Circular Motion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Multiple Correct: A person stands on a merry-go-round which is rotating at constant angular speed. Which of the following are true about the frictional force exerted on the person by the merry-go-round? Select two answers.
(A) The force is greater in magnitude than the frictional force exerted on the person by the merry-go-round.
(B) The force is opposite in direction to the frictional force exerted on the merry-go-round by the person.
(C) The force is directed away from the center of the merry-go-round.
(D) The force is dependent on the person's mass
B, D
A ball attached to a string is whirled around in a horizontal circle having a radius R. If the radius of the circle is changed to 4R and the same centripetal force is applied by the string, the new speed of the ball is which of the following?
(A) One-quarter the original speed
(B) One-half the original speed
(C) The same as the original speed
(D) Twice the original speed
(D) Twice the original speed
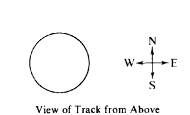
A racing car is moving around the circular track of radius 300 meters shown above. At the instant when the car's velocity is directed due east, its acceleration is directed due south and has a magnitude of 3 meters per second squared. When viewed from above, the car is moving
(A) clockwise at 30 m/s
(B) clockwise at 10 m/s
(C) counterclockwise at 30 m/s
(D) counterclockwise at 10 m/s
(A) clockwise at 30 m/s
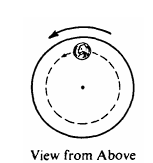
The horizontal turntable shown above rotates at a constant rate. As viewed from above, a coin on the turntable moves counterclockwise in a circle as shown. Which of the following vectors best represents the direction of the frictional force exerted on the coin by the turntable when the coin is in the position shown?
C
In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? Select two answers.
(A) It moves in a straight line at constant speed.
(B) It moves with uniform circular motion.
(C) It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance.
(D) It is at rest.
B, C
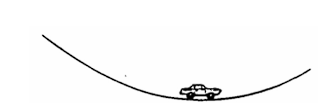
An automobile moves at constant speed down one hill and up another hill along the smoothly curved surface shown above. Which of the following diagrams best represents the directions of the velocity and the acceleration of the automobile at the instant that it is at the lowest position. as shown?
B
A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding?
(A) The force is directed away from the center of the circle.
(B) There is not enough force directed north to keep the package from sliding.
(C) There is not enough force tangential to the car's path to keep the package from sliding.
(D) There is not enough force directed toward the center of the circle to keep the package from sliding.
(D) There is not enough force directed toward the center of the circle to keep the package from sliding.
A child has a toy tied to the end of a string and whirls the toy at constant speed in a horizontal circular path of radius R. The toy completes each revolution of its motion in a time period T. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the toy?
B
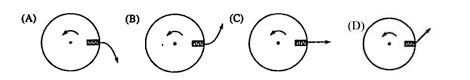
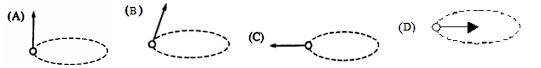
A compressed spring mounted on a disk can project a small ball. When the disk is not rotating, as shown in the top view above, the ball moves radially outward. The disk then rotates in a counterclockwise direction as seen from above, and the ball is projected outward at the instant the disk is in the position shown above. Which of the following best shows the subsequent path of the ball relative to the ground?
D
A steel ball supported by a stick rotates in a circle of radius r, as shown above. The direction of the net force acting on the ball when it is in the position shown is indicated by which of the following?
C
Inside a washing machine, the radius of the cylinder where the clothes sit is 0.50 m. In one of its settings the machine spins the cylinder at 2.0 revolutions per second. What is the acceleration of an item of clothing?
(A) 0.080 m/s2 (B) 1.6 m/s2 (C) 8.0 m/s2 (D) 79 m/s2
(D) 79 m/s2
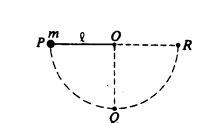
A ball of mass m is attached to the end of a string of length Q as shown above. The ball is released from rest from position P. where the string is horizontal. It swings through position Q. where the string is vertical, and then to position R. where the string is again horizontal. What are the directions of the acceleration vectors of the ball at positions Q and R?
Position Q
(A) Position Q: Downward - Position R: Downward
(B) Position Q: Downward - Position R: To the right
(C) Position Q: Upward - Position R: Downward
(D) Position Q: Upward - Position R: To the left
(C) Position Q: Upward - Position R: Downward
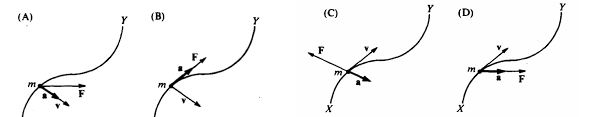
A mass m moves on a curved path from point X to point Y. Which of the following diagrams indicates a possible combination of the net force F on the mass, and the velocity v and acceleration a of the mass at the location shown?
D
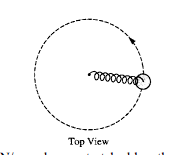
A spring has a force constant of 100 N/m and an unstretched length of 0.07 m. One end is attached to a post that is free to rotate in the center of a smooth table, as shown in the top view above. The other end is attached to a 1 kg disc moving in uniform circular motion on the table, which stretches the spring by 0.03 m. Friction is negligible. What is the centripetal force on the disc?
(A) 0.3 N (B) 3N (C) 10 N (D) 300 N
(B) 3N
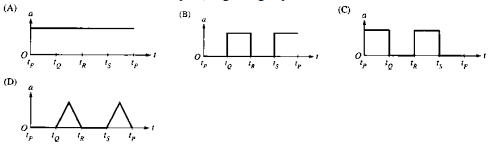
A figure of a dancer on a music box moves counterclockwise at constant speed around the path shown above. The path is such that the lengths of its segments, PQ, QR, RS, and SP, are equal. Arcs QR and SP are semicircles. Which of the following best represents the magnitude of the dancer's acceleration as a function of time t during one trip around the path, beginning at point P?
B
A car travels forward with constant velocity. It goes over a small stone, which gets stuck in the groove of a tire. The initial acceleration of the stone, as it leaves the surface of the road, is
(A) vertically upward
(B) horizontally forward
(C) horizontally backward
(D) zero
(A) vertically upward
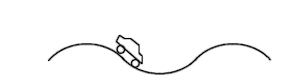
A car is traveling on a road in hilly terrain, see figure to the right. Assume the car has speed v and the tops and bottoms of the hills have radius of curvature R. The driver of the car is most likely to feel weightless:
(A) at the top of a hill when v GREATER THAN (sqrt)gR
(B) at the bottom of a hill when v GREATER THAN (sqrt)gR
(C) going down a hill when v EQUAL TO (sqrt)gR
(D) at the top of a hill when v EQUAL TO gR
(A) at the top of a hill when v GREATER THAN (sqrt)gR
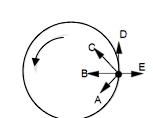
An object shown in the accompanying figure moves in uniform circular motion. Which arrow best depicts the net force acting on the object at the instant shown?
(A) A
(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
(B) B
Multiple Correct: A child whirls a ball at the end of a rope, in a uniform circular motion. Which of the following statements is true? Select two answers.
(A) The speed of the ball is constant
(B) The velocity is of the ball is constant
(C) The magnitude of the ball's acceleration is constant
(D) The net force on the ball is directed radially outwards
A, C
An astronaut in an orbiting space craft attaches a mass m to a string and whirls it around in uniform circular motion. The radius of the circle is R, the speed of the mass is v, and the tension in the string is F. If the mass, radius, and speed were all to double the tension required to maintain uniform circular motion would be
(A) F (B) 2F (C) 4F (D) 8F
(C) 4F
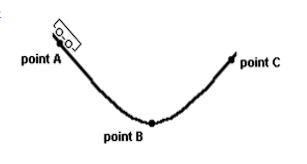
Assume the roller coaster cart rolls along the curved track from point A to point C under the influence of gravity. Assume the friction between the track and the cart is negligible. What would be the direction of the cart's acceleration at point B?
(A) upward
(B) downward
(C) forward
(D) backward
(A) upward
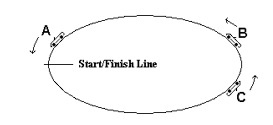
Questions 22 - 23
Which car has had the lowest average speed during the race so far?
(A) car A
(B) car B
(C) car C
(D) all three cars have had the same average speed
C) car C
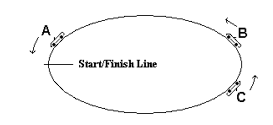
Questions 22 - 23
Which car at the moment of the snapshot MUST have a net force acting on it?
(A) car A
(B) car B
(C) car C
(D) all three cars have net forces acting on them
(D) all three cars have net forces acting on them
A centripetal force of 5.0 newtons is applied to a rubber stopper moving at a constant speed in a horizontal circle. If the same force is applied, but the radius is made smaller, what happens to the speed, v, and the frequency, f, of the stopper?
(A) v increases and f increases
(B) v decreases and f decreases
(C) v increases and f decreases
(D) v decreases and f increases
(D) v decreases and f increases
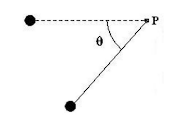
Astronauts on the Moon perform an experiment with a simple pendulum that is released from the horizontal position at rest. At the moment shown in the diagram with 0° <θ < 90°, the total acceleration of the mass may be directed in which of the following ways?
(A) straight to the right
(B) straight upward
(C) straight downward
(D) straight along the connecting string toward point P (the pivot)
(A) straight to the right
A 4.0 kg mass is attached to one end of a rope 2 m long. If the mass is swung in a vertical circle from the free end of the rope, what is the tension in the rope when the mass is at its highest point if it is moving with a speed of 5 m/s?
(A) 5.4 N (B) 10.8 N (C) 50 N (D) 65.4 N
(B) 10.8 N
A ball of mass m is fastened to a string. The ball swings at constant speed in a vertical circle of radius R with the other end of the string held fixed. Neglecting air resistance, what is the difference between the string's tension at the bottom of the circle and at the top of the circle? (A) mg (B) 2mg (C) 4mg (D) 8mg
(B) 2mg
An object weighing 4 newtons swings on the end of a string as a simple pendulum. At the bottom of the swing, the tension in the string is 6 newtons. What is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the object at the bottom of the swing?
(A) 0.5 g (B) g (C) 1.5 g (D) 2.5 g
(A) 0.5 g
Riders in a carnival ride stand with their backs against the wall of a circular room of diameter 8.0 m. The room is spinning horizontally about an axis through its center at a rate of 45 rev/min when the floor drops so that it no longer provides any support for the riders. What is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rider required so that the rider does not slide down the wall?
(A) 0.056 (B) 0.11 (C) 0.53 (D) 8.9
(B) 0.11