Gross Anatomy 12: Respiratory System
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What layers make up the mucosa?
Epithelium, basal lamina, and lamina propria.
What is the function of the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
Warms, moistens, and filters air.
What structures help warm and moisten air?
Cavernous/erectile tissue and mucous and serous glands.
What structures help filter air?
Nose hairs, cilia, secretions, and alveolar macrophages.
What are general histologic features of the conducting portion?
Mucus and serous glands and ciliary movement.
What structures make up the extrapulmonary respiratory tract?
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and primary bronchi.
What structures make up the intrapulmonary respiratory tract?
Bronchial tree.
What histologic feature allows gaseous exchange?
Thin and highly permeable epithelium.
What is epithelium?
A covering or lining tissue.
What type of epithelium is respiratory epithelium?
Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium.
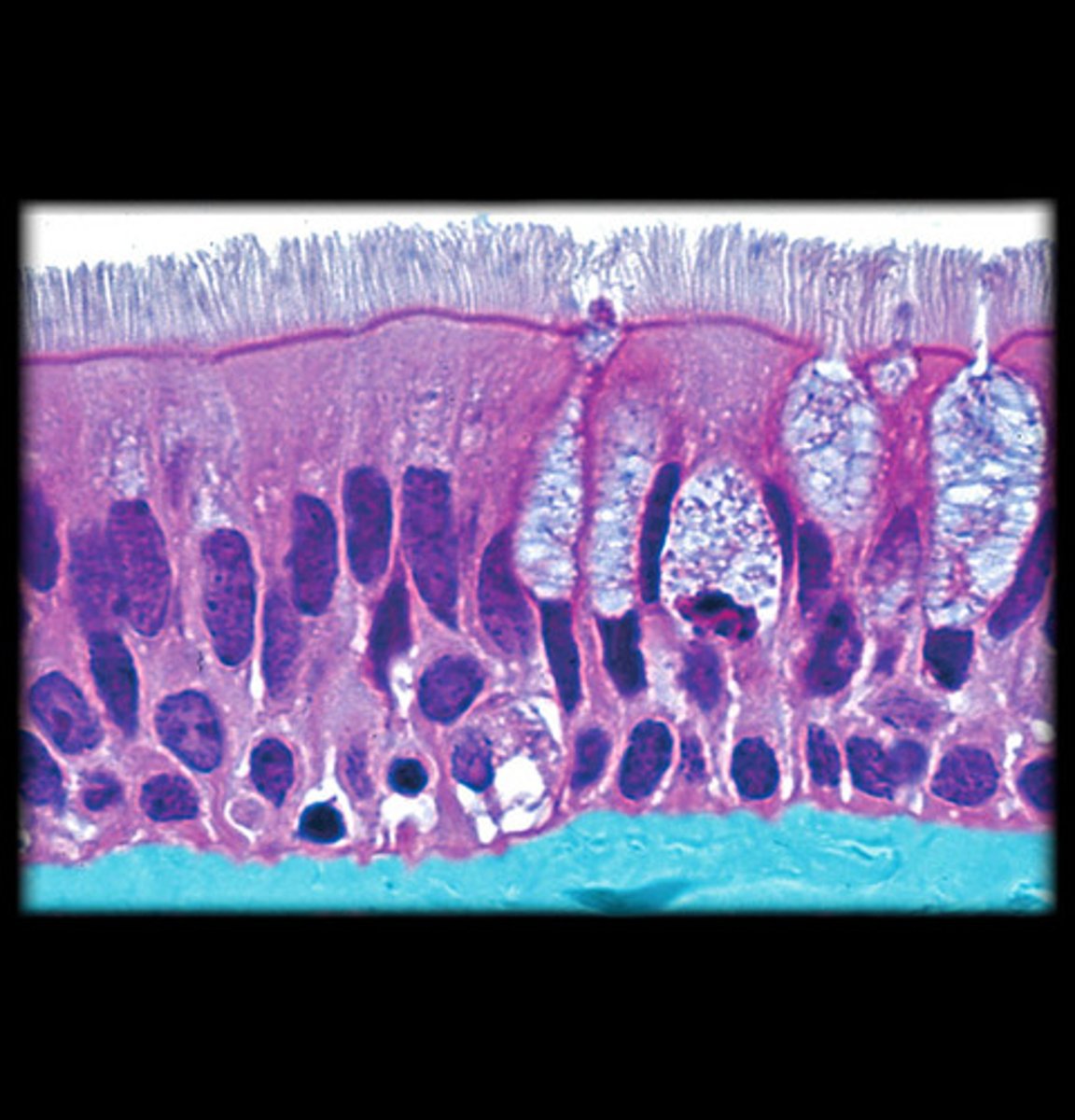
What cell types are found in respiratory epithelium?
Ciliated, goblet, brush, small granule, and basal cells.
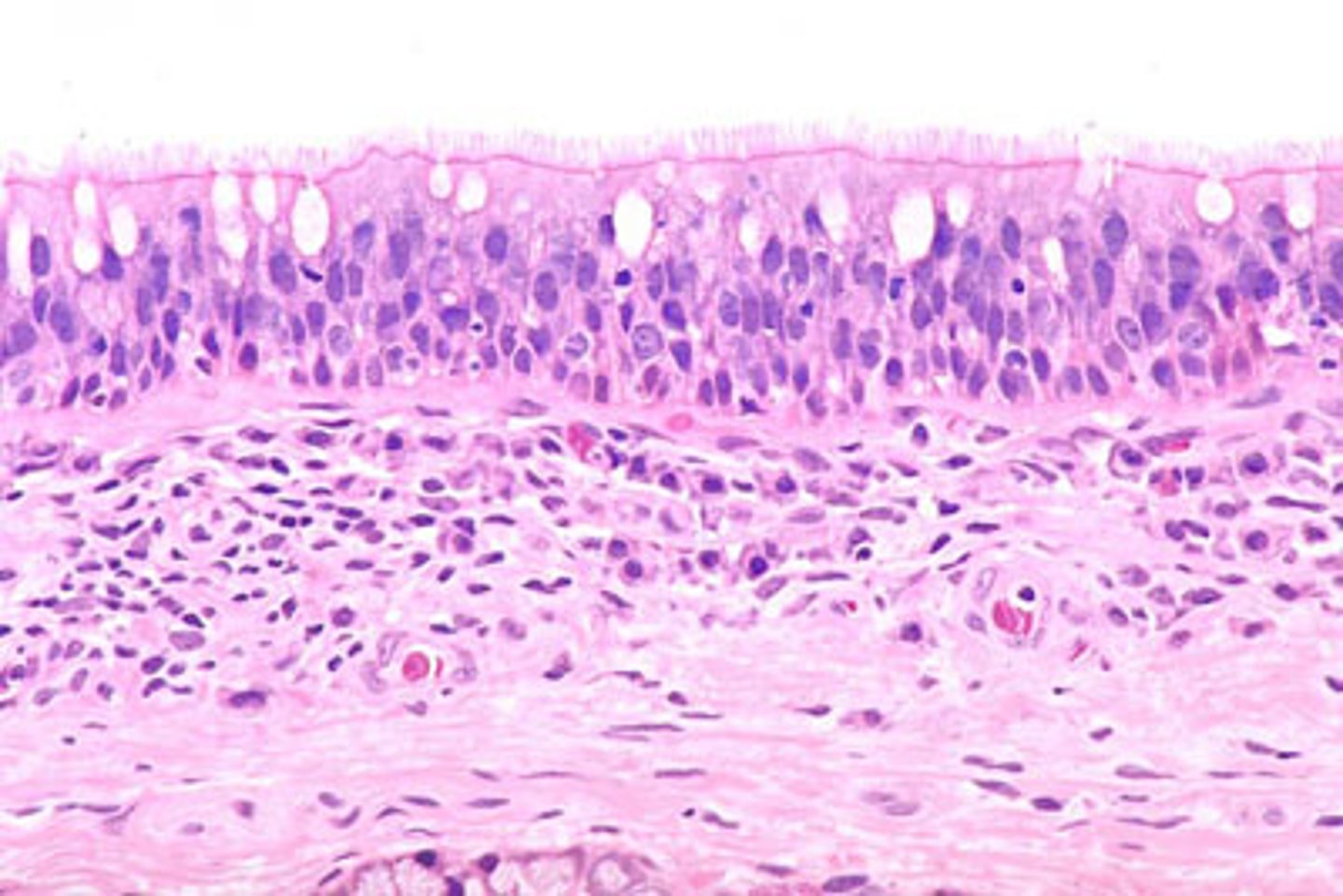
What is the function of ciliated cells?
Ciliary movement.
What is the function of goblet cells?
Mucus secretion.
What is found on the brush border?
microvilli
What is the function of small granule cells?
Secretory/endocrine.
What are basal cells?
stem cells for renewal of other cells
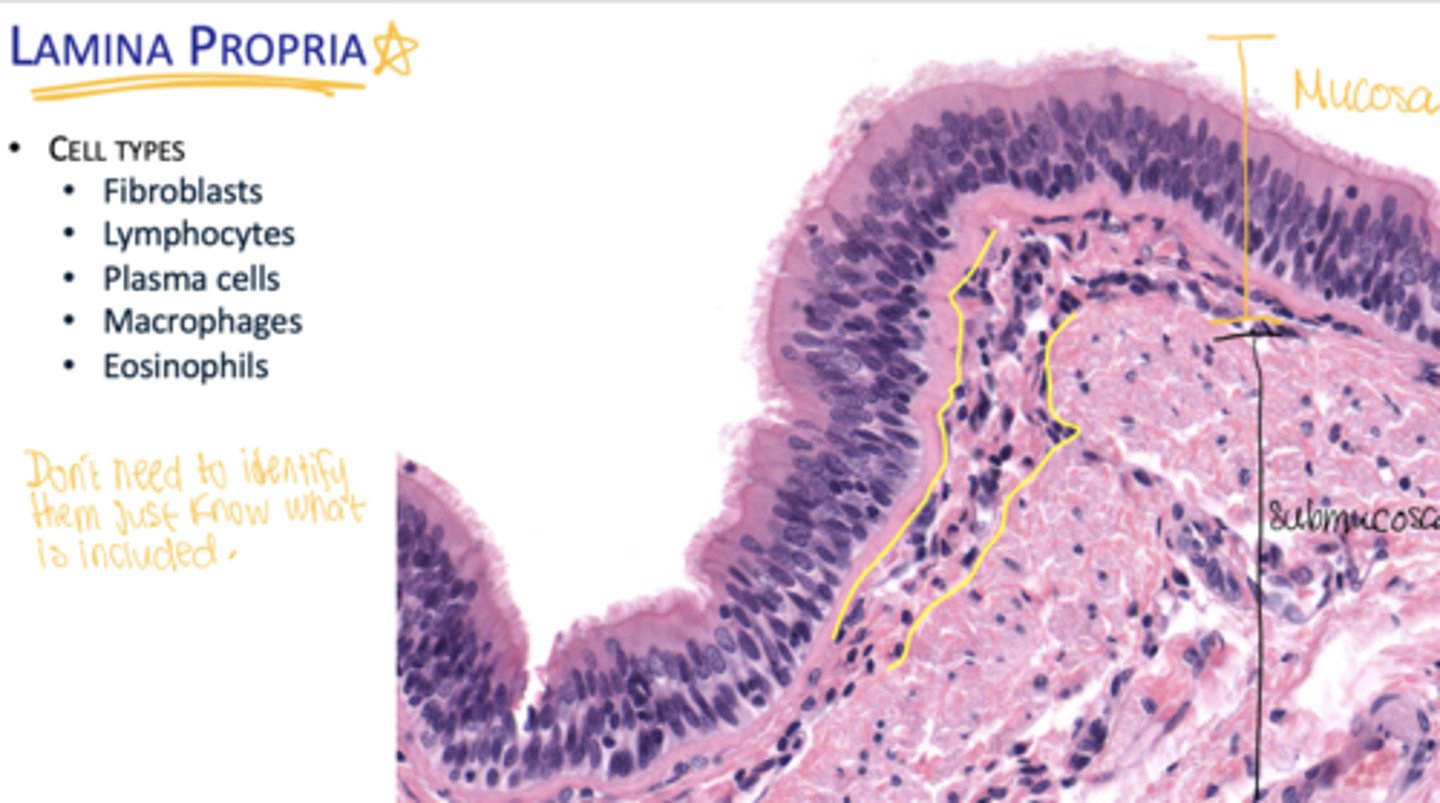
What cells are found in the lamina propria?
Fibroblasts, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, eosinophils.
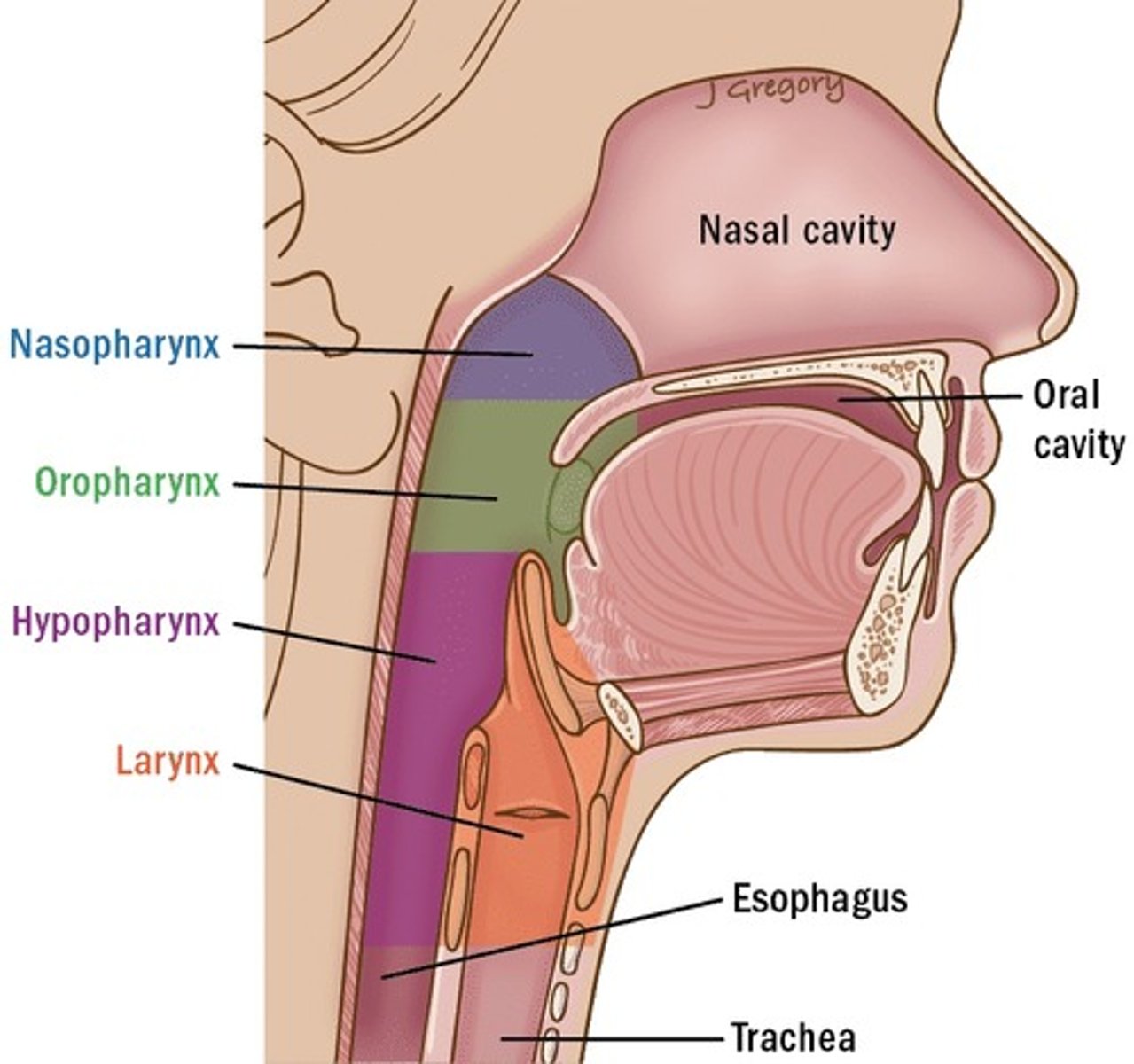
What is Waldeyer's ring?
A ring of lymphoid tissue surrounding openings into digestive and respiratory tracts.
What structures are included in Waldeyer's ring?
Pharyngeal (adenoid), tubal, palatine, lingual tonsils, and diffuse lymphatic tissue.
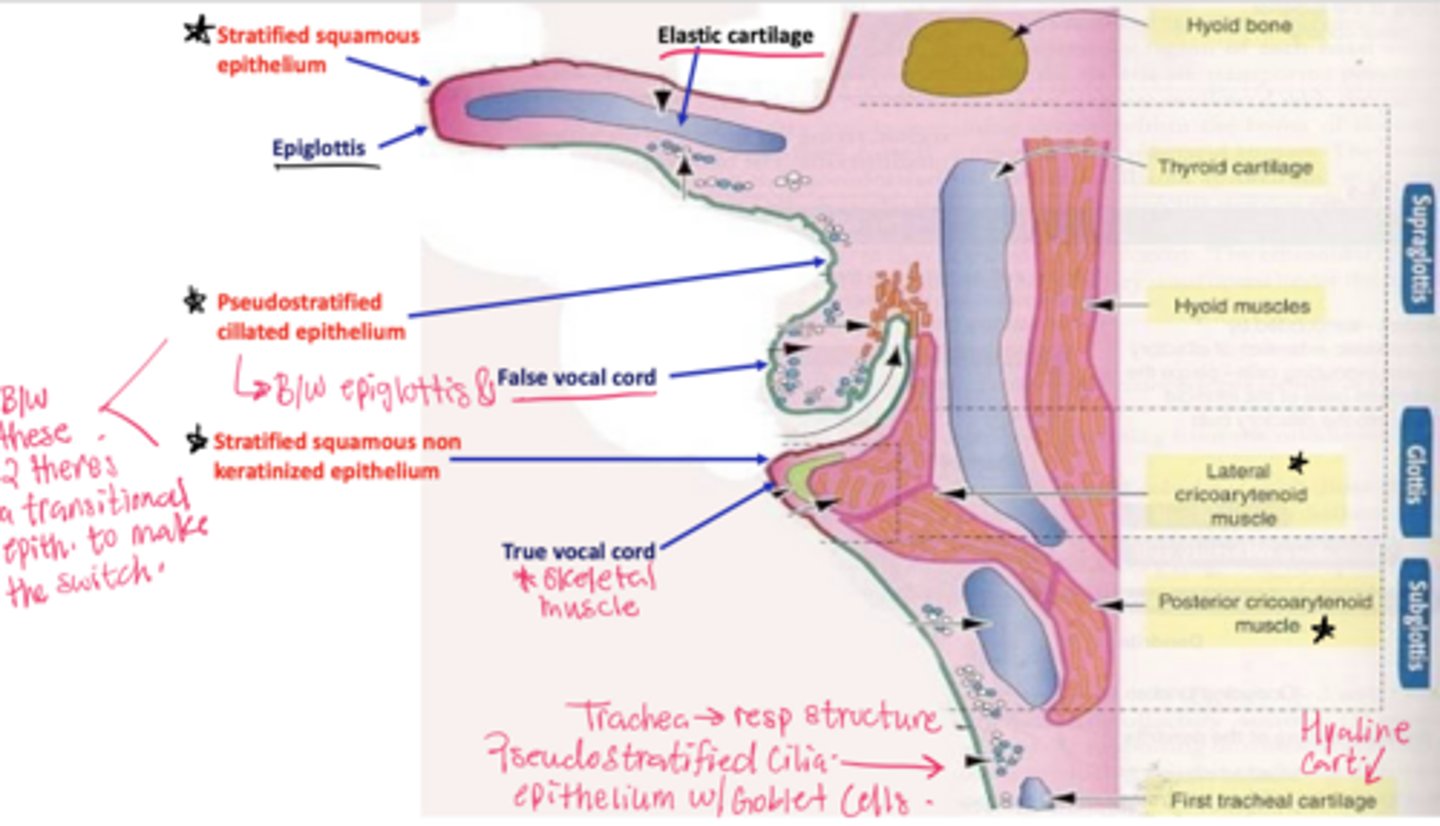
Where is the larynx located?
Between the oropharynx and trachea.
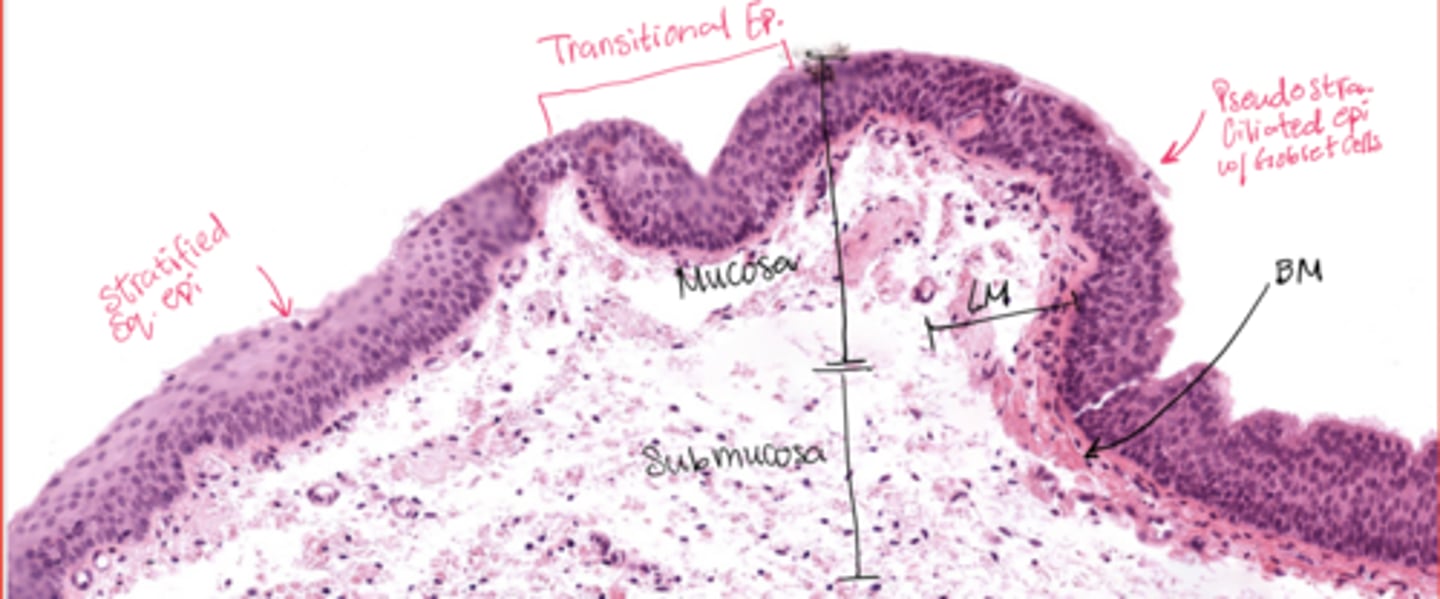
What epithelial transition occurs in the larynx?
Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium -> stratified squamous epithelium (image is at the vestibular folds)
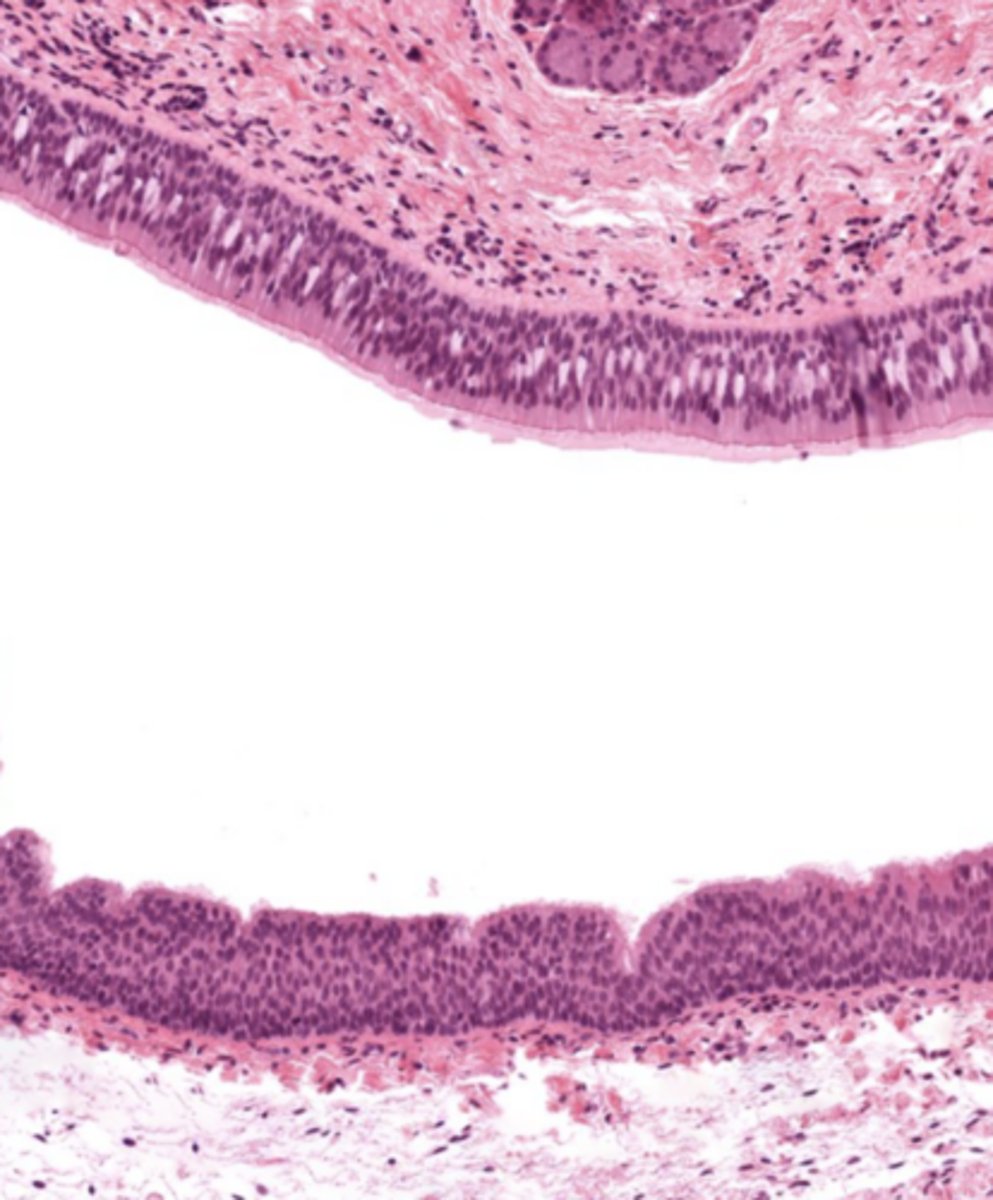
What tissue composes the vestibular folds?
Loose connective tissue with glands and lymphoid aggregations.
What epithelium covers vestibular folds?
Respiratory epithelium.
What muscle is found in the true vocal cords?
Vocalis muscle (skeletal muscle).
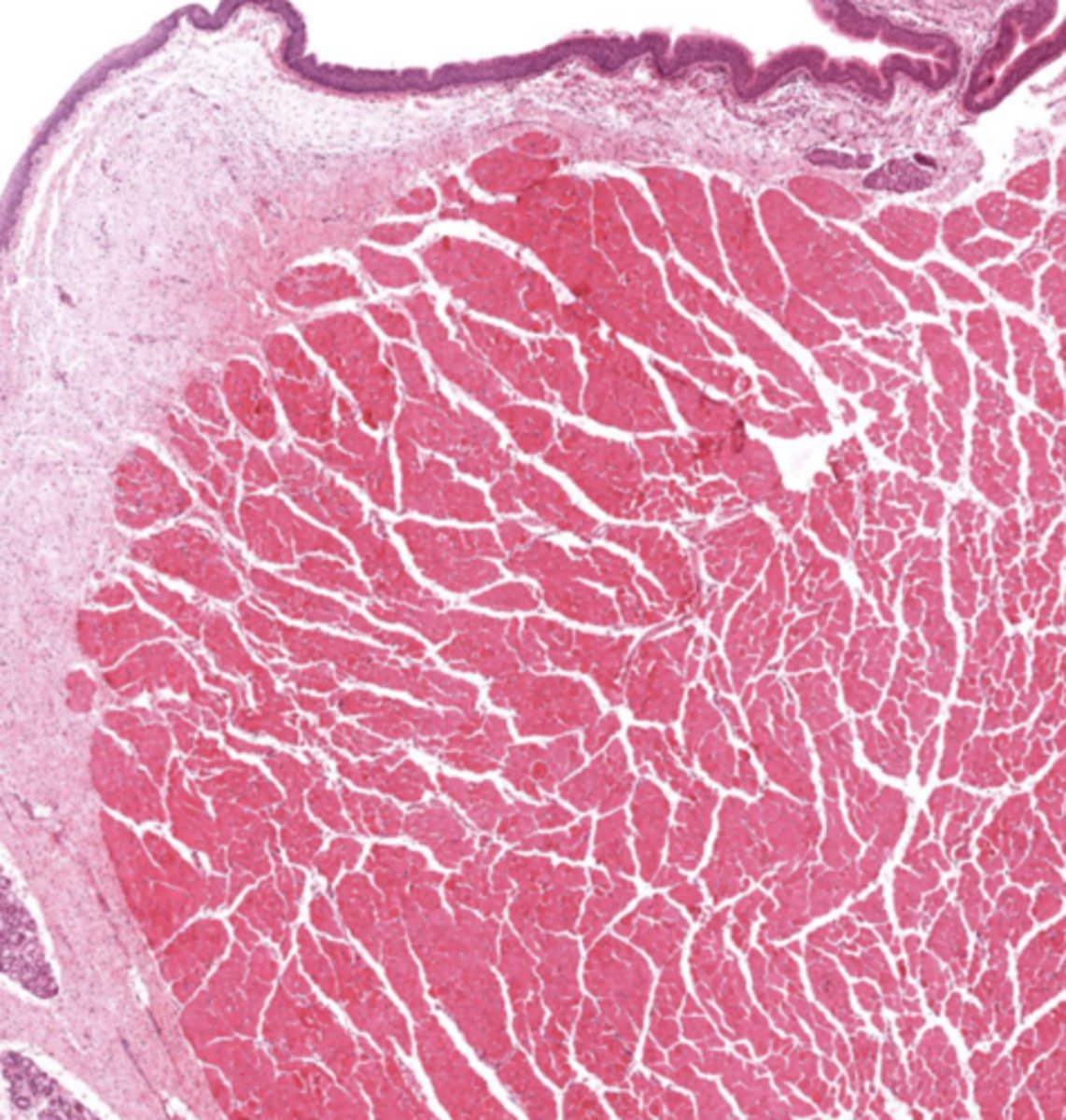
What forms the vocal ligament?
A band of elastic fibers.
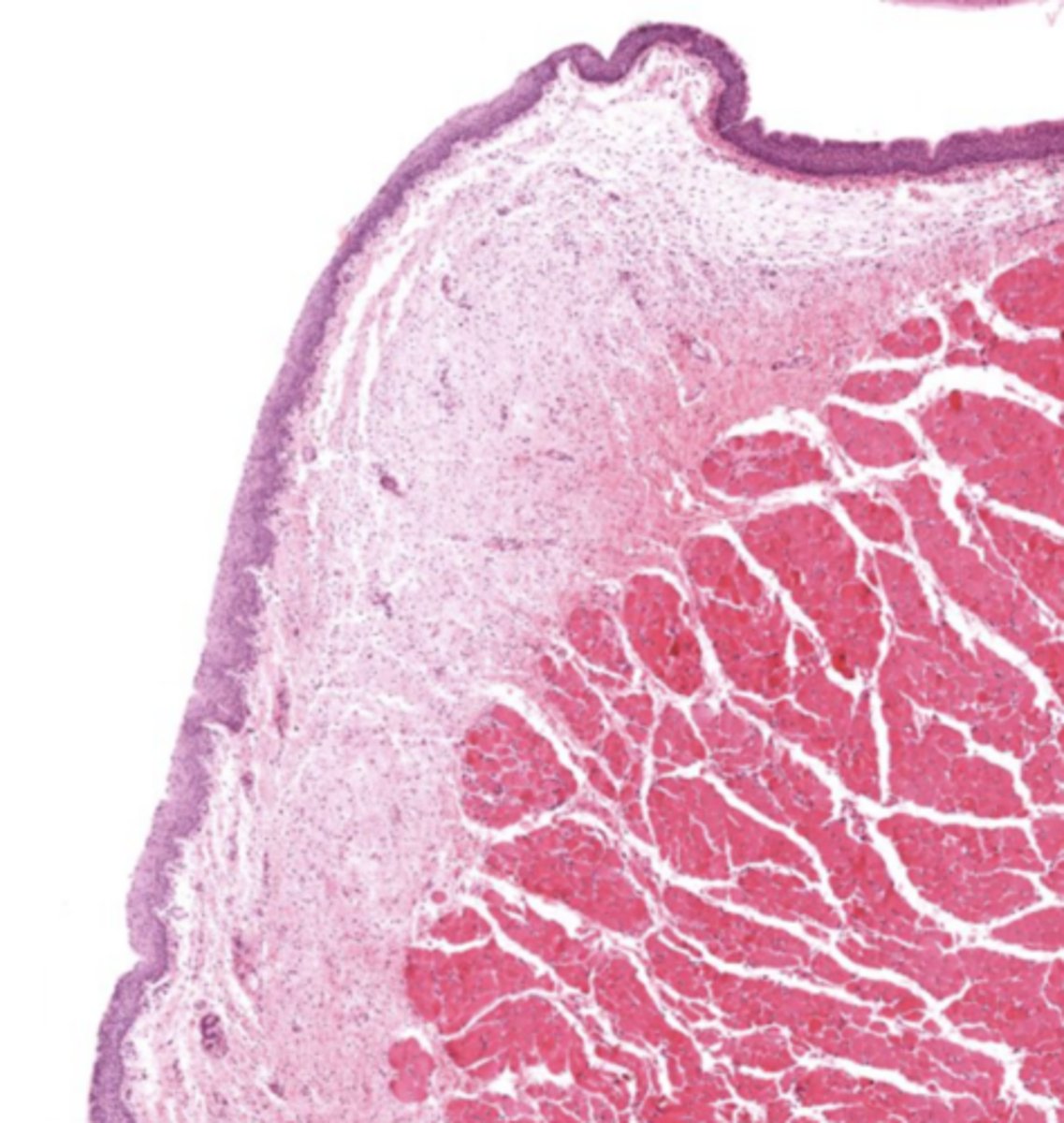
What epithelium lines the true vocal cords? and why is it this specific epithelium?
Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
so we can speak if we had any other lining the voice will be distorted
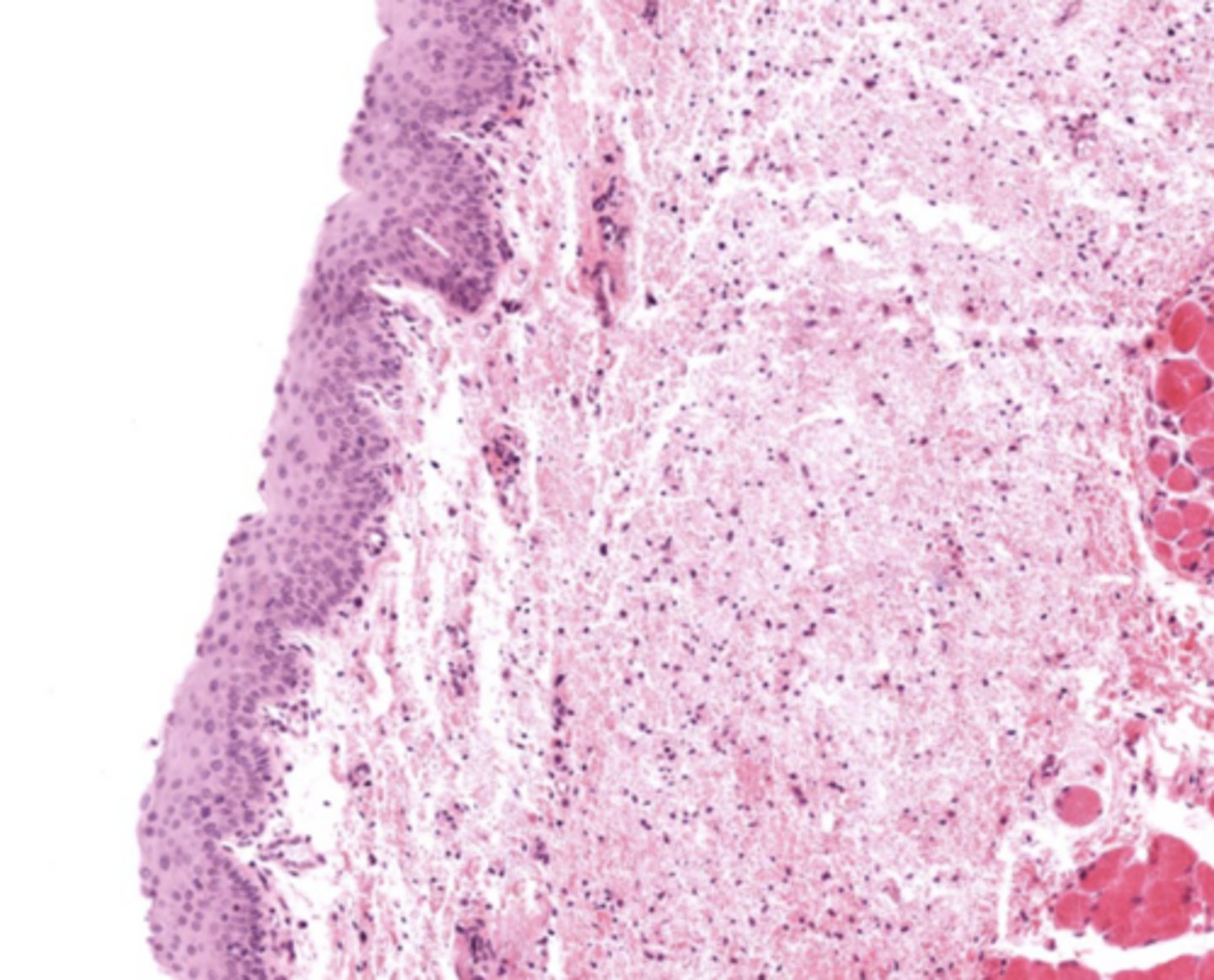
Why is Reinke's space clinically important?
No lymphatic vessels -> Reinke's edema.
Understand how the epithelium changes from epiglottis to treachea`
Epiglottis - stratified squamous epithelium with elastic cartilage
False vocal cords - pseudostra. cillated epithelium
True vocal cords - stratified sq. non keratinized epithelium with skeletal muscle
Trachea - pseudostra. ciliated epithelium with goblet cells (respiratory structure)
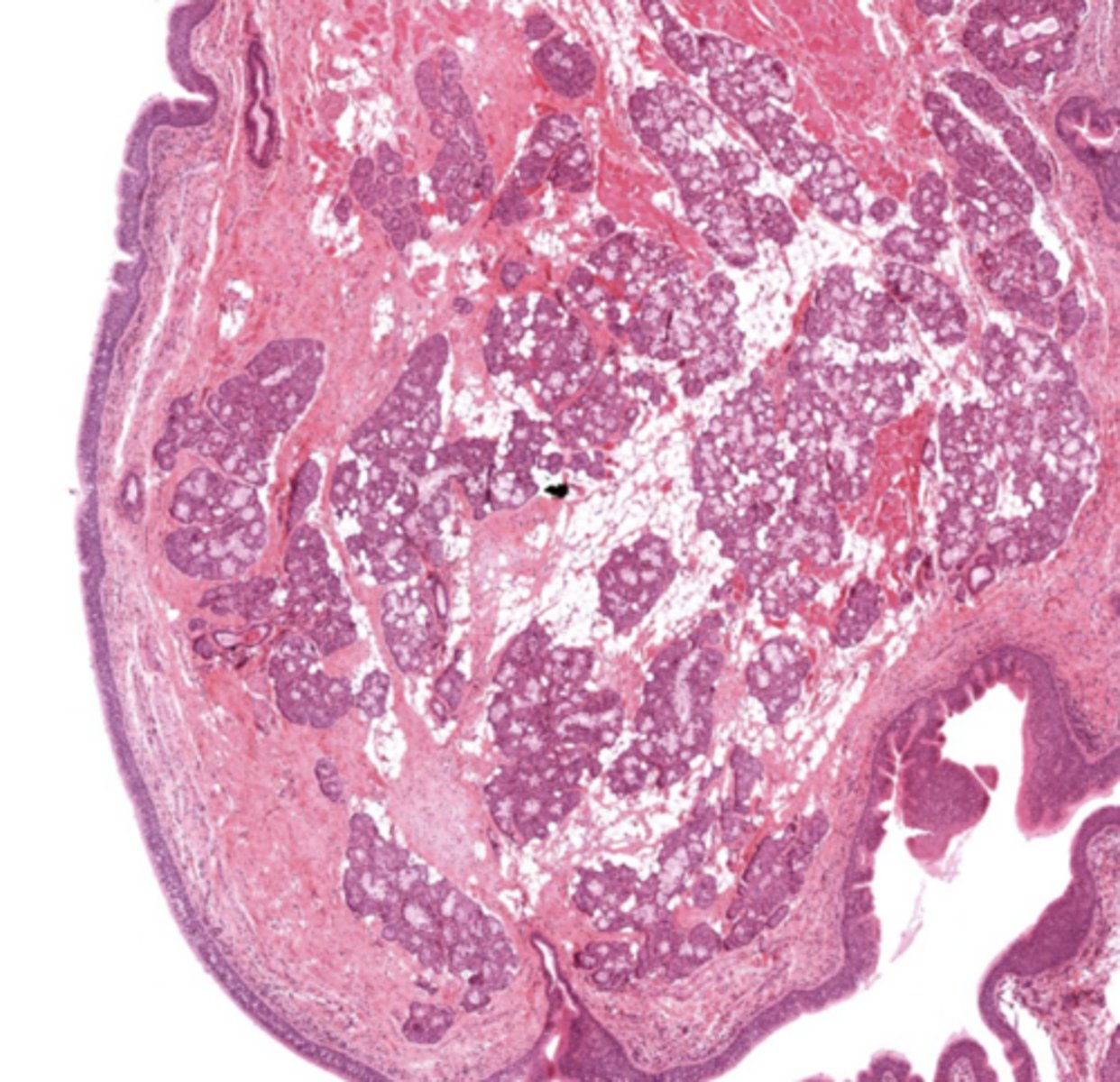
False cords of the larynx
Identify the image
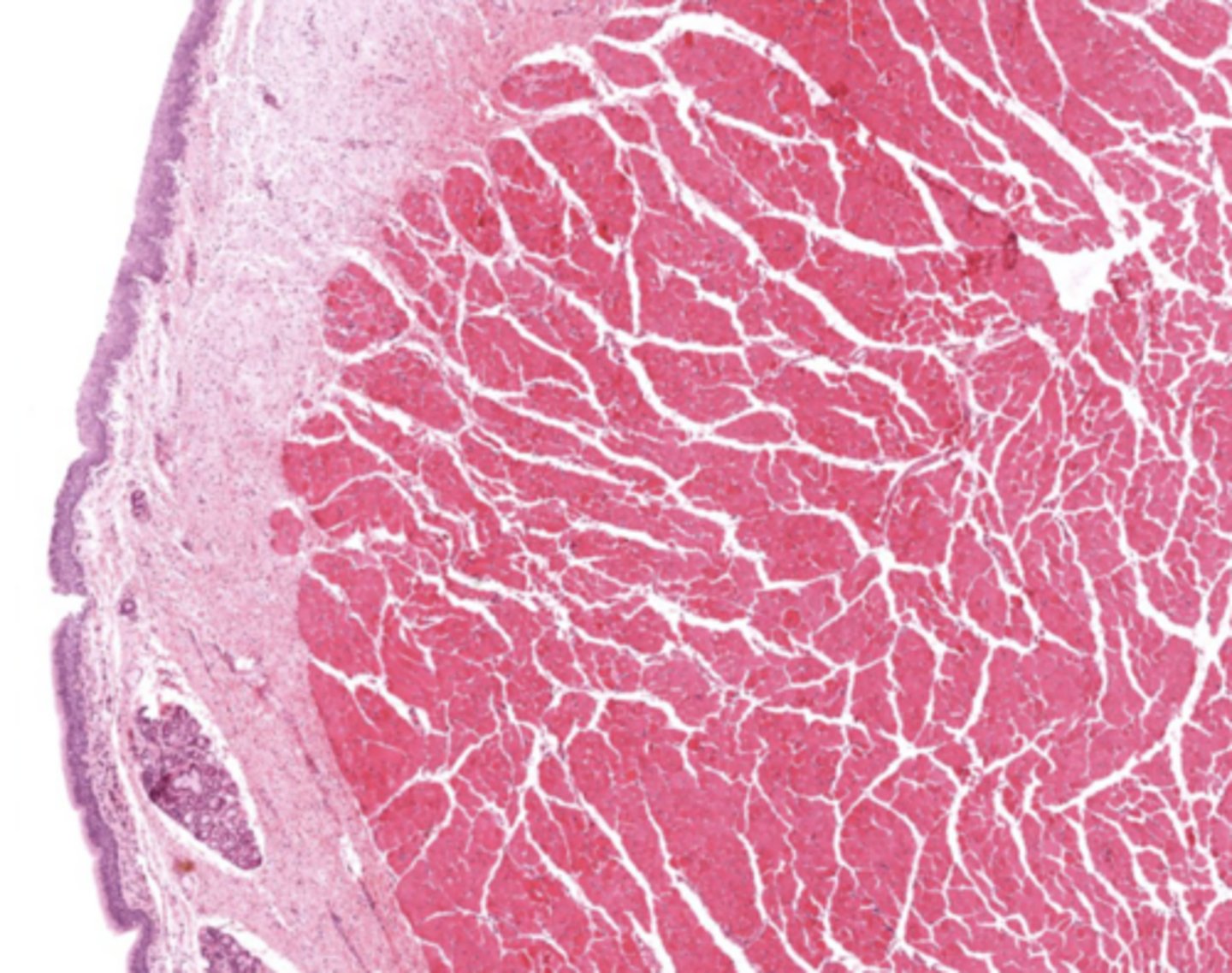
True cords of the larynx
Identify the image
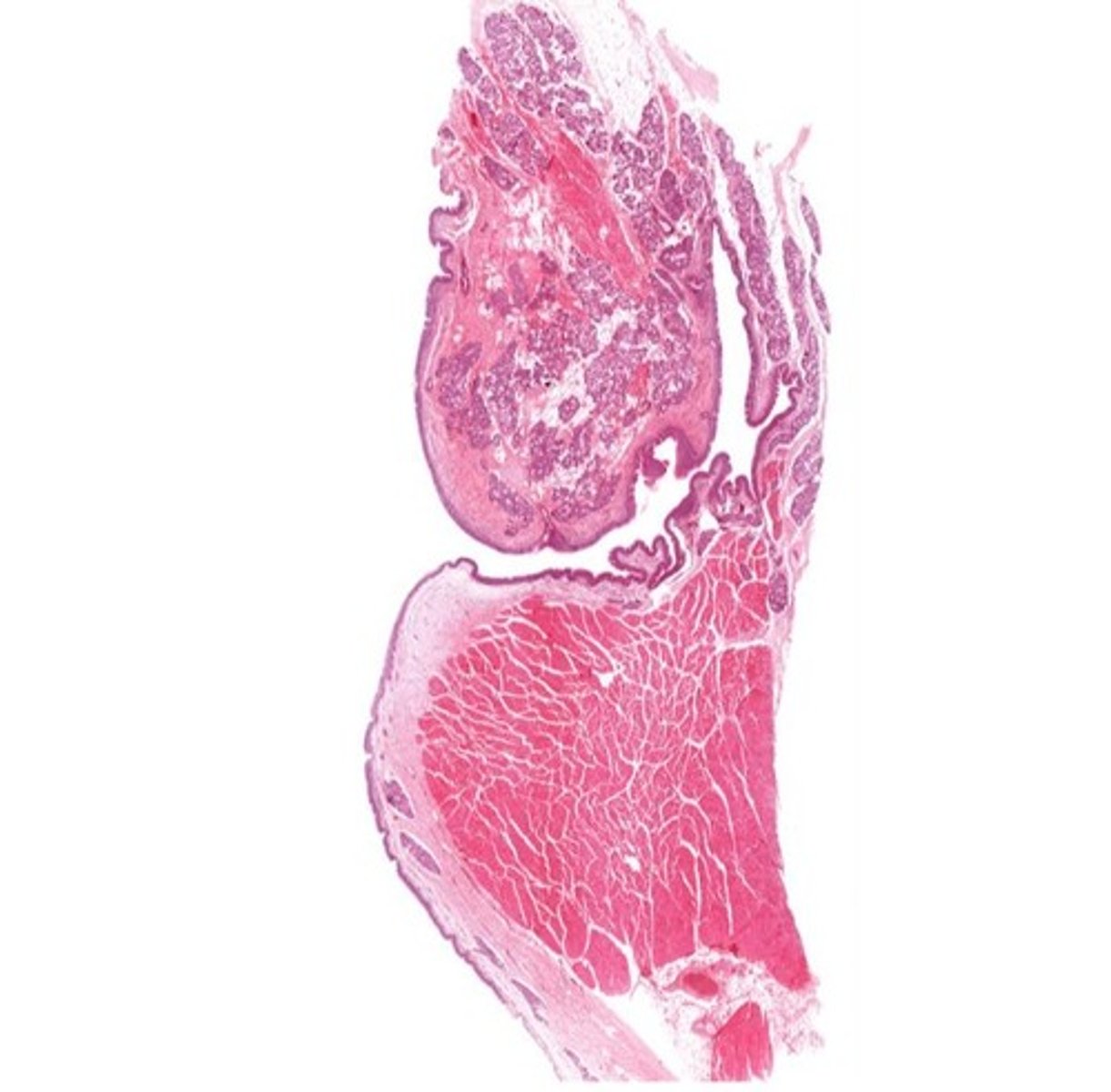
Larynx (voice box)
Identify the entire structure
Describe the transitional epithelium of the larynx
The main transition occurs near the vocal cords, separating the squamous epithelium of the true vocal cords from the respiratory epithelium pseudostratified ciliated
From what embryologic structure is the trachea derived?
Primordial foregut, its a 10 cm flexible tube which extends from the larynx to the bronchioles
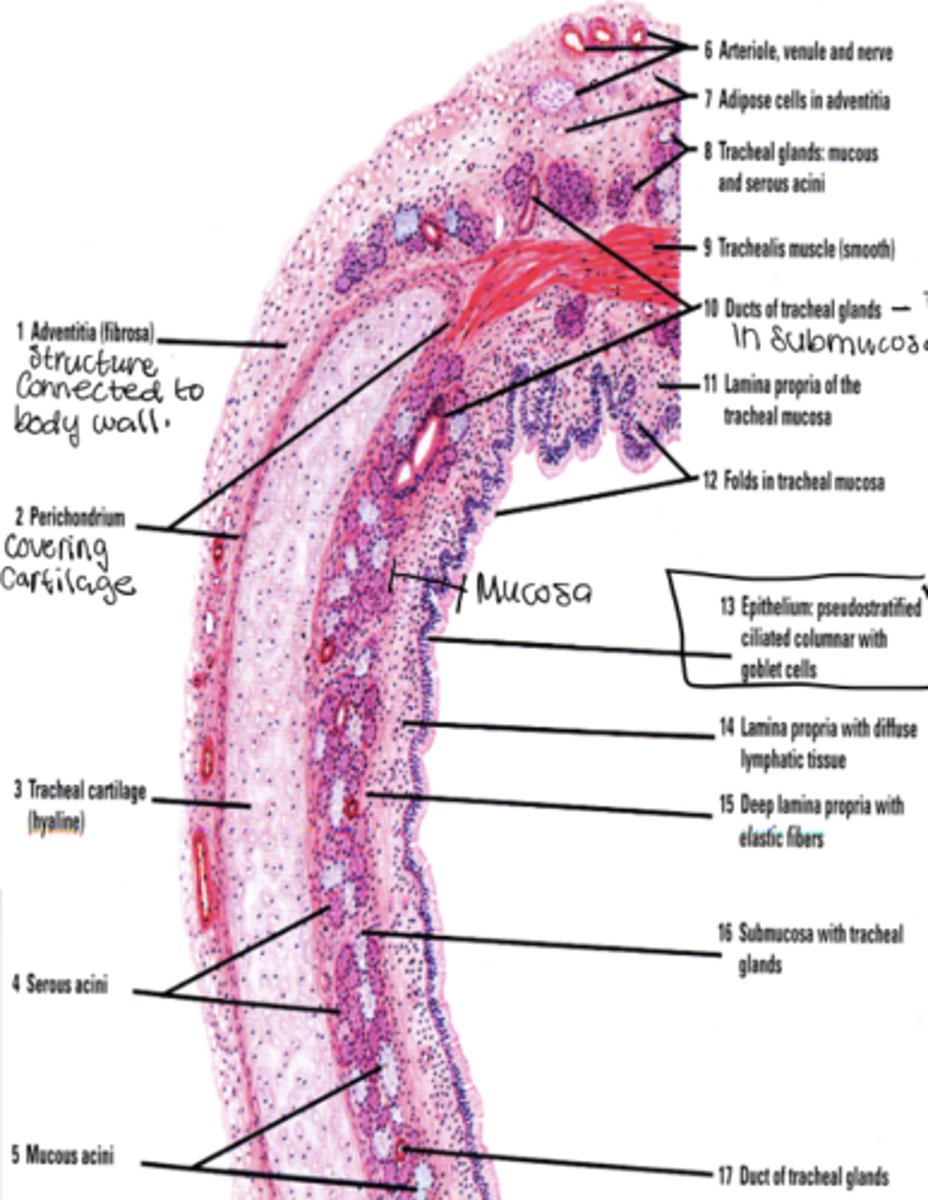
What layers make up the trachea?
Mucosa, submucosa, cartilaginous layer, adventitia.
What cell types are found in tracheal epithelium?
Goblet, basal, brush, small granule, and ciliated columnar cells.
What is another name for mucus cells?
Goblet cells.
Where are goblet cells located?
Between ciliated cells and extending from basal lamina to apex.
What happens to goblet cells in chronic inflammation?
They increase in number
What do brush cells synapse with?
Afferent nerve endings at their base
What type of regulation do small granule cells perform? What do they produce?
Paracrine regulation, diffuse neuroendocrine (Polypeptide hormones (calcitonin, serotonin, catecholamines)
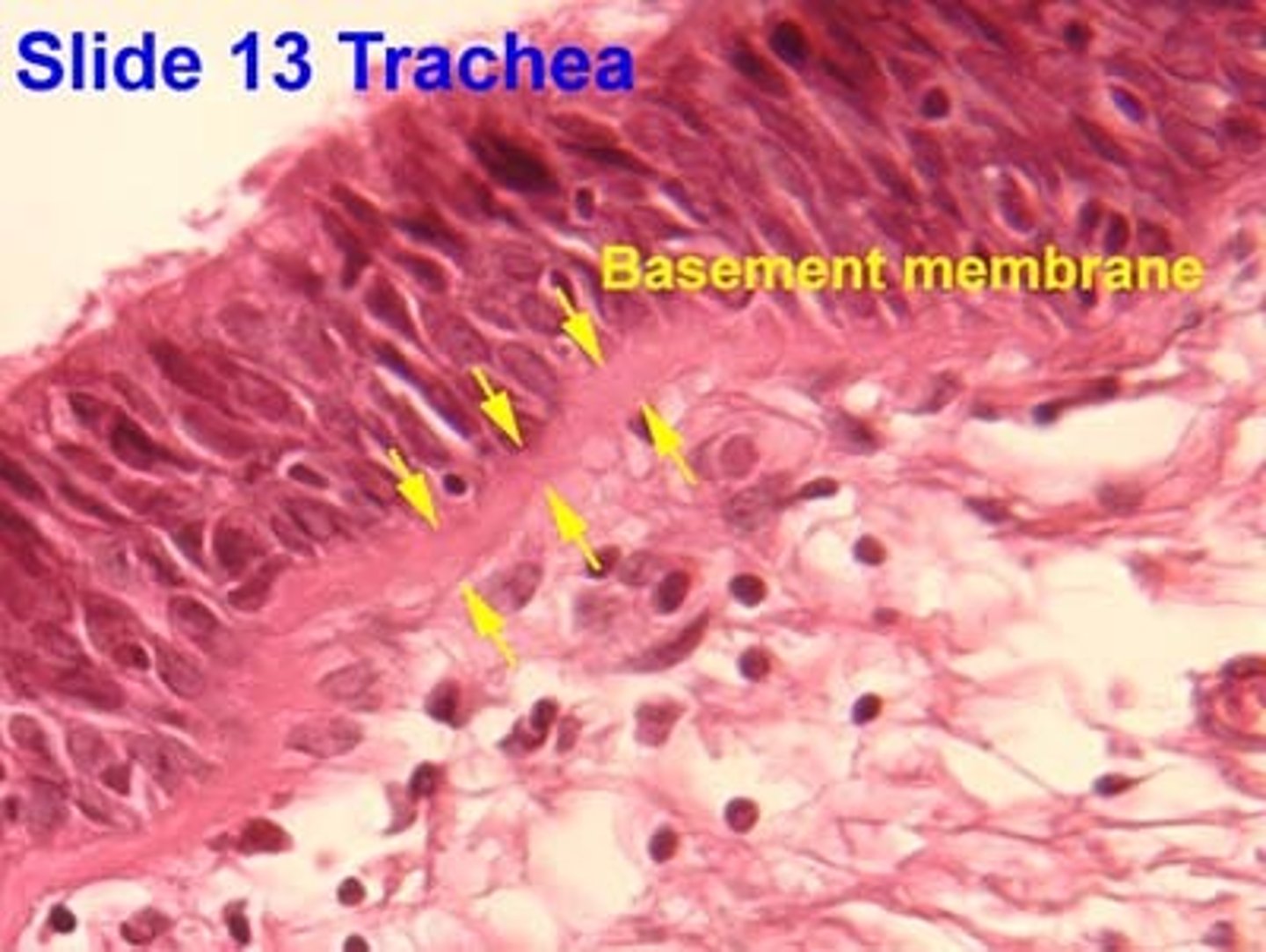
Why does the basement membrane appear thick and glossy?
Densely packed collagen fibers below basal lamina.
What is characteristic of the lamina propria in the trachea?
Very cellular loose CT with BALT.
What does the submucosa contain?
Dense irregular CT and glandular elements.
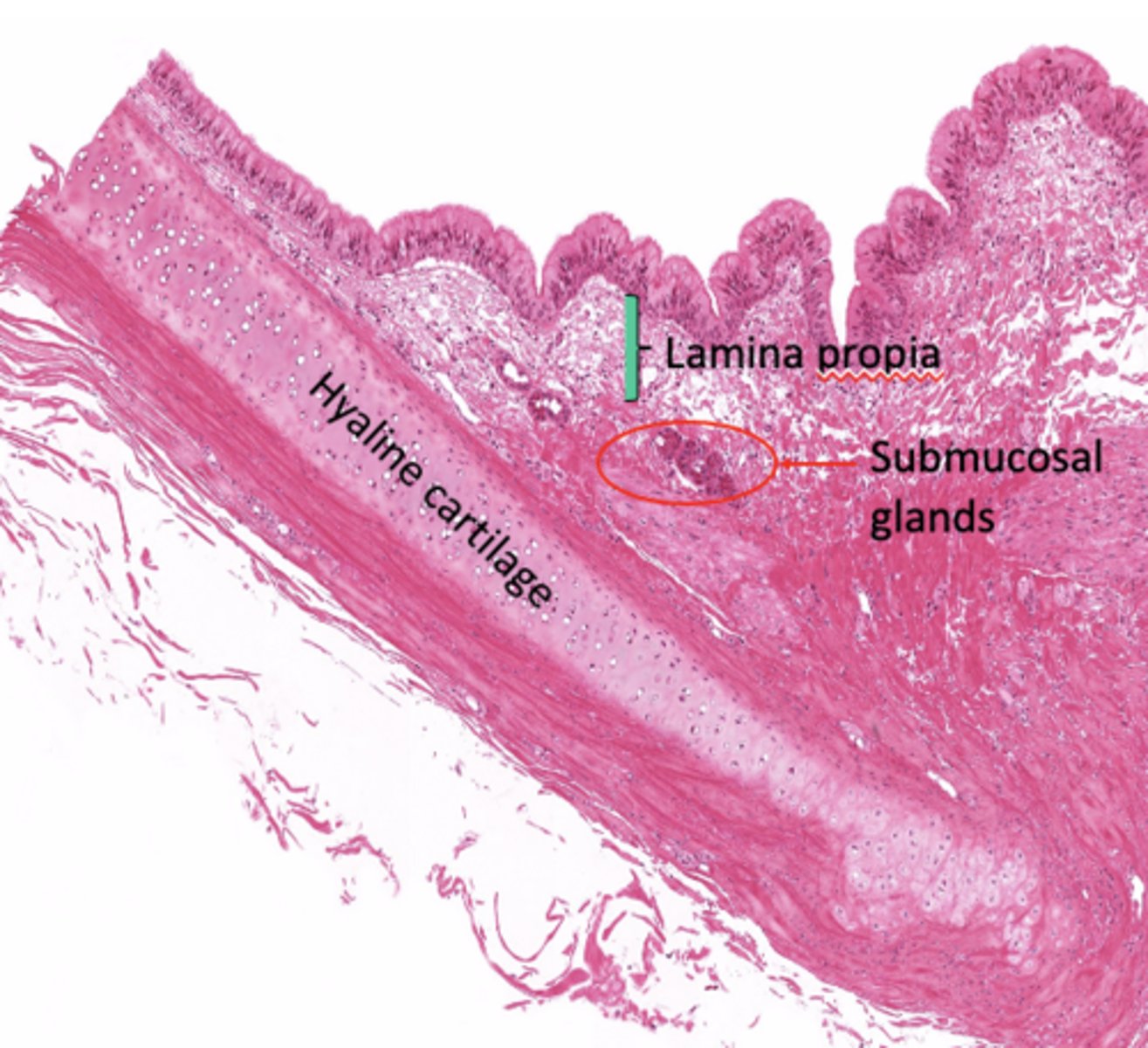
What type of cartilage supports the trachea?
Hyaline cartilage (16-20 C shaped rings)
Why are the cartilage rings open posteriorly?
To allow flexibility next to the esophagus.
What completes the posterior gap of the cartilage ring?
Fibroelastic membrane with trachealis muscle.
What is the adventitia?
Connective tissue layer deep to cartilage
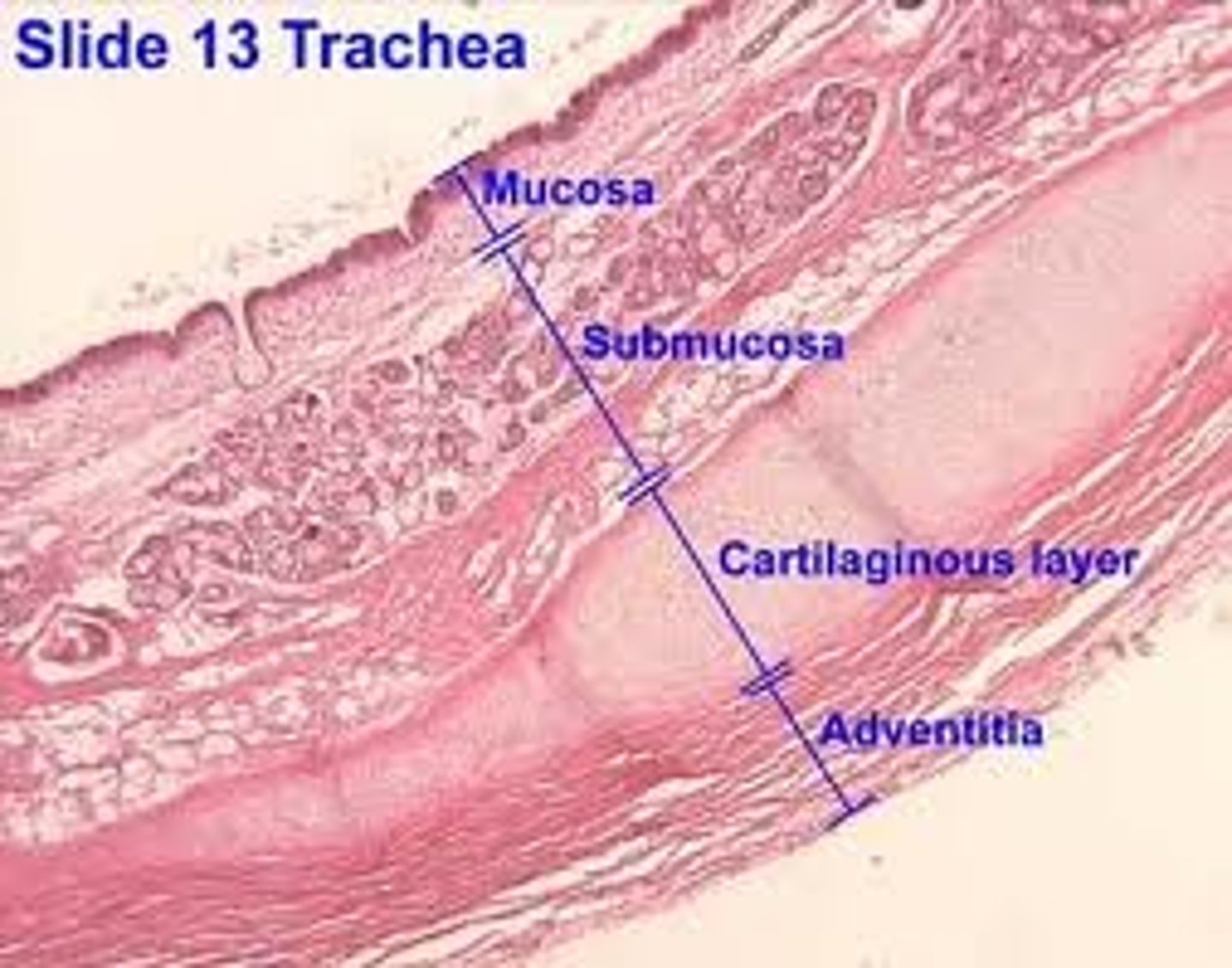
What does the adventitia contain?
Large blood vessels and lymphatic tissue.
How many primary bronchi are present?
Two
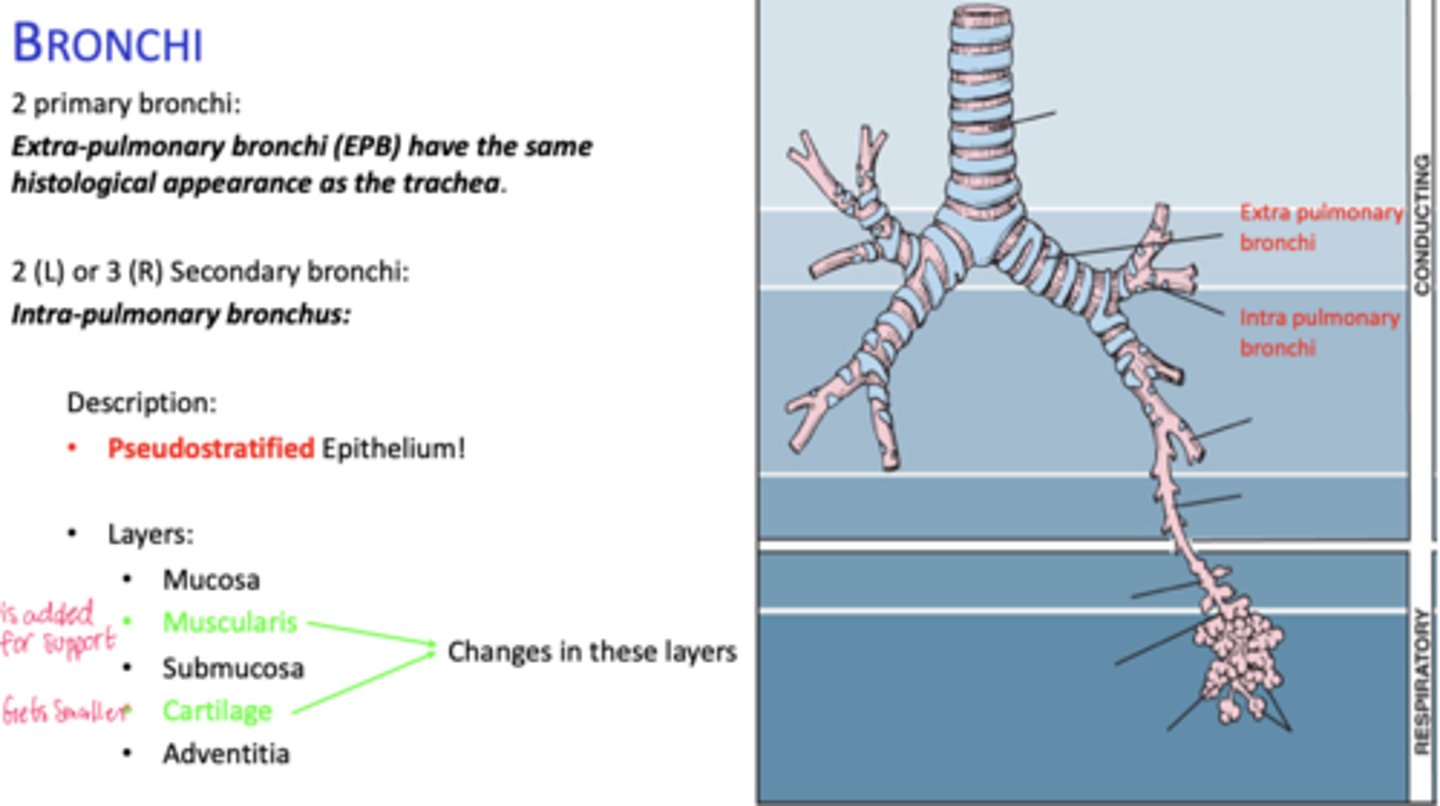
How do extrapulmonary bronchi compare histologically to the trachea?
Same histological appearance.
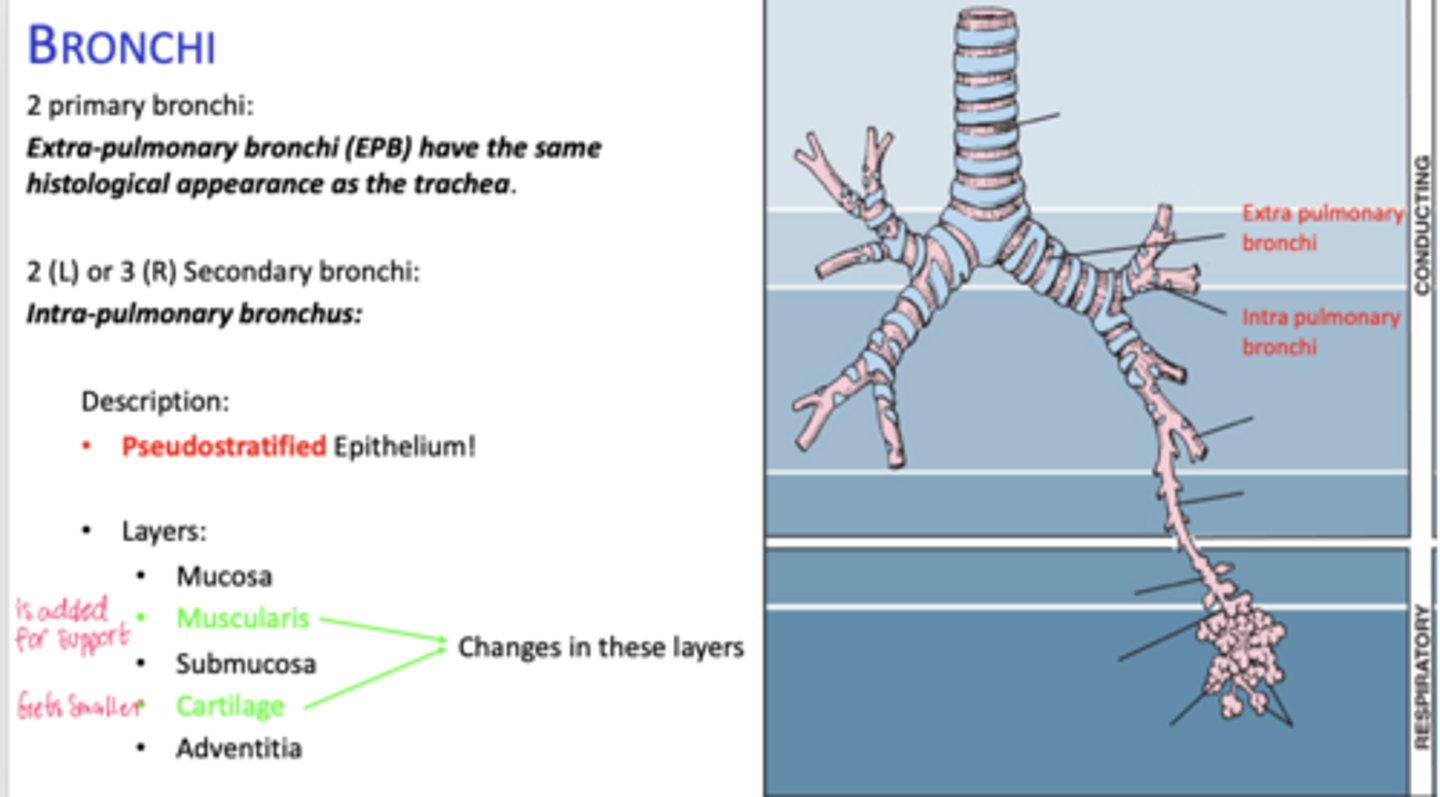
How many secondary bronchi are in the lungs?
Two on the left, three on the right (intrapolumanry bronchus)
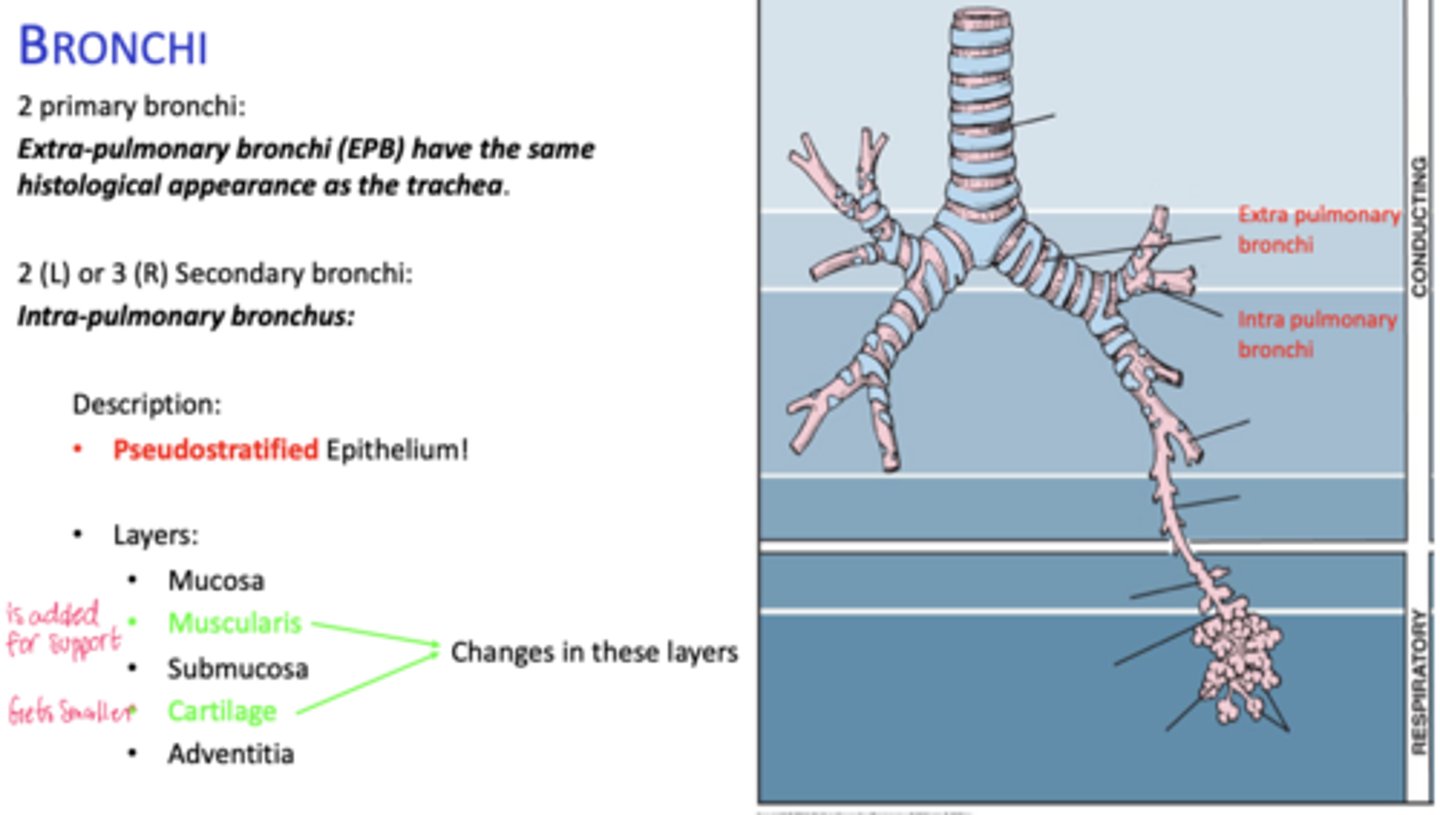
What happens to epithelial height as bronchial diameter decreases?
Cell height decreases.
What happens to cartilage in intrapulmonary bronchi?
Becomes discontinuous plates.
What muscle layer is present in intrapulmonary bronchi?
Spirally oriented smooth muscle.
How does epithelium change in bronchioles?
Pseudostratified -> stratified columnar -> stratified cuboidal.
What cells replace goblet cells in bronchioles?
Clara cells
What cartilage feature is seen in bronchioles?
No cartilage
What epithelium lines terminal bronchioles?
Simple cuboidal with ciliated and Clara cells
What muscle surrounds terminal bronchioles?
Circumferential smooth muscle
What is the first site of gaseous exchange?
Respiratory bronchioles.
What interrupts the walls of respiratory bronchioles?
Alveoli.
What do respiratory bronchioles transition into?
Alveolar ducts.
What structures are found between alveoli in ducts?
Rings of smooth muscle.
What do alveolar ducts terminate in?
Alveolar sacs.
What are Type I alveolar cells?
Simple squamous; 40% of cells, 95% of lining; cannot divide.
What are Type II alveolar cells?
Dome-shaped; 60% of cells, 5% of lining; produce surfactant.
What organelles are found in Type II cells?
Lamellar bodies.
What is the function of alveolar macrophages?
Found in CT; extend into air space.
What do lamellar bodies contain?
Phospholipids, neutral lipids, and proteins.
When is adequate surfactant produced?
After the 35th week of gestation.
What condition results from inadequate surfactant?
Respiratory distress syndrome of the newborn.
What structures form the thin air-blood barrier?
Surfactant, Type I pneumocyte, fused basal lamina, endothelium.
What structures form the thick air-blood barrier?
Surfactant, Type I pneumocyte, connective tissue, basal lamina, endothelium.
What are pores of Kohn?
Interruptions in interalveolar septa.
What is the function of pores of Kohn?
Collateral air flow but spread of infection.