Molecular orbitals
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
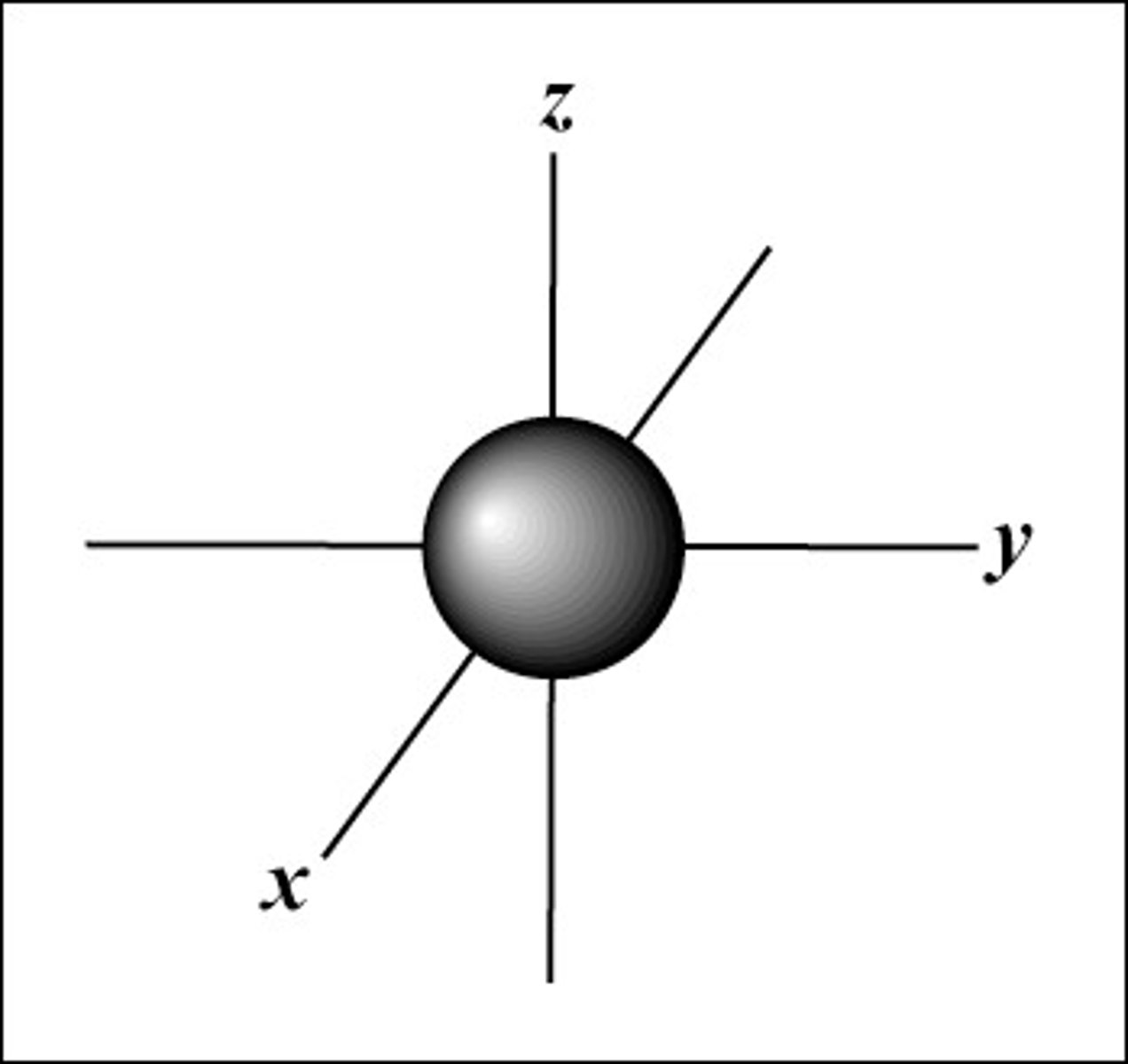
s orbital
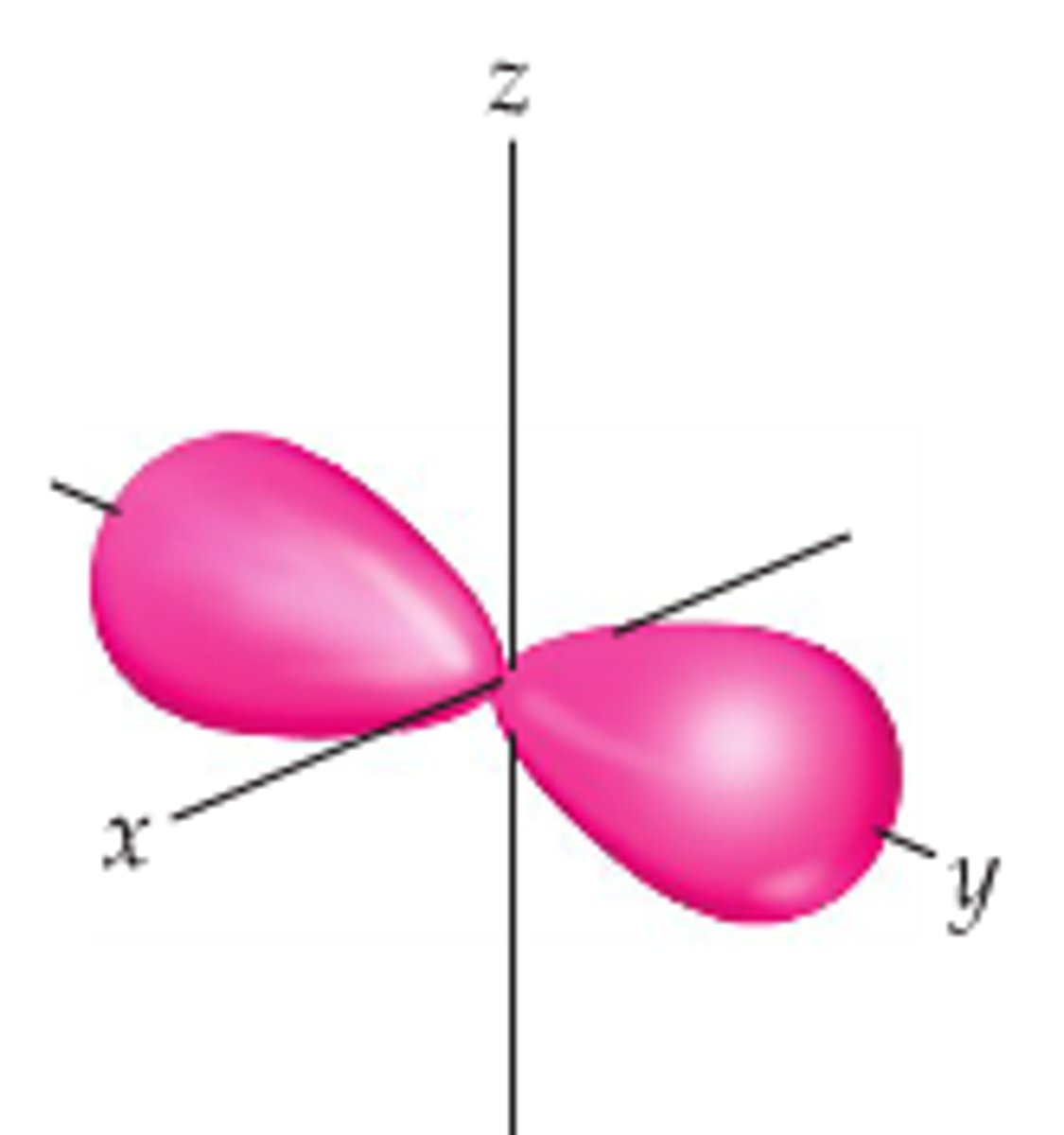
Py orbital
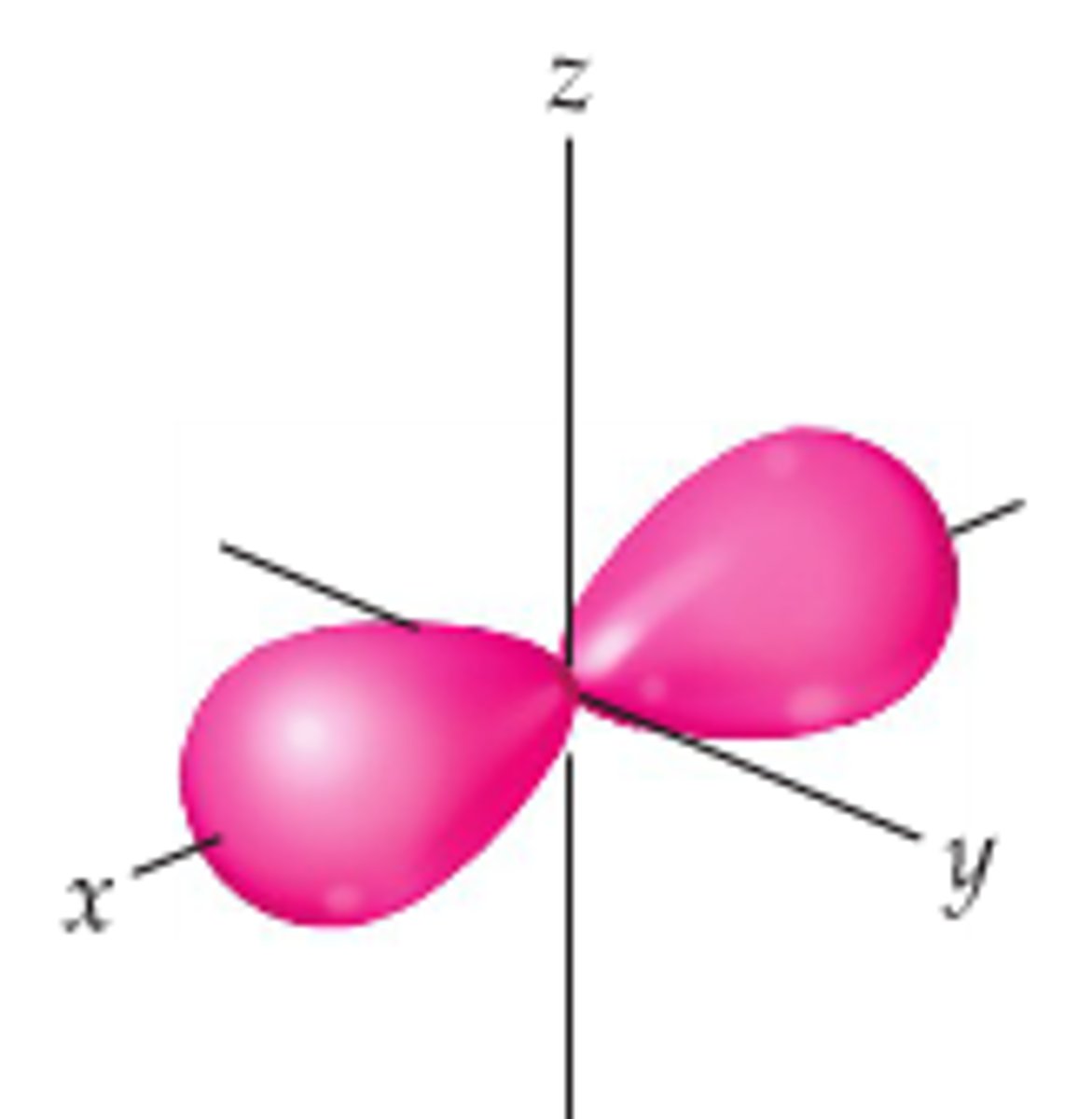
Px orbital
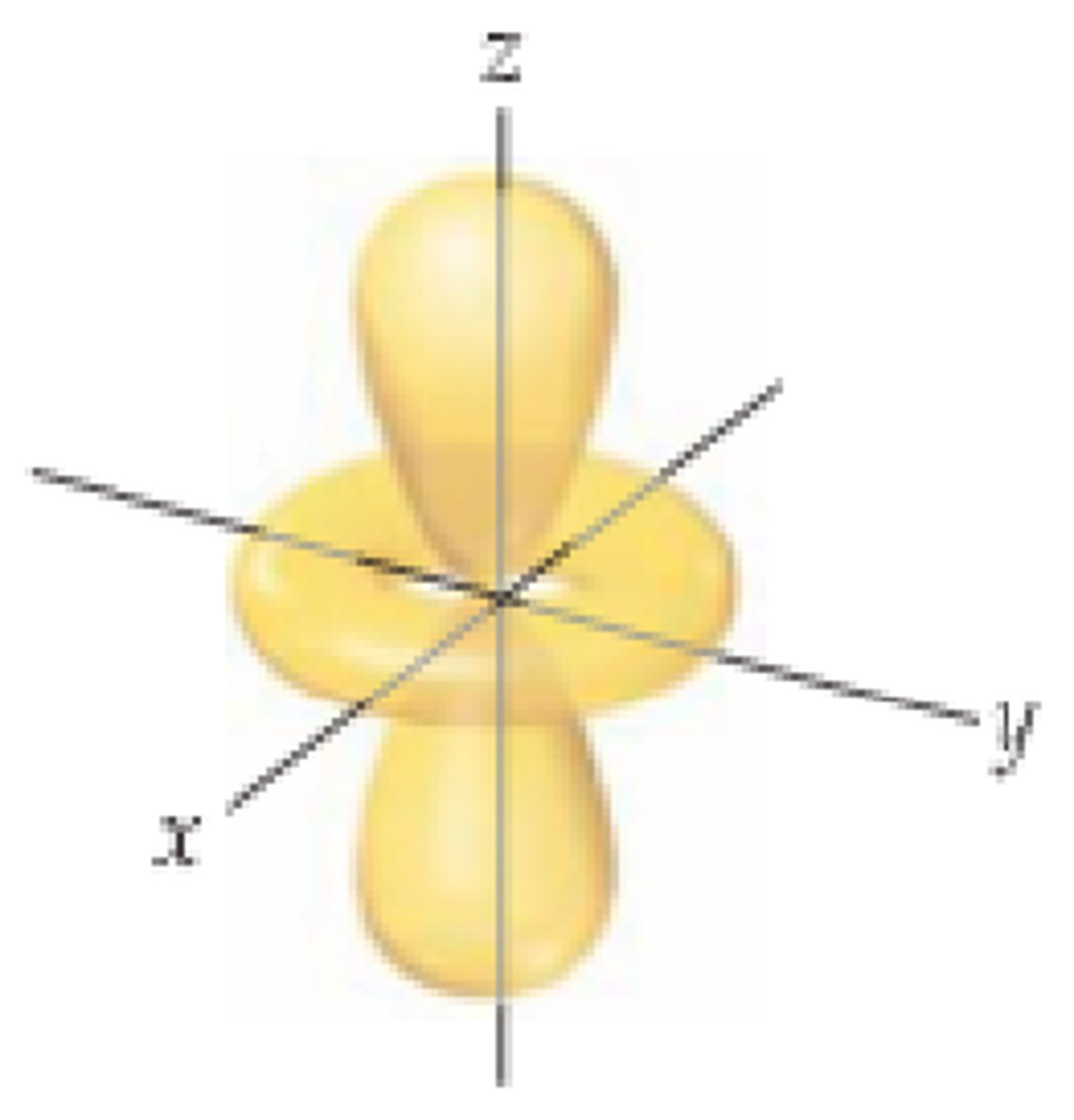
Pz orbital
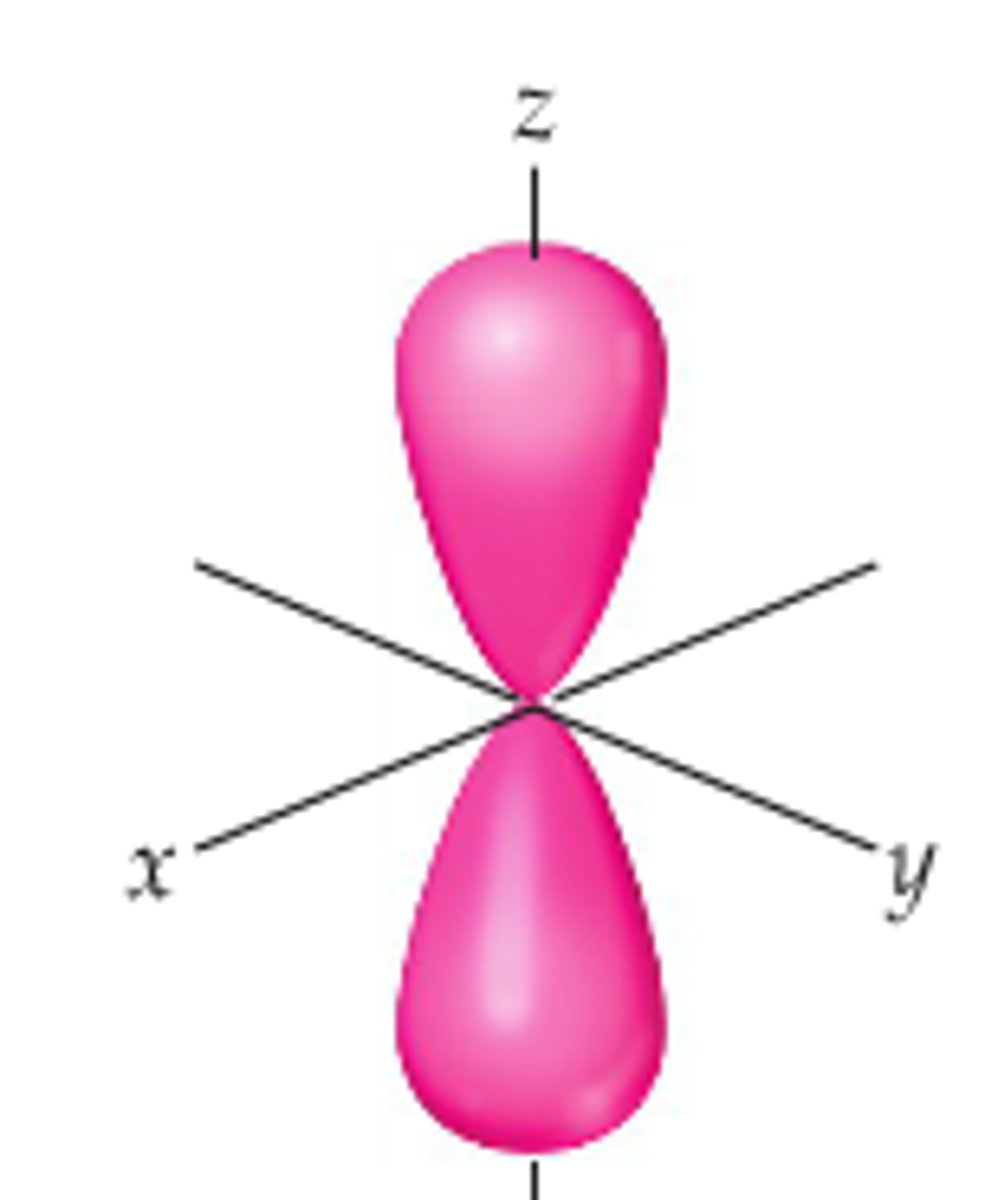
d xy orbital
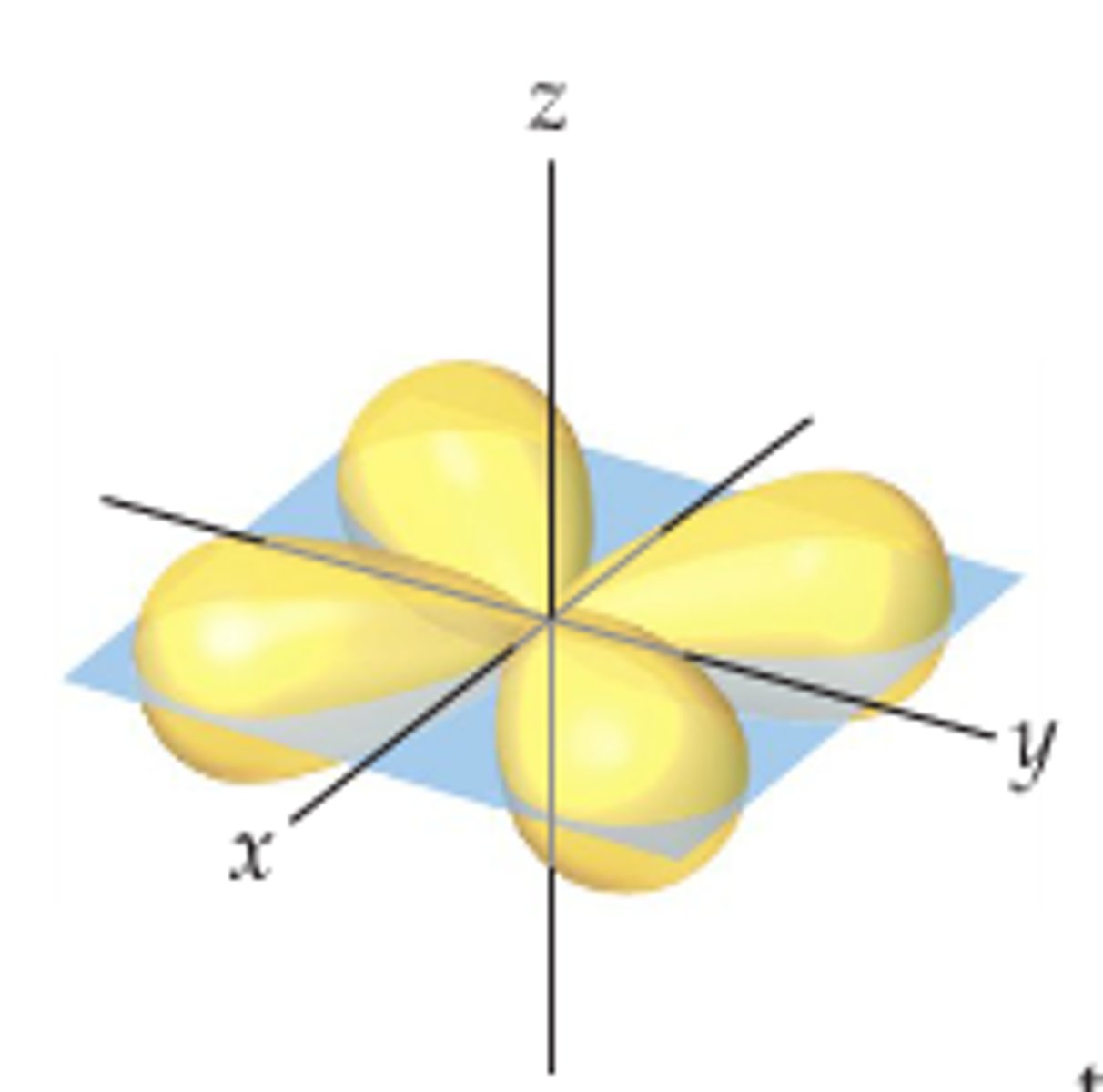
d xz orbital
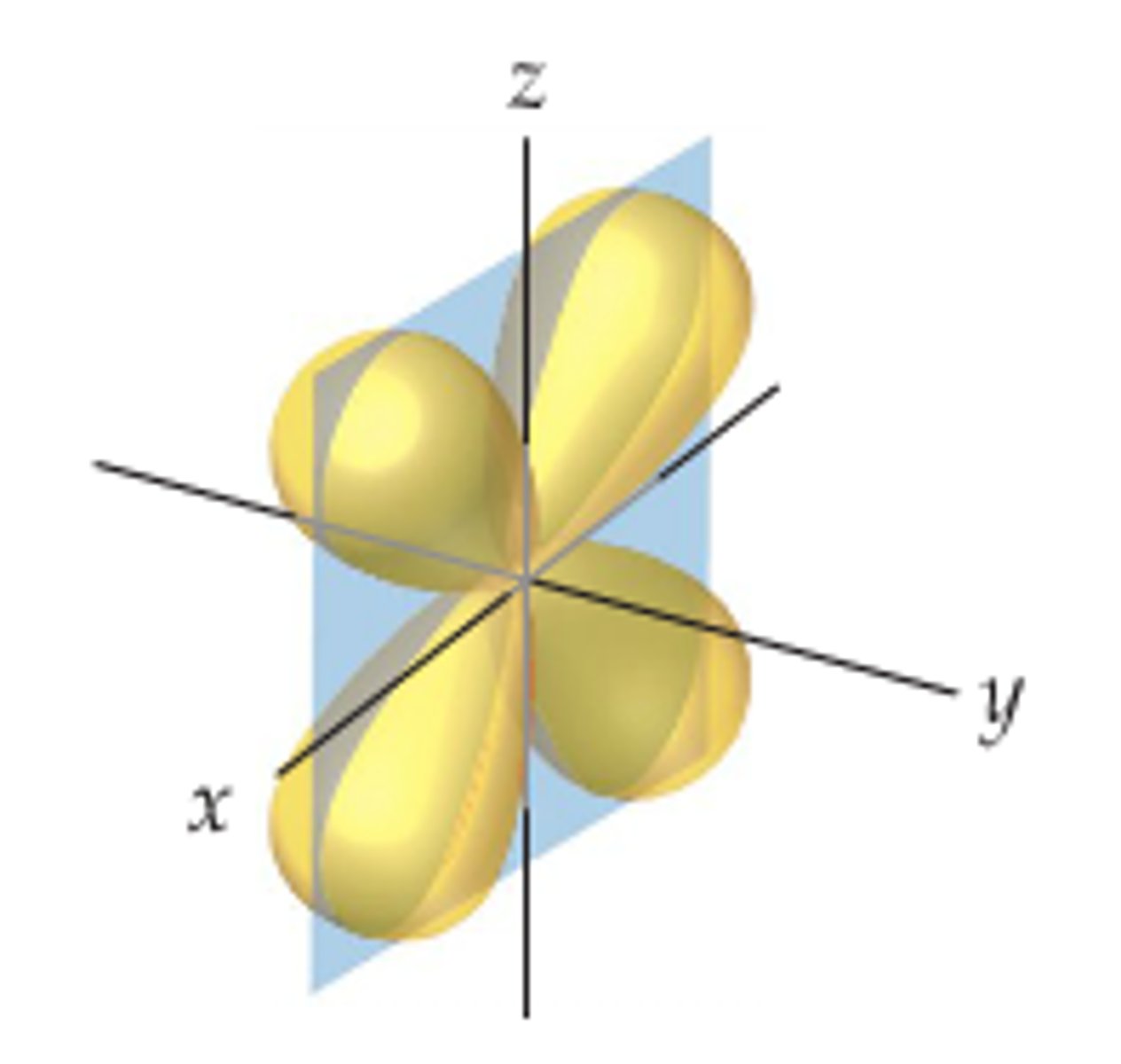
d yz orbital
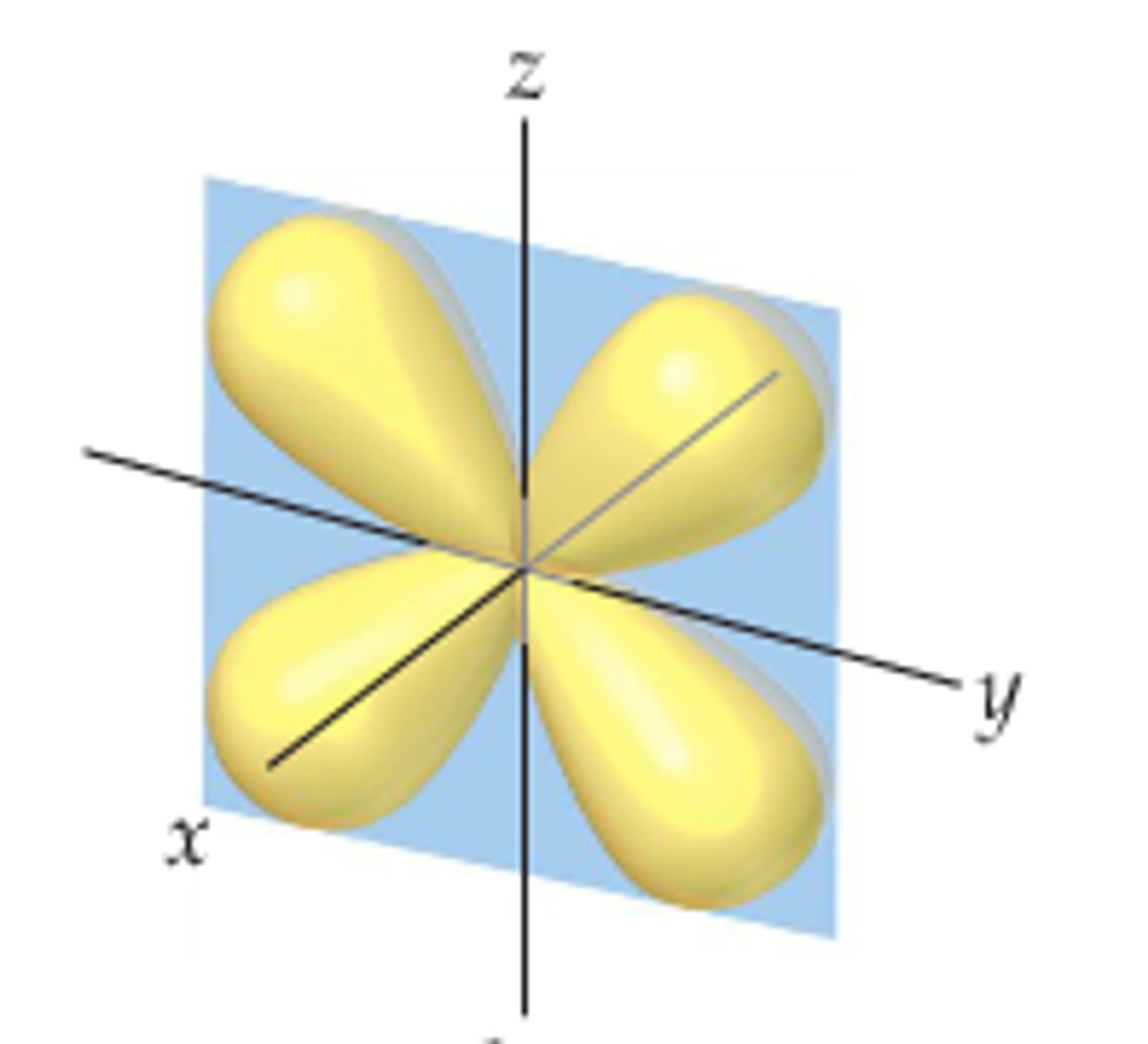
d x2-y2 orbital
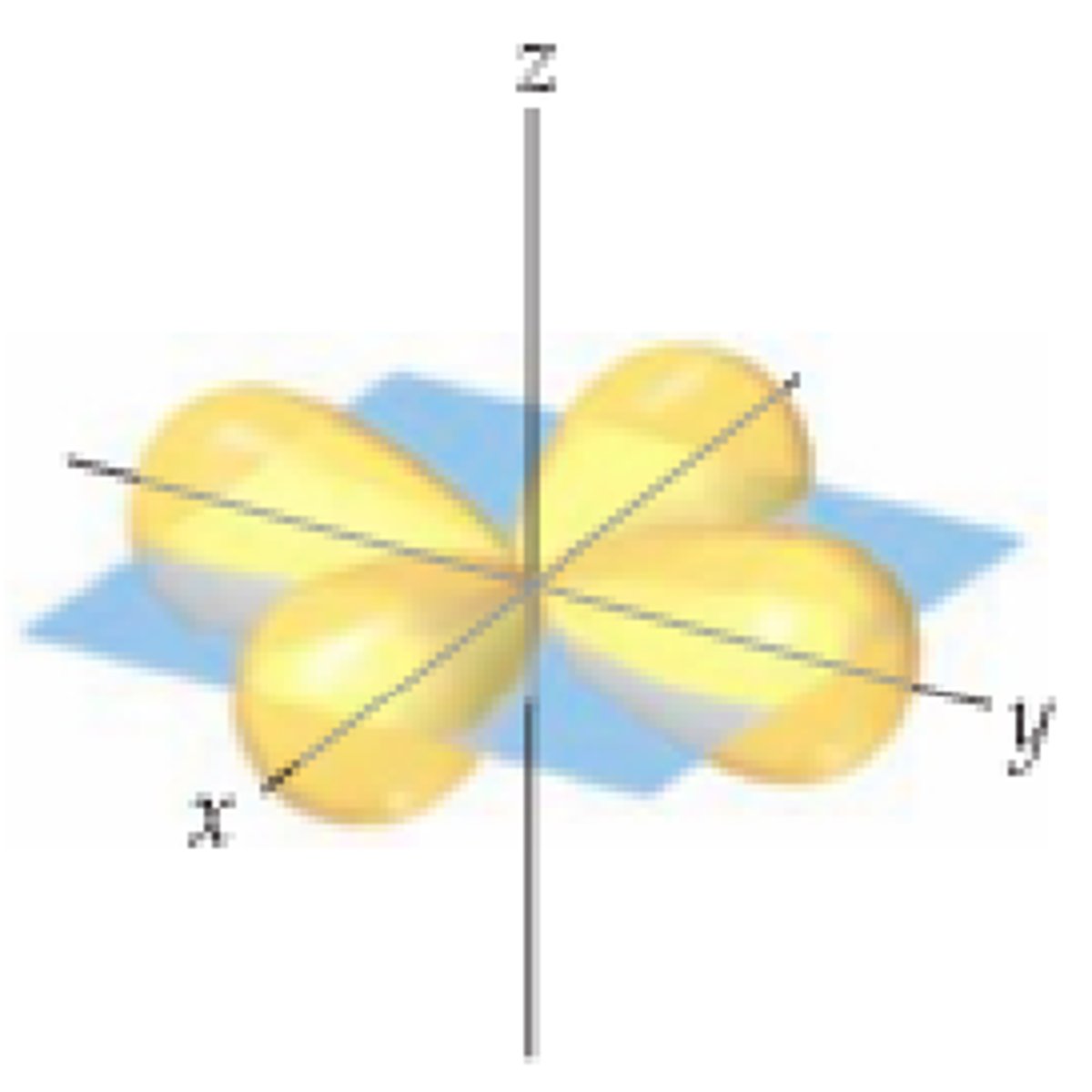
d z2 orbital
Bonding orbitals: energy
Bonding
- lower in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they were formed
-due to increase in shielding by nucleus
Antibonding orbitals: energy
Antibonding
-higher in energy than the atomic orbitals from which they were formed
-due to decrease in nuclear shielding
Constructive and destructive interference in bonding and antibonding
-Bonding: constructive interference of AO'S so they come together.
-antibonding: destructive interference of AO'S so they repulse each other
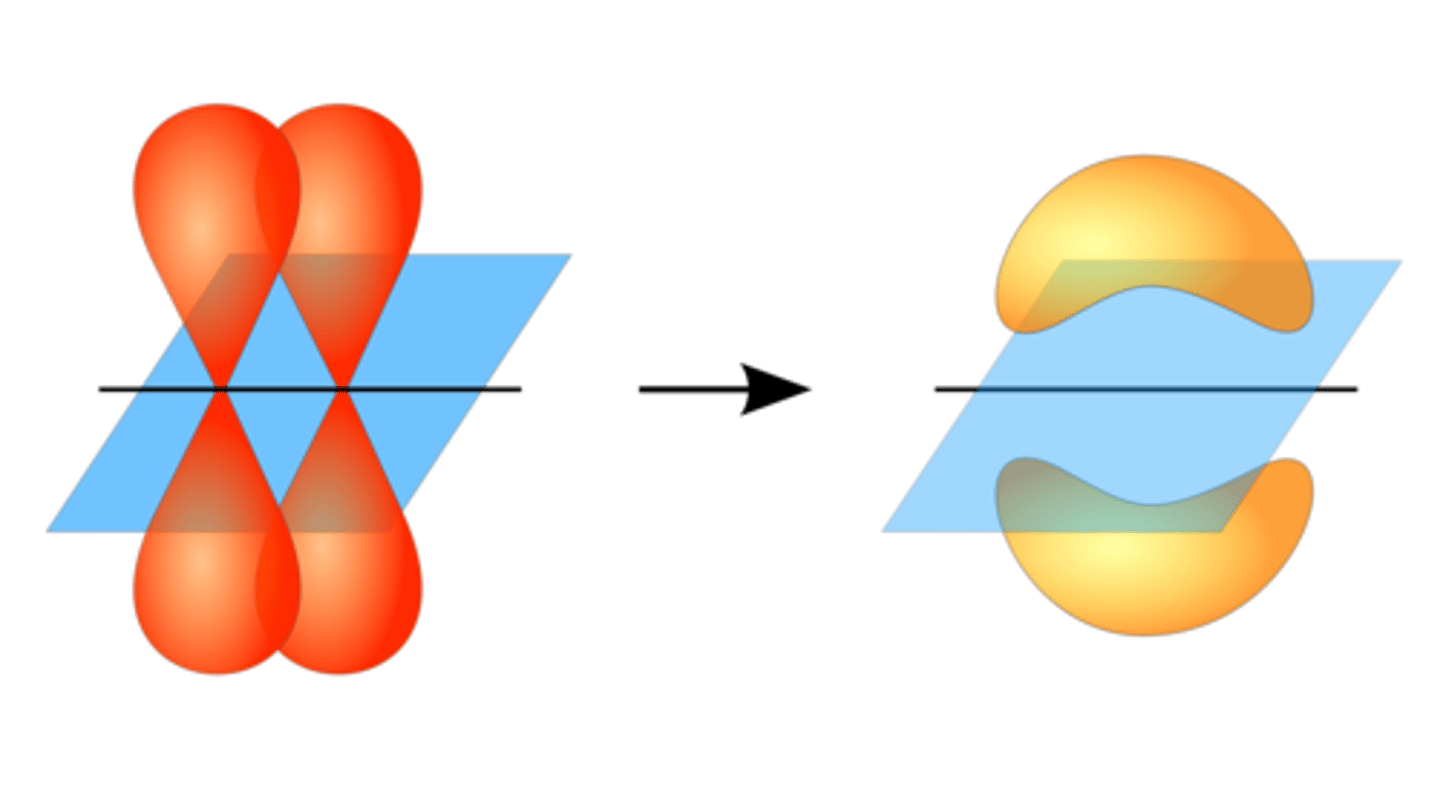
Pi bonding
electron density is above/below the bonding axis
sigma bonding
electron density is along the bonding axis
Bond order
1/2 (# electrons in bonding - # electrons in antibonding)
Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
--The motion of the nuclei and the electrons can be separated and the nuclear, electronic, and spin parts of the wavefunction can can be solved with independent wavefunctions
gerade
-German for even, these configurations are symmetrical relative to i (inversion)
ungerade
-German for uneven, these configurations are asymmetric relative to inversion
symmetry-adapted linear combination of atomic orbitals (SALCs)
--determined from overlapping orbitals with same symmetry
-Gives you the wave functions for MOs
-gives a qualitative picture of the MOs in a molecule and provides a good way of predicting bonds
sigma bonding molecular orbital
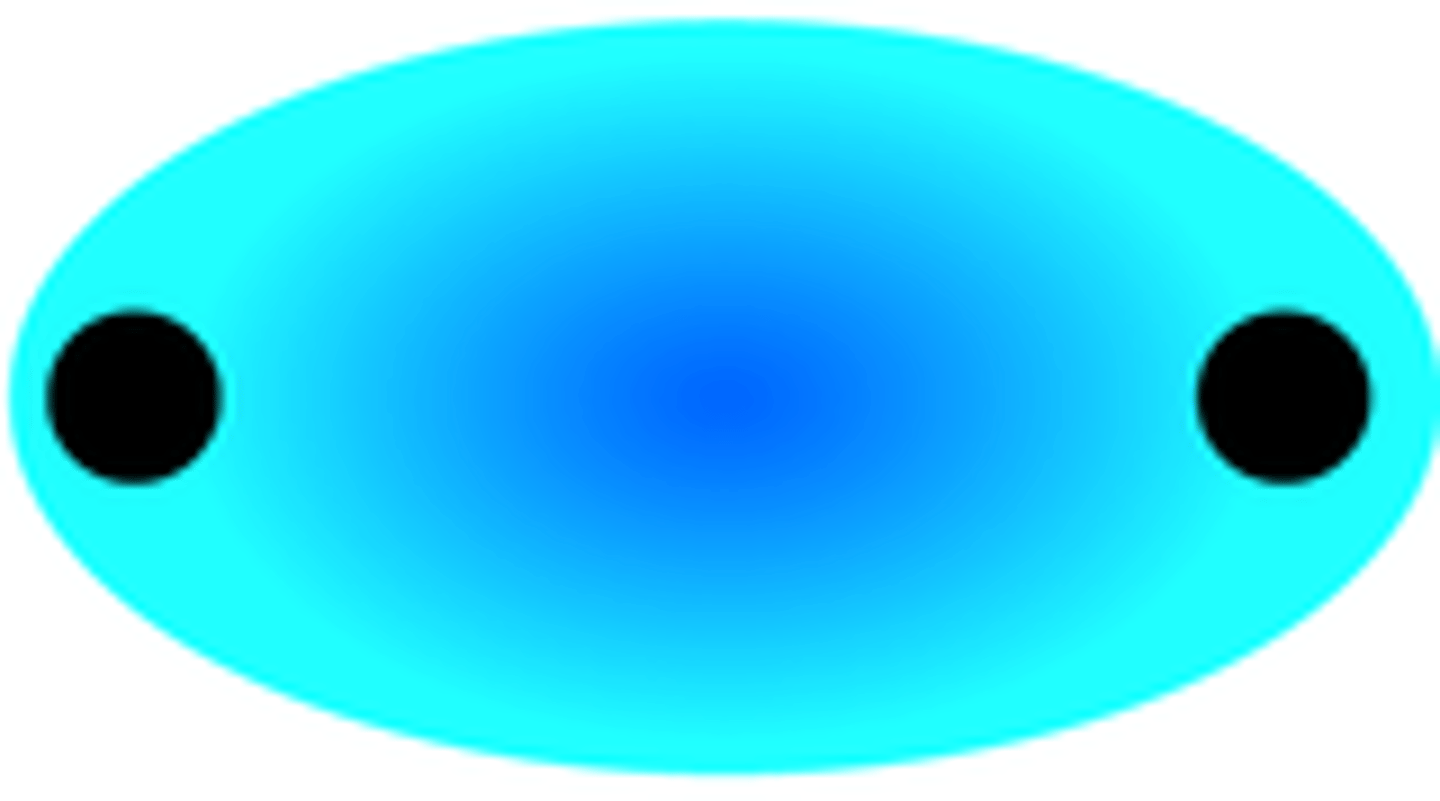
formation of a pi bonding molecular orbital