carbohydrates: disaccharides and polysaccharides
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
maltose
glucose + glucose
sucrose
glucose + fructose
lactose
glucose + galactose
non reducing sugar
a carbohydrate that cannot donate electrons
test for non reducing sugars
negative initial benedict’s est
take sample, adding hcl and heat until boiling (breaks glycosidic bods by hydrolysing it)
use a universal indicator to check the solution is alkaline
do benedict’s test and heat
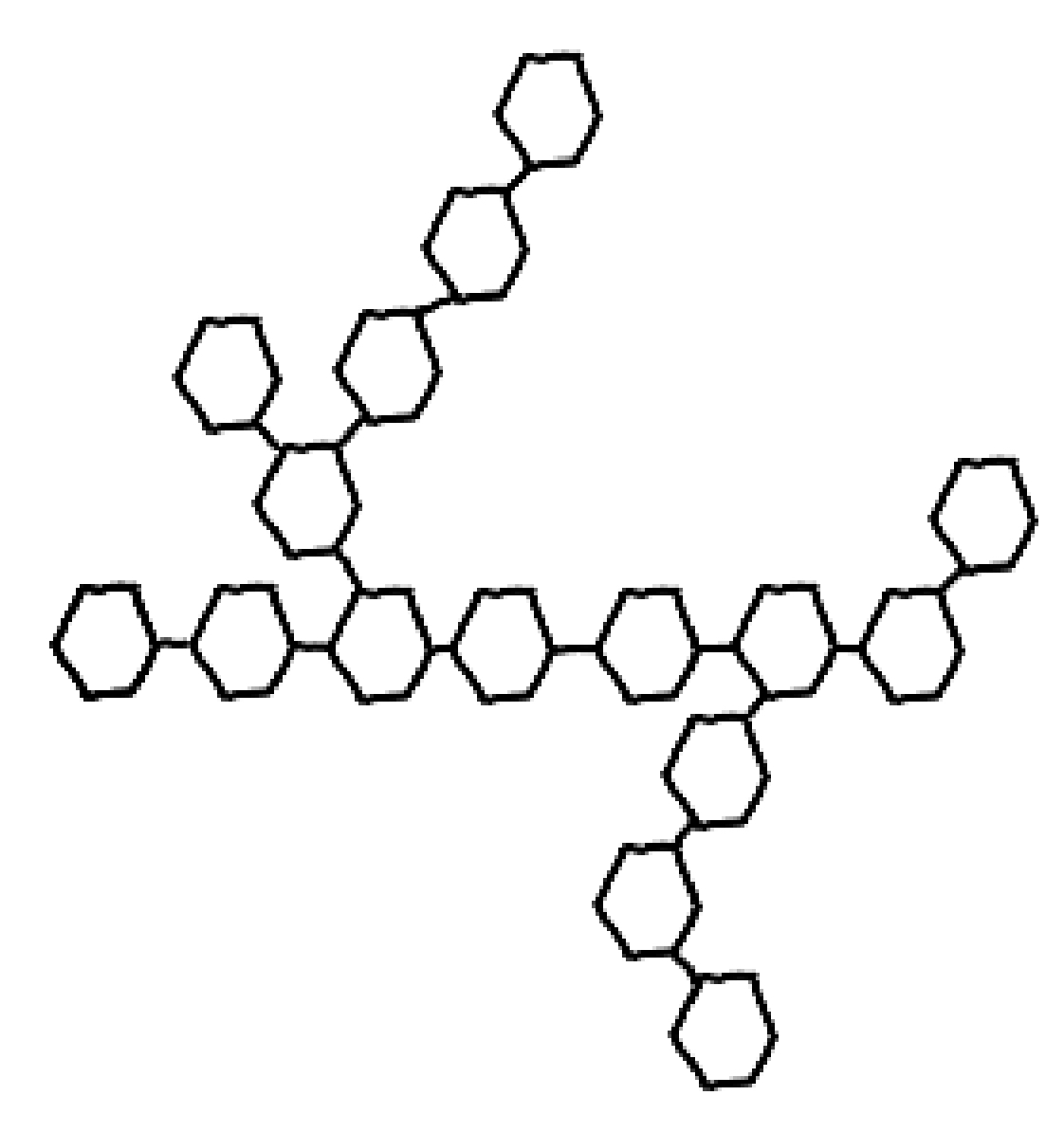
starch and glycogen properties
alpha glucose polysaccharide
insoluble and large, no diffusion, doesn’t affect water potential
osmosis is not affected
compact, stores lots in a small space, has lots of ends for enzyme action
cellulose properties
beta glucose polysaccharide
provides structure, strength and stability in a cell wall
starch structure
can be branched or unbranched
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
coiled
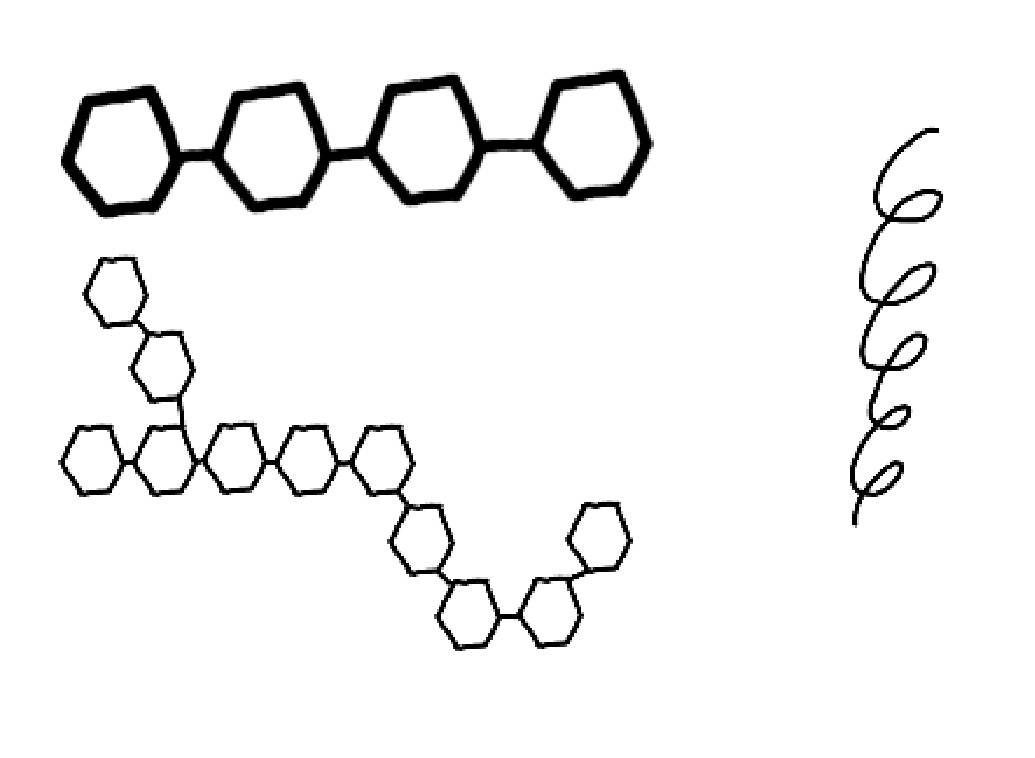
glycogen structure
shorter chains
1,4 or 1,6 glycosidic bonds
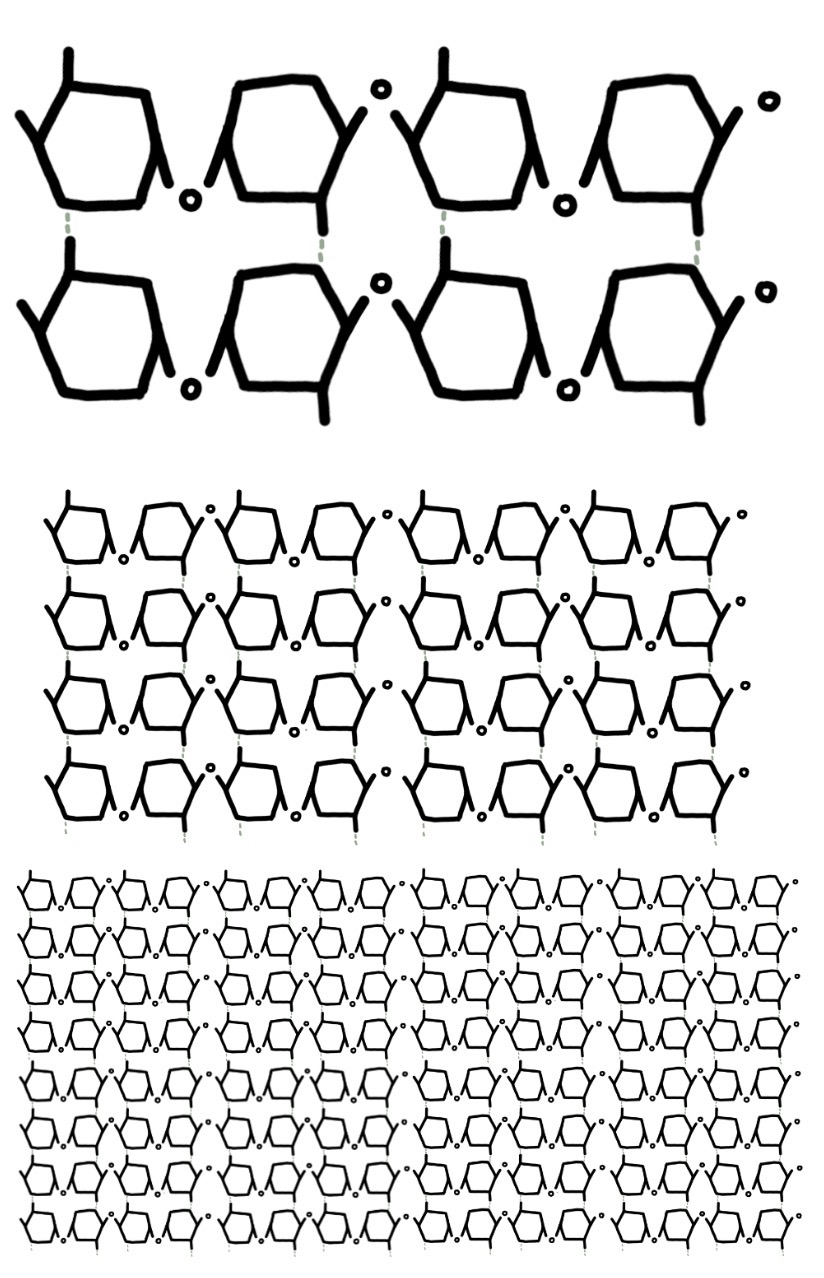
cellulose structure
each glucose molecule flips 180 degrees
beta glucose chain, long and unbranched
parallel chains, cross linking hydrogen bonds
microfibrils, lots of parallel chains grouped together
forms fibres, microfibrils groups together
lattice structure in cell wall