BIOL 314 LAB WK 11, 13, & 14
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/184
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:22 AM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
1
New cards
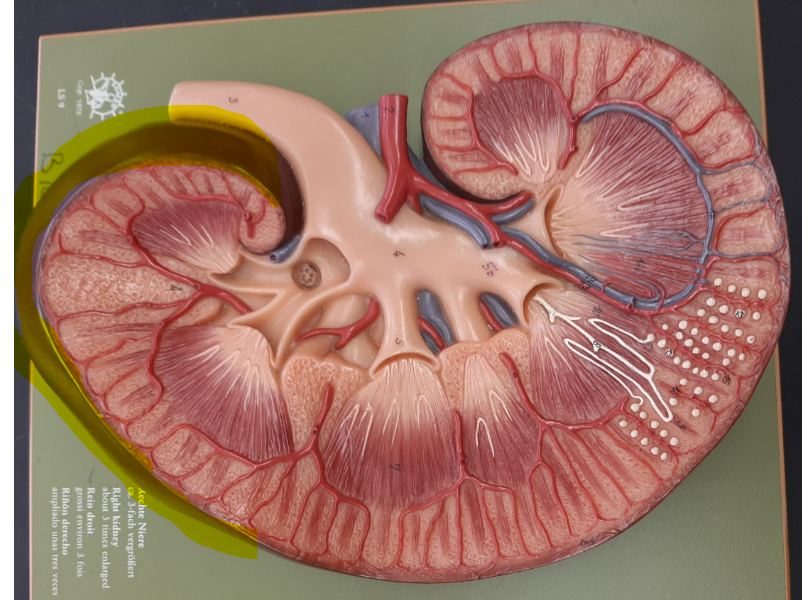
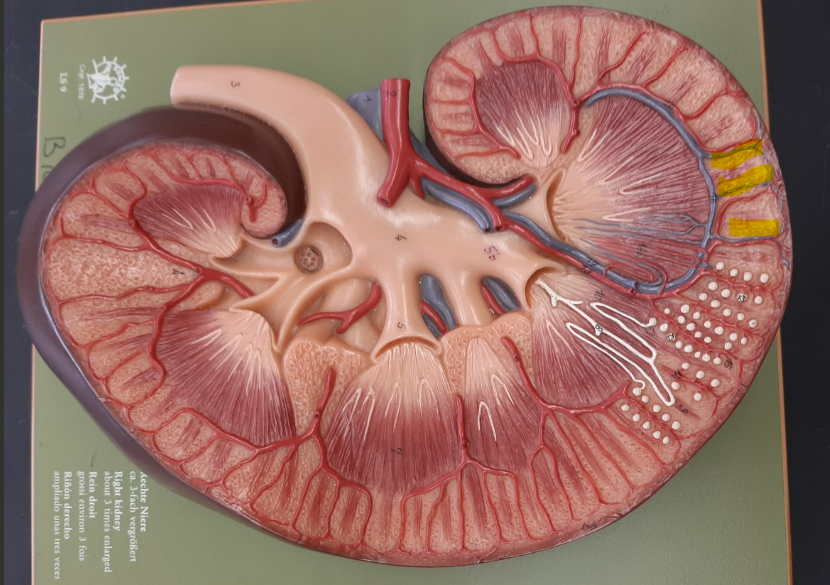
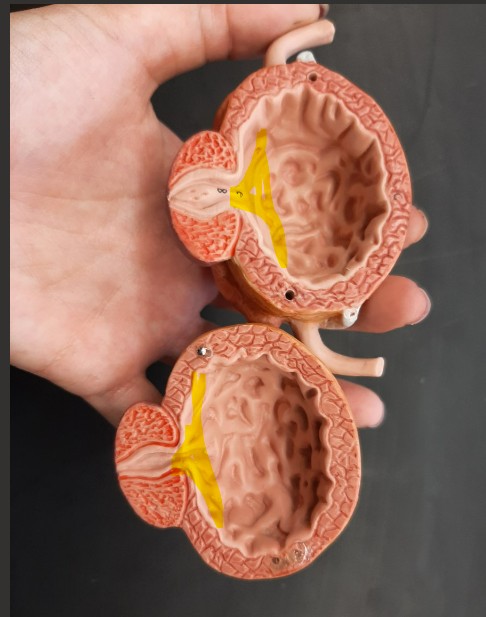
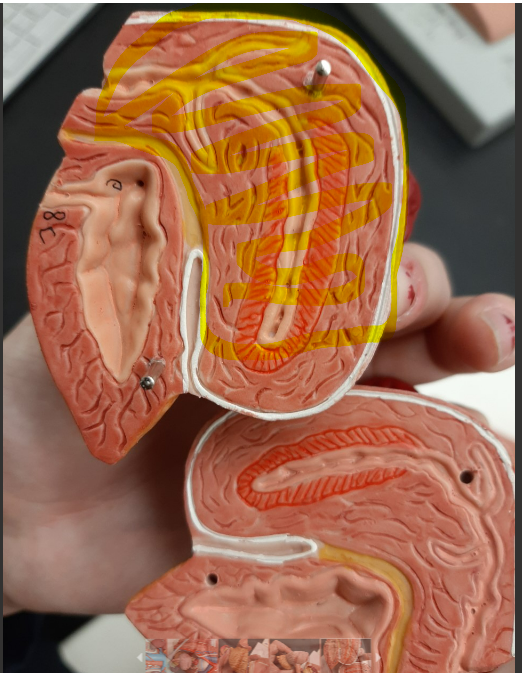
renal hilum
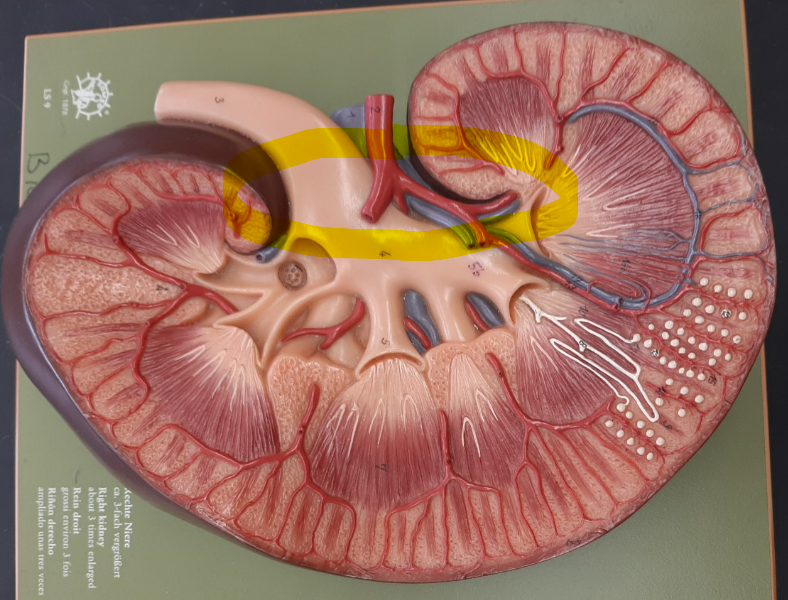
2
New cards
fibrous capsule
3
New cards
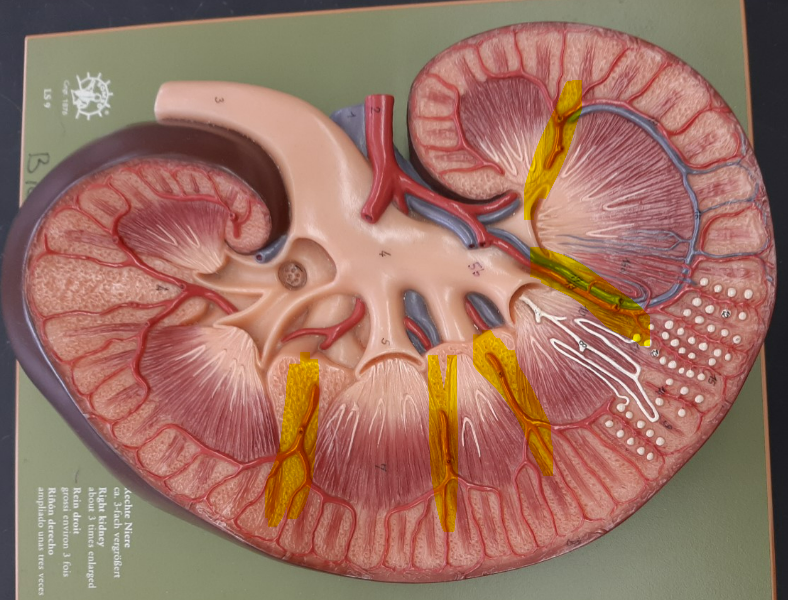
renal column
4
New cards
renal cortex
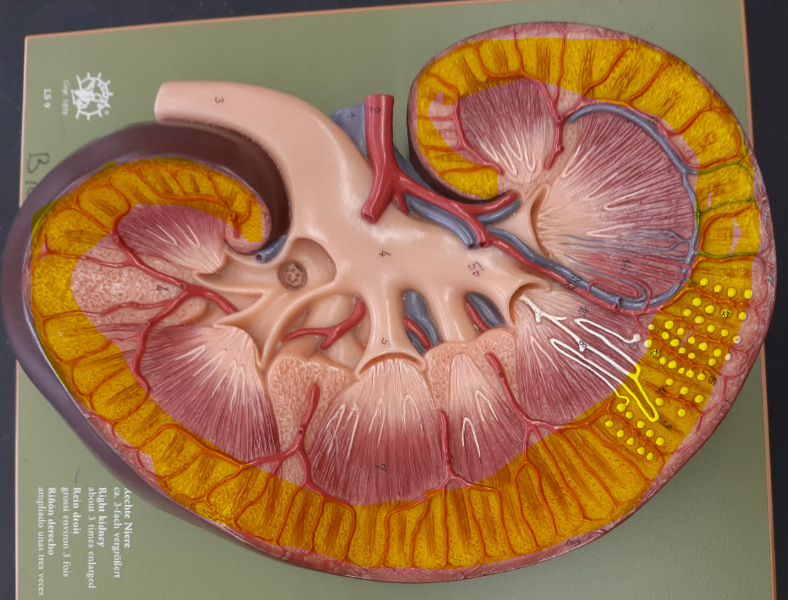
5
New cards
renal medulla
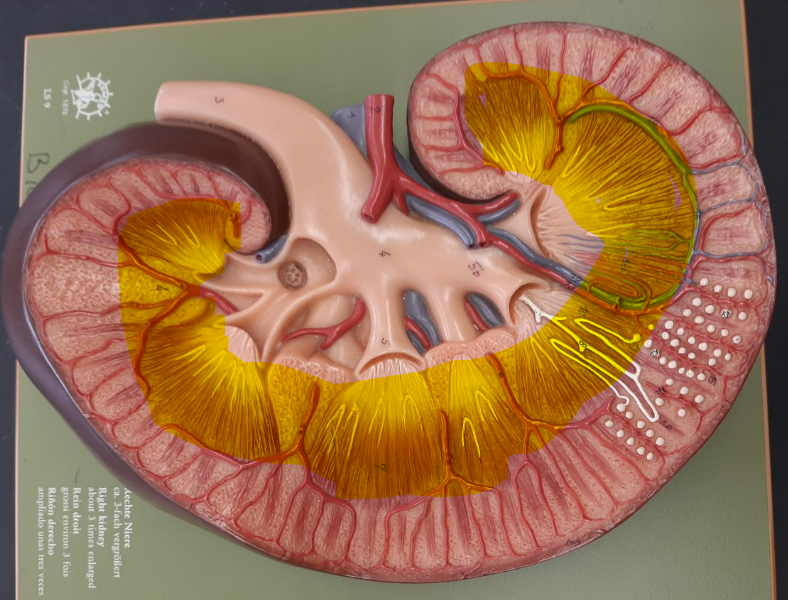
6
New cards
renal pyramid
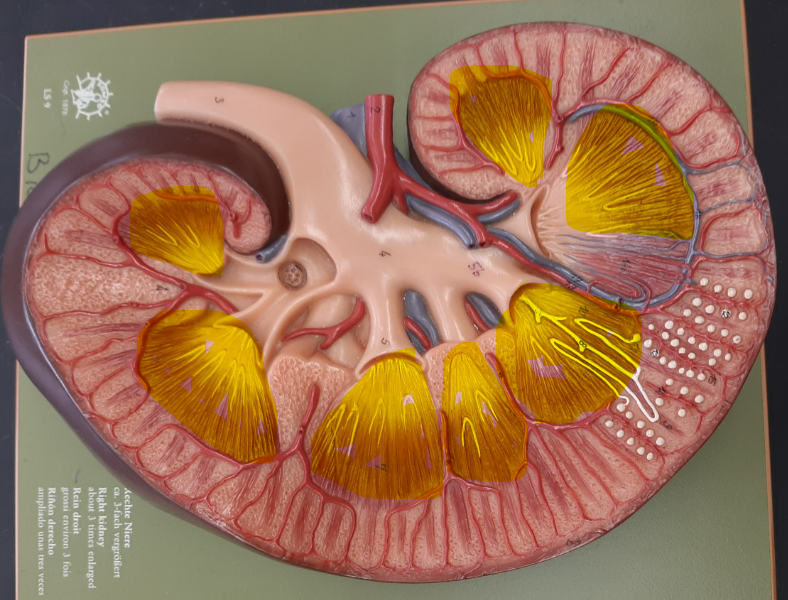
7
New cards
renal papilla
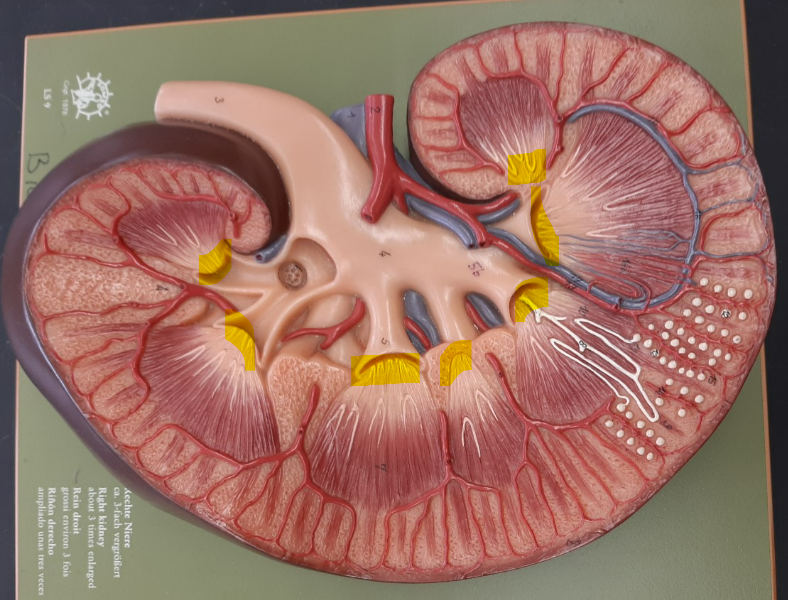
8
New cards
renal pelvis
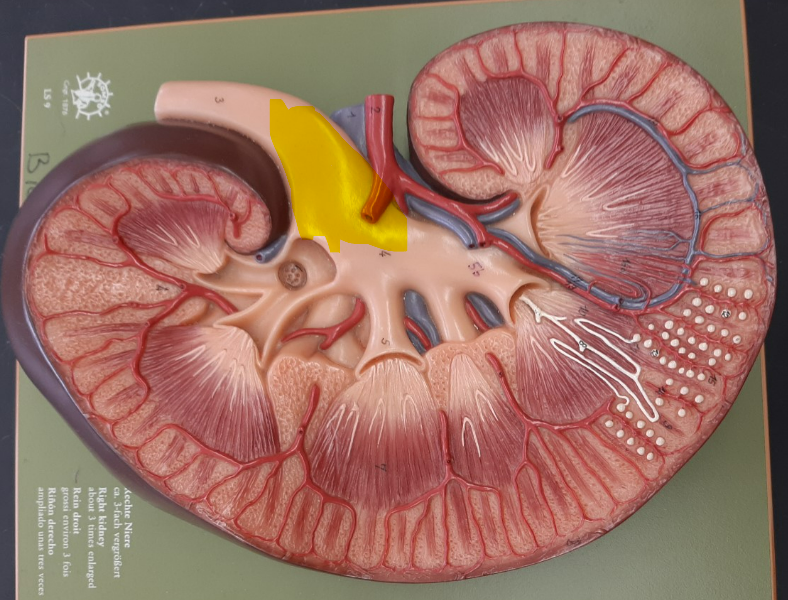
9
New cards
major calyx
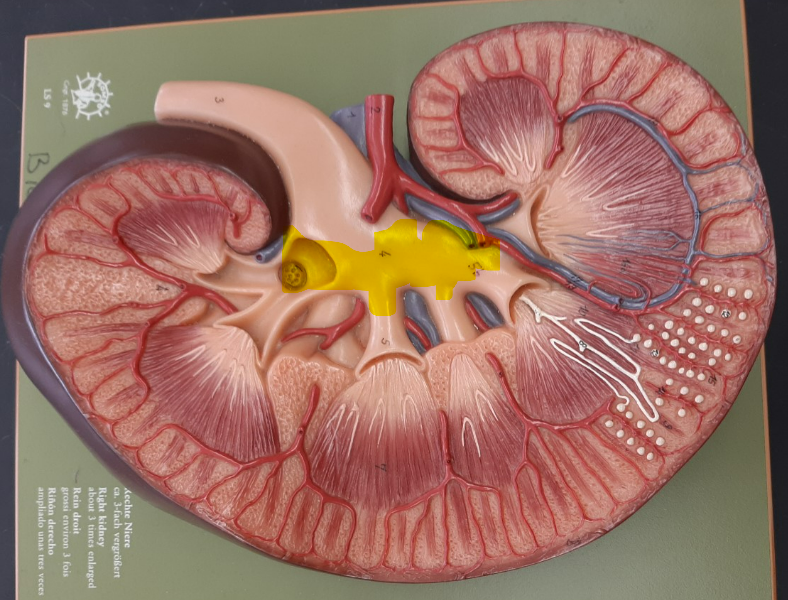
10
New cards
minor calyx
11
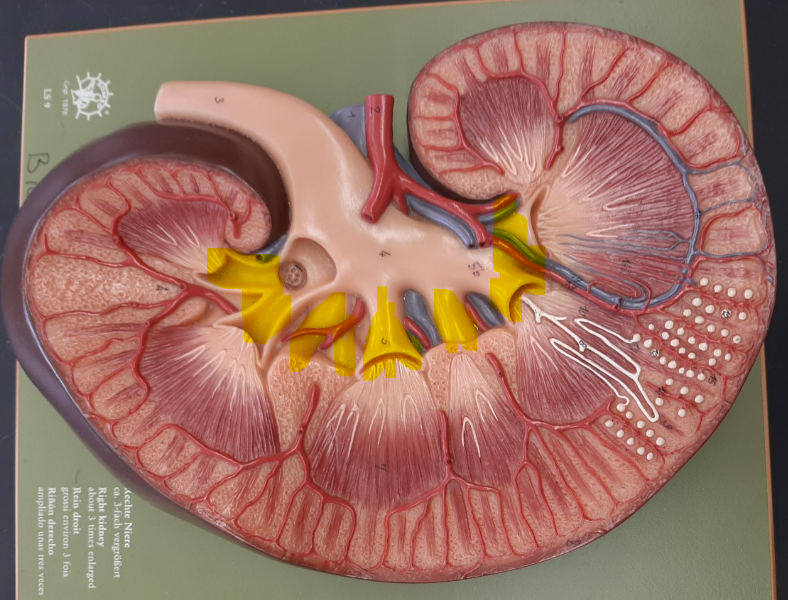
New cards
arcuate artery
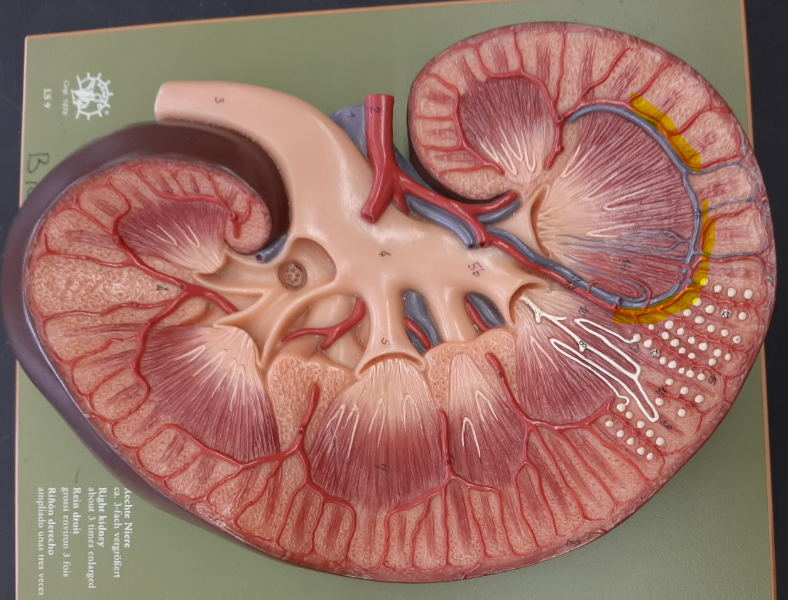
12
New cards
segmental artery
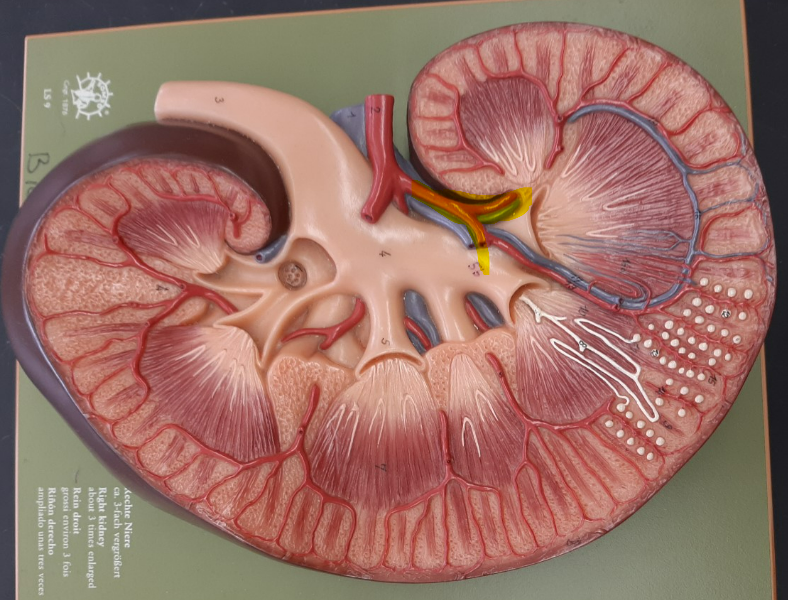
13
New cards
renal artery
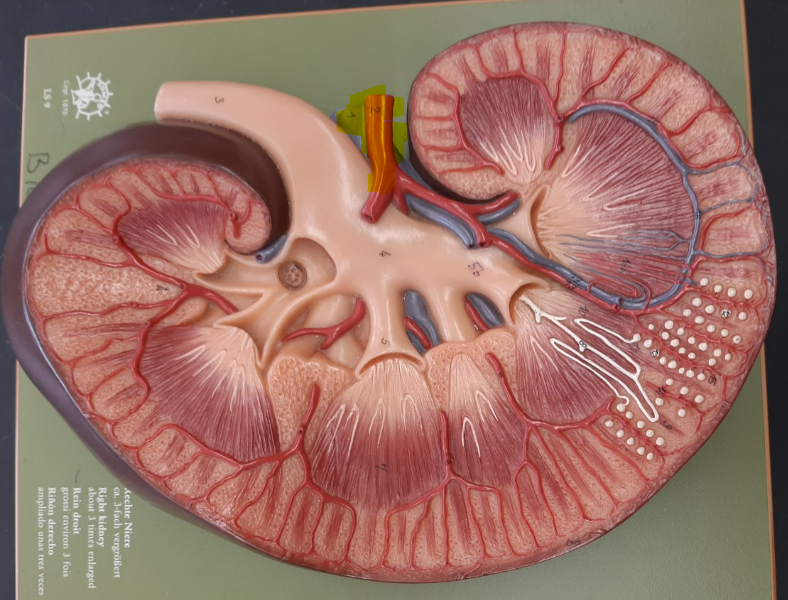
14
New cards
interlobar artery
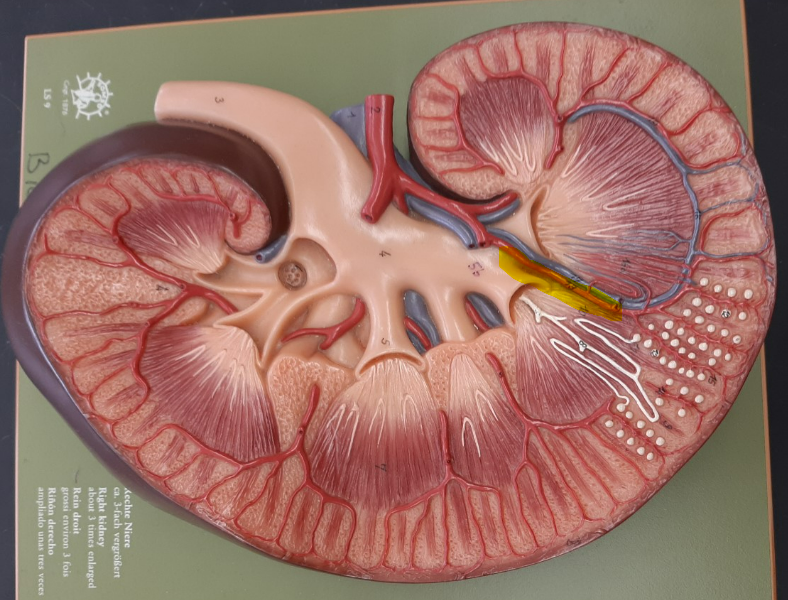
15
New cards
cortical radiate artery
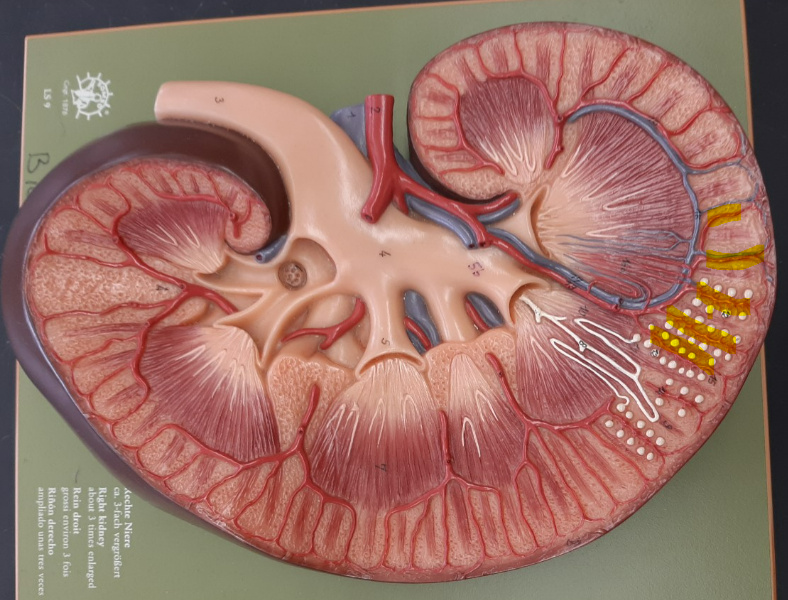
16
New cards
afferent arteriole
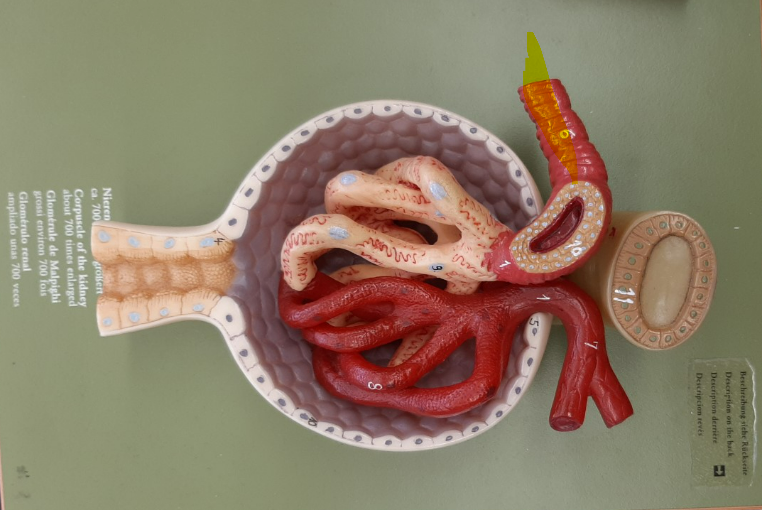
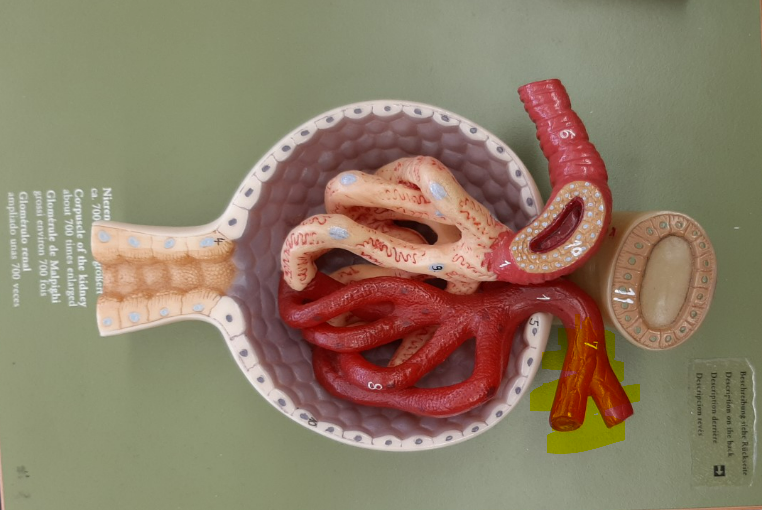
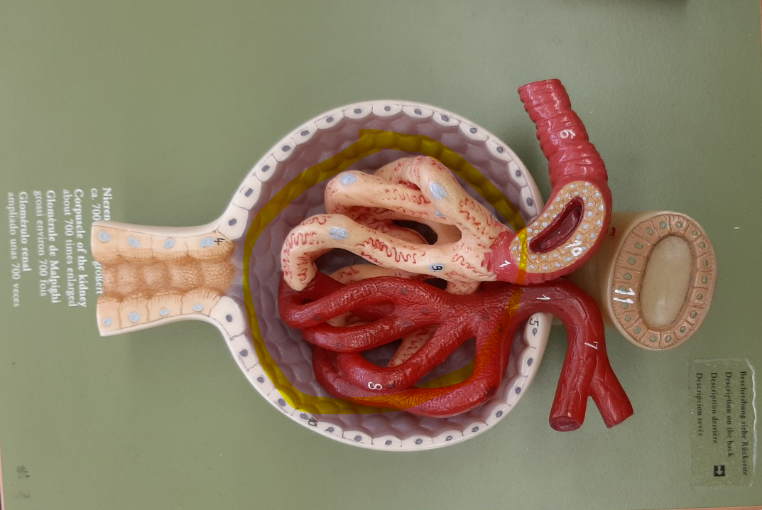
17
New cards
efferent arteriole
18
New cards
glomerulus
19
New cards
peritubular capillaries
20
New cards
vasa recta
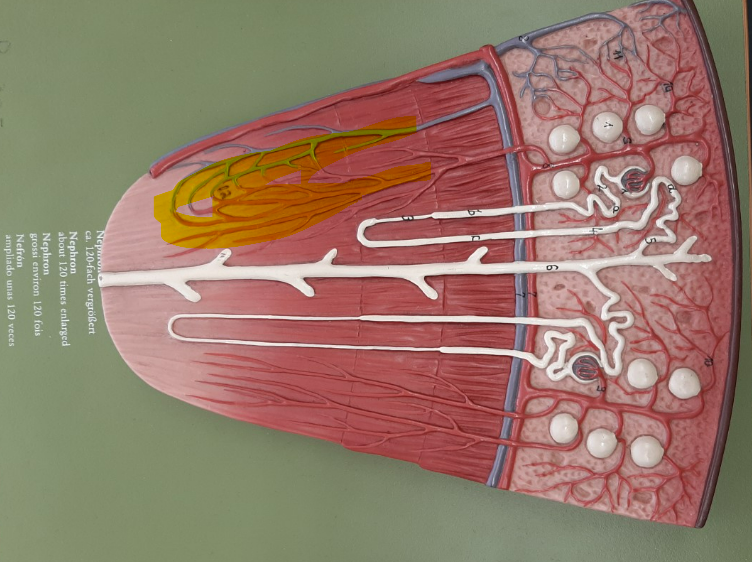
21
New cards
arcuate vein
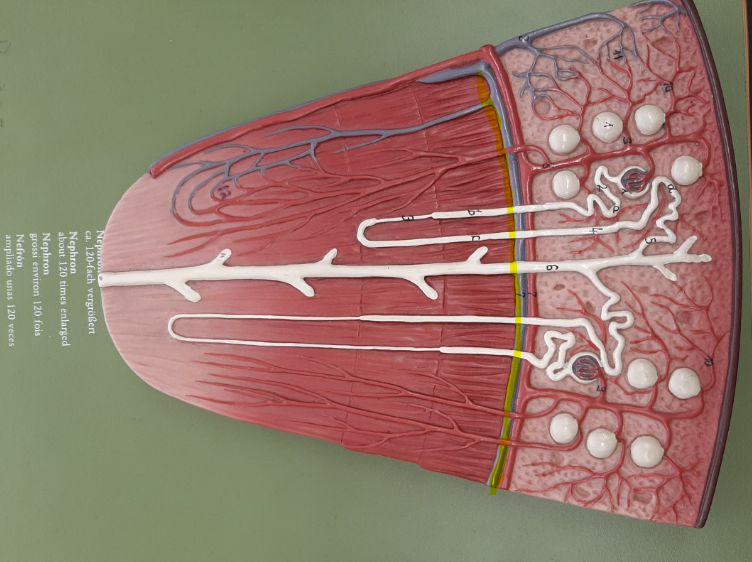
22
New cards
renal vein
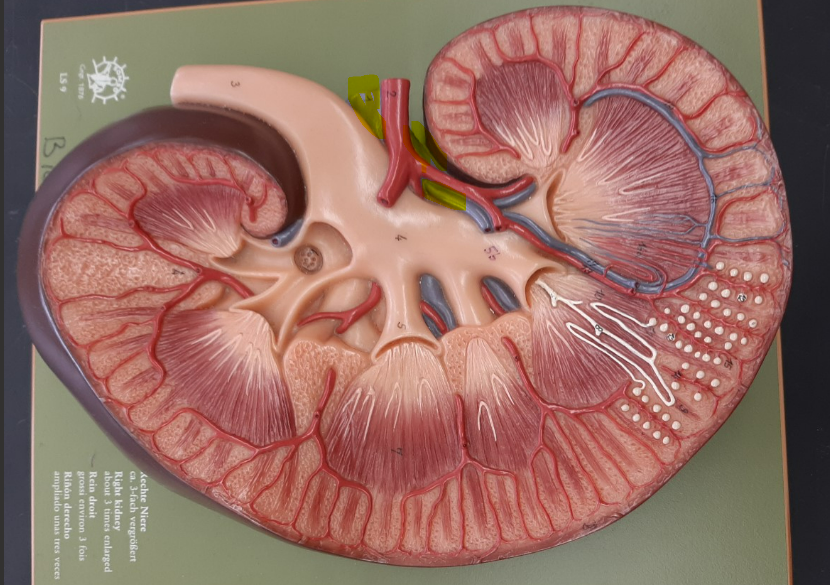
23
New cards
interlobar vein
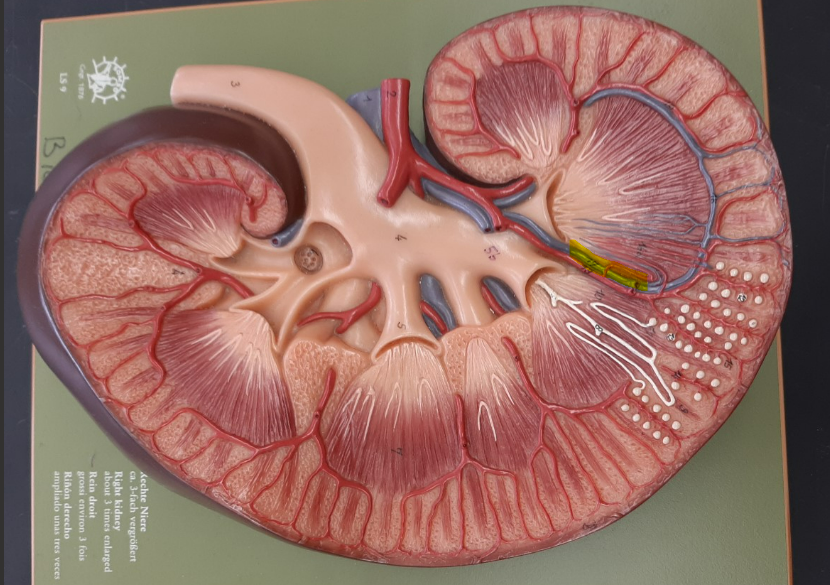
24
New cards
cortical radiate vein
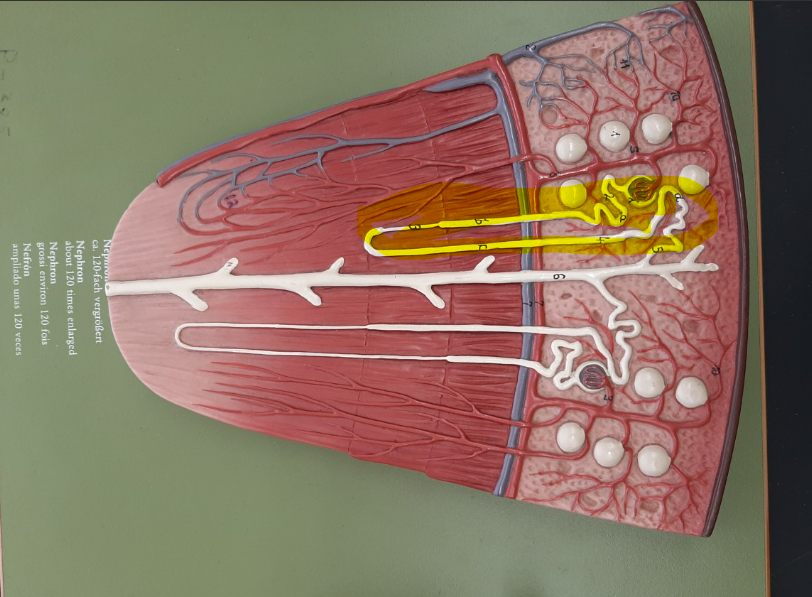
25
New cards
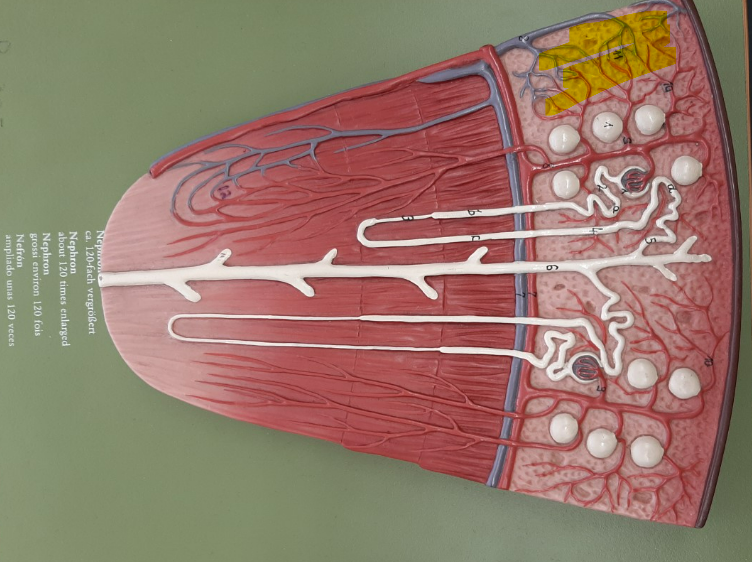
cortical nephron
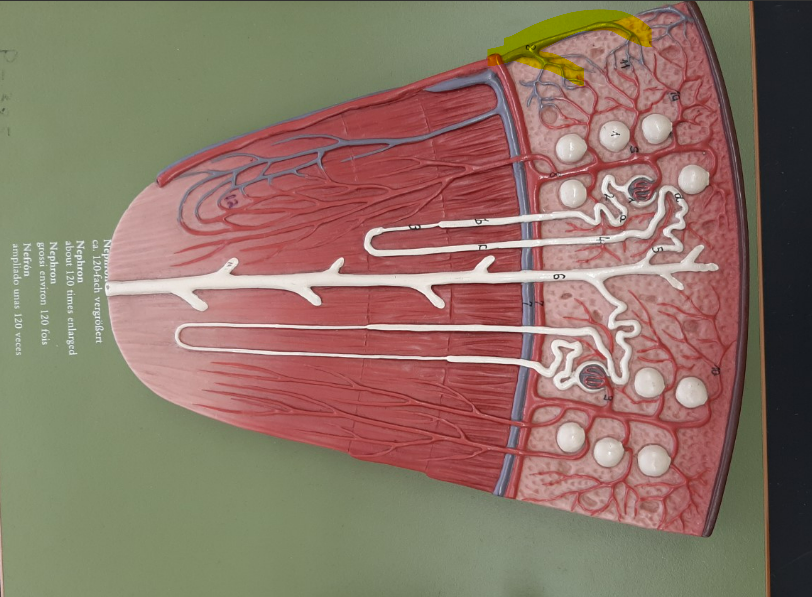
26
New cards
peritubular capillaries
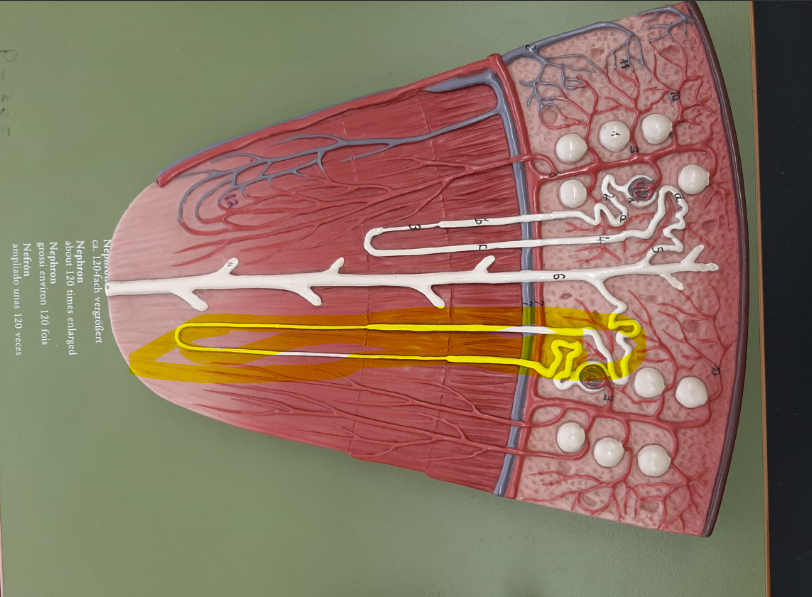
27
New cards
juxtamedullary nephron
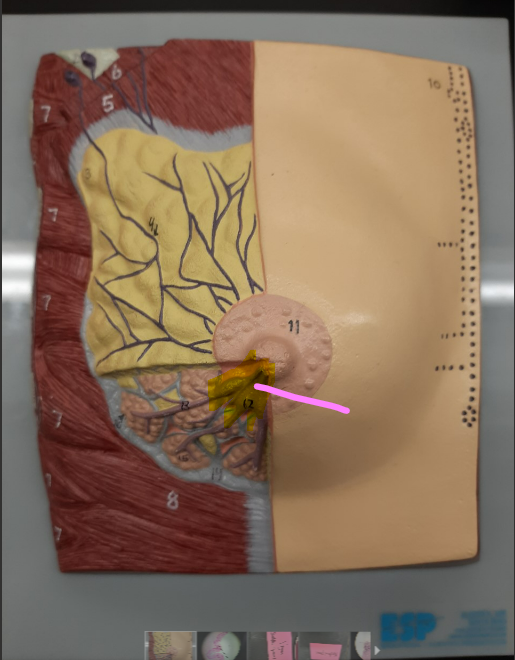
28
New cards
vasa recta
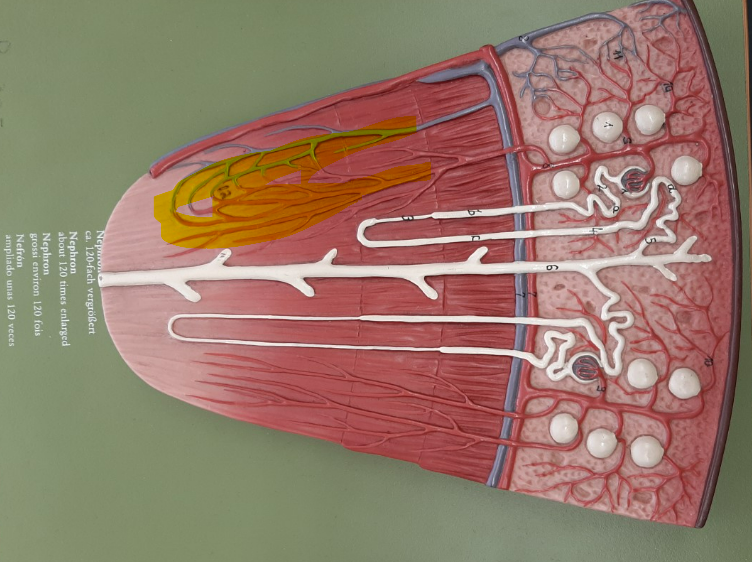
29
New cards
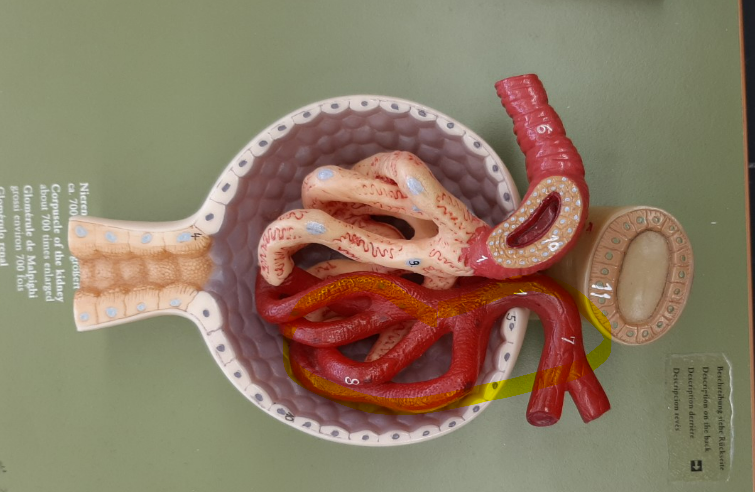
renal corpuscle
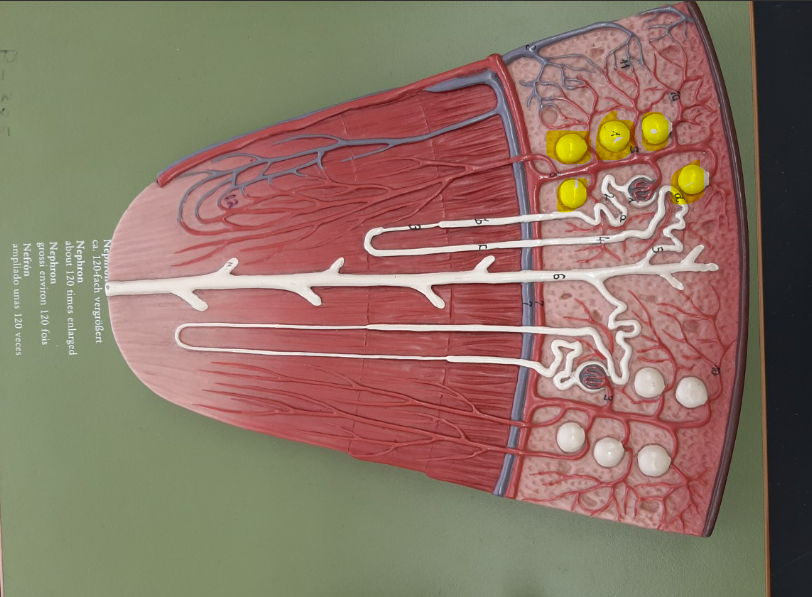
30
New cards
glomerular capsule
or bowman's capsule
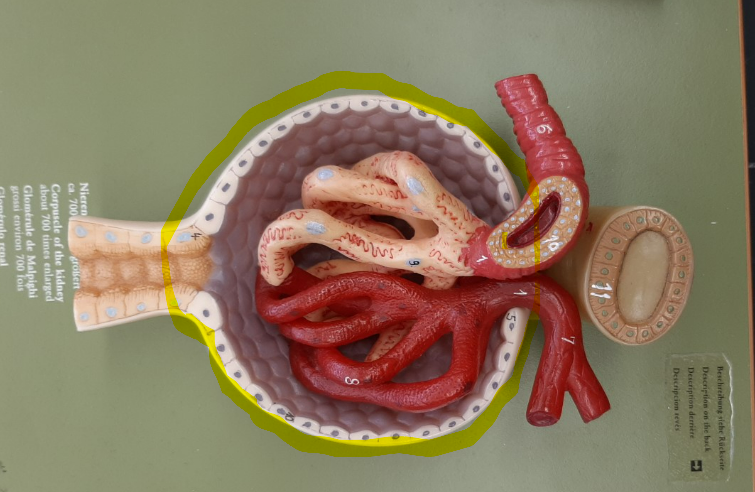
31
New cards
glomerular capsular space
bowman's capsular space
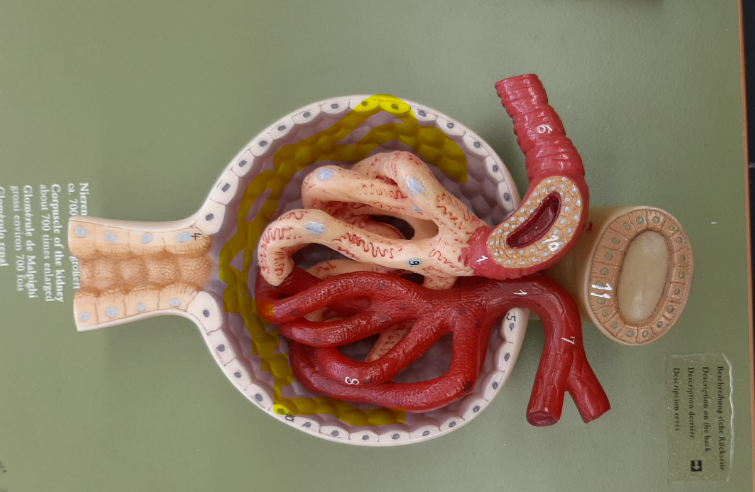
32
New cards
glomerulus
or glomerular capillaries
33
New cards
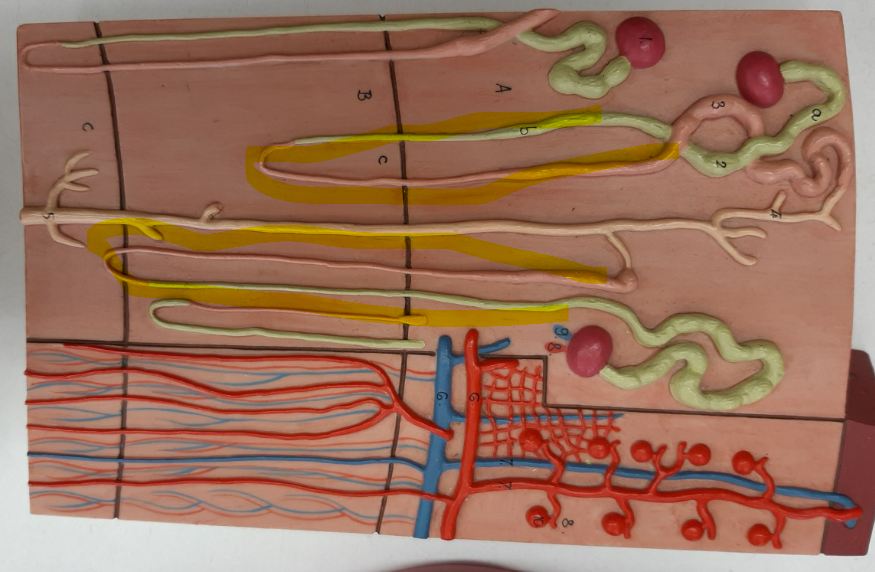
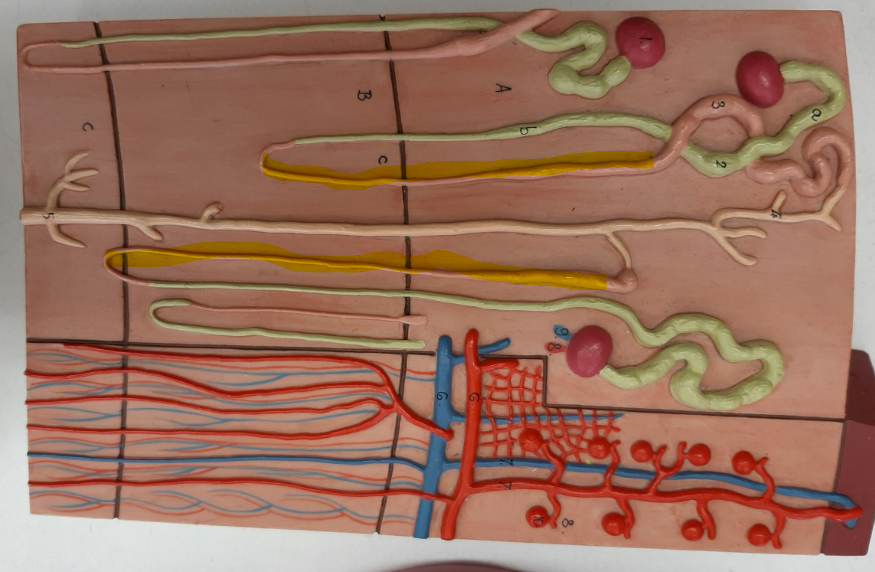
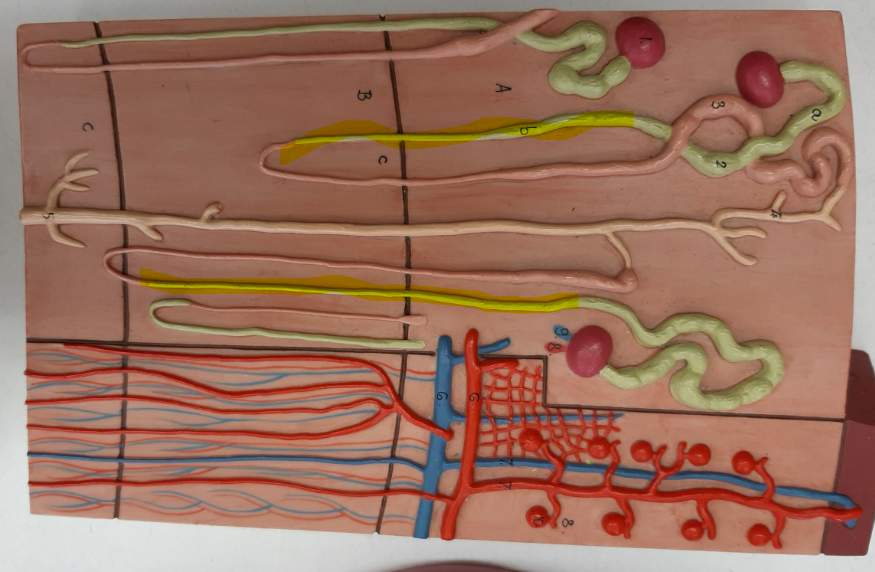
nephron loop
or loop of henle
34
New cards
ascending limb of the nephron loop
35
New cards
descending limb of the nephron loop
36
New cards
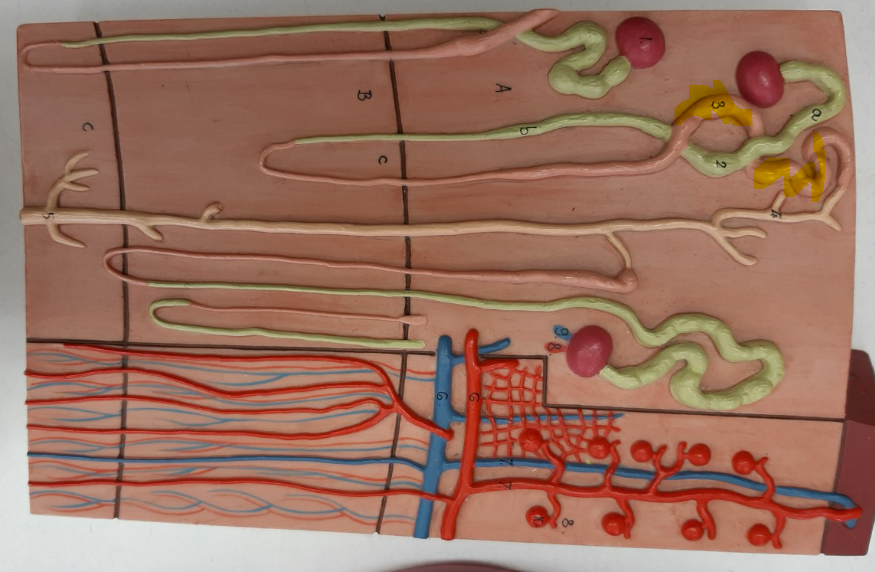
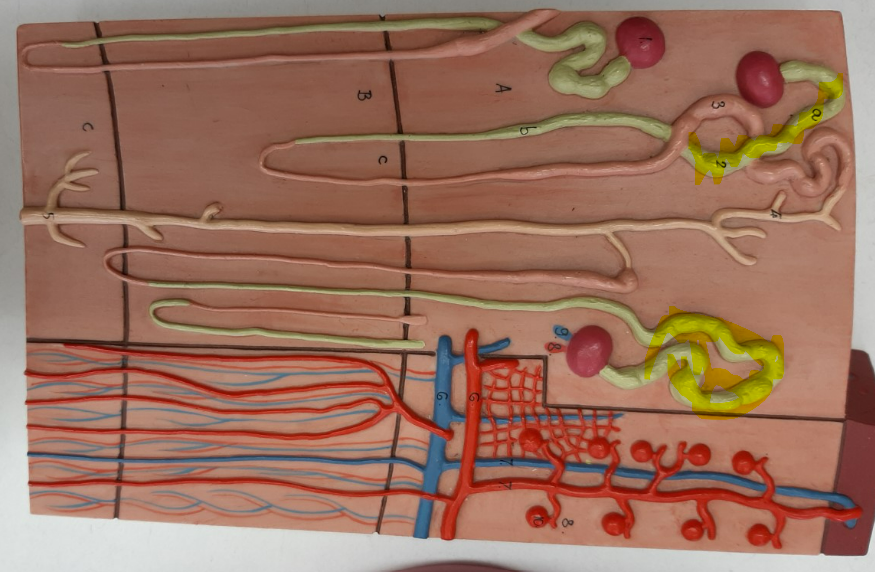
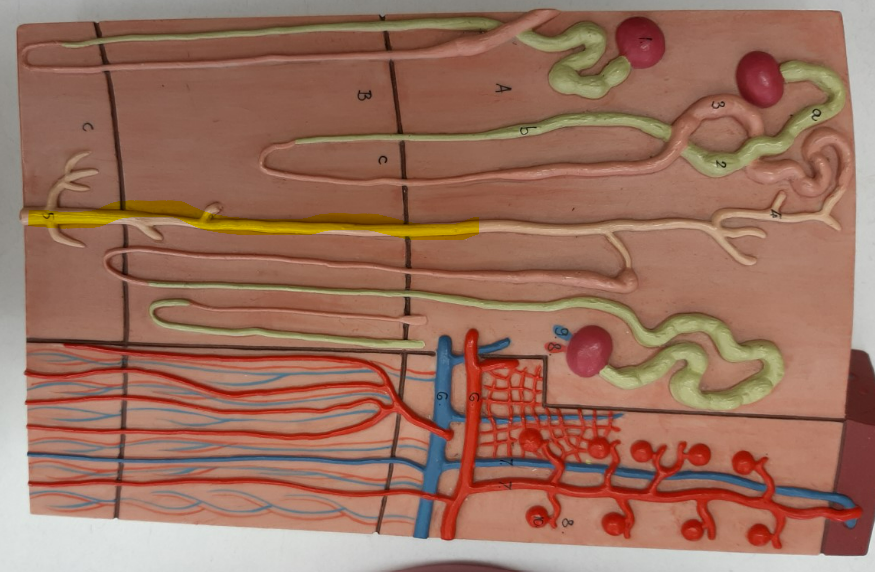
distal convoluted tubule
37
New cards
proximal convoluted tubule
38
New cards
collecting duct
39
New cards
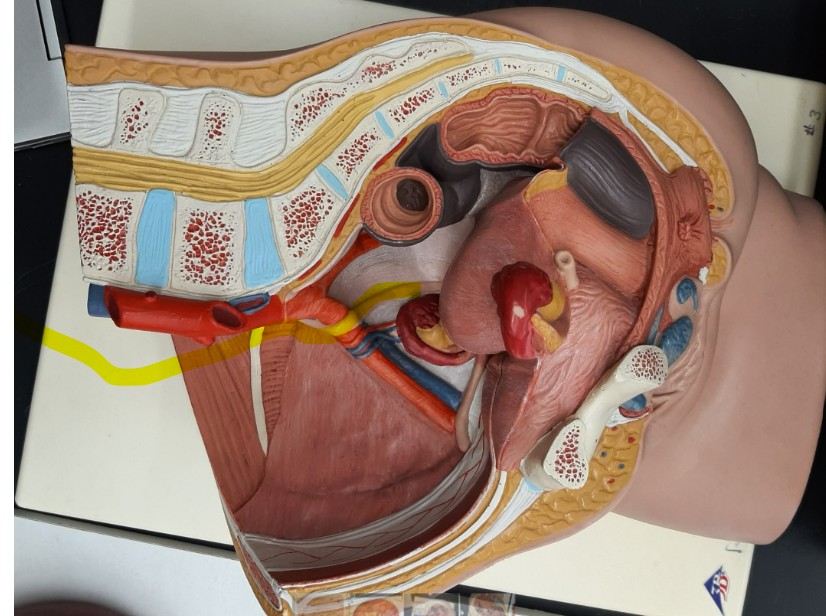
ureter
40
New cards
urinary bladder
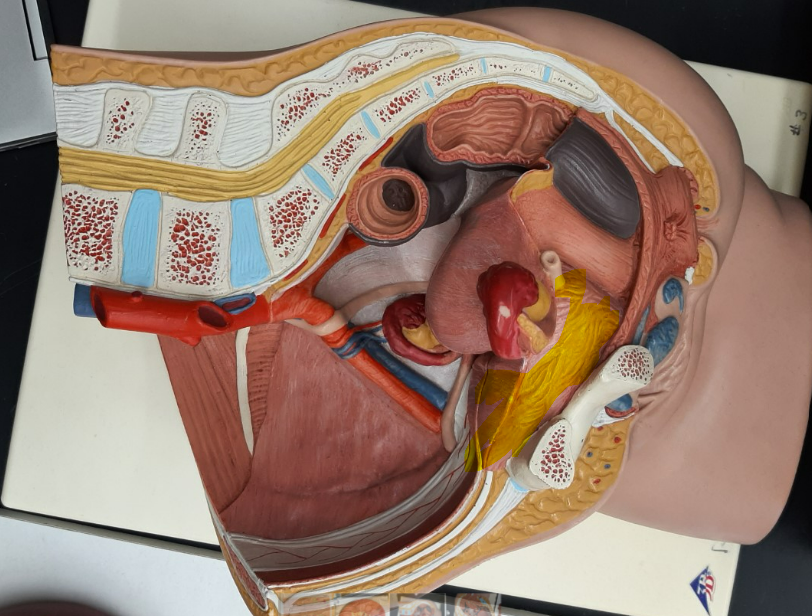
41
New cards
detrusor muscle
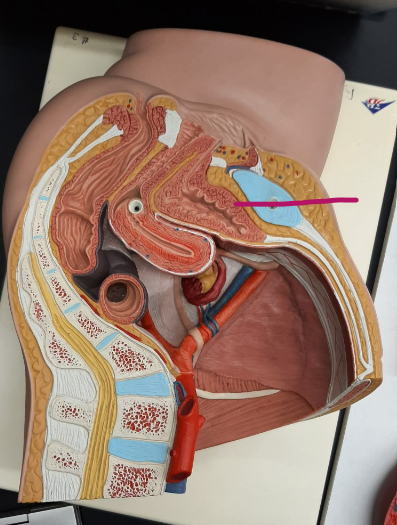
42
New cards
trigone
43
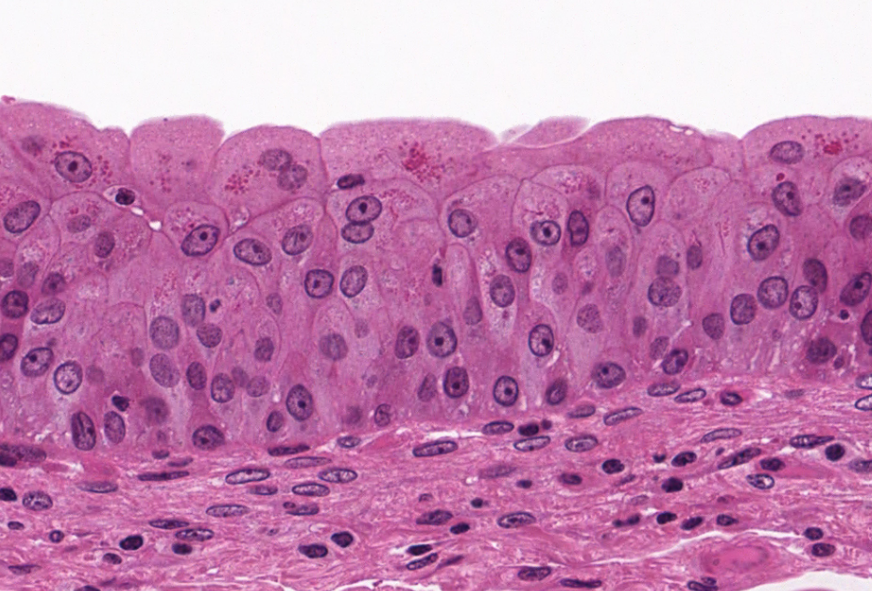
New cards
urothelium
or transitional epithelium
44
New cards
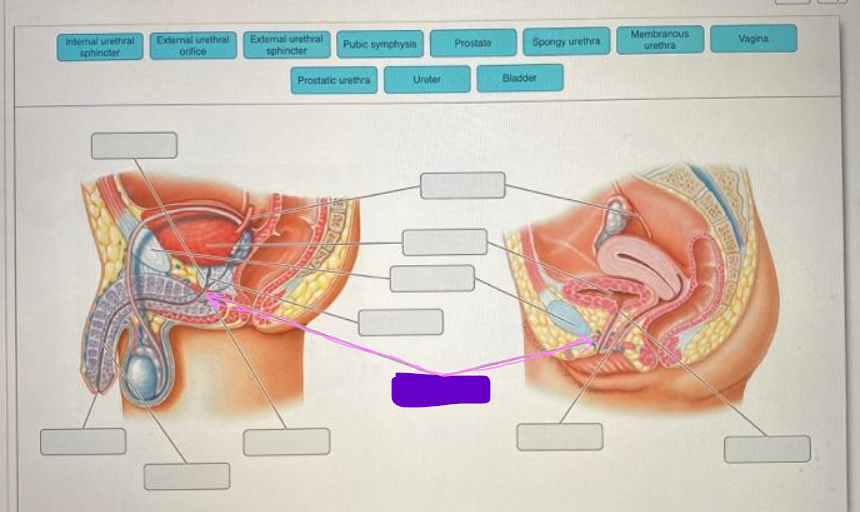
internal urethral sphincter
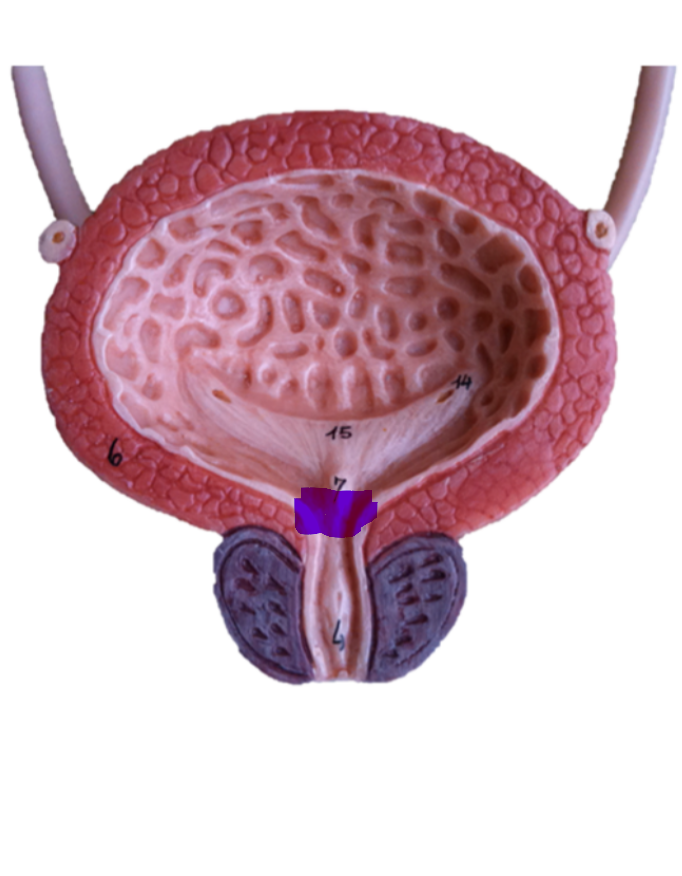
45
New cards
external urethral sphincter
46
New cards
pH range of normal urine
4.5-8.0
47
New cards
factors which influence color and transparency of urine
Diseases of the liver or obstructions of bile drainage from the liver impart a dark “tea” or “cola” hue to the urine. Dehydration produces darker, concentrated urine that may also possess the slight odor of ammonia.
48
New cards
factors which influence specific gravity of urine
Increased urine specific gravity may be due to conditions such as:
* Adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones (Addison disease)
* Heart failure
* High sodium level in the blood
* Loss of body fluids (dehydration)
* Narrowing of the kidney artery (renal artery stenosis)
* Shock
* Sugar (glucose) in the urine
* Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)
Decreased urine specific gravity may be due to:
* Damage to kidney tubule cells (renal tubular necrosis)
* Diabetes insipidus
* Drinking too much fluid
* Kidney failure
* Low sodium level in the blood
* Severe kidney infection (pyelonephritis)
* Adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones (Addison disease)
* Heart failure
* High sodium level in the blood
* Loss of body fluids (dehydration)
* Narrowing of the kidney artery (renal artery stenosis)
* Shock
* Sugar (glucose) in the urine
* Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH)
Decreased urine specific gravity may be due to:
* Damage to kidney tubule cells (renal tubular necrosis)
* Diabetes insipidus
* Drinking too much fluid
* Kidney failure
* Low sodium level in the blood
* Severe kidney infection (pyelonephritis)
49
New cards
cause of renal calculi
Kidney stones (also called renal calculi, nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. Diet, excess body weight, some medical conditions, and certain supplements and medications are among the many causes of kidney stones.
50
New cards
cause of glycosuria
Conditions with problems using or making the hormone insulin. Conditions with the kidney where the tubules are damaged, or other kidney defects. Eating more sugars than the body can process at once.
51
New cards
cause of proteinuria (albuminuria)
Causes typically include intense exercise, stress, fever and prolonged exposure to cold temperatures.
52
New cards
cause of ketonuria
Fasting for long periods of time or the intermittent fasting diet can lead to ketonuria. During fasting, your liver starts to use up fat and protein reserves in your body to keep it going.
53
New cards
cause of hematuria
The causes of hematuria include vigorous exercise and sexual activity, among others. More serious causes of hematuria include kidney or bladder cancer; inflammation of the kidney, urethra, bladder, or prostate; and polycystic kidney disease, among other causes.
54
New cards
cause of hemoglobinuria
Hemoglobinuria may be a result of any of the following: Burns. Crushing injury. Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a disorder that occurs when an infection in the digestive system produces toxic substances.
55
New cards
cause of nitrituria
Bacteria in the urinary tract turn nitrates into nitrites, creating nitrite-positive urine. Nitrites in urine (nitrituria) only occur when you have a urinary tract infection (UTI).
56
New cards
cause of bilirubinuria
The most common cause of bilirubinuria is hepatocellular disease. More rare causes include inherited disorders, such as Dubin–Johnson syndrome and Rotor syndrome.
57
New cards
cause of pyuria
Pyuria is a condition in which you have pus in your pee. UTIs are the most common cause, but other causes include STIs, viral infections and chronic use of some medications. The most common symptom is cloudy, foul-smelling pee.
58
New cards
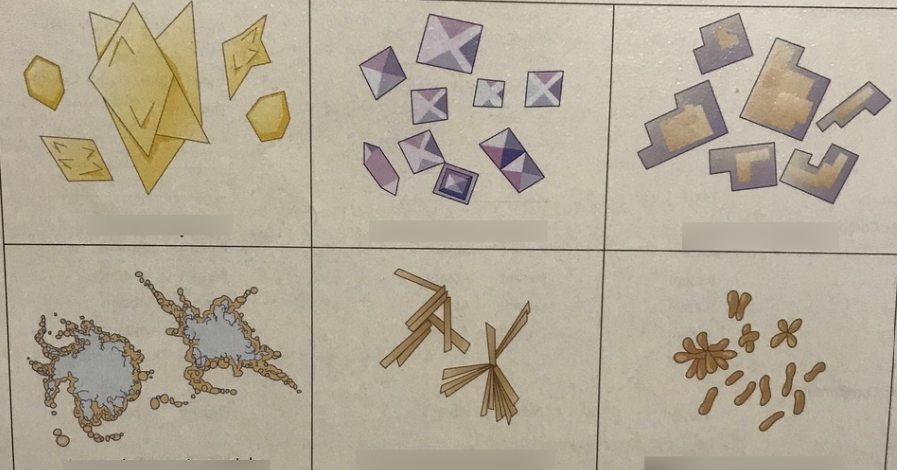
unorganized sediment

59
New cards
organized sediment
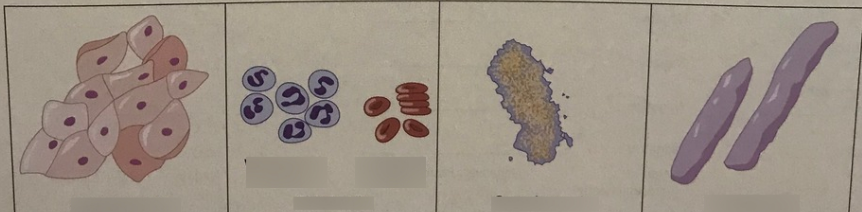
60
New cards
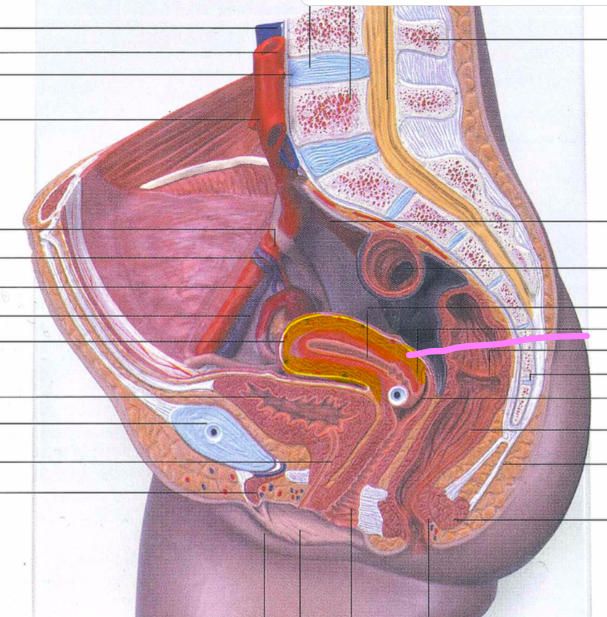
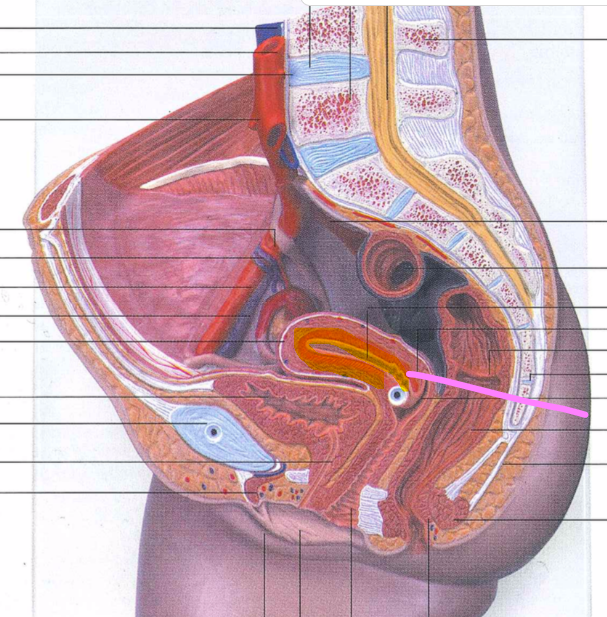
vagina
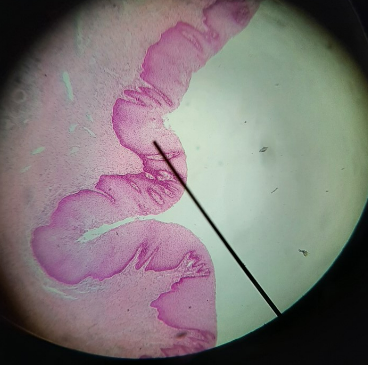
61
New cards
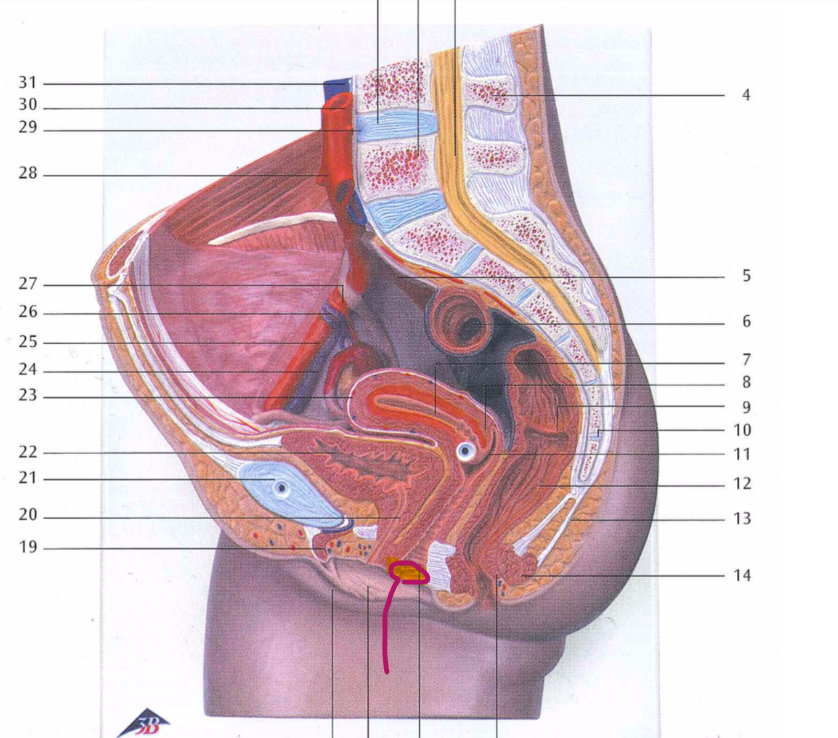
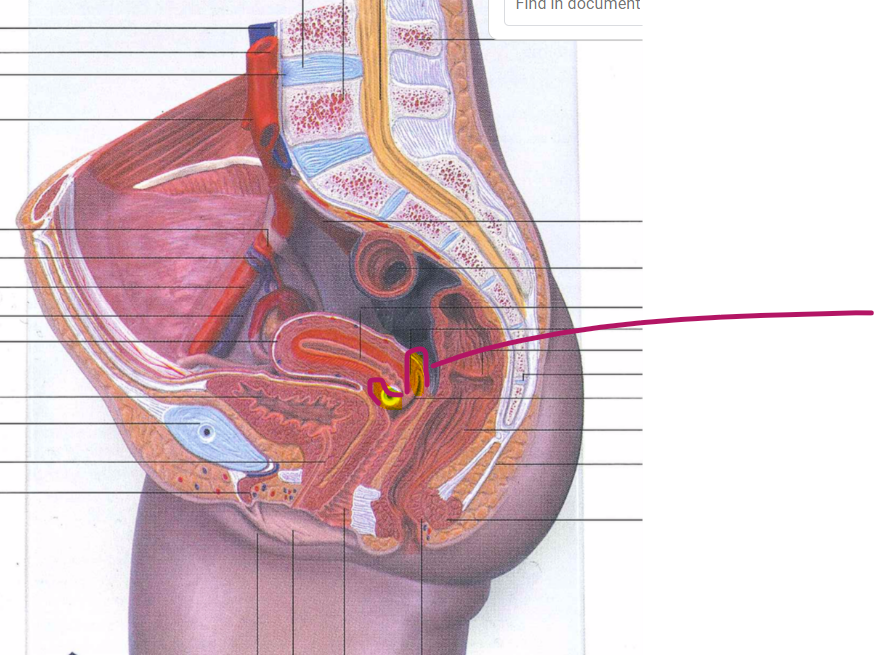
vaginal orifice
62
New cards
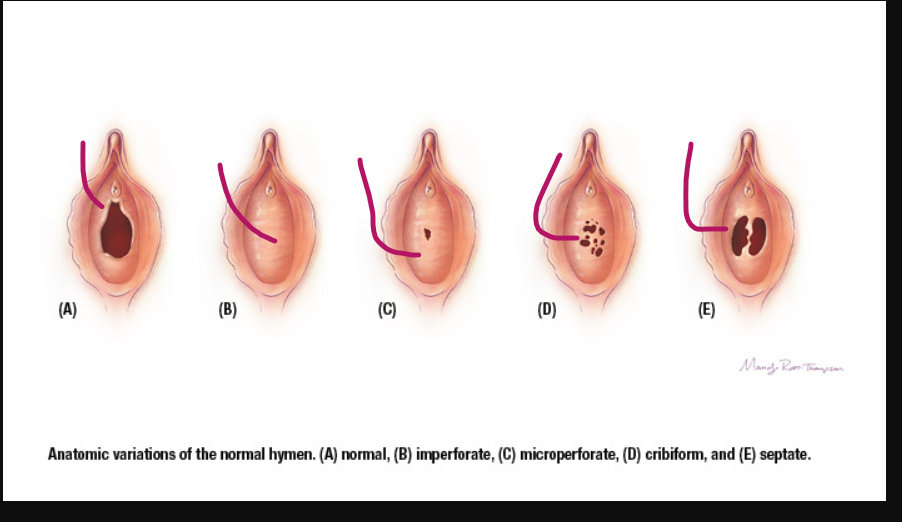
hymen
63
New cards
vaginal fornix
64
New cards
ovary
65
New cards
uterine tube
(general)
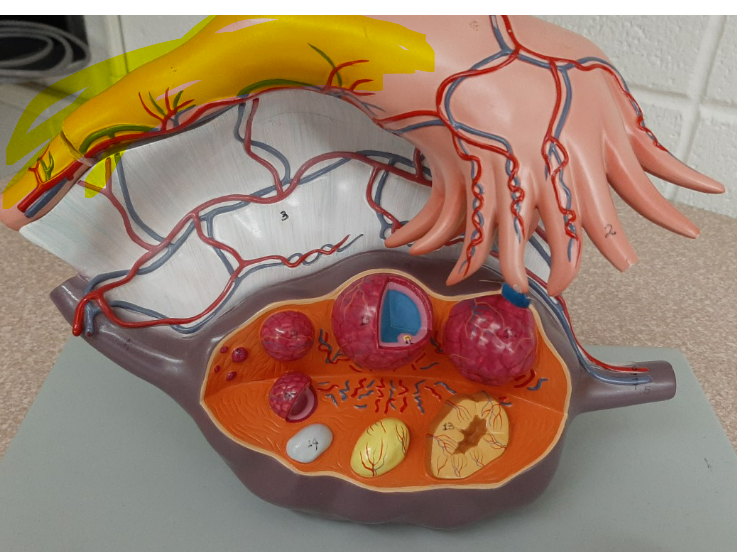
66
New cards
fimbriae
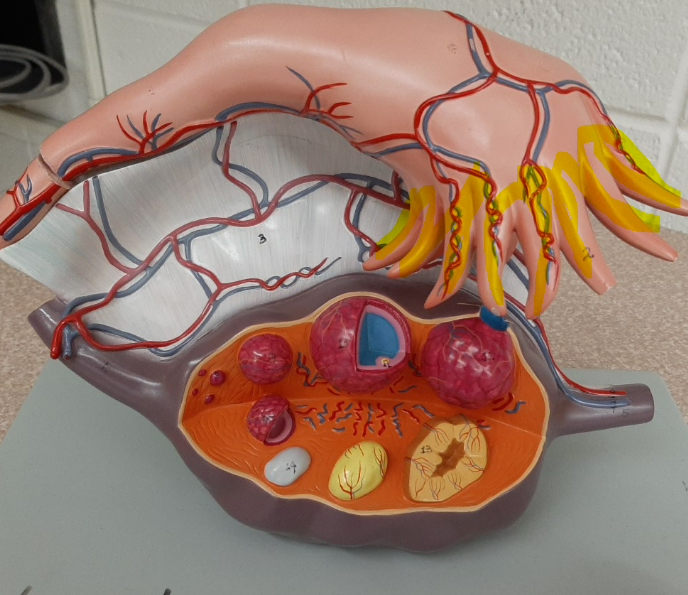
67
New cards
infundibulum
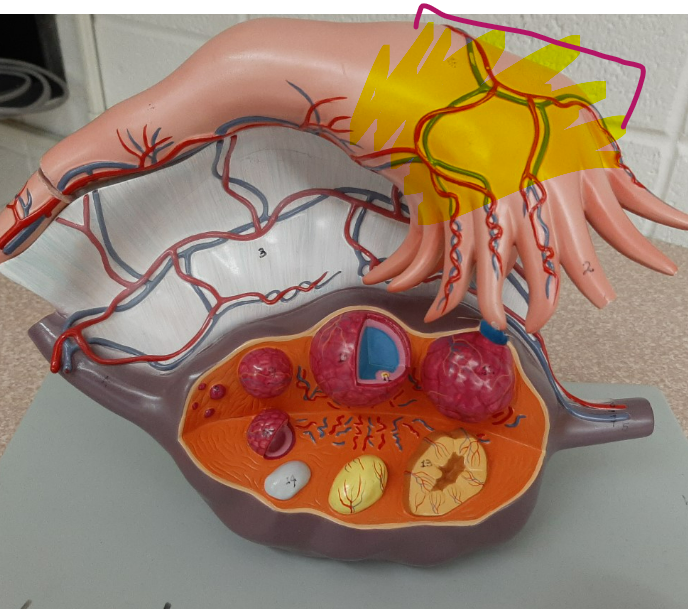
68
New cards
ampulla
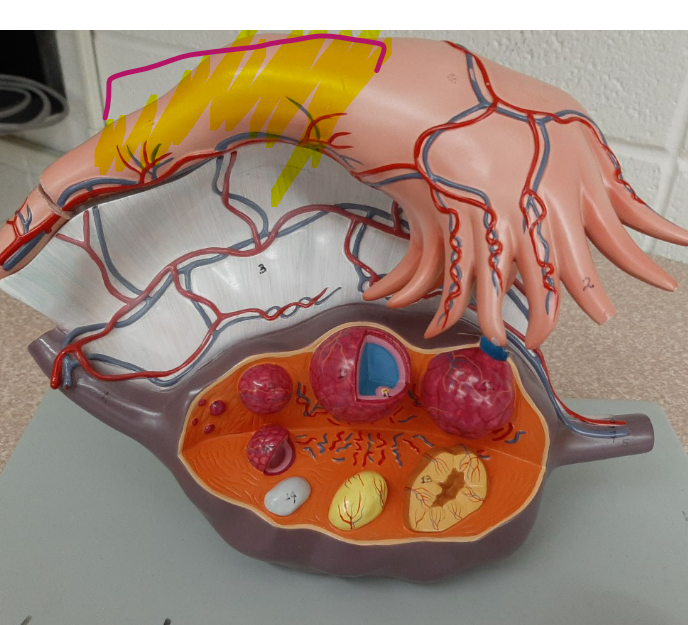
69
New cards
isthmus
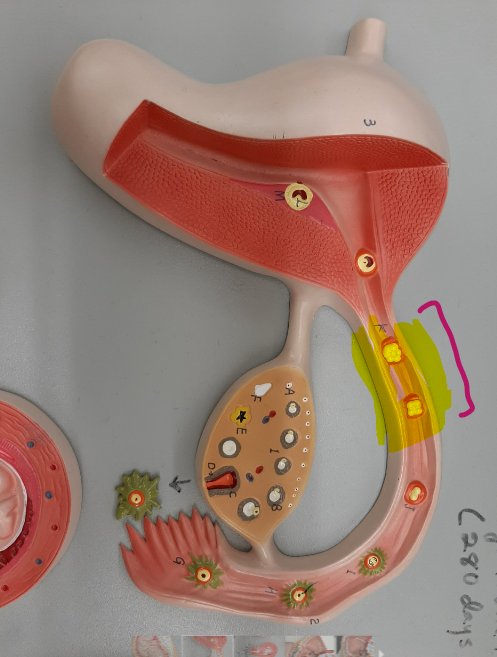
70
New cards
uterus
71
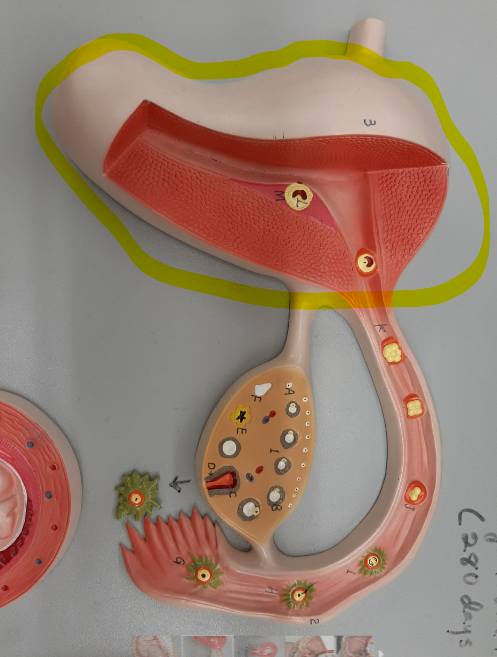
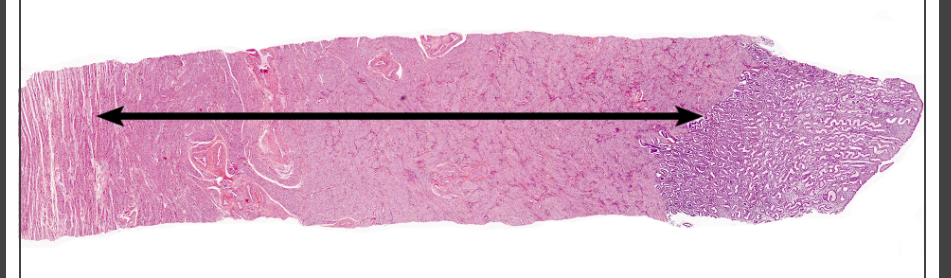
New cards
perimetrium
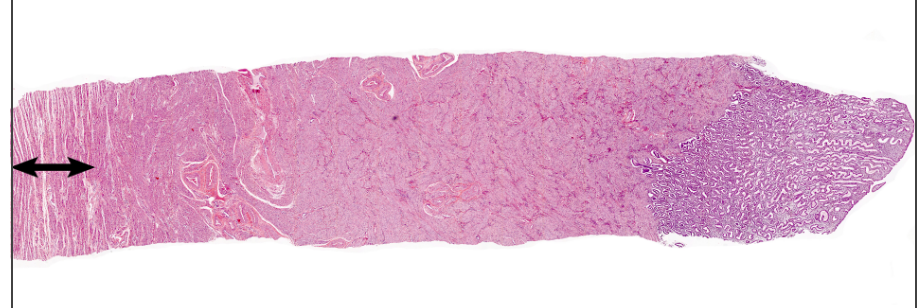
72
New cards
myometrium
73
New cards
endometrium
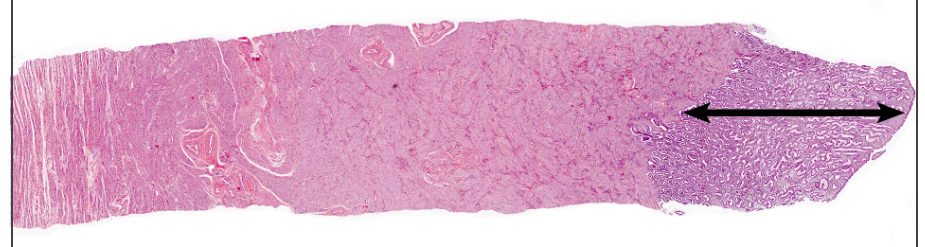
74
New cards
perimetrium
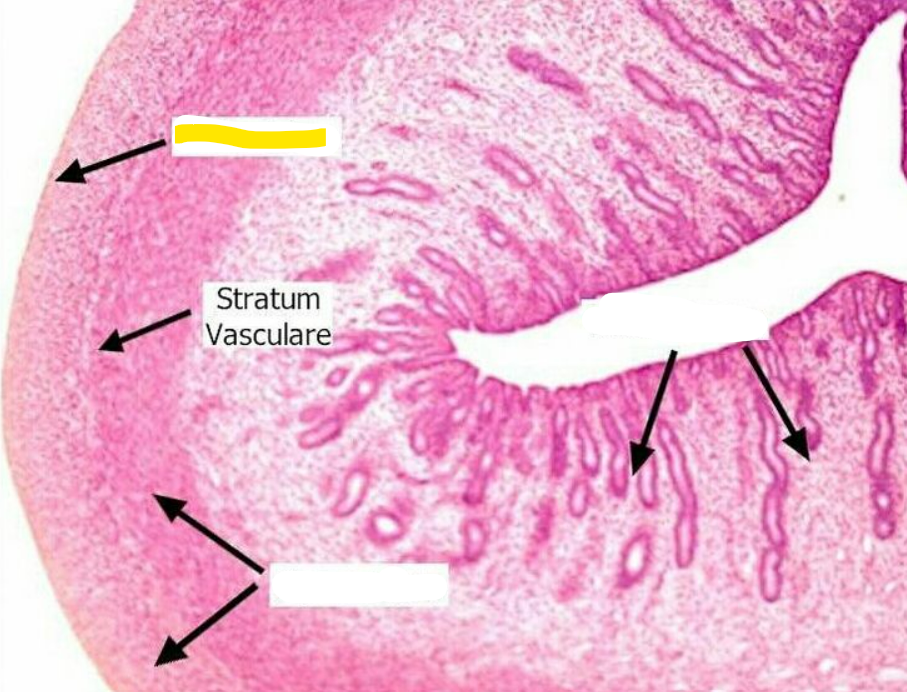
75
New cards
myometrium
76
New cards
endometrium
77
New cards
functional layer
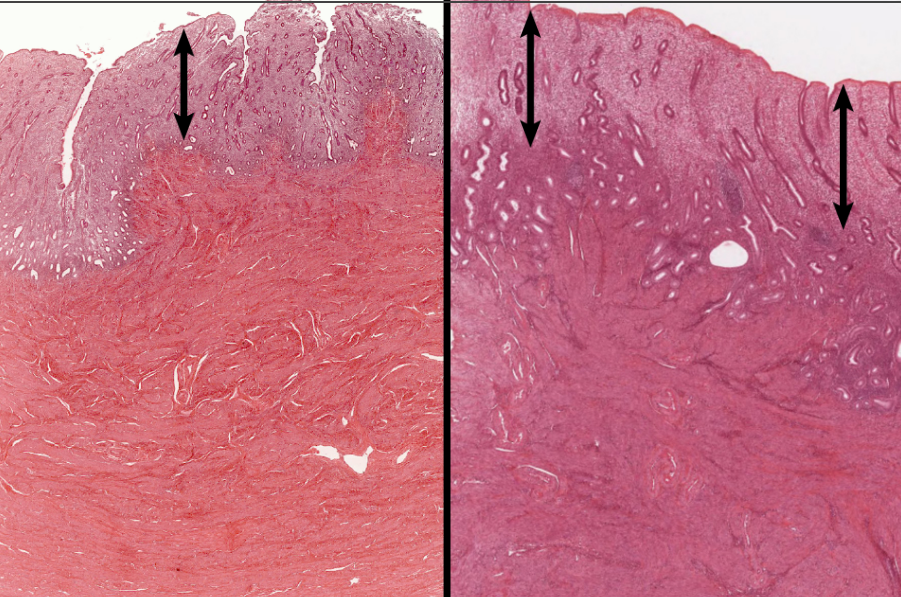
78
New cards
basal layer
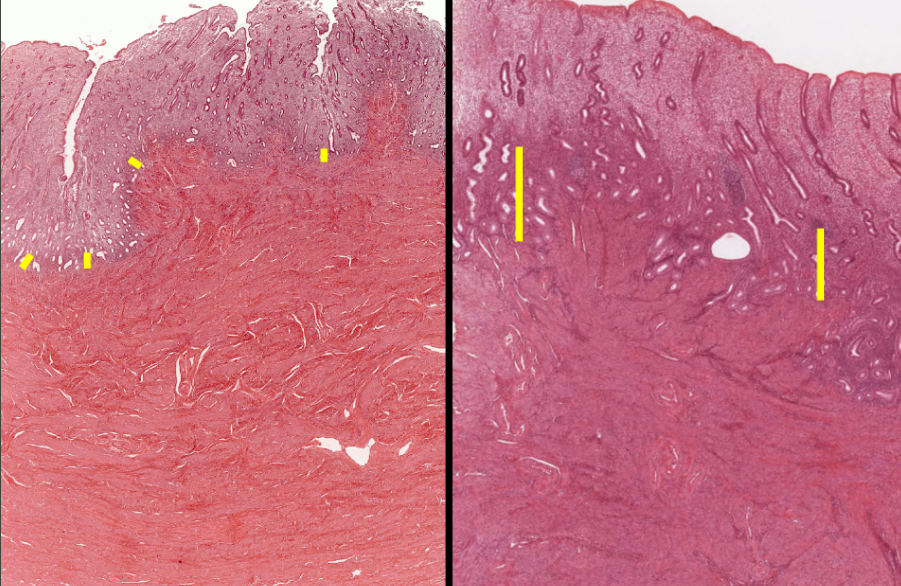
79
New cards
uterine gland
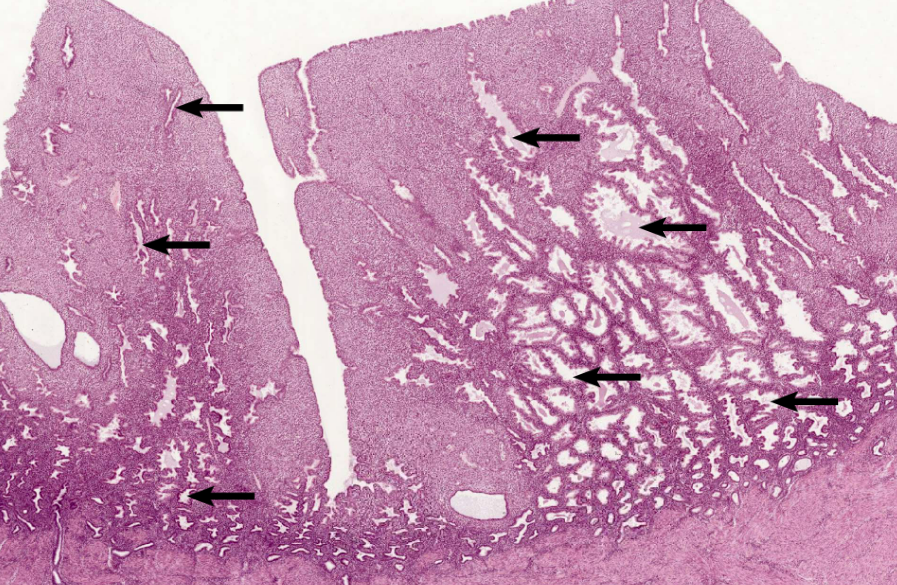
80
New cards
fundus
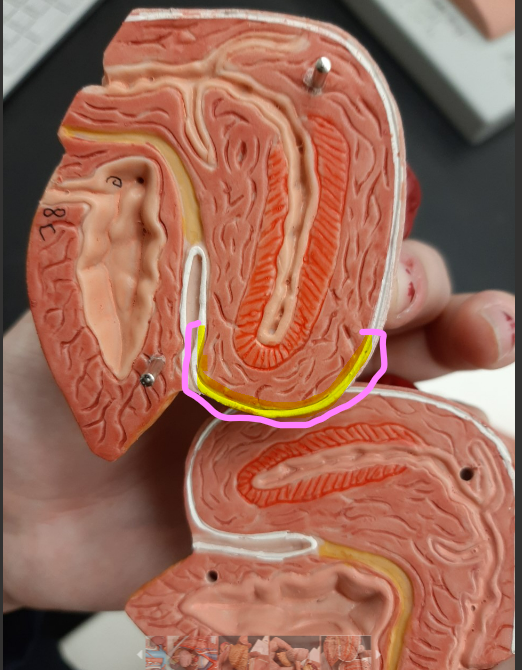
81
New cards
body of uterus
82
New cards
cervix
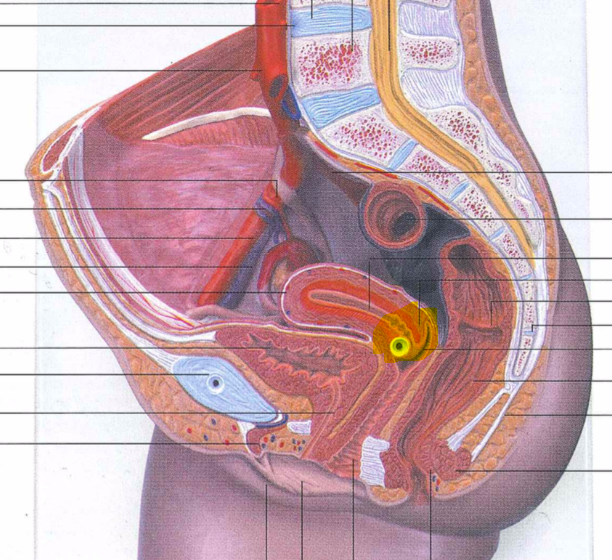
83
New cards
internal os
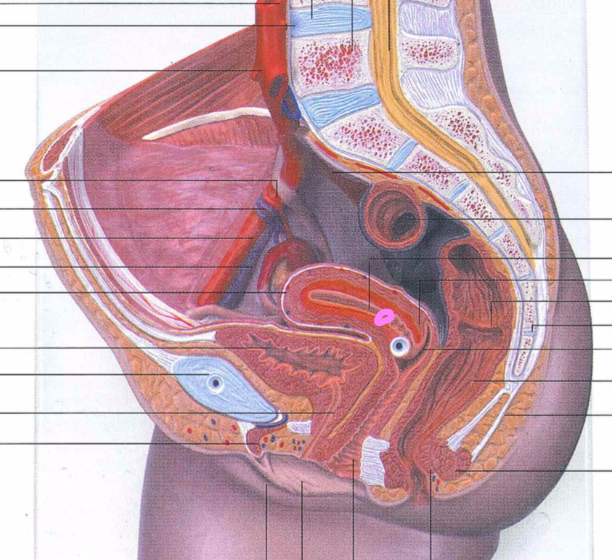
84
New cards
cervical canal
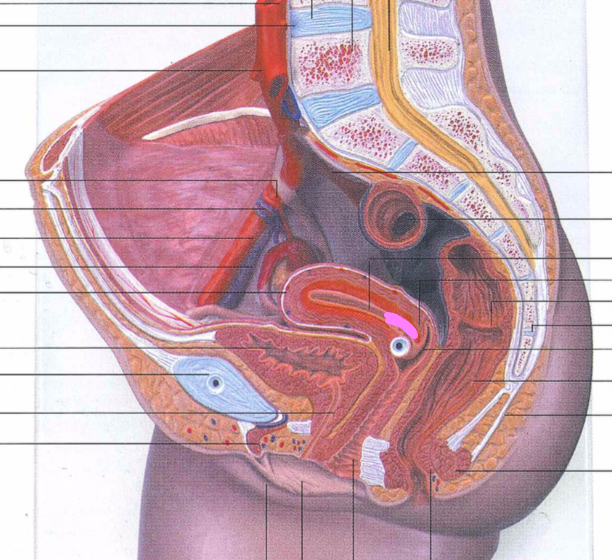
85
New cards
external os
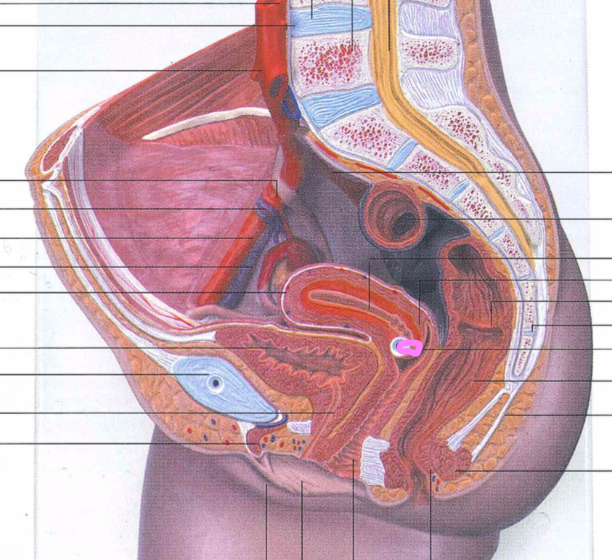
86
New cards
labium majus
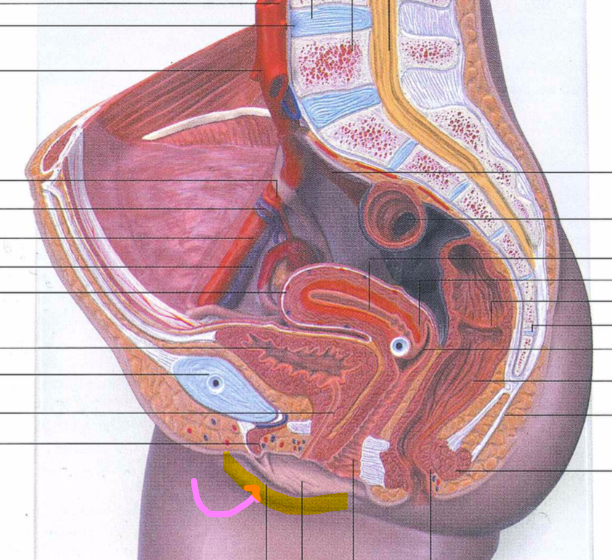
87
New cards
labium minus
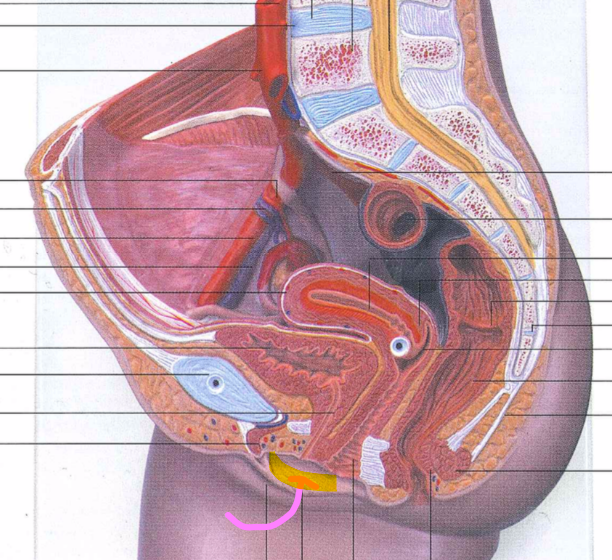
88
New cards
prepuce
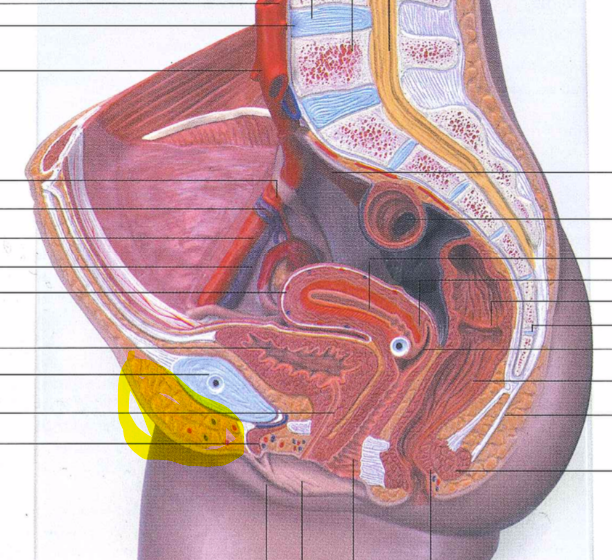
89
New cards
vestibule
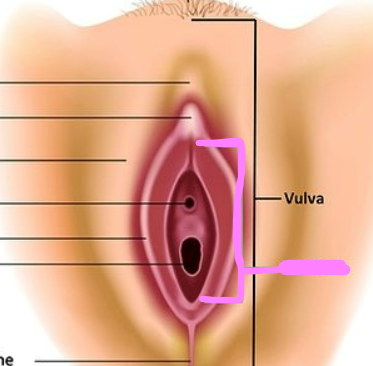
90
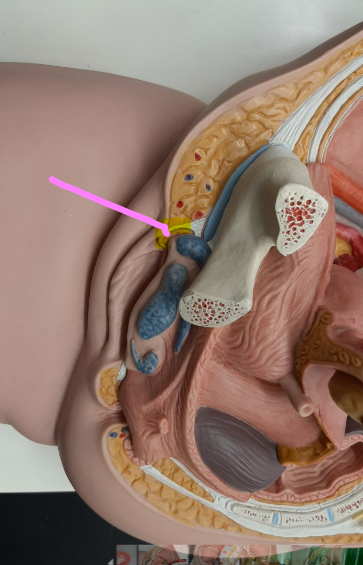
New cards
clitoris
91
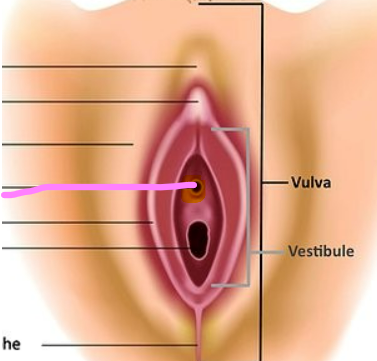
New cards
external urethral orifice
92
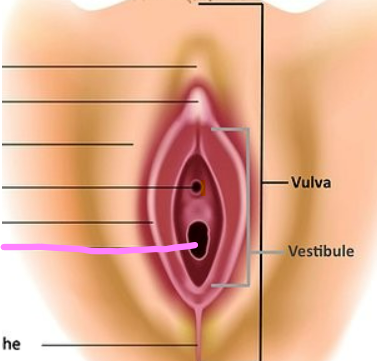
New cards
vaginal orifice
93
New cards
breast
(general)
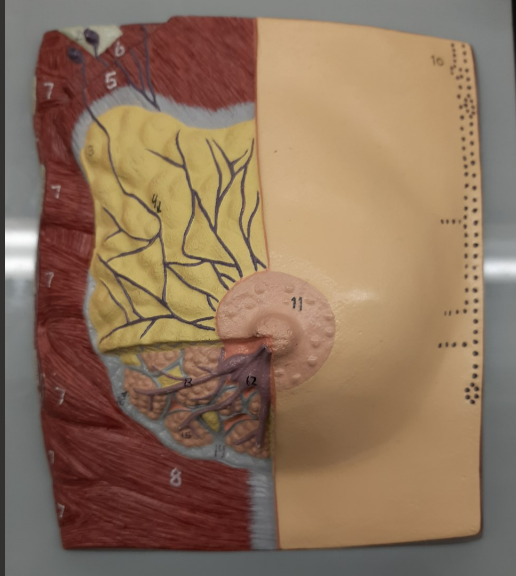
94
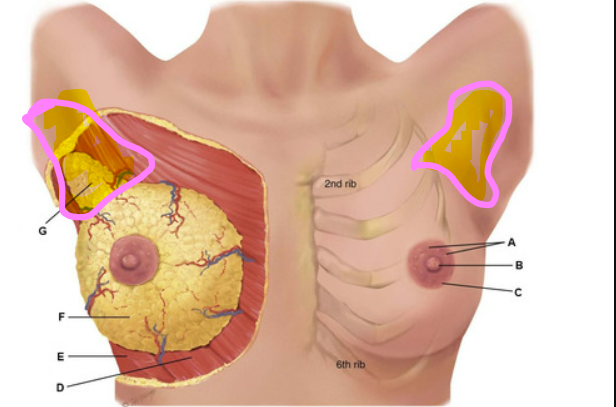
New cards
axillary tail
95
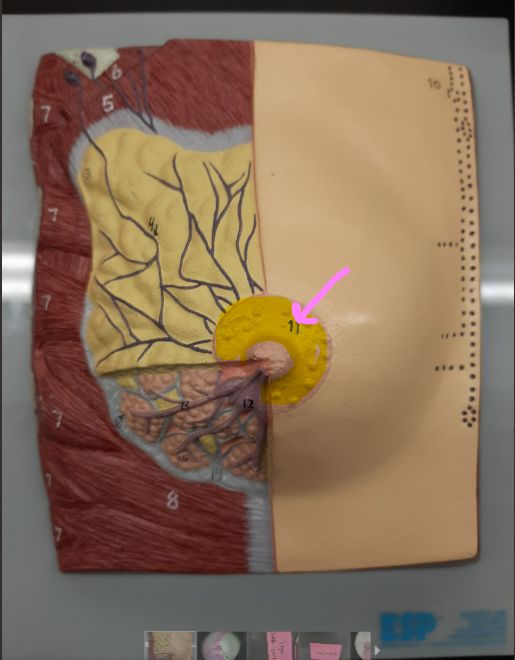
New cards
areola
96
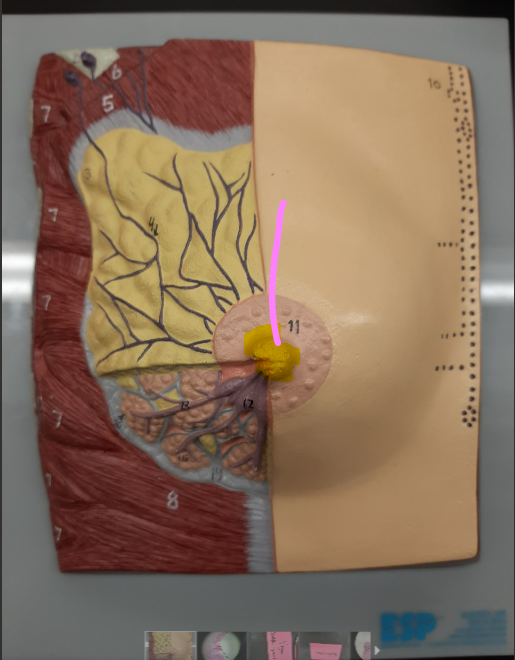
New cards
nipple
97
New cards
mammary gland
(general)
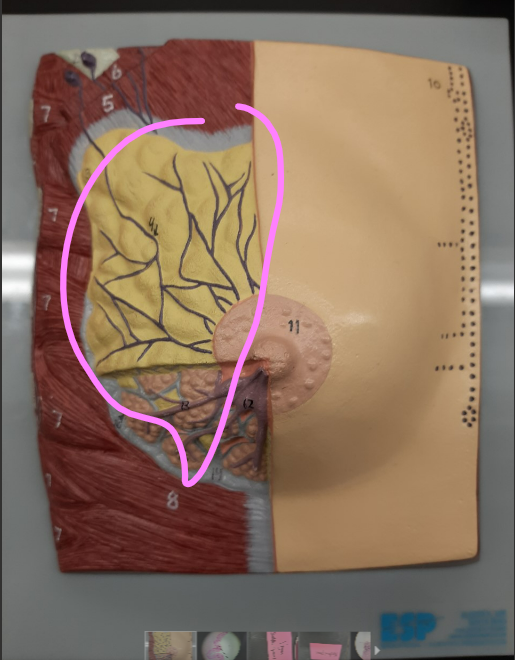
98
New cards
suspensory ligament
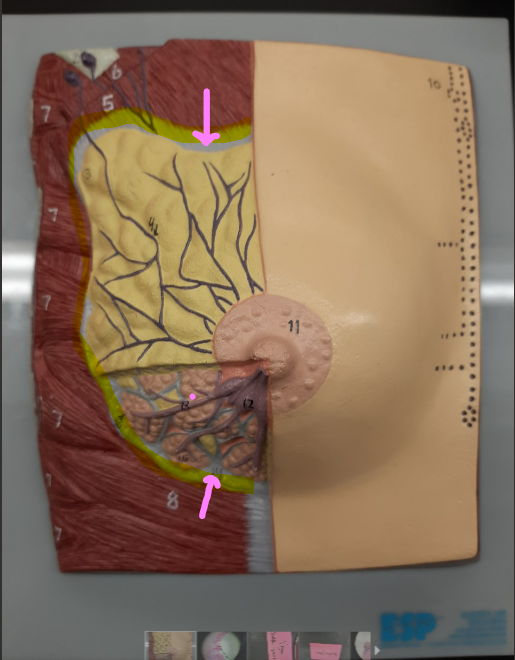
99
New cards
adipose tissue
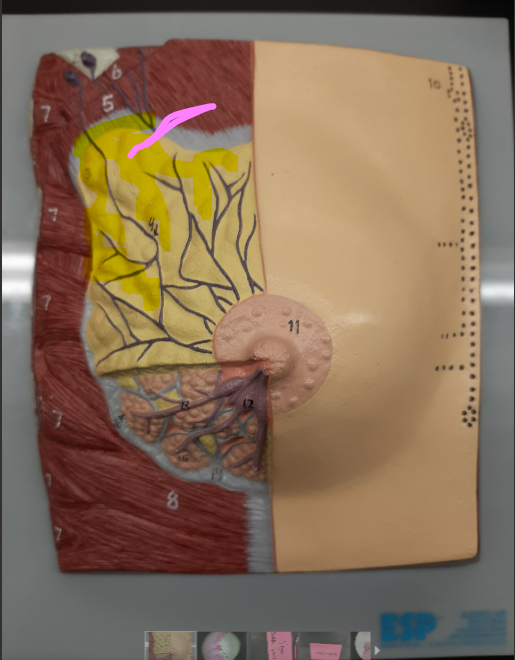
100
New cards
lactiferous sinus