The Constraints on Growth and Development
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Education and skills: What is the impact of low productivity?
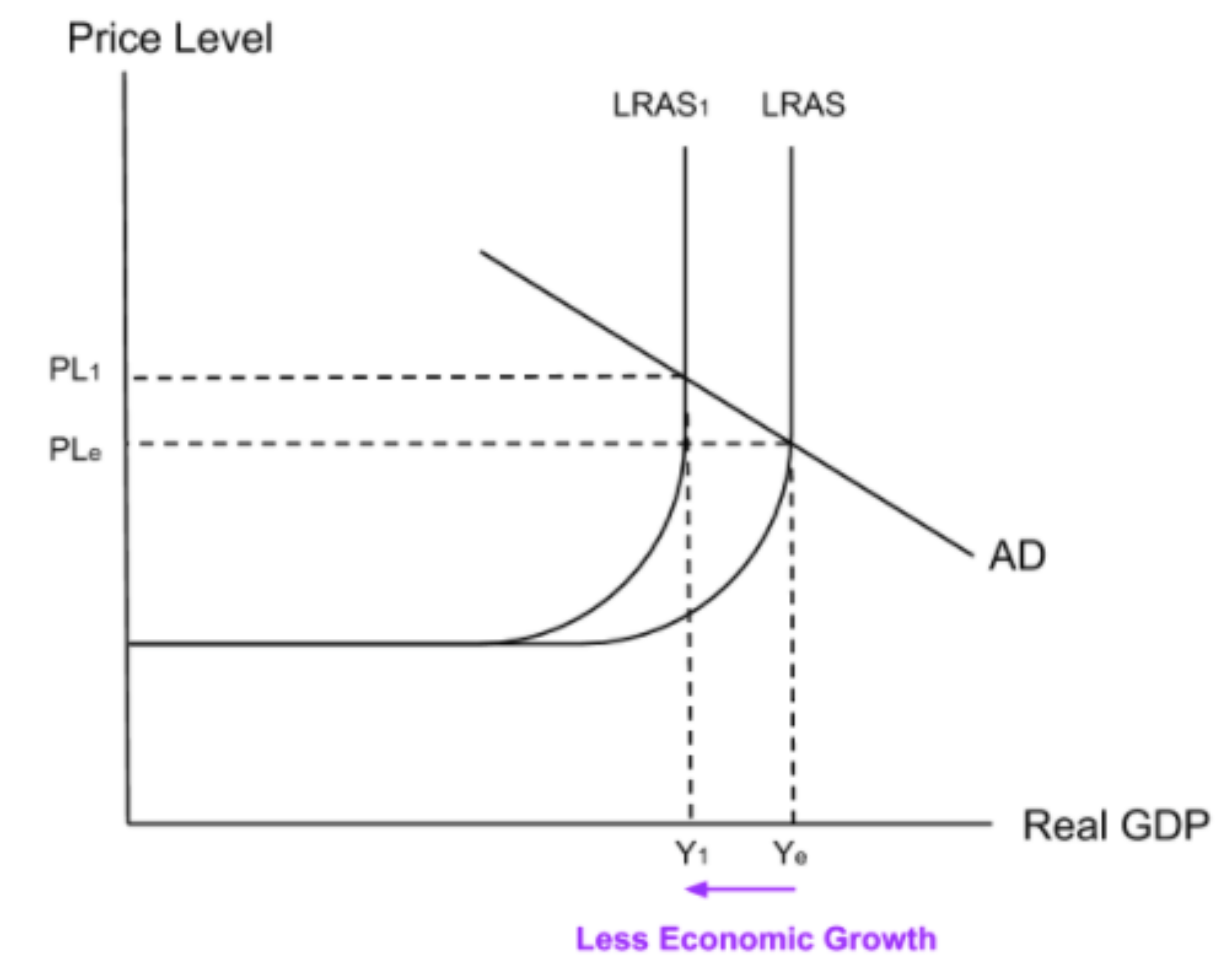
Low productivity causes a left shift in LRAS meaning the economy has a lower productive capacity. This will limit real GDP and therefore limit economic growth.
The chain of reasoning is as follows:
Low human capital → Low productivity → Keeps LRAS to the left → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Education and skills: the definition of: Low Human Capital
When workers don’t have the necessary knowledge, skills or assets to be productive.
Education and skills: What does it mean for the government if incomes are low?
the government will unable to collect much income tax revenue which means that it has less money available to invest in development.
Education and skills: In 1980, the GNI per capita for Madagascar was $460. What was the GNI per capita for Madagascar in 1990?
Between 1980 and 1990, GNI per capita in Madagascar fell from $460 to $240.
Education and skills: What is the impact of an improvement in human capital?
When people receive a better education, they leave school with higher human capital which means that they have the knowledge and skills to make them more productive workers.
Education and skills: reference to an example, explain how improvements in education can lead to growth and development.
In Madagascar in 2002, the President trained thousands of teachers and built hundreds of new schools. This improved the standard of education. When people receive a better education, they leave school with higher human capital meaning they have the knowledge and skills to make them more productive workers.
An increase in productivity shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the rightand increases real GDP, thereby increasing economic growth.
Higher productivity also means that workers’ incomes will increase. This means that they will pay more income tax and so the government will receive more revenue. This gives them more money to spend on development.
Education and skills: Evaluation point
A low standard of education means that students will not acquire the knowledgeor skills they need. In other words, they will have low human capital meaning there will not be a significant increase in worker productivity.
Lower productivity will shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the left and decrease real GDP and therefore decrease economic growth.
Lower productivity also means that workers’ incomes will decrease. This means that they will pay less income tax and so the government will receive less revenue. This gives them less money to spend on development.
The two chains of reasoning here are:
Low human capital → Low productivity → Keeps LRAS to the left → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Low human capital → Low productivity → Low incomes → Less income tax revenue → Less government spending on development → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Infrastructure: Impact of poor infrastructure on the economy
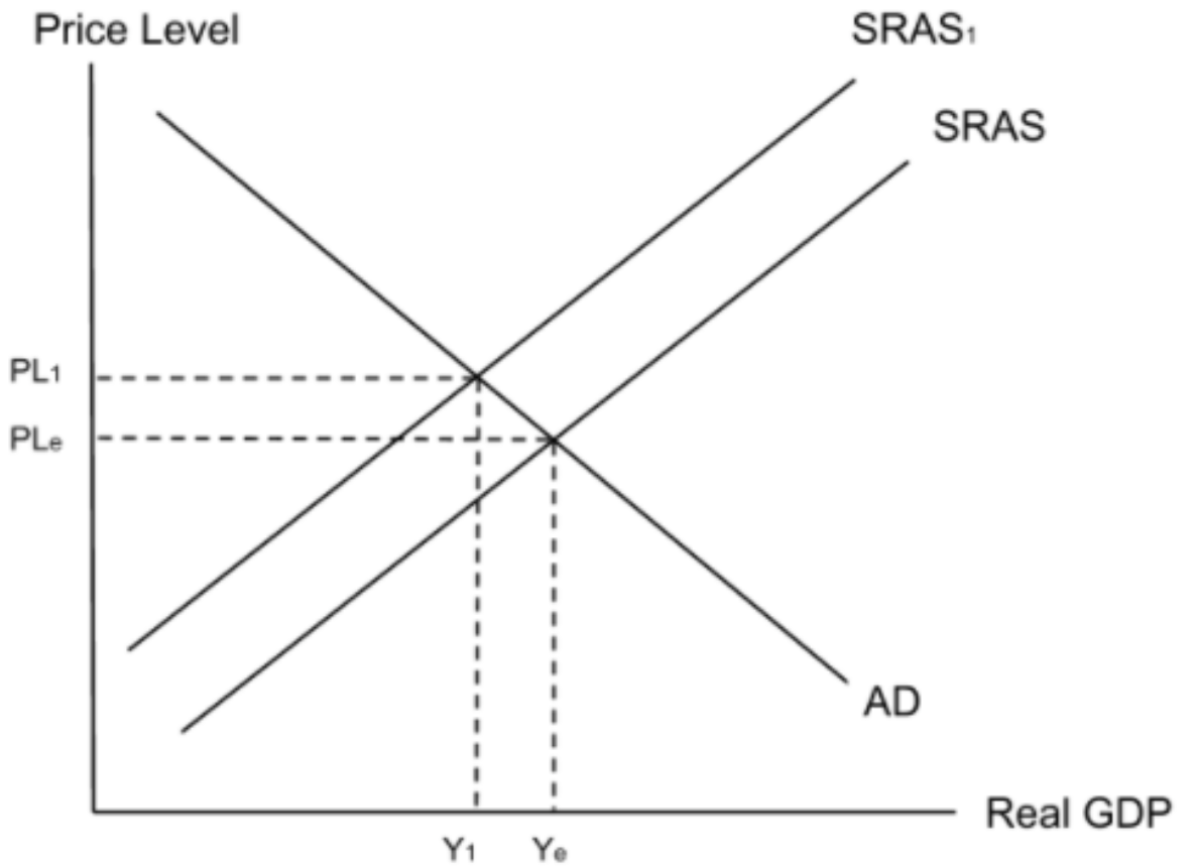
Poor infrastructure will make firms less productive as it takes workers longer to get everything done.This increases costs. Higher costs force firms to increase prices which makes them less competitive meaning people demand less of their products. This decreases their profits. As a result, the government will receive less corporation tax revenue meaning it has less money to spend on development. The chain of reasoning is:
Poor infrastructure → Increases costs → Shifts SRAS to the left →Increases prices → Decreases competitiveness → Less profit → Less corporation tax revenue → Less government spending on development.
Infrastructure: Impact of improved infrastructure on an economy
Improved infrastructure → Decreases costs → Right shift of SRAS → Decreases prices → Increases competitiveness → More profit → More corporation tax revenue → More government spending on development.
Improved infrastructure → Higher productivity → Shifts LRAS to the right → Increases real GDP → Increases economic growth
Infrastructure: How can a country promote FDI?
A country can promote FDI by either reducing corporation tax which means that firms can keep more of their profit
OR
by reducing wage costs which will enable firms to make more profit
Infrastructure: How much Foreign Direct Investment did Indian firms receive in 2015?
31 billion dollars
Infrastructure: Evaluation of FDI
However, promoting FDI may not lead to development. Reducing the minimum wage means that consumers will have lower income which will reduce income tax revenues and limit economic growth and development. Moreover, reducing corporation tax means that the government will receive less tax revenue which means that they have less money to spend on development.
Poor Health: Reasons for poor health in developing countries
poor healthcare and poor sex education.
Poor Health: example of poor health in Kenya
As of 2025, over 1.3 million people in Kenya are HIV positive
Poor Health: immediate impact of a reduction in workers’ productivity?
Poor health → Low productivity → Keeps LRAS to the left → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Poor health → Low productivity → Increases costs → Less profit → Less corporation tax revenue → Less government spending on development.
Poor Health: immediate impact of a reduction in workers’ productivity?
Poor health → Low human capital → Low productivity → Low incomes →Less income tax revenue → Less government spending on development →Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Poor health → Low human capital → Low productivity → Keeps LRAS to the left → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Poor Health: What is the impact of an improvement in health from things like foreign aid?
Improved health → Higher productivity → Shifts LRAS to the right →Increases real GDP → Increases economic development
Improved health → Higher productivity → Decreases costs → More profit → More corporation tax revenue → More government spending on development.
mproved health → More children in school → Higher human capital →Higher productivity → Shifts LRAS to the right → Increases real GDP →Increases economic development
Improved health → More children in school → Higher human capital →Higher productivity → Higher incomes → More income tax revenue → More government spending on development → Increases real GDP → Increases economic development
Poor Health: evaluation of aid
Aid may not lead to growth and development if the money ends up being spent by corrupt government officials rather than being spent on areas that will have a positive impact such as health/education/infrastructure/development.
Population growth: How is it negative?
Parents stay at home to look after even more children, so they can’t develop their career, which means that they often end up earning low incomes.
Schools and hospitals can become overrun. This starts to reduce the quality of education, which can lower human capital and reduce productivity.
Population growth: Negative impact
Low human capital → Low productivity → Keeps LRAS to the left → Limits real GDP → Limits economic growth
Low human capital → Low productivity → Low incomes → Less income tax revenue → Less government spending on development → Limits real GDP → Limits economic development
Population growth: Improvement in education impact
Improved education → Higher human capital → Higher productivity → Higher incomes → Decrease birth rate (as more women become career focused) → Higher quality education → Increases economic development
mproved sex education → Decrease birth rate → More time to focus on education/career → Increases incomes → Increases economic development
Population growth: Improvement of education evaluation
Some religions can teach that contraception shouldn’t be used. This can contribute to higher levels of population growth even after education has improved.
Population growth: What is the savings gap?
A savings gap is when there is a gap between the amount of money held at banks, in the form of savings, and the amount of money that firms want to borrow from banks.
Population growth: What are the two main reasons for low savings?
Low income- many people in developing countries don’t earn enough to have money left to save
Limited access to banks which are often far away and not always seen as secure
Savings gaps: What are the two main reasons for low savings?
low incomes - many people in developing countries don’t earn enough to have money left to save.
low access to banks - they are often far away and not always seen as secure.
Savings gaps: What is a savings gap?
A savings gap is when there is a gap between the amount of money held at banks, in the form of savings, and the amount of money that firms want to borrow from banks.
What does a large savings gap mean for firms?
banks will not have enough money to lend to firms who want to borrow money.
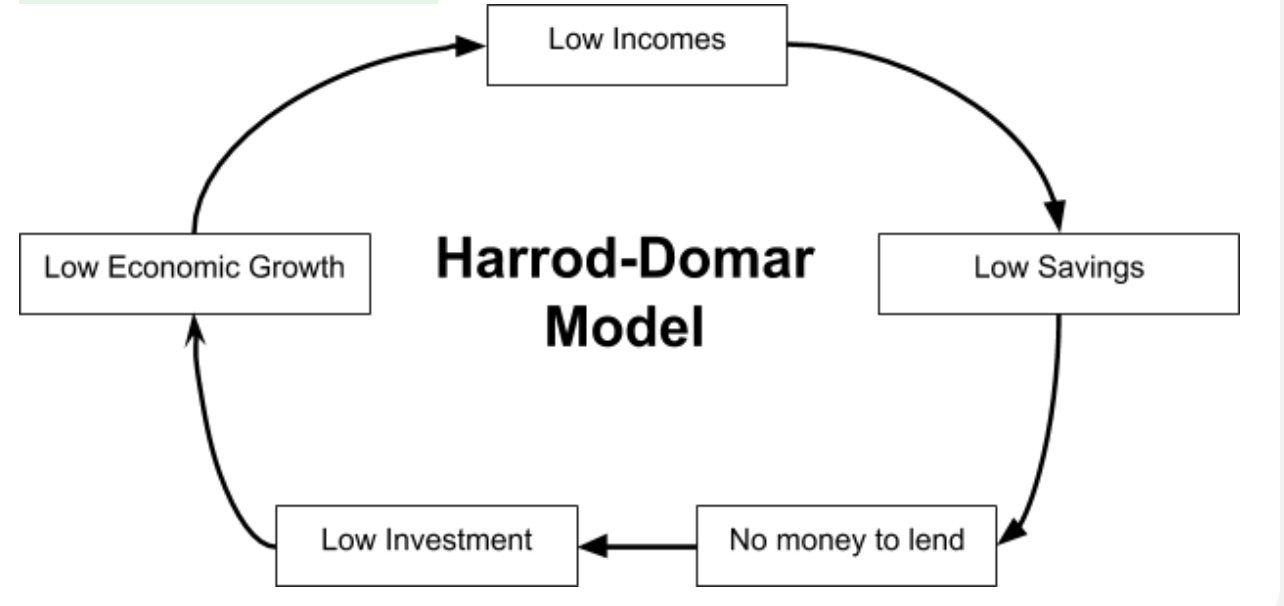
Savings gaps: What is the Harrod dormer model?
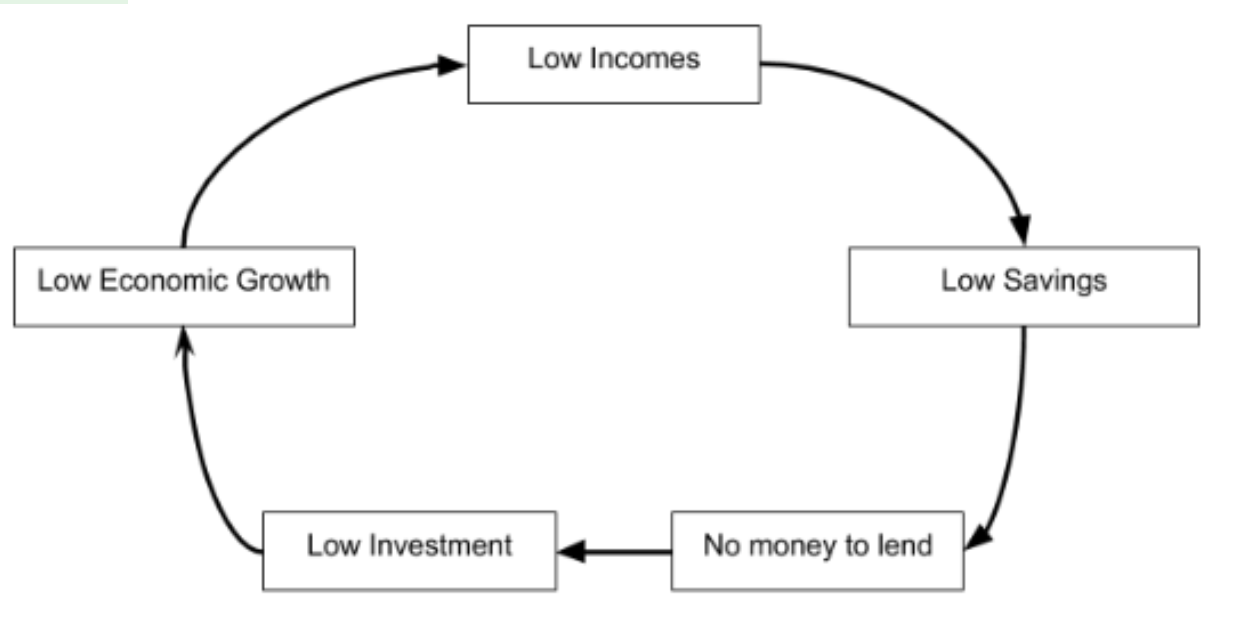
A model to explain how low savings make it difficult for firms to be able to invest which limits economic growth.
Low incomes → Low savings → No money in the bank to lend → Low investment → Low AD and low LRAS → Low economic growth → Low incomes
Savings gaps: Microfinance
Small loans provided to small businesses who otherwise would have no access to financial services
Savings gaps: impact of micro finance
When people use microfinance loans to invest into their small businesses, their productivity increases. This reduces their costs and means they can charge lower prices which makes them more competitive meaning they will earn more in profits and income.
If incomes are higher then savings will be higher as people have more sparemoney to save after they have bought all the necessities.
Savings will increase and so the savings gap will begin to decrease as the bank has more money available to lend out to firms wishing to invest.
The savings gap will begin to decrease as the bank has more money available to lend out to firms wishing to invest. This in turn means that banks lend out more money which leads to an increase in investment.
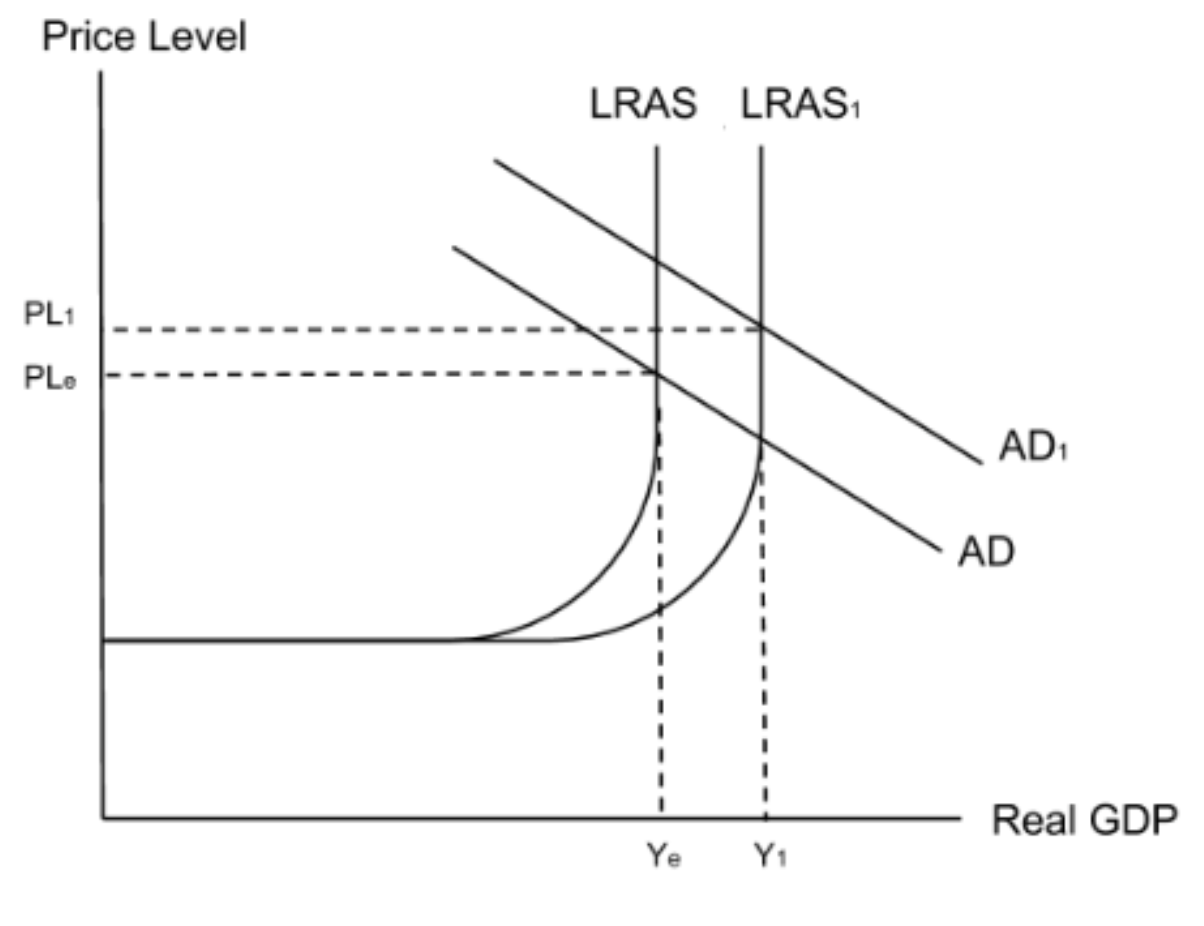
High levels of investment will shift AD to the right as investment is a component of AD.
High levels of investment will also shift LRAS to the right as high investment will increase productivity which increases the productive capacity of the economy.
Both an increase in AD and an increase in LRAS will increase economic growth and development. Moreover, as a firm invests it becomes more productivemeaning costs will decrease. The firm will then be in a position to lower the prices of its product, thereby making it more competitive. As a result, profits will increase and so will corporation tax revenues.
Savings gaps: Evaluation of micro financing
Microfinance lenders can often charge very high interest rate so borrowers have to pay back more, this means that if they do not start earning quickly they will not have any extra income.
With no extra income, they won’t be able to save money in the bank. This means that there will still be a savings gap and that firms won’t be able to borrow more money. As a result, investment will stay low. Since investment is a component of aggregate demand, this means that economic development will stay limited.
If people can’t pay back their loans they may go bankrupt which means that they would have to sell off their business and become unemployed. As a result, they will have lower incomes and the harried dormer theory occurs.
Property rights: What are they?
give people legal rights over their own property meaning they can go to court if their property is stolen.
Property rights: What are possessions without property rights are called?
dead capital
Property rights: Dead capital can not be used as:
Collateral is an asset that the bank requires if you take out a loan. It is used to ensure that the bank is not out of pocket if you don’t pay back the loan, in which case they will take ownership of the asset. If you do not have the property rightsto this asset then it is dead capital and can’t be used as collateral. If the bank can’t take ownership of it (as you don’t own it) it is of no use to them.
Property rights: impact of giving people property rights
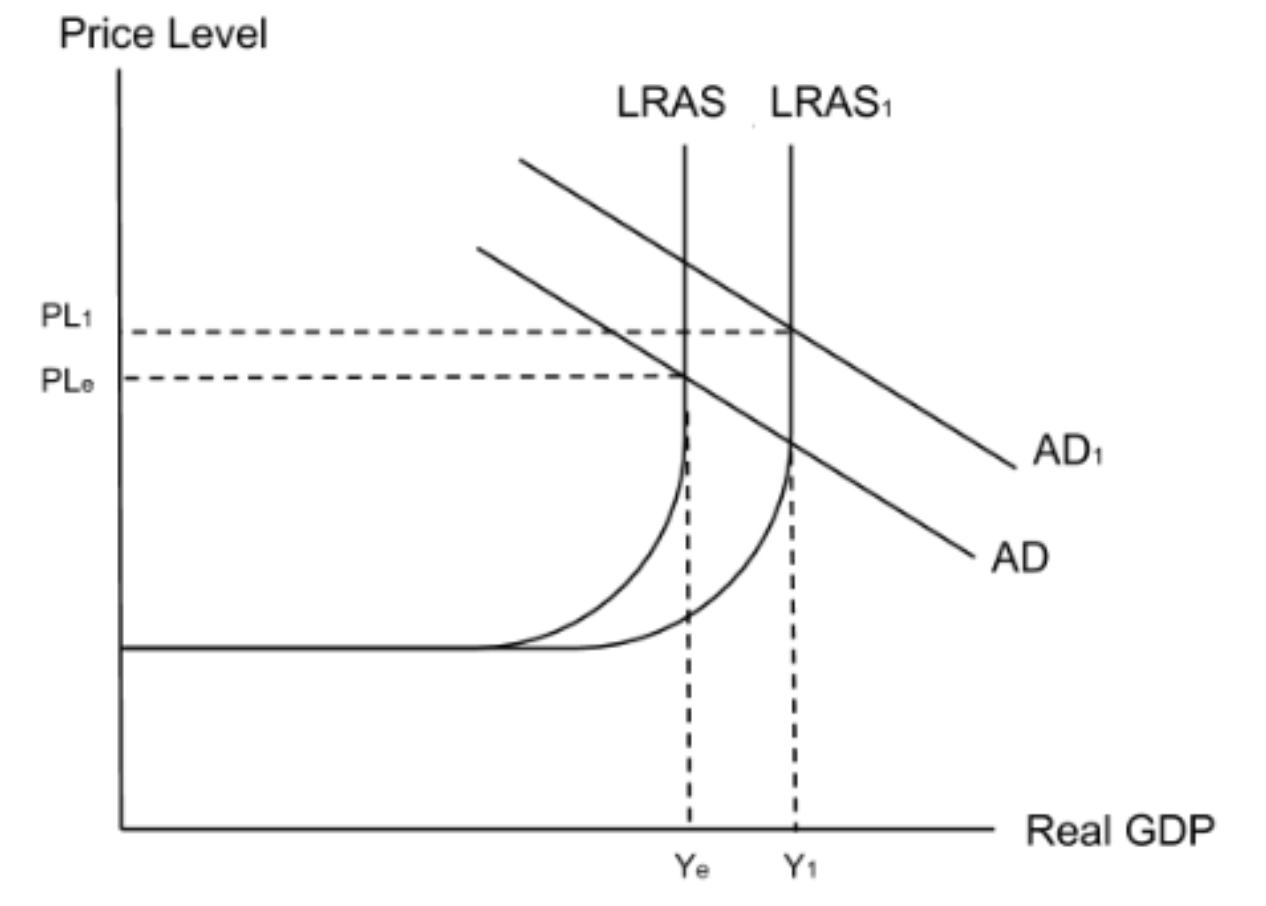
Increase investment → Increase AD → Increase economic growth → Increase economic development
Increase investment → Increase productivity → Right shift of LRAS → Increase economic growth → Increase economic development
Increase investment → Higher incomes → More income tax revenue → More government spending on development
Property rights: studies in Argentina and Peru have found that
Poor people with property rights are no more likely to take out loans
Corruption: What is it?
Corruption is when people working for the government use public funds for their own private expenses.
Corruption: fair trade schemes
When you buy fair trade products, part of the fair trade price you pay goes directly to the producers and so it increases their incomes.
Corruption: Fair Trade Premium
A communal fund that fair trade farmers can spend on whatever will develop their communities the most.
Corruption: Impact of fair trade schemes
Money goes straight to farmers → Increases their incomes → Increases consumption → Increases AD → Increases economic growth
Money goes straight to farmers → Increases their incomes → Increases income tax revenue → Increases government spending on development → Increases economic development
Corruption: Evaluation of fair trade schemes
Less money goes straight to farmers → Less increase in their incomes → Less increase in consumption → Less increase in AD → Limited economic development
Less money goes straight to farmers → Less increase in their incomes → Less increase in income tax revenue → Less increase in government spending on development → Limited economic development
Landlocked: What does being landlocked mean?
Countries are landlocked if they are surrounded by other countries - they have no coasts.
Landlocked: negative impact
increasing shipping costs- estimated 2x more expensive then non landlocked countries
Being landlocked means that the country is surrounded by other countriesand has no coast. This will Increase shipping costs. High costs will force firms to keep prices high which will make them less competitive meaning people will demand less of their products and profit will decrease. A decrease in profit will then mean the government collects less corporation tax and has less money to spend on development.
The chain of reasoning is:
Landlocked → Increases costs → Left shift of SRAS → Increases prices → Decreases competitiveness → Less profit → Less corporation tax revenue → Less government spending on development → Limits development
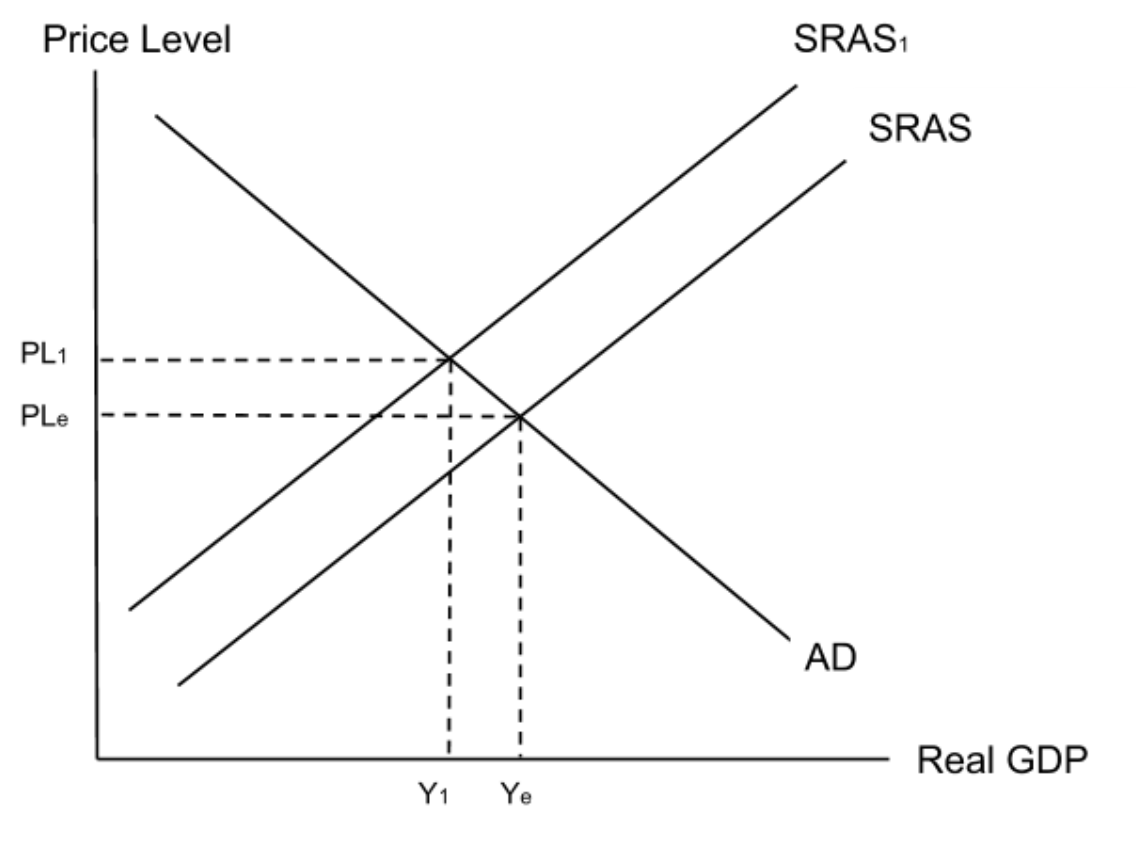
Landlocked: What is debt relief?
someone who has borrowed money no longer have to pay it back.
HOWEVER, corrupt officials may not spend this money on development
Infant industries: What are they?
Industries that are too small to benefit from economies of scale.
Infant industries: What is the impact?
High costs will force firms to keep prices high, which will make them less competitive, meaning people will demand less of their products and profit will decrease. A decrease in profit will then mean the government collects less corporation tax and has less money to spend on development.
The chain of reasoning is:
Infant industry → Low output → High average costs → Left shift of SRAS → Increases prices → Decreases competitiveness → Less profit → Less corporation tax revenue → Less government spending on development → Limits development
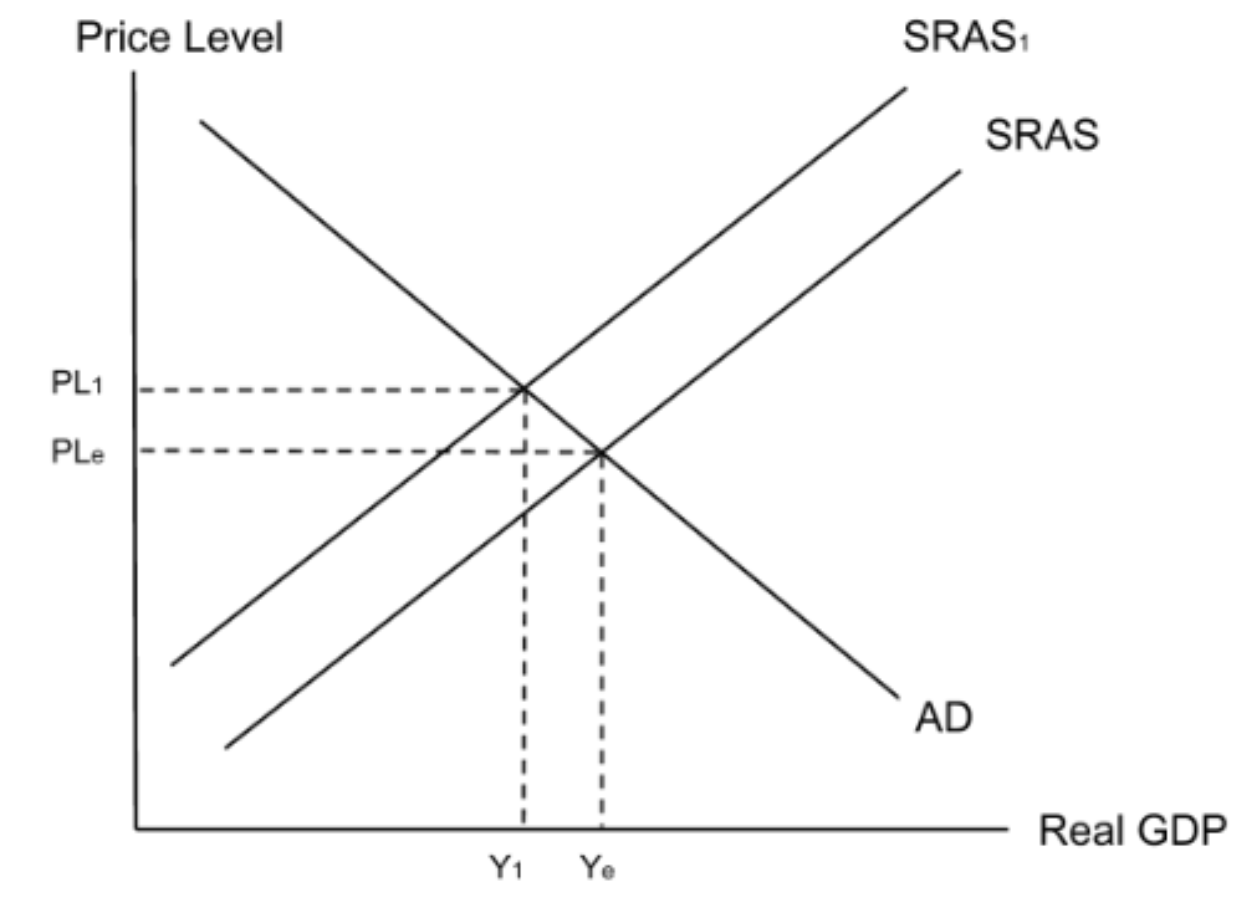
Infant industries: impact of protectionism on infant industries
Right shift of SRAS → Decreases price level → Increases competitiveness → More profit → More corporation tax revenue → More government spending on development → More development
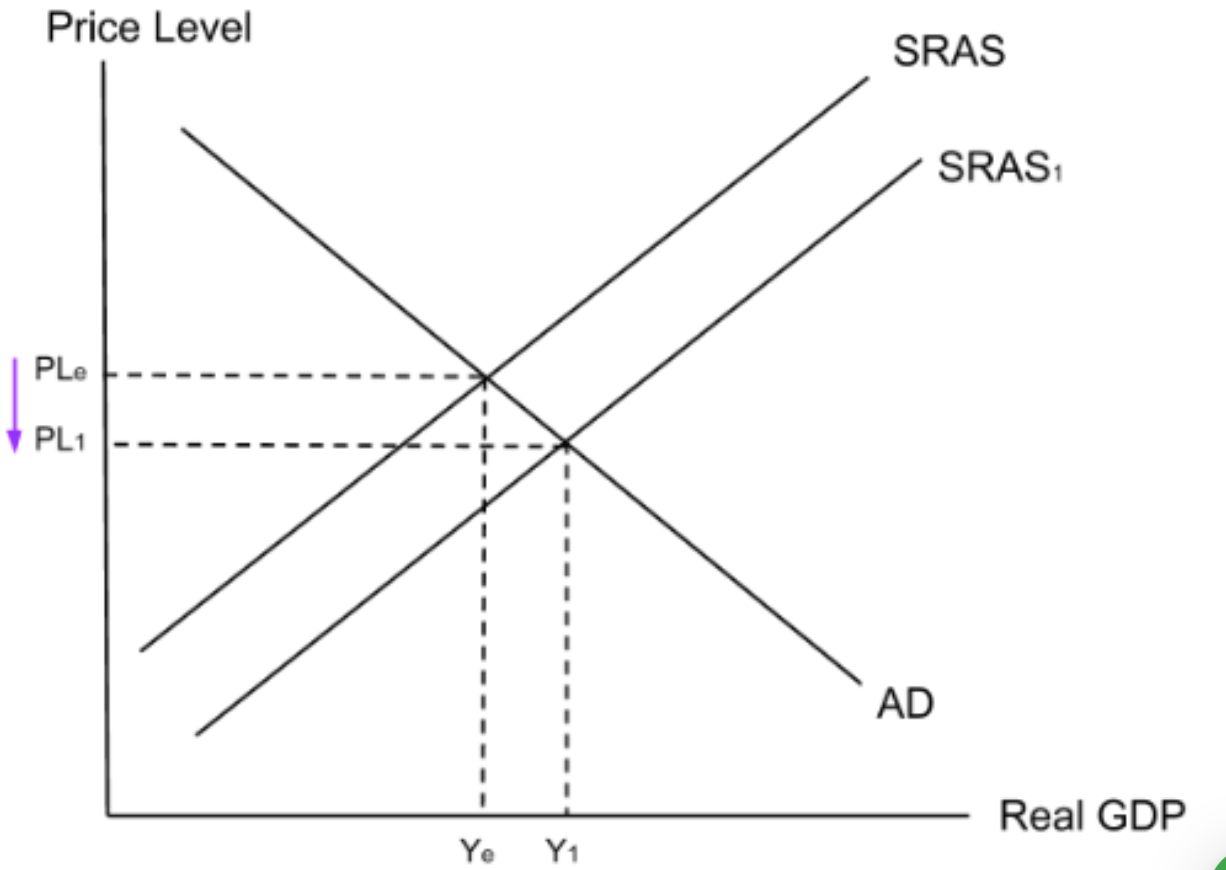
Infant industries: Why may protectionism like subsidies not result in development?
can create a culture where businesses become overly dependent on government support, which can mean that they become inefficient.
Infant industries: Competitive devaluation
A competitive devaluation is when you devalue your fixed exchange rate in order to keep your exports competitive.
through decreasing interest rates or selling domestic currency.
Infant industries: impact of competitive devaluation
Once a country has devalued their exchange rate, their exports will become cheaper and more competitive. This makes it easier for infant industries to compete with larger industries and so infant industries make more profits. They can use this profit to invest, which will eventually lower their own costs and cause the SRAS to shift to the right.
Infant industries: What are the two effects of an outward shift of a country’s short run aggregate supply curve?
Right shift of SRAS → Decreases price level → Increases competitiveness → More profit → More corporation tax revenue → More government spending on development → More development
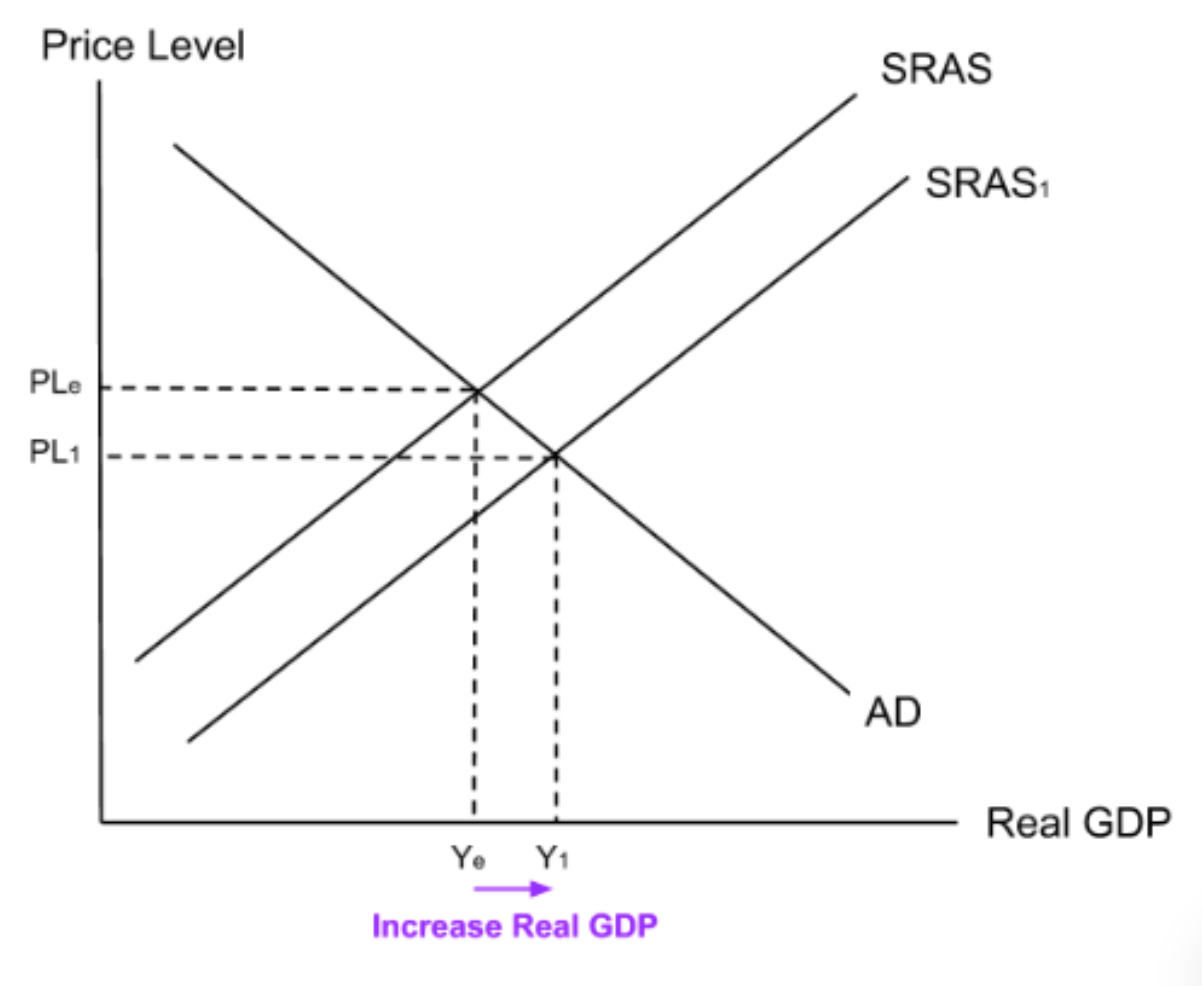
Infant industries: Evaluation of devaluation
May lead to a currency war causing imports to become extremely expensive
Foreign currency gap: What is it?
When the amount of foreign currency in a country decreases. When net imports exceed exports.
What does a foeign currency gap lead to?
A depreciation- makes imports more expensive causing cost such inflation