Leadership & Cooperation and Competition
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
what quality promotes perceived leadership status?
communication; leaders of groups engage in more communication than nonleaders.
Kurt Lewin’s study on leadership styles
situation: boys in an after-school program were organized into groups with three different leadership styles: autocratic, democratic, and laissez-faire.
findings:
1) laissez-faire groups were less efficient, less organized, and less satisfying for the boys than democratic groups;
2) autocratic groups were more hostile, more aggressive, and more dependent on their leader, with greater quantity of work;
3) democratic groups were more satisfying and more cohesive, with stronger work motivation and interest
cooperation
acting together for mutual benefit so that everyone can obtain a goal
competition
acting for one’s individual benefit so that they can obtain a goal that has limited availability
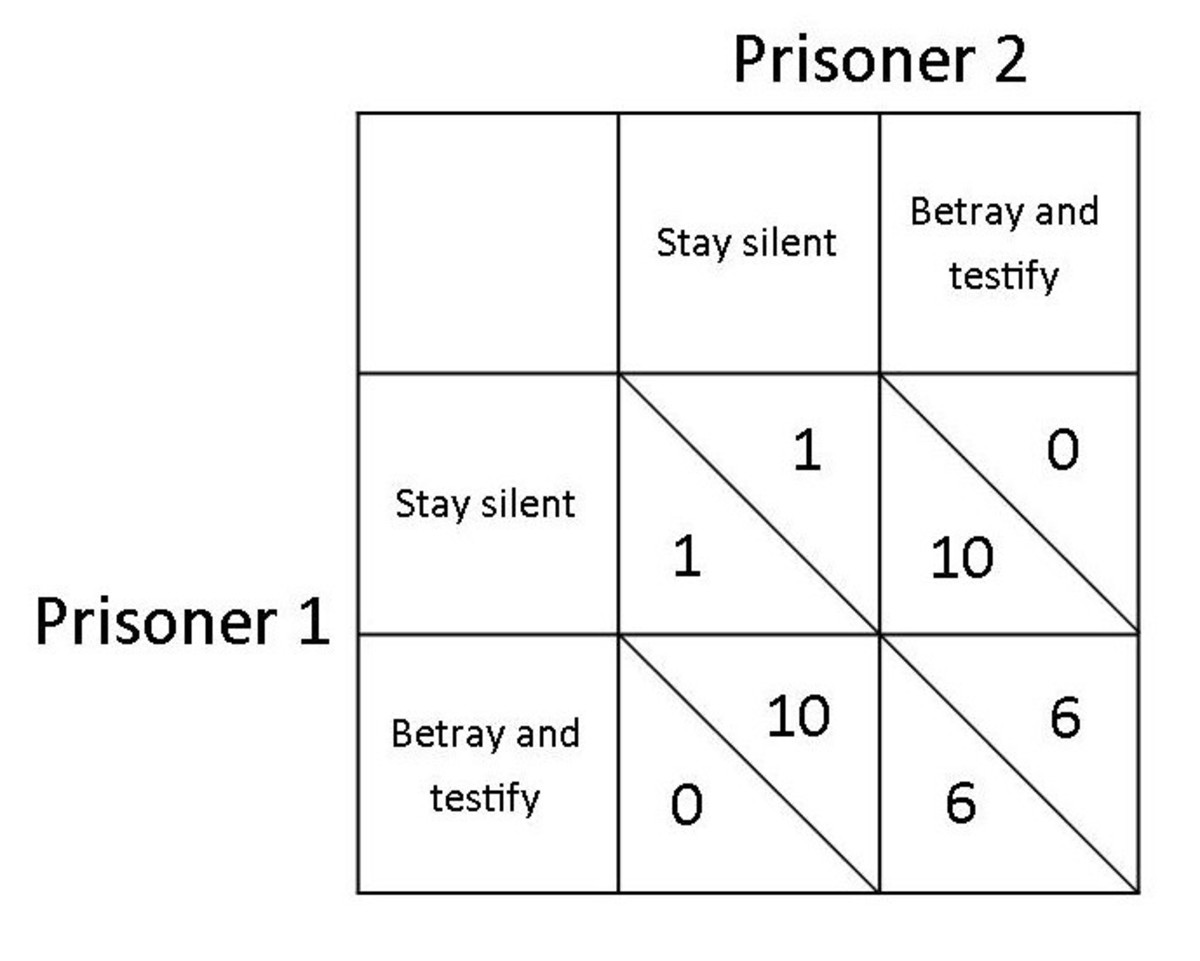
the prisoner’s dilemma
Muzafer Sherif’s Robber’s Cave experiment
situation: group of 12-year-old boys at a boys’ camp were split into two groups; tasks where given in order of within-group cooperation, between-group competition, and between-group cooperation.
findings:
1) within-group cooperation: emergence of status hierarchy, role differentiation for various tasks, and norms for behaviors.
2) between-group competition: generation of between-group hostility, desire for no further contact, and ineffectiveness of mere contact
3) between-group cooperation: joint effort on superordinate goals (goals best obtained through intergroup cooperation) dramatically improved intergroup relations