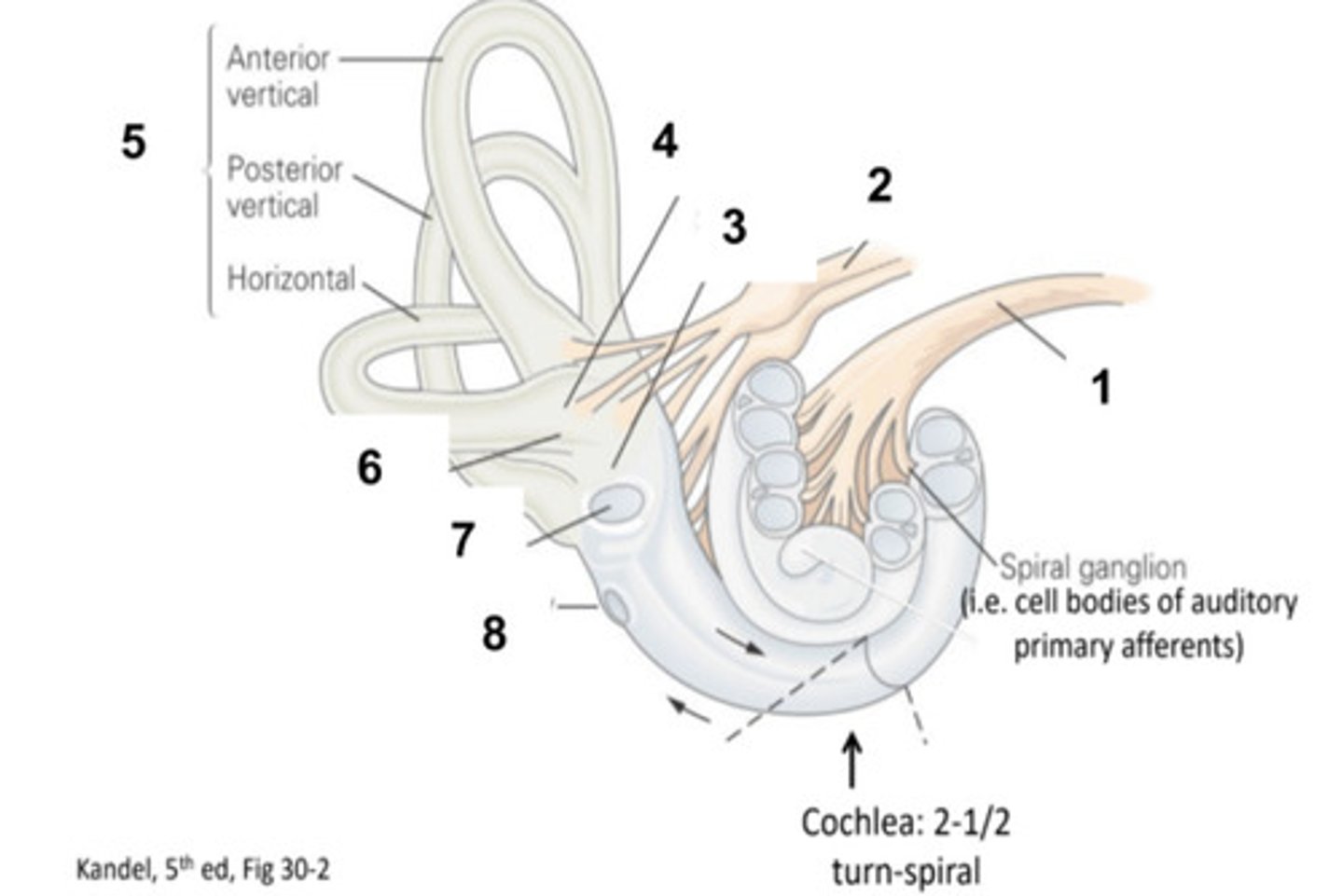
Vestibular Nerve
What is structure #2?
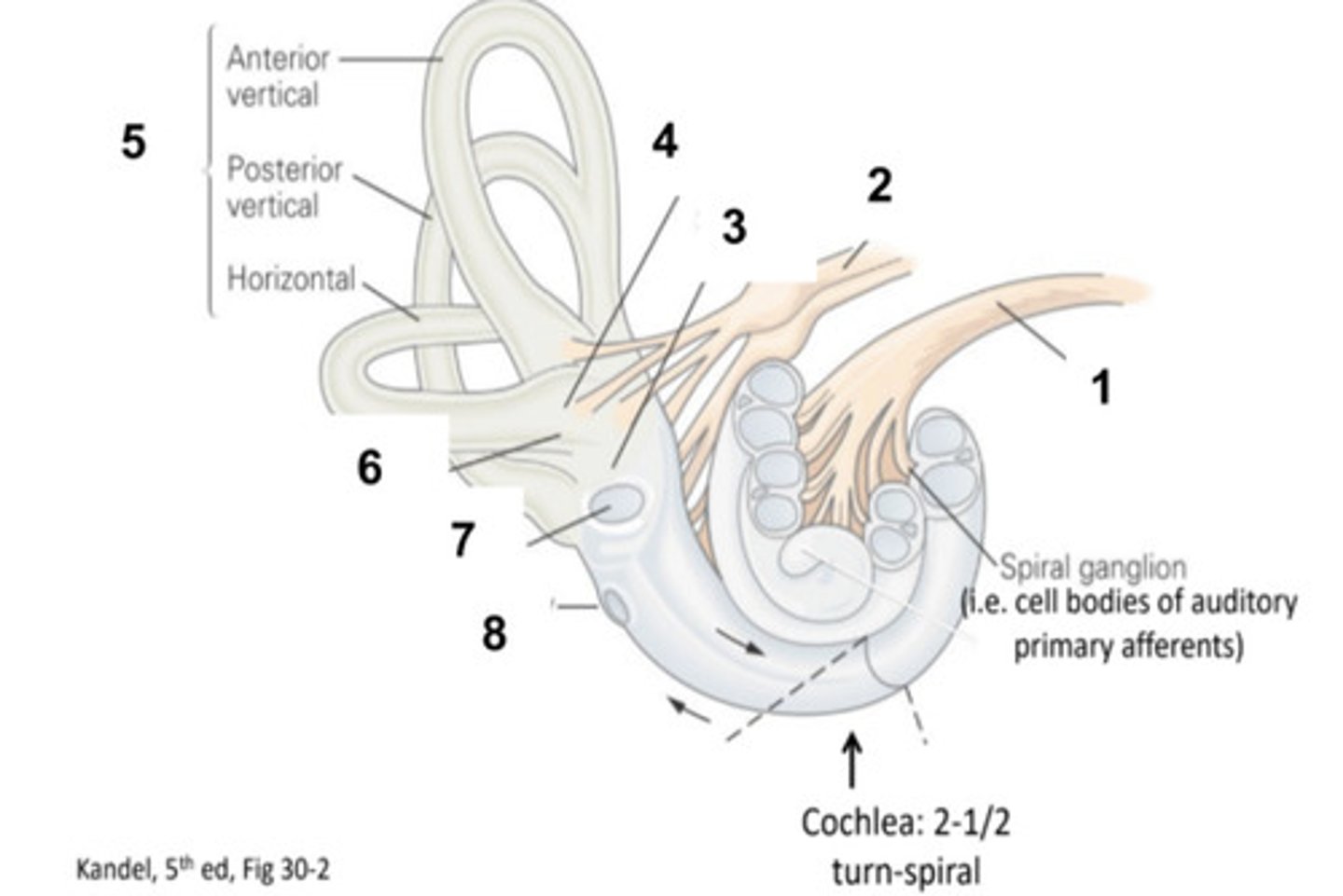
Saccule
What is structure #3?
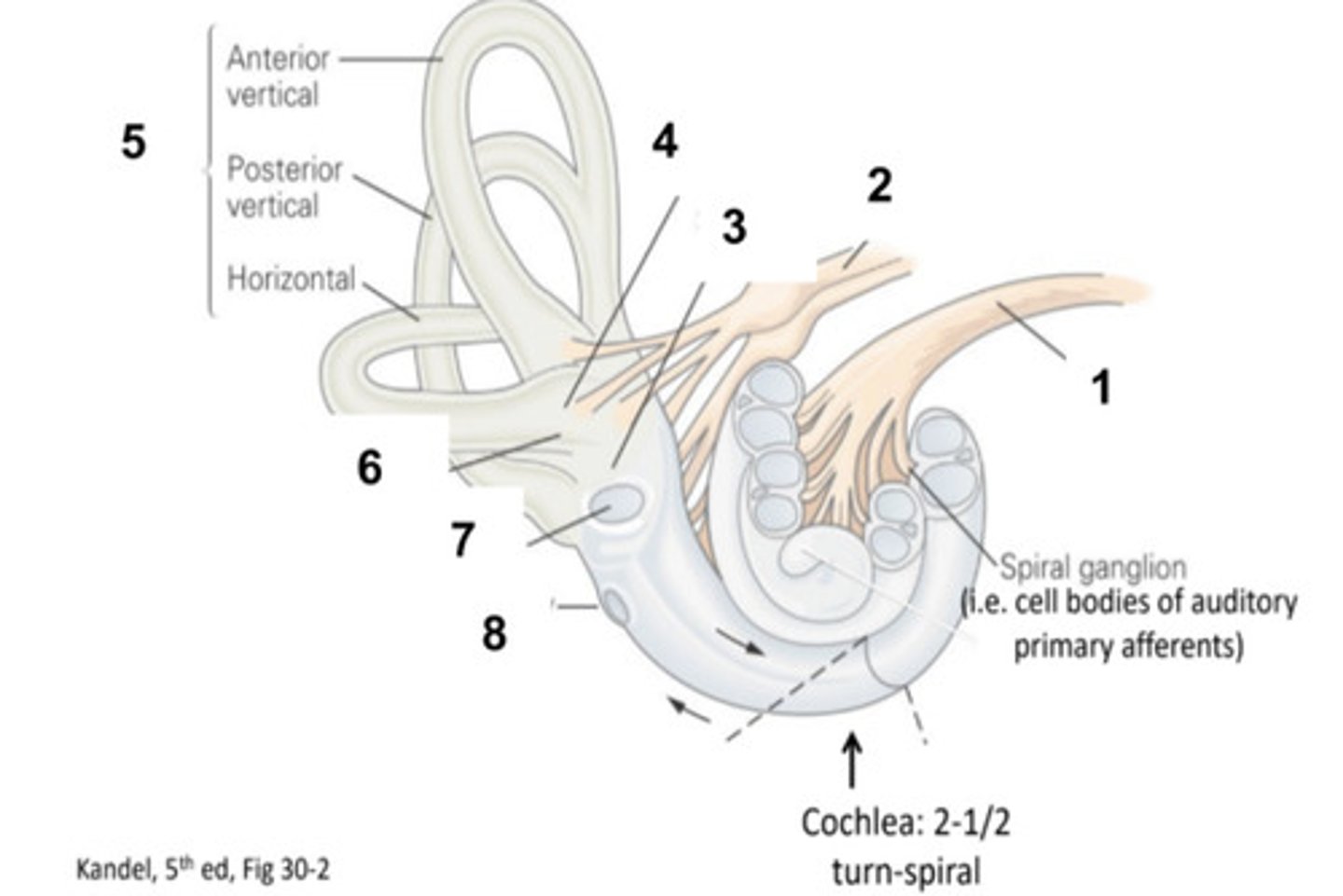
Utricle
What is structure #4?
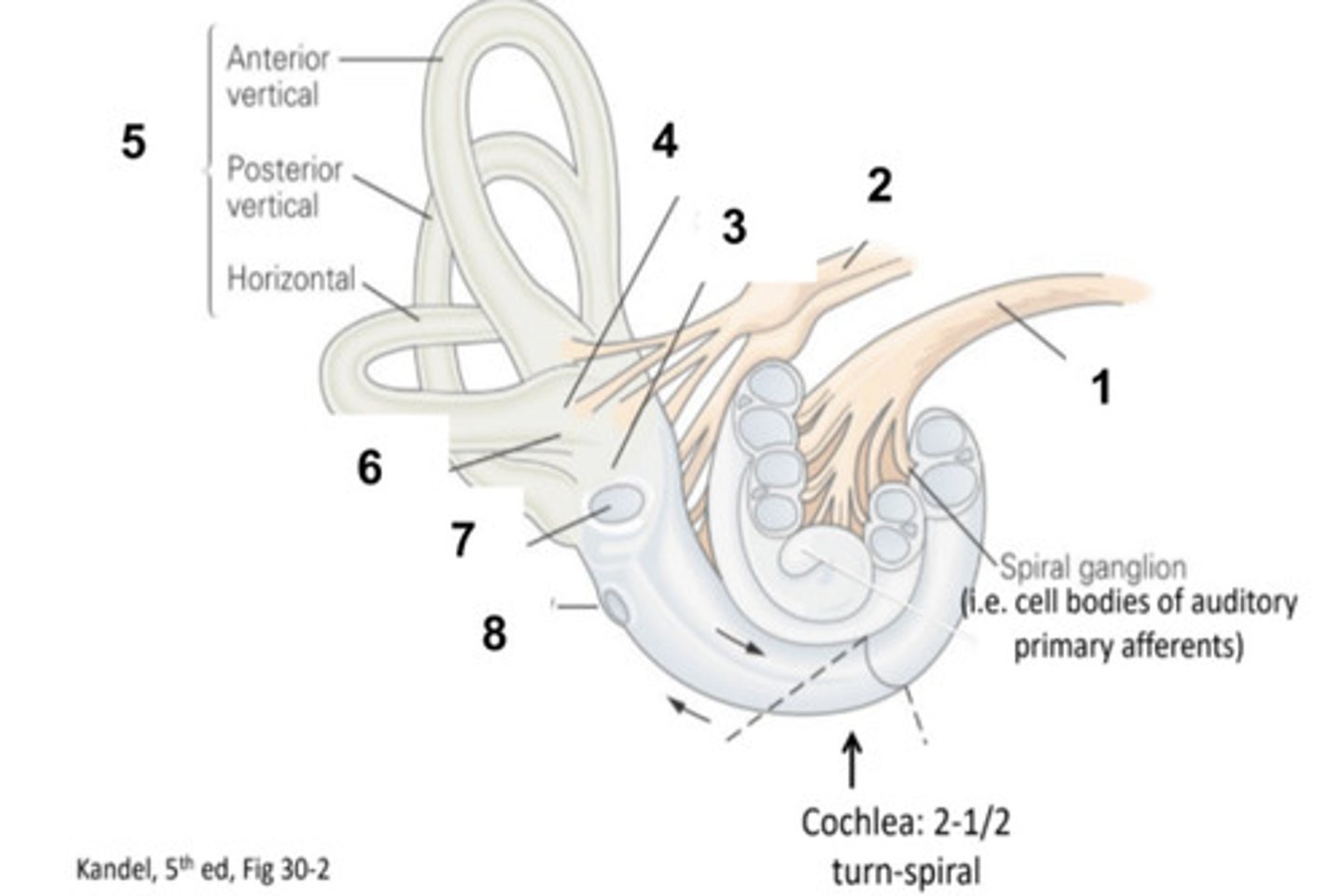
Semicircular Canals
What is structure #5?
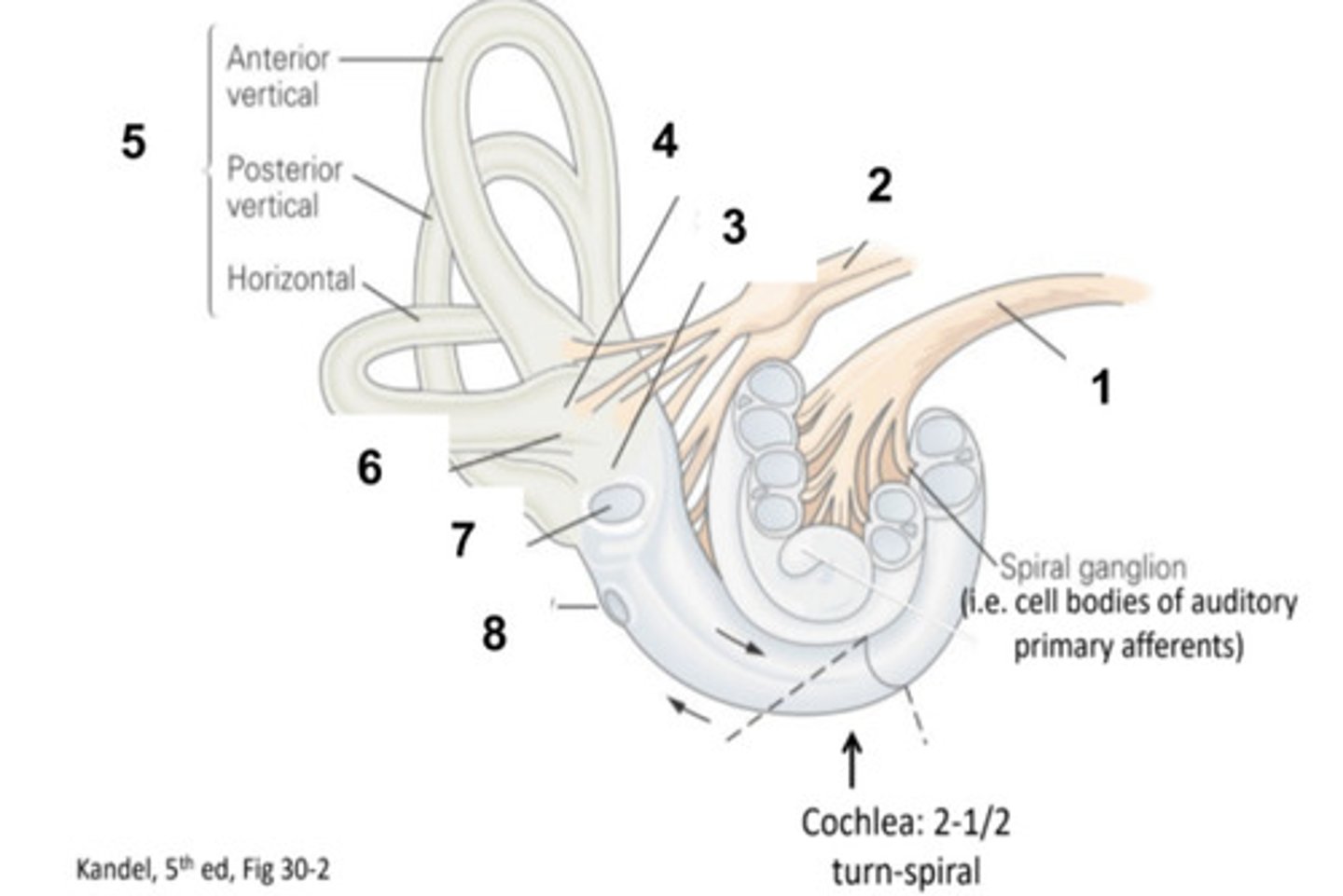
Ampulla
What is structure #6?
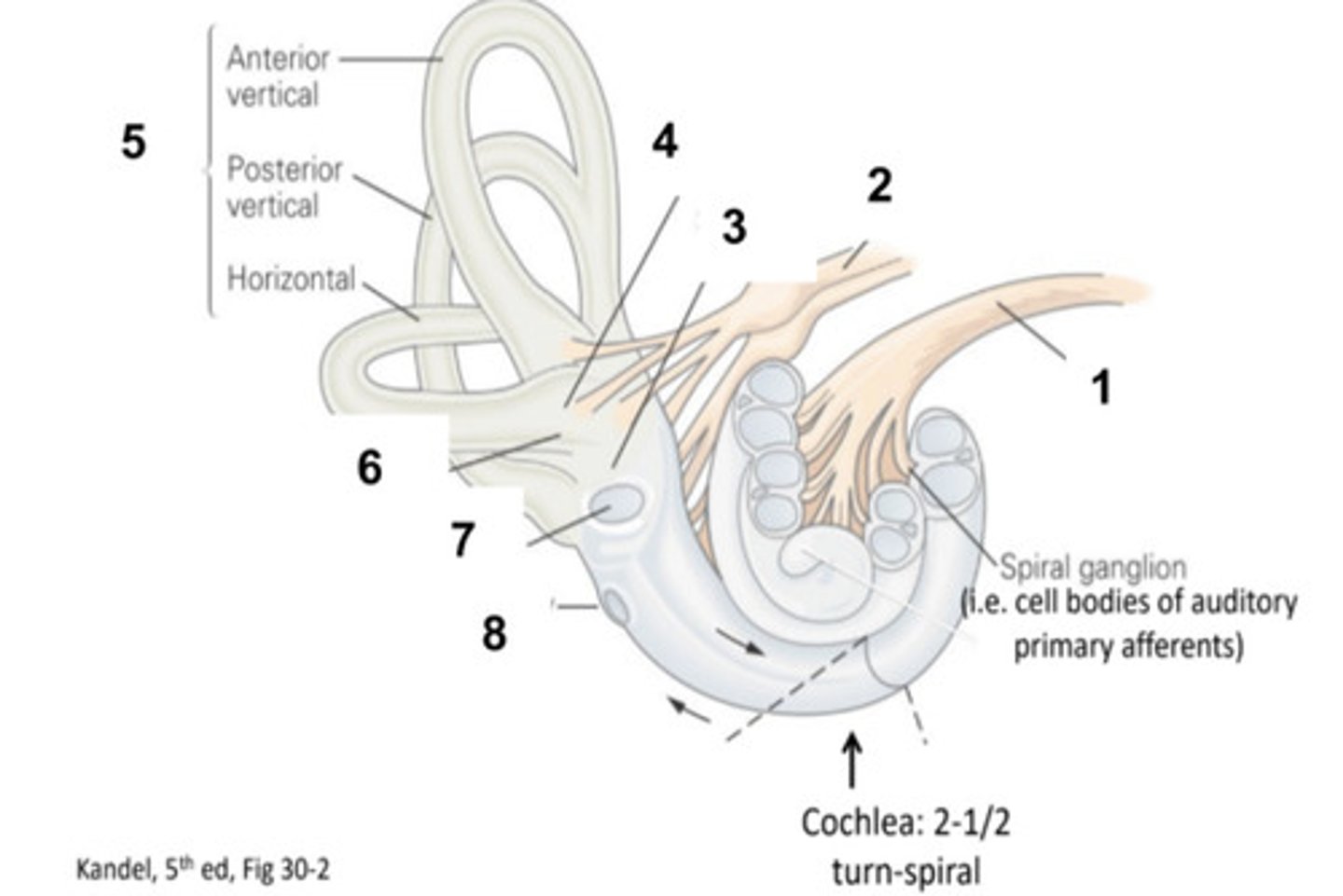
Oval Window
What is structure #7?
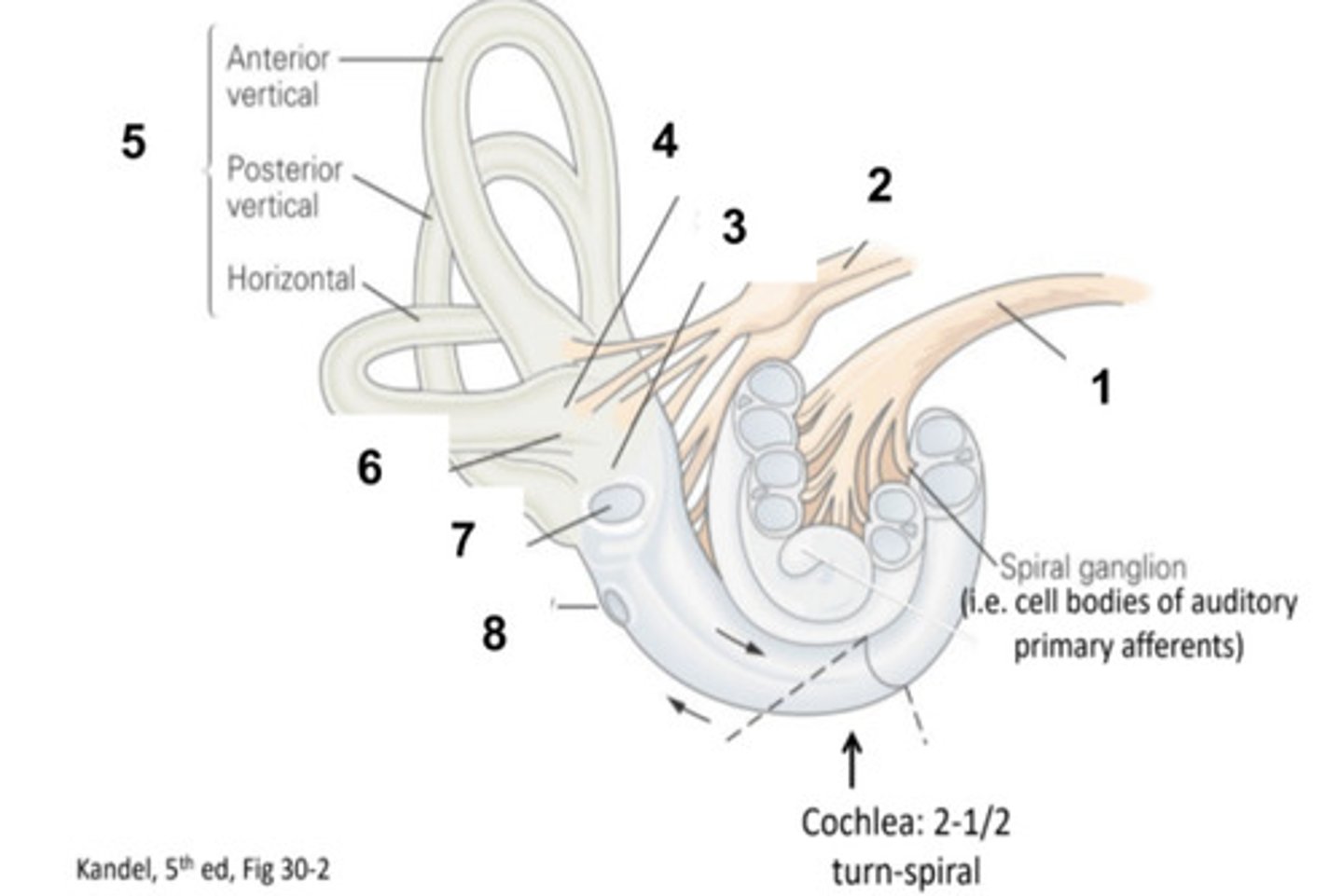
Round Window
What is structure #8?
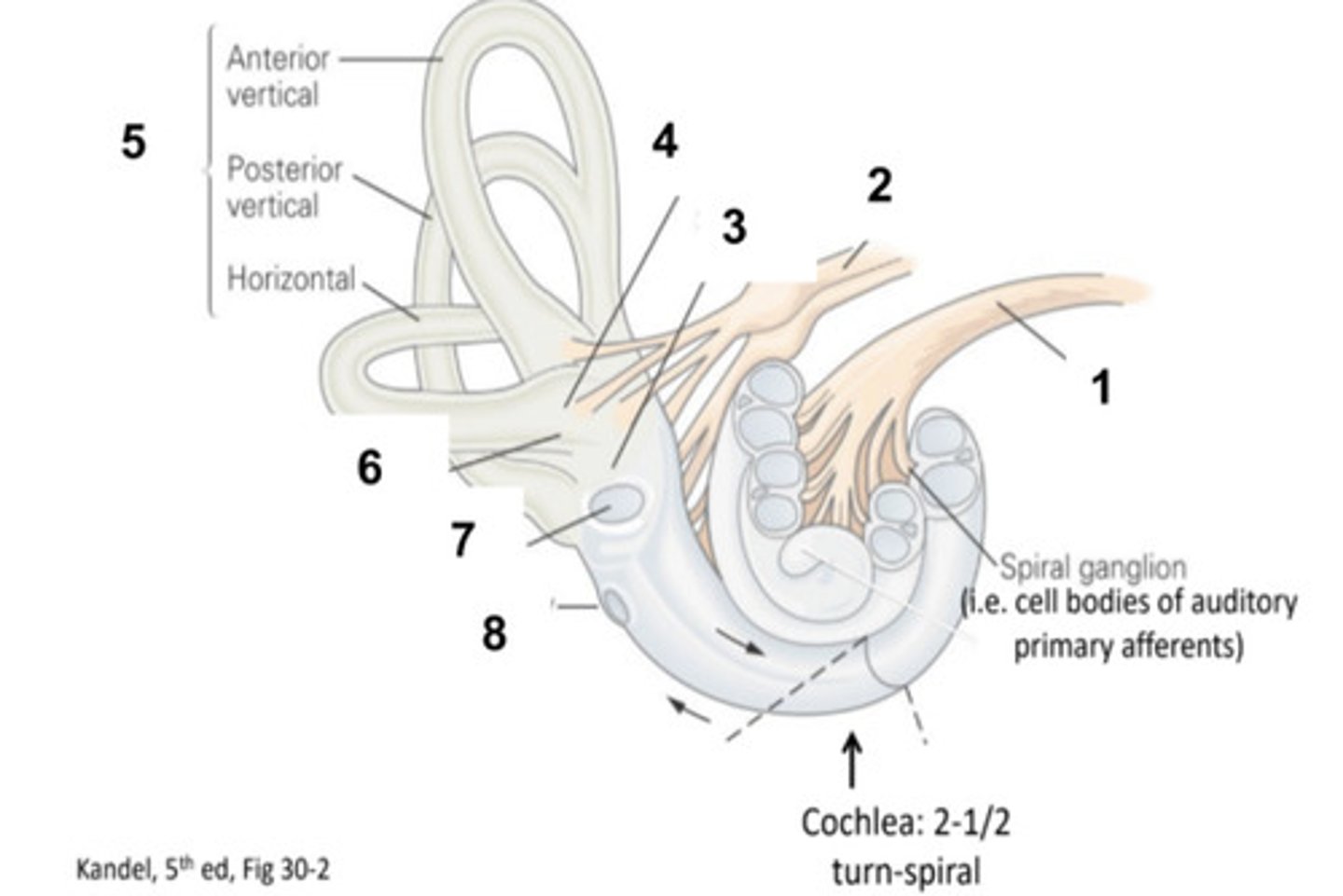
Hair Cells
What is structure #1?
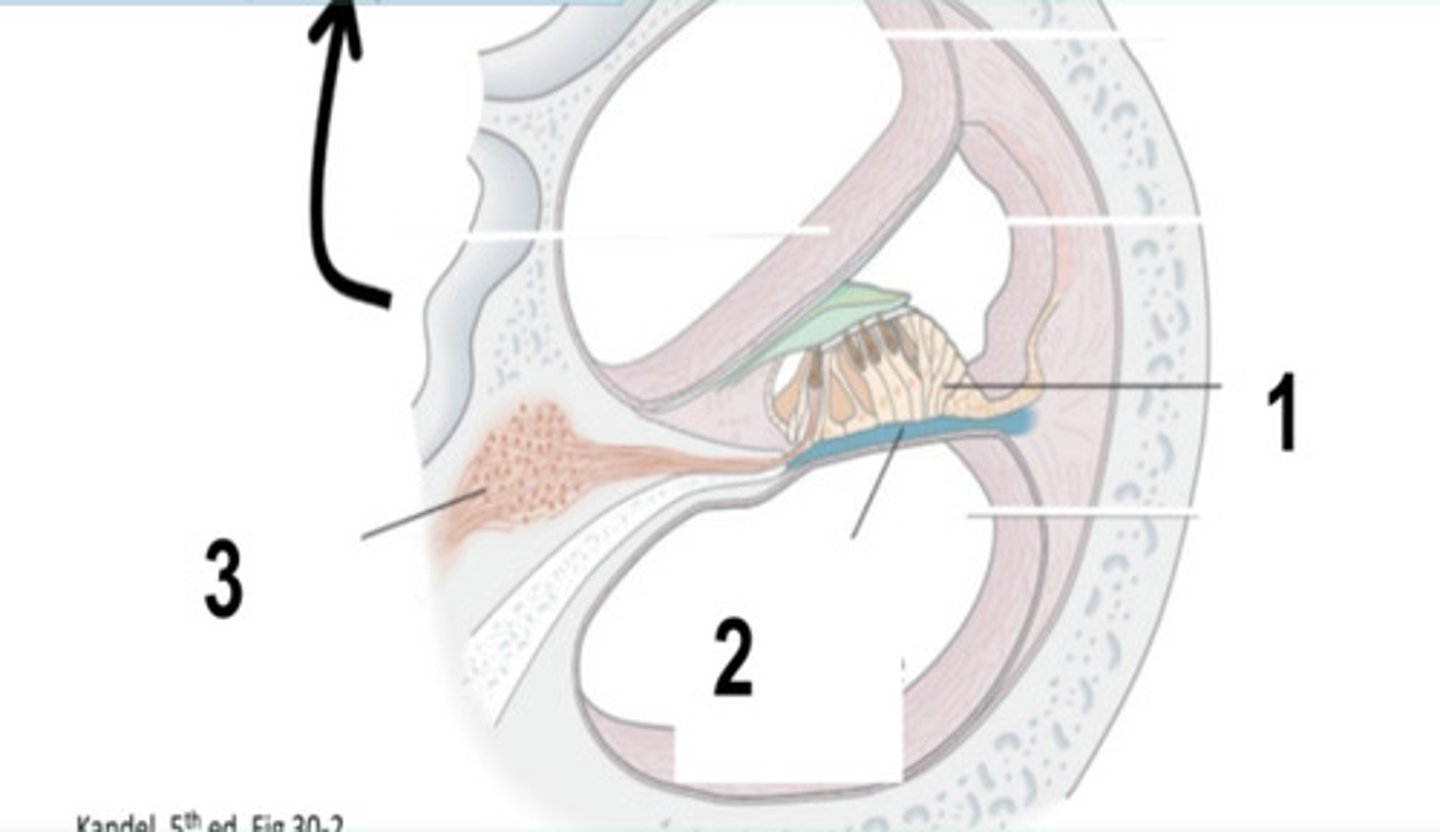
Hair Cells Function
where sound transduction occurs
Basiliar Membrane
What is structure #2?
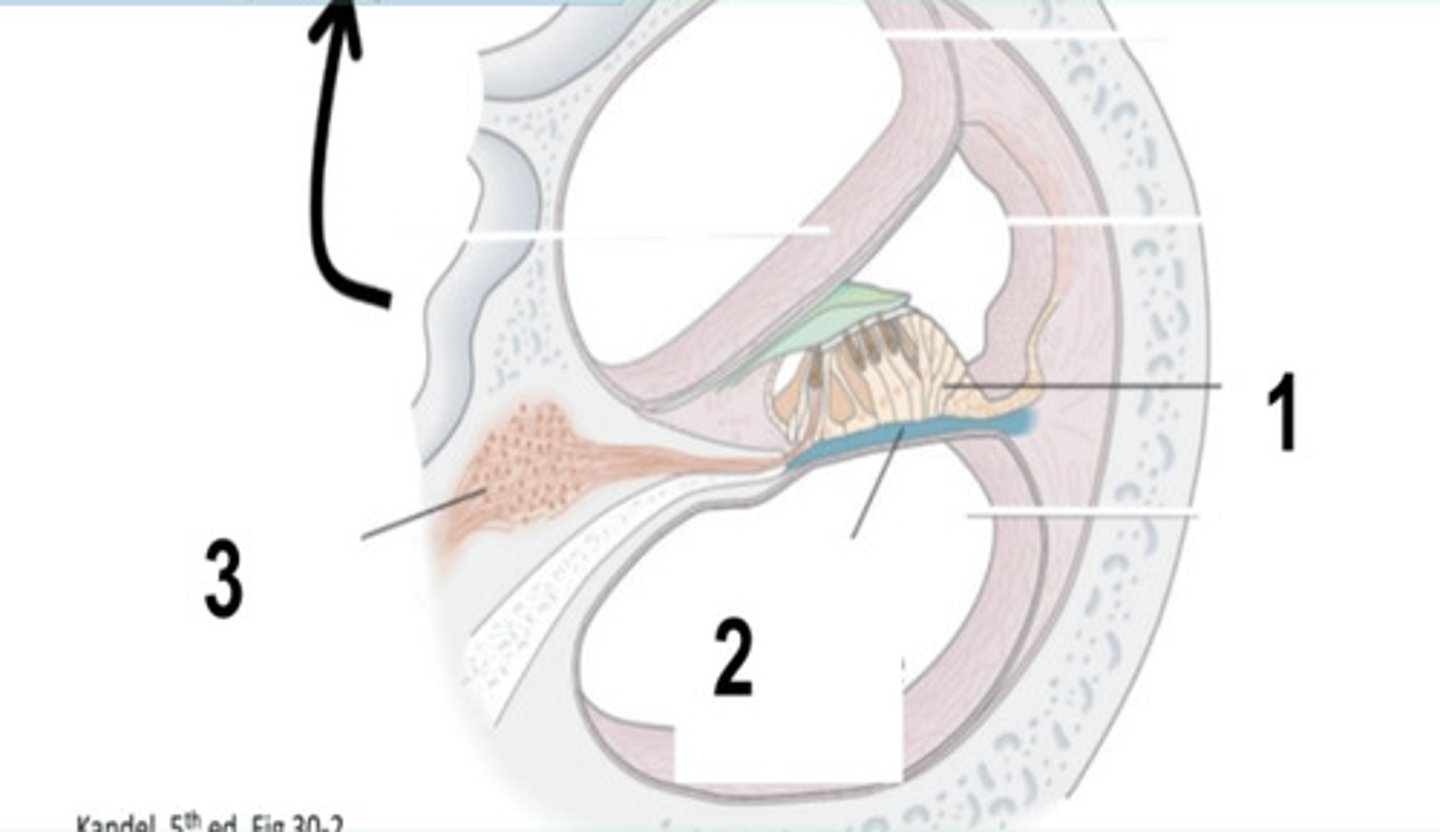
Basiliar Membrane Function
membrane transmitting sound vibrations to hair cells
Spiral Ganglion
What is structure #3?
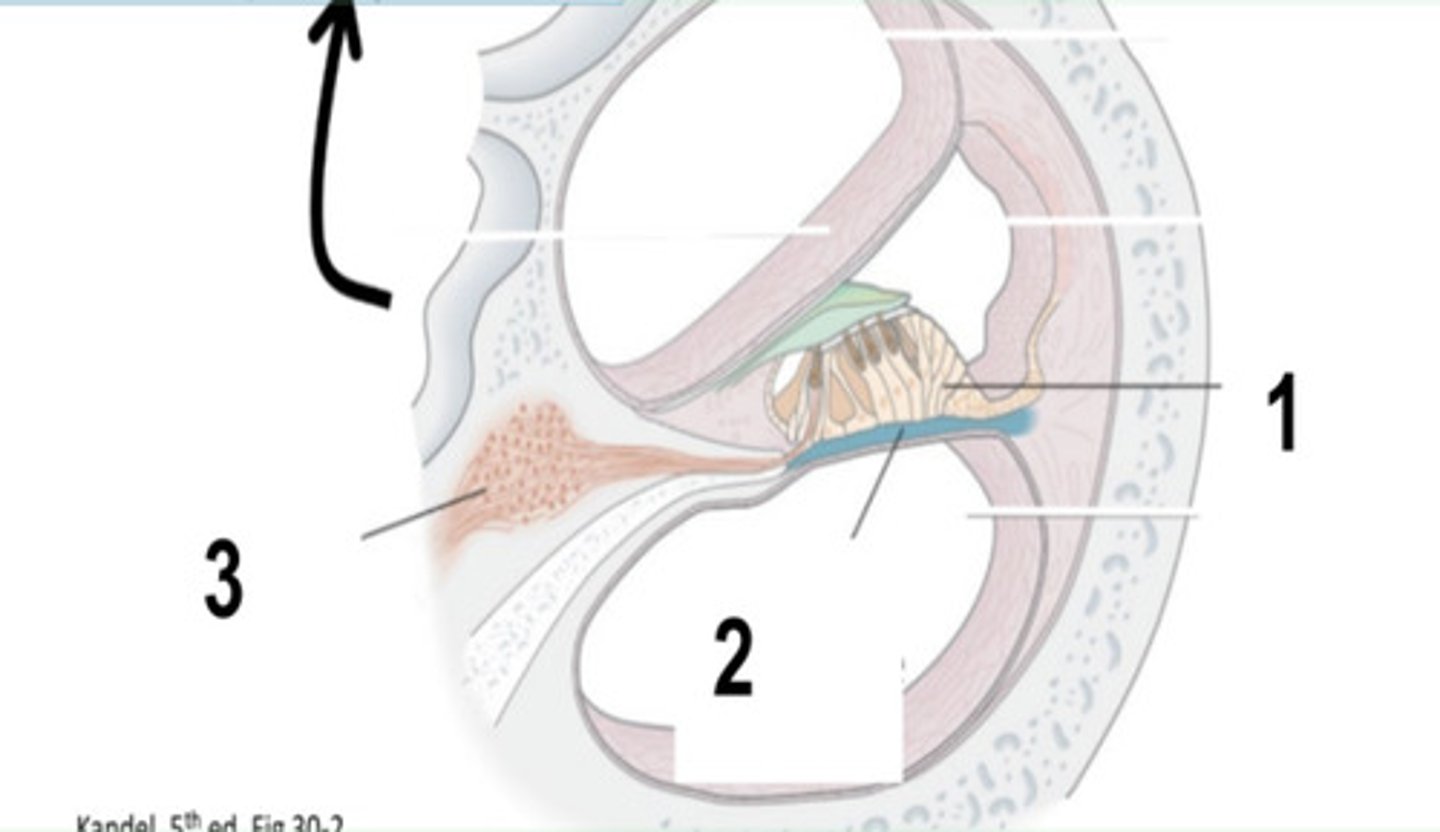
Spiral Ganglion Function
primary afferent neurons for hearing
Wide, thin, flaccid
What is the width and tension of the basiliar membrane at the apex?
Narrow, thick, tense
What is the width and tension of the basiliar membrane at its base?
Low
The apex of the basiliar membrane has ____ resonant frequency.
High
The base of the basiliar membrane has ____ resonant frequency.
100 Hz
low frequency
1000 Hz
medium frequency
10,000 Hz
high frequency
Basiliar
Every frequency resonates at a unique point along the _____ membrane.
Excitation of Hair Cells
- depolarization
- increased impulse frequency
Inhibition if Hair Cells
- hyperpolarization
- decreased impulse frequency
Spinal Ganglion Neuron
bipolar neuron found in the inner ear whose axons form the auditory nerve
Cochlear Nuclei
sound localization & identification: medulla
Olivary Nuclei
sound localization and volume control: pons
Inferior Colliculus
identification of and reflexive responses to sounds: midbrain
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
thalamus relay nucleus
Auditory Cortex
tonotopic organization, sound identification
Pitches
Sounds usually consist of multiple ____.
Single
A pitch is a _____ frequency.
Deafness
loss of the ability to hear
Conduction Deafness
- ear wax
- issues w/ ossicles
Sensorineural
- most common form of deafness
- can be result from exposure to loud noises
- age-related loss of high-frequency hearing
- treated w/ hearing aids
Tinnitus
- ringing in the ears
- associated w/ hearing loss
- difficult to treat
Rotation
Semicircular canals sense ____.
Endolymph
fluid within the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear
Ampulla
the connection of the semicircular canals
Cupula
a gelatinous mass found in the ampulla of the semicircular canals; moves in response to the flow of the fluid in the canals
Cupula
The flow of fluid causes the ____ to move.
Angular
Semicircular canals sense ____ acceleration.
Linear
Utricle and saccule sense ____ acceleration.
Horizontal
The utricle is hair cells in the ____ sheet.
Vertical
The saccule is hair cells in the ___ sheet.
Vestibular; Flocculonodular
The vestibular apparatus projects its axons to:
- the _____ nuclei in dorsal brainstem
- part of the cerebellum involved in balance (the
_____ lobe)
Cerebellum; Eye Movements
The vestibular nuclei project axons to:
- spinal cord
- ______
- Cranial nerve nuclei controlling _____ (i.e. oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nuclei--CN 3, 4, 6).
Functions of Vestibular Nuclei
Projections to spinal cord & cerebellum:
- Coordinate eye movements with head & neck
movements
- Coordinate vestibular input with “anti-gravity” muscles
(i.e. reflexively catch yourself if you trip)
Projections to nuclei innervating extraocular
muscles:
- Track objects while turning your head
3
The vestibular system provides only one of __ inputs
that tell us how our body is oriented.
Proprioception
uses gravity, e.g., the force exerted between our feet and the floor
Vision
orients us relative to the earth (down), the sky (up), and what's horizontal
False
(True/False) People can typically function with only one of the three senses.
Vertigo
sensation of turning in the absence of motion
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
the sensation of spinning with certain head movements as a result of a problem in the inner ear (fancier medical term)
Ménière's Disease
results in a degeneration of inner ear structures that can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo, and an increase in pressure within the inner ear
Nystagmus
repetitive rhythmic movements of one or both eyes in the absence of movement
Motion Sickness
effect when visual and/or motor feedback (autonomic centers) is inconsistent with vestibular input to reticular formation