Hemolytic Anemias-Hemoglobinopathies (Chapter 11)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Hemoglobinopathies
A group of genetic disorders caused by structural abnormalities in the hemoglobin
What is the frequent cause of Hemoglobinopathies?
Single amino acid substitutions in the globin chains
There are _____ hemoglobin variants
1,000
The majority of hemoglobin variants are clinically _______
Insignificant
There are ___ known polypeptide chains that make up the different globin portions of the hemoglobin molecule
Six
Hemoglobinopathies do not have an amino acid substitution or deletion
False, hemoglobinopathies do have an amino acid substitution/deletion
Hgb A is:
A normal Hgb allele
Hgb S is:
An abnormal Hgb allele
Hgb C is:
An abnormal Hgb allele
Most hemoglobinopathies result from:
β-chain abnormalities
What causes Hemoglobin S (HbS) to occur?
Position 6 of the β chain, valine replaces glutamic acid
What causes Hemoglobin C (HbC) to occur?
At position 6 of the β chain, lysine replaces glutamic acid
Sickle cell disease (SCD)
Group of genetic disorders characterized by the production of abnormal HbS
Sickle cell anemia (HbSS disease)
Most common type of sickle cell disease; most severe form
What represents the homozygous form of sickle cell, in which the individual inherits a double dose of the abnormal gene that codes for HbS?
Sickle cell anemia (HbSS disease)
Sickle cell trait (HbAS)
Occurs when a person inherits one HbS gene and one normal HbA gene (heterozygous)
Which sickle cell is usually asymptomatic, but may have mild symptoms under extreme stress
Sickle cell trait (HbAS)
When properly oxygenated, HbS should usually does not cause any issues
True
HbS is soluble
True
What occurs when oxygen tension decreases (low O2 environment)?
HbS molecules to stick together when they release O2, forming long, rigid rods
Causes the RBC to deform into the characteristic sickle shape
What triggers an aplastic crisis?
Usually viral infections (especially parovirus B19)
What effect does an aplastic crisis have?
Temporary suppression of erythropoiesis (bone marrow stops making new RBCs)
What triggers a hemolytic crisis?
Medications
Autoimmune disorders
Viral infections
Low O2 state
Acidosis
Cold exposure
The lab findings for an individual going through a hemolytic crisis shows ______ H&H and _____
Decreased, jaundice
Lab findings for a patient experiencing hemolytic crisis would show ______ reticulocyte count
Increased
A patient experiencing a hemolytic crisis would have what kind of symptoms?
Sudden weakness
Rapid pulse
Faintness
Pallor (lips & mucous membranes)
Abdominal fullness from splenic enlargement
What is the most common type of sickle crisis?
Vaso-occulsive crisis (pain crisis)
Which sickle crisis is associated with severe pain, caused by occlusion (blockage) of small blood vessels?
Vaso-occulsive crisis (pain crisis)
Dactylitis (painful swelling of the hands/feet is more common in ____ & ________ with HbSS anemia?
Infants & young children
What is the major cause of morbidity and mortality for those with HbSS anemia?
Serious bacterial infections
____ occurs in up to 22% of patients with HbSS anemia?
Stroke
How is sickle cell trait inherited?
One normal β-globin gene (HbA) + one sickle β-globin gene (HbS)
Individuals with HbS trait are usually ______
Asymptomatic
Individuals with sickle cell trait produce both HbA and HbS in a ratio of __:__ (HbA, HbS)
60,40
Newborns suspected of HbS in the U.S. and territories are routinely screened
False, every newborn is screened regardless of race or ethnicity
What is the gold standard for confirming HbS?
Hemoglobin electrophoresis (performed on cellulose acetate and citrate agar)
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Separates hemoglobin types based on their charge
Sickle cell anemia (HbSS) & stickle cell trait are most commonly found in populations with ancestry from?
Regions where malaria is or was historically prevalent
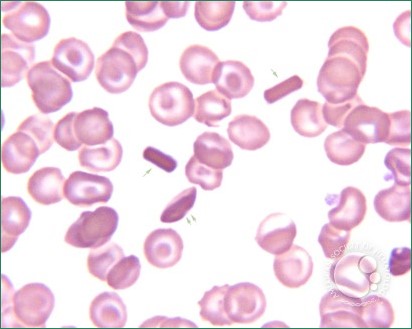
What is in the center of this slide?
HbC crystals “bar of gold”
Hemoglobin C Disease and traits are almost exclusive to:
African & African American populations
HbC disease presents with:
Normocytic & Normochromic or hyperchromic anemia
HbC crystals “bars of gold”
Electrophoresis results:
95% Hbc (dominant form)
Some HbA2 present
<7% HbF
What could these results indicate?
Hemoglobin C Disease/trait
Hemoglobin Disease/Trait is more common in
Asian populations
Especially SE Asia
What kind of cells would an individual with Hemoglobin E disease/trait have?
Microcytosis, target cells
What protective effect does Hemoglobin E disease/trait have?
HbE alters the RBC environment, making it less favorable for Plasmodium falciparum
As a result, the parasite multiplies more slowly in HbAE (trait) or HbEE (disease) cells
HbD
Non-sticking soluble hemoglobin
Hemoglobin D Disease/Trait
Causes mild hemolytic anemia
Has variations (name may include area of prevalence)
Hemoglobin OArab Disease/Trait
Exhibits a mild hemolytic anemia with slight splenomegaly & target cells
Has a distinct electrophoresis pattern
Those with the trait are asymptomatic
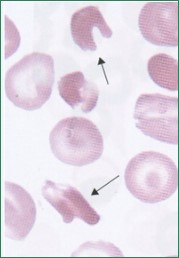
What could this indicate?
Hemoglobin SC disease
The gene for HbS and HbC are inherited from one parent only in the case of Hemoglobin SC disease
False, the gene for HbS is inherited from one parent and HbC from the other
Hemoglobin SD disease
Combination of HbS and HbD disease, rare
How does hemoglobin SD disease present a diagnostic problem?
Hemoglobin migrates together at alkaline pH, the electrophoretic pattern is similar to that of HbSS disease; alternative testing is needed
Thalassemia
Decrease in Hgb production due to decrease production of globin chains
HbS/β0 thalassemia
Severe condition that clinically resembles sickle cell anemia (Zero = no synthesis of beta chains)
HbS/β+ thalassemia
Generally milder clinical presentation (plus = reduced synthesis of beta chains)
Unstable hemoglobins may cause Hgb to ____ & precipitate in RBCs as _______
Denature, Heinz bodies
Isopropanol stability/Heat stability testing
Detects unstable Hgbs (also, gene sequencing)
Unstable hemoglobins are not hemoglobin variants
False, they are