GI E2- ID of GI tract
1/79
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What. is inflammation of the stomach lining?
Gastritis
What is inflammation of the stomach and intestines?
Gastroenteritis
What term refers to diseases caused after consuming toxins in food?
Food poisoning
What kind of food poisoning?
can be detected in food
shorter incubation- 1-6 hrs
ssx: usually vomiting, fever not usually present
ex: s. aureus, b. cereus
Preformed toxins
What kind of food poisoning?
toxin detected in stool specimens
longer incubation- 8-16 hrs
ssx: less vomiting, more abd cramping, ± fever
ex: c. perfringens
Microbe produces toxin after ingestion
Acute diarrhea lasts ______
< 2 weeks
Persistent diarrhea lasts _______
> 2 weeks
Chronic diarrhea lasts _____
> 30 days
What term describes ≤ 3 stools/day?
Mild diarrhea
What term describes ≥ 4 stools/day with local symptoms (abd cramps, N, tender)?
Moderate diarrhea
What term describes ≥ 4 stools / day with systemic symptoms (fever, chills, dehydration)?
Severe diarrhea
What kind of diarrhea?
involve invasion of colon by bacteria, parasites, or toxin production
complaints of frequent bloody, small volume stools
common sx: fever, abd cramps, tenesmus, fecal urgency
Inflammatory/bloody diarrhea
Pathogens that cause inflammatory diarrhea
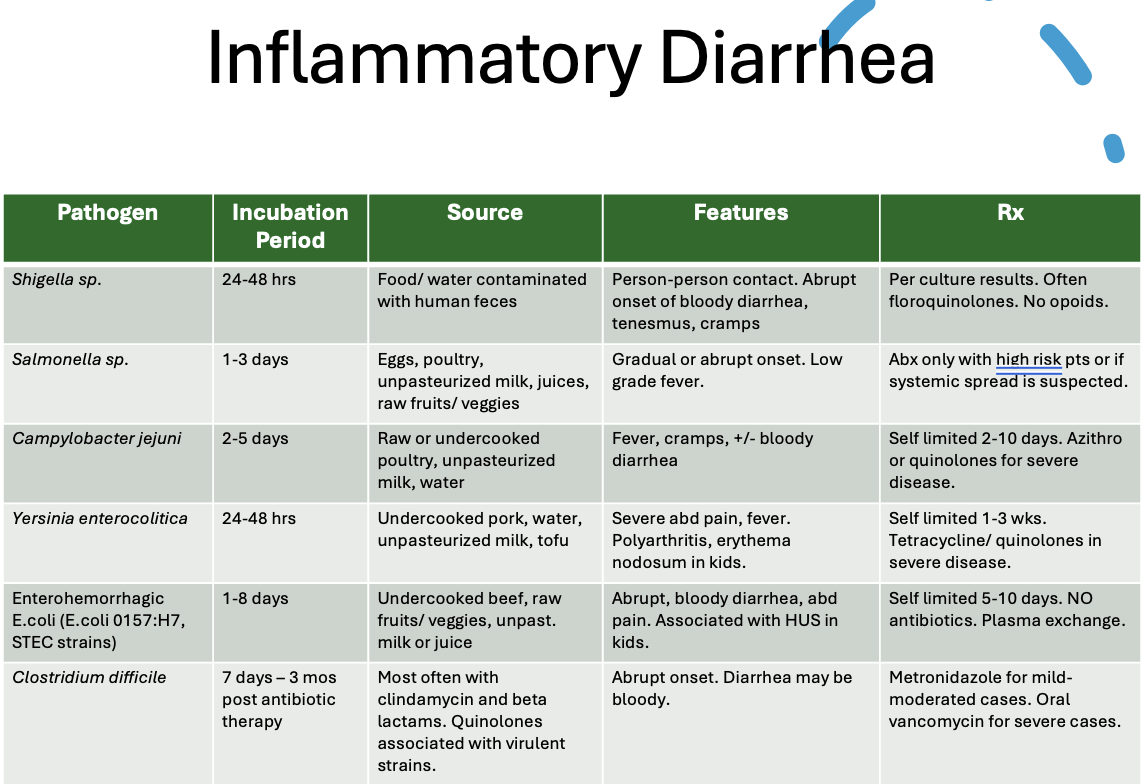
What kind of diarrhea?
milder; caused by viruses or toxins that invade small intestine
interfere with salt & water balance → large volume watery diarrhea
local sx: N, V, cramps
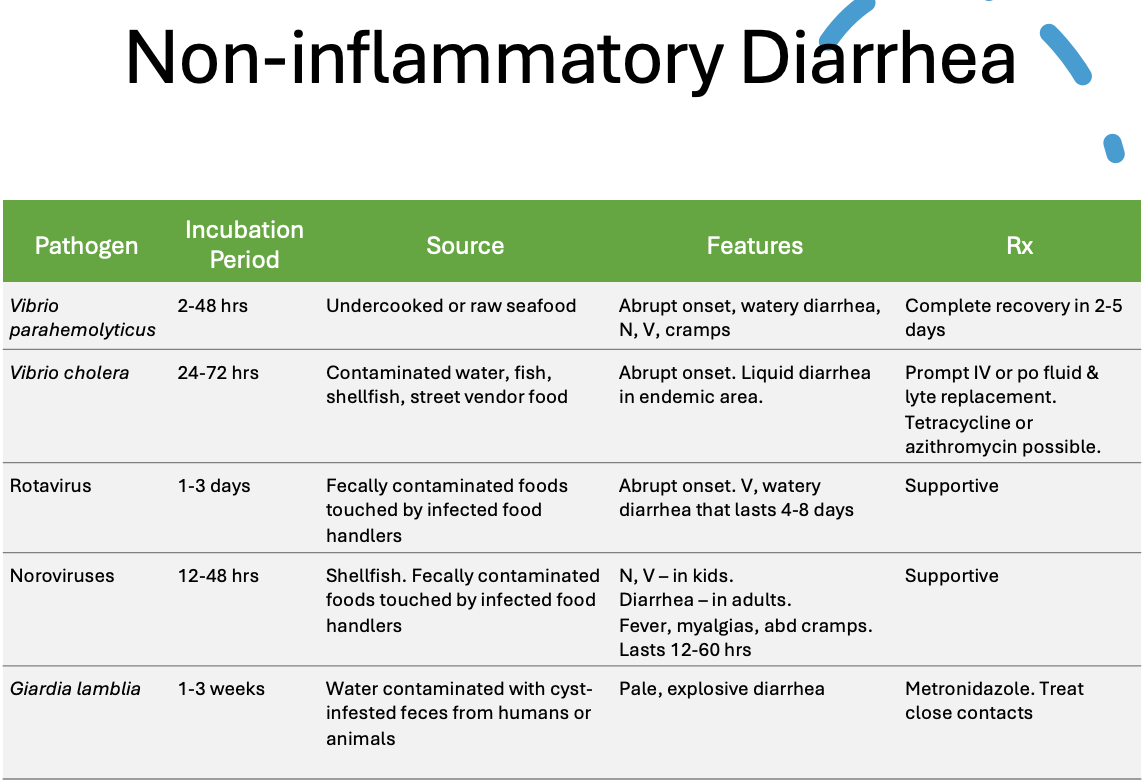
Non-inflammatory, non-bloody, watery diarrhea
Pathogens that cause non-inflammatory diarrhea
Food/water borne pathogens that cause non-inflammatory diarrhea
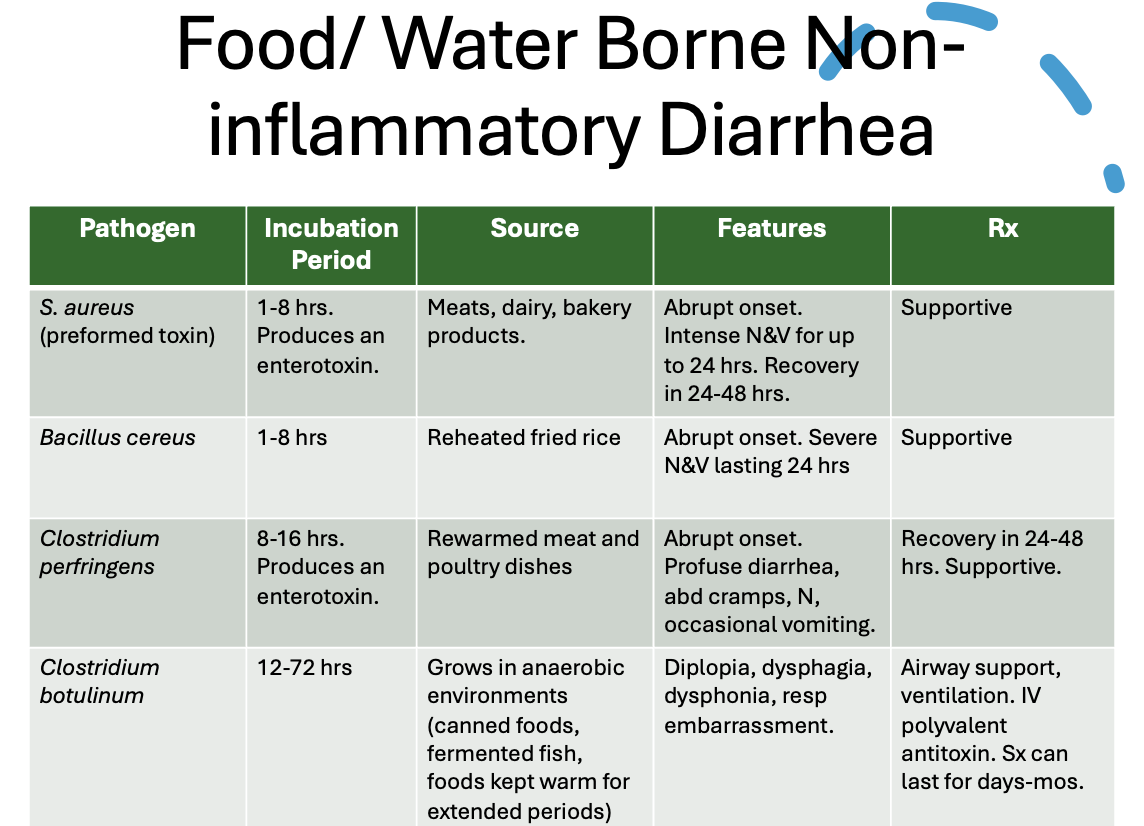
What condition?
transmitted by food and water (both types)
12-72 hr incubation
profuse watery diarrhea that is prolonged but self limited (1-2 wks)
*can be longer if immunocompromised
Acute infectious diarrhea
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does recent hospitalization or abx use suggest?
C. diff
What pathogens for acute infectious diarrhea do recent foreign travel suggest?
Salmonella, shigella, campylobacter, e. coli or v. cholerae
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does an undercooked hamburger suggest?
E. coli 0157:H7
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does an outbreak in a longterm care facility, school, or on a cruise ship suggest?
Norovirus
What pathogen for acute infectious diarrhea does the consumption of fried rice suggest?
B. cereus toxin
How is acute infectious diarrhea diagnosed?
Clinical- look at history and environmental factors
What is the treatment for acute infectious diarrhea?
RX not recommended → most self limited
Fluid/elyte replacement, oral glucose based rehydration solns (pedialyte, ceralyte, gatorade), antiemetics
What should be done for acute infectious diarrhea if symptoms last > 1 wk, the initial onset is of fever or bloody stools, or patient is immunocompromised?
Stool cultures- WBC, O&P, etc
can order specific tx if specific organism identified and sx persist (but most resolve by time culture is returned)
Antibiotics for acute infectious diarrhea would be helpful for with pathogens?
Shigella or campylobacter infections
Acute infectious diarrhea caused by which pathogens would antibiotics worsen the disease?
E. coli 0157:H7 (risk developing HUS)
C. diff (prolongs dz)
What pathogen?
affects all ages, esp kids
frequently in summer mos
transmission: ingestion of contaminated food, drink
vector: domestic pets (dogs, cats, turtles)
large numbers must be ingested to produce illness
Salmonella (salmonellosis)
What are sources that can contain salmonella?
Unpasteurized milk, turkey, chicken, duck, eggs (esp raw), hollandaise sauce, homemade eggnog, caesar salad dressing
What can decrease the possibility of salmonella infection but doesn’t eliminate it?
Cooking contaminated foods (might not reach lethal temperature range or deep in foods like large turkeys or soft cooked eggs)
How much salmonella must be ingested to produce illness?
Large numbers
In general, what amount of shigella is sufficient to induce symptoms?
10-100 bacteria
What pathogen?
Worldwide distribution; common in countries w/o effective sanitation
fecal oral route
source: food or water contaminated with human feces
Shigella aka bacillary dysentery
What pathogen?
infx MC in children and elderly
produces cytotoxin (shiga toxin/STEC) → endothelial damage, hemolysis and renal damage
uncomplicated infx resolves spontaneously in 5-10 days
E. coli 0157:H7 (enterohemorrhagic)
What have E. coli 0157:H7 outbreaks been attributed to?
Undercooked ground beef, unpasteurized apple juice and milk, raw fruits and vegetables
What are complications of E. coli 0157:H7?
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), esp in kids < 5 y/o
Why are antibiotics contraindicated in e.coli 0157:H8 infx?
increases risk of HUS
What does the CDC recommend for all patients with bloody diarrhea or HUS?
Test for E. coli 0157:H7
What pathogen is an enterotoxin forming strain of staphylococcus that multiplies in food before ingestion and is commonly found on skin?
S. aureus
What are the sources of growth for s. aureus?
Protein rich foods- ham, eggs, hardboiled eggs, mayonnaise, custard filled pastries, potato salad
Also cold ready to eat foods and raw milk
What pathogen?
typical sx: stomach pain and vomiting
average onset period- 1-6 hrs
recovery- usually 4-6 hrs, occasionally 24 hrs
dx: high suspicion; multiple cases in people eating the same meal
S. aureus
What is the most common botulism in the US?
Infant botulism
What causes infant botulism?
ingestion from honey & spores in the environment
What pathogen?
3 types of botulism- food, infant, wound
grows in anaerobic acidic environemnts- canned foods, fermented fish, foods kept warm for extended periods
sx begin 12-36 hrs after ingestion
may occur up to 14 days after in infants
Clostridium botulinum
What are sx of botulism?
Double or blurred vision, droopy eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, muscle weakness that starts in shoulders and descends through body
What is the treatment for c. botulinum?
maintain airway and breathing, may require ventilator, IV polyvalent antitoxin
What condition?
majority caused by Enterotoxigenic e coli, shigella species, or c. jejuni
onset 5-15 days, can occur w/in 2-10 days of travel, esp in area of poor sanitation
contaminated foods or drinks- unpeeled fruits, leafy vegetables, unsanitary drinking water or ice
Traveler’s diarrhea
What is there a significant risk of developing with traveler’s diarrhea?
IBS
What sx are associated with traveler’s diarrhea?
Watery diarrhea (≥ 10 loose stools/day), nausea, abd cramping, fever (< 1/3 of pts)
Are stool cultures needed for travelers diarrhea?
Nope- no blood or leukocytes present
How long does traveler’s diarrhea last?
Usually spontaneously resolves in 5 days
What is the treatment/prevention for traveler’s diarrhea?
Give antimicrobials to take if diarrhea occurs during trip
loperamide 4mg loading dose following by 2mg after each loose stool (max 16 mg/day)
peptobismol
What antimicrobials can be given to a patient about to travel to prevent traveler’s diarrhea?
Cipro (or levo or ofloxacin) single dose
Azithro 1g single dose
Rifaximin
What is a broad spectrum abx that is specific for enteric pathogens of the GI tract?
Rifaximin
What condition?
toxin mediated disease causes severe inflammatory response w/ formation of pseudomembranes made of necrotic debris, mucus, inflammatory cells
cause- C. diff
MC in hospitalized patients - 20% of those after taking abx
fecal oral transmission
Pseudomembranous colitis (PMC)
How can abx cause pseudomembranous colitis?
Disrupts normal bowel flora → overgrowth of C. difficile
What pathogen is an obligate anaerobe, gram positive, spore forming bacilli?
C. difficile
What antibiotics cause pseudomembranous colitis?
Ampicillin, lincosamides (clindamycin), 3rd gen cephalosporins, FQs
Describe the toxins associated with PMC
Destroy colonic mucosa, don’t induce fluid or elyte secretion, & appear as raised yellowish white plaques (pseudomembranes) loosely adherent to the mucosa, occurring in patches MC in the rectosigmoid area
The following sx are associated with what condition?
mild-mod greenish, foul smelling, watery diarrhea
5-15 stools/day
lower abd cramping, LLQ tenderness
positive for mucous in stool but no blood
PMC
What is the diagnostic workup for PMC?
Cytotoxicity assay (definitive), rapid EIA for toxin A & B, rapid PCR (preferred), fecal WBCs, flex sigmoidoscopy (white or yellow fluffy loose plaques + copious mucus), and abd XR/CT if megacolon suspected
What is the treatment for PMC?
D/c offending antibiotic
Vancomycin PO or fidaxomicin (if both not available → flagyl)
Fecal microbiota transplant
What should be avoided in PMC?
Antimotility agents and narcotics → delays clearance of toxin
What complications area associated with PMC?
Fulminant disease → hemodynamic instability, resp failure, metabolic acidosis, megacolon. perforation, deaeth
Chronic untreated dz → wt loss, protein losing enteropathy
Why do 25% of patients with PMC relapse within 1-2 weeks after discontinuing the initial rx?
Re-infection or failure to eradicate organism, spores can recreate disease
What is the treatment for a relapse of PMC?
Retreat with same therapy
Multiple relapses → 7 week tapering regimen of vancomycin & concomitant probiotics
What condition?
common cause of illness
transmission: person to person, fecal oral route, or water or food borne outbreaks
rotavirus or norovirus
Viral gastroenteritis
Which virus is associated with viral gastroenteritis in infants and young children?
Rotaviruses
Which virus is associated with viral gastroenteritis in adults and older children?
Noroviruses
Rotavirus or norovirus (Norwalk)?
outbreaks typically in winter months
infants & children 6-24 mos
24-72 hr incubation
abrupt onset of vomiting, watery diarrhea, low grade fever, ± abd pain
Rotavirus
Rotavirus or norovirus (Norwalk)?
family and community wide outbreaks, esp on cruiseships
school age children, family contacts, and adults
1-3 day incubation
abrupt onset of diarrhea, N, V, mild abd cramps
Norovirus (Norwalk)
What is the MC protozoan GI infx in the US?
Giardia lamblia
What pathogen?
prevalent in areas with poor water treatment
contamination of water supplies with cyst-infested feces from humans or animals
beavers, muskrats, dogs, cats, raccoons, deer
Giardia lamblia
What type of infection occurs in these areas?
mountainous west → backpackers diarrhea
from drinking fecally contaminated water from mountain streams
former Soviet Union - Armenia, Georgia, Ukraine, Russia (esp st petersburg)
Protozoal infx
What condition?
1-3 week incubation
half of pts are asx
sx: pale, explosive diarrhea w/ cysts or trophozoites found in stool
Treat empirically if high suspicion + treat close contacts + report to board of health
Protozoal gastroenteritis
What is the treatment for protozoal gastroenteritis?
Tinidazone (TOC) or metro
What are supportive treatment options for GI infectious diseases?
Bowel rest, hydration w/ clear fluids, antiemetics, BRAT diet (bananas, white rice, apple sauce, tea/toast)
What should clear fluids used to hydrate patients with infectious disease contain?
Glucose, sodium, K, Cl, bicarb (ex- pedialyte, gatorade, or IV lactate ringers if severe)
What antiemetics can be used in the supportive treatment of GI infectious diseases?
PO or suppository phenergan, promethazine, zofran
What should be avoided in patients with GI infectious diseases?
Lactose products, fried or fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, whole wheat or high fiber products