Comprehensive Guide to Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPX/CPET) in Cardiology and Pulmonology
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the primary goal of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPX)?
To evaluate the physiologic response to an increase in physical stress.
What type of analysis does CPX provide?
Real-time respiratory analysis.
What are the advantages of using a cycle ergometer for CPX?
Cheaper, safer, can stop anytime, holding bars has no effect, requires less space, and less noise.
What is a key advantage of using a treadmill for CPX?
Attains higher VO2 and provides a more 'real world' exercise experience.
What are indications for performing CPX?
Evaluation of dyspnea, distinguishing causes of exercise limitation, detection of exertional desaturation, rehabilitation, and pre-op evaluation.
What are some contraindications for CPX?
Acute MI, unstable angina, unstable arrhythmia, acute endocarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis, syncope, severe symptomatic aortic stenosis, uncontrolled CHF.
What is one reason to exercise high-risk patients in CPX?
The prognostic data and potential for patient management outweigh the risks involved.
What are common reasons for terminating a CPX?
Patient's request due to fatigue, dyspnea, pain, ischemic ECG changes, chest pain, significant ectopy, and significant changes in blood pressure.
What can CPX help identify when initial tests are inconclusive?
Cardiac, pulmonary, psychological issues, or conditions like hyperventilation and anxiety.
What are mechanisms of exercise impairment in CPX?
Pulmonary impairment, cardiovascular issues, peripheral inactivity, and motivational factors.
What does CPX provide that resting tests cannot predict?
Exercise tolerance.
What is the significance of VO2max in CPX?
It defines the limits of the cardiopulmonary system and is a predictor of exercise capacity.
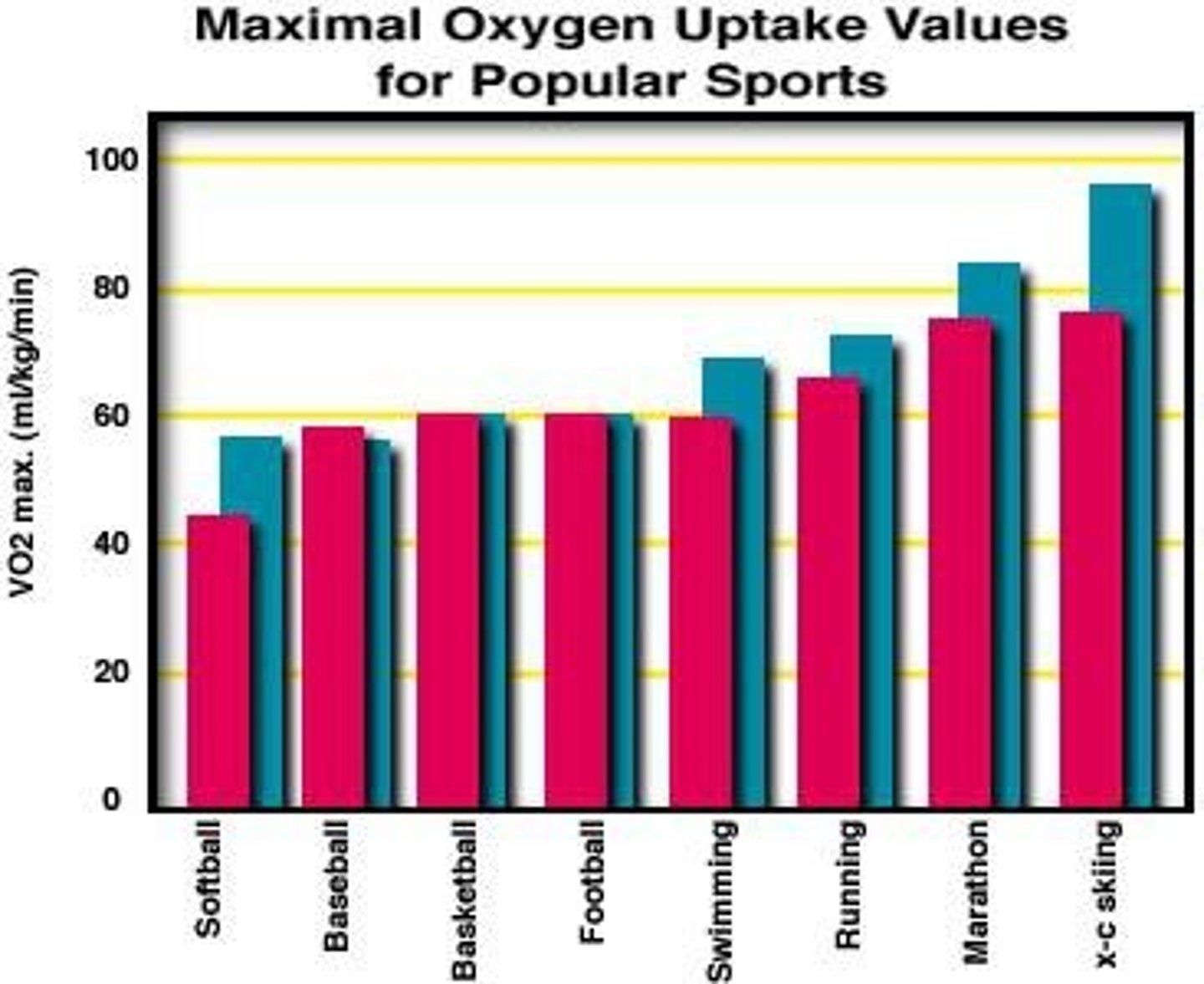
How is VO2max expressed for inter-subject comparison?
In mL/kg/min to normalize for body weight.
What is the anaerobic threshold (AT) in CPX?
The point during exercise at which lactic acid starts to accumulate in the blood.
What does the Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) indicate?
The ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed during exercise.
What is the role of CPX in preoperative evaluation?
Predicting post-operative cardiopulmonary complications.
What is the relationship between predicted VO2max and post-operative outcomes?
Predicted VO2max <50-60% is linked to high morbidity and mortality post lung resection.
What does CPX measure in terms of cardiovascular response?
Heart rate (HR), ECG, and blood pressure (BP).
What are common exertional symptoms that correlate poorly with resting symptoms?
Leg pain or fatigue.
What is the significance of CPX in monitoring patients undergoing fitness training?
It helps determine the patient's functional capacity and response to exercise.
What is the importance of the minute ventilation-carbon dioxide output relationship (Ve/VCO2 slope)?
It provides insights into ventilatory efficiency during exercise.
What is the role of CPX in evaluating patients with cardiovascular disease?
It is used in evaluation for heart transplants and as a predictor of cardiac death.
What does VO2max represent?
Maximal oxygen uptake; the highest rate of oxygen consumption during exercise.
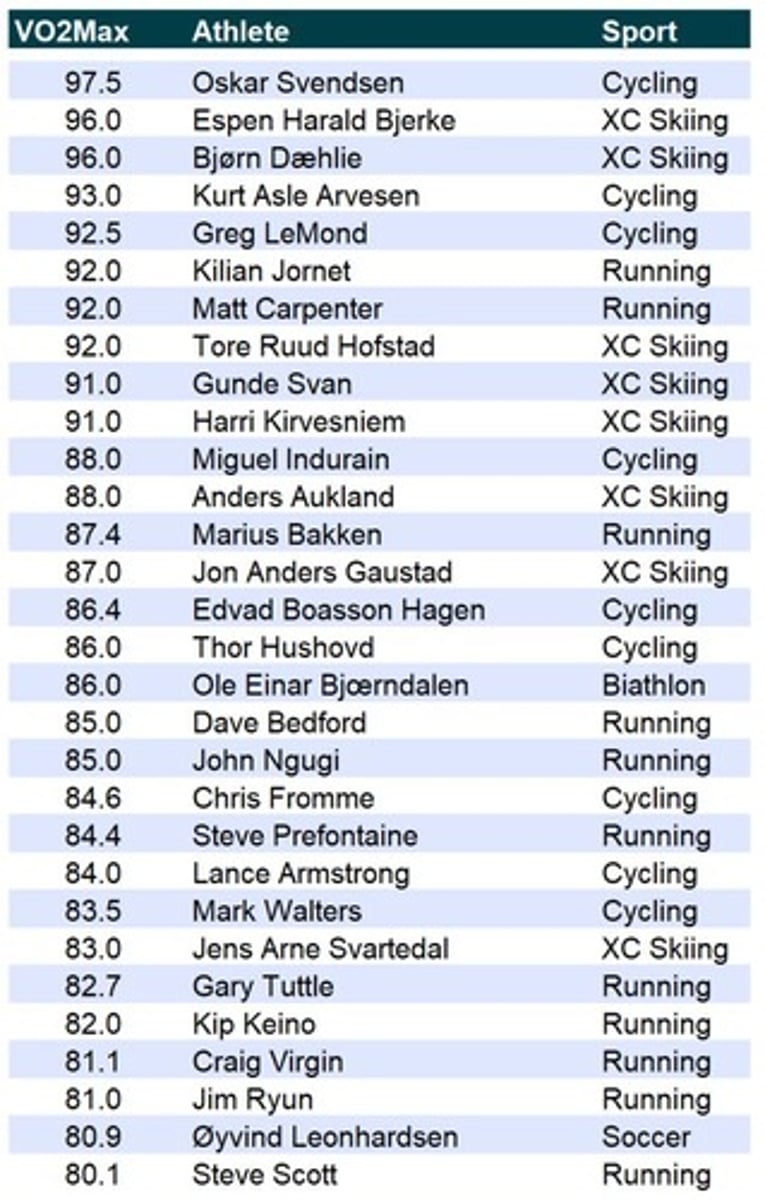
What is the significance of a plateau in VO2?
It indicates that an individual's physiological limit has been reached.
What is the difference between VO2max and peak VO2?
VO2max implies a physiological limit reached, while peak VO2 is more commonly used clinically and may not indicate a true maximum.
What does the respiratory exchange ratio (RER) measure?
The ratio of carbon dioxide produced to oxygen consumed.
What is a normal resting RER range?
0.75 to 0.85.
What RER value indicates maximal exercise?
An RER greater than 1.10.
What does the anaerobic threshold (AT) indicate?
The point where oxygen supply to the muscle does not meet oxygen demand, leading to increased reliance on anaerobic metabolism.
At what percentage of VO2max does AT typically occur in a sedentary person?
50-60% of VO2max.
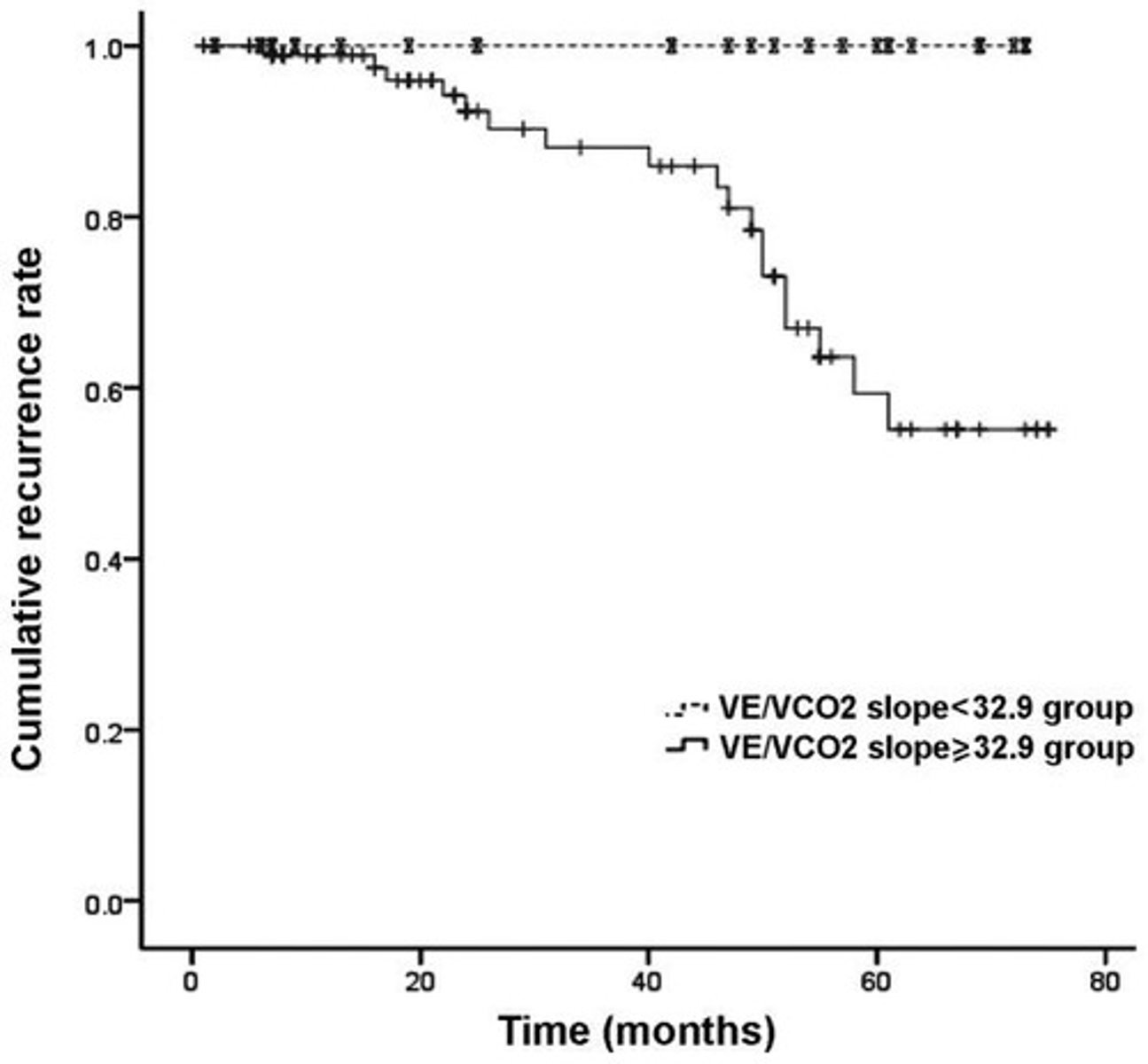
What is the significance of the VE/VCO2 slope?
It predicts outcomes in heart failure and reflects the relationship between minute ventilation and carbon dioxide output.
What is the normal PETCO2 range?
Greater than 35 mmHg.
What does a VE/VCO2 slope greater than 34 indicate?
A worse prognosis in patients.
What is tidal volume (Vt)?
The volume of air a patient consumes during exercise.
What is the relationship between VE and VCO2 during exercise?
They are tightly coupled, with VE modulated by VCO2 production.
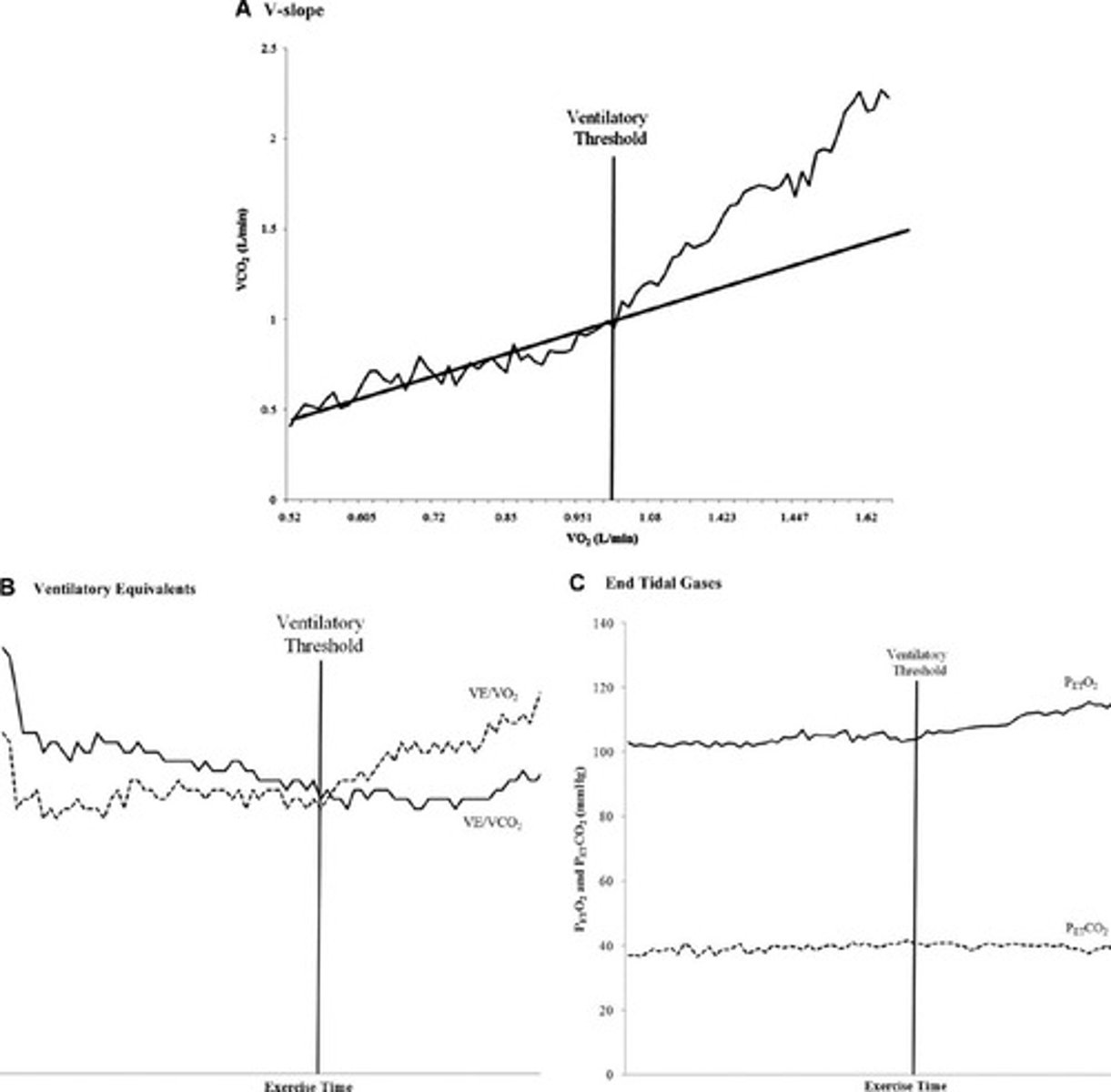
What is the V-slope method used for?
To determine the point at which the slope of the relationship between VCO2 and VO2 changes.
What can cause elevated VE/VCO2 in heart failure?
Ventilation-perfusion mismatching and increased chemoreceptor sensitivity.
What is the role of arterial lactate in determining anaerobic threshold?
It helps assess the metabolic acidosis onset during exercise.
What is the clinical significance of peak VO2?
It is used to assess exercise capacity and guide treatment decisions in heart failure patients.
What does a normal cardiovascular response to exercise indicate?
It suggests normal aerobic capacity and fitness levels.
What is the impact of hyperventilation on PETCO2?
PETCO2 lowers during hyperventilation.
What is the significance of the anaerobic threshold in exercise testing?
It helps determine the exercise intensity at which anaerobic metabolism begins to dominate.
What is the clinical relevance of determining AT?
It can indicate limitations in oxygen supply to tissues and guide exercise prescription.
What factors can affect the accuracy of the V-slope method?
Operator experience and the patient's ventilation status.
What does a pVO2 of 9.6 ml/kg/min indicate in a patient?
A severely reduced exercise capacity, often seen in heart failure.
What is the importance of case studies in understanding CPX results?
They provide real-world examples of how exercise testing can inform clinical decisions.