AP Psychology Ch 7 Cognition - Unit 2 (updated for 25/26 SY)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
storage
the retention of encoded information over time
retrieval
the process of bringing to mind information that has been previously encoded and stored
Explicit memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
Episodic Memory
the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at a particular time and place
Semantic memory
a network of associated facts and concepts that make up our general knowledge of the world
Implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection
Procedural memory
a type of implicit memory that involves motor skills and behavioral habits
Prospective memory
remembering to do things in the future
Long-term potentiation
gradual strengthening of the connections among neurons from repetitive stimulation
Working memory model
describes short-term memory as a system with multiple components; suggests that short-term memory is dynamic and multifaceted
Primary memory system
hippocampus
working memory
A newer understanding of short-term memory that involves conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory.
Central executive
the part of working memory that directs attention and processing
phonolgical loop
holds and retains verbal information. rehearsal. uniquely human characteristic. thought to evolve for learning of new languages.
Visuospatial sketchpad
A component of working memory where we create mental images to remember visual information
Long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.
Multi-store model
An explanation of memory based on three separate memory stores, and how information is transferred between these stores.
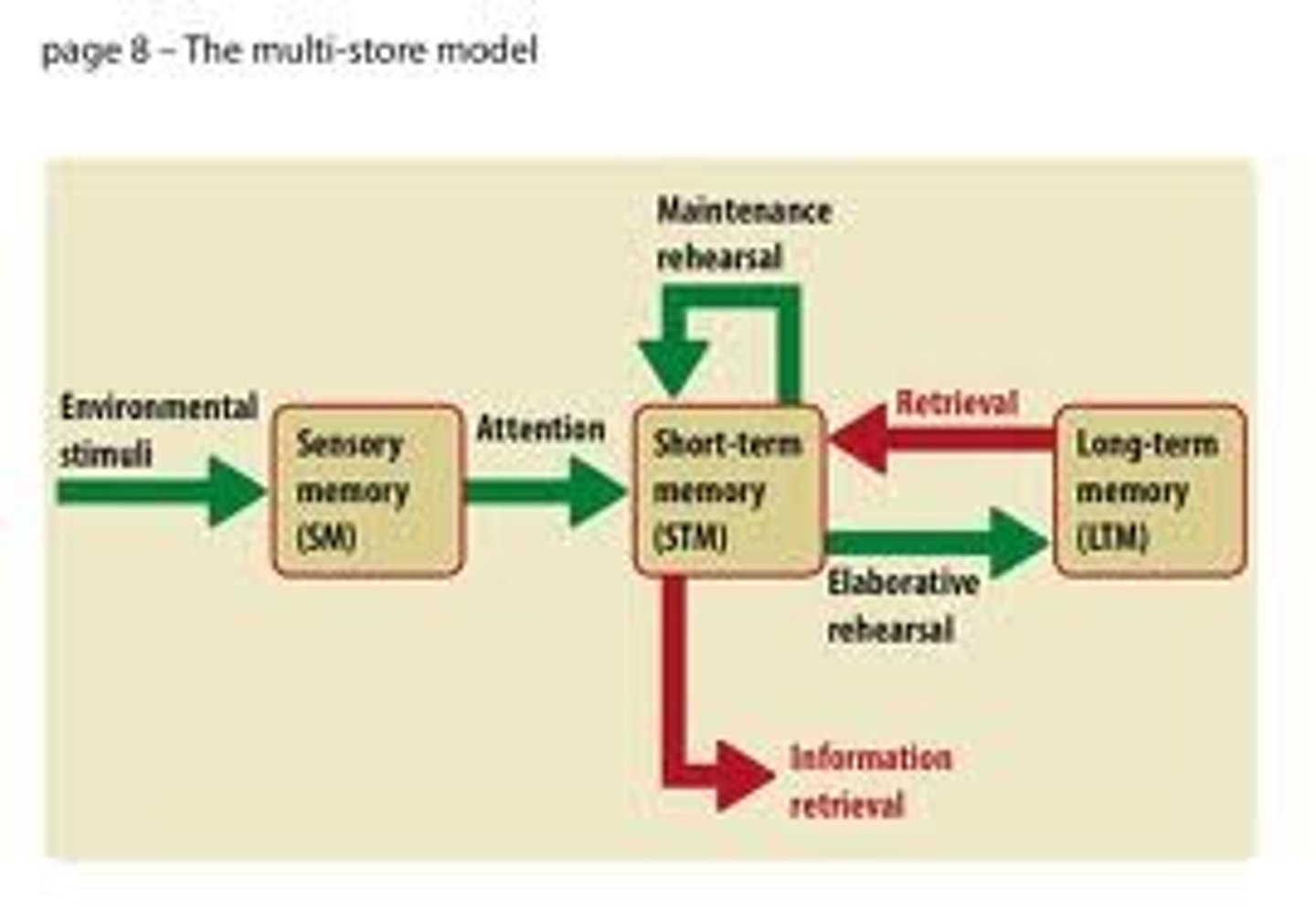
Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
Echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
Automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings
Effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Encoding
the processing of information into the memory system
Levels of processing model
the more deeply an item is encoded, the more meaning it has and the better it is remembered
Shallow encoding
encoding based on sensory characteristics, such as how something looks or sounds
Deep encoding
encoding based on an event's meaning as well as connections between the new event and past experience
Structural, phonemic, and semantic
three levels of processing
Mnemonic devices
techniques for using associations to memorize and retrieve information
Method of loci
A mnemonic technique that involves associating items on a list with a sequence of familiar physical locations
Chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
Categories
clusters of interrelated concepts
Hierarchies
A Social structure that organizes ranks people such as in a class system.
Spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
Memory consolidation
the gradual, physical process of converting new long-term memories to stable, enduring memory codes
Massed practice
a practice schedule in which studying continues for long periods, without interruption
Distributed Practice
spacing the study of material to be remembered by including breaks between study periods
Serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last and first items in a list
Primacy effect
tendency to remember information at the beginning of a body of information better than the information that follows
Recency effect
tendency to remember recent information better than earlier information
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, such as the seven digits of a phone number while dialing, before the information is stored or forgotten
Maintenance rehearsal
A system for remembering involving repeating information to oneself without attempting to find meaning in it
Elaborative rehearsal
a method of transferring information from STM into LTM by making that information meaningful in some way
memory retention
ability to recall information
Autobiographical memory
the memory for events and facts related to one's personal life story
Retrograde amnesia
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
Anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
Infantile amnesia
the inability to retrieve memories from much before age 3
Recognition
the ability to match a piece of information or a stimulus to a stored image or fact
Retrieval cues
Stimuli that are used to bring a memory to consciousness or into behavior
Context-dependent memory
The theory that information learned in a particular situation or place is better remembered when in that same situation or place.
Mood-congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood
State-dependent memory
The theory that information learned in a particular state of mind (e.g., depressed, happy, somber) is more easily recalled when in that same state of mind.
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information
metacognition
awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes.
Forgetting curve
a graphic depiction of how recall steadily declines over time
Encoding failure
the inability to recall specific information because of insufficient encoding of the information for storage in long-term memory
Proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
Retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
Tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
the temporary inability to remember something you know, accompanied by a feeling that it's just out of reach
Repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
Misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event
Source amnesia
attributing to the wrong source an event we have experienced, heard about, read about, or imagined
Constructive memory
memory that utilizes knowledge and expectations to fill in the missing details in retrieved memory traces
Imagination inflation
a memory phenomenon in which vividly imagining an event markedly increases confidence that the event actually occurred
Structural processing
type of shallow processing that focuses on the physical structure of information.
phonemic processing
shallow processing that focuses on the auditory aspects of information
semantic processing
processing the meaning of information for a deeper level of memory encoding
recall
the memory process of retrieving stored information from long-term memory without the use of any external cues or hints
automatic processing
the unconscious encoding of information about space, time, frequency, and well-learned tasks.