HSC 214 Vertebral Column / Thorax
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
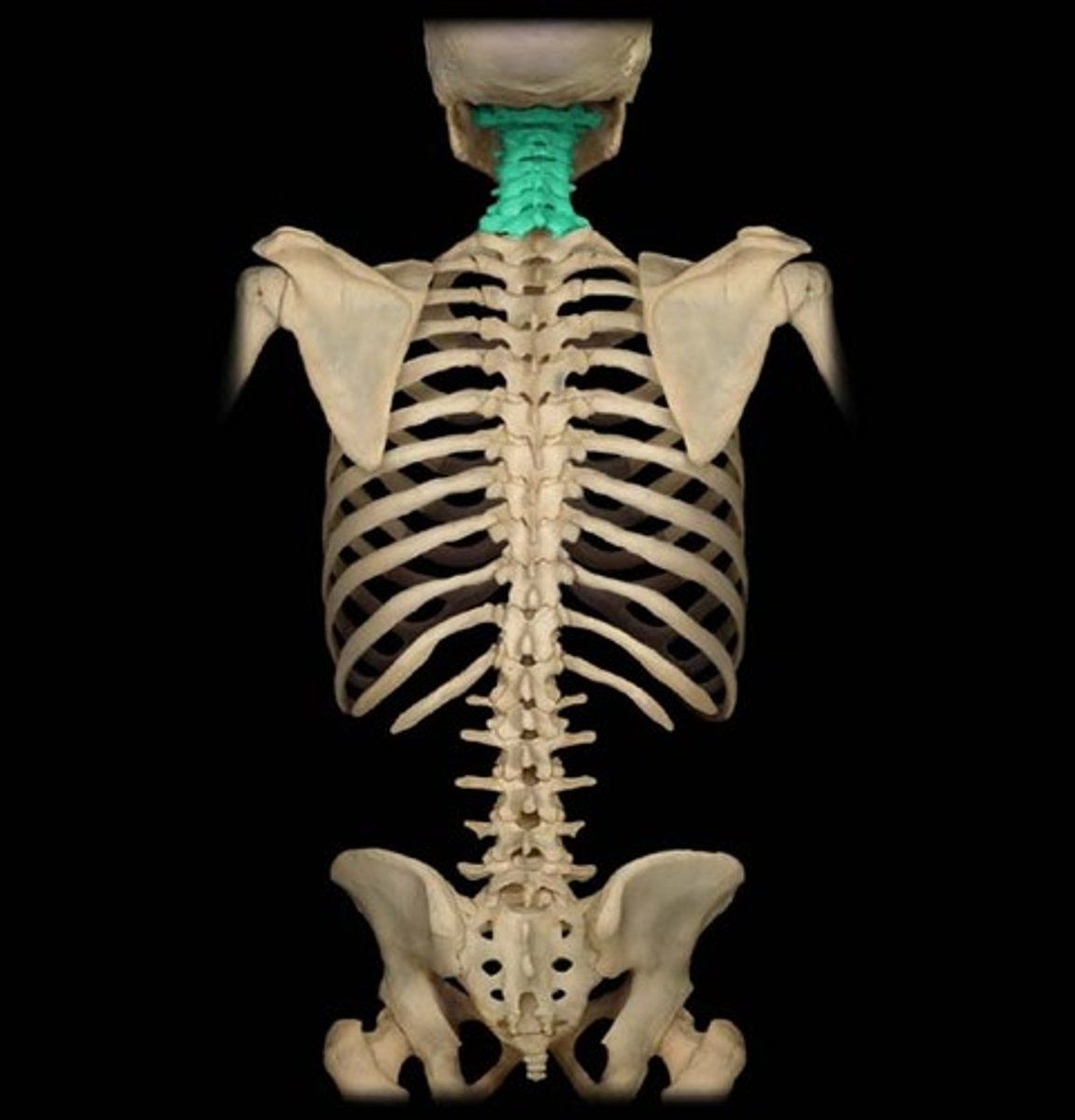
Cervical
- first seven vertebrae (C1-C7)
- "breakfast at 7" for 7 cervical vertebrae
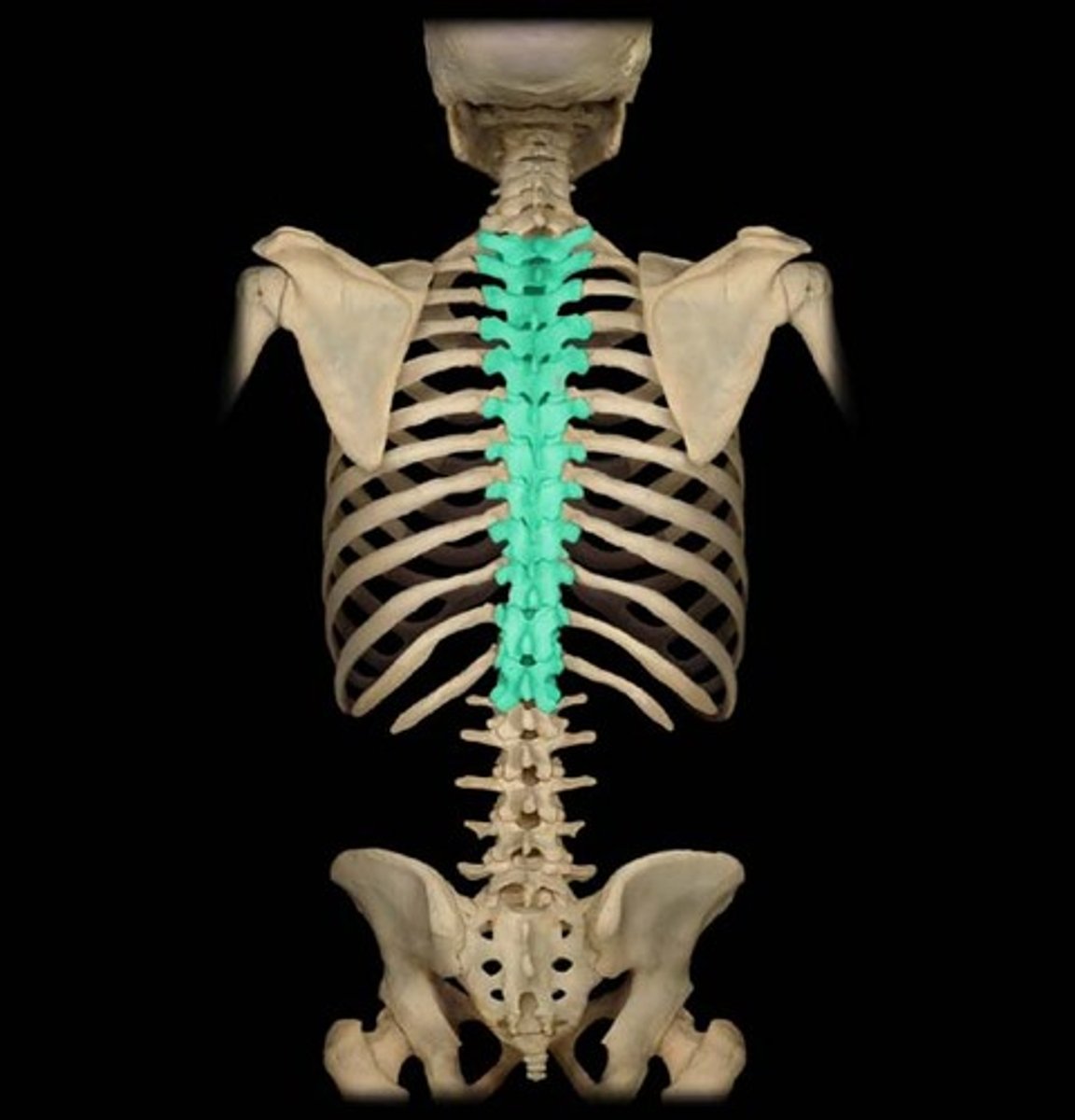
Thoracic
- twelve vertebrae where the ribs attach (T1-T12), together forming a kyphosis curve of the spine
- "lunch at 12" for 12 thoracic vertebrae
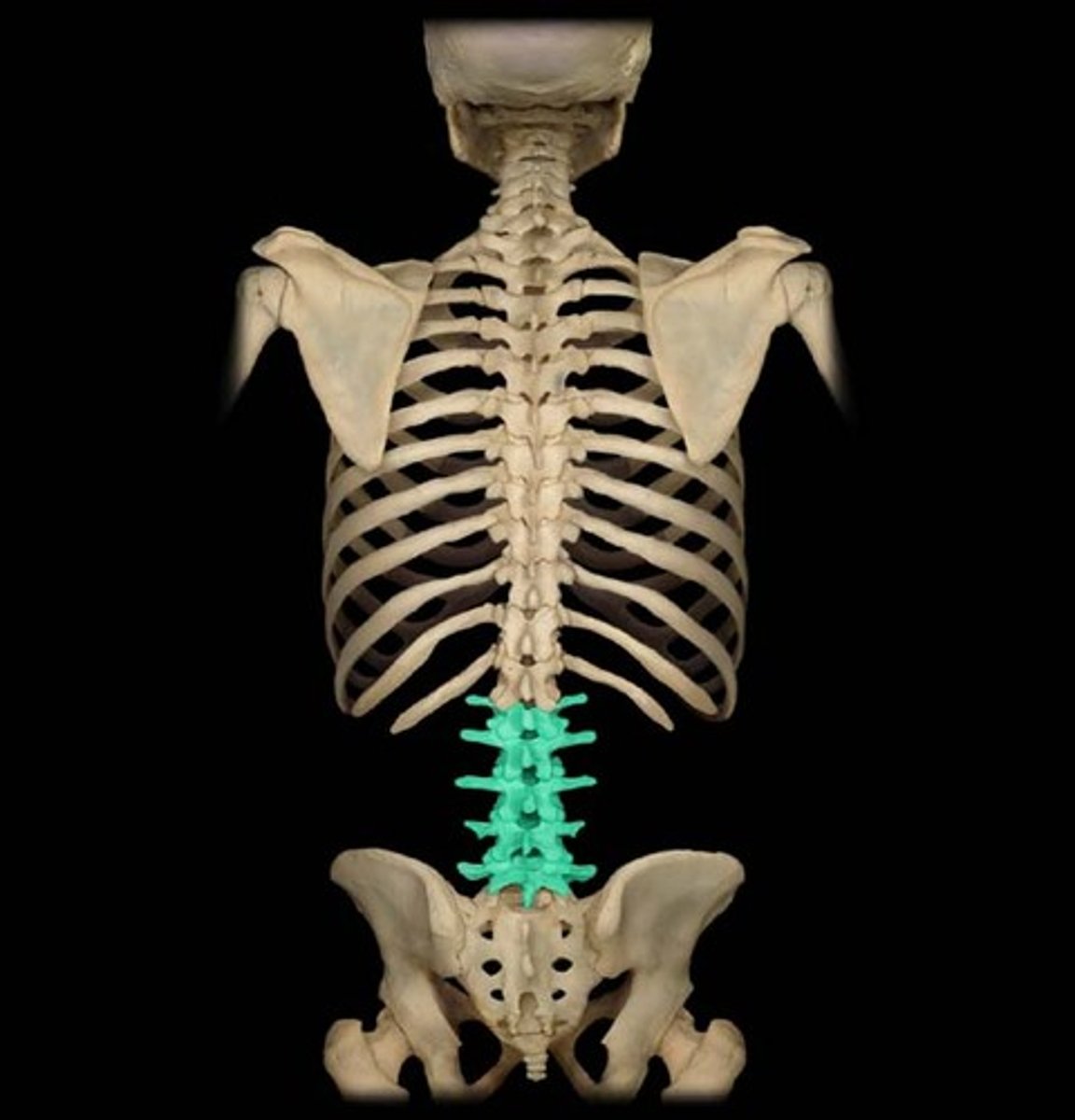
Lumbar
- five weight-bearing vertebrae (L1-L5), together forming a lordosis curve of the spine
- "dinner at 5" for 5 lumbar vertebrae
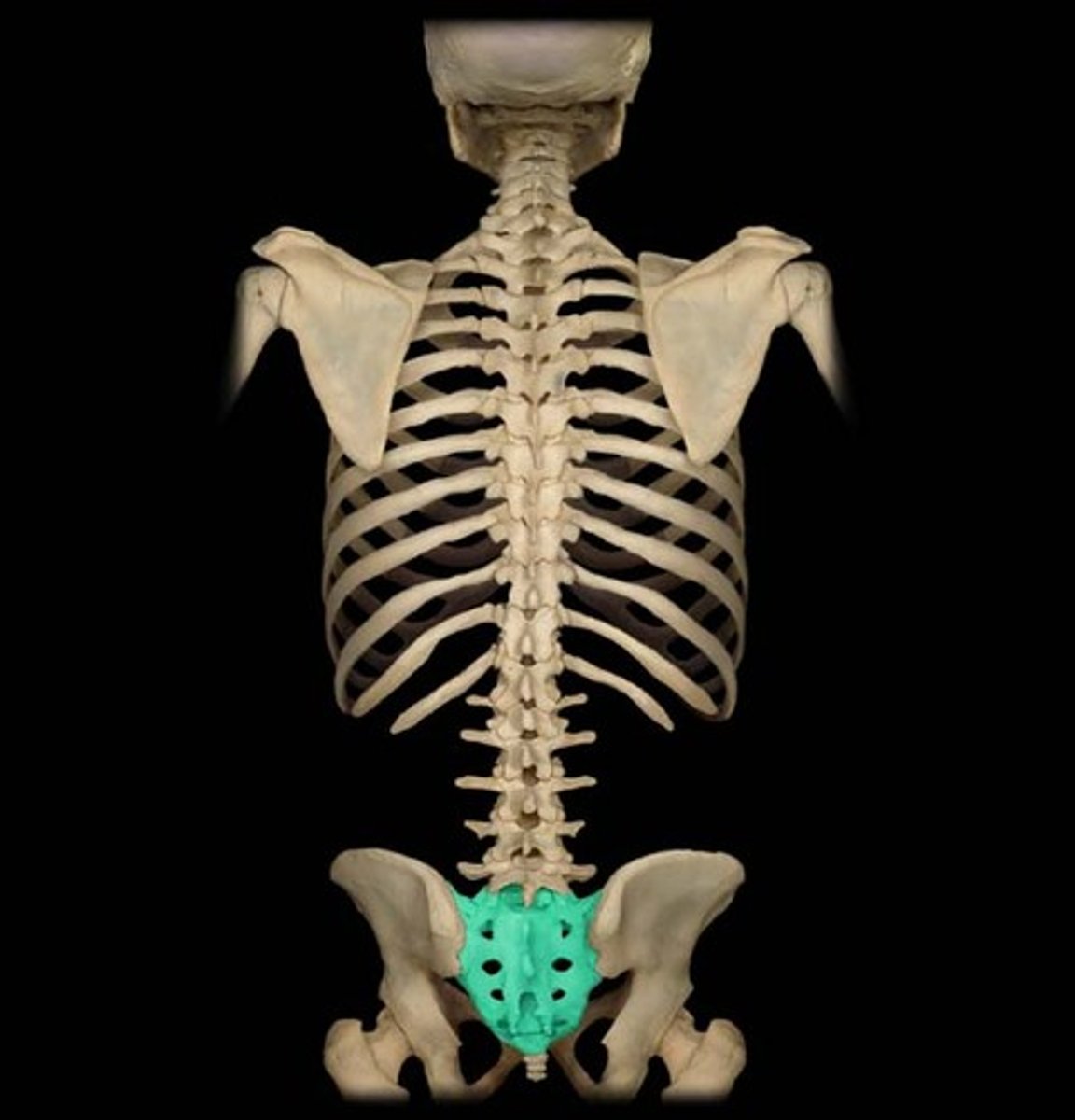
Sacrum
- Five fuse vertebrae (S1-S5), forming one triangular bone
- between the hip bones
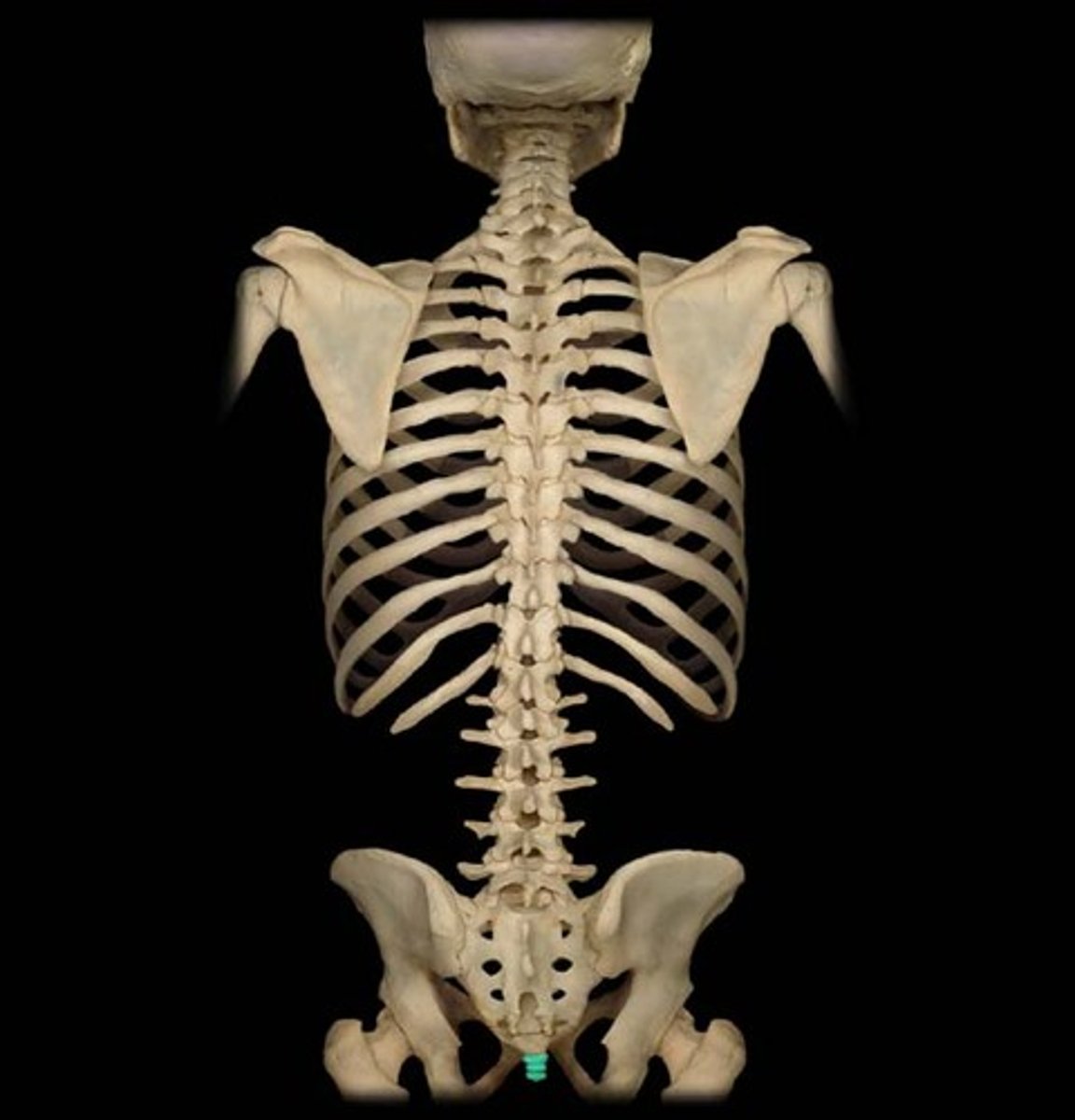
Coccyx
- Three or four fused vertebrae (C1), forming one small, triangular bone
- "tailbone"
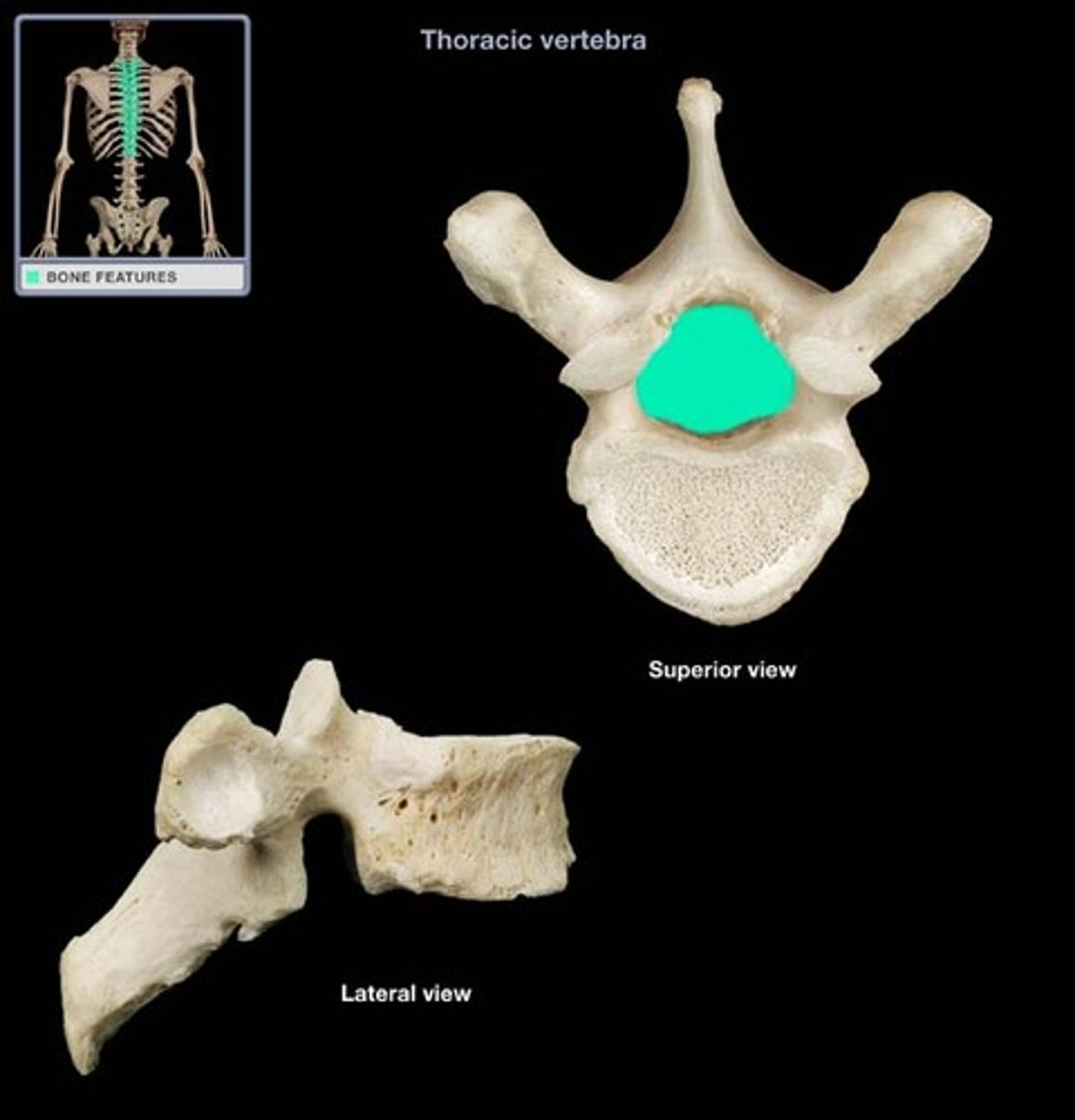
Vertebral body
- large, anterior rounded bone masses
- together form the vertebral column
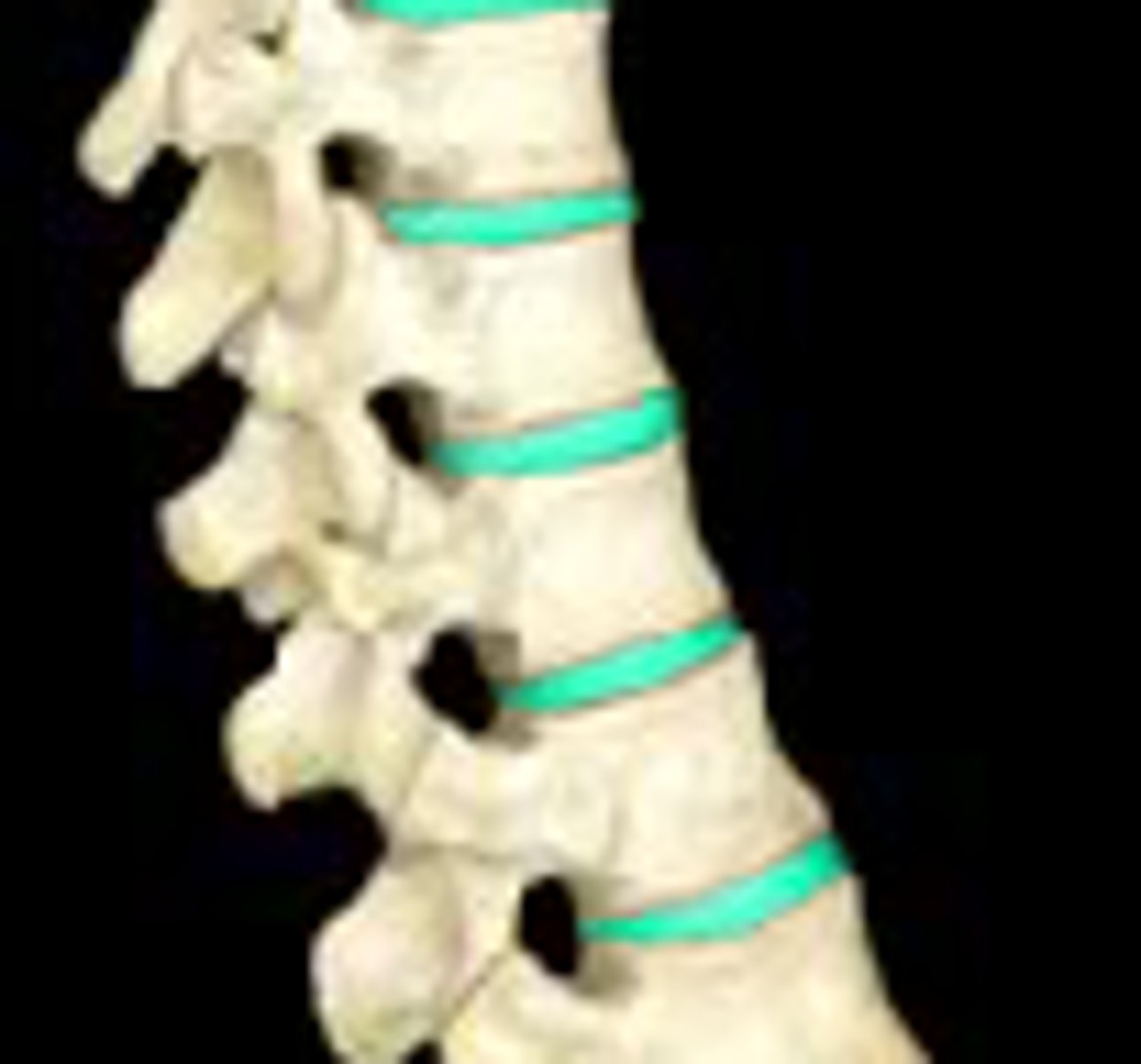
intervertebral disc
- fibrocartilage discs between vertebral bodies
- "shock absorbers"
pedicle
- short, thick, pillar of bone between the vertebral body and transverse process
- directly connected to the vertebral bodies
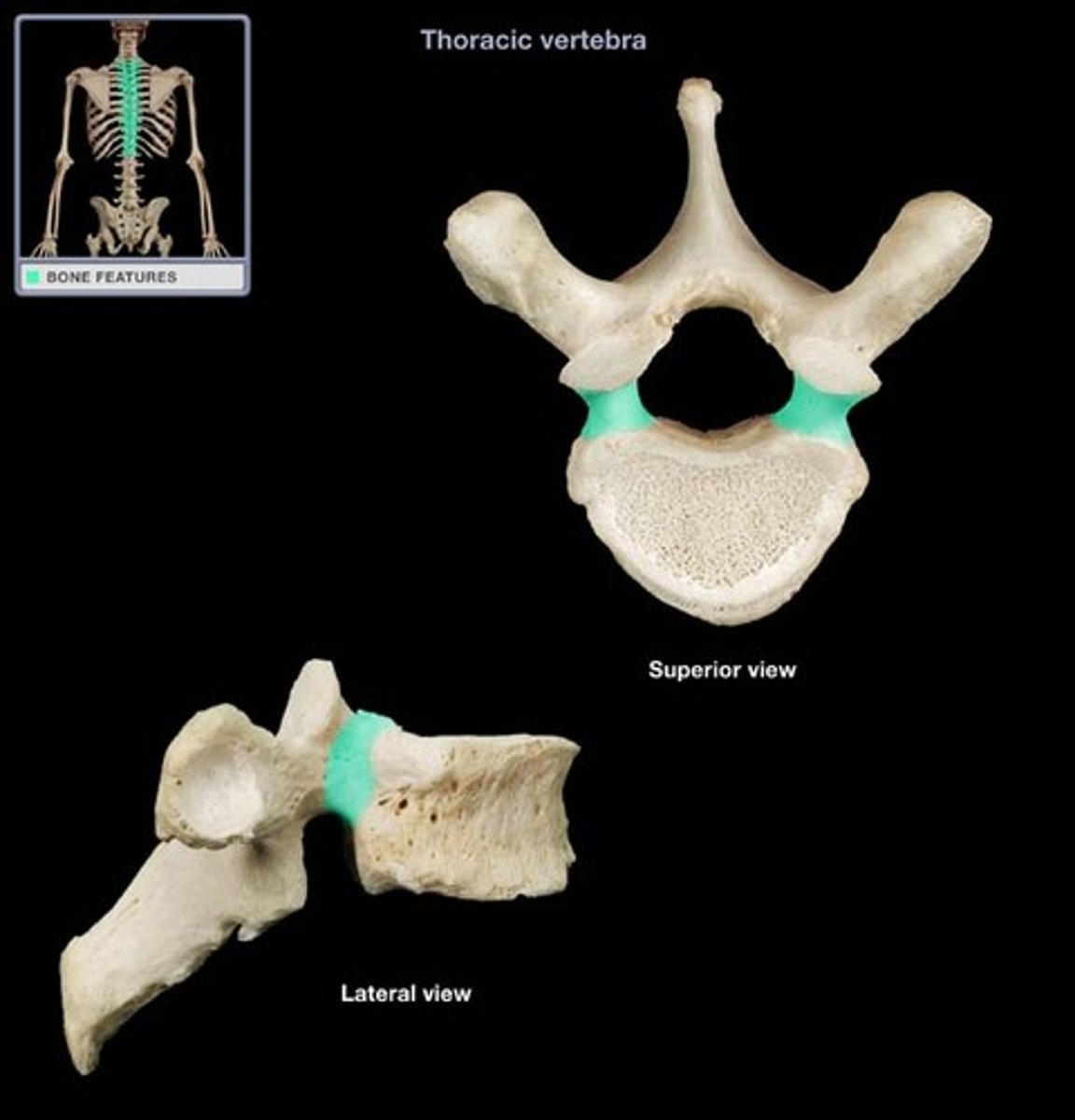
transverse process
- prominent, paired, laterally projections
- between the lamina and pedicle
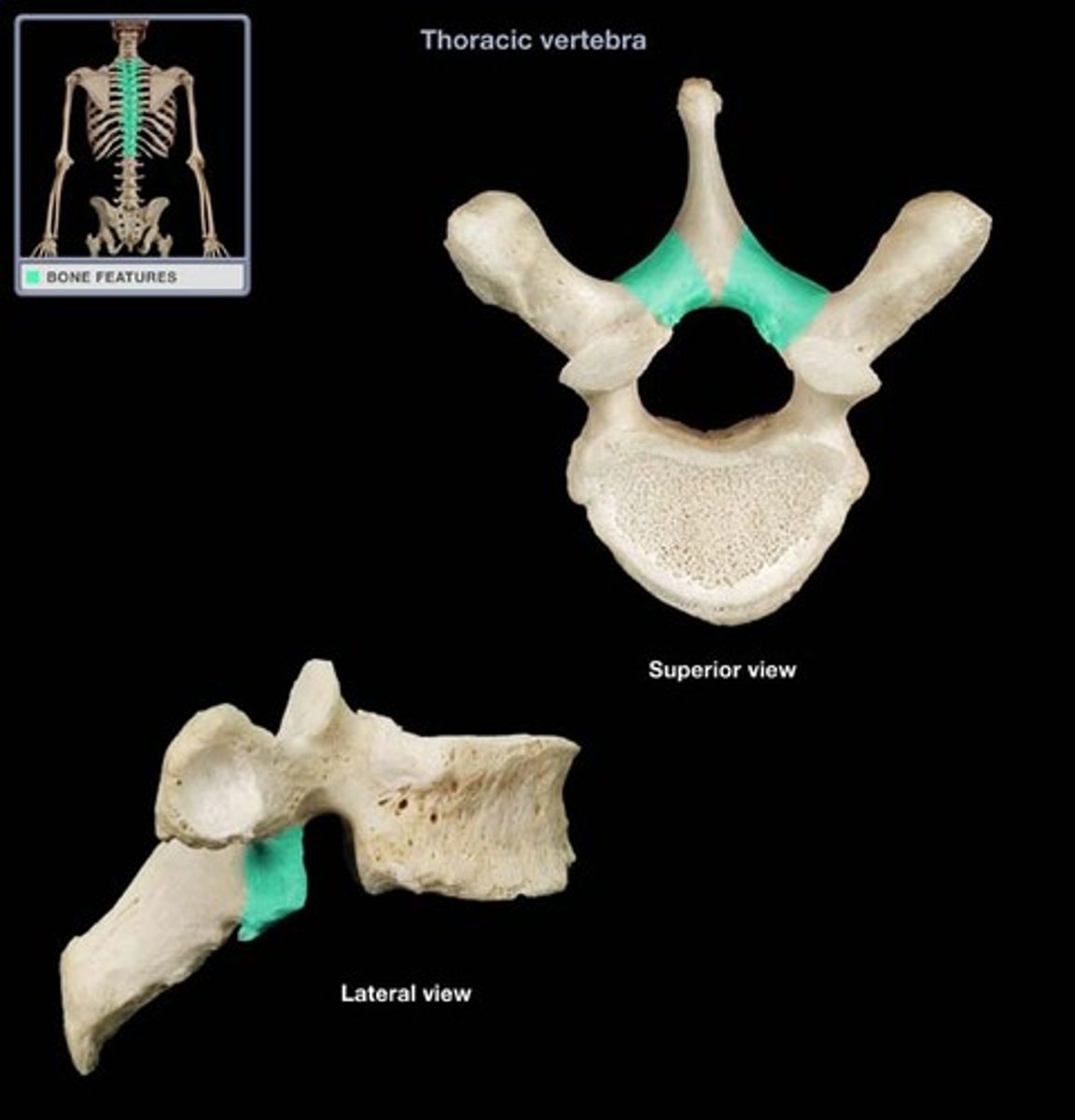
lamina
- broad, flat piece of bone between the transverse and spinous process
- not attached directly to the vertebral bodies
- Site of Laminectomies
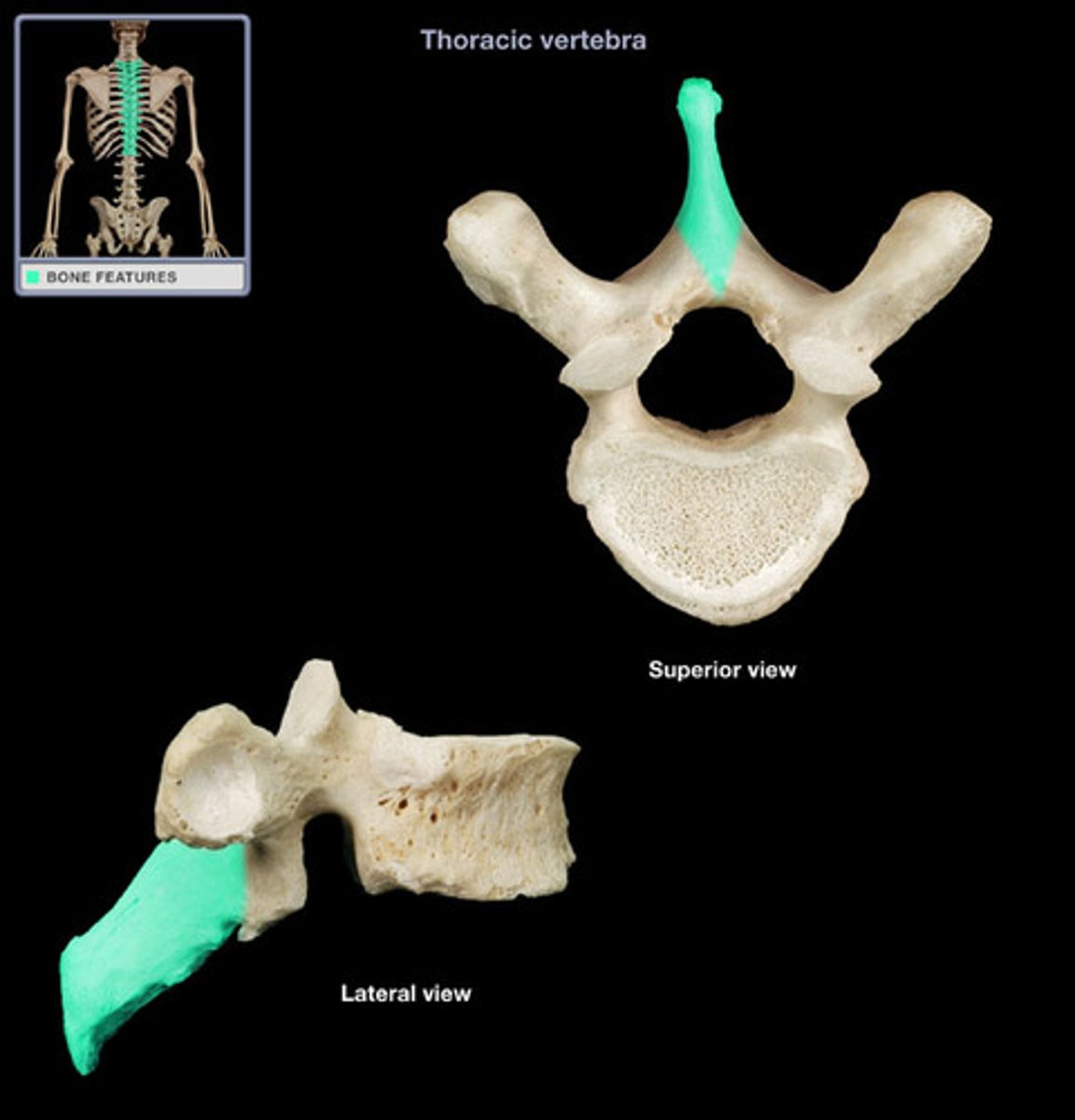
spinous process
- midline, posterior projection formed by the fusion of the lamina
- failure of fusion results in the condition called spina bifida Bifid (split) in the cervical region
vertebral (neutral) arch
- posterior ring of bone formed by the pedicles and lamina
- excludes the vertebral body
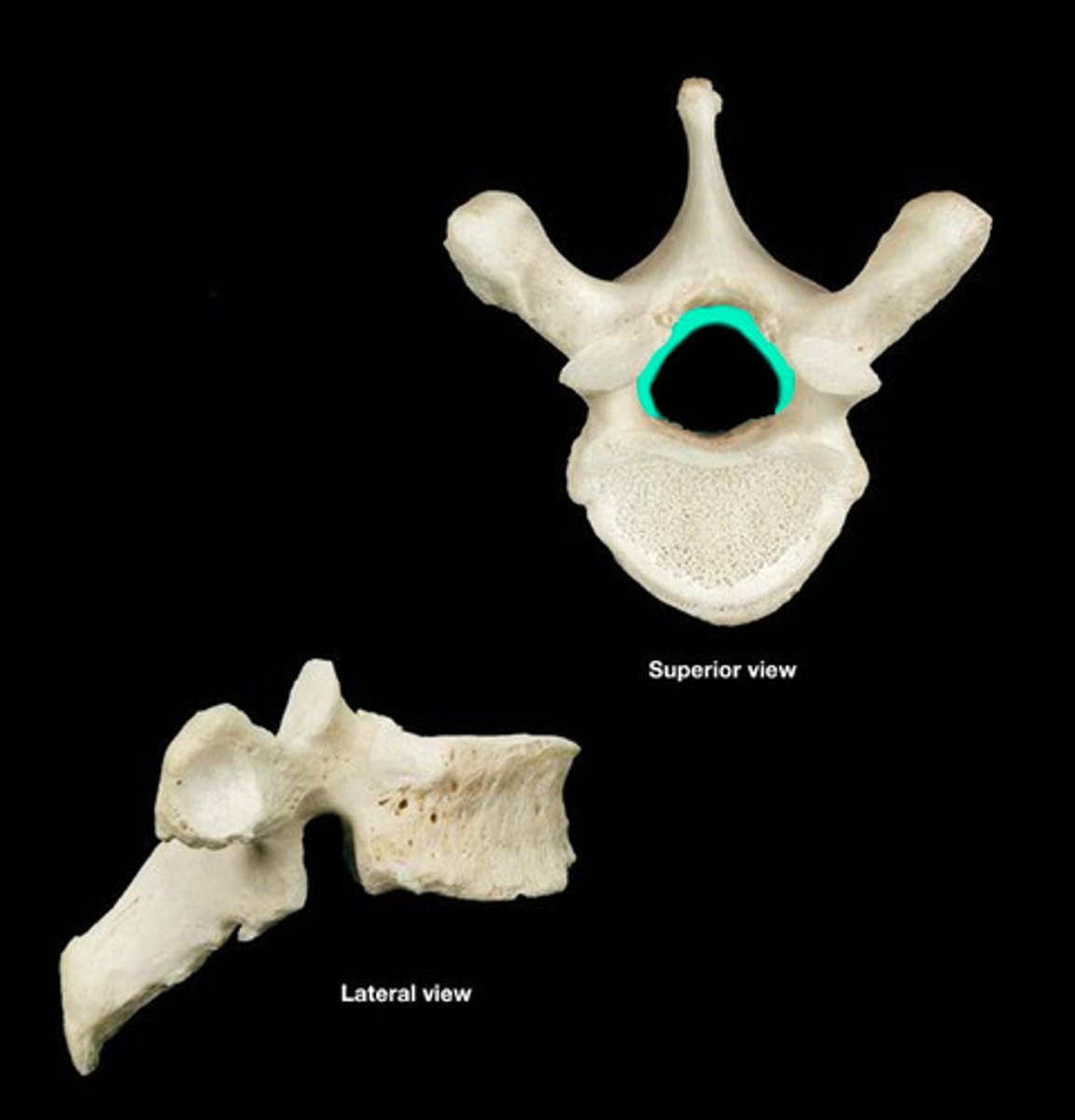
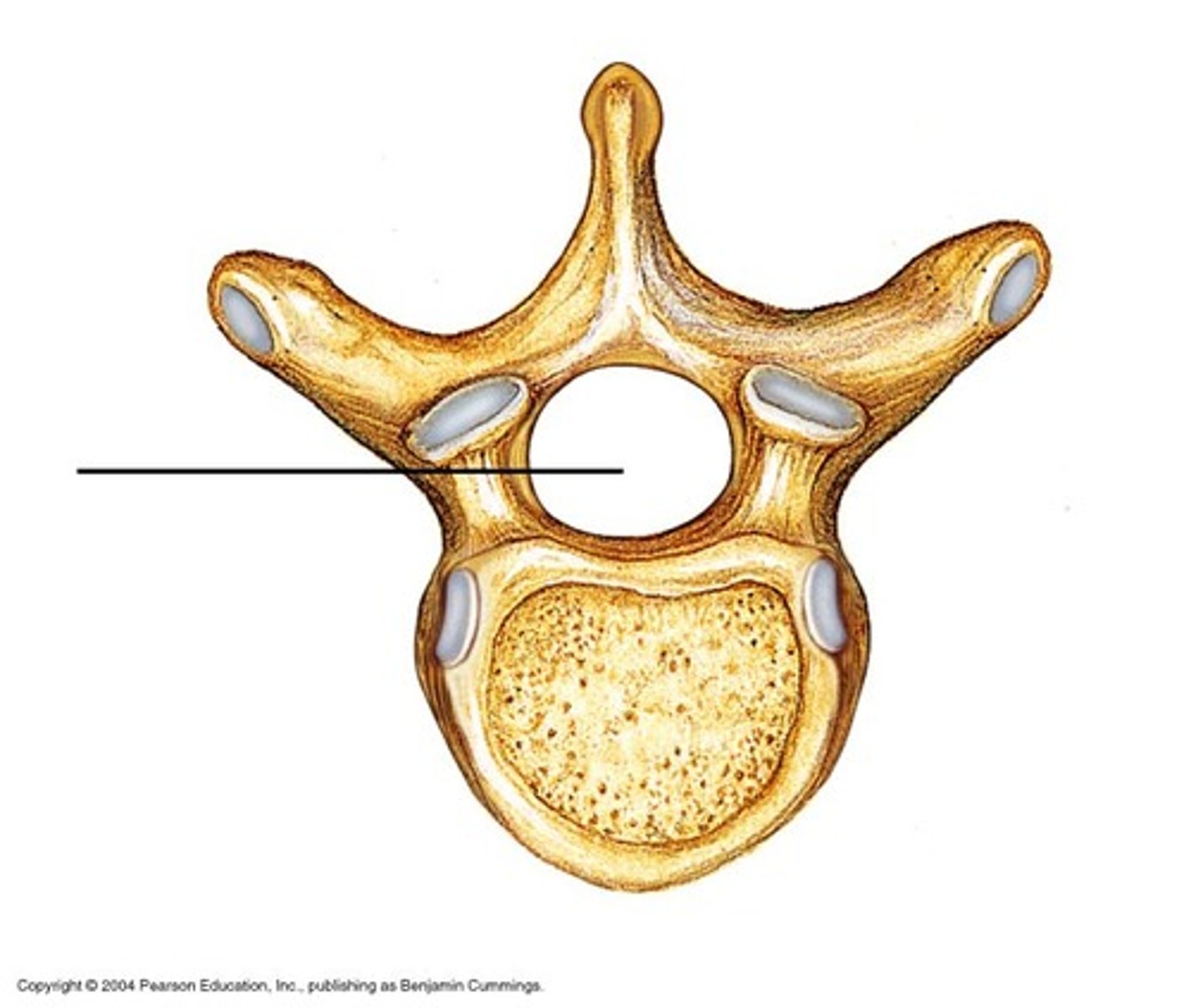
vertebral foramen
- large space formed by the vertebral arch and posterior aspect of the vertebral body
- single vertebrae
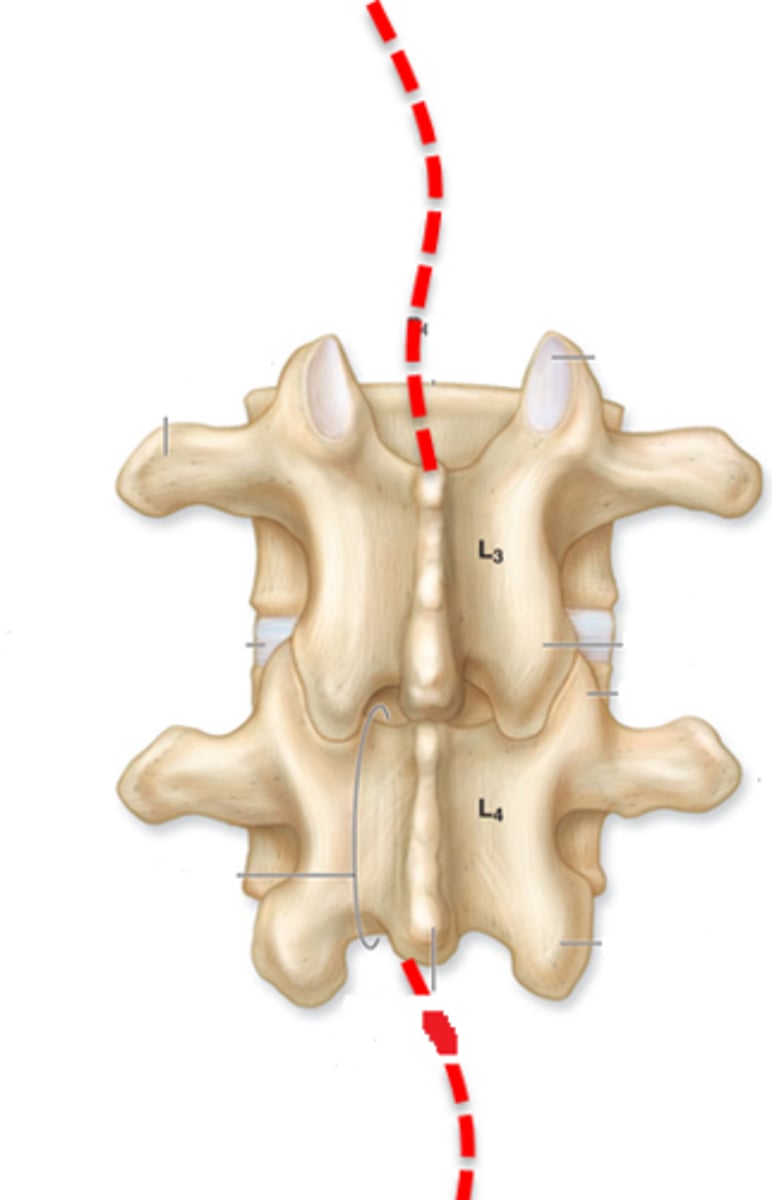
vertebral canal
- space of multiple vertebral foramen together in which the spinal cord passes through
- multiple vertebrae
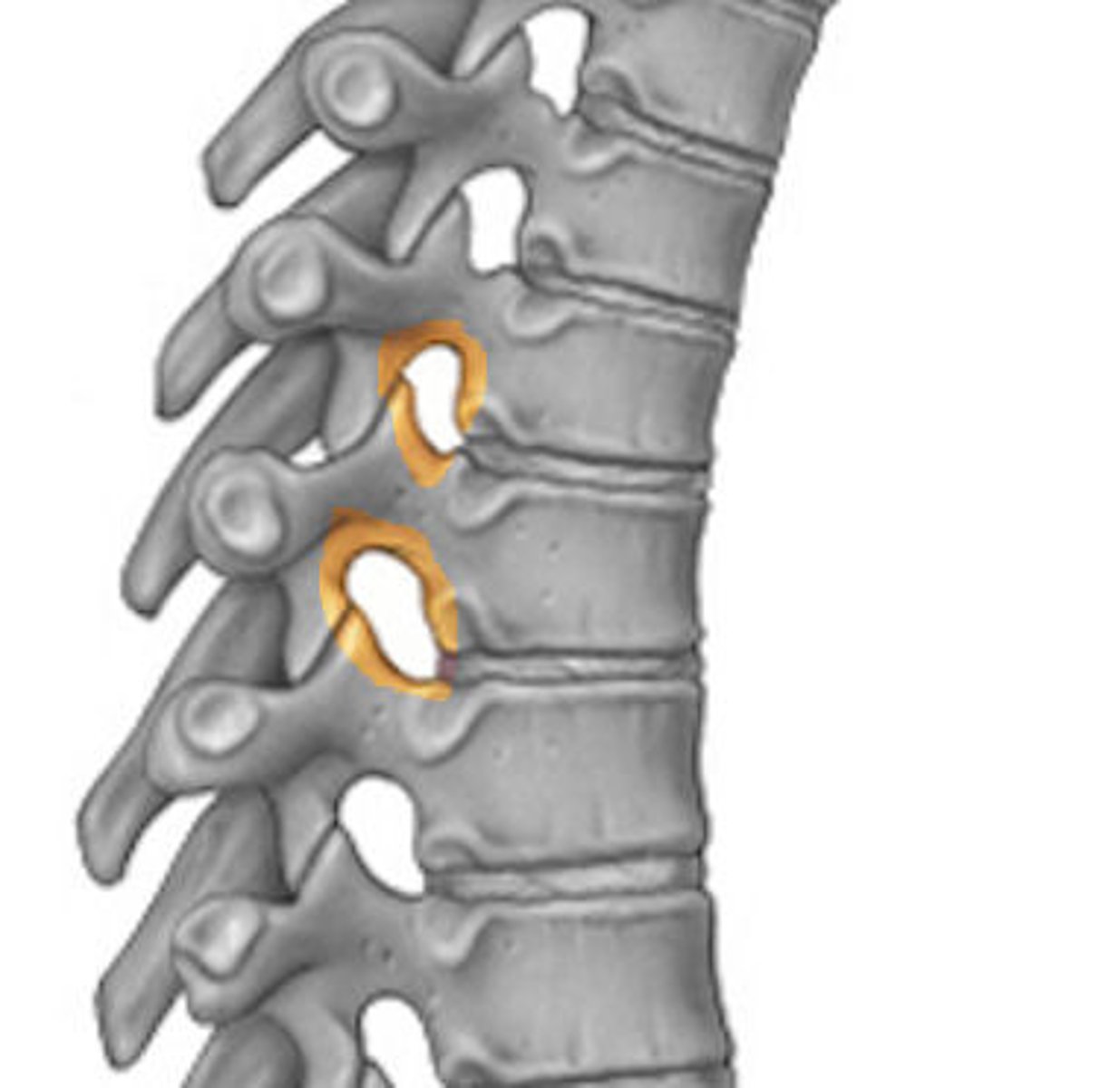
intervertebral foramen
- lateral space formed by the pedicles of two adjacent vertebrae
- passageway for spinal nerves
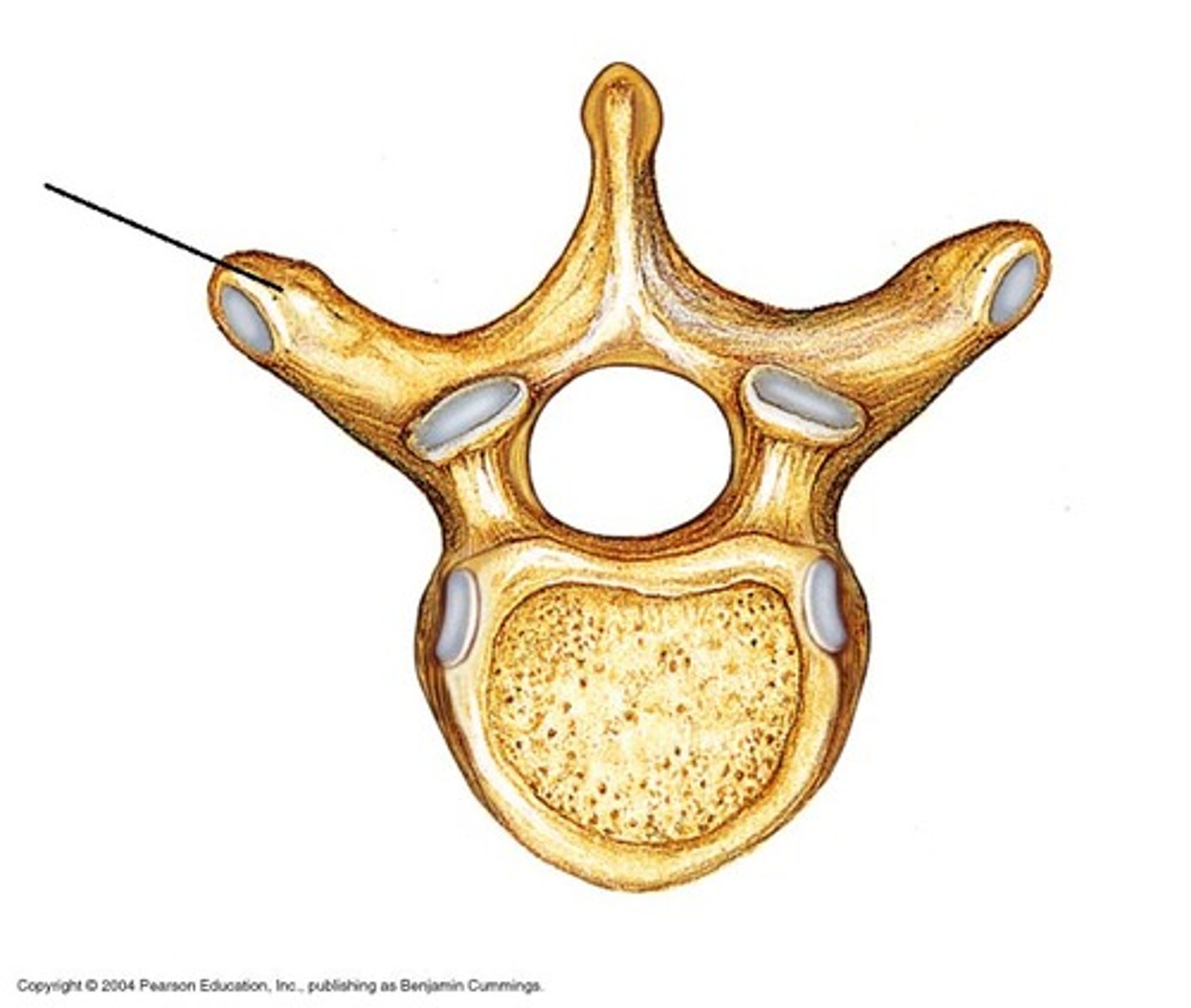
superior articular process
superior boney projection at the junction of the pedicle and lamina
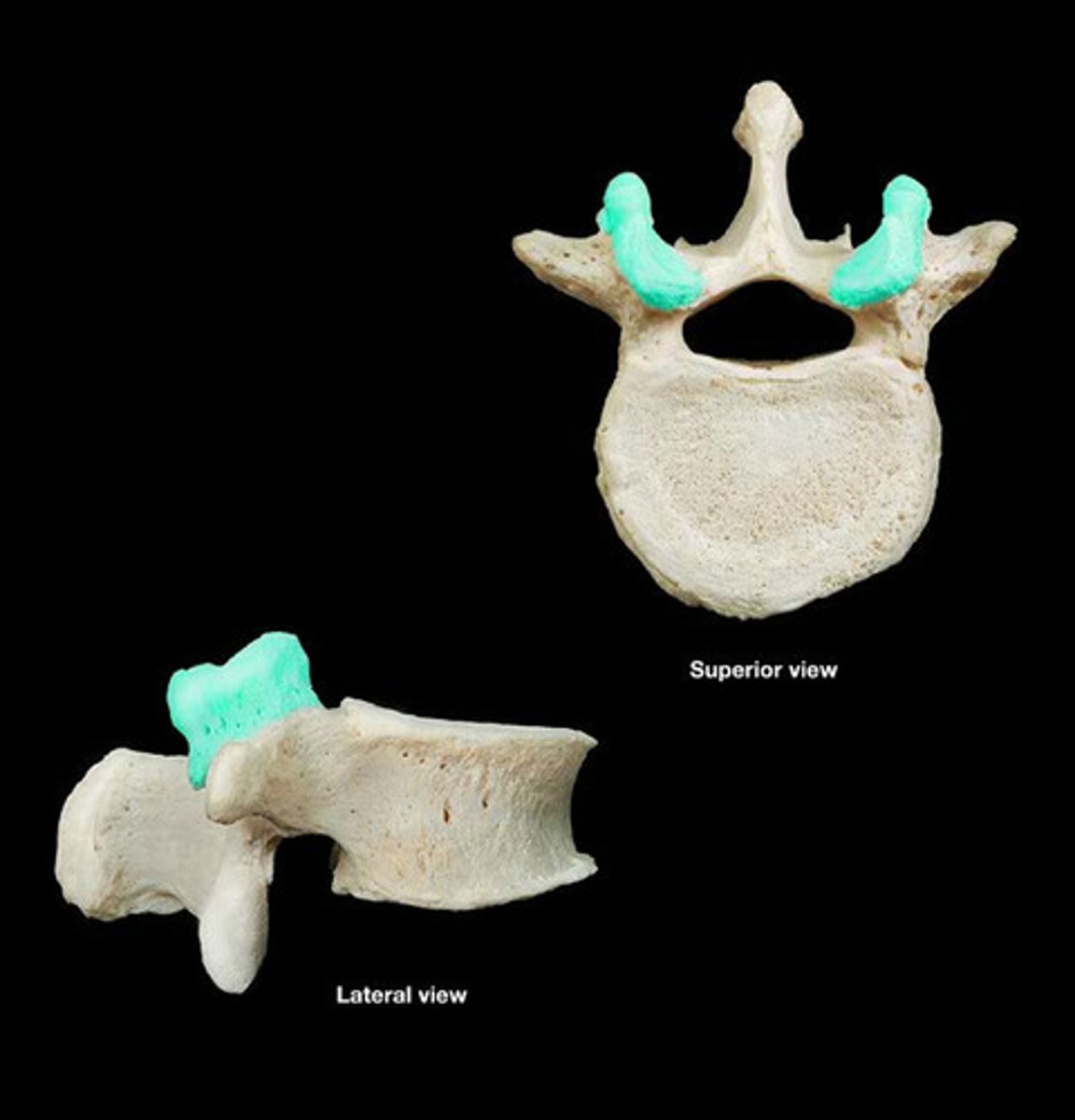
superior articular facet
- smooth surface on the superior articulating process that articulates with the adjacent vertebrae's inferior articulating facet
- in thoracic vertebrae the facets face posteriorly
- in lumbar vertebrae the facets face medially
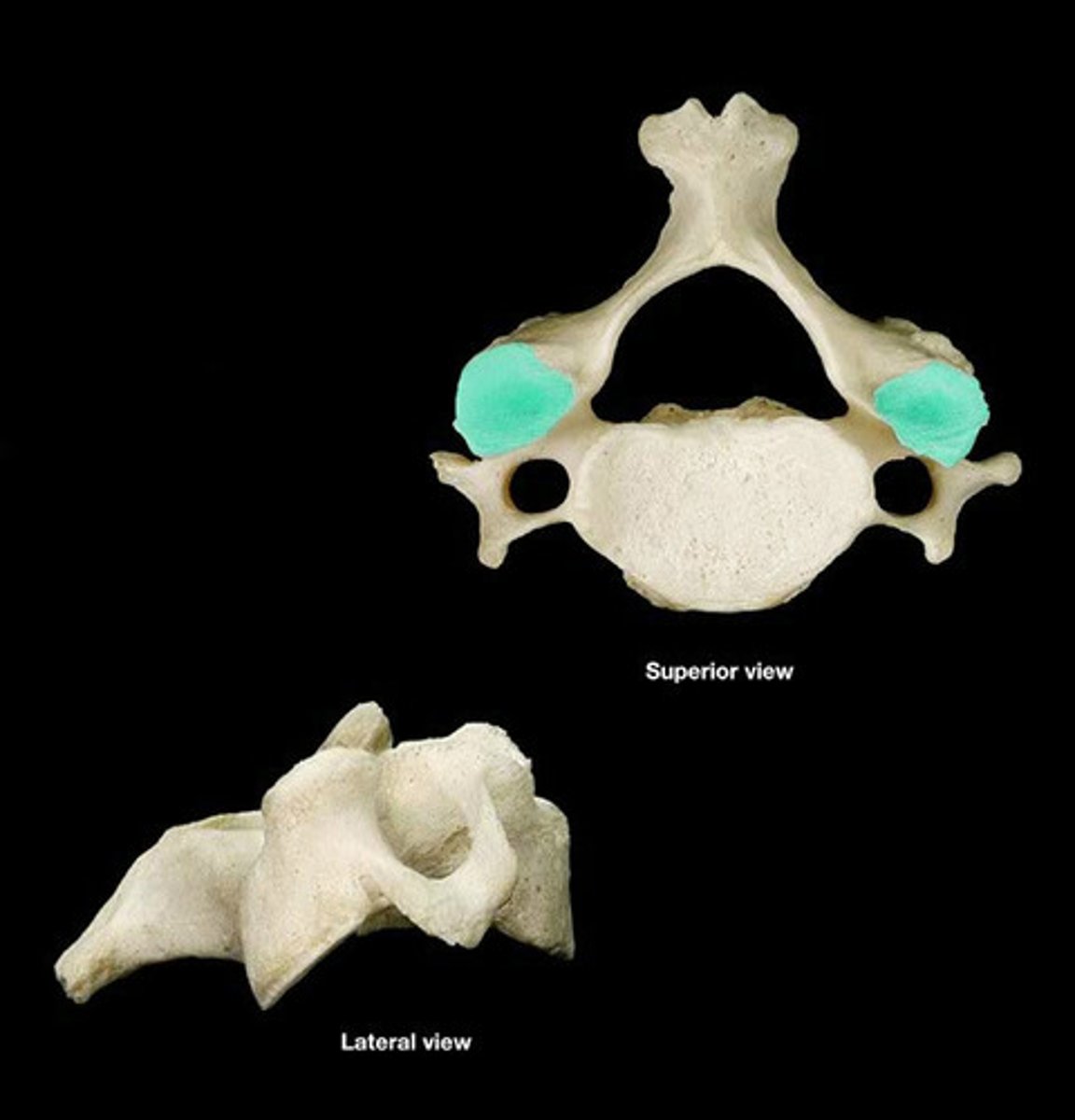
inferior articular process
inferior boney projection at the junction of the pedicle and lamina
inferior articular facet
- smooth surface on the inferior articulating process that articulates with the adjacent vertebrae's superior articulating facet
- in the thoracic vertebrae, the facets face anteriorly
- in the lumber vertebrae, the facets face laterally
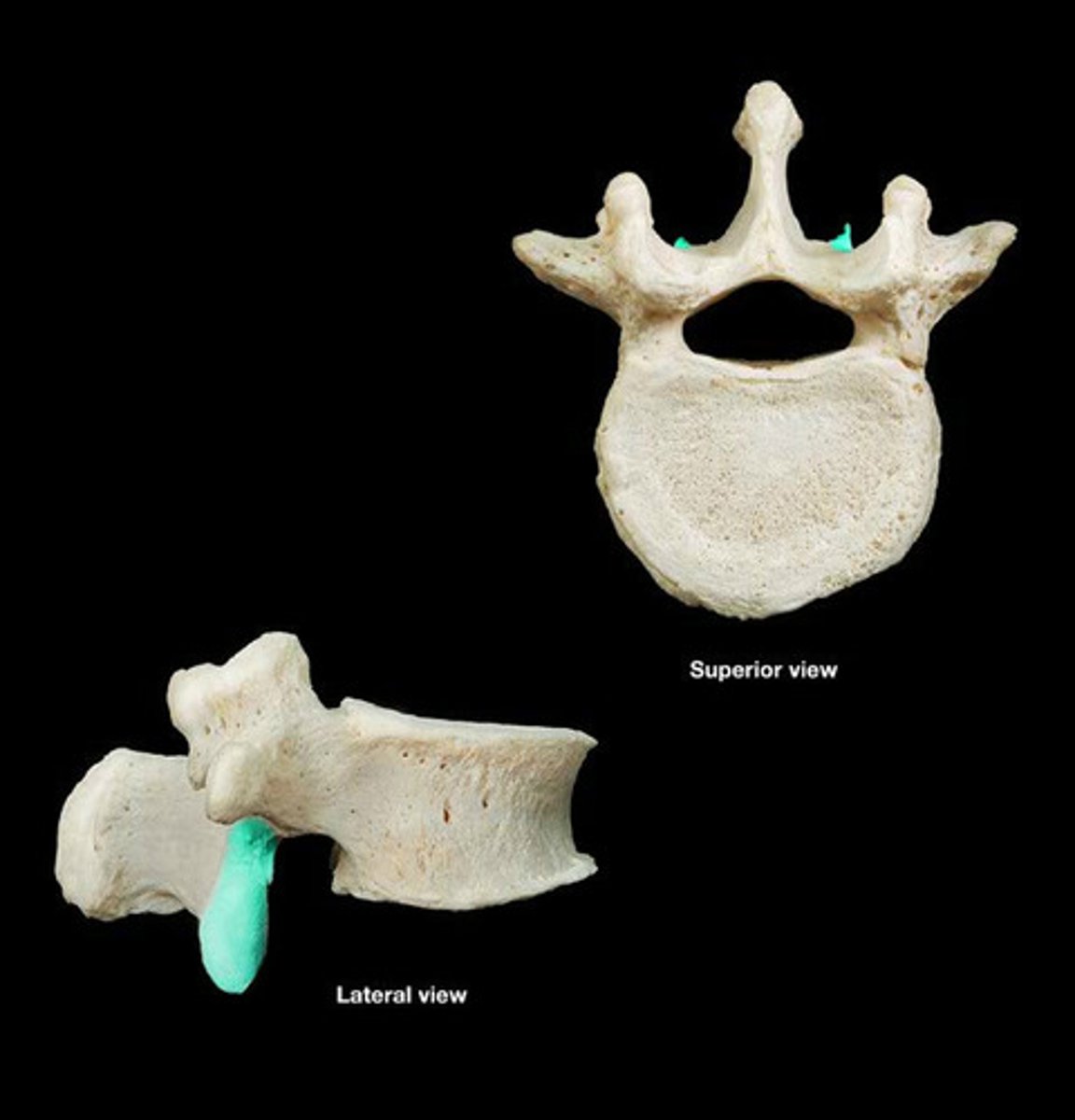
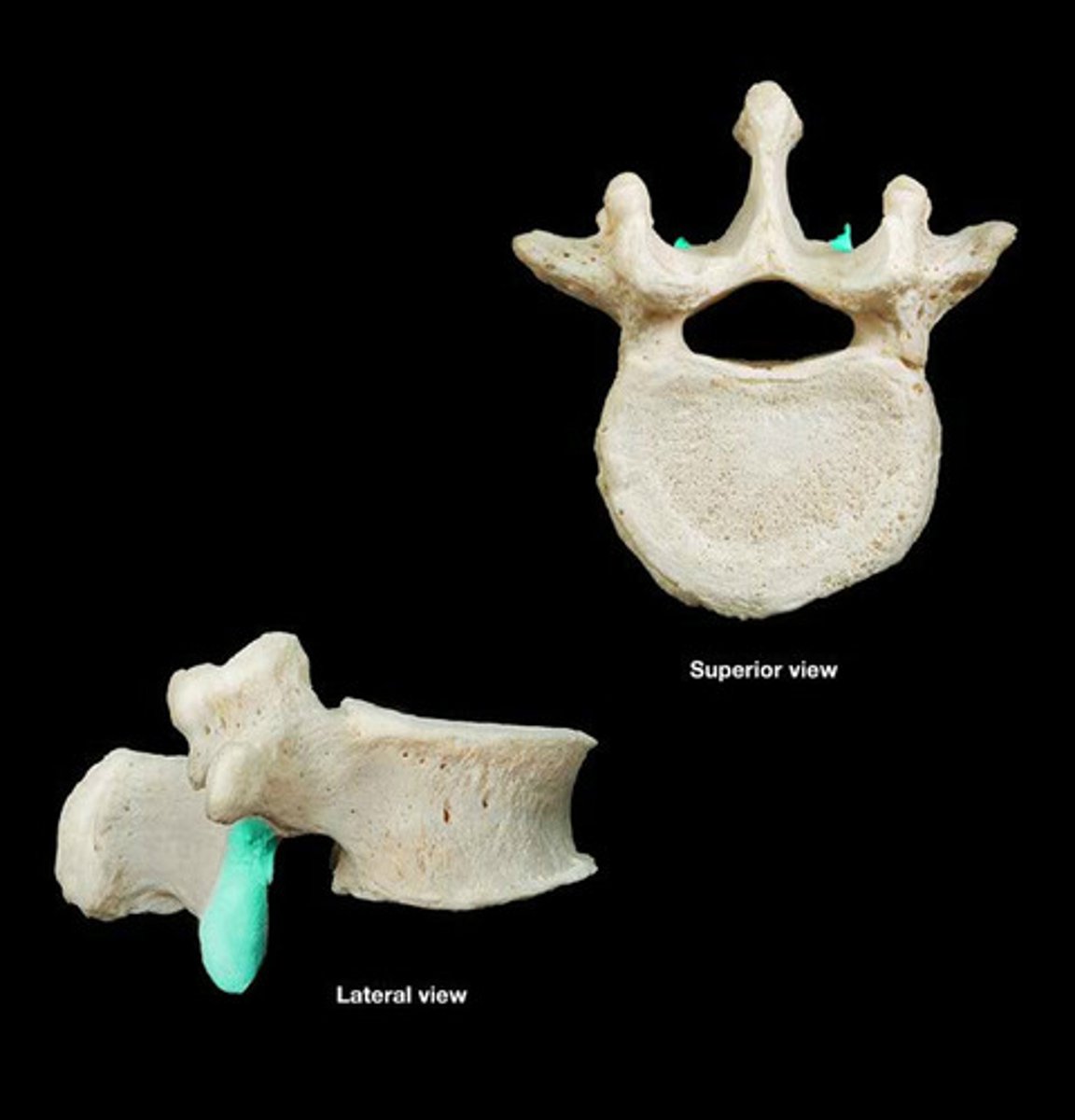
transverse foramen
- space within transverse process
- passageway for vertebral arteries
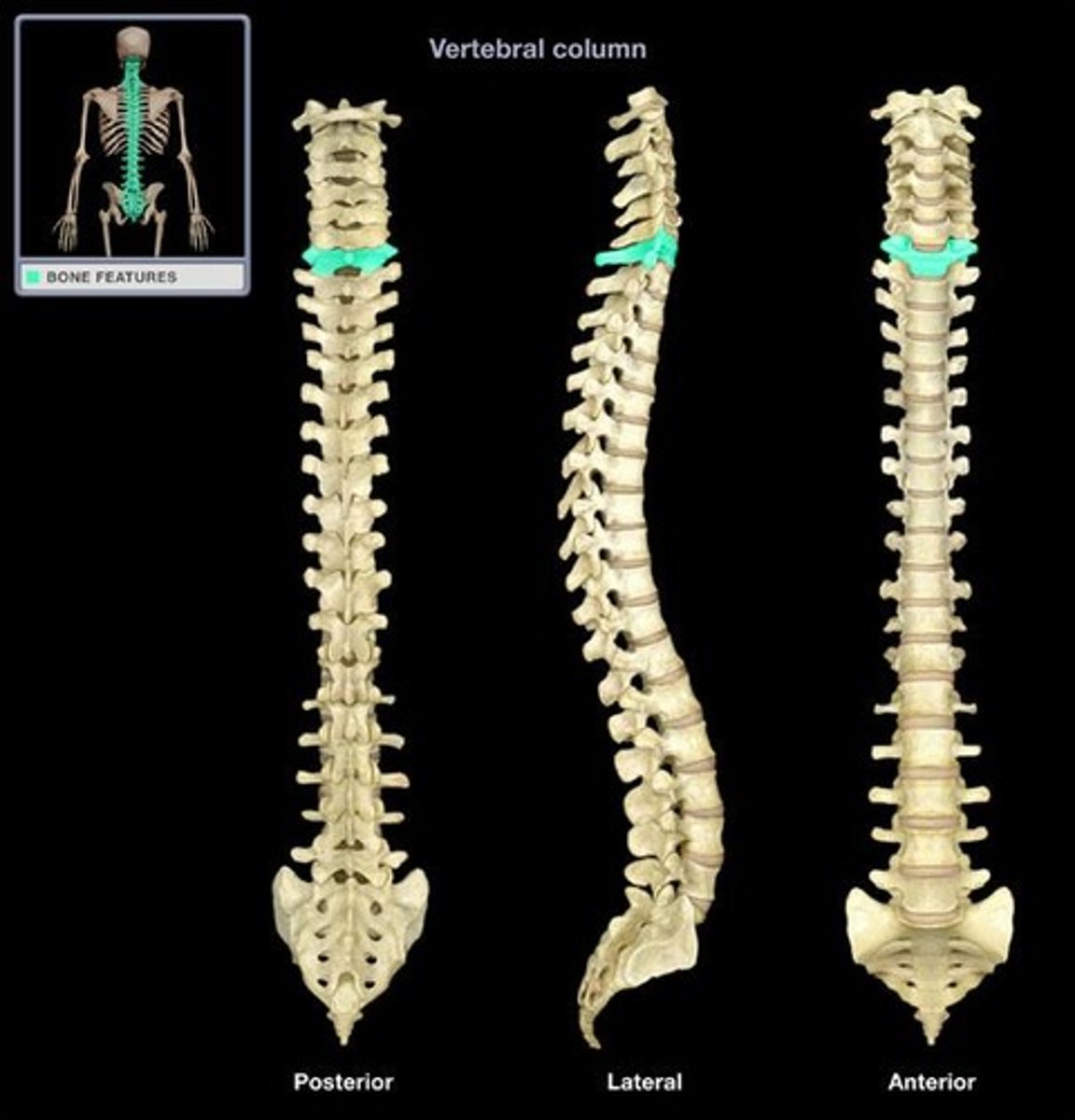
vertebra prominens
- specific spinous process of C7
- posterior neck landmark
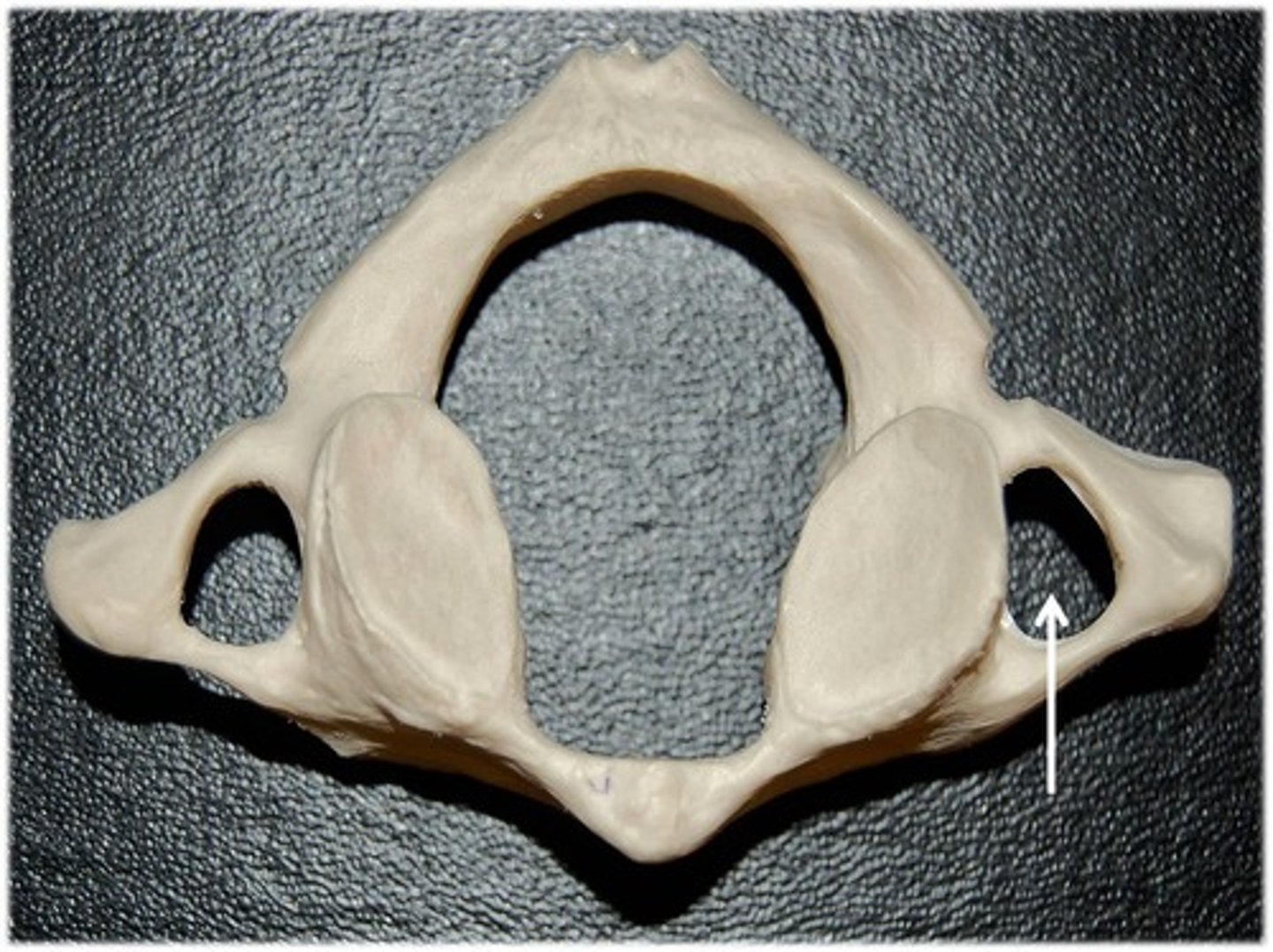
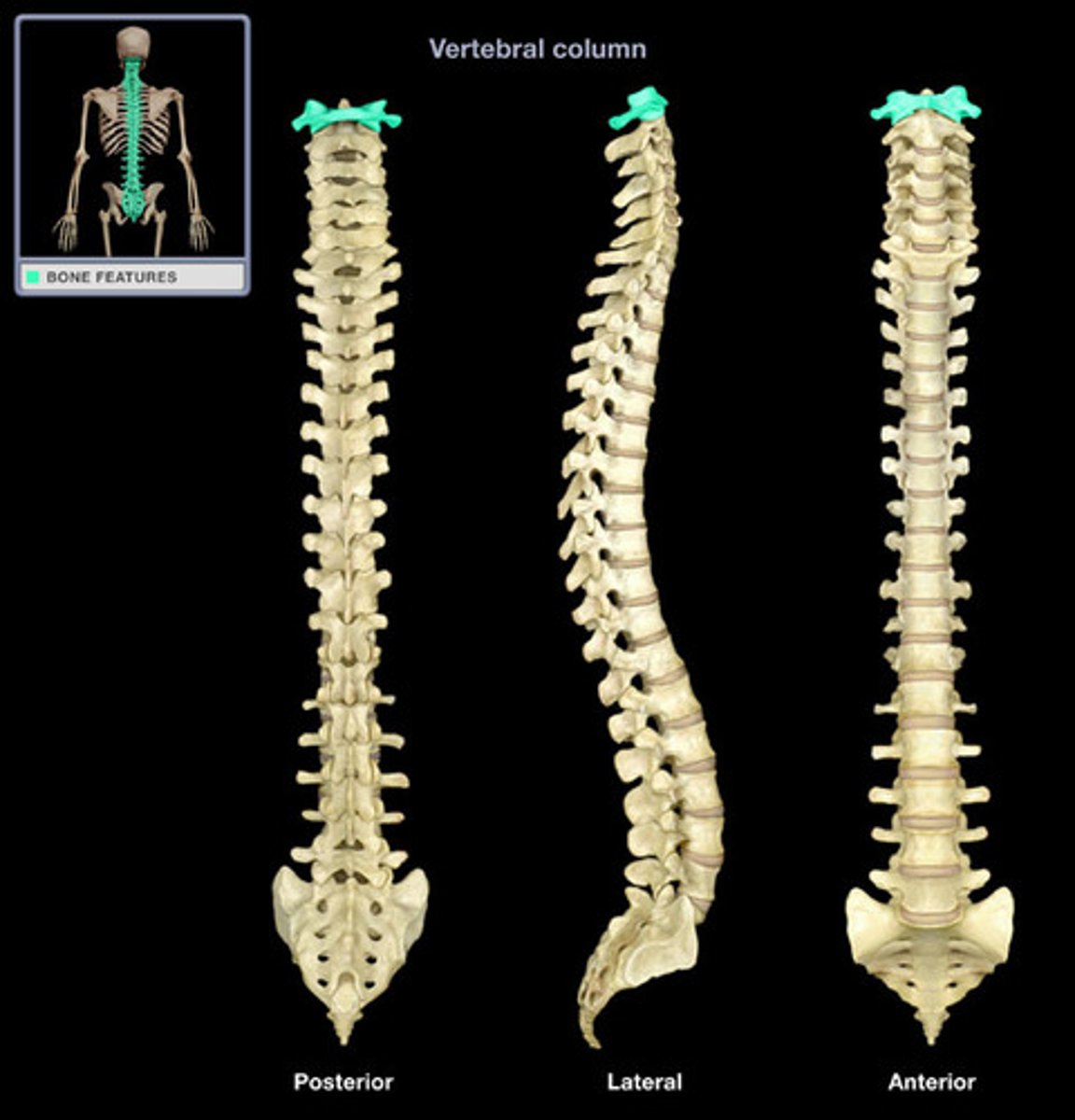
atlas
- specific name for C1 vertebrae
- ring-like vertebra articulating with the occipital condyles to support the skull
- lacks a vertebral body, spinous process, and lamina
axis
- specific name for C2 vertebrae
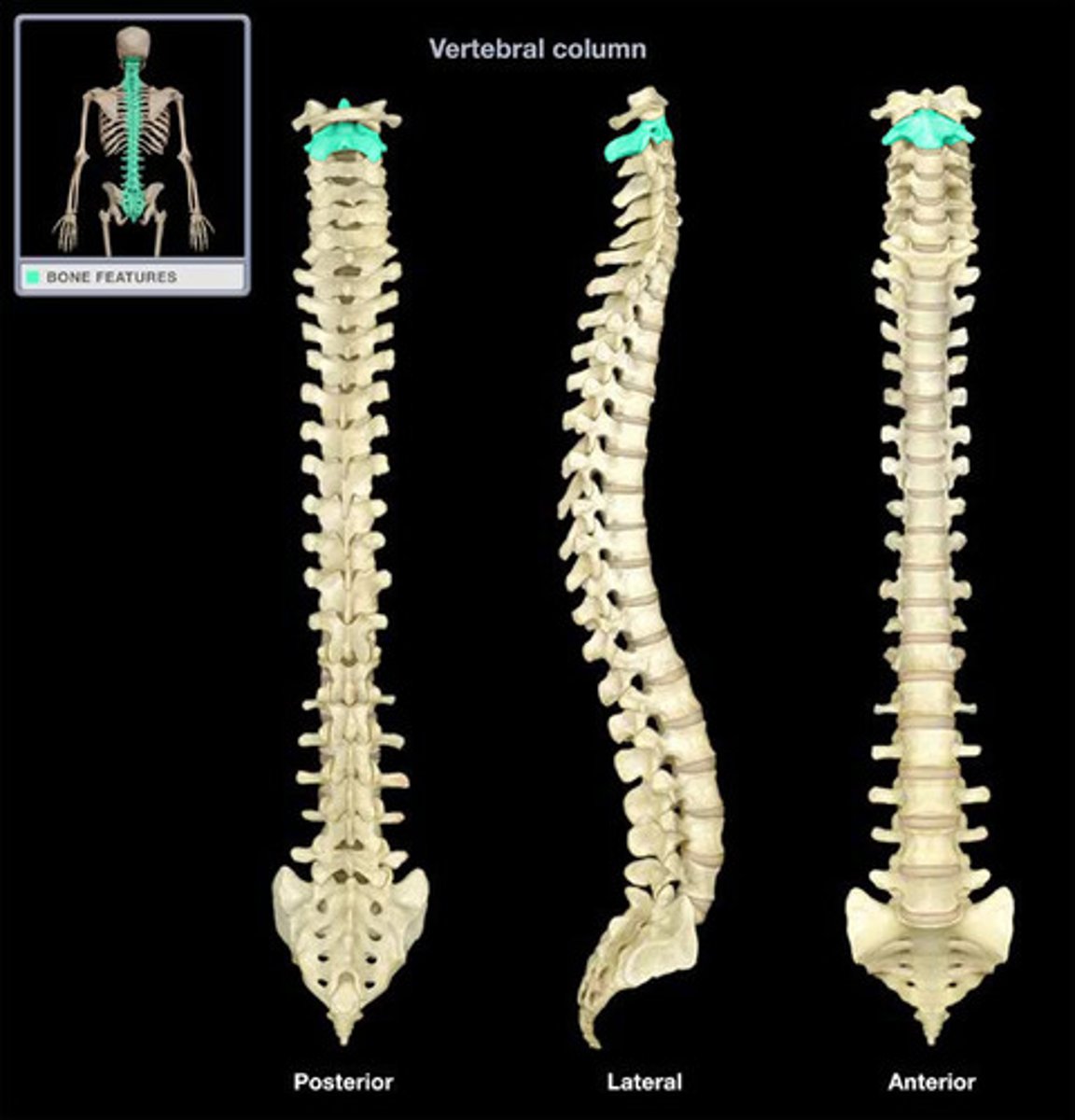
dens
- superior boney projection from the vertebral body
- pivot point articulating with the atlas (C1)
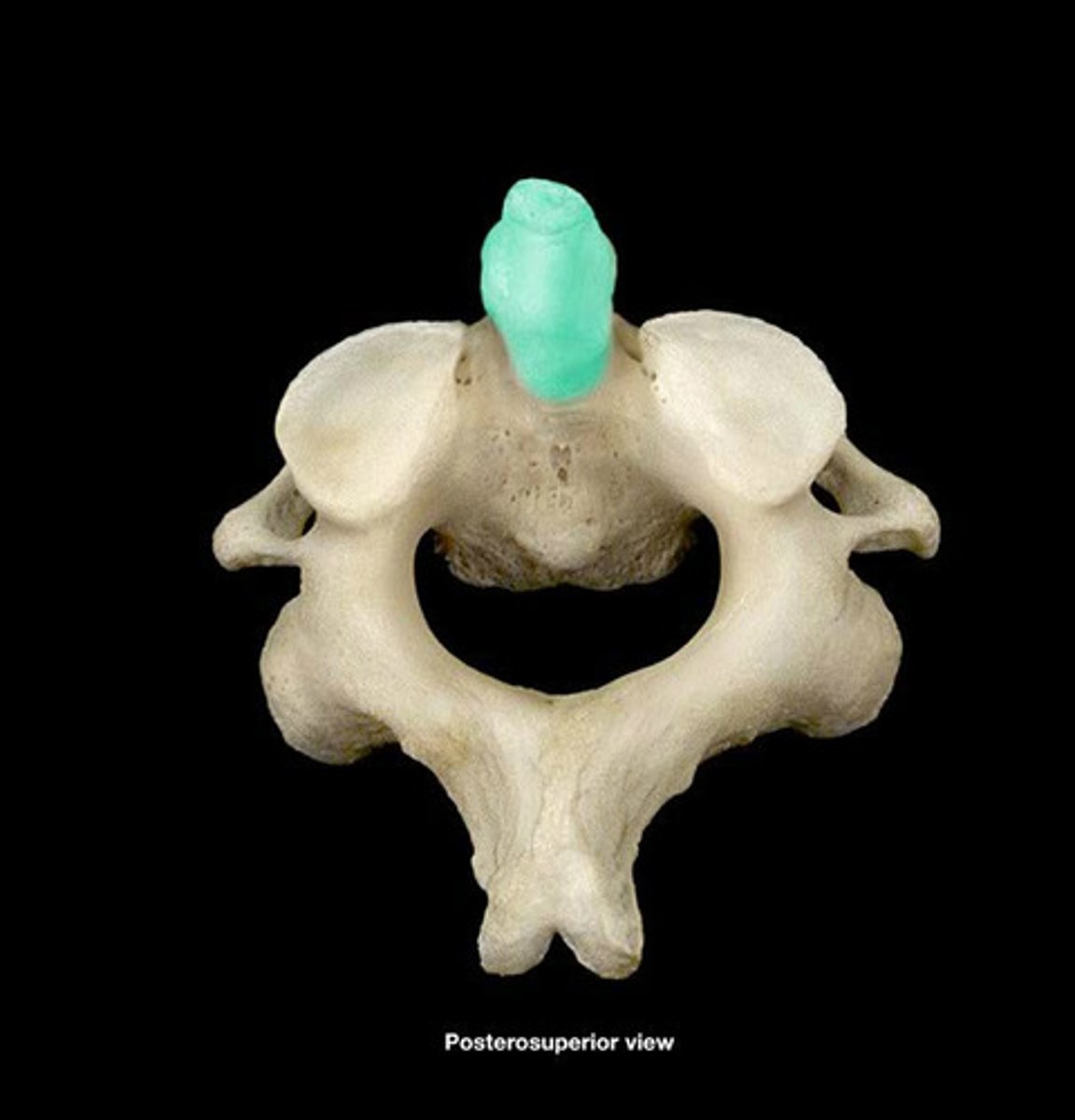
sacral canal
- opening in center of the sacrum
- continuation of the vertebral canal
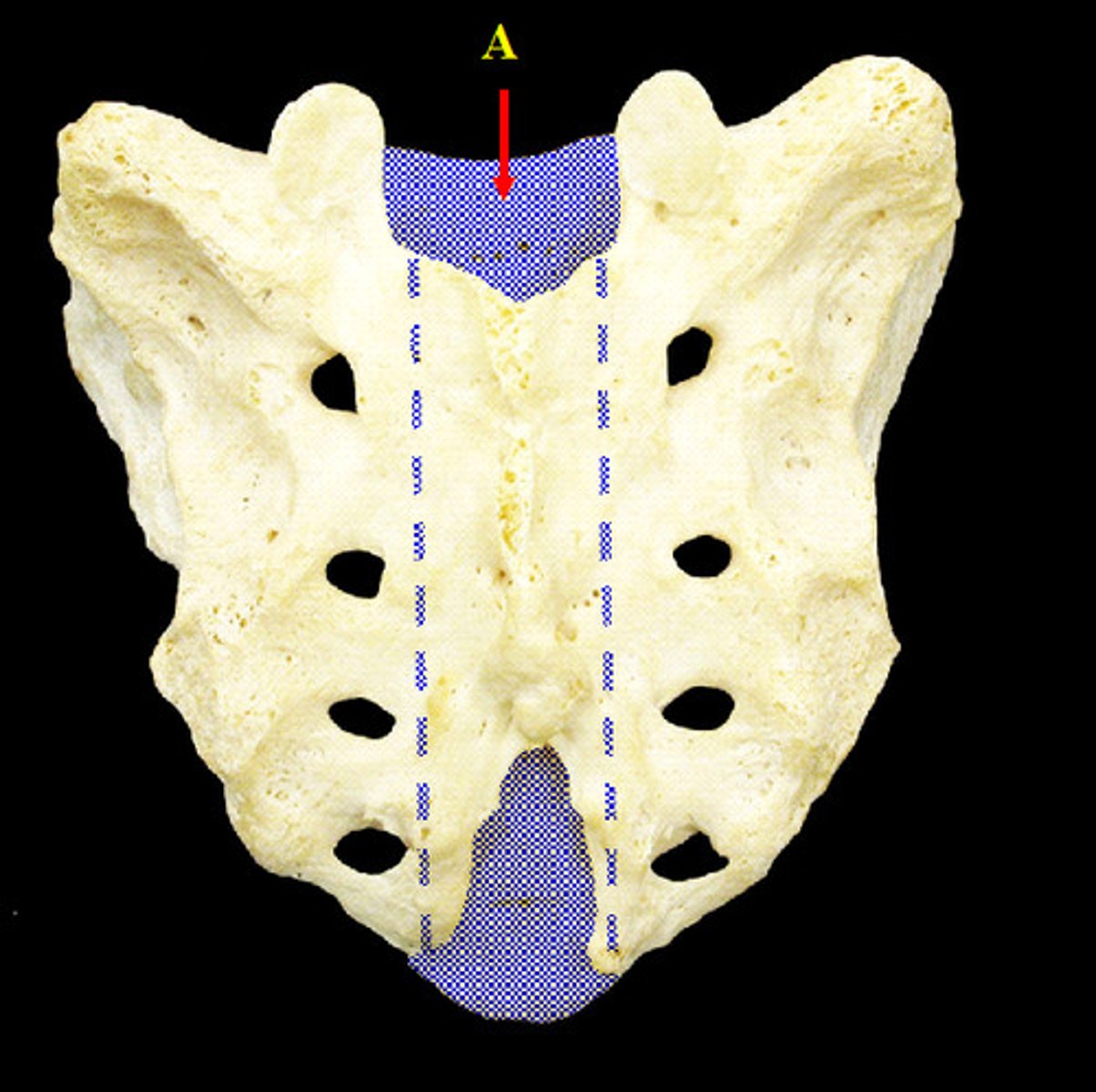
sacral promontory
- anteriorly projecting ridge on the superior aspect of the sacrum
- formed by the superior border of the S1 vertebral body
auricular surface
- lateral surfaces articulating with the ilium
- ear-like shape
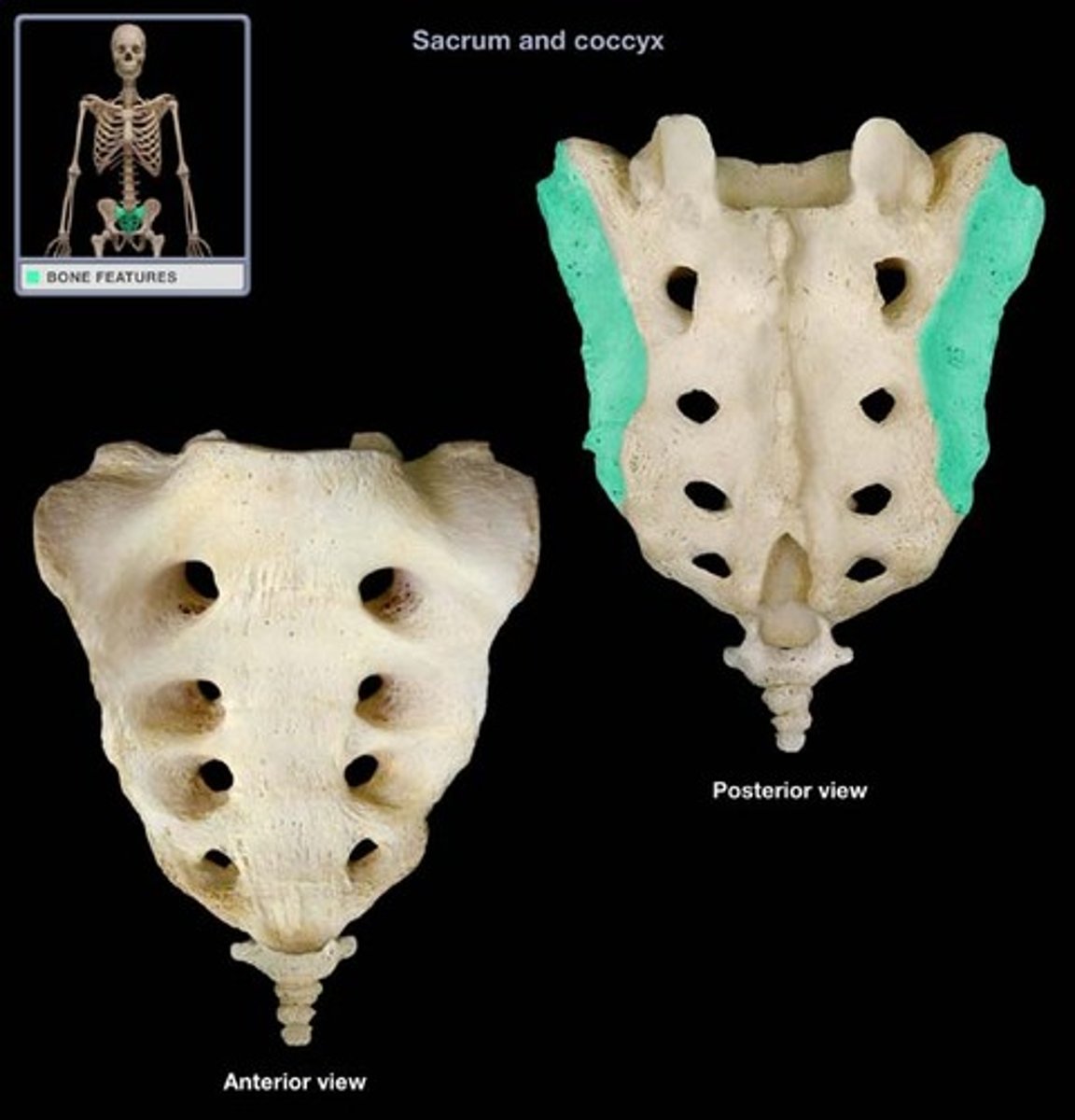
sacral tuberosity
- roughened surface immediately posterior to the auricular surface
- attachment site for sacroiliac ligaments
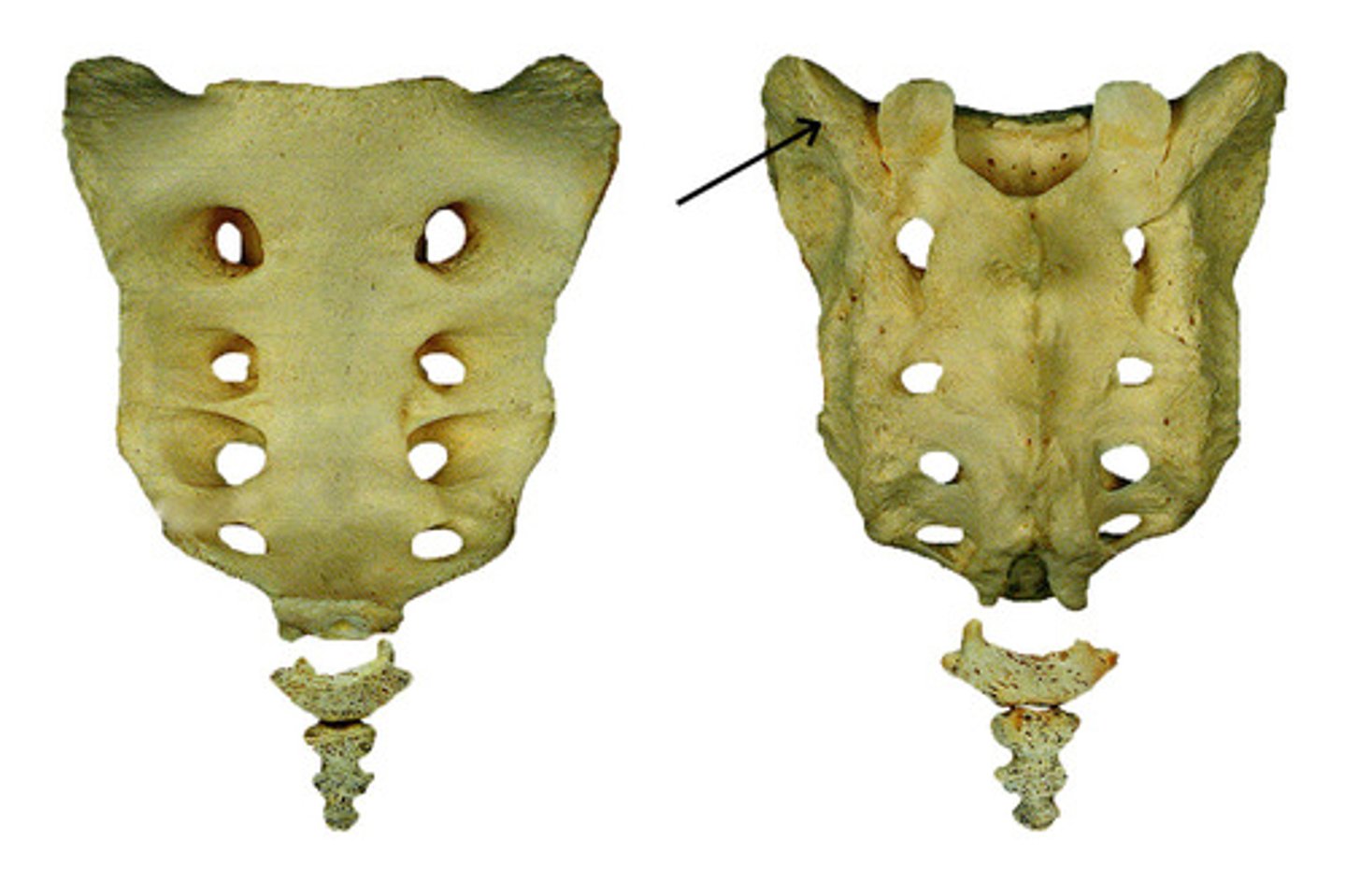
anterior sacral foramina
- four paired spaces on the anterior surface of the sacrum
- passageway for the ventral rami of S1-S4 spinal nerves
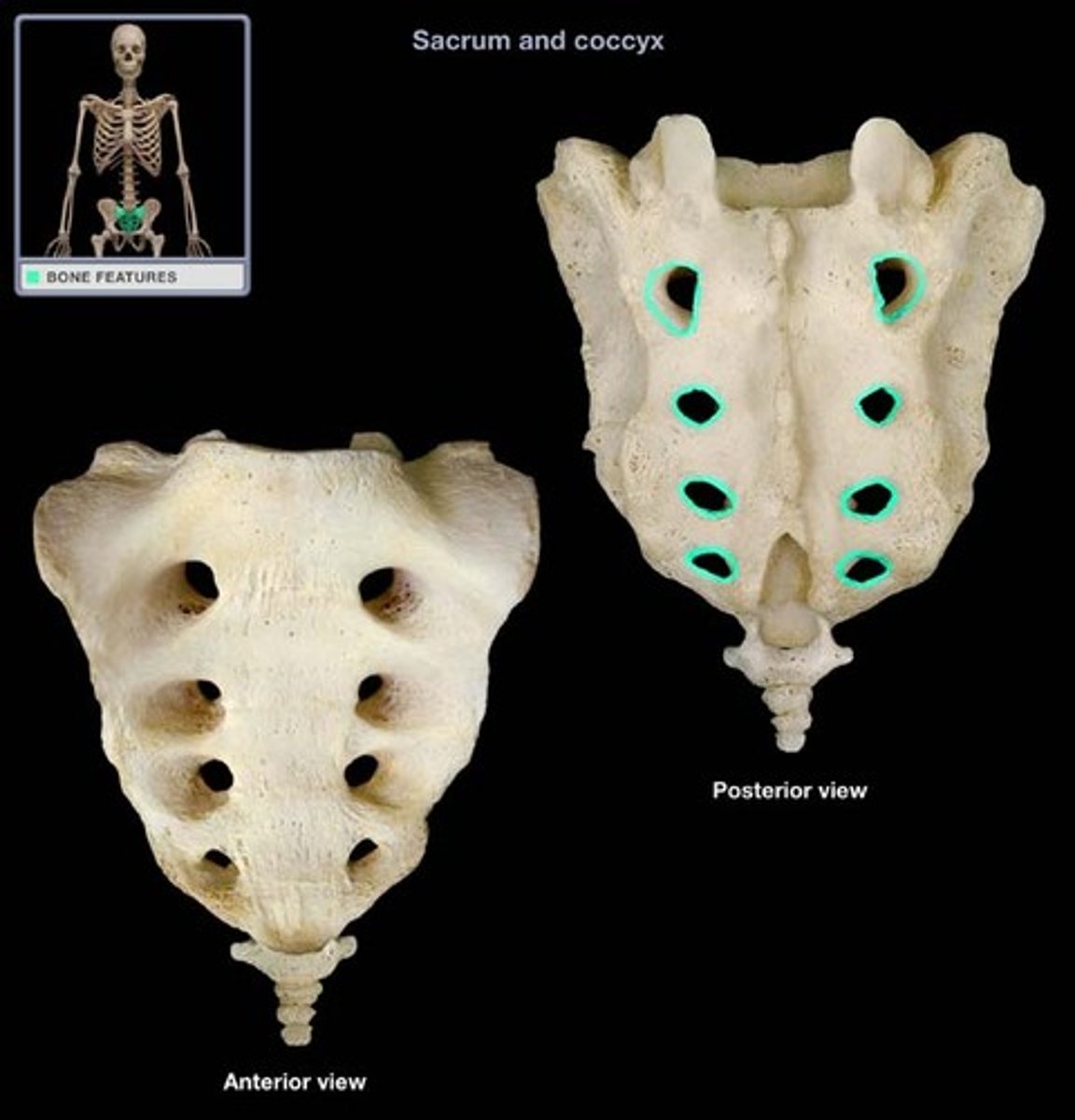
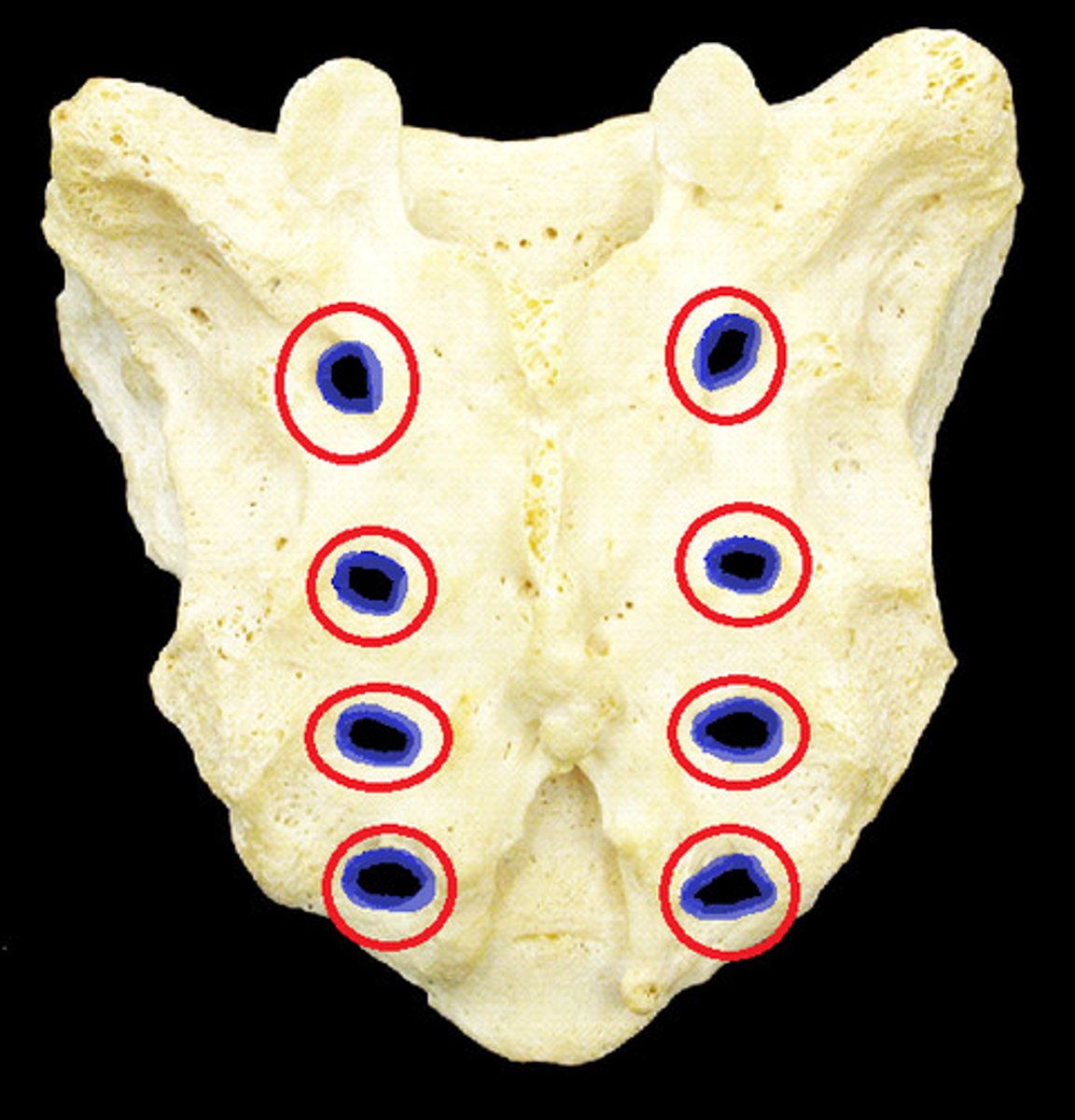
posterior sacral foramina
- four paired spaces on the posterior surface the sacrum
- passageway for the dorsal rami of S1-S4 spinal nerves
ribs
- twelve pairs of curved, flat bones forming the lateral thoracic walls
- articulate with thoracic vertebrae
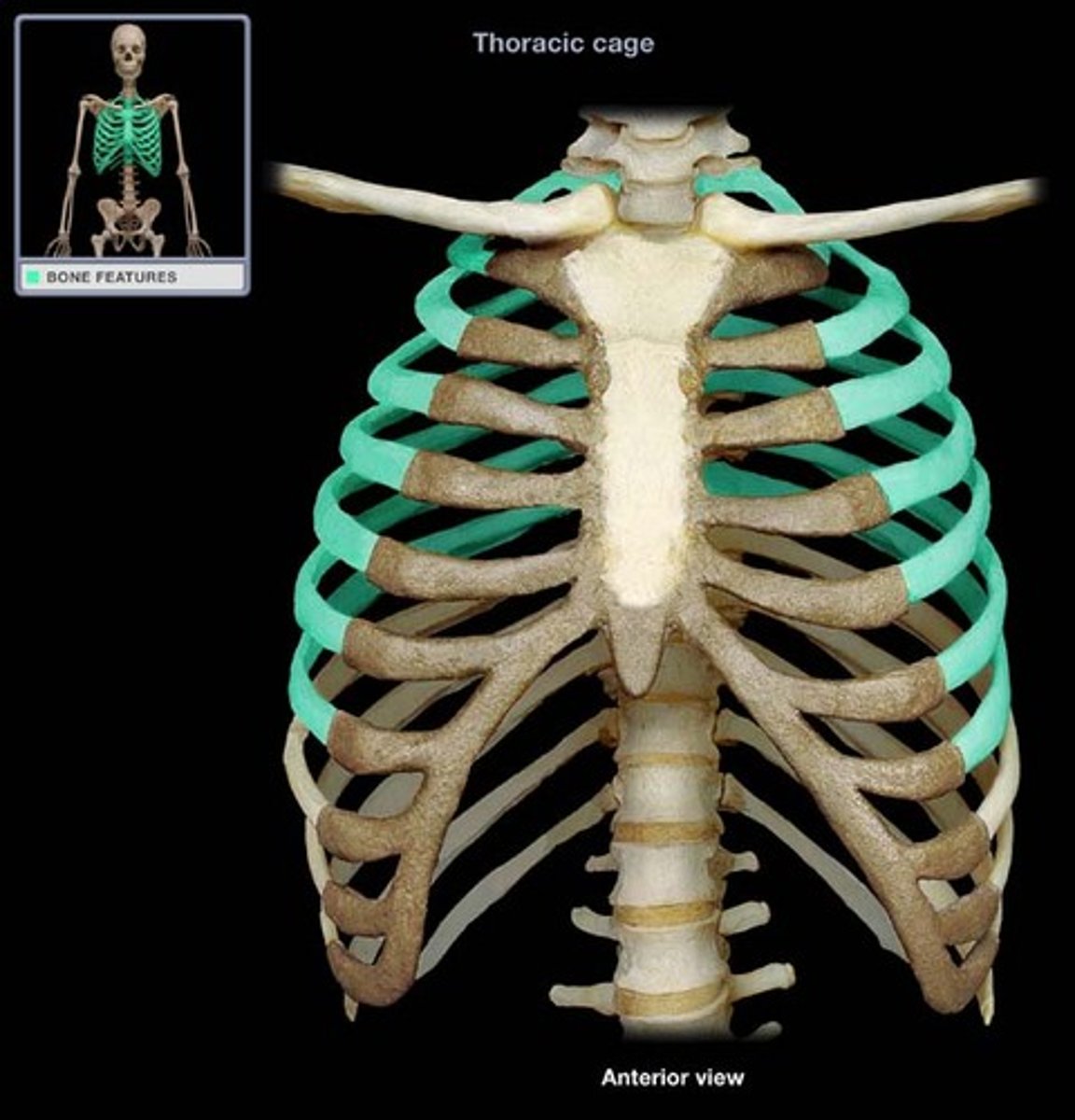
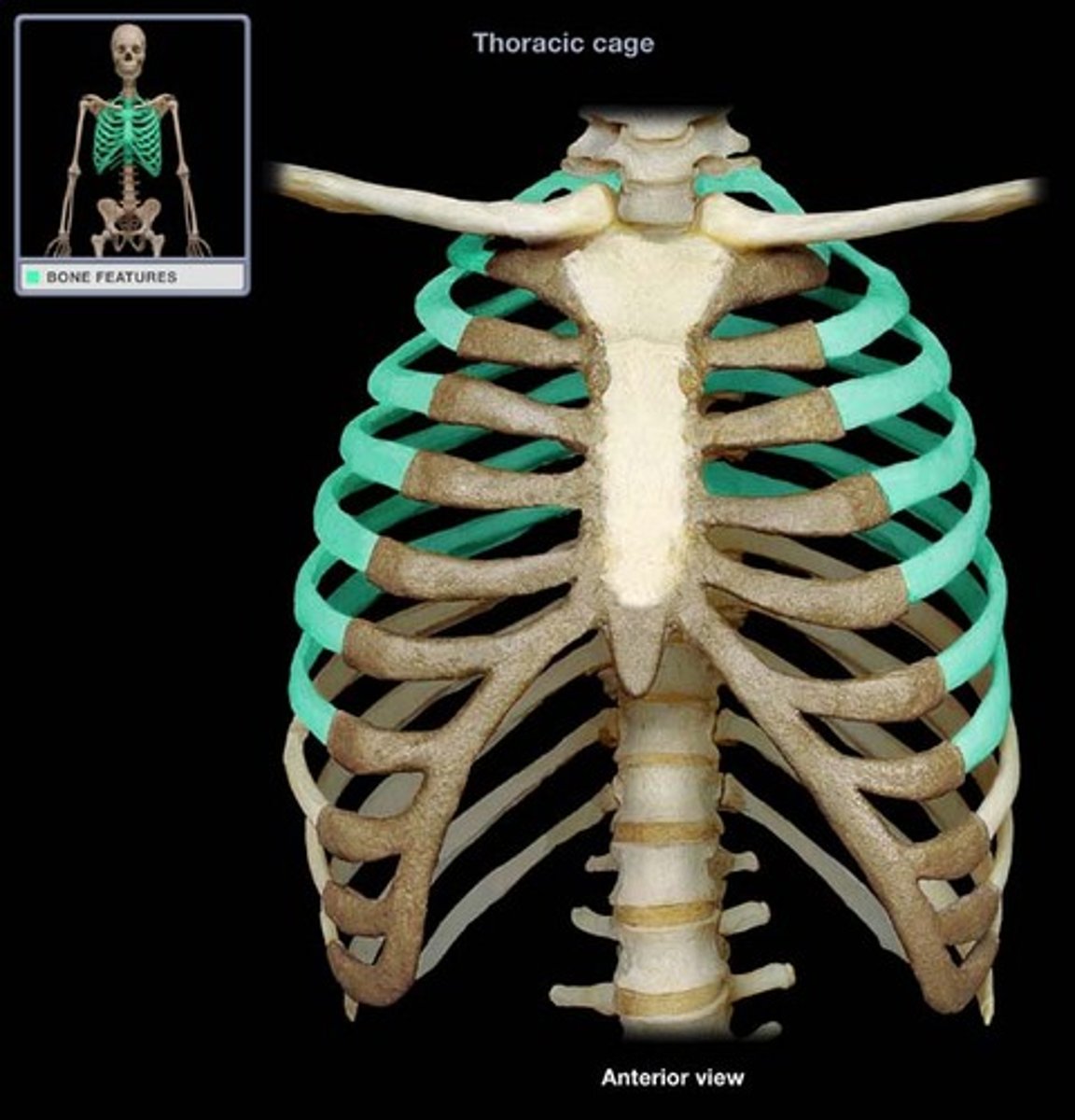
true rib
- first seven pairs directly attaching to the sternum by costal cartilages
- ribs 1-7
false rib
- three pairs indirectly attaching to the sternum via shared costal cartilage
- ribs 8-10
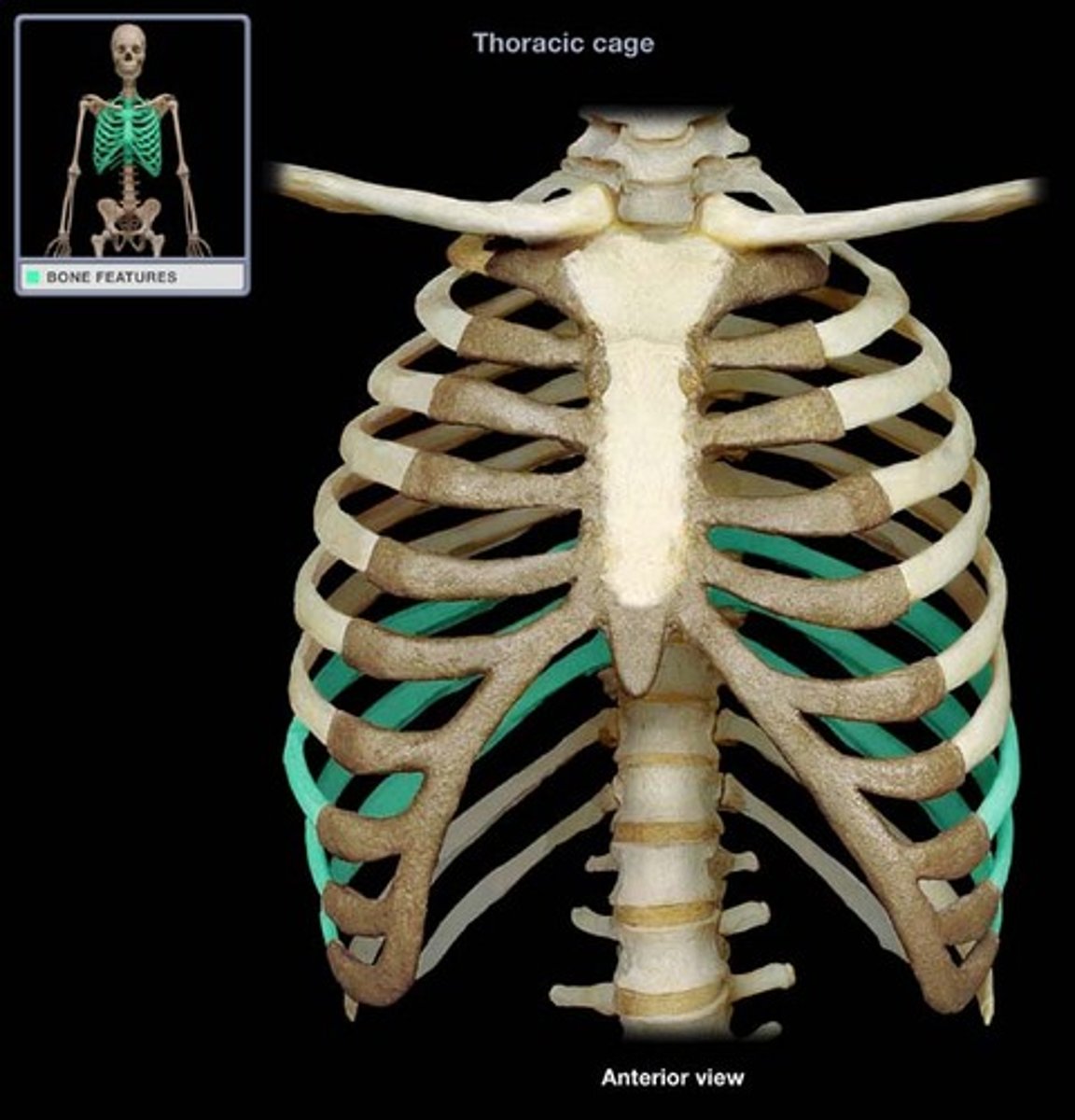
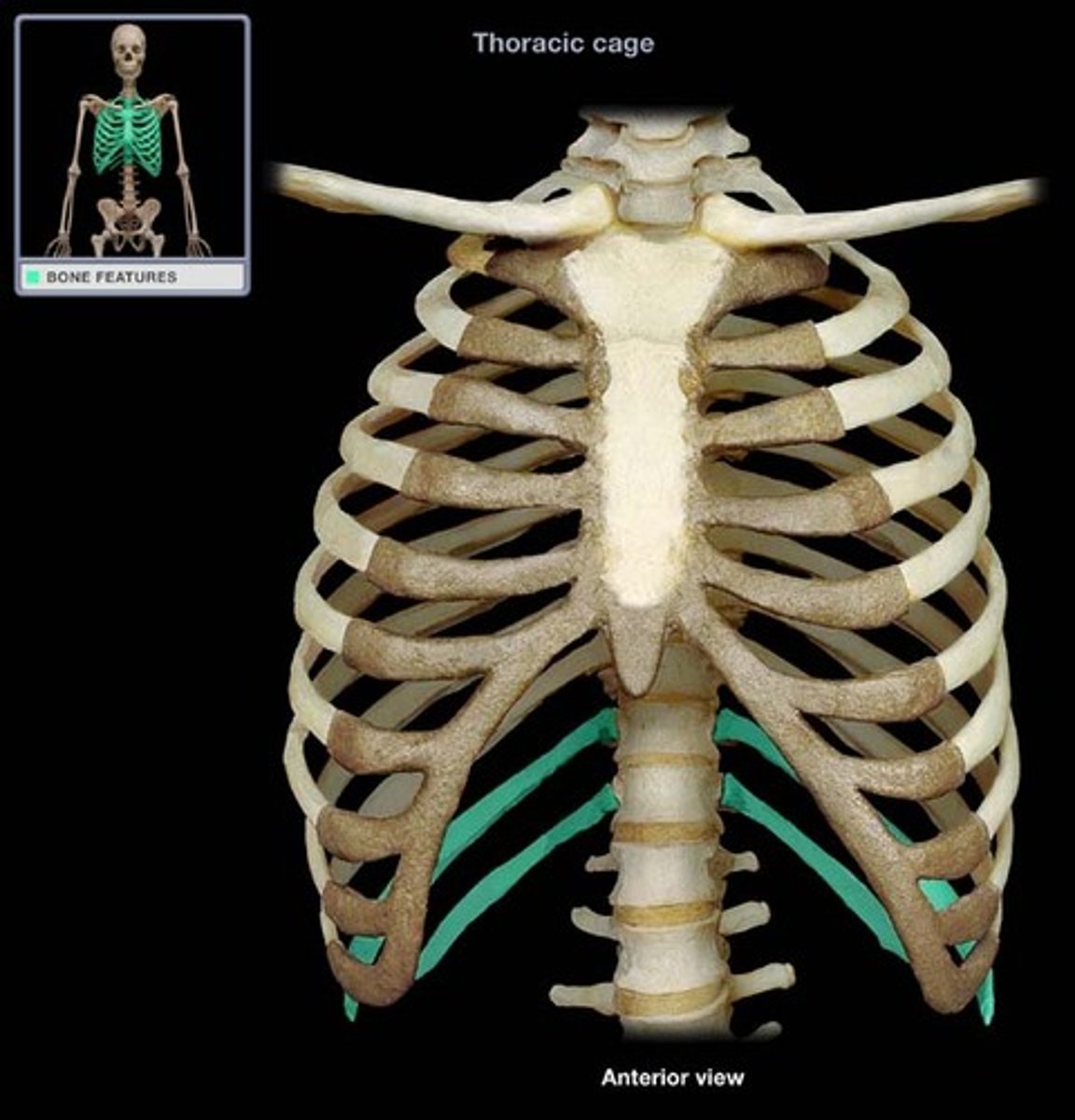
floating rib
- last two pairs that do not attach to the sternum
- ribs 11-12
- considered false ribs
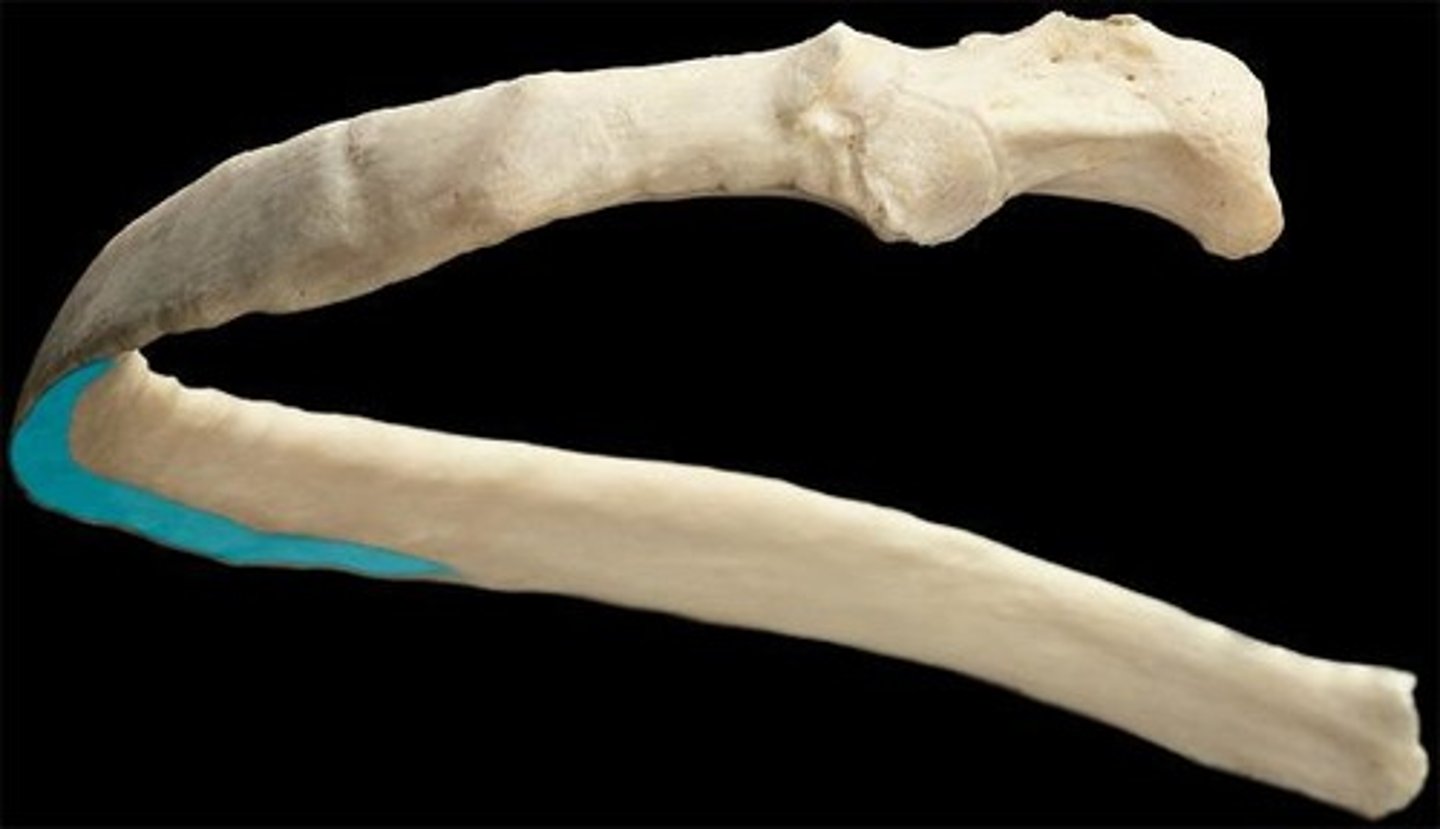
costal groove
- indent on the inferior border of ribs 2-10
- where the intercostal nerves, arteries, and veins run
costal angle
area where the rib begins to curve sharply anteriorly
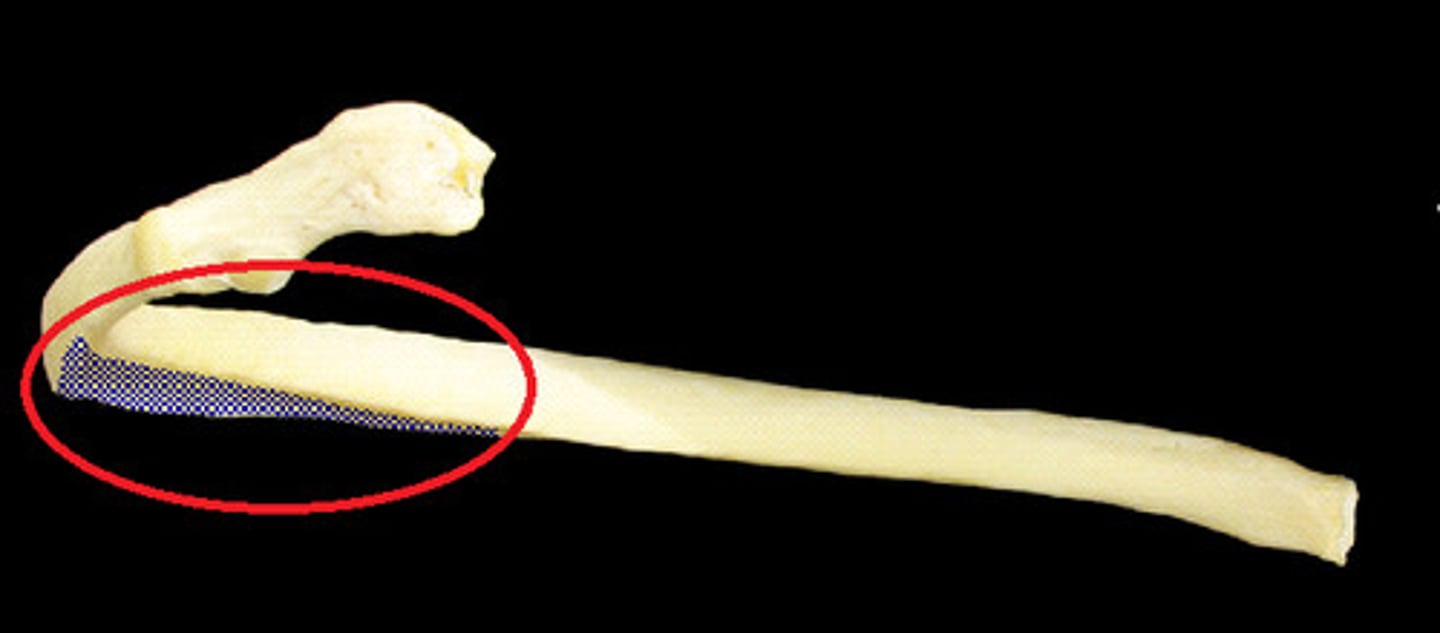
costal cartilage
- hyaline cartilage attaching ribs to the sternum
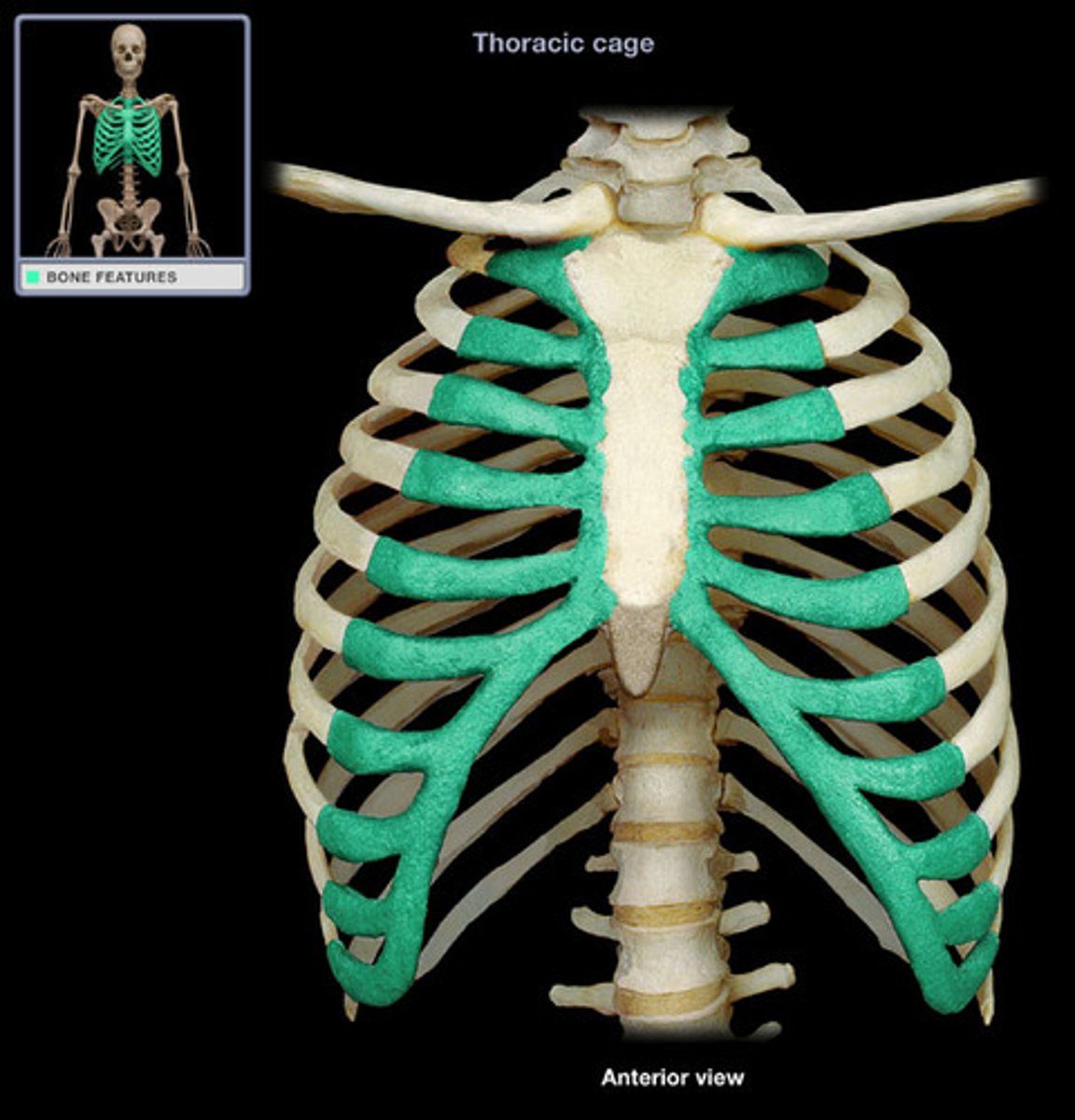
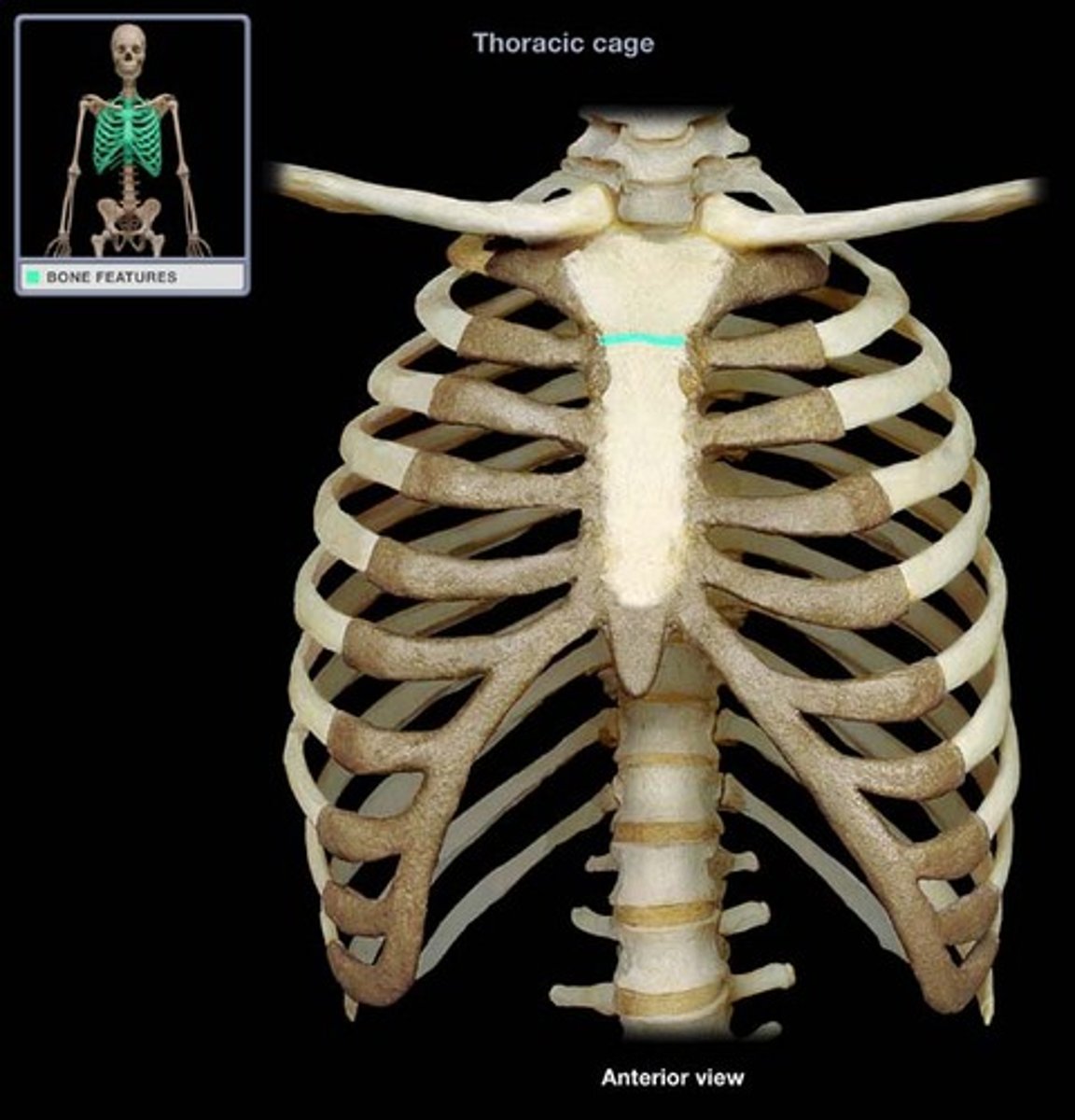
sternum
- broad, flat bone forming the anterior thoracic wall
- "breastbone"
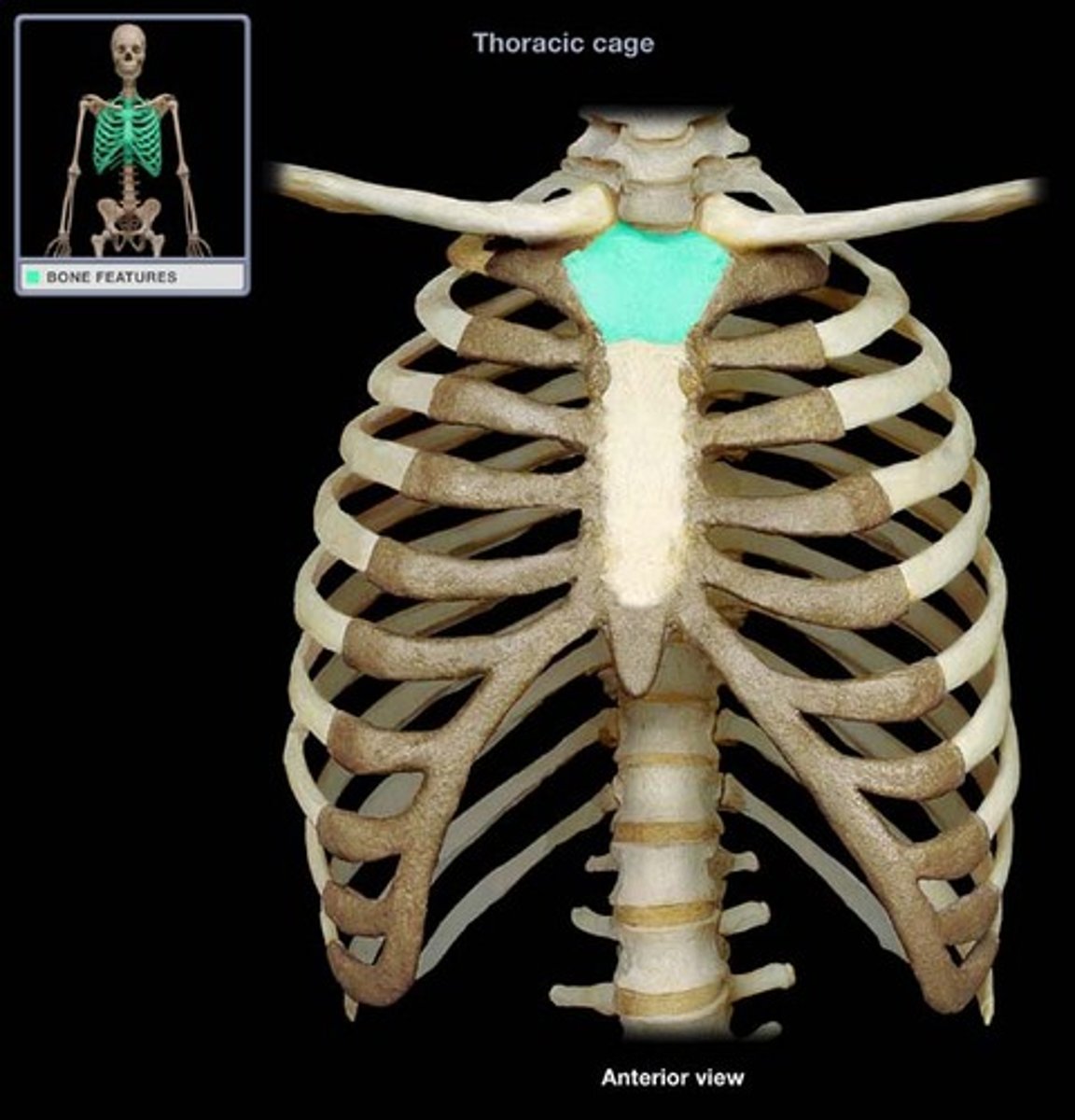
manubrium
- triangular shaped, superior part of the sternum
- articulates with costal cartilages of ribs 1-2 and clavicles
jugular (suprasternal) notch
- depression in the superior border of the manubrium
- between the clavicle notches
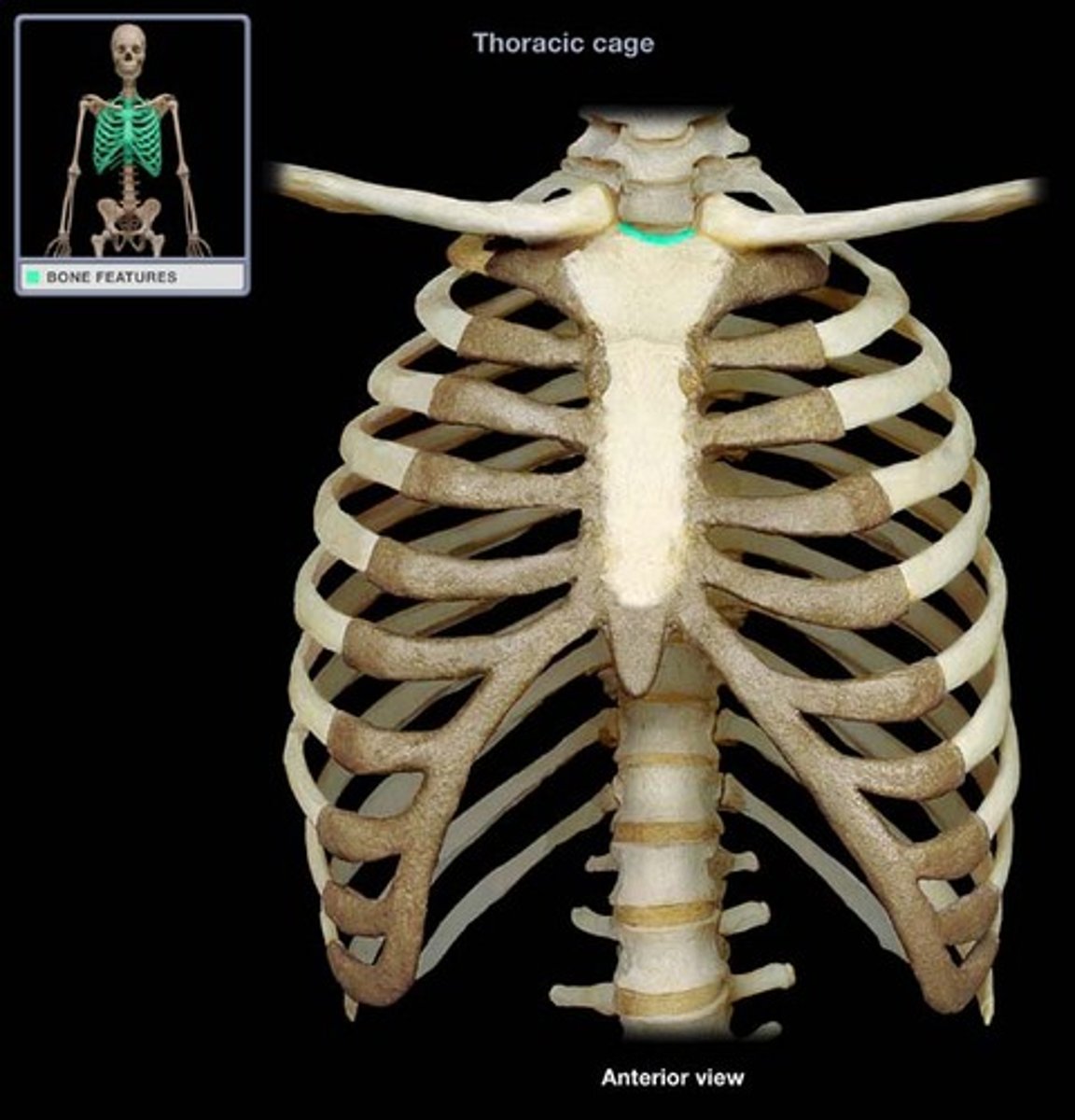
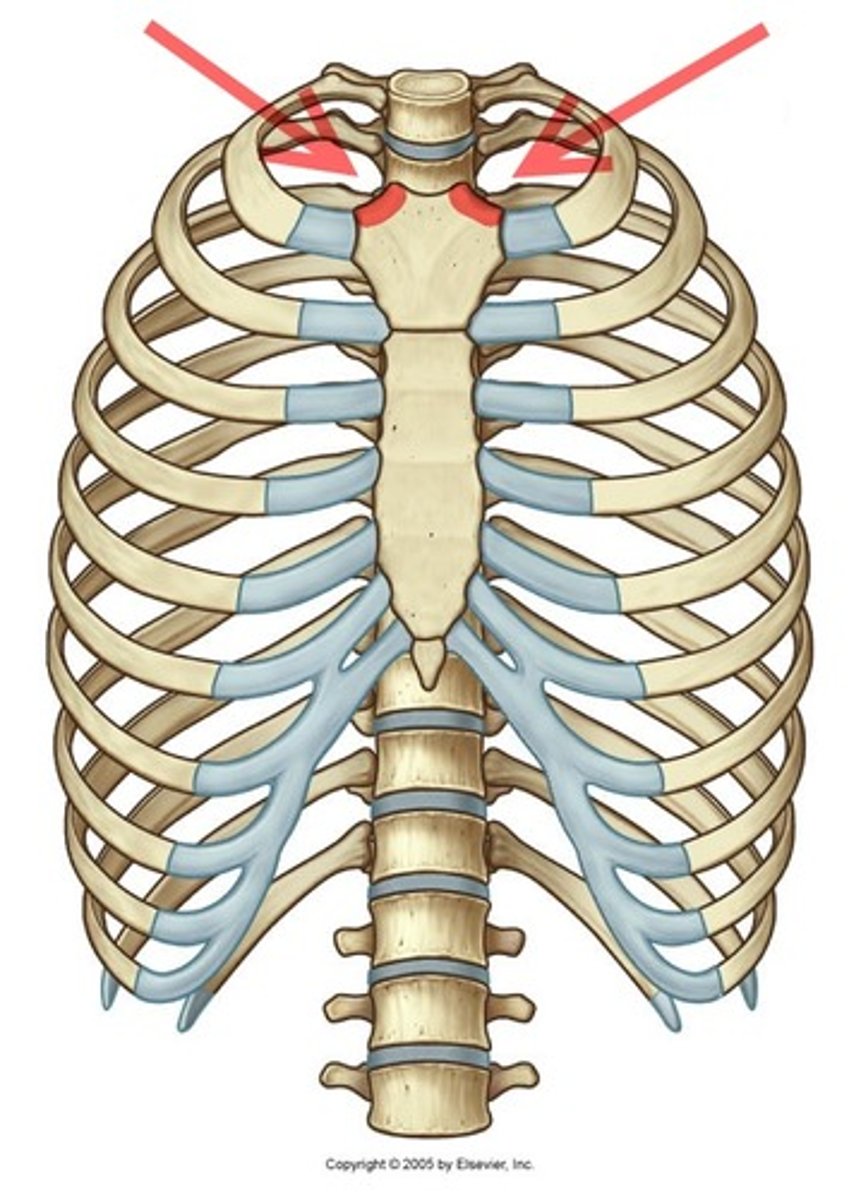
clavicular notch
- lateral depressions in the superior border of the manubrium
- where the clavicles articulate with sternum
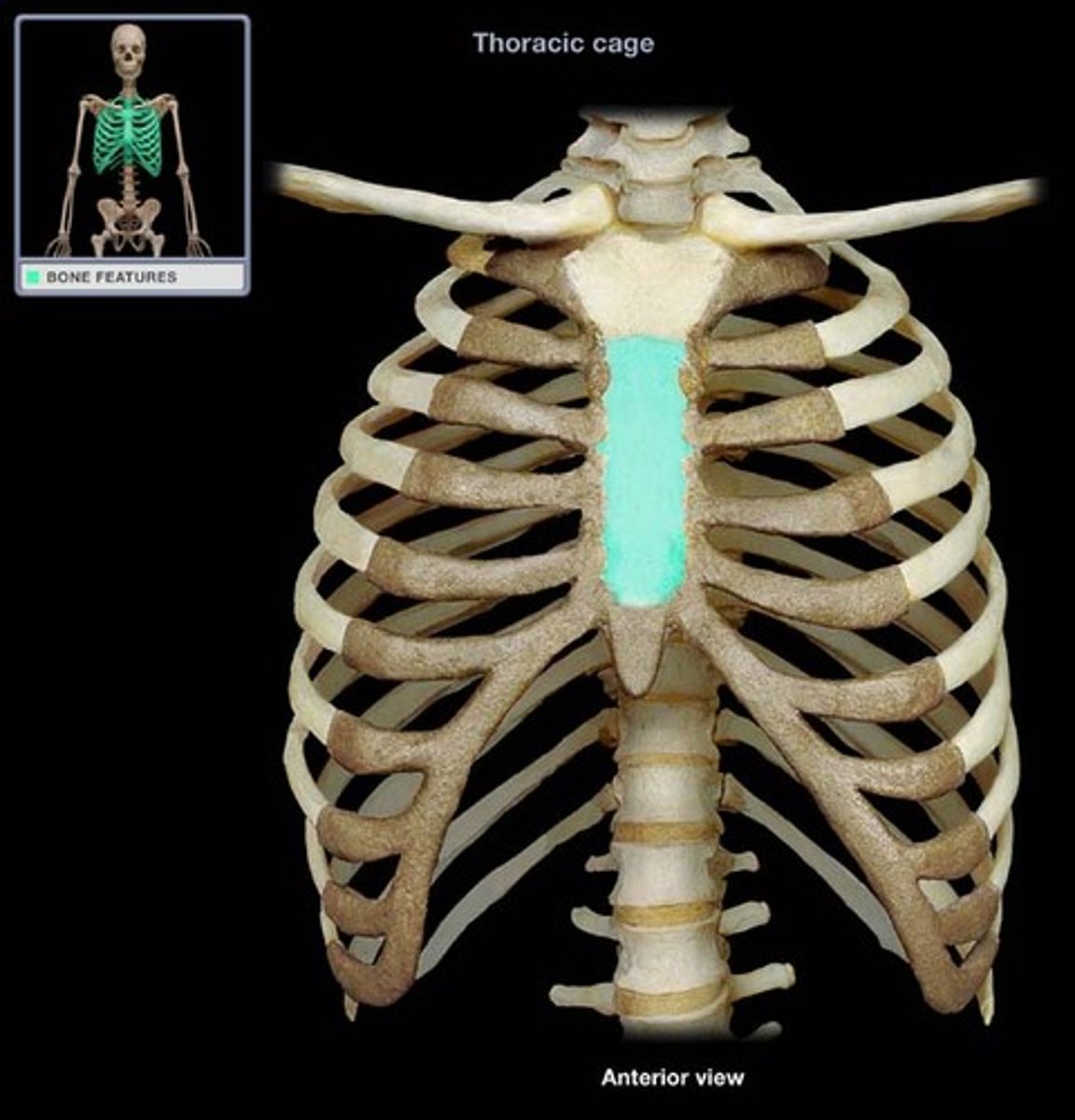
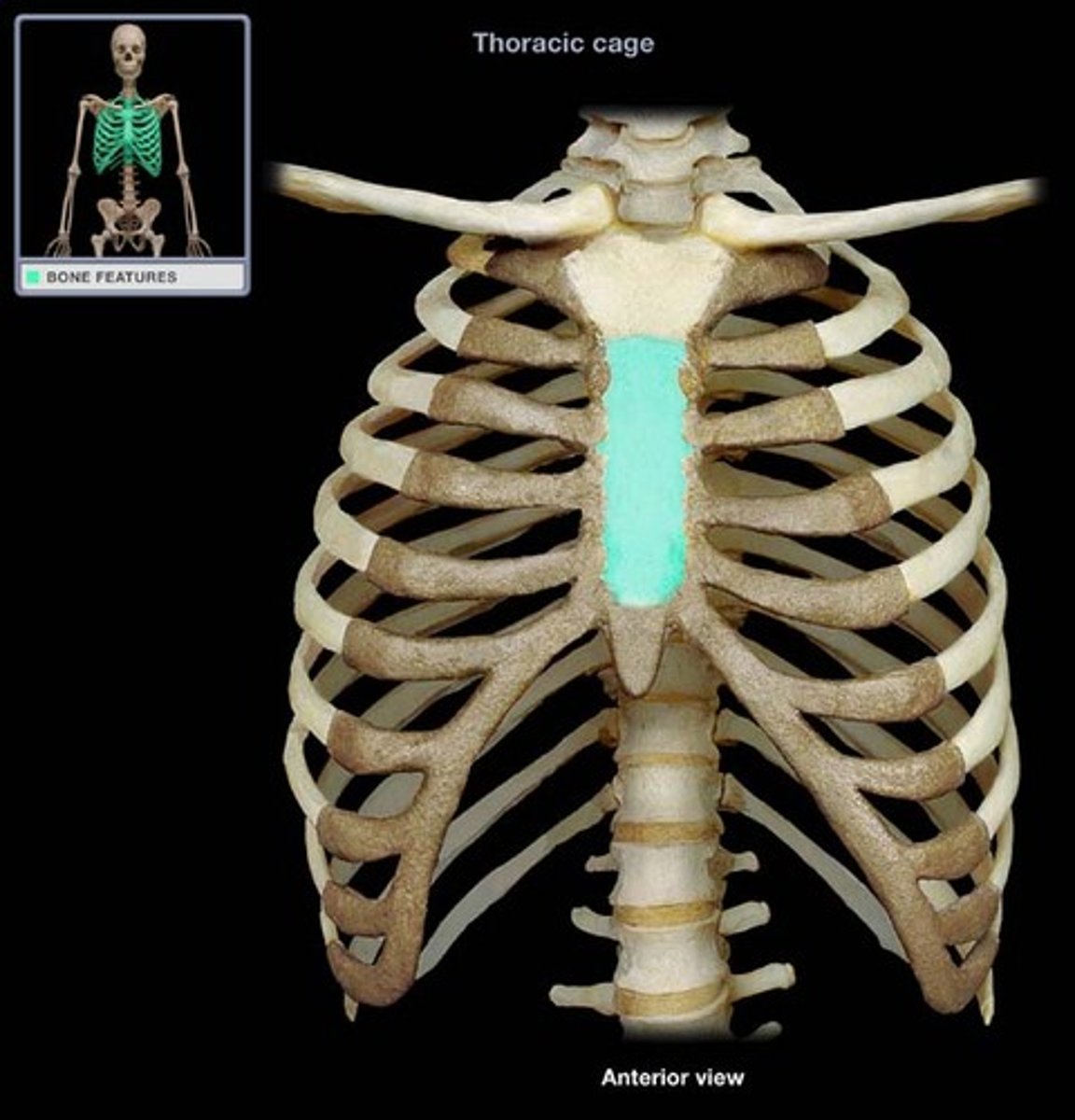
body (gladiolus) of sternum
- long flat part of the sternum between the manubrium and xiphoid process
- articulates directly with the costal cartilage of ribs 2-7
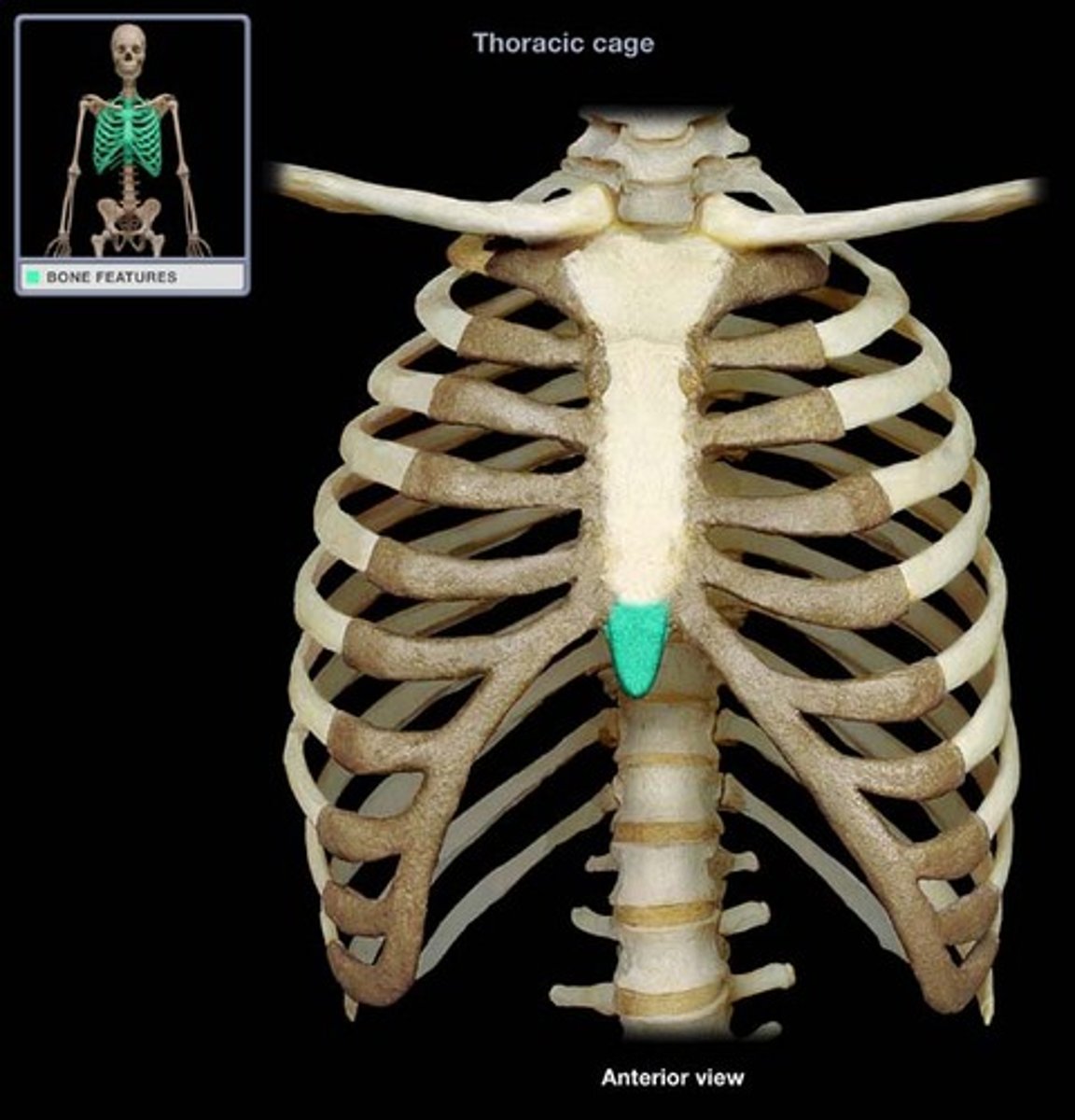
xiphoid process
- inferior pointed tip of the sternum
- CPR landmark
sternal angle
- horizontal ridge formed by the junction of manubrium and body of sternum
- level of C2