Bontrager Chapter 15
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Fracture resulting in multiple (two or more) fragments
Comminuted fx
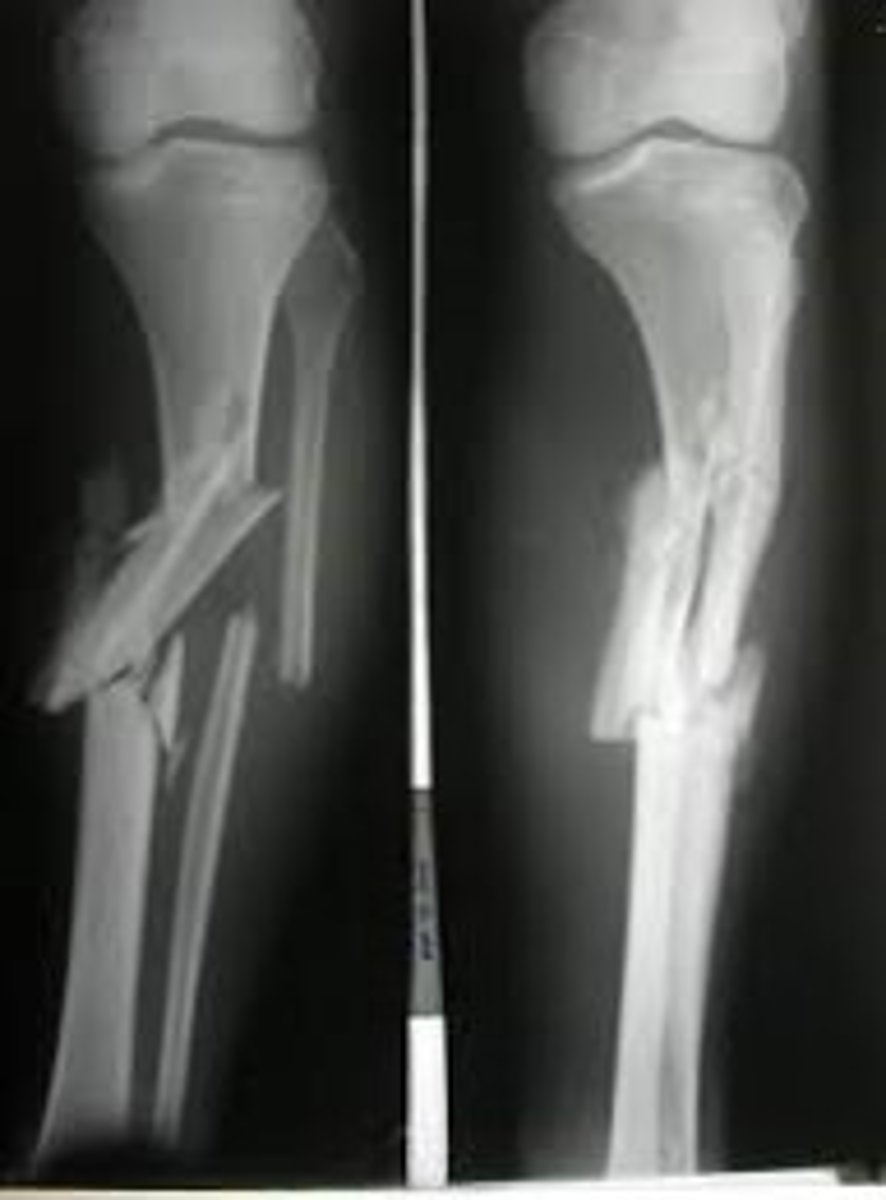
Incomplete fracture with broken cortex on one side of bone only
Greenstick fx
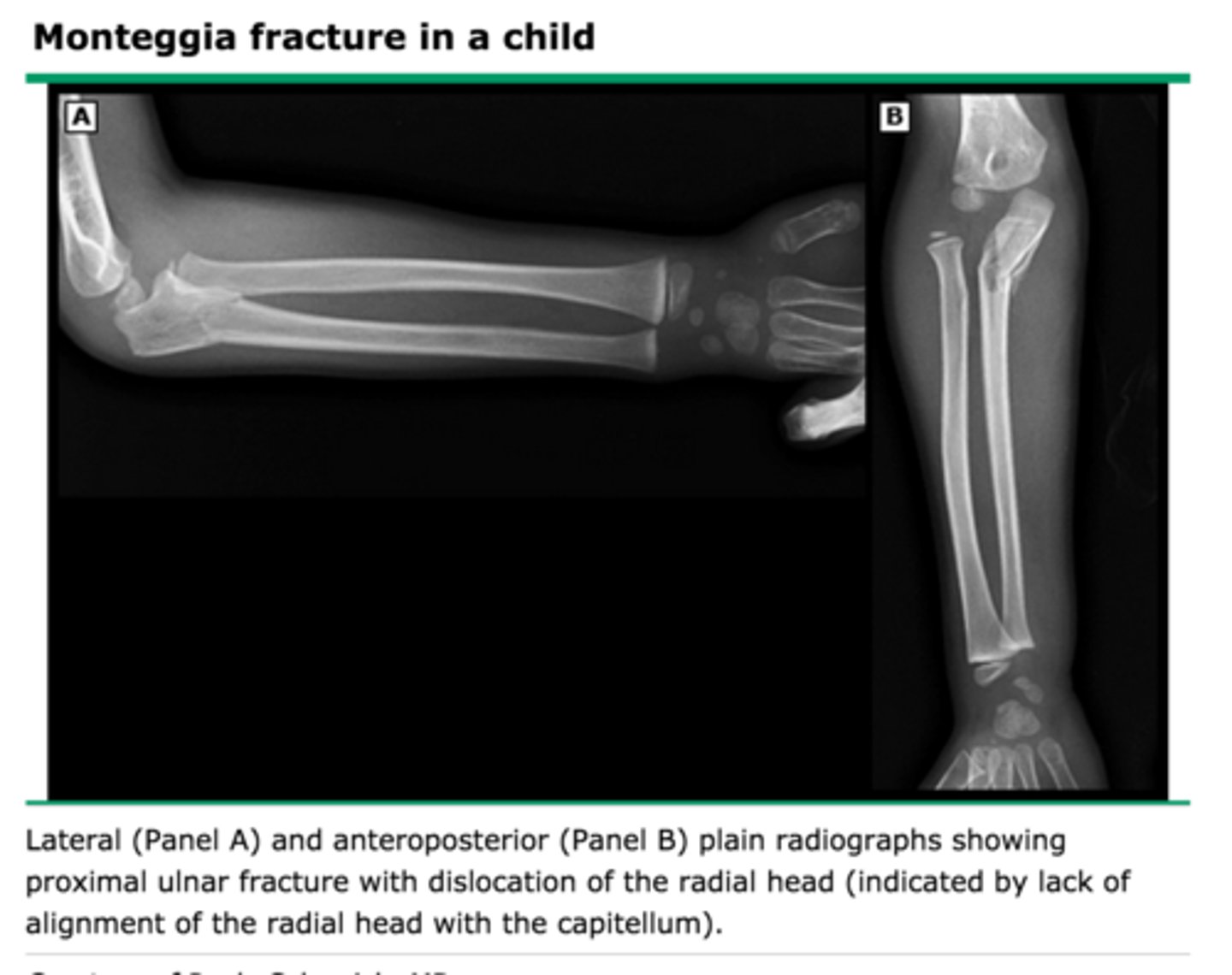
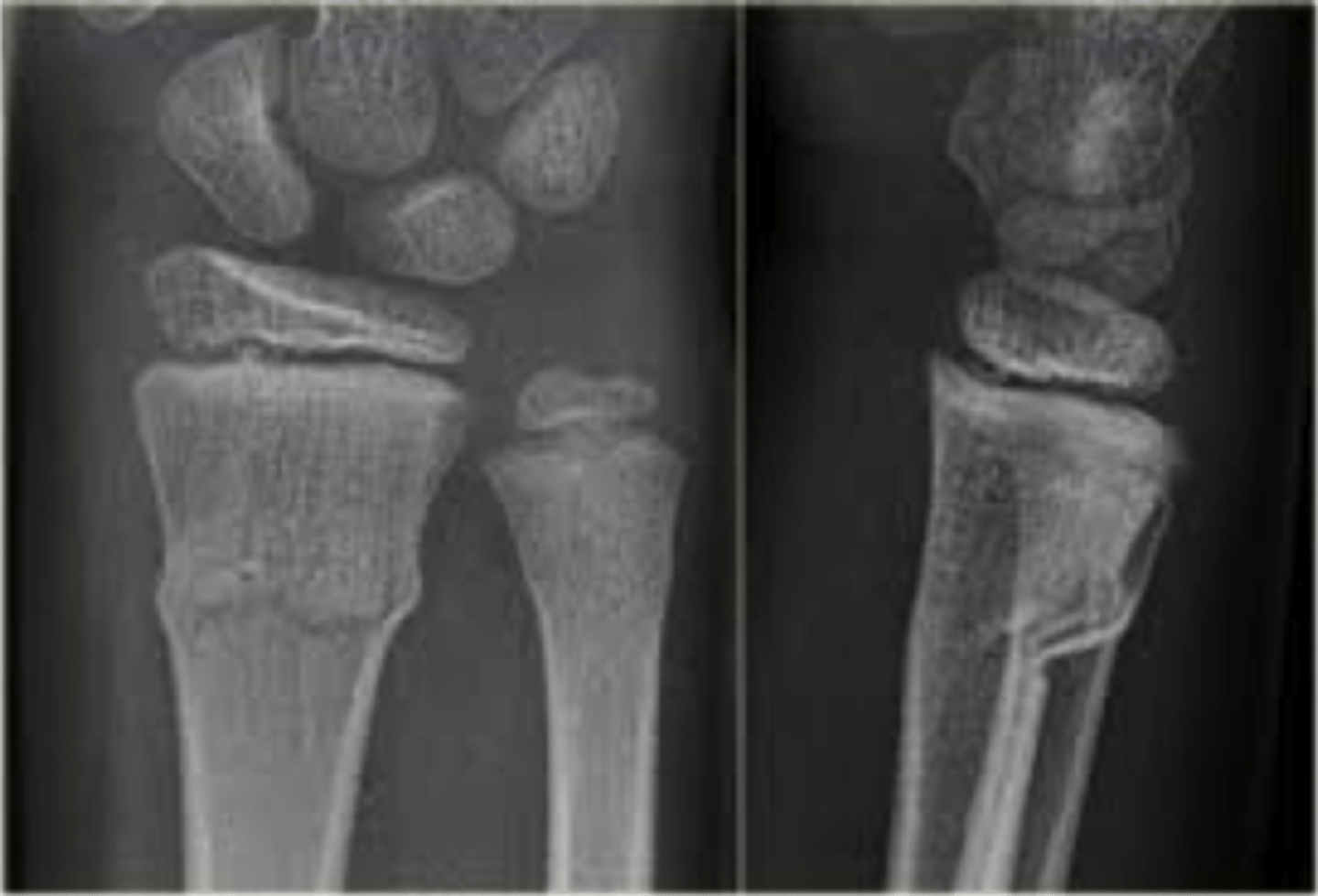
Fracture of proximal half of ulna with dislocation of radial head
Monteggia fx
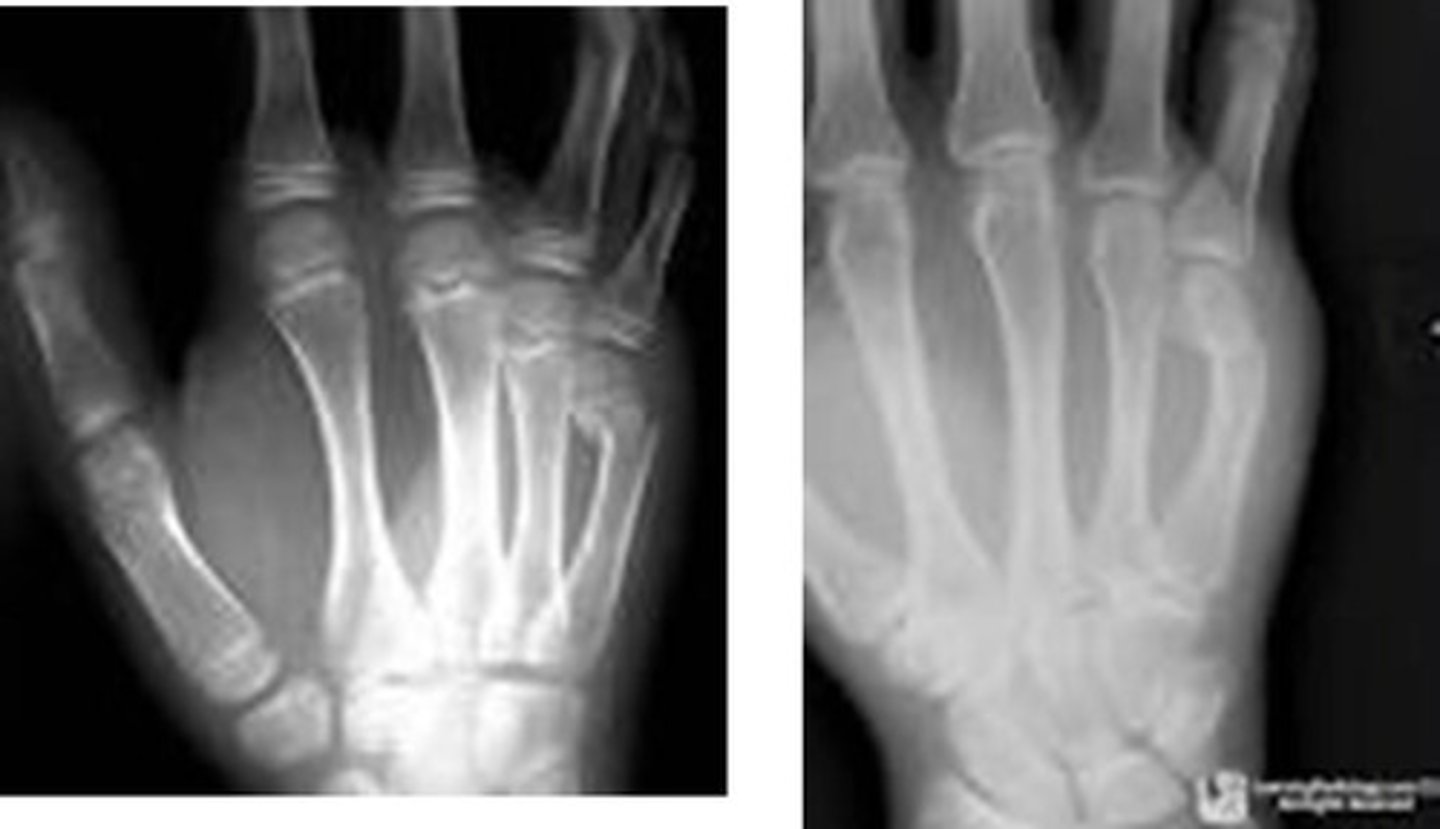
Fracture of distal fifth metacarpal
Boxer's fx
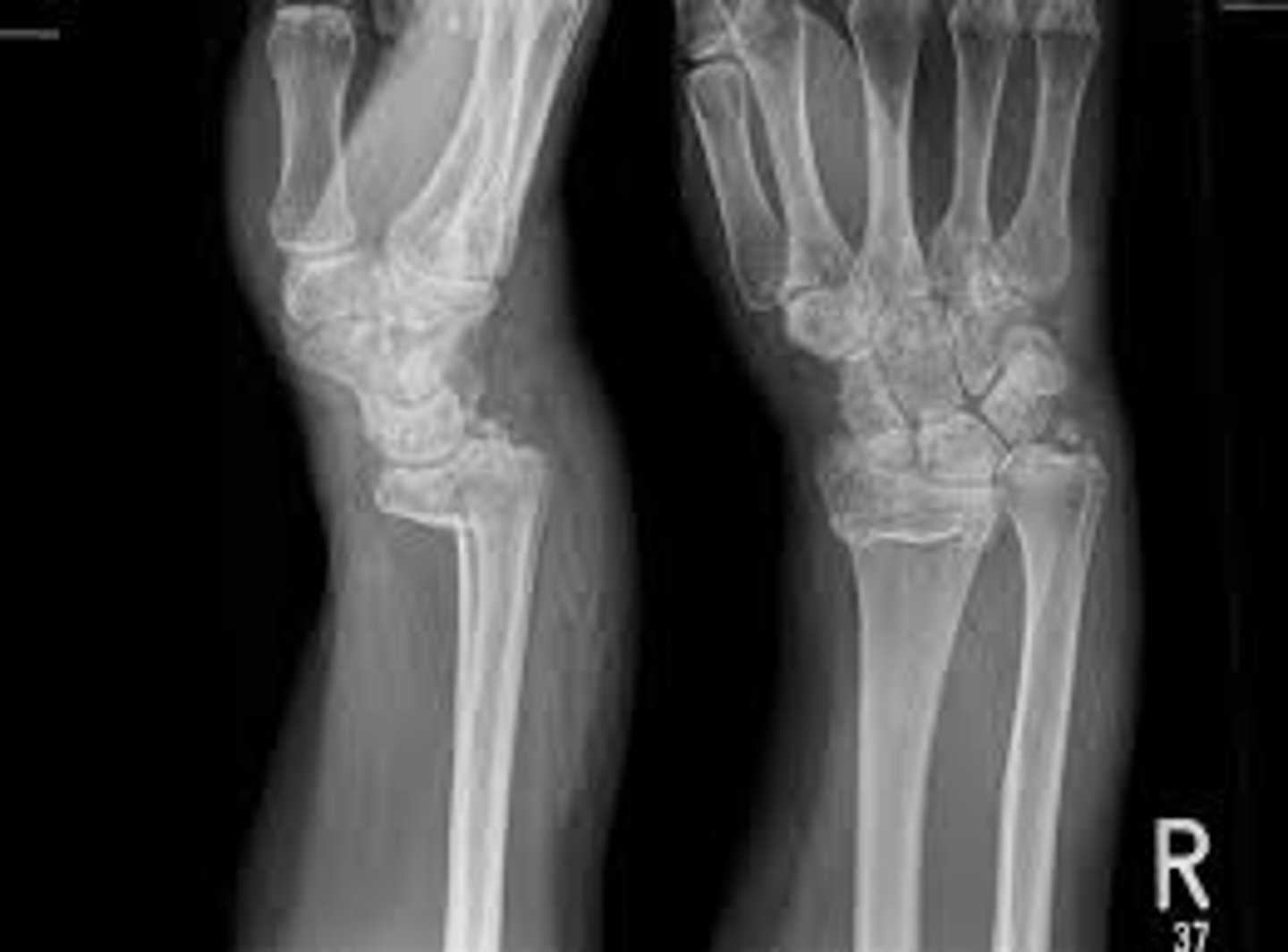
Fracture of distal radius with anterior displacement
Smith's fx
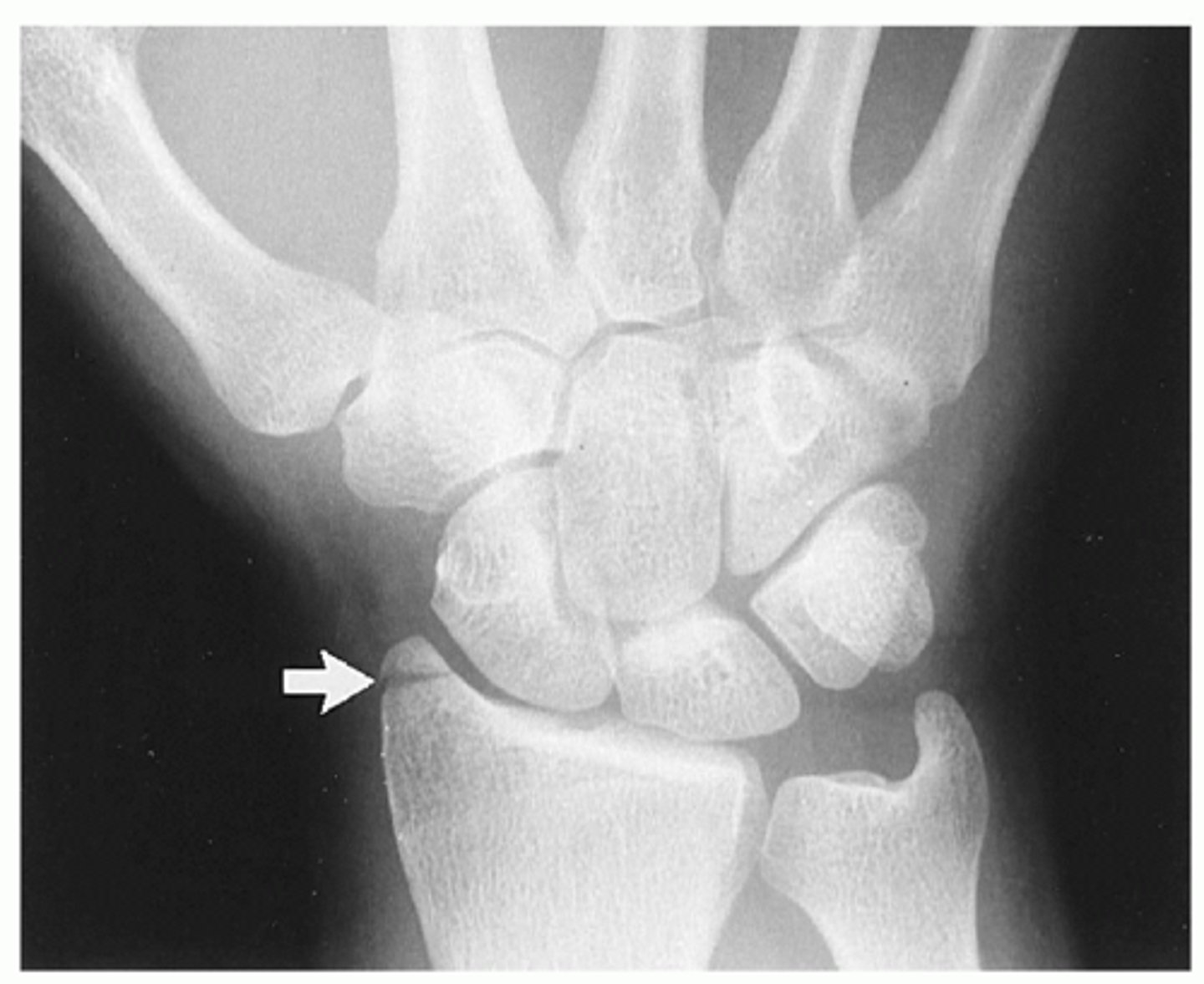
Intraarticular fracture of radial styloid process. Also called a chauffeur's fracture.
Hutchinson's fx
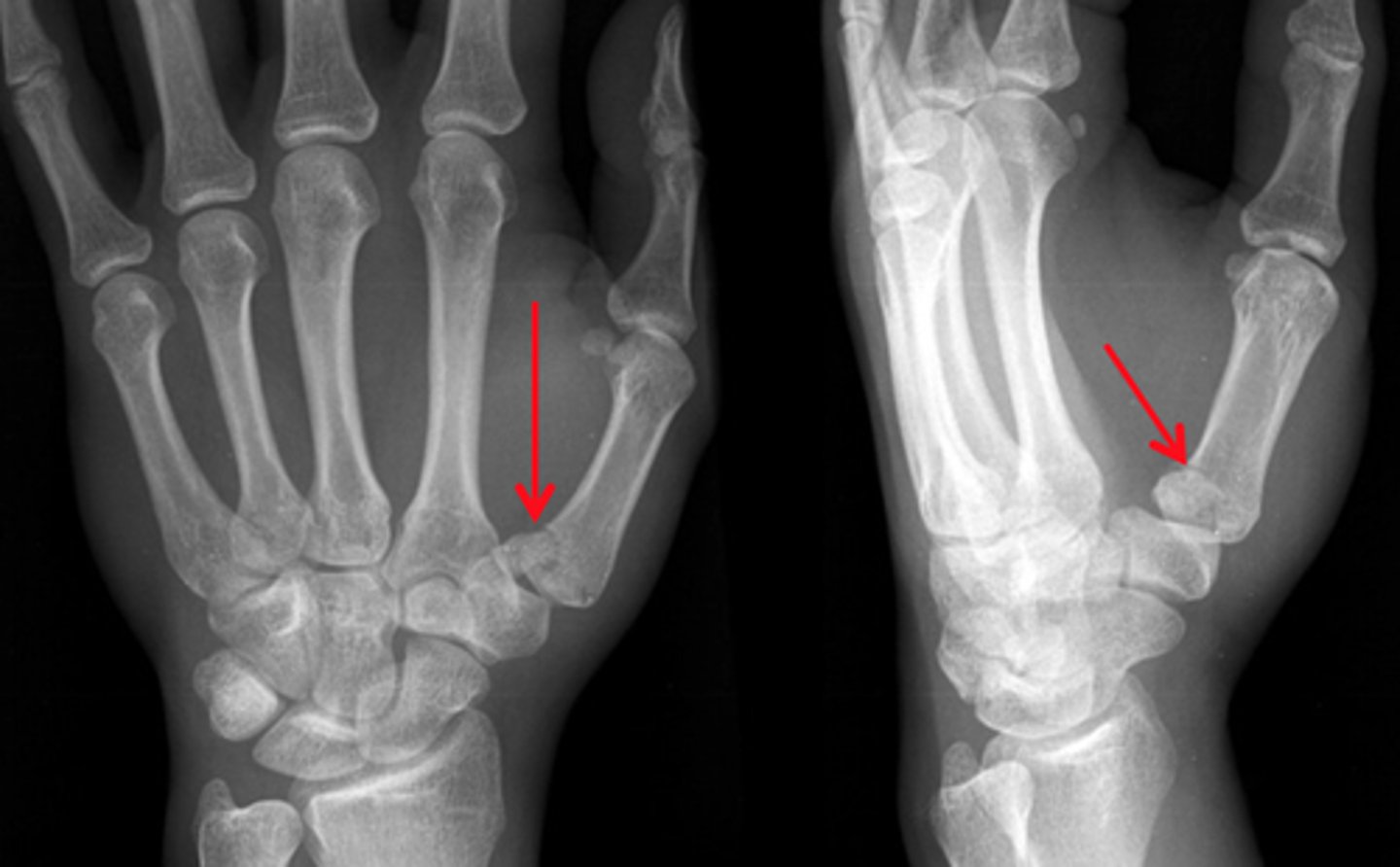
Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal
Bennett's fx
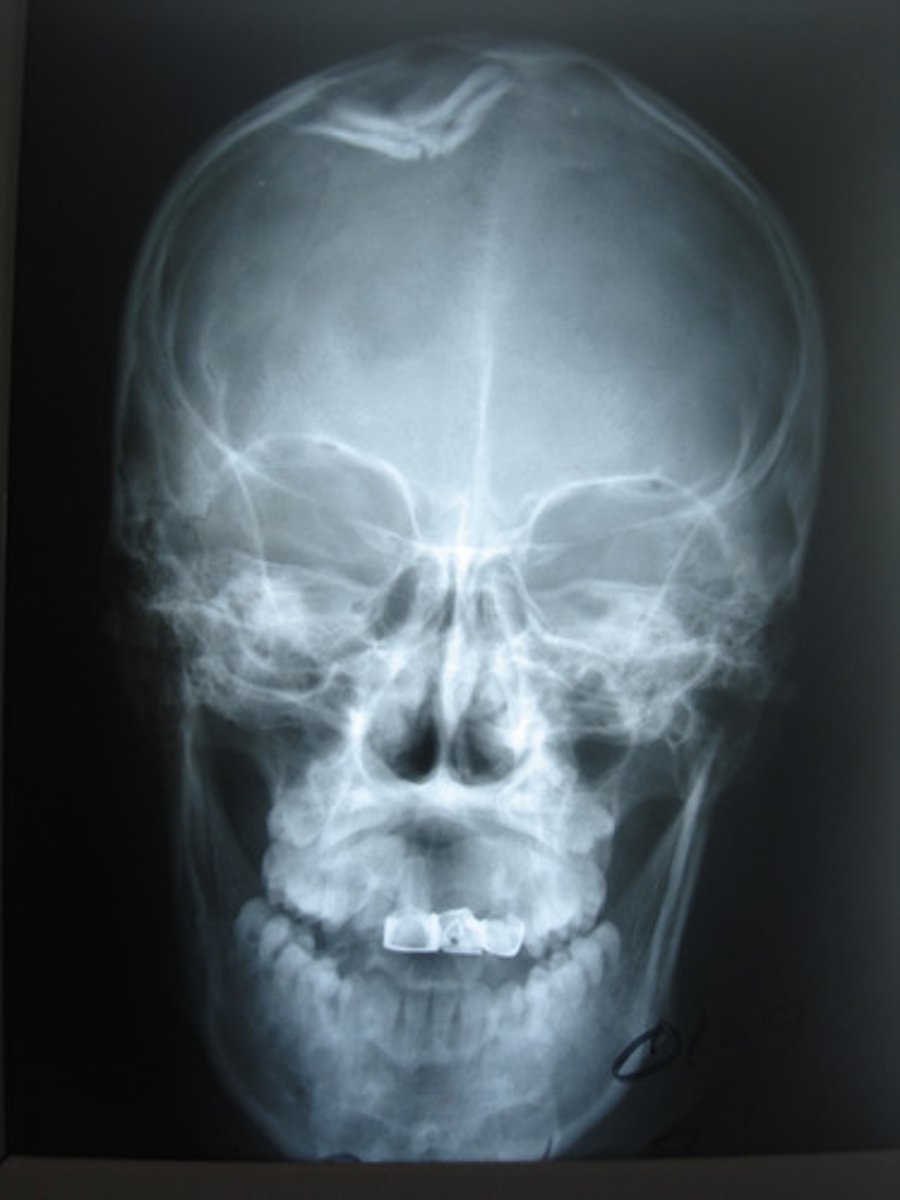
Fracture due to a severe stress to a tendon. A fragment of bone is separated or pulled away by the attached tendon or ligament.
Avulsion fx

A fracture of the skull, a fragment is depressed
Depressed fx (ping-pong fx)
Fracture with fracture lines radiating from center point of injury in a starlike pattern
Stellate fx
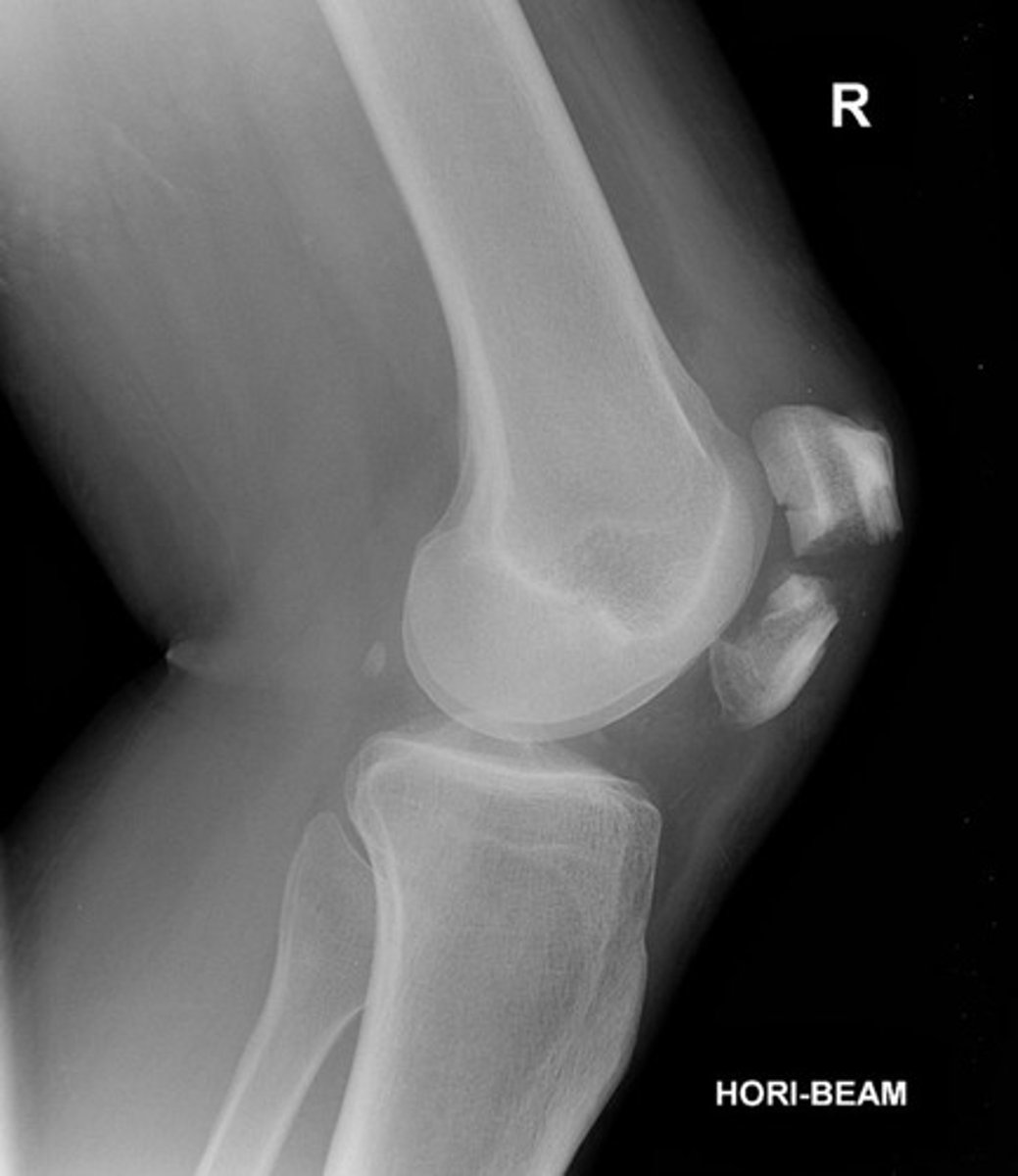
Fracture of the lateral malleolus, medial malleolus, and distal posterior tip of tibia
Trimalleolar fx
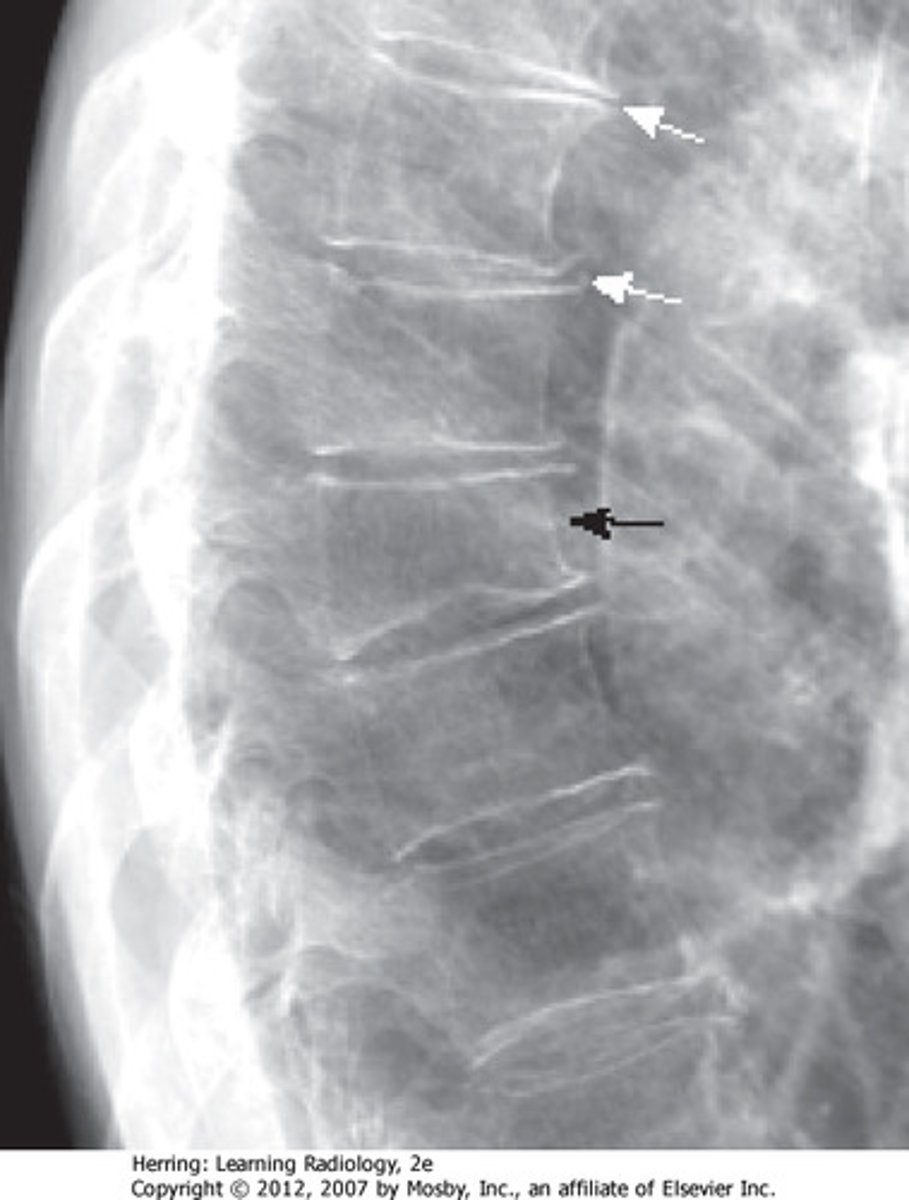
Fracture protruding a reduced hight of the anterior vertebral body
Compression fx
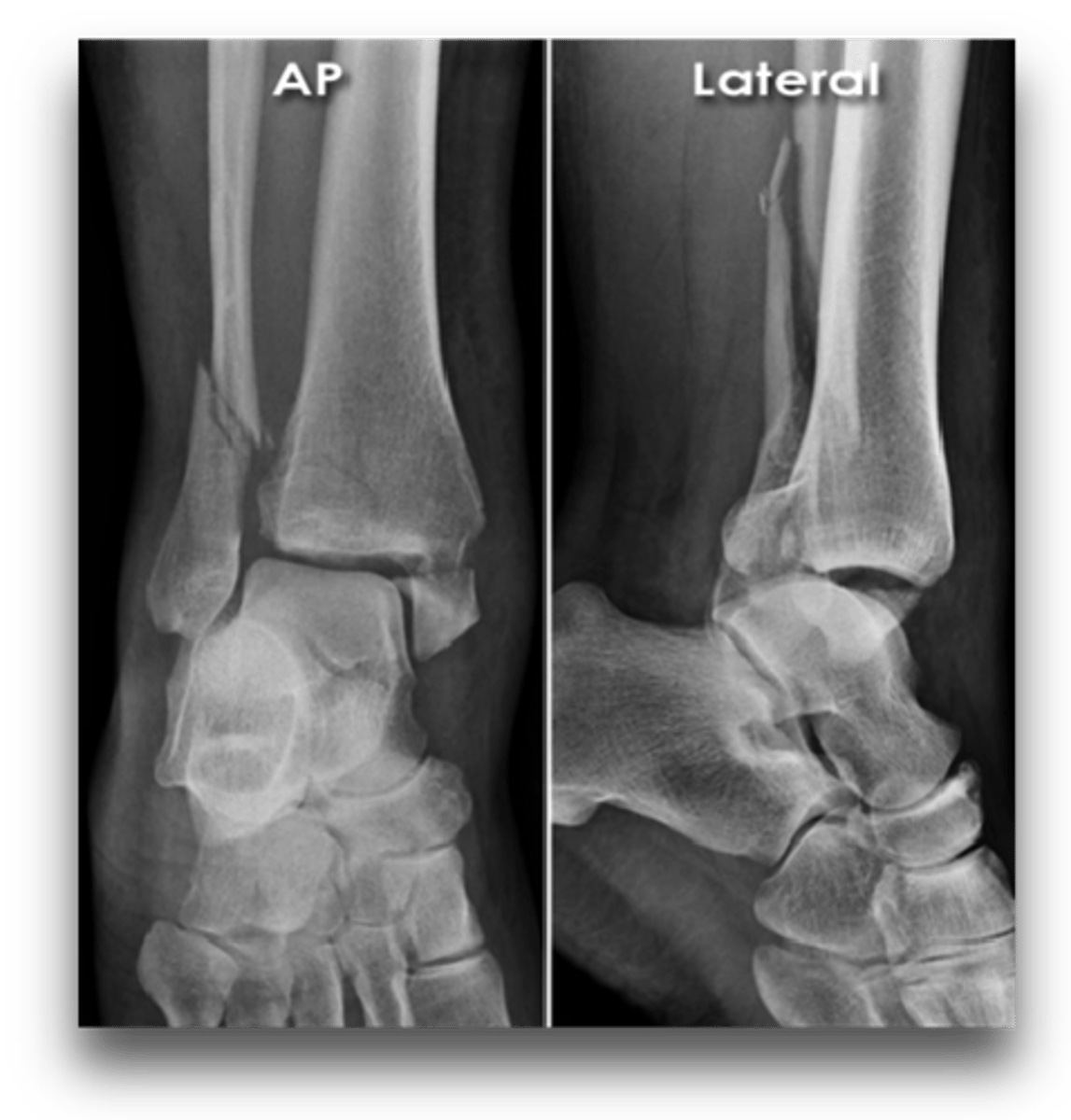
Complete fracture of distal fibula, frequently with fracture of medial malleolus
Pott's fx
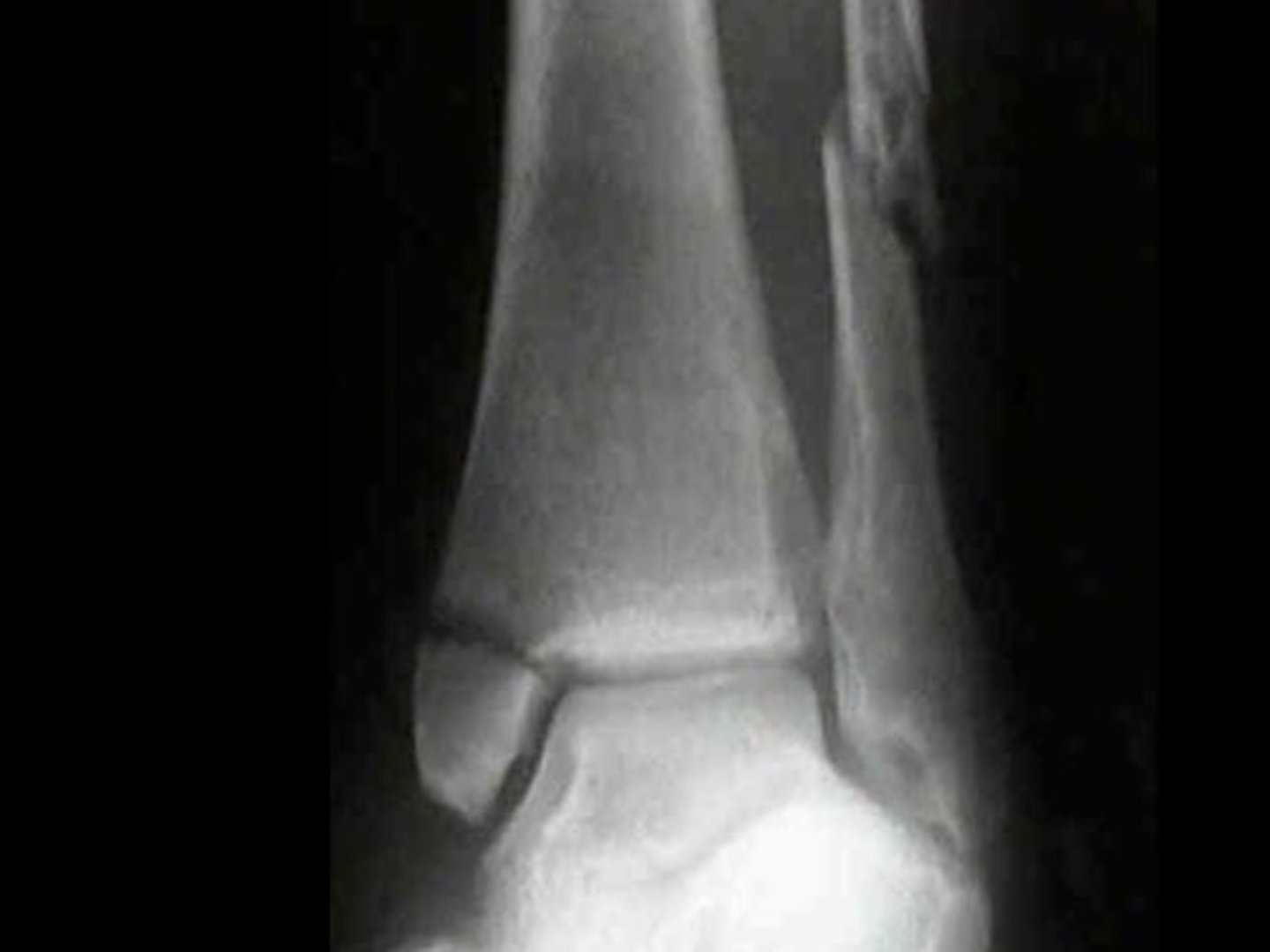
Fracture of distal radius with posterior displacement
Colles' fx
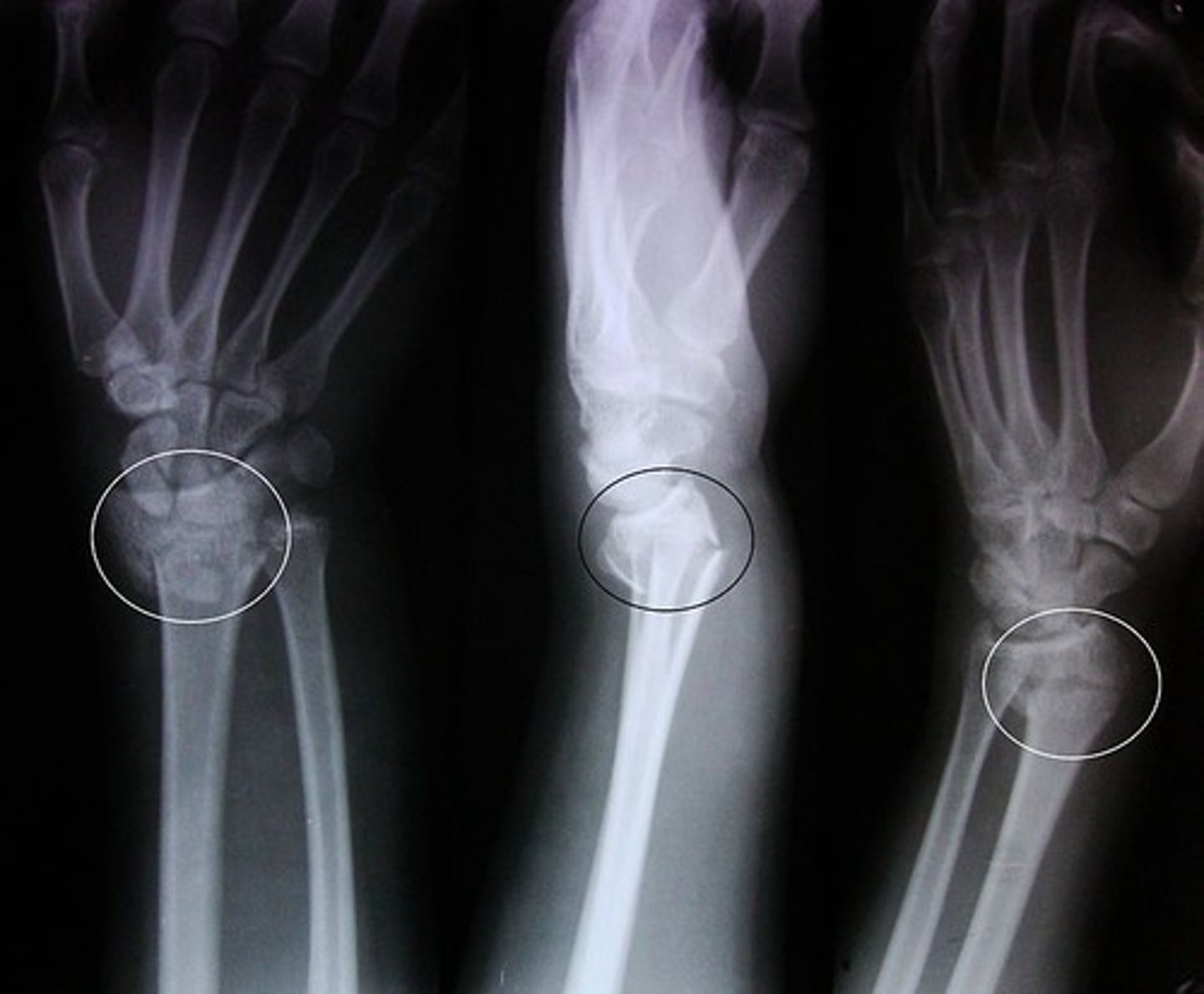
Fracture of the pedicles of C2
Hangman's fx
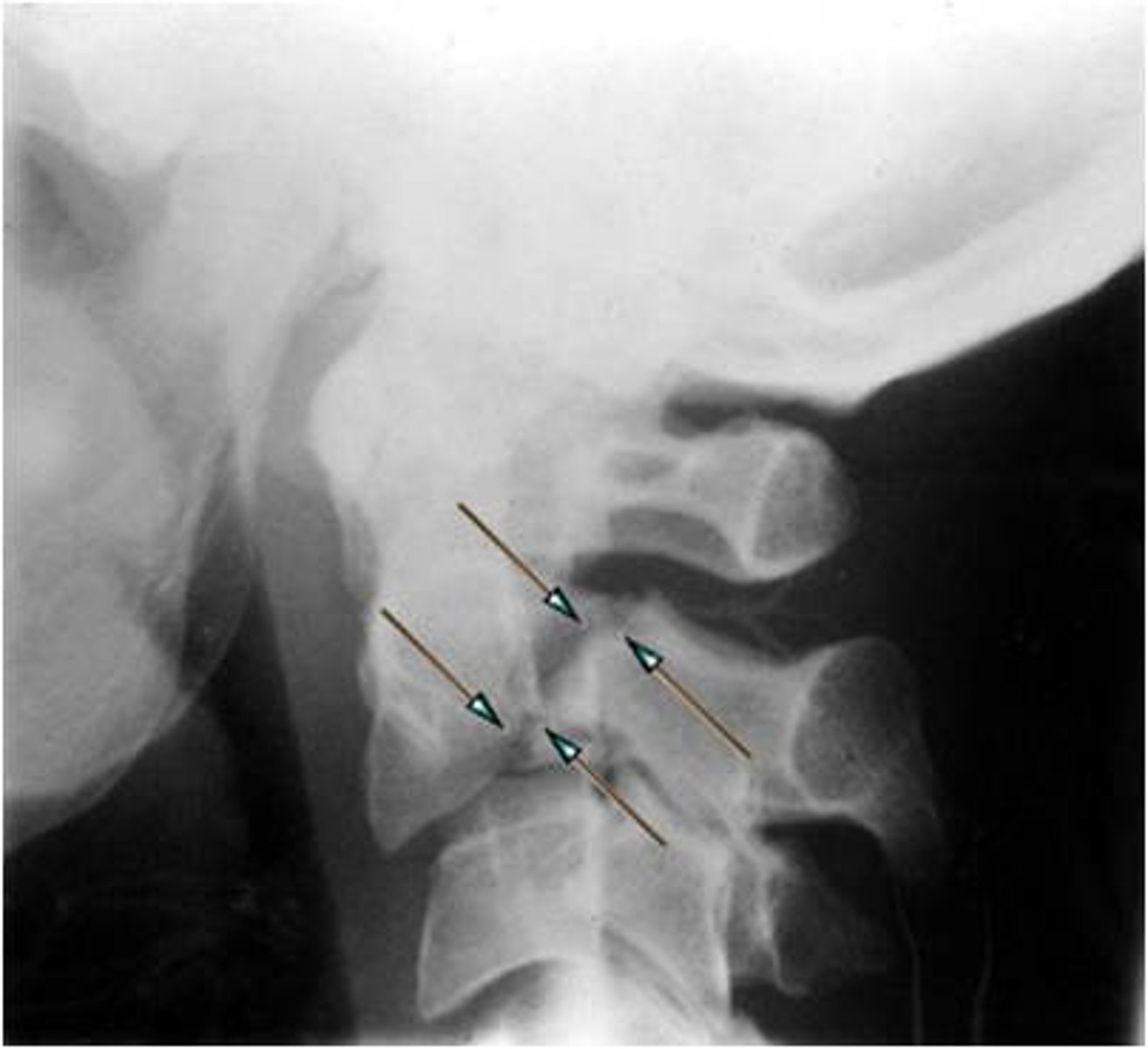
Fracture where the bone has been twisted apart and spirals around the long axis.
Spiral fx
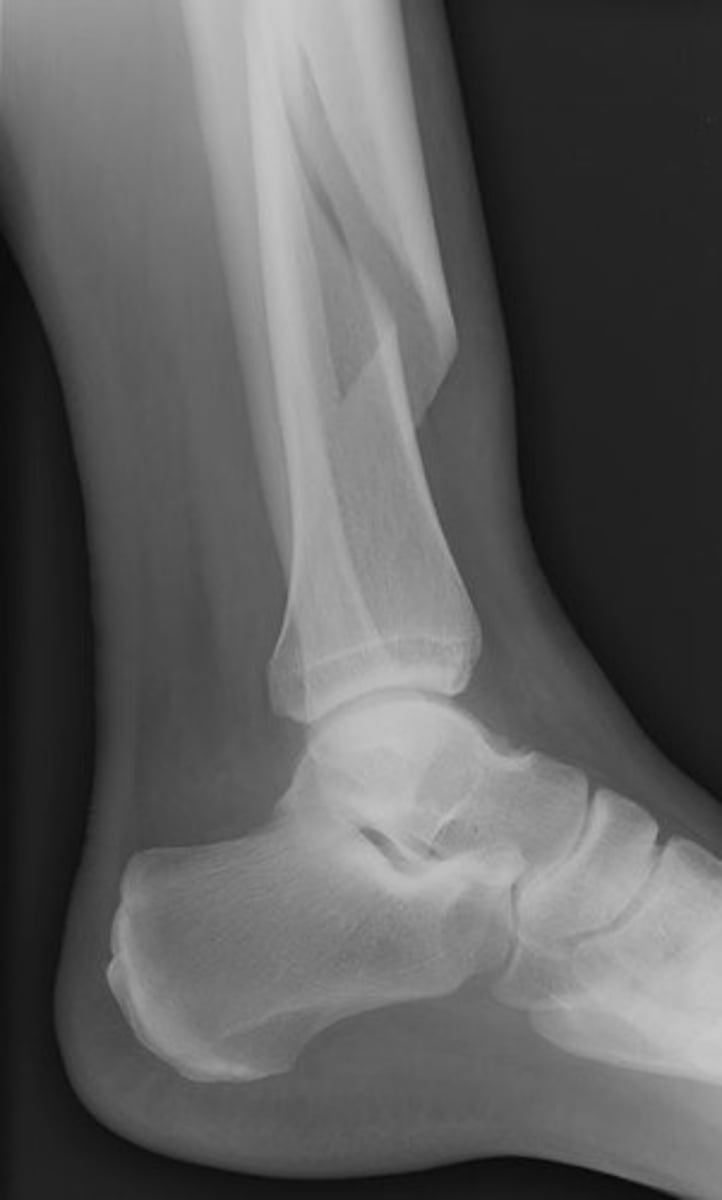
Fracture in which a portion of the bone (usually the fragmented end) protrudes though the skin
Compound fx
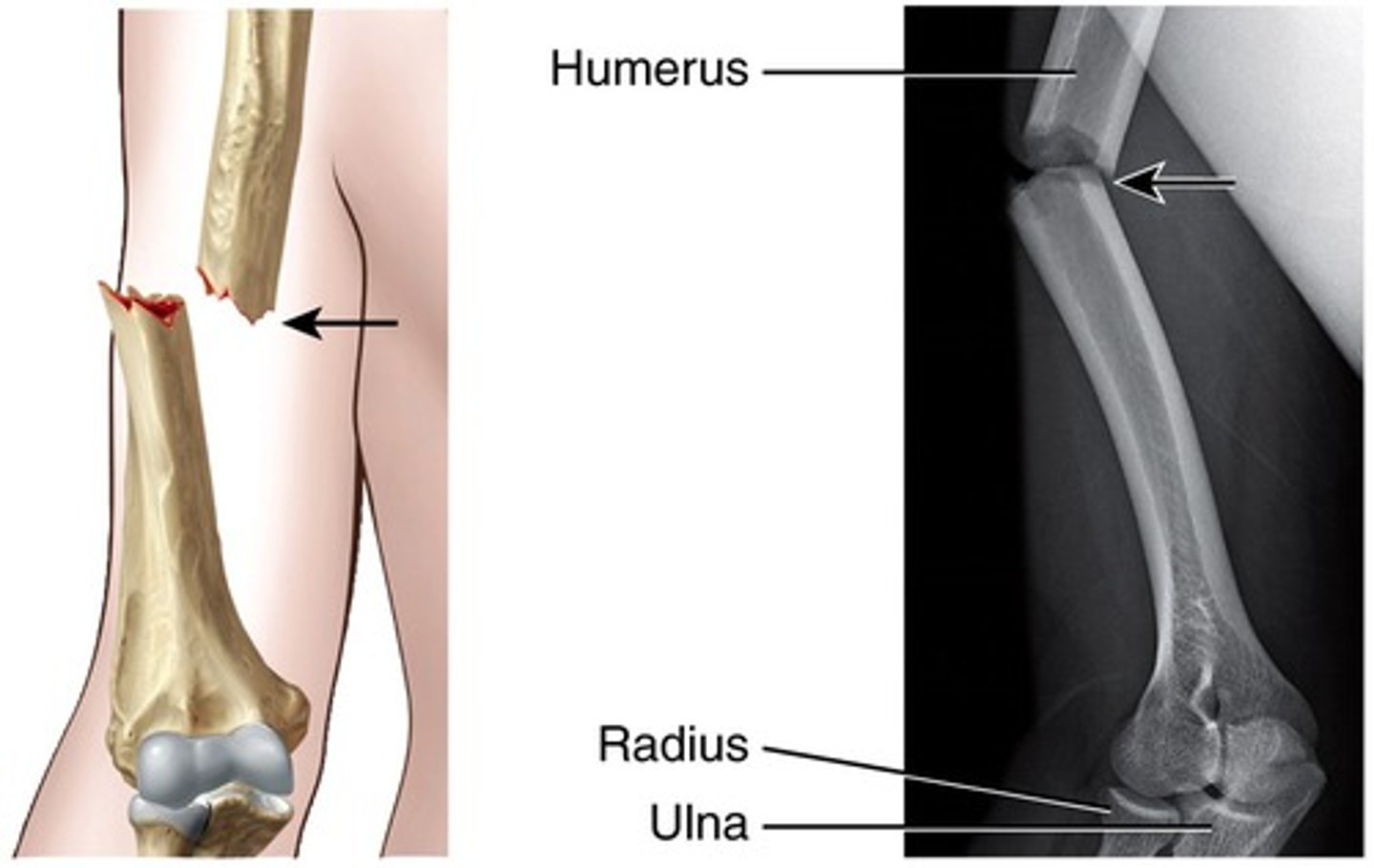
Fracture in which the bone does not break through the skin
Simple fx
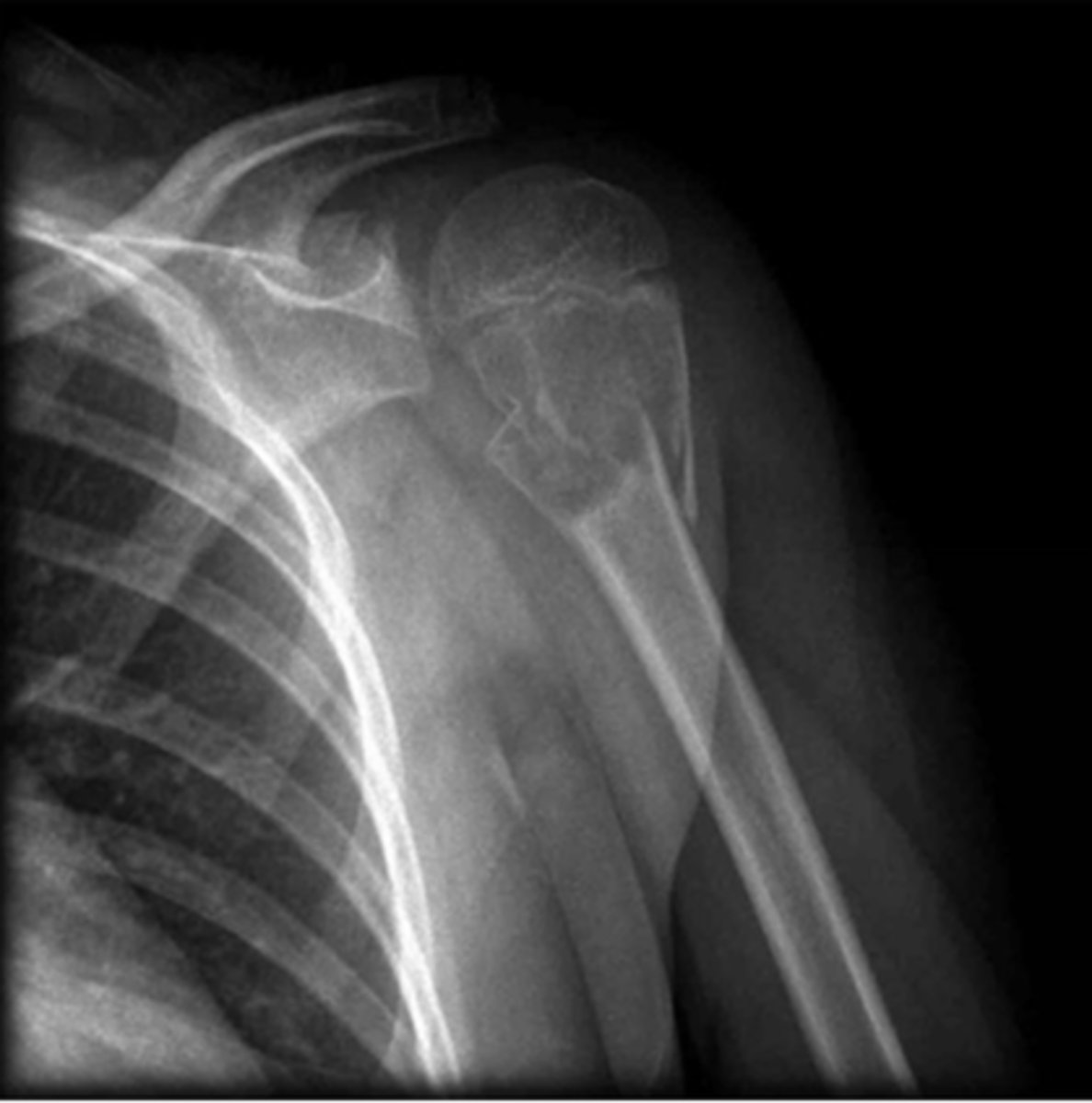
Fracture does not transverse through the entire bone.
Incomplete fx
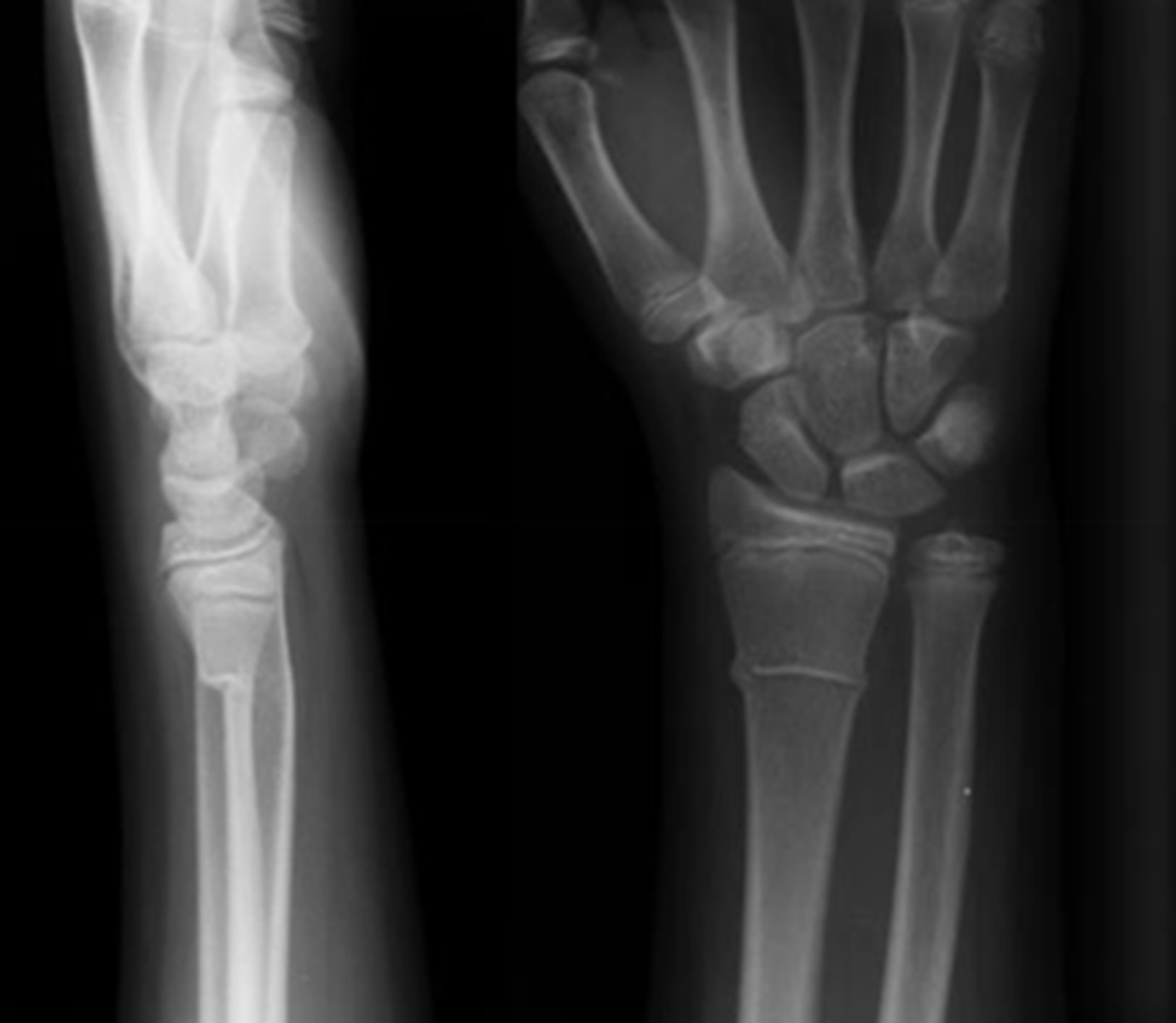
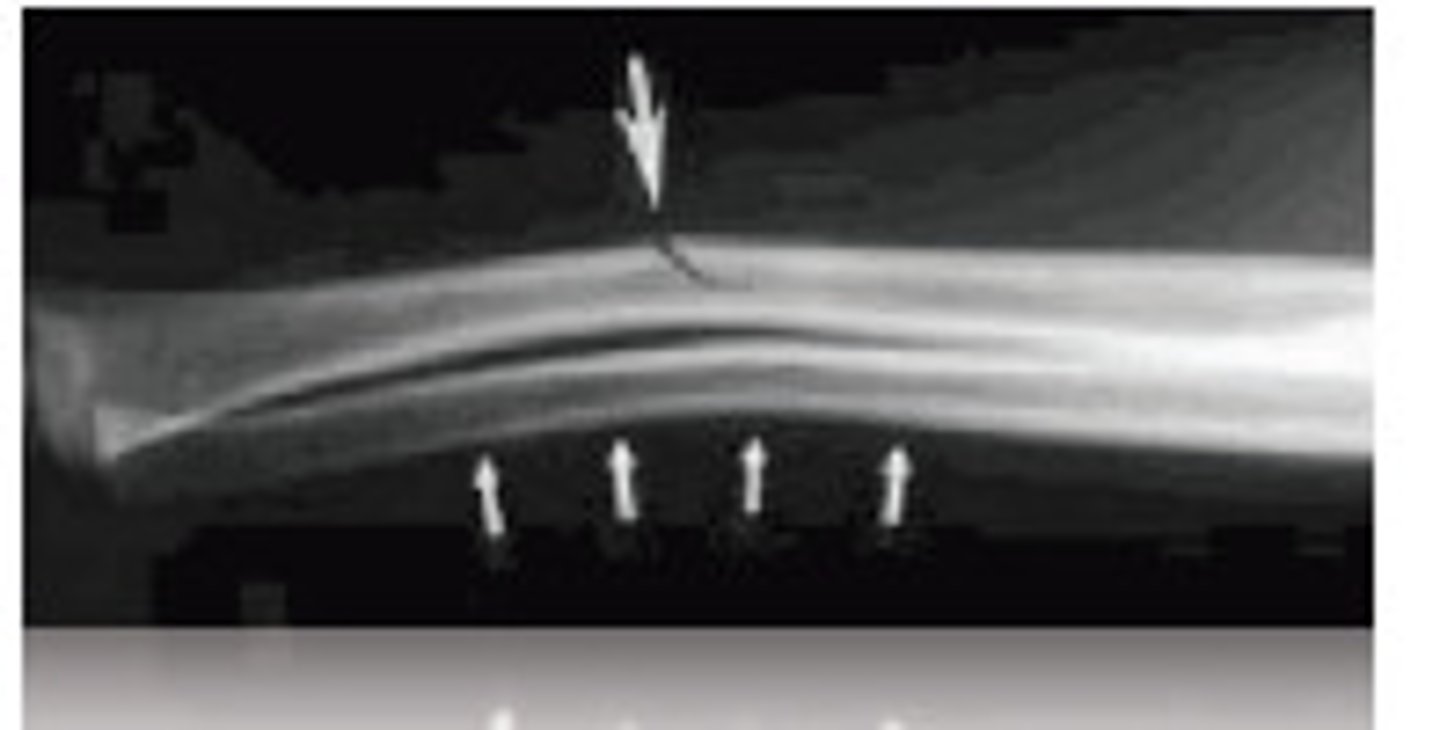
Incomplete fracture in which there is no complete break in the cortex
Torus fx
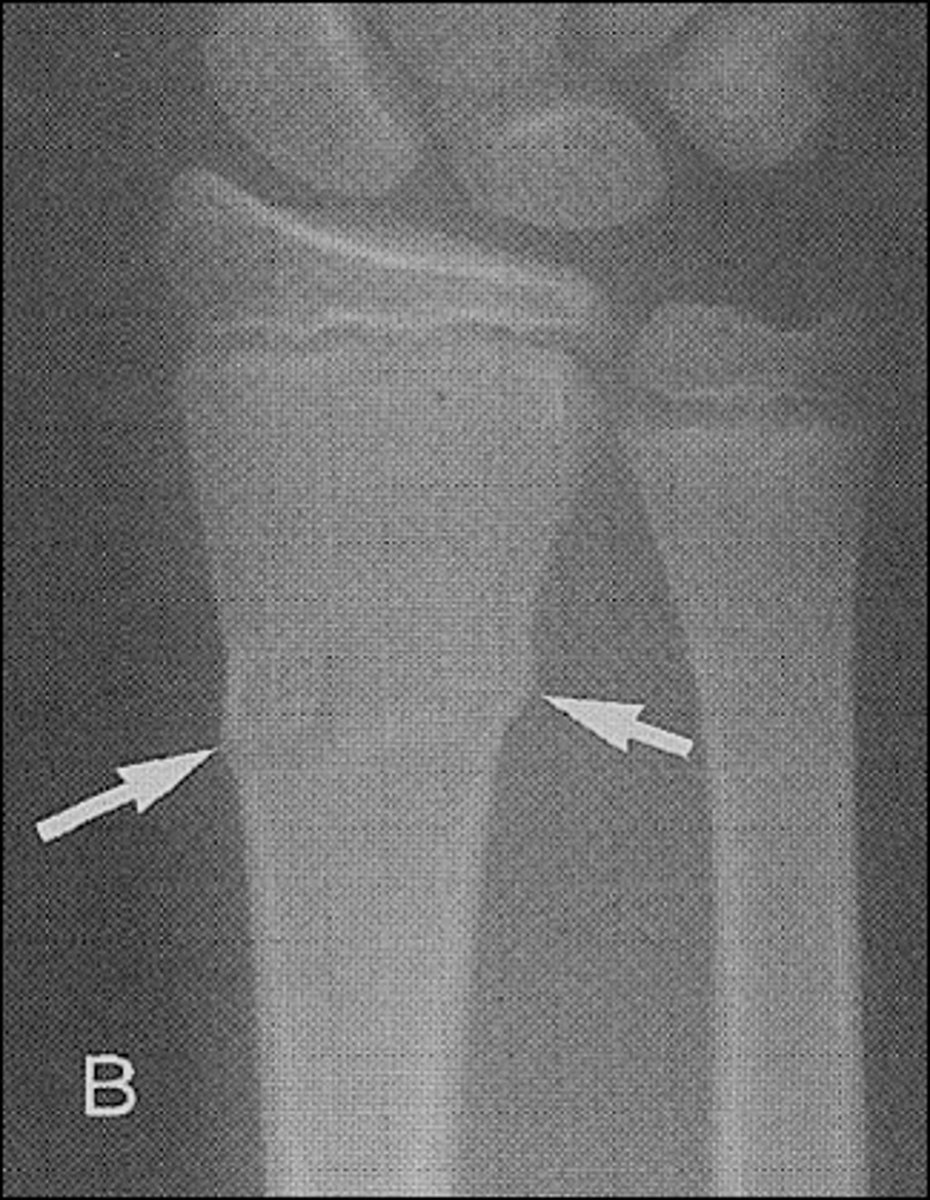
Fracture where the bone is broken into two places
Complete fx
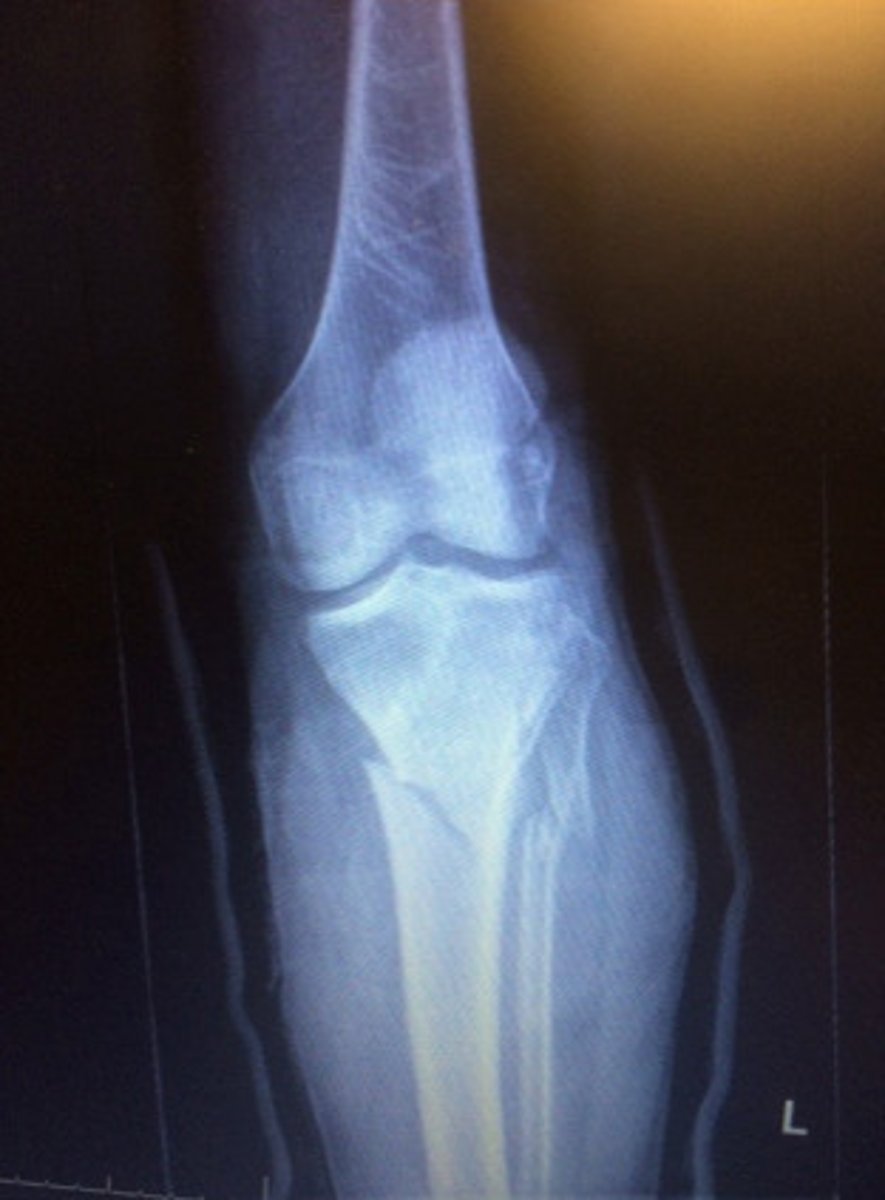
Fracture where one fragment is driven into the other.
Impacted fx
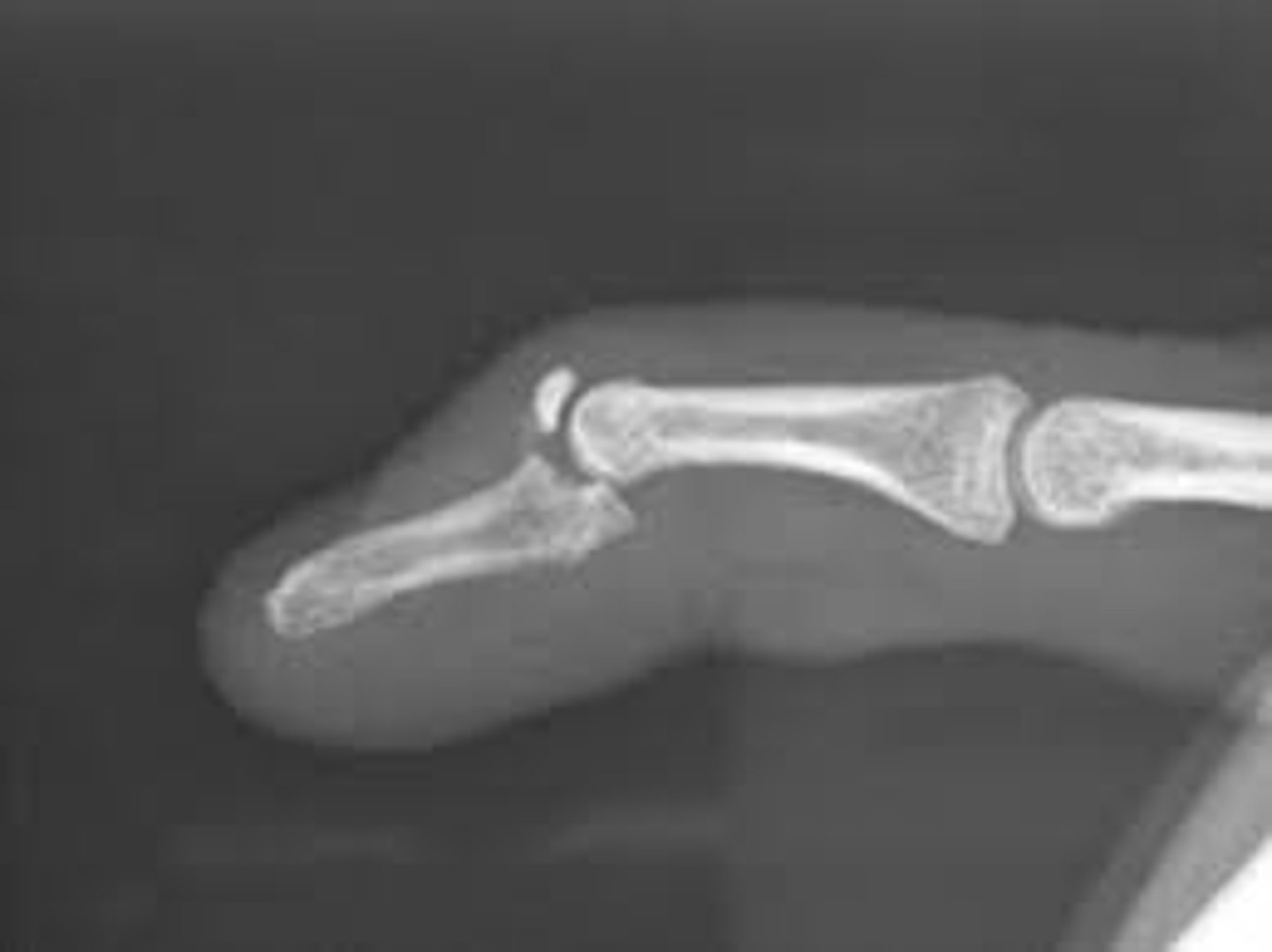
Fracture of the distal phalanx with finger extended
Baseball fx
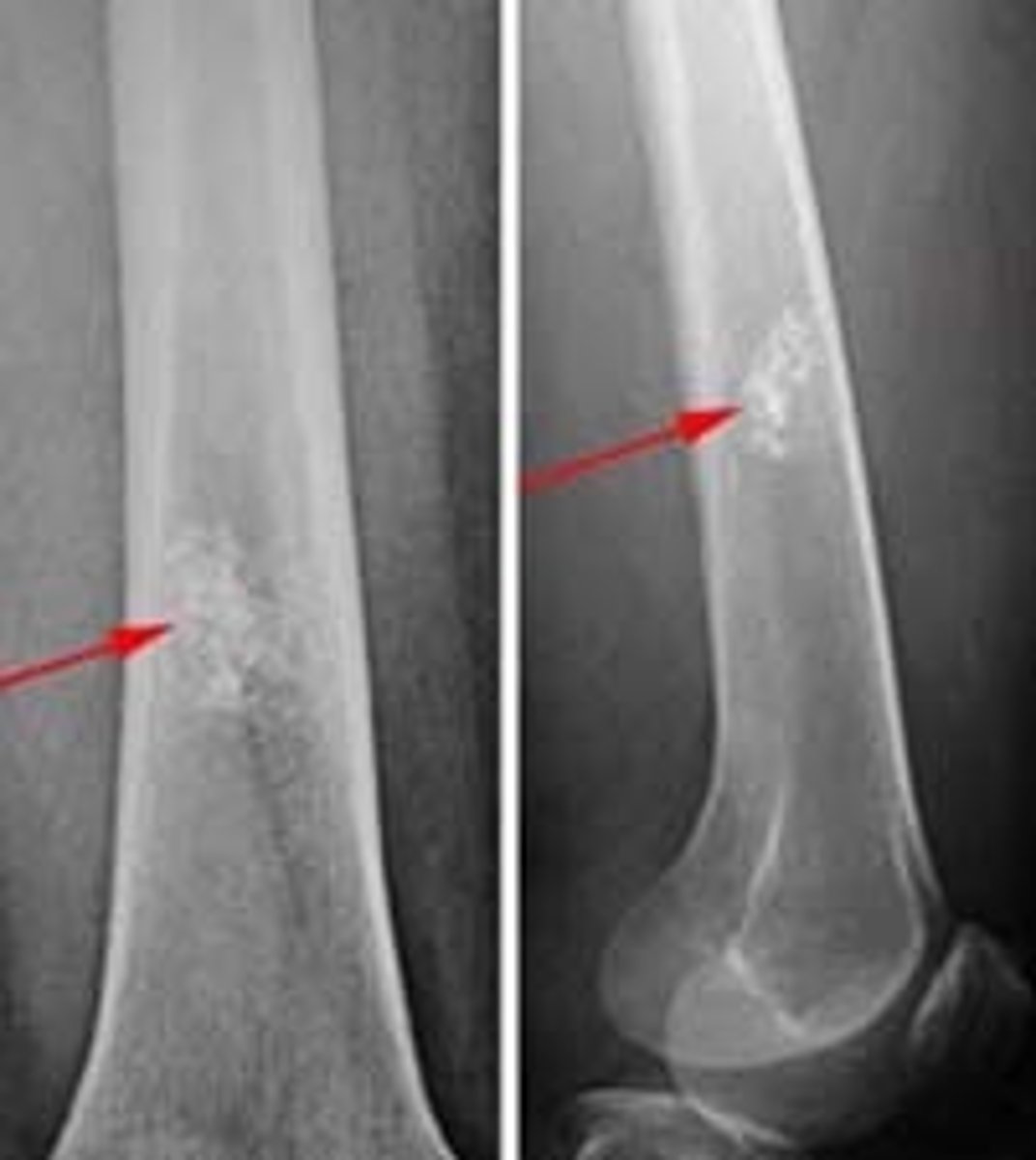
Fracture is nontraumatic in origin, resulted from repeated stress on a bone such as marching or running.
Stress or fatigue fx (march fx)
Fracture due to a disease process
Pathologic fx
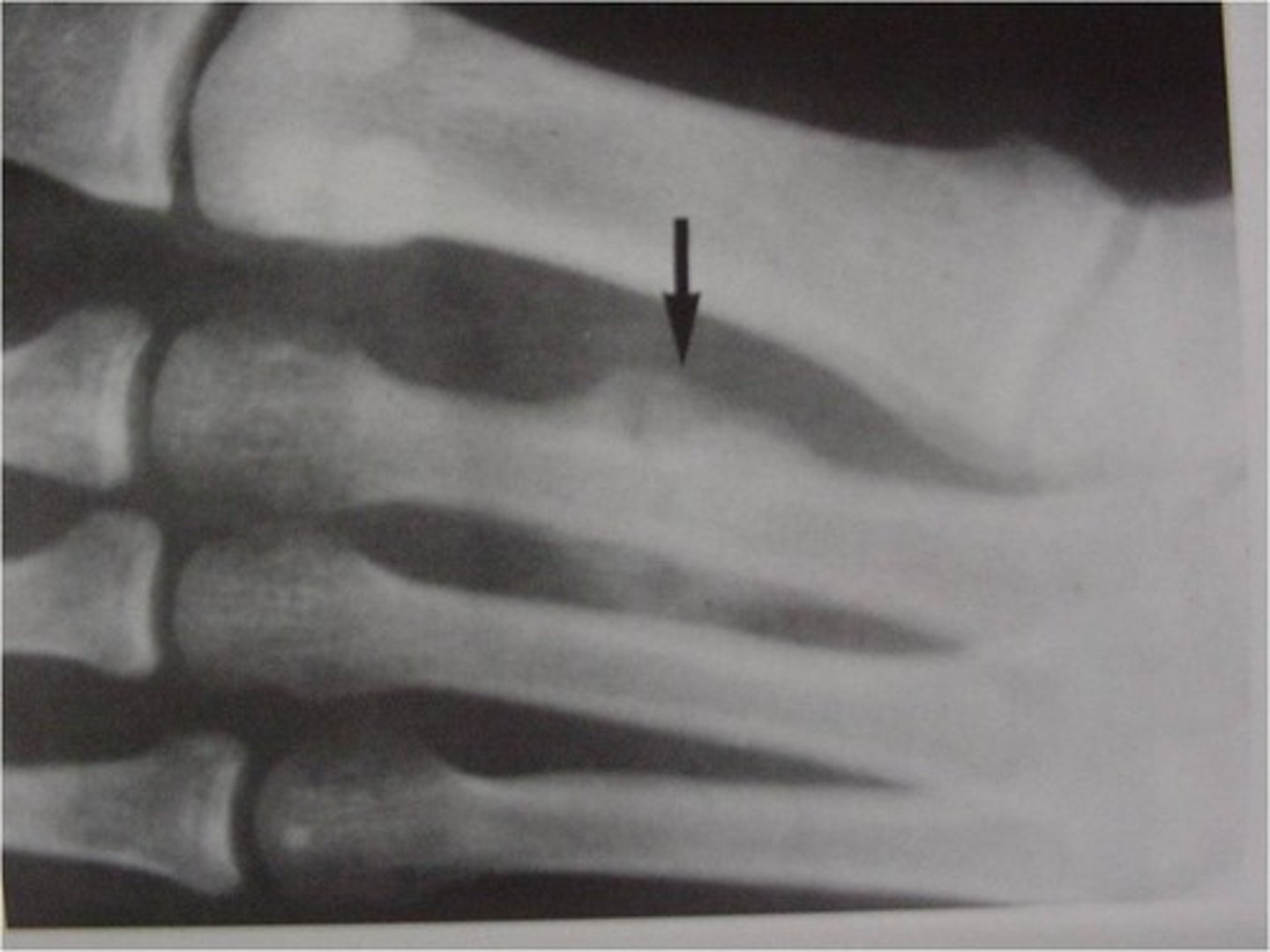
Fracture resulting in an isolated bone fragment
Chip fx
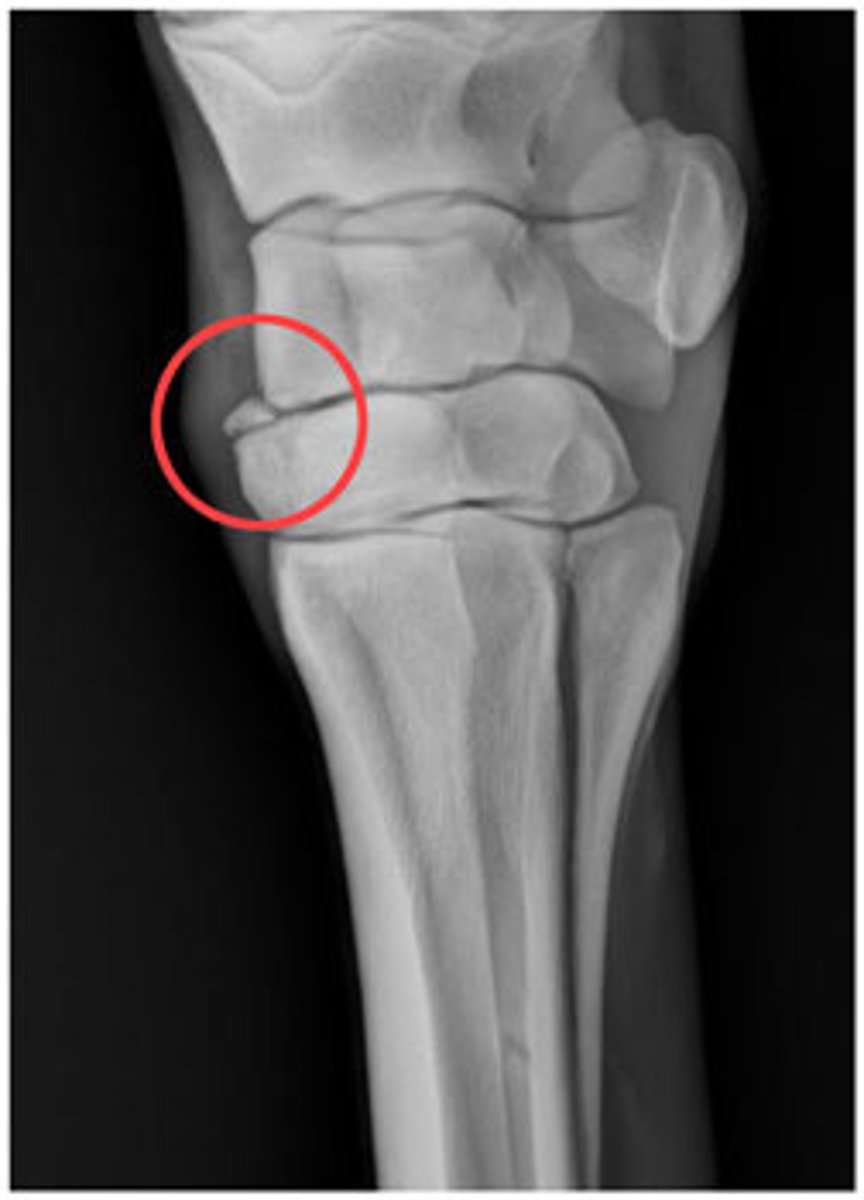
Subluxation of the radial head on a child
Nursemaids' elbow
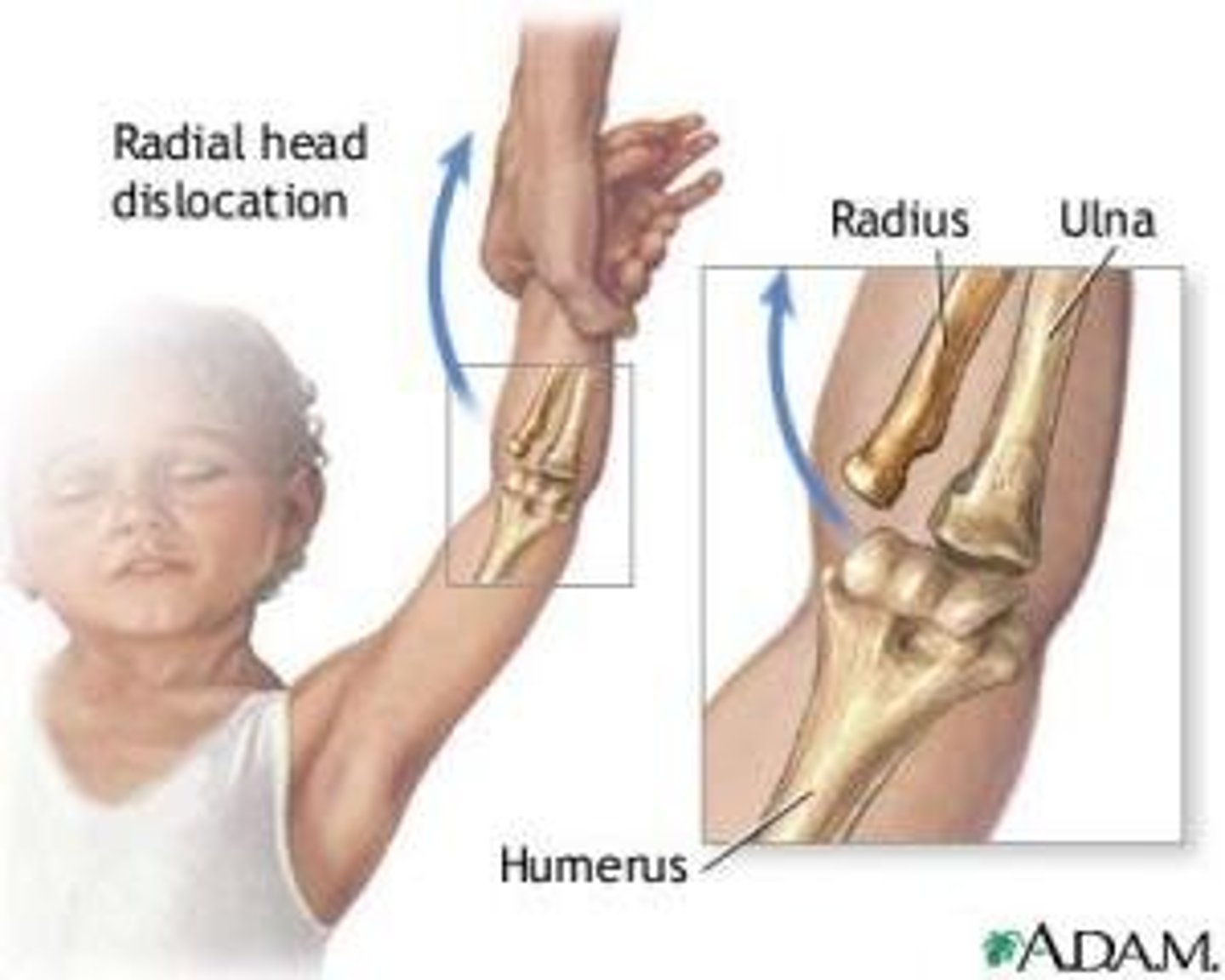
Which one of the following terms describes a poor alignment between the end of a fractured bone?
Lack of apposition
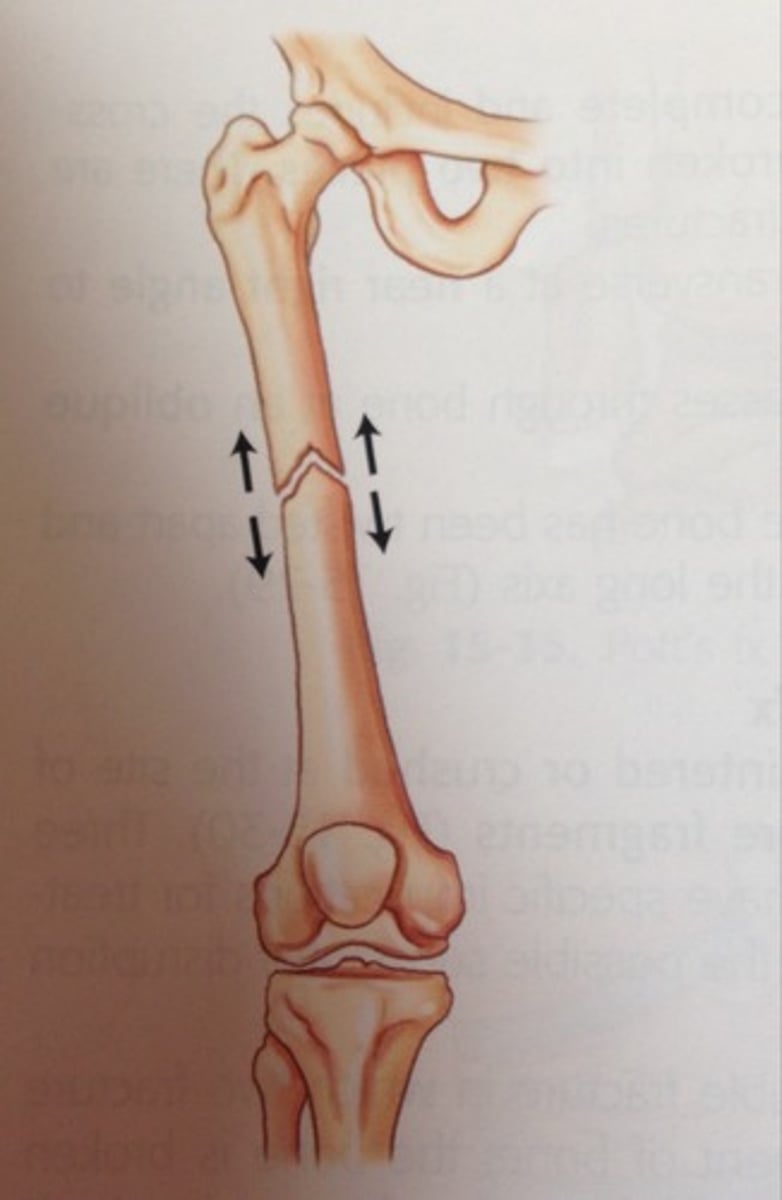
What is the correct term for the displacement of a bone from a joint?
Dislocation or luxation
Which of the following terms best describes a partial dislocation of a joint?
a. Subluxation
b. Luxation
c. Apposition
d. Angulation
a. Subluxation
A bruise type of injury with a possible avulsion fracture is termed a(n):
a. Subluxation
b. Luxation
c. Apposition
d. Contusion
d. Contusion
Which type of fracture is defined as being crushed at the site of impact, producing two or more fragments?
a. Comminuted
b. Compound
c. Complete
d. Torus
a. Comminuted fx
Which of the following fractures is described as an incomplete fracture with the cortex broken on one side of the bone?
a. Bayonet
b. Torus
c. Avulsion
d. Greenstick
d. Greenstick fx
Which of the following is not a fracture but a subluxation?
a. Hutchinson's
b. Nursemaids' elbow
c. Monteggia's
d. None of the above
b. Nursemaids' elbow
Which of the following fractures is often called a reverse Colles' with anterior displacement of the distal radius?
a. Pott's
b. Trimalleolar
c. Tripod
d. Smith's
d. Smith's fx
Which of the following fractures involves the distal fifth metacarpal?
a. Boxer's
b. Barton's
c. Pott's
d. Smith's
a. Boxer's fx
A boxer's fracture best describes a fracture of the:
a. metacarpals.
b. metatarsals.
c. phalanges.
d. navicular.
a. metacarpals.
Which of the following fractures usually involves the spine?
a. Depressed
b. Comminuted
c. Stellate
d. Compression
d. Compression fx
Which type of procedure would be performed in surgery to realign a fracture?
a. Open reduction
b. Closed reduction
c. Internal fixation
d. Compound reduction
a. Open reduction
A fracture that occurs through the pedicles of the axis (C2), with or without displacement of C2 or C3, is termed _____ fracture.
a. Odontoid
b. clay shoveler's
c. Jefferson
d. hangman's
d. hangman's fx
Which fracture is also called a "march fracture"?
a. Pott
b. Stress
c. Trimalleolar
d. Burst
b. Stress fx
A fragment of bone that is separated or pulled away by the attached tendon or ligament is termed a(n) _____ fracture.
a. Avulsion
b. Chip
c. Depressed
d. Epiphyseal
a. Avulsion fx
Which definition best describes an impacted fracture?
a. The bone is splintered or crushed.
b. The bone is fractured in two places.
c. One fragment is firmly driven into the other.
d. The distal radius is fractured with posterior displacement.
c. One fragment is firmly driven into the other.
A hangman's fracture refers to a fracture of which bony structure?
a. symphysis pubis
b. C-7
c. dens
d. gonion
c. dens
Which type of mobile radiography x-ray unit is self-propelled?
Battery operated, battery driven
Which type of mobile x-ray unit is lighter weight?
Standard power source
T/F C-arms are most generally stationary fluoroscopy units used in surgery.
False, mobile fluoroscopy units
T/F The C-arm fluoroscopy unit can be rotation a minimum of 180°
True
What is true of a capacitor discharge portable machine?
a. It does not have to be plugged in.
b. It stores enough energy for about 50 chest exams.
c. It must be charged immediately before each exposure.
d. It allows higher mA and kV than other types.
c. It must be charged immediately before each exposure.
In battery-powered mobile units, the type of battery used is usually?
a. nickel-cadmium.
b. cellular.
c. QC type.
d. capacitation.
a. nickel-cadmium.
Which type of mobile x-ray machine is the most common?
a. battery powered
b. conventional
c. capacitor discharge
d. hybrid
a. battery powered
Mobile techniques often differ from techniques used in the radiology department because :
a. available mA and kV are limited.
b. SID may be longer or shorter than usual.
c. the patient may be more severely ill.
d. all of the above.
d. all of the above.
Portable radiographic equipment which does not have to be plugged in during the exposure is :
a. operated by magnetism.
b. of very low capacity.
c. battery powered.
d. of the capacitor discharge type.
c. battery powered.
T/F Because of radiation exposure to the head and neck region, the C-arm should not be placed in the PA projection tube alignment.
False
T/F The AP projection with the x-ray tube placed directly above the anatomy during a C-arm procedure is recommended to minimize OID
False, PA is recommended because of less exposure to operator and less OID
What is the term for the process of holding one image on the C-arm monitor while also providing continuous fluoroscopy?
Road-mapping
Which one of the three cardinal rules of radiation protection is the most effective means of reducing exposure during mobile and surgical procedures?
a. Time
b. Distance
c. Shielding
d. None of the above; all are equally effective.
b. Distance
T/F Any trauma study requires at least two projections as close to 90° opposite from each other as possible
True
T/F On an initial study of a long bone, both joints should be included for each projection
True
T/F Collimation on trauma cases can lead to cutoff of key anatomy and pathology, therefore it should be limited to the size of the IR.
False
What is the shortest distance from the tube to the patient when employing a C-arm unit?
a. 6 inches
b. 9 inches
c. 12 inches
d. 18 inches
a. 6 inches
T/F Wearing a protective lead apron is optional if the technologist is at least 8ft from both the x-ray tube and the patient during a mobile radiographic procedure
False
T/F The exposure dose is greater on the image intensifier side than on the x-ray tube side with the C-arm in the horizontal configuration
False, greater on the tube side
What should be the final step that the technologist takes before returning a trauma patient to the ER following a radiographic procedure?
a. Review patient history
b. Review examination requisition
c. Check patient armband/identification
d. Ensure the side rails are up on the patients cart
d. Ensure the side rails are up on the patients cart
Radiologists often use the Salter-Harris system to classify _________ fractures.
Epiphyseal fx
A patient with possible pleural effusion in the right lung enters the emergency room. The patient is unable to stand or sit erect. What position would best demonstrate this condition?
Right lateral decubitus
Where is the CR centered for an AP semi erect projection of the chest?
3-4'' below the jugular notch
A patient with a crushing injury to the thorax enters the emergency room. The patient is on a backboard and cannot be moved. Which projections can be performed to determine whether the sternum is fractured?
15° to 20° mediolateral angle and horizontal beam lateral projections
What is the minimum number of projections required for a post reduction study of the wrist?
two projections
To ensure that the CR is aligned properly for an AP trauma projection of the foot, the CR is angled:
10° posteriorly from perpendicular to the plantar surface of the foot
A patient with a possible fracture of the ankle enters the emergency room. The patient cannot rotate the lower limb. What can be done to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a mortise projection of the ankle?
Perform a cross-angle CR projection of the ankle, with CR 15° to 20° lateromedial from the long axis of the foot.
Following a post reduction of a fractured tibia/fibula, a post reduction study is ordered. A fiberglass cast was placed on the fractured leg. The original technique was 70kV @ 4mAs (film/screen system). How much should the technologist increase their factors from the original technique?
Up to 74 kV OR 5 mAs
Which projection demonstrates the C1-C2 vertebra if the patient cannot open their mouth?
35° to 40° cephalad AP axial projection
A patient with a possible fracture of the cervical spine pedicles enters the emergency room. Which one of the following projections will best demonstrate this region of the spine without moving the patient?
a. Perform a swimmer's lateral
b. Perform an articular pillar projection
c. Perform a Fuchs method
d. Perform AP axial trauma oblique projections
Perform AP axial trauma oblique projections
Which one of the following facial bone projections will best demonstrate air-fluid levels in the maxillary sinuses for a patient unable to stand or sit erect?
a. AP acanthioparietal
b. Trauma, horizontal beam lateral
c. AP modified acanthioparietal
d. AP axial
b. Trauma, horizontal beam lateral
On a horizontal beam lateral trauma skull projection, the IR should be placed crosswise with the CR centered:
2'' superior to the EAM
A patient with a possible compression fracture of the lumbar spine enters the emergency room. Which specific projection of the lumbar spine series would best demonstrate this fracture?
Lateral projection
For a successful radiographic exposures, clear communication must be established between the surgeon, technologist, and:
Anesthesiologist
CST is the acronym for:
Certified surgical technologist
The absence of infectious organisms is the definition for:
Asepsis
What portion of the OR table is considered sterile:
a. Only the level of the tabletop
b. Entire table
c. Tabletop and half base
d. None of the table
a. Only the level of the tabletop
T/F Scrubs worn in radiology may also be worn in surgery
False
T/F Scrub covers must be removed before entering the surgical suite
True
T/F The technologist can wear non sterile gloves when handling the IR and surgical cover following a procedure
True
Imaging equipment permanently stored in surgery must be cleaned at least:
Weekly
Which one of the following techniques will best reduce dose to the surgical team during a C-arm procedure?
a. Use boost function whenever possible
b. Place tube in vertical position above patient
c. Use intermitten fluoroscopy
d. Lower kV as low as possible
c. Use intermitten fluoroscopy
Which of the C-arm orientations in general results in the greatest exposure to the operator's head region if the distance from the patient is unchanged (patient is supine)?
a. Anteroposterior (AP) projection (x-ray tube above anatomy)
b. PA projection (x-ray tube below anatomy)
c. PA, 30° tilt away from operator
d. No significant difference
a. Anteroposterior (AP) projection (x-ray tube above anatomy)
A 30° tilt of the C-arm x-ray tube from the vertical position will increase radiation exposure to the face and neck region of the operator standing next to the C-arm by approximately a factor of:
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
c. 4
A patient enters the ED with a possible pneumothorax of the right lung. The patient is unable to stand or sit erect. Which specific position should be performed to diagnose this condition?
a. Left lateral decubitus
b. Right lateral decubitus
c. Ventral decubitus
d. AP supine
a. Left lateral decubitus
A patient enters the ED with a possible fractured sternum. The patient is supine and unable to lie prone. Which of the following routines best demonstrates the sternum?
a. RPO and lateral recumbent
b. AP and horizontal beam lateral
c. AP and LPO
d. LPO and horizontal beam lateral
d. LPO and horizontal beam lateral
A patient enters the ED with a possible fractured scapula. Because of her multiple injuries, the patient is on a backboard. Which of the following techniques is most helpful in providing a lateral view of the scapula if the patient is unable to rotate the affected shoulder adequately?
a. Perform a horizontal beam lateral.
b. Angle the CR parallel to the scapular spine.
c. Angle the CR lateromedial and parallel to the scapular body.
d. Angle the CR mediolateral and perpendicular to the scapular body.
c. Angle the CR lateromedial and parallel to the scapular body.
A patient enters the ED with a possible greenstick fracture. Which age group does this type of fracture usually affect?
a. Pediatric
b. Young adult
c. Middle-age
d. Geriatric
a. Pediatric
What should a technologist do if the sterile environment is violated during a surgical procedure?
a. Note the violation on the examination requisition.
b. Inform the radiology supervisor.
c. Notify a member of the surgical team once the procedure has been completed.
d. Notify a member of the surgical team immediately.
d. Notify a member of the surgical team immediately.
Which procedure introduces orthopedic cement directly into the weakened vertebrae?
a. Vertebroplasty
b. Microdiskectomy
c. Spinal fusion
d. Scoliosis corrective surgery
a. Vertebroplasty
Which of the following procedures is a nonsurgical procedure?
a. Closed reduction
b. Open reduction
c. Internal fixation
d. Intramedullary fixation
a. Closed reduction
T/F Shoe covers are not required in the presurgical or recovery areas.
False
Which device is utilized to promote proper bone alignment and immobilization as part of proper healing?
a. retractor
b. splint
c. traction
d. cast
c. traction
A trauma patient should only be left in the room alone in which of the following cases?
a. when accompanied by a family member
b. when he or she says he or she will be fine to be left alone
c. when the pain is gone
d. never
d. never
In the event a trauma patient arrives in the emergency room secured in a neck brace and backboard, when is it safe to remove both items?
a. immediately after radiographs are completed
b. immediately after patient requests it off
c. upon review of films and cleared by EMT
d. upon review of films and cleared by the attending physician
d. upon review of films and cleared by the attending physician
(A patient is never stripped of his or her neck brace or backboard until films are reviewed and cleared by the attending physician. )
In the case where there are suspected bilateral fractures of the femoral necks, which of the fol- lowing positions should be imaged?
1. AP 2. Danelius-Miller 3. Clements-Nakayama
a. 1 only
b. 1 and 2 only
c. 1 and 3 only
d. 1, 2, and 3
c. 1 and 3 only