Understanding Acute Coronary Syndromes and Management
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the leading cause of death in the United States?
Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
How many deaths per day were attributed to CVD in 2017?
2,354 deaths per day
What percentage of CVD deaths are due to coronary heart disease (CHD)?
Approximately 50% of all CVD deaths
How many Americans experience a new myocardial infarction each year?
605,000 Americans
What are the three components of Acute Coronary Syndromes?
Unstable angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction (MI), and sudden cardiac death due to myocardial ischemia.
What is the most common underlying mechanism for Acute Coronary Syndromes?
Atherosclerotic plaque erosion, rupture, or other types of plaque disruption.
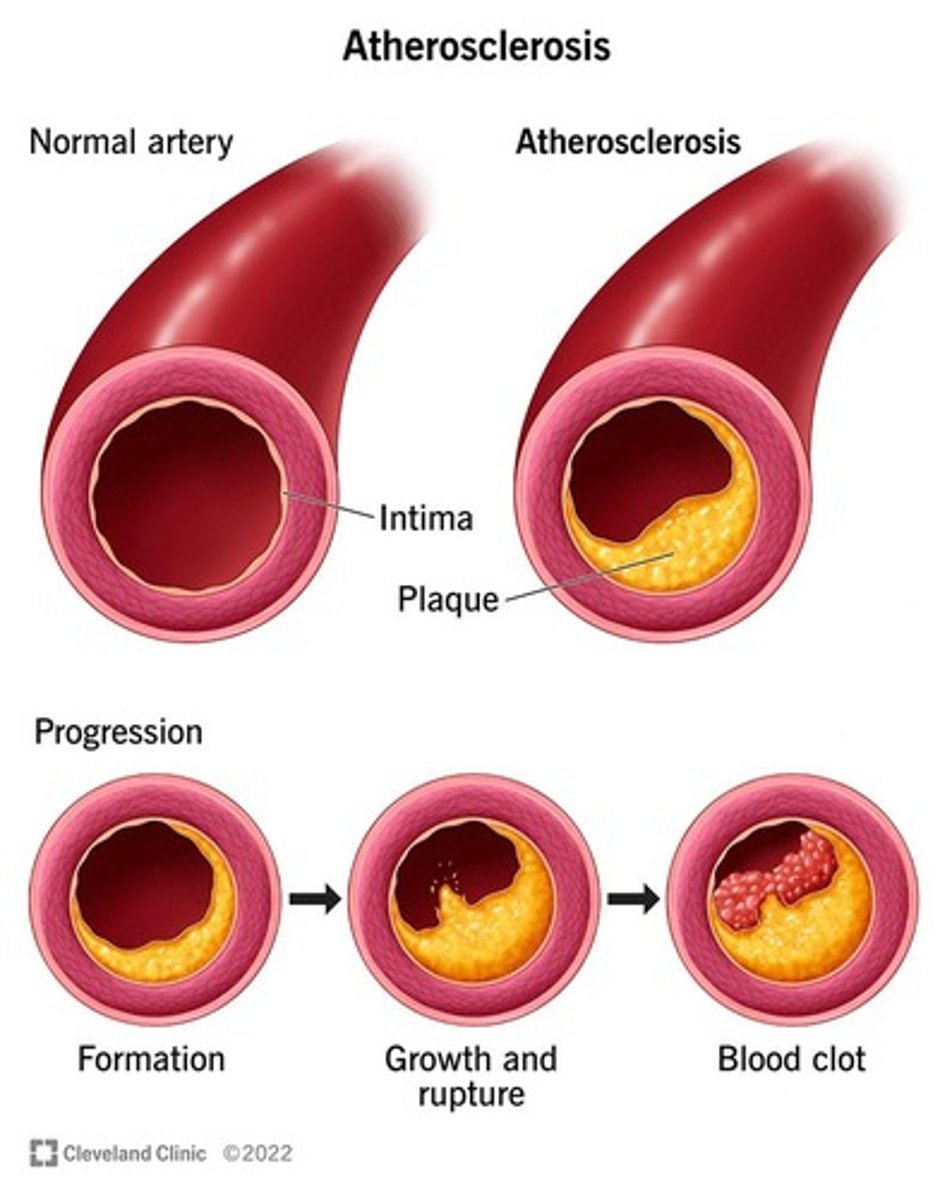
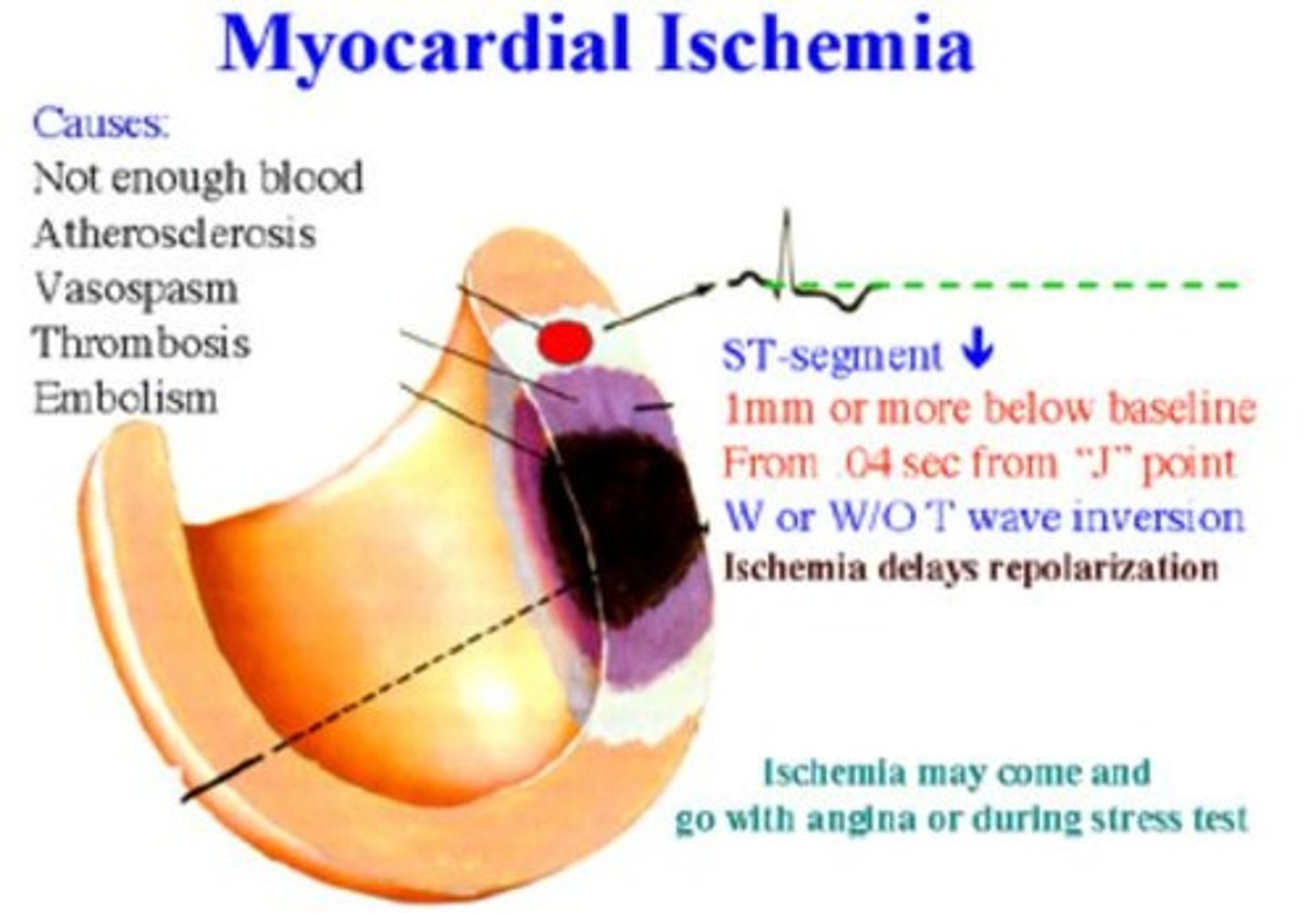
What are the EKG signs associated with Acute Coronary Syndromes?
ST to T wave abnormalities.
What is the difference in occlusion time between unstable angina and myocardial infarction?
Unstable angina is typically less than 10 minutes, while occlusion greater than 60 minutes results in MI.
What is the key event that leads to myocardial infarction?
Disruption of the myocyte membrane.
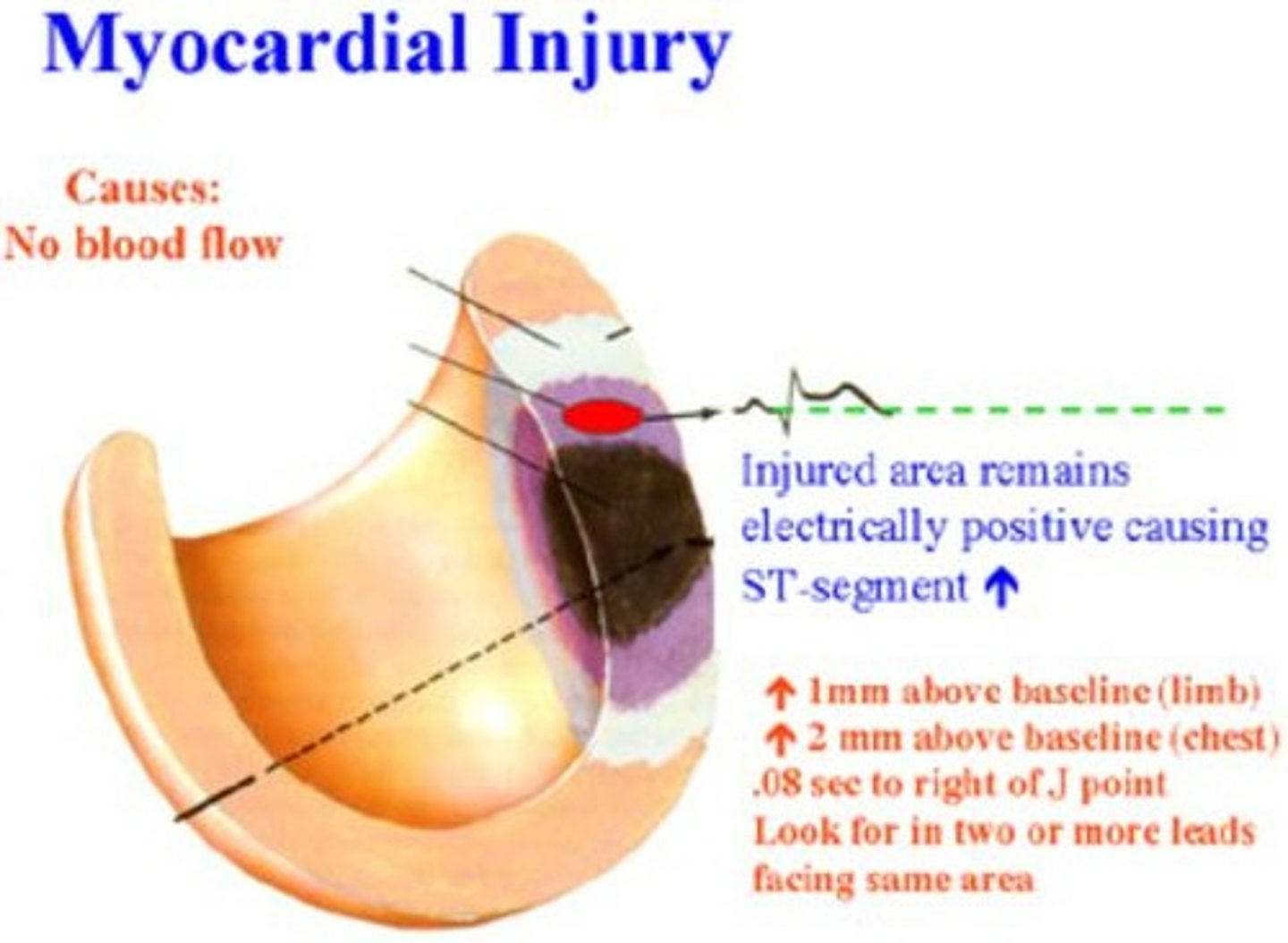
What is the preferred biomarker for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction?
Cardiac troponin (cTn).
How long after the onset of infarction does cardiac troponin elevation occur?
2-3 hours after onset.
What is the significance of a pathological Q wave in an ECG?
It indicates myocardial infarction if it lasts 0.03 seconds or longer and has a vertical deflection of at least 1/3 of the R wave.
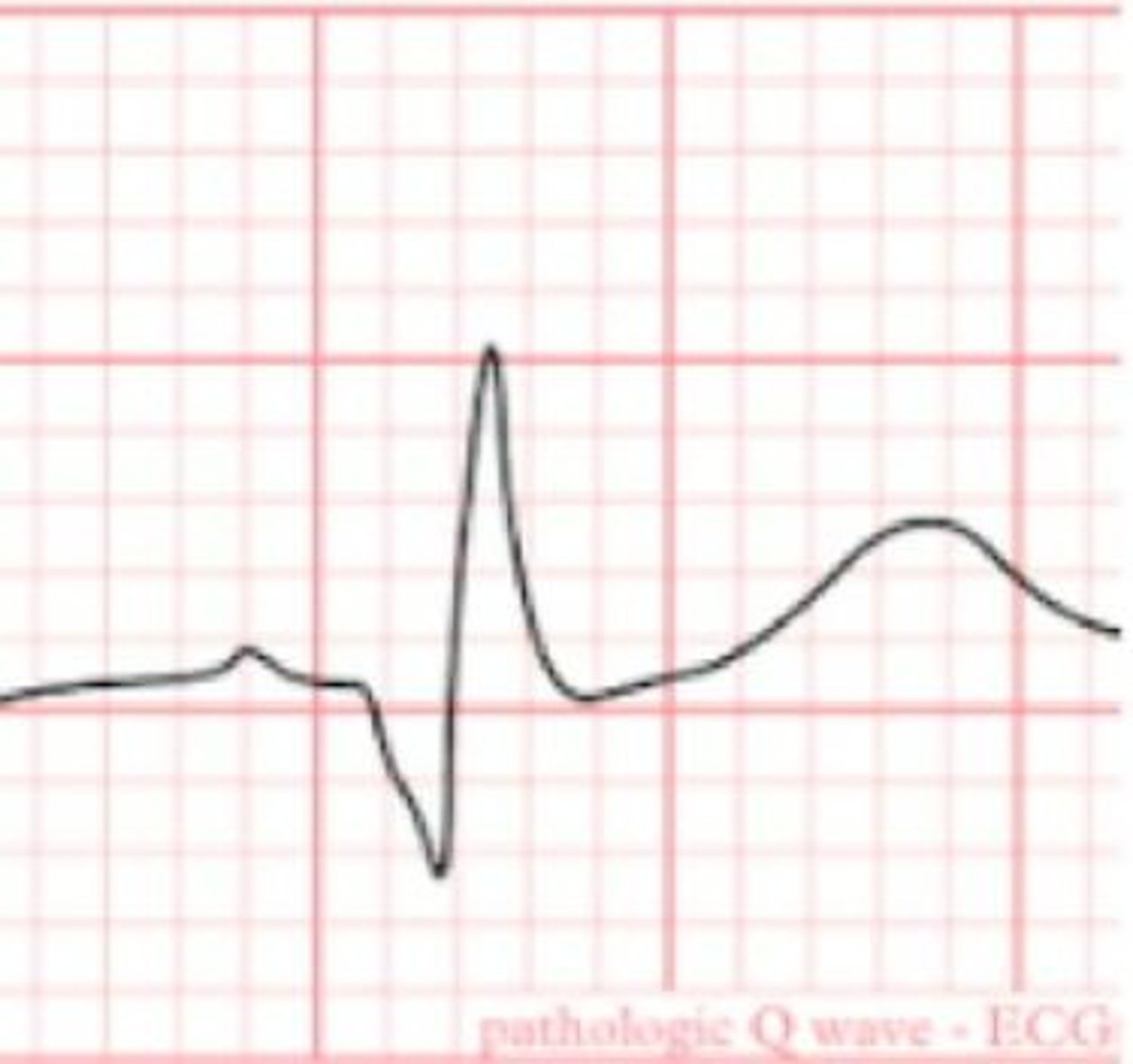
What are the two classifications of myocardial infarction based on EKG findings?
STEMI (ST-segment elevation) and NSTEMI (ST-segment depression or T wave inversion).
What are the management strategies for Acute Coronary Syndromes?
Anti-ischemic therapy, dual antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulants, pain relief, and reperfusion therapy.
What is an early invasive strategy for managing non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction?
Percutaneous coronary intervention within 24 hours of hospital presentation.
What is the recommended therapy for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction?
Reperfusion strategies such as thrombolysis or primary PCI.
What is the relationship between right ventricular myocardial infarction and inferior wall myocardial infarction?
RV infarction is most associated with inferior wall myocardial infarction and occurs due to occlusion of the proximal right coronary artery.
What are signs of poor prognosis in stress testing?
Inability to exercise, substantial exercise-induced ischemia, and a capacity of less than 5 METs.
What is the recommended timing for early outpatient cardiac rehabilitation after hospital dismissal?
1-2 weeks after hospital dismissal.
What are some benefits of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) for cardiac patients?
Improved cardiovascular fitness, VO2 peak, endothelial function, left ventricular function, and mitochondrial density/function.
What is the significance of supervised exercise training for coronary patients?
It has been demonstrated to be safe and effective.

What percentage of eligible Medicare beneficiaries participate in cardiac rehab services?
Only 19%.
What is the conclusion regarding acute coronary syndromes?
They result from atherosclerotic plaque development leading to plaque disruption and thrombus formation, causing myocardial ischemia and potential necrosis.
What characterizes unstable angina pectoris?
Transient coronary artery occlusion with spontaneous clot dissolution and no demonstrable myocardial necrosis.
What are the overall benefits of cardiac rehabilitation for patients?
Significant reductions in mortality and improved health outcomes.