2.2 2.3 aggregrate demand aggregate supply
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
difference between a movement and a shift on a curve
When the curve is affected due to the price change, we see a movement along the curve. However, when the curve is affected due to any change other than any change in the price of a given product, we see the shift of the curve itself.
how does disposable income effect consumer spending
- Consumers are likely to buy non-essential items when they have extra income. increasing consumption,shifting AD to the increasing GDP and increasing growth
- Lower disposable income can lead to reduced spending, causing consumers to prioritize necessities.
- Overall, disposable income plays a crucial role in influencing both short-run AD and long-term economic growth, but its impact is influenced by broader economic conditions.
how can the rate if savings effect consumer spending
Savings represent the portion of disposable income not spent on consumption. A higher savings rate typically means households are spending less, leading to a fall in consumption (C) — a major component of aggregate demand (AD). This can cause the AD curve to shift left, potentially reducing real GDP and slowing economic growth in the short run.
When consumers prioritise saving over spending, demand for goods and services falls. This can lead to lower revenue for businesses, discouraging investment (I) and possibly leading to reduced employment and output.
On the other hand, a lower savings rate indicates that consumers are spending a larger proportion of their income, increasing consumption and boosting aggregate demand, which may stimulate economic growth.
if savings are later spent (e.g. during retirement or uncertainty passes), they can still contribute to AD over time.
how can interest rates effect consumer spending
When the central bank lowers interest rates, the cost of borrowing falls, making loans for consumption (e.g. credit cards, car finance, mortgages) more attractive. As a result, consumers are likely to increase spending on durable goods and housing, which raises consumption (C) — a major component of AD. This shift in behavior leads to a rightward shift in the AD curve, potentially increasing real GDP and promoting economic growth.
In contrast, higher interest rates increase borrowing costs and raise the incentive to save, discouraging consumer spending. Monthly repayments on mortgages and loans also rise, which reduces disposable income and suppresses demand for goods and services, shifting AD to the left.
how can consumer confidence effect consumer spending
- High consumer confidence generally leads to increased consumer spending, as people feel secure in their financial situation.
- When consumers are optimistic about the economy, they are more likely to make larger purchases.
- Low consumer confidence can result in reduced spending, as individuals may prioritize saving in uncertain times.
how does economic performance of other nations impact the UK
The slow growth of the Eurozone in 2012 to 2014 affected the UK's export sales (we require demand from Europe for our financial services)
difference between gross investment and net investment
- Gross investment is the total money spent on new assets.
- Net investment is what’s left after accounting for the loss of value in old assets.
- So, gross shows total spending, and net shows real growth.
how does the rate of economic growth effect investment
Economic growth tends to boost investment as firms expect higher future demand. This links to the accelerator effect, where rising output leads to increased capital spending. Strong growth also improves business confidence, making firms more willing to invest.
In contrast, during periods of low or negative growth, firms may delay investment due to uncertainty and spare capacity.
However, investment decisions also depend on other factors such as interest rates, government policy, and access to credit. So while growth encourages investment, it’s not the only influence.
how does business confidence effect investment
- High confidence boosts investment.
- Firms expand when they feel secure.
- Low confidence holds back investment.
- Confidence is crucial for investment decisions.
how does animal spirits effect investment
- Animal spirits influence investment through emotions.
- High spirits boost investment due to optimism.
- Low spirits lead to cautious investment.
- They significantly shape investment trends.
how does demand for exports influence investment
When demand for a country’s exports increases, foreign consumers are buying more of its goods and services. This leads to:
Higher revenue for exporting firms
→ Firms see rising profits and stronger sales.Greater expected future demand
→ Firms anticipate continued growth in orders from abroad.Increased need for capacity
→ To meet this demand, businesses may invest in:New machinery
More workers
Expanding factories
The accelerator effect
→ Investment increases because output is rising due to export demand.
how do interest rates influence investment
- Low rates lower borrowing costs, encouraging investment.
- High rates increase costs, deterring investment.
- The relationship affects overall economic growth.
how does access to credit influence investment
- Easy access encourages borrowing for projects and expansion.
- Limited access restricts investment opportunities.
- Overall, credit availability affects business growth.
how do government regulations influence investment
- Favorable regulations can encourage more investment.
- Strict regulations may increase costs and deter investment.
how does real income effect trade balance
- Higher Real Income: Boosts imports, worsening trade balance.
- Lower Real Income: Reduces imports, improving trade balance.
.
how do exchange rates effect trade balance
- Strong Currency: Exports more expensive; imports cheaper, worsening trade balance.
- Weak Currency: Exports cheaper; imports more expensive, improving trade balance.
- Inflation: Higher inflation can weaken currency, affecting trade dynamics. .
how does state of world economy effect the trade balance
- Global Demand: Increases exports, improves trade balance.
- Recessions: Decrease demand, worsen trade balance.
- Trade Agreements: Influence trade balance positively or negatively.
how does degree of protectionism effect trade balance
- High Protectionism: Reduces imports, can improve trade balance.
- Tariffs: Increase costs of imports, encouraging local consumption.
- Trade Barriers: Limit foreign competition, benefiting domestic localities
how do non price factors influence the trade balance
- Quality: Higher quality goods attract more exports.
- Brand Reputation: Strong brands can boost sales overseas.
- Consumer Preferences: Changes in tastes affect import and export levels.
how many work visas issued in 2023
just under 500,000!
what causes the SRAS to shift right
Lower production costs (e.g. wages, raw materials)
Improved productivity or technology
Lower business taxes
Cheaper imported inputs (due to currency appreciation)
Favourable supply-side shocks (e.g. good weather)
effect on higher wages on SRAS
- Increased production costs for businesses
- Potential decrease in short run aggregate supply (SRAS)
- Could incentivize firms to invest in labor-saving technology in the long run
a fall in cost of raw materials on SRAS
- Lower production costs
- Increase in short run aggregate supply (SRAS)
- Potential for lower prices and higher demand
- Encourages expansion and hiring for firms
a rise in the value of pound on SRAS
- Increased cost of exports
- Decreased competitiveness of domestic goods abroad
- Potential decrease in short run aggregate supply (SRAS)
- Lower import costs may benefit consumers
- Could lead to trade balance adjustments
a fall in productivity on SRAS
- Increased production costs
- Decrease in short run aggregate supply (SRAS)
- Lower output levels for businesses
- Potential for higher prices due to reduced supply
- May lead to inflationary pressures in the economy
define short run aggregate supply
SRAS is the total output of goods and services at a given price level, with some factors of production fixed. It can change with demand and productivity.
define LRAS
Long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) is the total output an economy can produce when resources are fully utilized, unaffected by the price level.
how do technological advances influence the LRAS of an economy
- Increasing productivity through more efficient production.
- Reducing production costs, encouraging output expansion.
- Creating new products and markets, shifting the LRAS right.
- Enhancing labor force efficiency, leading to higher output.
how will increases in the level of productivity influence LRAS
allowing more output with the same resources.
- Shifts LRAS to the right, indicating higher potential output.
- Stimulates economic growth and improves living standards.
- Enhances overall efficiency in the economy.
how does improving standards of education and skills in an economy effect LRAS
- Enhances workforce productivity, leading to increased output.
- Shifts LRAS to the right, indicating higher potential economic growth.
- Fosters innovation and adaptability in the labor market.
- Contributes to higher living standards and economic stability.
how does a rise in migration of working age people influence LRAS of an economy
- Increases the labor supply, providing more workers for businesses.
- Shifts LRAS to the right, indicating higher potential output.
- Stimulates economic growth through increased consumption and demand.
why may a government value happiness
happiness includes the quality of life rather than the income alone. Government policy can have a significant impact on happiness, for example, by spending money on sporting and leisure facilities. Happiness may be associated with a more productive economy.
how does access to borrowing on credit cards affect consumer consumption
When consumers can borrow on credit, they are able to spend more than their current income allows.leads to higher spending on goods and services. However, if borrowing becomes excessive, it can lead to debt potentially reducing future consumption as consumers allocate more income toward repaying credit card debt.
aggregate demand
I + C + G + (X-M)
C - 60 % of AD
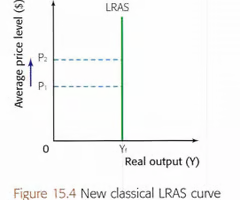
Classical LRAS
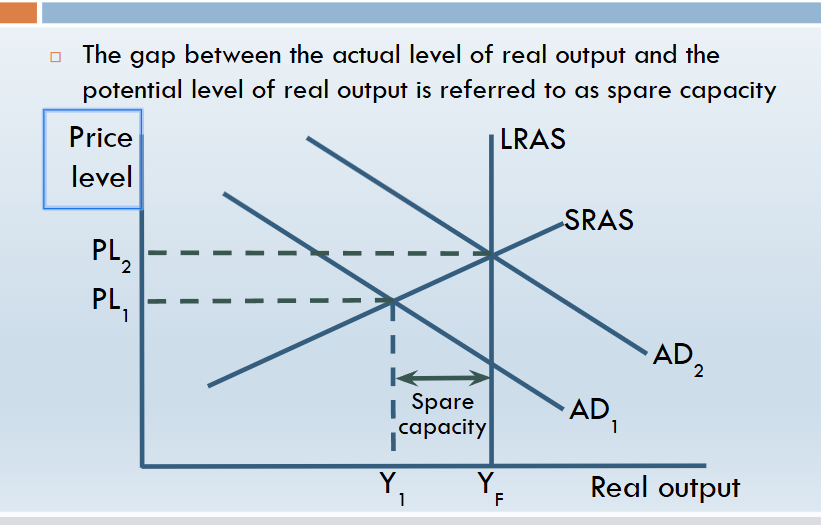
Keynesian LRAS – rise in AD
evaluation against the wealth effect
Liquidity constraints: Some households might be asset-rich but cash-poor, so they can’t easily convert wealth (e.g., housing) into spending money.
Explain the difference between a movement along the AD curve and a shift of the AD curve
A movement along the AD curve occurs when there is a change in the price level. E.g., a fall in the price level causes an expansion in AD.
A shift of the AD curve happens when there is a change in a non-price factor, such as a rise in government spending, which shifts AD to the right.
Explain how increased business confidence might affect aggregate demand.
When business confidence is high, firms are more likely to invest in new projects, expecting future returns. This increases investment (I), which is a component of AD, causing AD to rise.
Discuss one reason why an increase in government spending may not result in a large increase in aggregate demand.
If the increase in government spending is offset by higher taxes or cuts elsewhere, the overall impact on AD may be limited. Alternatively, if the economy is already at full capacity, increased government spending may cause inflation rather than real output growth.
what is fiscal drag
It is the phenomenon where wage and salary increases due to inflation push individuals into higher income tax brackets, resulting in a larger portion of their income being taxed at a higher rate, even without a real increase in their purchasing power
what is balance of payments
The Balance of Payments is a record of all economic transactions between a country and the rest of the world over a period of time (usually a year).
what are the components of the balance of payments
current Account – day-to-day trade:
Trade in goods (e.g. cars, food)
Trade in services (e.g. tourism, finance)
Primary income (interest, dividends, profits from abroad)
Secondary income (transfers like aid or remittances)
Capital Account – small flows:
One-off transfers (e.g. debt forgiveness, patents)
Financial Account – investment flows:
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Portfolio investment (buying shares/bonds)
Reserves (foreign currency held by the Bank of England)
can you define a current account deficit
A current account deficit occurs when the value of a country’s imports of goods, services, income, and transfers is greater than the value of its exports over a given period.
what are the benefits to an economy of export led growth
Increases national income and GDP through higher demand for domestic goods.
Improves employment by creating jobs in export industries.
negatives to an economy on export led growth
Over-reliance on external demand makes the economy vulnerable to global downturns.
Can lead to neglect of domestic markets, causing imbalances.May cause exchange rate appreciation, making exports less competitive.
explain how the uk current account may improve when there is economic growth in other EU countries
Economic growth in EU countries increases their income, so they demand more goods and services.
As a result, UK exports to these countries rise because British goods and services become more attractive.
Higher exports improve the UK’s trade balance within the current account.
This raises export revenues, helping to reduce the UK’s current account deficit or even create a surplus.
define consumption
The total spending by households on goods and services within a given period.
define disposable income
Disposable income is the income households have left to either consume (spend on goods and services) or save.
higher interest rates on consumption
When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive (higher loan repayments).
This discourages consumers from taking loans to spend on big-ticket items.
Also, higher interest rates increase the incentive to save rather than spend.
As a result, consumption tends to decrease.
an increase in households wealth - how does it effect consumption
When household wealth rises (e.g., through higher house prices or stock market gains), consumers feel richer.
This wealth effect encourages them to spend more, even if their income hasn’t changed.
As a result, consumption increases, boosting aggregate demand.
define investment
Spending by firms on capital goods such as machinery, buildings, and technology to increase future productive capacity.
spare capacity in the economy how does it impact investment
Spare capacity means there are unused resources (like idle factories or unemployed workers) in the economy.
When spare capacity is high, firms can increase output without investing in new capital.
Therefore, high spare capacity tends to reduce the incentive to invest, as firms don’t need extra machinery or buildings.
Conversely, when spare capacity is low, firms are more likely to invest to expand productive capacity.
a rise in demand for exports how does it effect investment
Increased demand for exports raises firms’ revenues and profits in export industries.
Higher profits improve business confidence and encourage firms to invest in expanding production capacity (e.g., new machinery or factories).
This leads to an increase in investment, boosting overall economic growth.
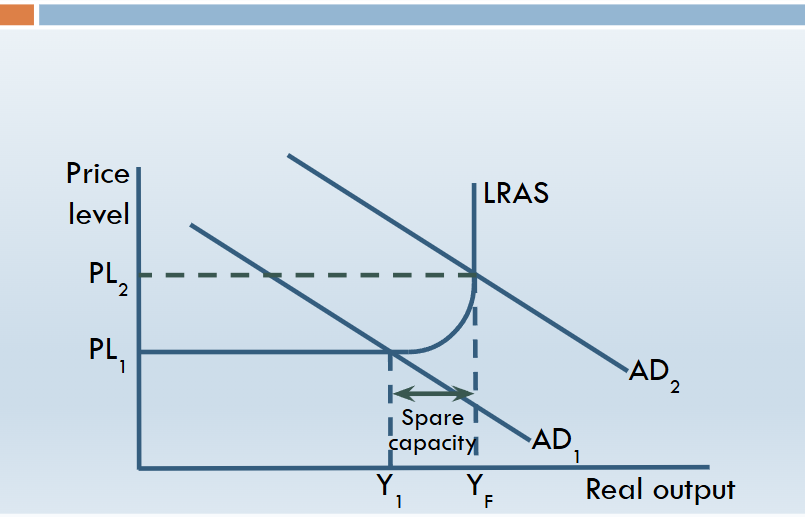
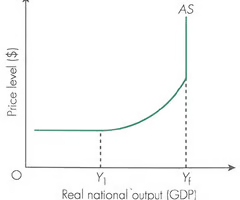
Draw a keynesian curve and explain
Keynesian LRAS suggests that there can be an output gap in the long run
At low levels of economic activity LRAS = elastic
Towards full employment - output at max - LRAS = inelastic
--> at this point LRAS can not be increased without an increase in quantity or improvement in quality of the factors of production
Classical
In the long run if the price level changes there will be no increase in output as it is assumed the economy is working at full potential
evaluate the wealth effect
Ricardo Sousa (economist) found that the wealth effect is negligible in some economies such as Europe, as many people rent rather than own housing. Thus, when house prices increase, they will actually spend more on rent than before, meaning they have less disposable income left, and thus consumption may actually decrease.
how does AS increase if imports get cheaper
If imports become cheaper, then it means that foreign suppliers are willing to sell their goods at lower prices. This creates a downward pressure on the prices of similar goods produced domestically. As a result, domestic producers will have to lower their prices in order to remain competitive with the cheaper imported goods.
how does increasing interest rates lead to more expensive exports
Two ways:
- Countries begin to save in UK which puts a lot of strain on the currency and appreciates its value which makes exports more expensive.
- Loans for businesses become more expensive, costs increase, shifting SRAS inwards, raising prices and decreasing exports
movements along the AS curve cause changes to
changes to price level
government spending in AD
20%
investment in AD
14
hot money flows
When you take advantage of other country's interest rates and exchange your currency for theirs (this can cause appreciation)
what is the current account
Measures the international trade in goods and services, investment income, and net transfer payments.
disadvantages of increasing corporation tax
Firms have to pay more tax on their profits.
This leaves them with less money to invest in new machinery, technology, or buildings.
If firms invest less, their productivity grows more slowly.
Over time, this can mean lower economic growth (GDP falls)