Week 2: Intro to macroeconomics and circular flow
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
microeconomics
the study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets

macroeconomics
the study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth

the goal of macroeconomics
to explain the economic changes that affect many households, firms, and markets simultaneously
the circular-flow diagram
a simplified representation of the macroeconomy
a visual model that shows connections between different sectors of our economic system
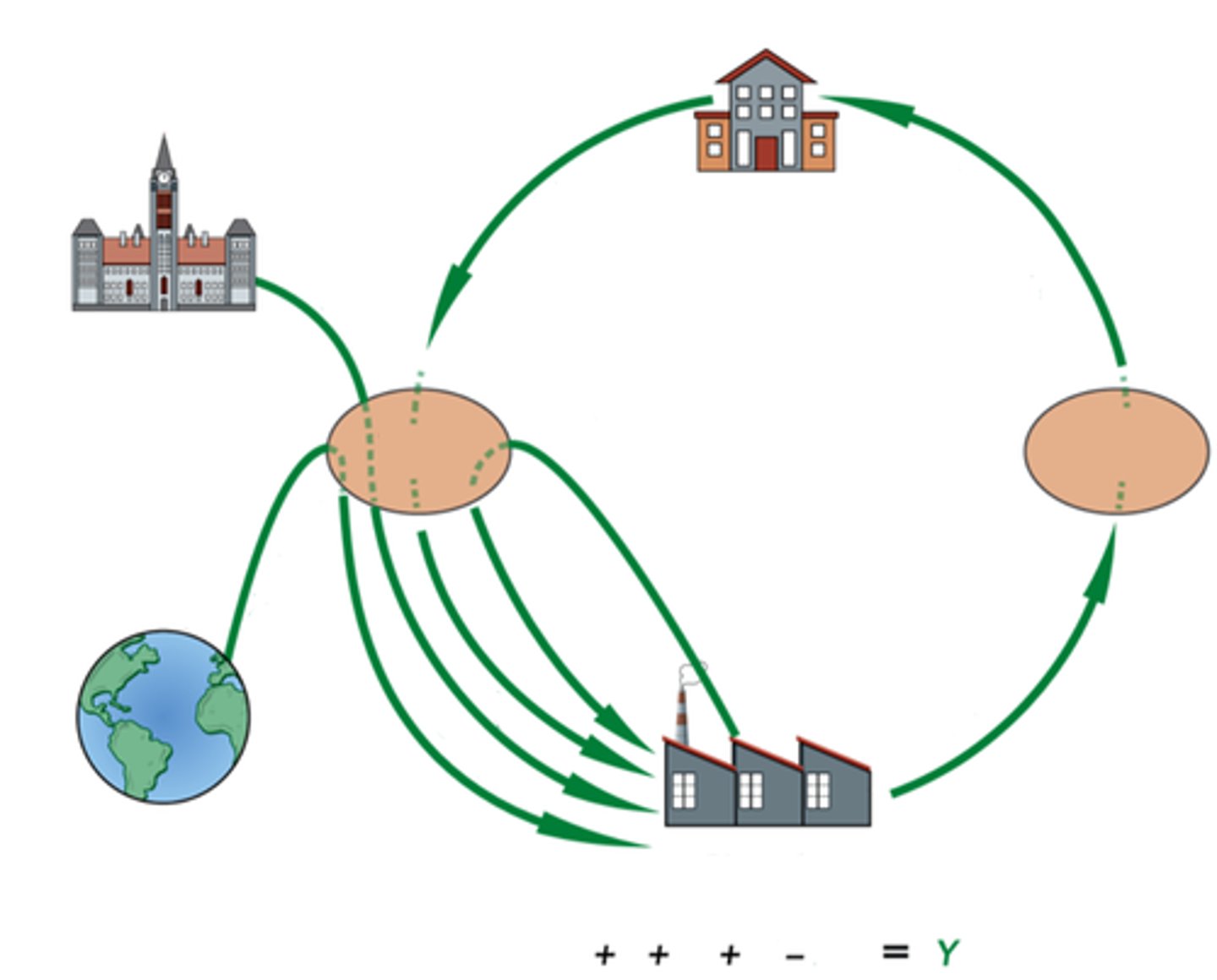
Product markets
markets where goods and services are bought and sold
Factor markets
markets where resources, especially capital and labour, are bought and sold
Consumer spending (C)
household spending on new (not used) goods and services from domestic and foreign firms. Usually make up over two-thirds of GDP spending.
Investment spending (I)
spending by firms on new productive physical capital, such as machinery, factories, equipment, tools, construction of new buildings*, and on changes in inventories
*it also includes expenditure on new homes by households
Taxes
required payments to the government
Tax revenue
the total amount of funds the government receives from taxes
Disposable income
the total amount of household income available to spend on consumption
equal to income plus government transfers minus taxes
Government purchases (G)
Spending by all levels of government on goods and services, including spending on the military, schools, and highways.
Does not include spending on transfer payments, such as Social Security payments.
Government transfers
payments that the government makes to individuals without expecting a good or service in return, such as benefits
Exports (X)
Resources, goods, or services that are produced domestically but sold abroad.
Includes final goods and services and intermediate goods.
Imports (IM)
Goods or services produced abroad but sold domestically.
IM is an accounting variable that is subtracted with the intent of correcting for the value of spending already counted as C, I, or G but actually spent on imported goods.
Includes intermediate goods.
X-IM
The balance of trade: (Exports - Imports)
Components of GDP (formula)
Y = C + I + G + (X - M)
injection
defined as spending in the circular flow that does not start with consumers.
Government purchases (G), business investment spending (I), and exports (X) are injections
leakage
defined as spending that leaks out of (leaves) the circular flow through savings (S), net taxes (T), or imports (IM)
equilibrium level of real GDP (formula)
I + G + X = S + T + IM