EKGs
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
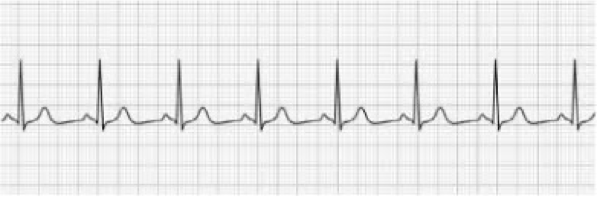
NSR - HR 75 bpm
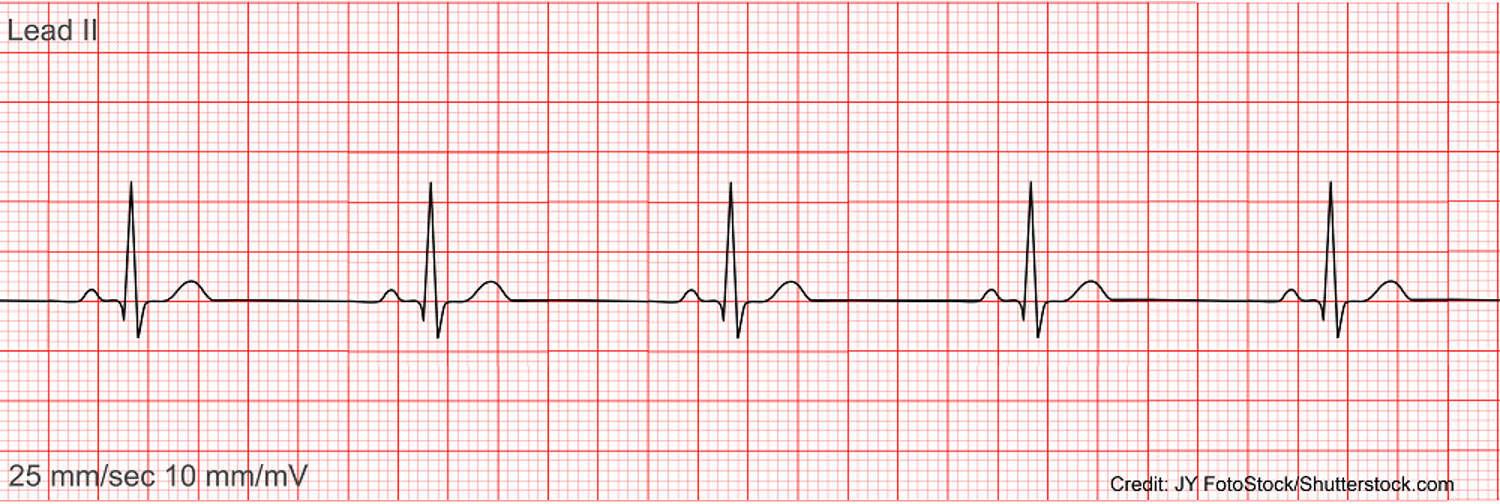
NSR - HR 50 bpm (sinus brady)
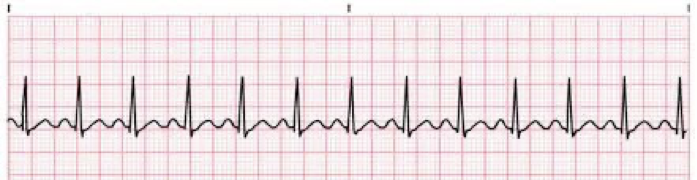
NSR - HR 140 (sinus tach)
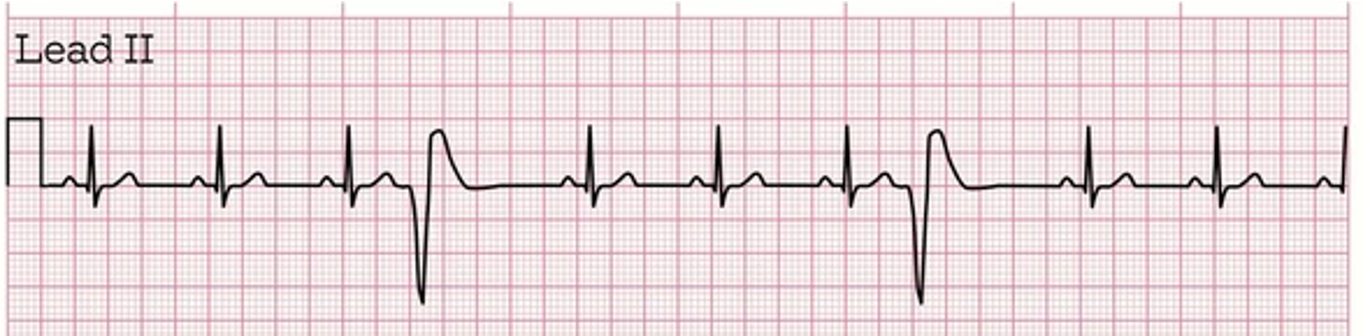
PVC
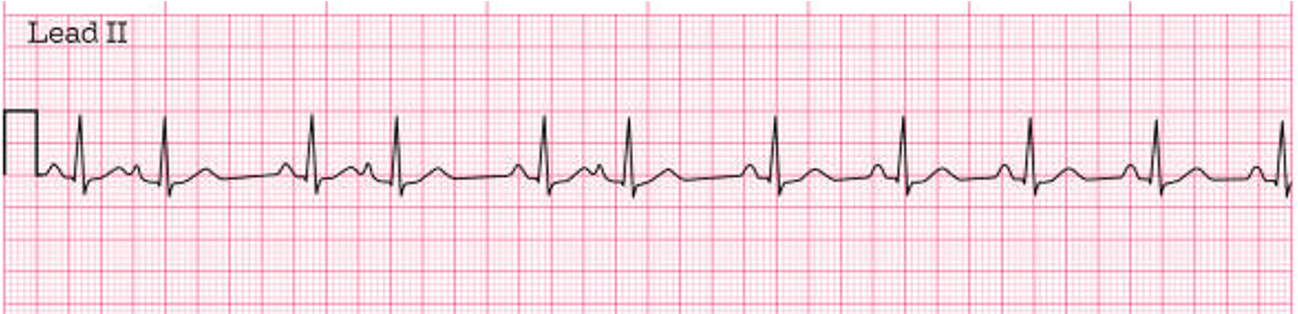
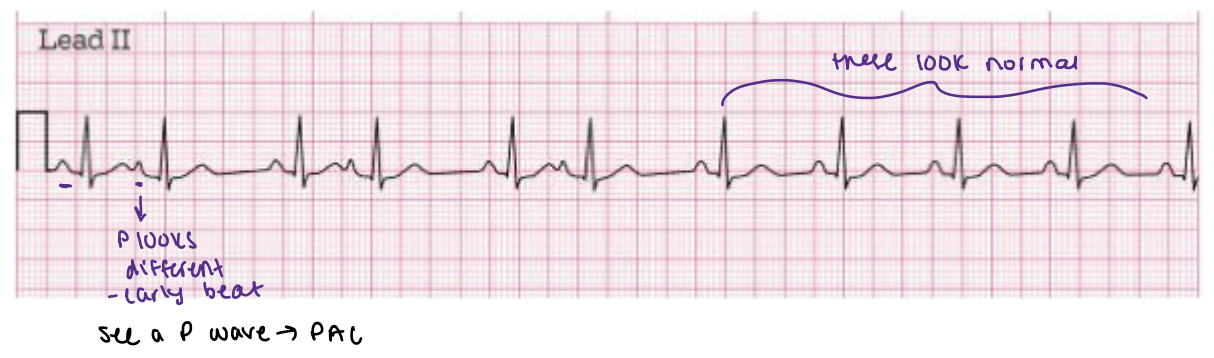
PAC
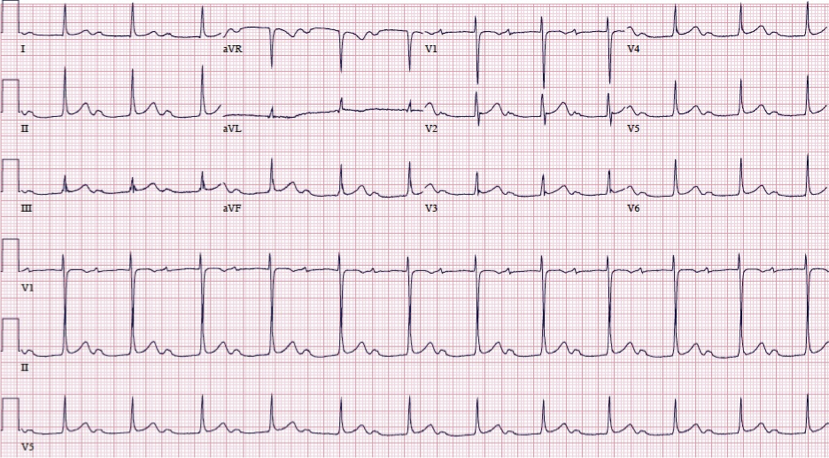
1st degree AV block
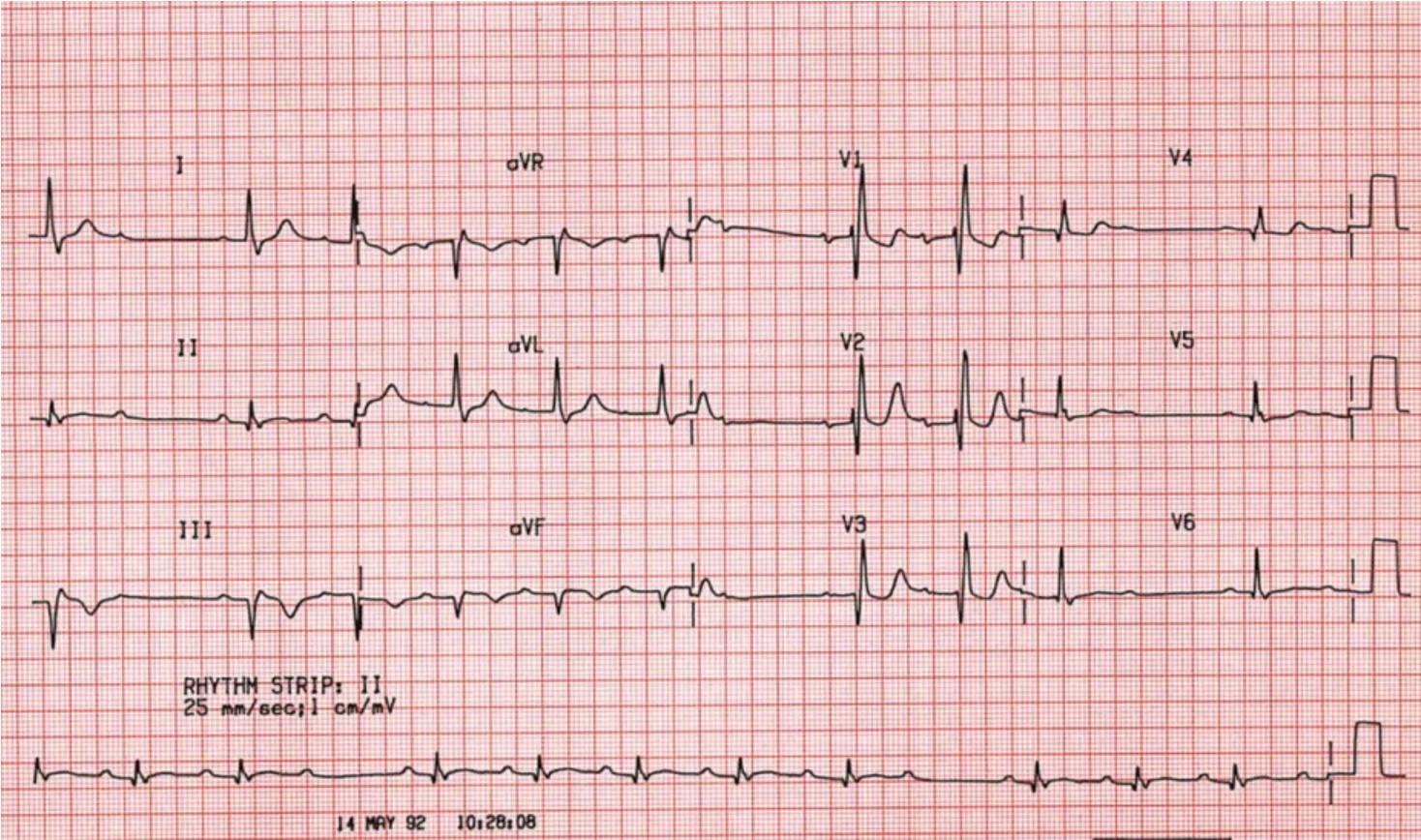
2nd degree AV block type I (Mobitz I/Wenckebach)
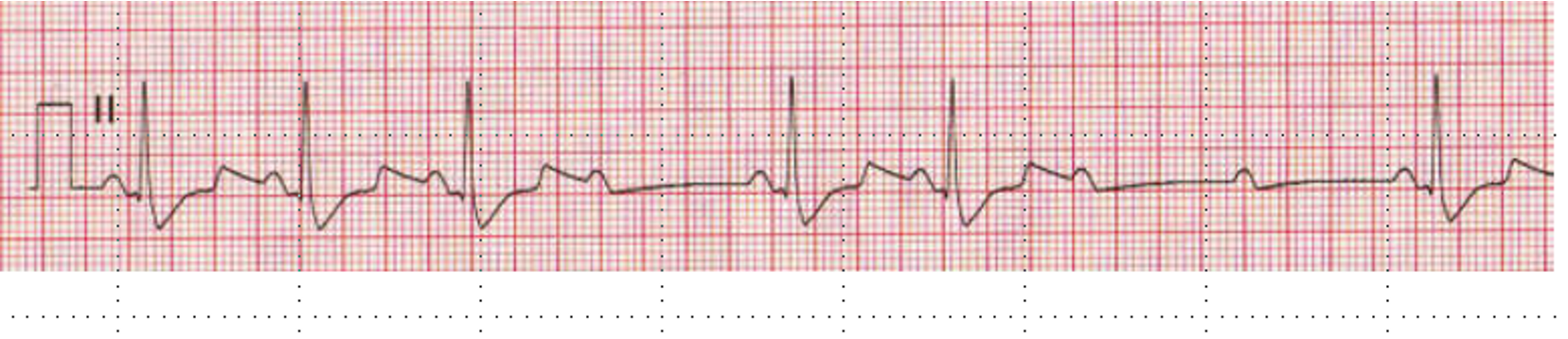
2nd degree AV block type II (Mobitz II)
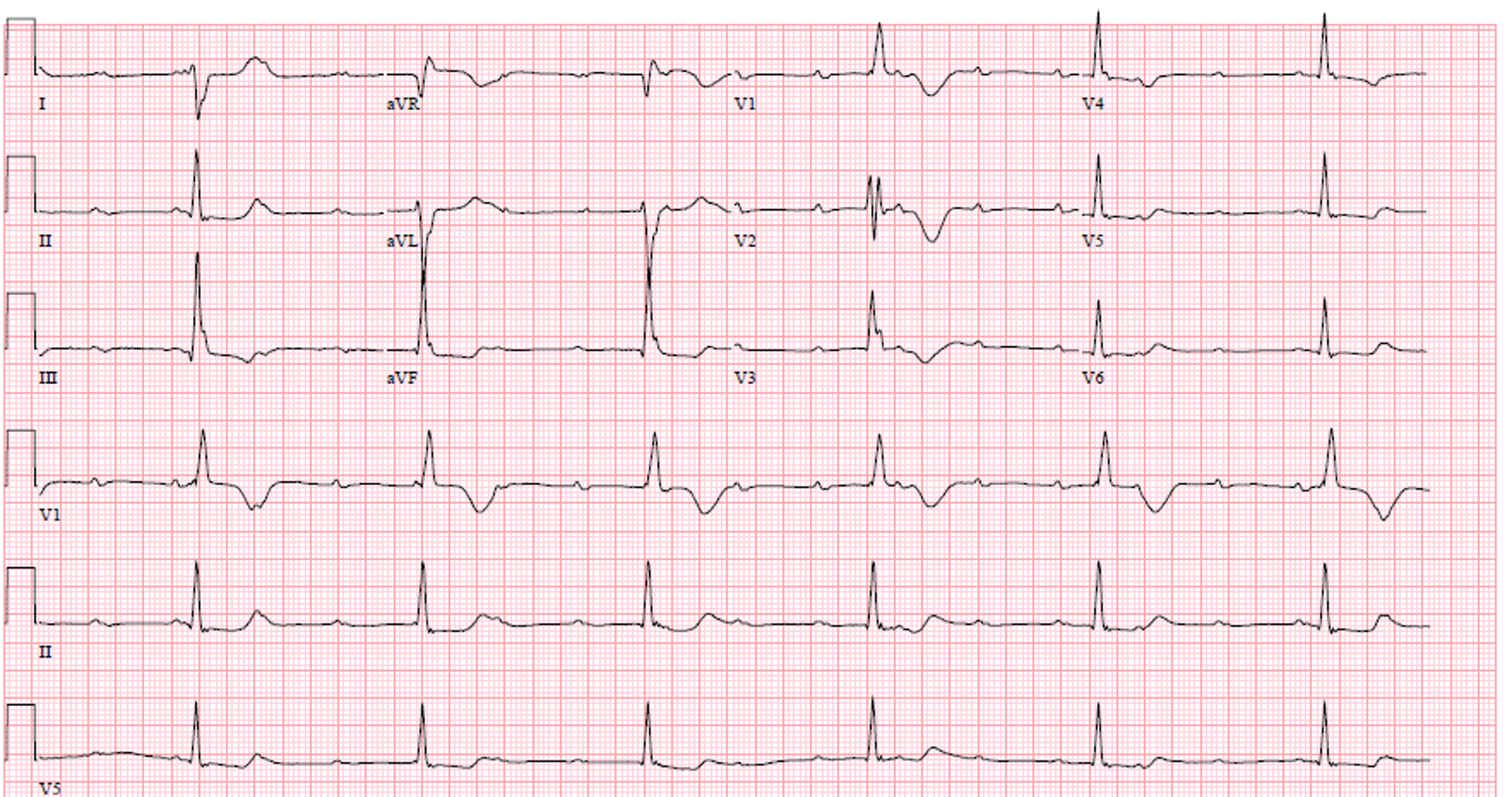
3rd degree heart block
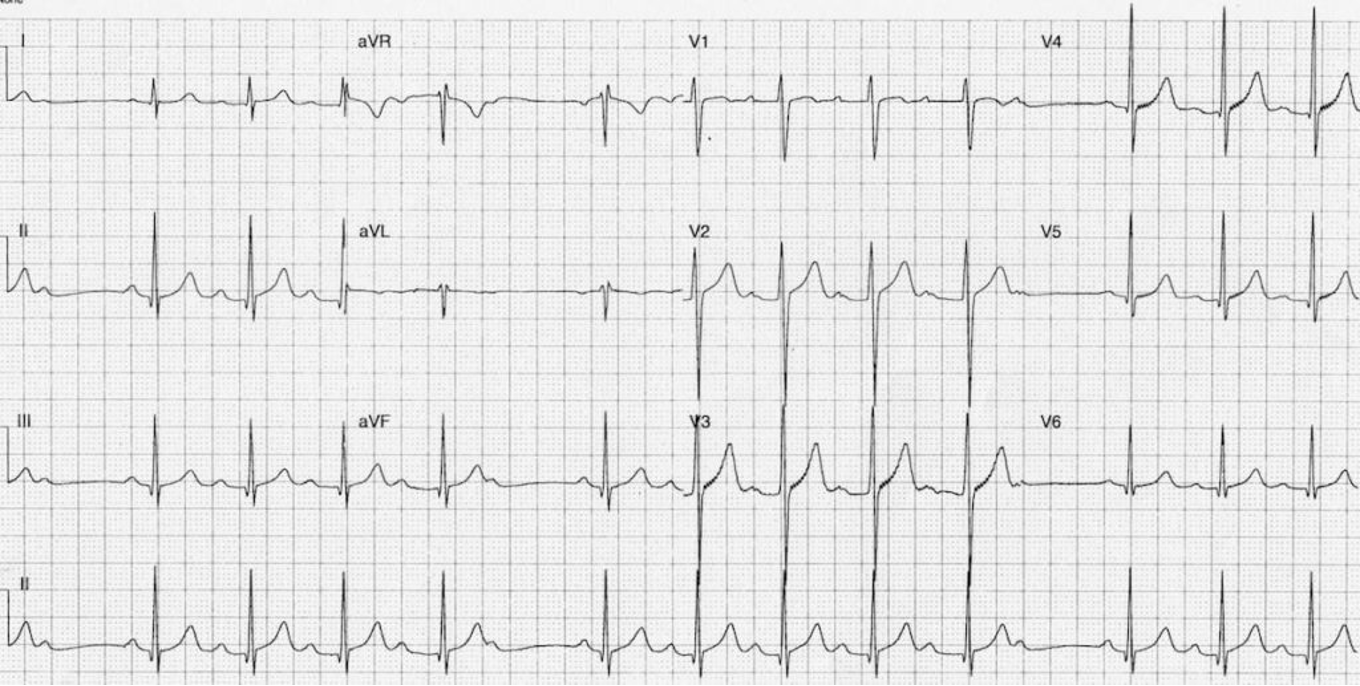
2nd degree heart block type I (mobitz I/wenckeback)
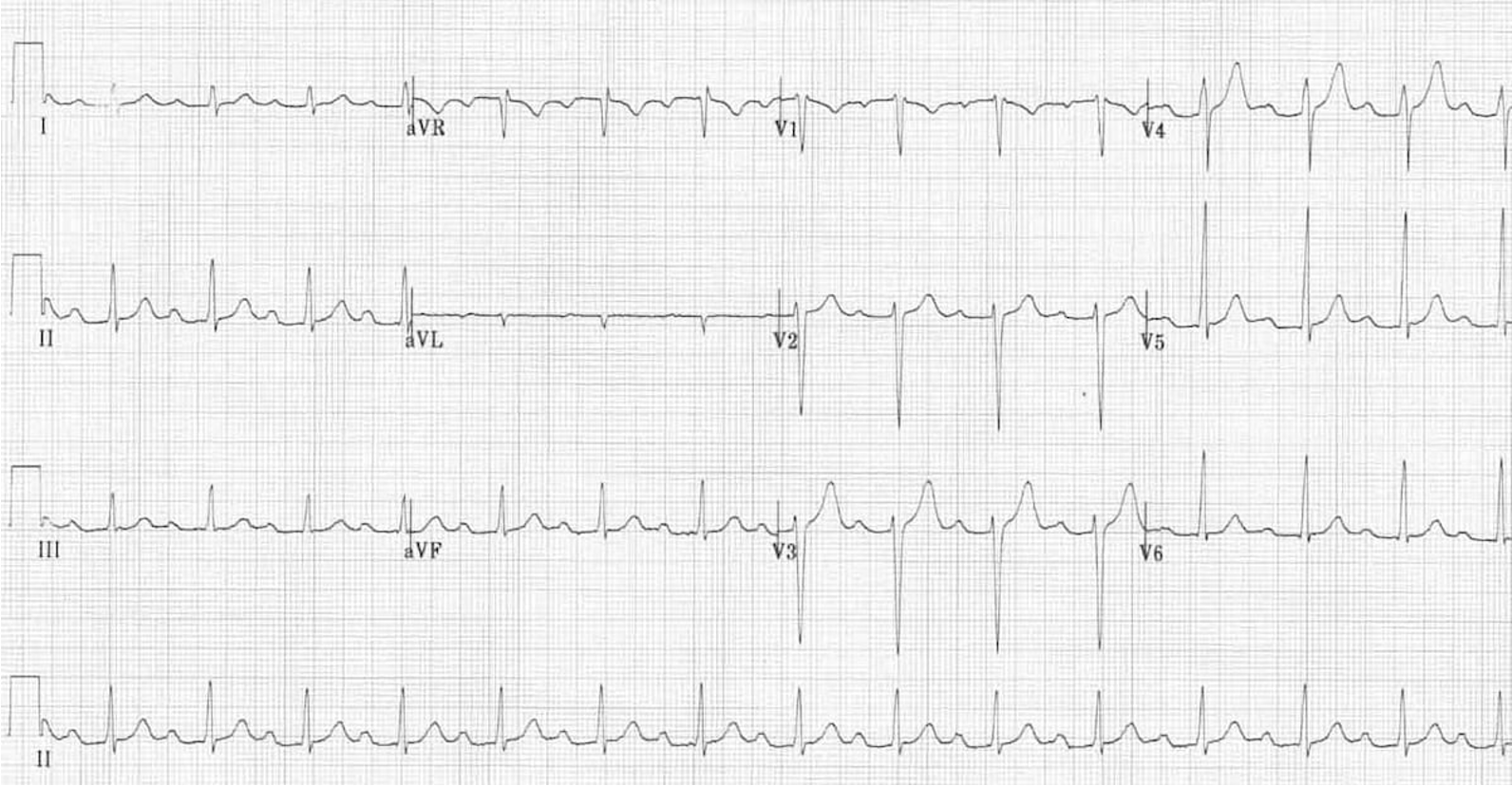
1st degree heart block
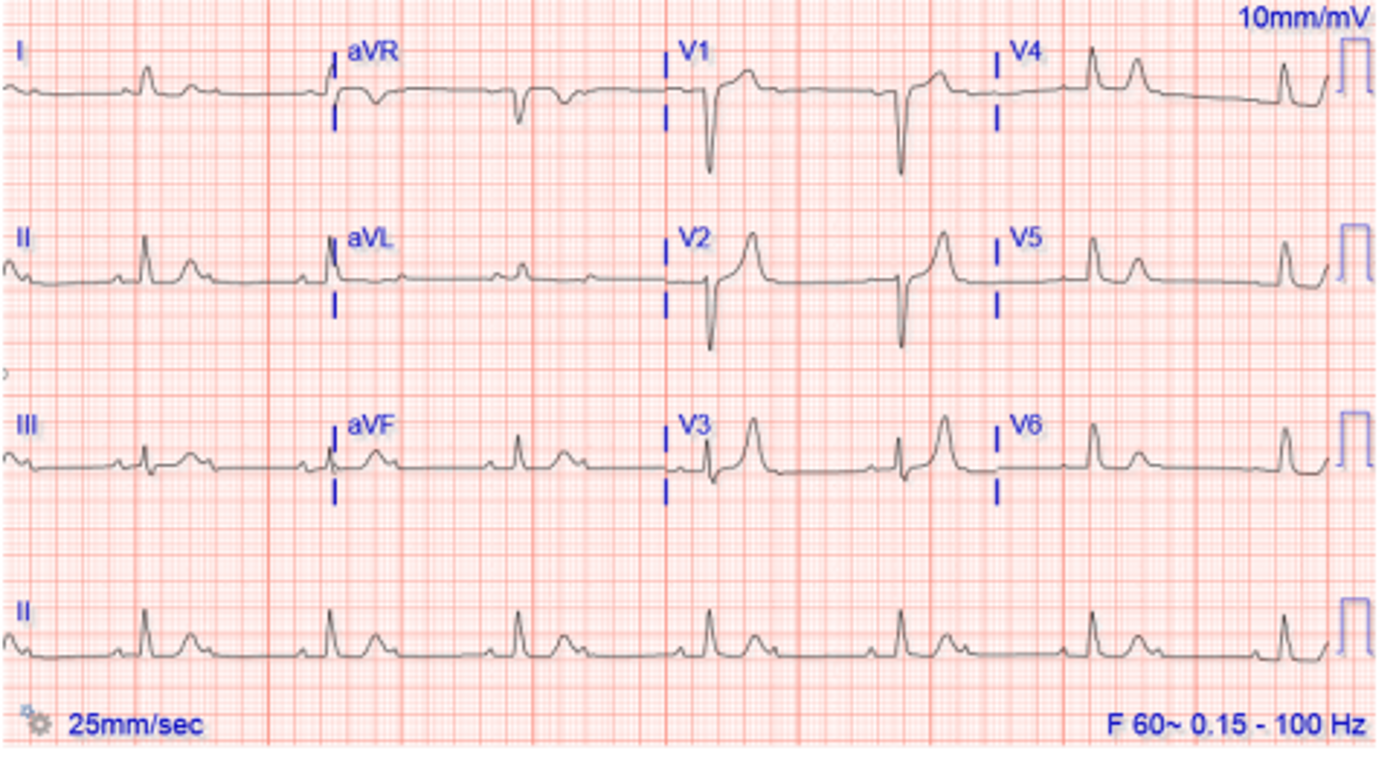
2:1 AV block (type of 2nd degree) - treated like CHB
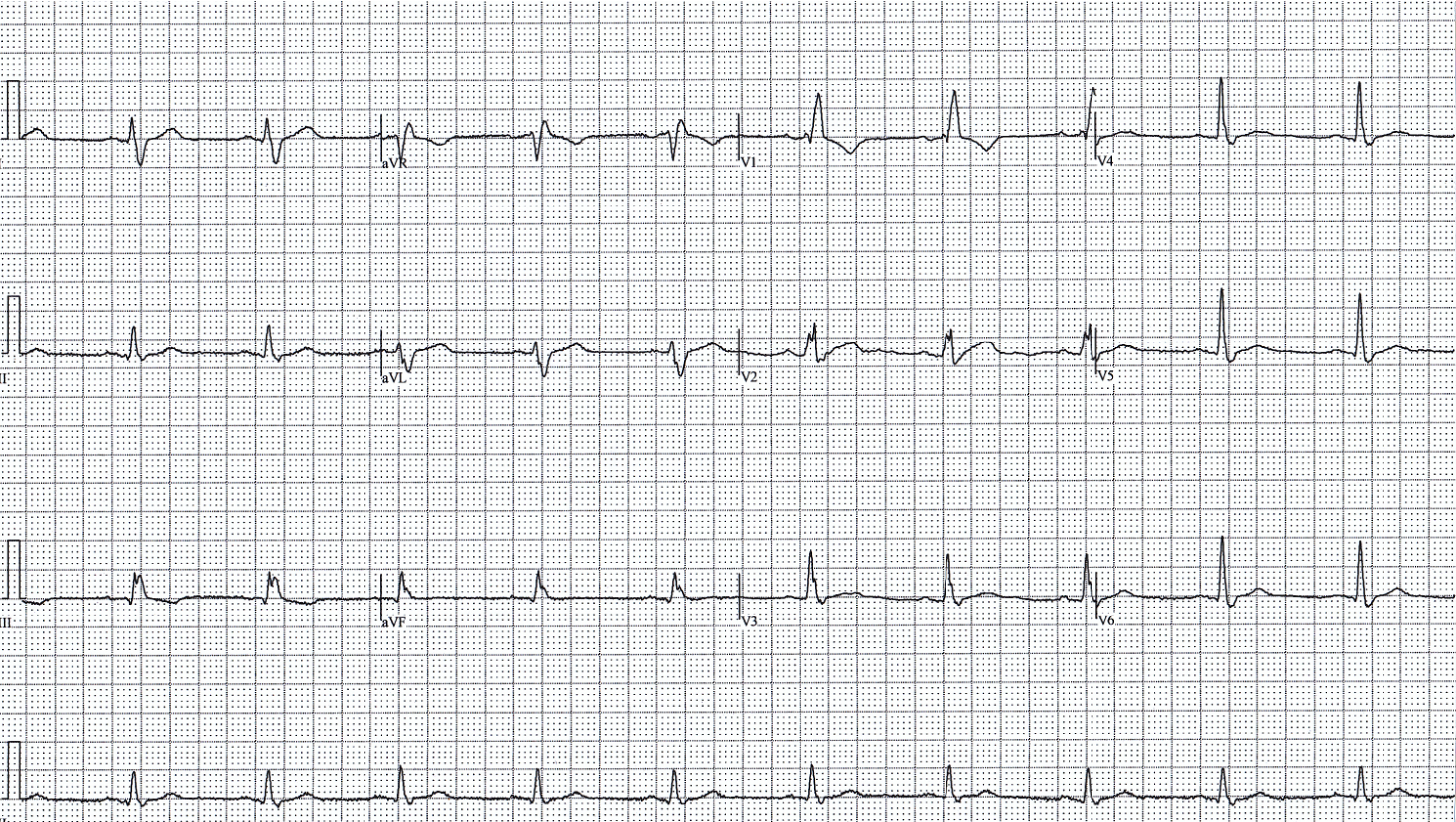
RBBB
RR’ in V1/V2
broad S wave in V6
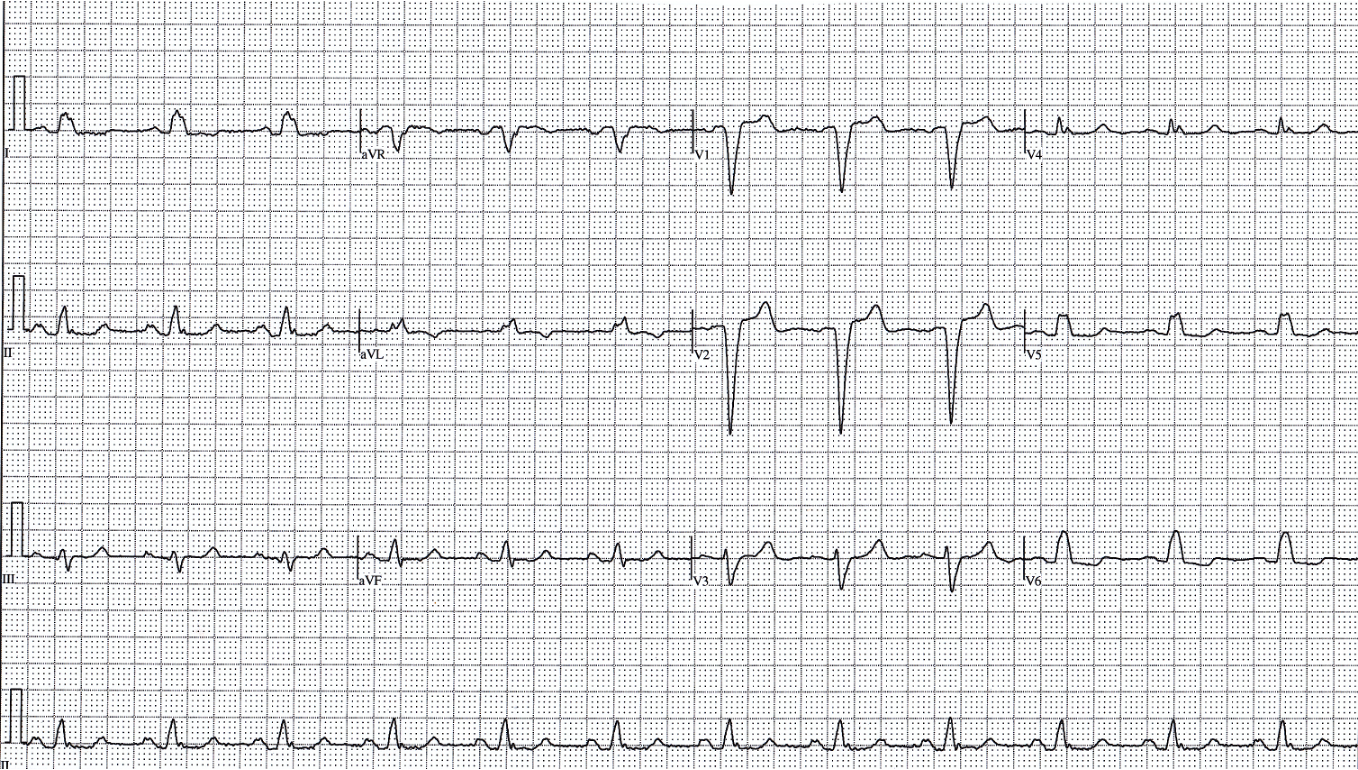
LBBB
rS in V1/V2 (negative)
R in V6 (positive)
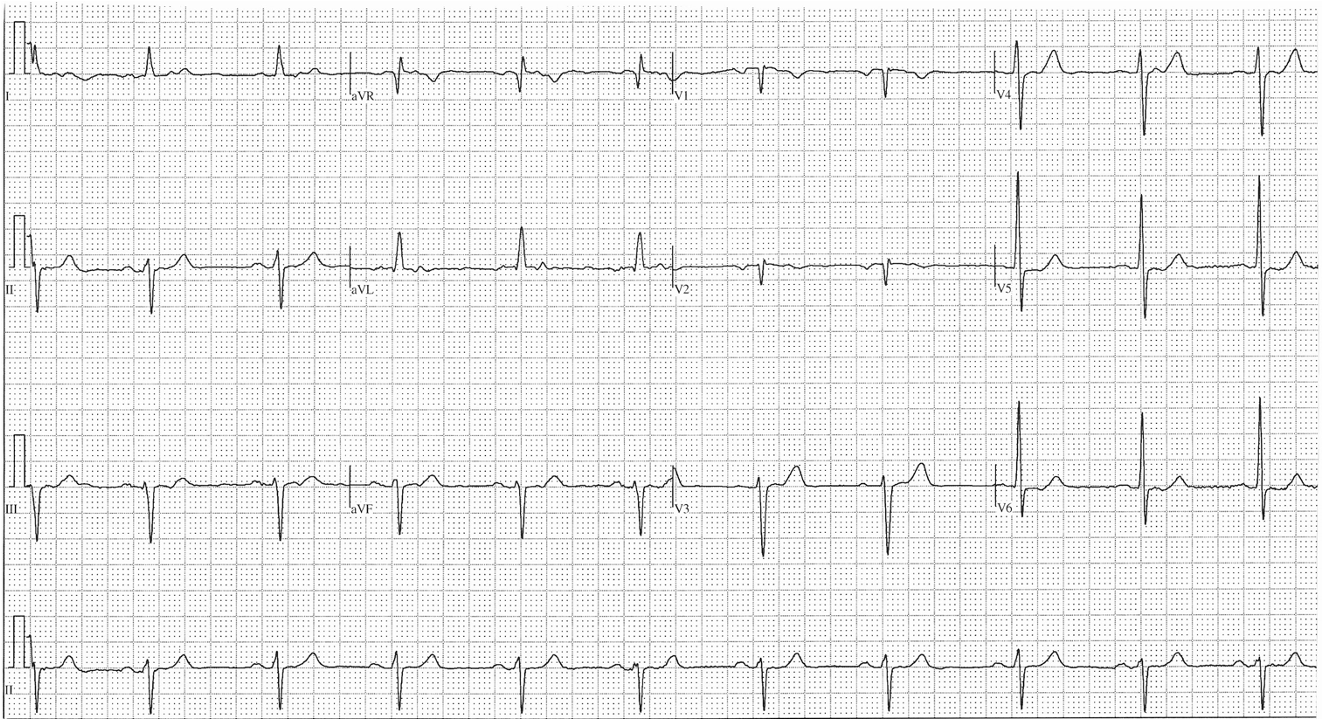
LAFB
LAD
inferior leads: rS (negative)
lateral leads: qR (positive)
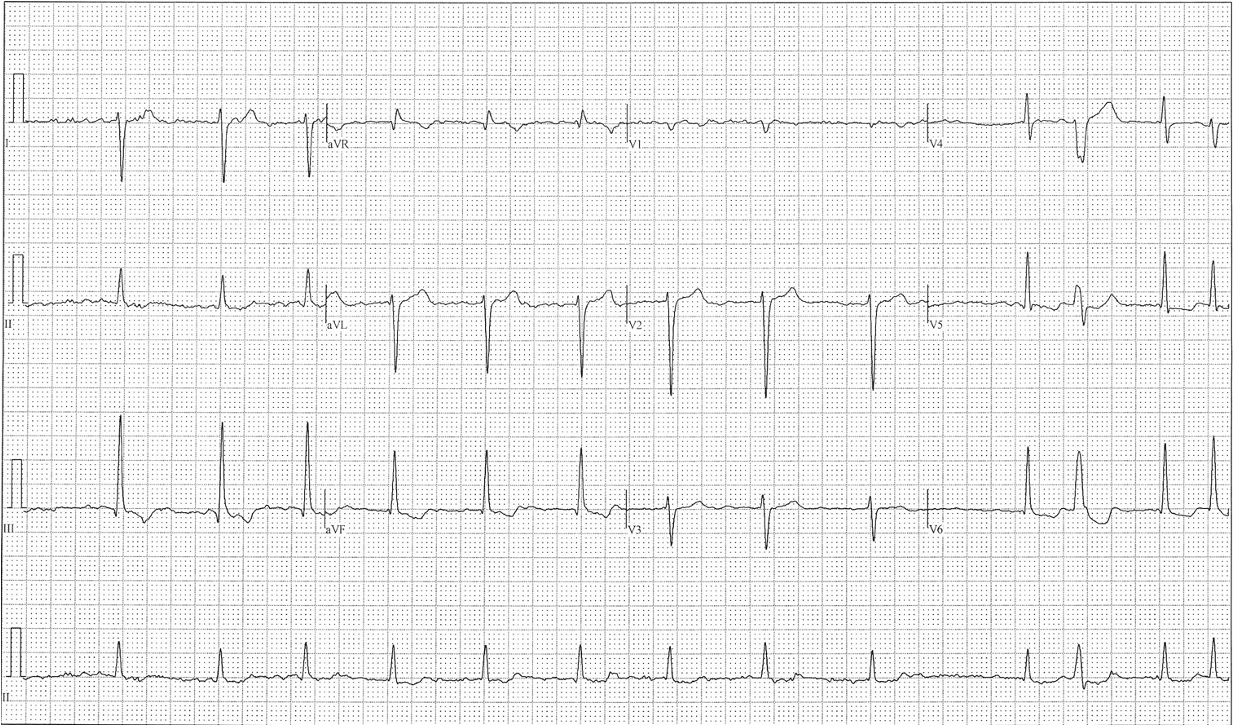
LPFB
RAD
inferior leads qR (positive)
lateral leads rS (negative)
P wave represents…
atrial depolarization
QRS represents…
ventricular depolarization
ST and T wave represents…
ventricular repolarization
phase 0 action potential
sodium channels open → rapid upstroke

phase 1 action potential
(initial) potassium efflux
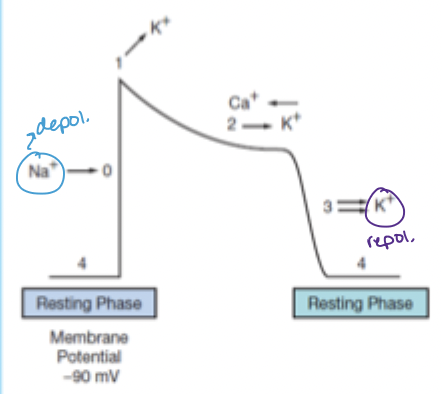
phase 2 action potential
calcium channels open → calcium in matches potassium out
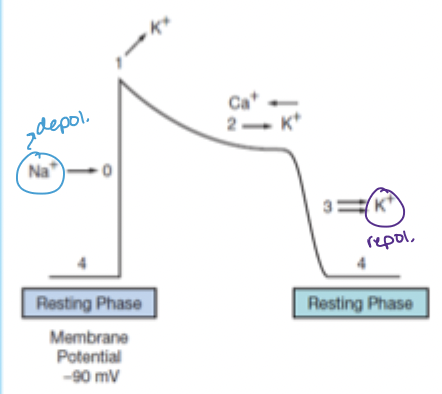
phase 3 action potential
potassium efflux predominates → repolarization
relative refractory period corresponds to which part of the EKG?
T wave (ventricular repolarization)
size of 1 large box (ms or s)
200 ms (0.2 s)
size of 1 small box
40 ms (0.04 s)
PR interval is from the beginning of the P wave to the start of __
QRS
PR interval represents the spread of electricity from ___ to ___
sinus node to AV node
normal PR interval (length)
120-200 ms (3-5 small boxes = <1 large box)
PR interval >0.2 seconds indicates…
1st degree AV block
if PR interval is depressed below baseline, think…
pericarditis
normal QRS length
80-120 ms (<3 small boxes)
**measure the end by the end of the S wave (when it returns back to baseline)
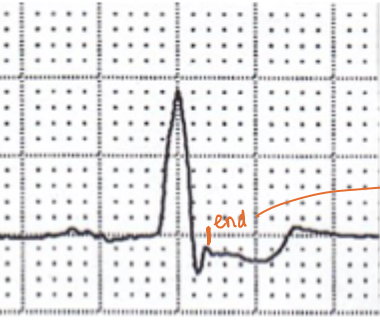
Q wave =
first downward deflection
R wave =
first upward deflection
S wave =
first downward deflection after an R wave
when to use capital vs. lowercase letters for QRS?
capital letter if the wave is 2+ small boxes in height
lowercase if <2 small boxes
pathologic ST segment looks like…
1-2mm above or below baseline in consecutive leads
**not J point elevation (J point = swooping up, ST elevation = immediate rise)
T wave inversion =
ischemia (first stage)
peaked T waves =
hyperkalemia
normal QT interval length
less than ½ of R-R interval
<500 ms/ 2.5 large boxes
as HR increases, QT (increases/decreases)
decreases
bipolar leads (list)
I, II, III
unipolar leads (list)
aVR, aVL, avF
lead I positive and negative
+: LA
-: RA
lead II positive and negative
+: LL
-: RA
lead III positive and negative
+: LL
-: LA
aVR combines leads:
I and II
aVL combines leads:
I and III
aVF combines leads:
II and III
V1 lead location
R 4th intercostal, sternal border
V2 lead location
L 4th intercostal, sternal border
V3 lead location
L, between V2 and V4
V4 lead location
L 5th intercostal, MCL
V5 lead location
even with V4 at anterior axillary line
V6 lead location
even with V4 and V5 at midaxillary line
which leads should have a deep S wave in a normal R wave progression?
V1 and V2
where should R and S waves be equal height in normal R wave progression?
V3
where should R wave be larger than S wave with normal R wave progression?
V4-V6
causes of poor R wave progression
anything that changes depolarization in either ventricle:
block
hypertrophy
infarct
300 rule for determining HR
300, 150, 100, 75, 60, 50
only use if regular rhythm, >40 bpm
count & multiply method for HR
count number of QRS complexes in the rhythm strip and multiply by 6
use for irregular rhythms, bradycardia
characteristics of low atrial focus escape rhythm (P wave, HR)
inverted P wave - because electricity has to move up the atrial walls (normally SA node is at the top)
HR 50-60 bpm
characteristics of AV junctional focus escape rhythm (P wave, HR)
no P wave (not originating in atria)
HR 40-60 bpm
characteristics of ventricular focus escape rhythm (P wave, HR)
no P wave
wide QRS
HR 20-40 bpm
key to determining diagnosing irregular rhythm:
relationship between P and QRS
PACs (do/do not) have a P wave before every QRS
they DO but usually it has a different morphology
can be visible or buried in the previous QRS
PVCs (do/do not) have a P wave before every QRS
do NOT - P waves will come at a regular interval but QRS is irregular
PVCs have a distinctly different appearance from sinus beats (wide QRS)
normal axis degrees
-30 (0) to 90
LAD degrees
-30 to -90
RAD degrees
90 to 180
indeterminate axis degrees
-90 to 180
which leads do you look at to determine axis?
lead I, aVF
lead I positive, aVF positive: axis?
normal
lead I positive, aVF negative: axis?
left axis deviation
lead I negative, aVF positive: axis?
right axis deviation
causes of LAD
left BBB
LVH
LAFB
obesity
inferior wall MI
causes of RAD
COPD
tall, thin frame
right BBB
RVH
LPFB
lateral wall MI
criteria for 1st degree AV block
PRi prolonged >200 ms (>1 big box) with normal QRS
technically a delay not a block
criteria for Type 1 2nd degree block (Mobitz 1)
PR interval progressively lengthening prior to a dropped QRS
→ the PRi of the beat after the dropped QRS will be significantly shortly than the PRi of the beat before the nonconducted P wave
dropped beat occurs when AVN is no longer able to conduct a stimulus from above
criteria for Type 2 2nd Degree block (Mobitz II)
fixed PRi with a P wave that is not followed by a QRS (dropped beat)
why is Mobitz II worse than Mobitz I?
mobitz II is infrahisian (block occurs in the bundle of His (lower than the AV node)) so it is a more unstable rhythm
mobitz I block occurs in AV node
criteria for 3rd degree/complete heart block
atrioventricular dissociation
regular atrial & ventricular rhythms but they are not associated with each other
no atrial depolarizations are able to penetrate AVN → junctional escape rhythm takes over in ventricles
which leads are better for seeing P waves?
V1 and V2
main criteria for bundle branch block
wide QRS
morphology will also be distinct (leads V1/V6)
QRSd in bundle branch block
>120 ms
hemiblock = 100-120 ms
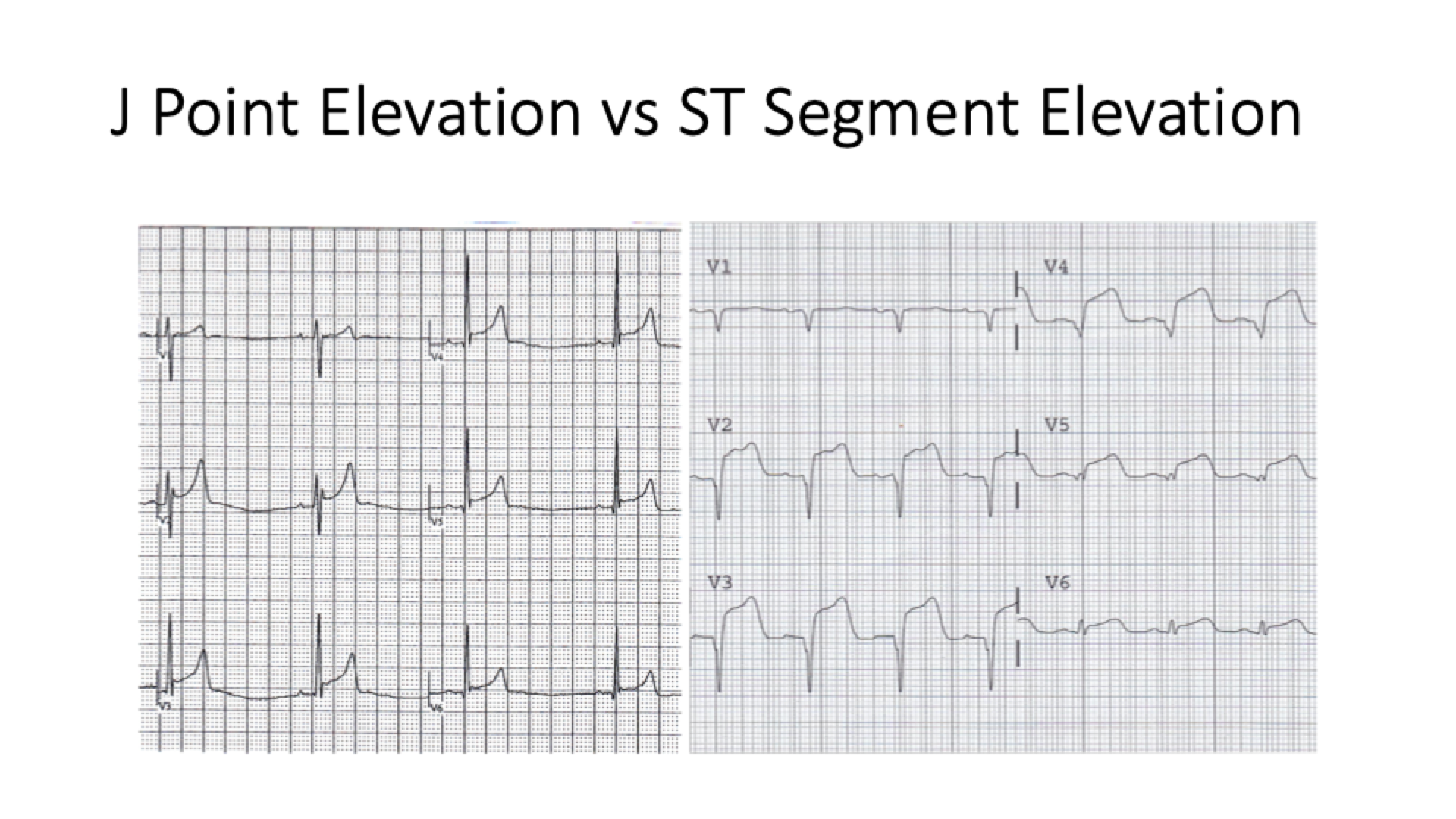
right chest leads in RBBB
“bunny ear” - RR’, rSR (V1 and/or V2)
due to LV contracting before RV → joined but out-of-sync QRS complexes
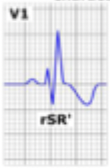
left chest leads in RBBB
broad S wave (V6)
due to slow diffusion of electricity away from LV towards RV
should you be concerned about RBBB?
not necessarily - be concerned if it is a new finding
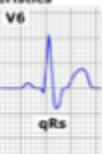
right chest leads in LBBB
QS (single negative deflection) or rS (V1)
may see inverted T
due to electricity moving away to passively depolarize the left
left chest leads in LBBB
tall R wave (often RR’ with no Q)
positive because all electricity is moving towards the left
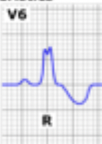
should you be concerned about a LBBB?
yes - always investigate
LAFB:
axis deviation?
inferior leads?
lateral leads?
LAD
negative (II, III, aVF)
positive (I, aVL)
LPFB
axis deviation?
inferior leads?
lateral leads?
RAD
positive (II, III, aVF)
negative (I, aVL)
inverted T waves indicates (ischemia/injury/infarction)
ischemia
ST segement elevation indicates (ischemia/injury/infarction)
injury (early stages of infarction)
infarction is ongoing or imminent
clinically significant ST segment elevation/depression = at least __ mm from baseline
2
Q waves represent (ischemia/injury/infarction)
infarction (scar tissue does not depolarize properly)
__ is often seen with Q waves
inverted T waves
issue with depolarization ←→ issue with repolarization
which vessel supplies the AV node? what can happen if there is an MI in this vessel?
RCA (supplies the inferior wall)
inferior wall MI can lead to complete heart block