AP BIO CELLULAR RESPONSE LOCK IN
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Animal cells communicate by
Direct contact (gap junctions)
Secreting local regulators (growth factors, neurotransmitters)
long distance (hormones)
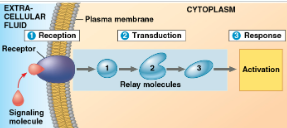
3 stages of cell signaling
reception
transduction
response
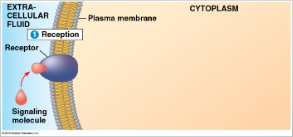
reception
detection of signal molecule (ligan) coming from outside the cell
transduction
convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response
response
specific cellular response to the signal molecule
Reception (image)
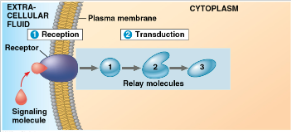
Transduction (image)
Response (image)
Reception: Binding between ___ ___ (ligand) + ____ is ____ _____
signal molecule; receptor; highly specific
Types of receptors
plasma membrane receptor (water soluble ligands)
Intracellular receptors (cytoplasm, nucleus)
- small or hydrophobic ligan molecules
- ex: testosterone or nitric oxygen
Reception steps
Ligand binds to receptor protein → protein changes shape → initiates transduction signal
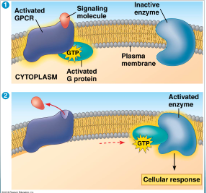
G-Protein-Coupled Receptor (image)
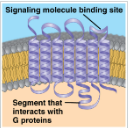
G-Protein Coupled Receptor (image #2)
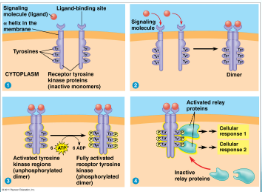
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (image)
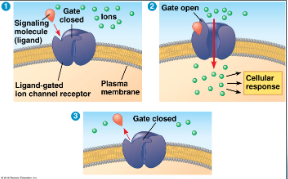
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel (image)
G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
7 transmembrane segments in membrane. G protein + GTP activates enzyme → cell response
Tyrosine Kinase
Attaches (P) to tyrosine. activate multiple cellular responses at once.
Plasma Membrane Receptors
Signal on receptor changes shape. Regulate flow of specific ions (Ca2+, Na+)
Transduction
cascades
protein kinase
phosphorylation cascade
Cascades
cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors → target molecules
Protein Kinase
enzyme that phosphorylates and activates proteins at next level
Phosphorylation cascade
enhance and amplify signal
Second messengers
small, nonprotein molecules/ions that can relay signal inside cell
ex: cyclic AMP (cAMP), calcium ions (CA2+), inositol triphosphate (IP3)
cAMP
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
GPCR → adenylyl cyclase (convert ATP → cAMP → activate protein kinase A)
Response
regulate protein synthesis by turning on/off genes in nucleus (gene expression)
regulate activity of proteins in cytoplasm
examples of signal transduction pathway problems/defects
diabetes
cholera
autoimmune disease
cancer
neurotoxins, poisons, pesticides
drugs (anesthetics, blood pressure meds)
Cholera
disease acquired by drinking contaminated water )human feces)
bacteria: vibrio cholerae
bacteria colonizes lining of small intestine and produces toxin
toxin modifies g protein
g protein stuck in active form
diarrhea
Apoptosis
cell suicide
triggered by signals that activate cascade of suicide proteins (caspase)
protects neighboring cells from damage
animal development and maintenance
may be involved in diseases like alzheimer’s
Cell cycle
life of a cell from its formation until it divides into two cells
Functions of cell division
reproduction, growth, and tissue repair
Genome
all of a cell’s genetic info (DNA)
prokaryote
single, circular chromosome
Eukaryote
more than one linear chromosomes
Human chromosome #
46
each chromosome must be ____ before cell division
duplicated (replicated)
Duplicated chromosomes
2 sister chromatids attached by a centromere
somatic cells
body cells
diploid (2n): 2 of each type of chromosome
divide by mitosis
Humans: 2n=46
Gametes
sex cells (sperm/egg)
Haploid (n): 1 of each type of chromosome
formed in meiosis
humans: n=23
the ____ phase alternates with ____
mitotic; interphase
cell cycle phsaes
G1 → S → G2 → mitosis → cytokinesis
Interphase makes up __% of the cell cycle
90
G1 Phase
cell grows and carries out normal functions
S Phase
duplicates chromosomes (DNA replication)
G2 phase
prepares for cell division, organelles copy
M phase (mitotic)
Mitosis + cytokinesis
Mitosis
nucleus divides
cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides
Mitosis phases
Prophase → metaphase → anaphase → telophase
prophase
the nuclear envelope begins to disappear, DNA coils into visible chromosomes, and fibers begin to move double chromosomes towards the center.
metaphase
Fibers align double chromosomes across the center of the cell
anaphase
Fibers separate double chromosomes into single chromosomes (chromatids). chromosomes separate at the centromere. migrate to opposite ends.
telophase
The nuclear envelope reappears and establishes two separate nuclei. each nucleus contains a complete genome. chromosomes will begin to uncoil.
Prophase (image)
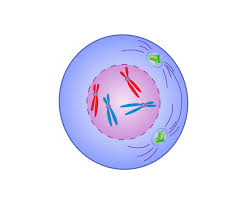
metaphase (image)
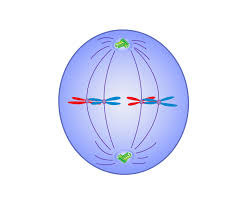
Anaphase (image)
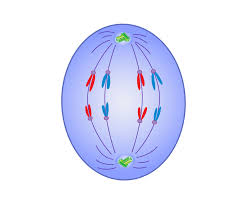
Telophase and Cytokinesis
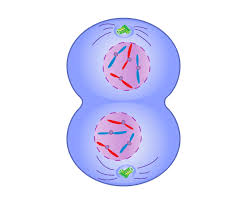
Cytokinesis
cytoplasm of cell divided
Animal cells cytokinesis
pinch at the cleavage furrow
Plant cells cytokinesis
cell plate forms and cuts cells apart
chromosomes are walked to poles by ____ during anaphase
motor proteins
Kinetochore microtubules shorten at ends as they ______
depolymerize
bacteria cells divide by ________
binary fission
other types of asexual reproduction used by other organisms
budding - yeast
sporation - mushrooms
regeneration - lizard, starfish
tubers - potatoes
runners - strawberries
bulb - onions or tulips
grafting - skin
cell cycle checkpoint
control point where stop/go signals regulate the cell cycle
G1 checkpoint
most important
controlled by cell size, growth size, growth factors, environment
go → completes whole cell cycle
stop → cell enters nondividing state (G0 phase)
G2 checkpoint
controlled by DNA replication completion, DNA mutations, cell size
M-spindle (metaphase) checkpoint
check spindle fiber (microtubules) attachment to chromosomes at kinetochores (anchor sites)
kinetochore
proteins associated with DNA at centromere
Kinases
(cyclin-dependent kinase, cdk), protein enzyme controls cell cycle; active when connected to cyclin
Cyclins
proteins which attach to kinases to activate them; levels fluctuate in the cell cycle
MPF
maturation-promoting factor
specific cyclin-Cdk complex which allows cells to pass G2 and go to M phase
anchorage dependence
cells must be attached to another cell or ECM to divide
density dependent inhibition
crowded cells normally to stop dividing; cell-surface protein binds to adjoining cell to inhibit growth
growth factor
proteins released by other cells to stimulate cell division
Cancer
disorder in which cells lose the ability to control growth by not responding to regulation.
multistep process of about 5-7 genetic changes for a cell to transform
what regulatory factors are affected by cancer
loses anchorage dependency and density-dependency regulation
transformation
process that converts a normal cell to a cancer cell
tumors
mass of abnormal cells
benign tumor
lump of cells remain at original site
malignant tumor
invasive - impairs functions of I+ organs (Called cancer)
metastasis
cells separate from tumor and travel to other parts of body
protein phosphates
remove phosphate groups from specific proteins to stop the signal or reset the pathway
Flow of ions into a cell
Ligand-gated ion channel receptor remains closed util bound by receptor. closed to stop ions from going in when they do not need to
the ligan-gated ion channel opens after being bounds to, specific ions can flow through and change the concentration
ligan dissociates from the receptor, causing the channel to close again, ending the cellular response
nerve cells are also called ___
neurons
parts of a neuron
dendrite, cell body, nucleus, schwann cell, myelin sheath, node of ranvier, axon terminal, axon.
endocrine distruptor
a natural or man-made chemical that mimics or interferes with the endocrine system
Multiple Sclerosis
a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord by damaging the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibers and disruption communication between the brain and body. T cells and B cells damage the nervous system.
example of an endocrine disruptor
phytostrogens, soy food
DDT
a synthetic insecticide that is largely outlawed because causes deformities in animals and hormonal signaling and reproduction.
Heroin
located on neurons of the brain which affects dopamine, the pleasure system, and endorphins. a part of the morphine group.
two hormones that regulate blood sugar
insulin and glucagon
what endocrine gland produces the glucose controlling hormones
the pancreas
when blood sugar is low, what hormone is secreted
glucagon
when blood sugar is high, what hormone is secreted
insulin
Type 1 diabetes
lowers blood sugar levels
Type 2 diabetes
cells struggle to use insulin
feedback mechanisms
used by organisms to maintain their internal environments and respond to environmental changes. increase or decrease cellular response to a certain event.
homeostasis
the maintenance of a stable internal environment
two examples of homeostasis
blood temperature and pH of blood
negative feedback
homeostasis is maintained by regulating a physiological process and returning a system back to its target set point.