AE2001 Fundamentals of ecology / 11 Predation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Predation
Interaction where one organism (predator) kills and consumes another (prey).
Regulates population size & shapes ecosystems.
True predator
Kills and consumes multiple prey over its lifetime.
Grazer
Consumes parts of many organisms without killing them, affecting plant growth and survival.
Example: cow feeding on grass
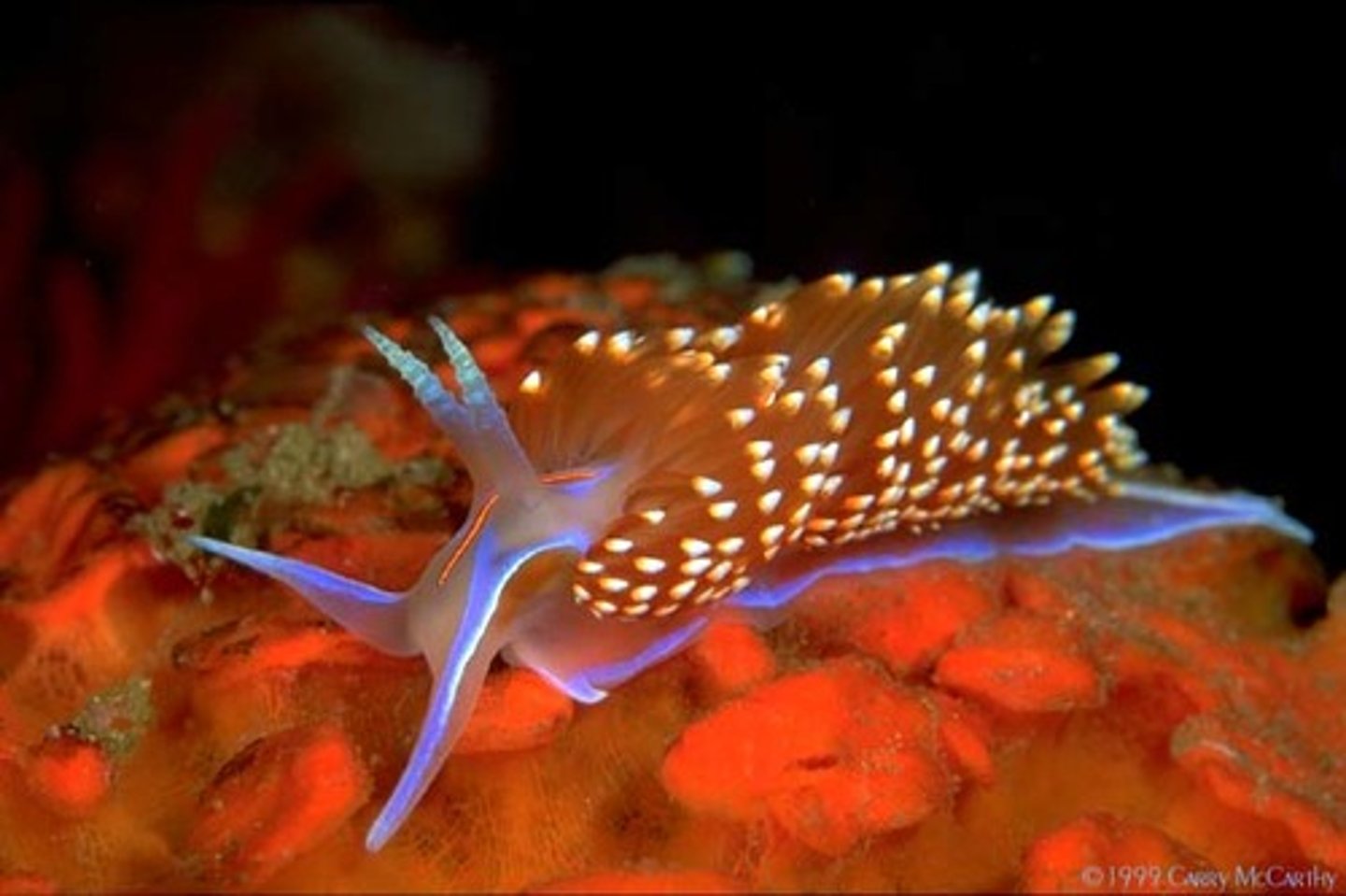

Parasite
Lives in or on a host, feeding slowly and weakening it without immediate lethality.
Example: tapeworm in intestines, louse on mammals
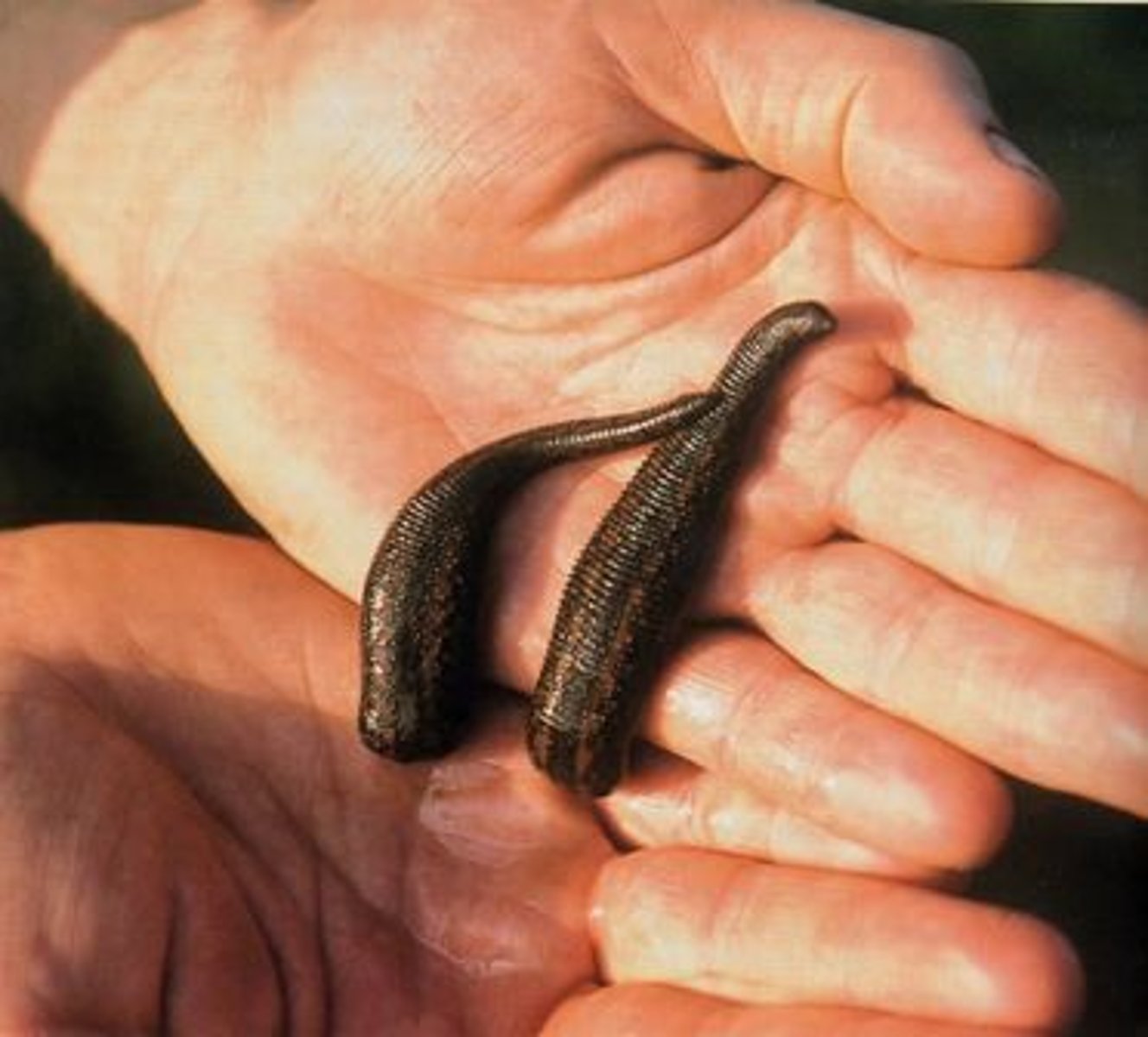

Parasitoid
Lays eggs inside or on a host, leading to its death when larvae develop and consume it from within.
Example: parasitic wasp targeting caterpillar
Trophic cascade
Chain reaction where a predator influences lower trophic levels by controlling prey population.
Example: wolf in Yellowstone reducing elk overgrazing
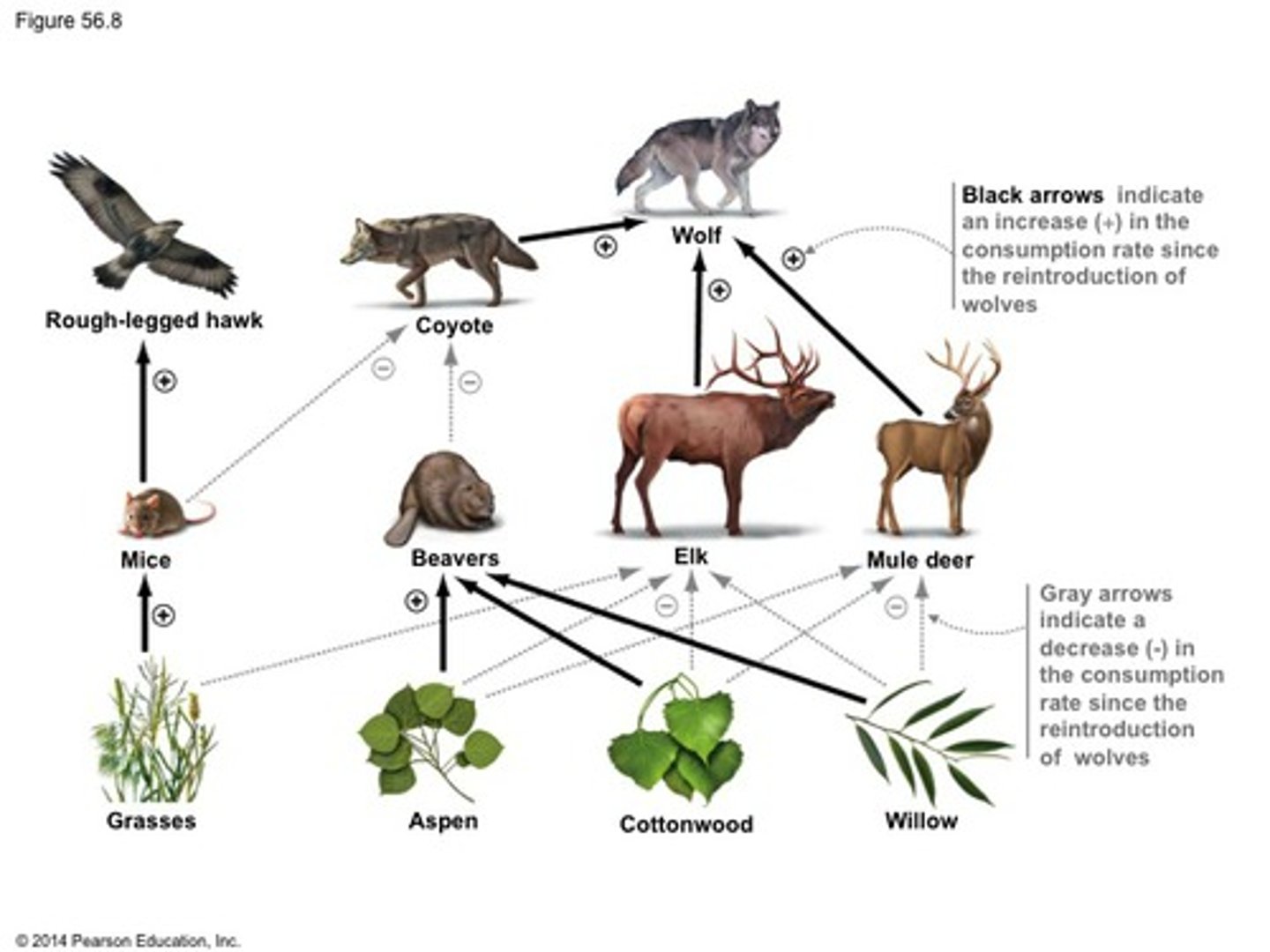
Top-down control
Predator regulates prey population, indirectly shaping vegetation and ecosystem stability.
Example: sea otter controlling sea urchin to protect kelp forests
Bottom-up control
Prey availability determines predator population size, impacting the food chain.
Example: fewer rabbits leading to a decline in fox population
Evolutionary arms race
Continuous adaptation between predator and prey, improving survival strategies.
Example: cheetah evolving speed to catch gazelle, gazelle developing agility to escape
Functional response
Change in a predator's feeding rate based on prey density.
Example: lynx consuming more hares when hare population increases
Numerical response
Change in predator population size based on prey availability.
Example: fox population increasing after boom in rodent numbers
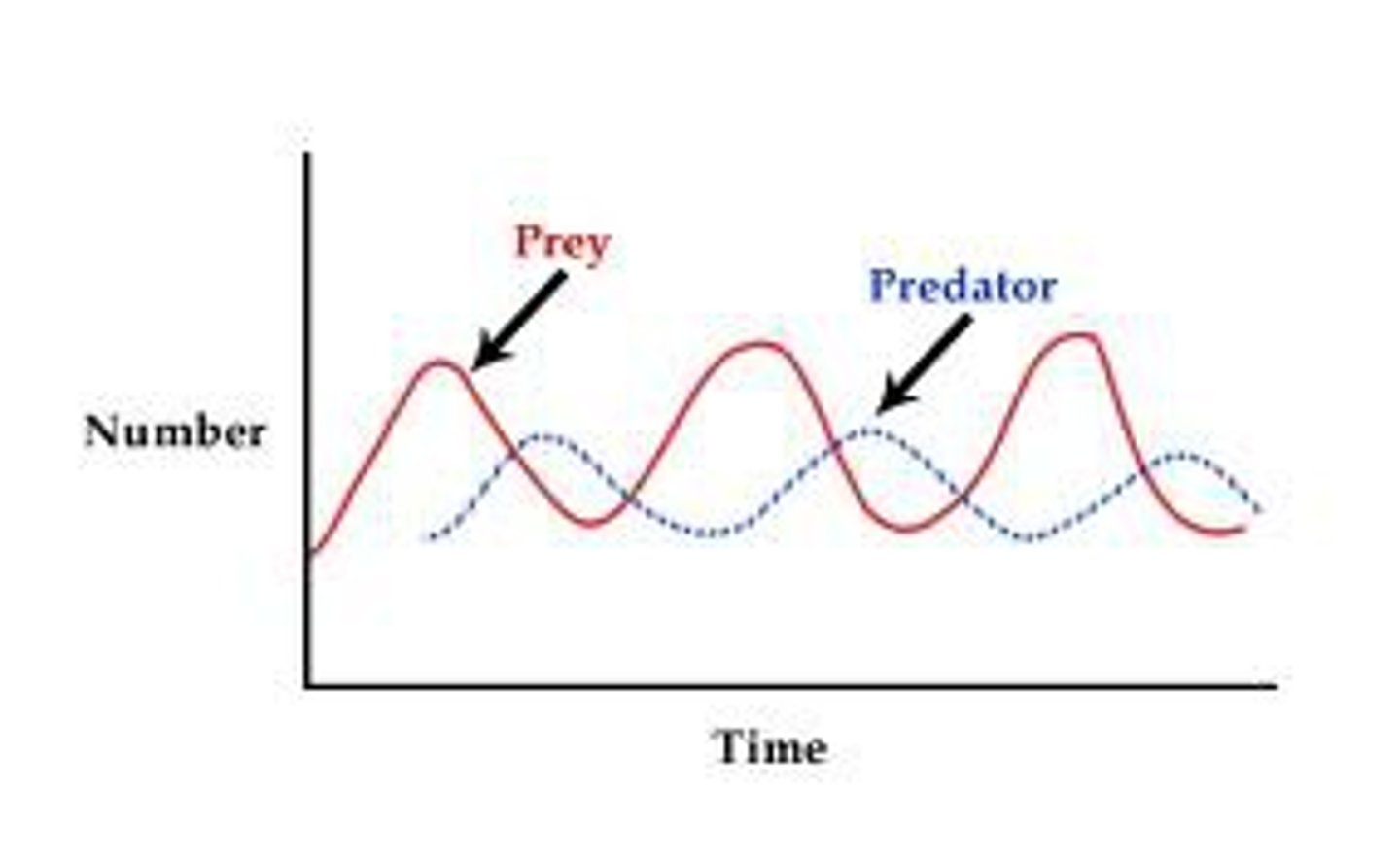
Lotka-Volterra model
Mathematical model describing cyclic predator-prey population fluctuations
Example: lynx and snowshoe hare populations rising and falling in predictable cycles
Optimal foraging theory
Predator maximises energy gain while minimising hunting effort.
Example: lion targeting weaker or slower prey to conserve energy
Sit-and-wait predator
Ambushes prey by remaining motionless until an opportunity arises.
Example: crocodile waiting near water edge.
Search-and-pursue predator
Actively hunts prey using speed, strategy, or teamwork.
(e.g., wolf hunting in a pack, cheetah sprinting to catch gazelle).
Specialist
Predator that focuses on one or a few prey species, often highly adapted.
Generalist
Predator that consumes a variety of prey, allows adaptation to changing food availability.
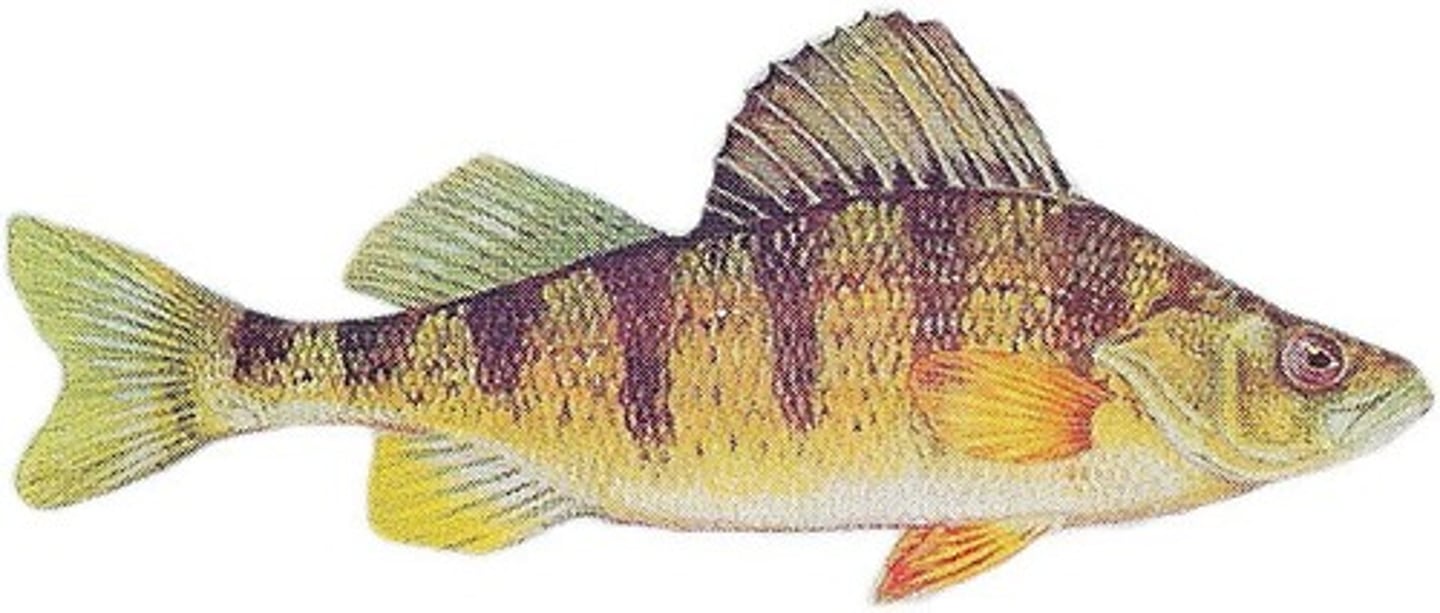
Introduced predator
Non-native predator disrupting an ecosystem by preying on species without natural defences.
Example: Nile perch in Lake Victoria leading to native fish extinctions

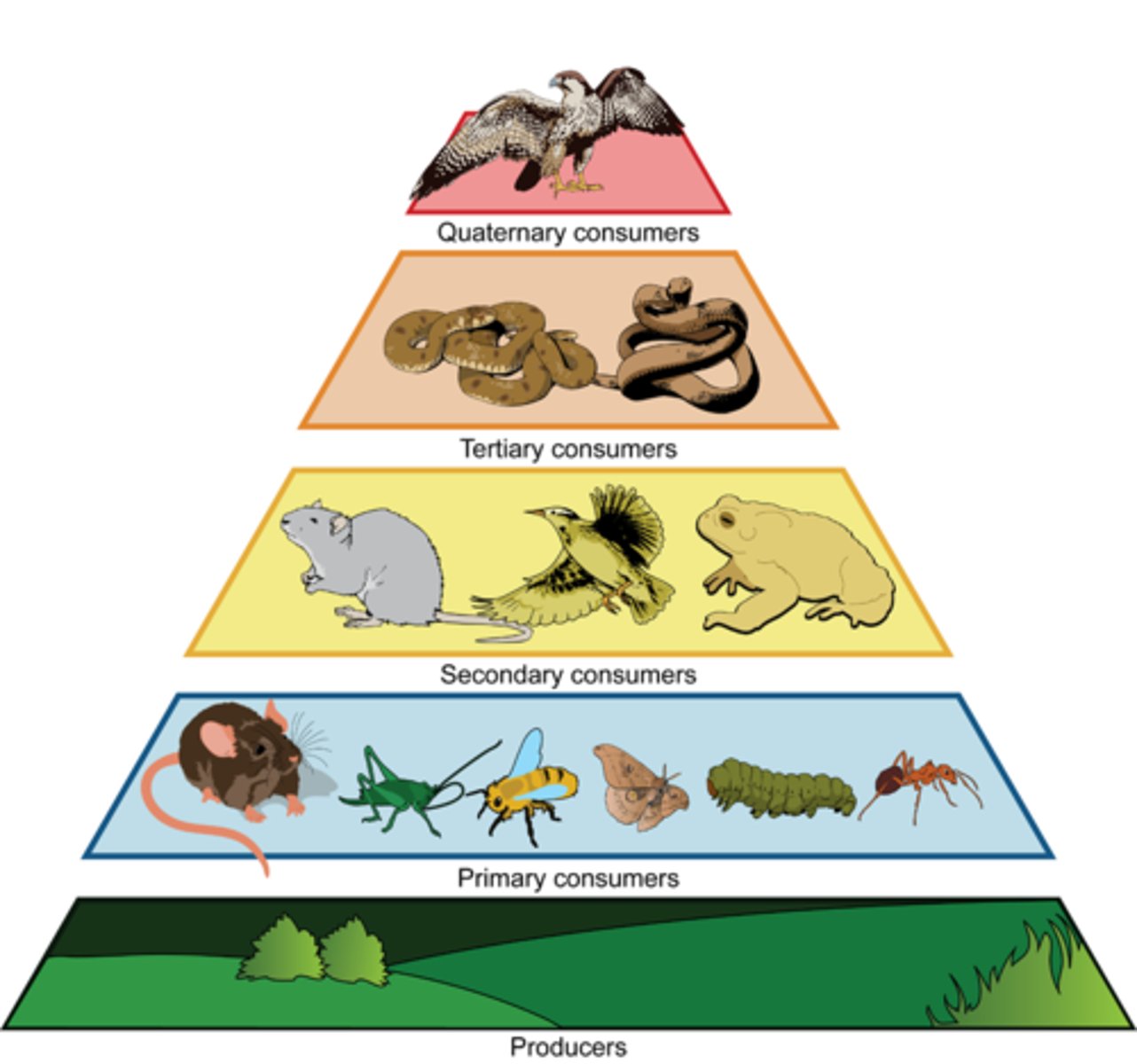
Trophic level
A stage in a food chain, from producers to top predators.
Example: plant → rabbit → fox
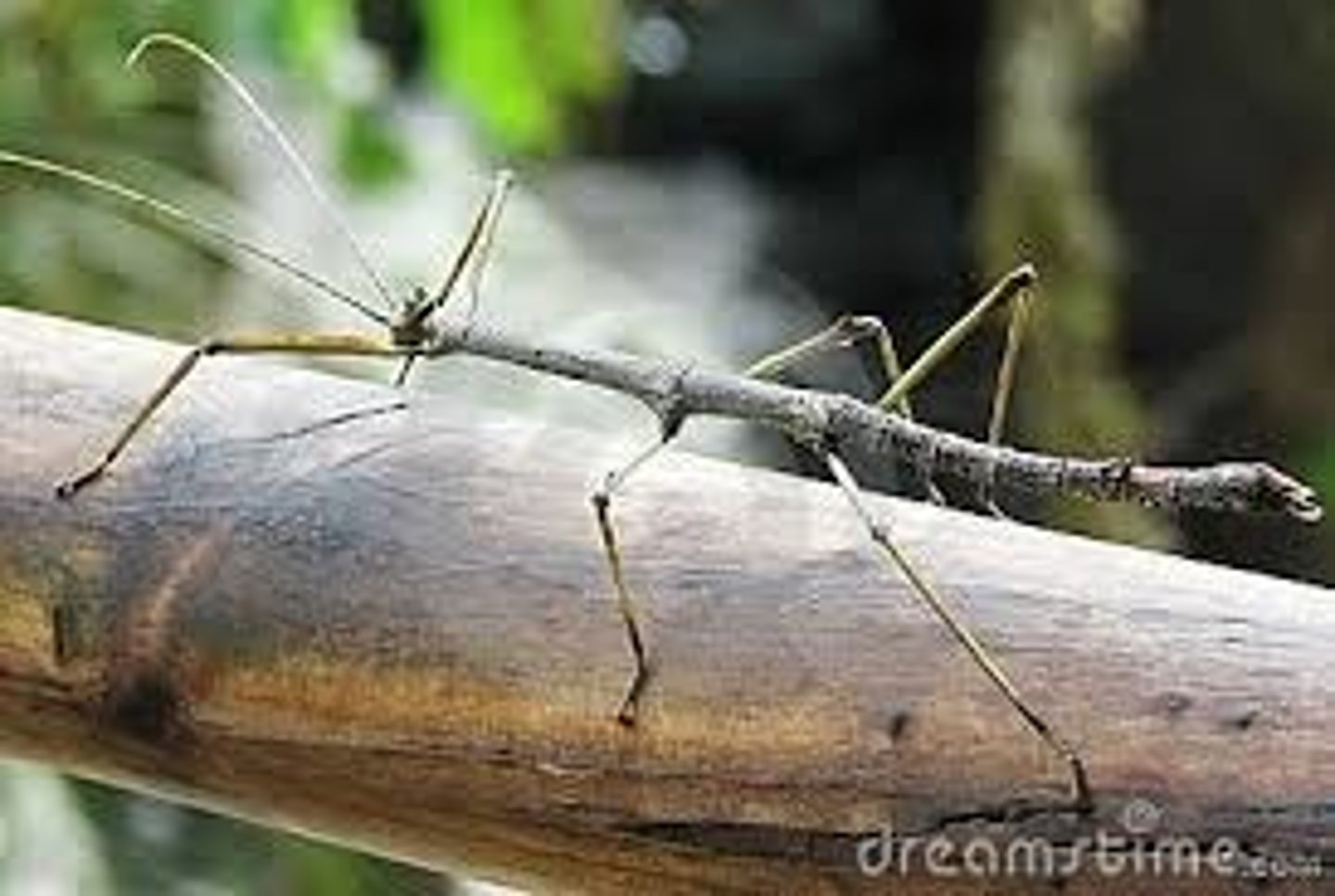
Crypsis
Camouflage to avoid detection by predator or prey.

Aposematism
Warning coloration signaling toxicity or danger to predators.
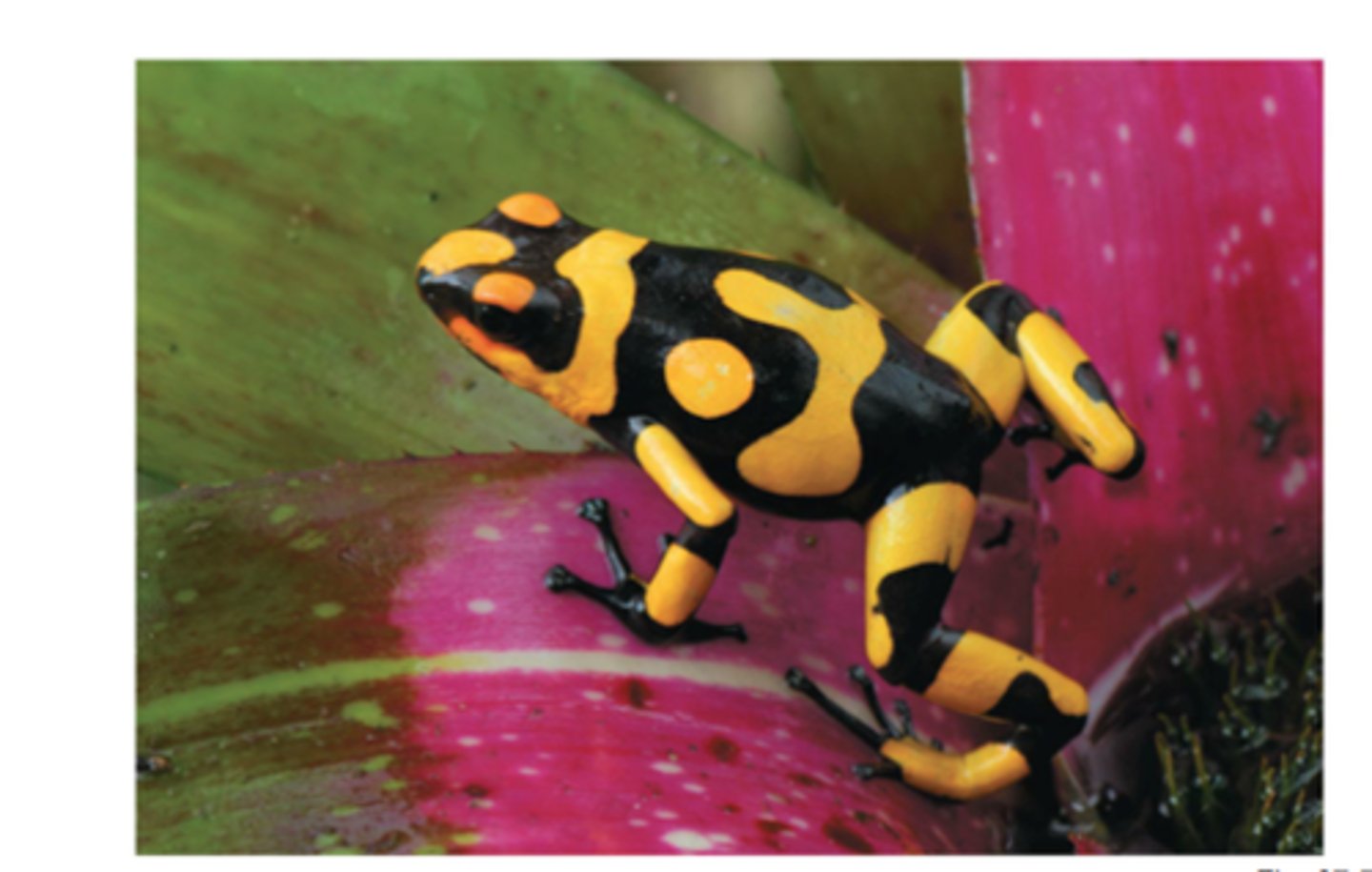

Mimicry
One species resembling another to gain protection.

Pike cannibalism
Ambush predators, consume prey nearly their own size, including other pike. (when resources are limited)

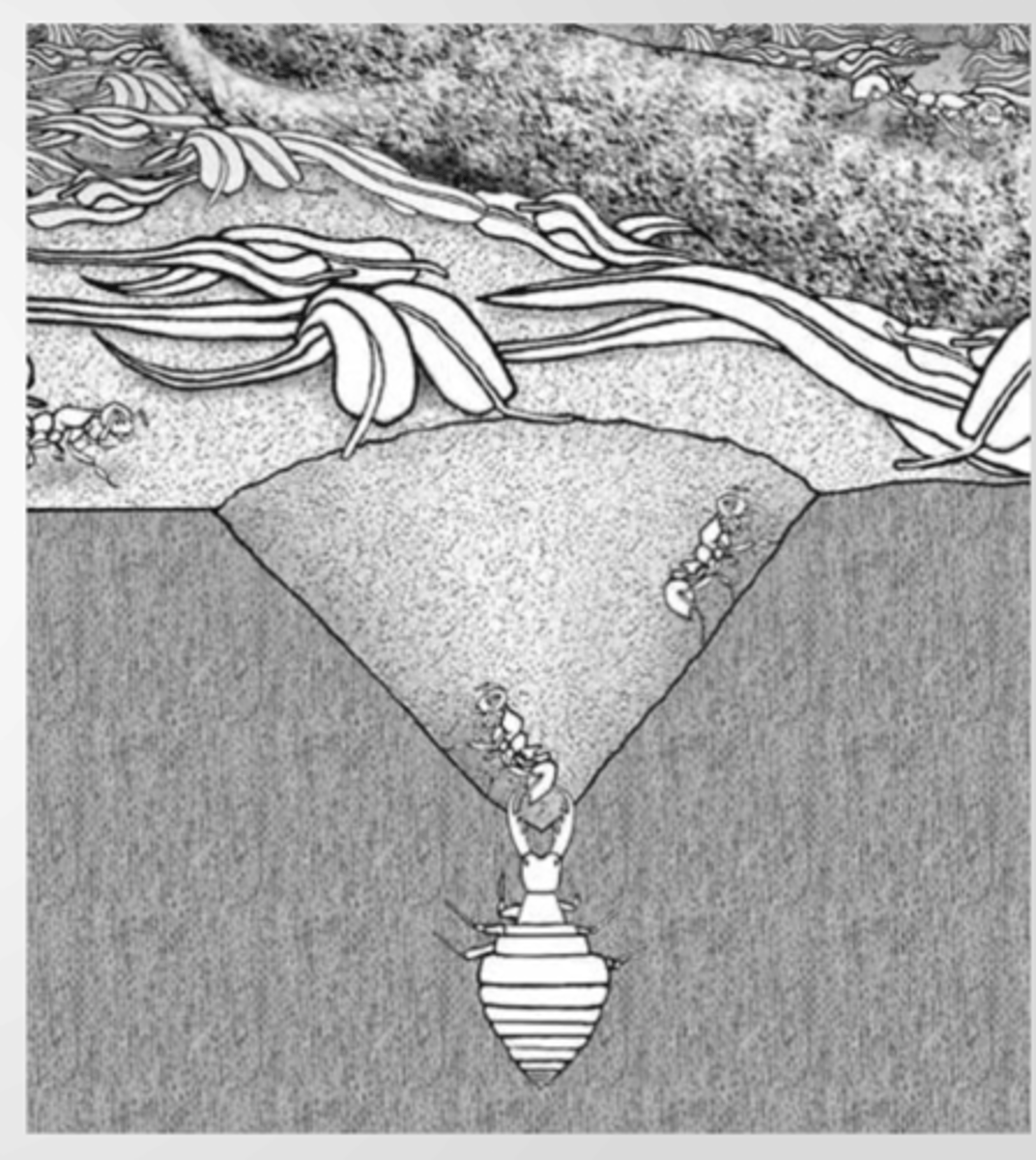
Antlion larvae
Sit-and-wait predators that dig sand pits to catch prey.
They wait for insects to fall into their traps and then consume them.
Sheep as predators
Sheep in Foula, Shetland, attack Arctic tern chicks due to a mineral deficiency.
Deficiency drives sheep to bite off the wings or legs of the chicks.
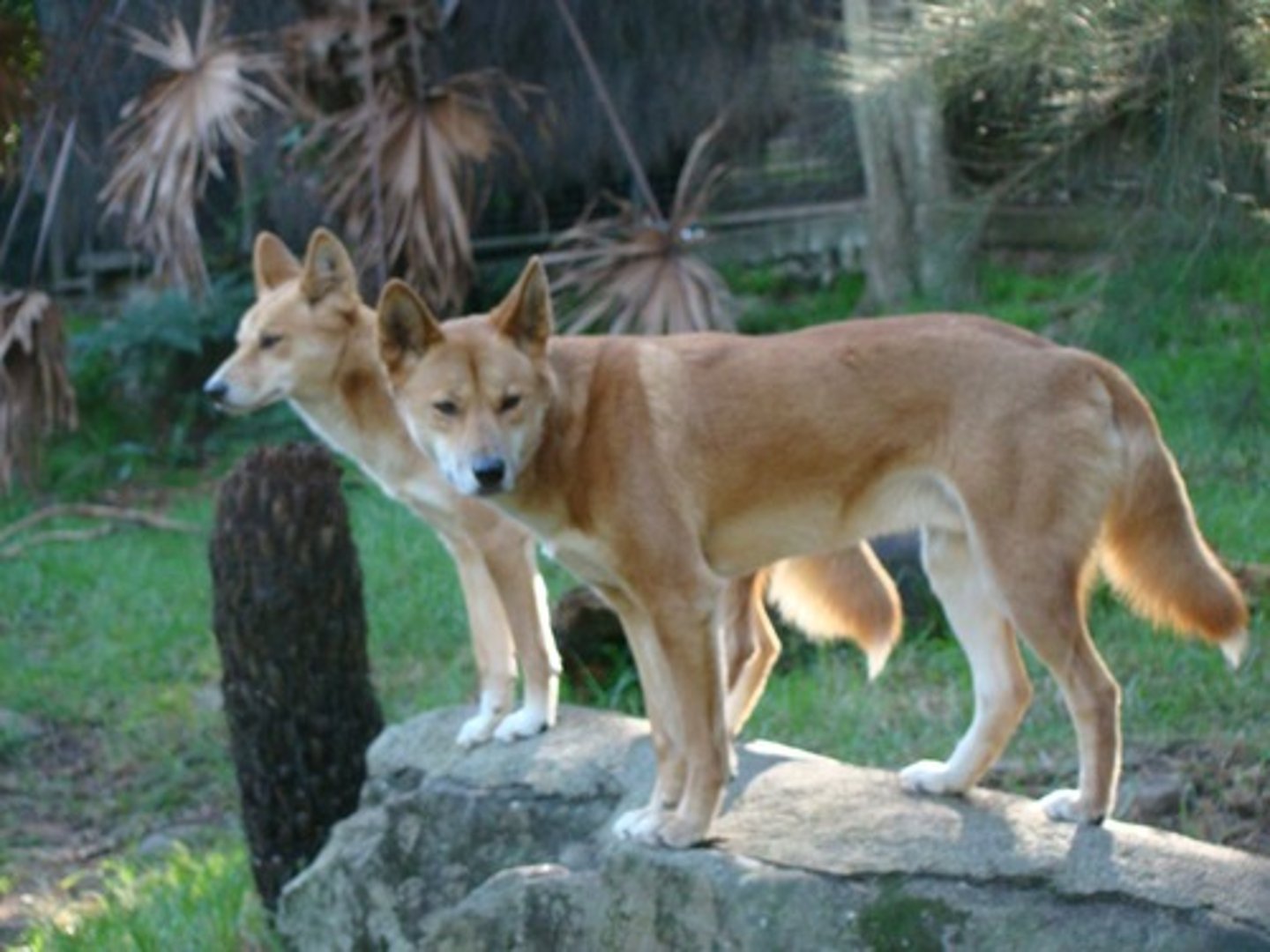
Dingoes & kangaroo control
Dingoes regulate kangaroo populations by hunting & predation.
In dingo-free zones, kangaroo populations grow uncontrollably.

Feral cats in Australia
Feral cats are a threat to biodiversity in Australia.
Dingoes help control feral cat populations, reduces impact on native species.

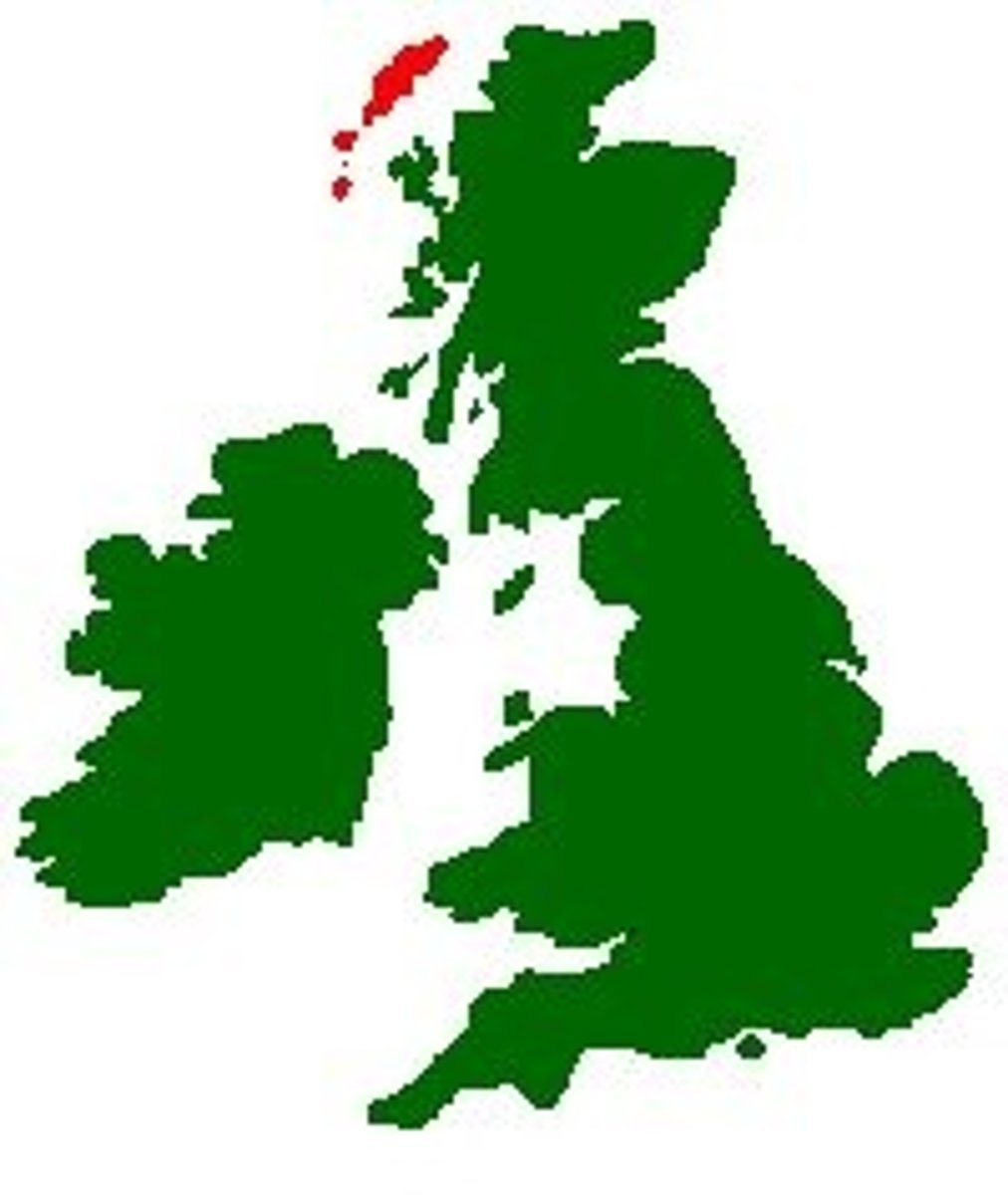
Hedgehogs in Outer Hebrides (Scotland)
Hedgehogs eat shorebird eggs = decline in bird populations.
Impact species like lapwings, redshanks, and dunlins.