AOS 3 - Enviro - Climate Change + Greenhouse Effect
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What factors are causing the earths temperature to rise?
Anthropogenic factors (environmental pollution and pollutants originating from human activity) are often to blame for Earth’s temperature and the greenhouse effect, natural factors include solar variability and volcanic eruptions
What is solar variability?
The changes in the Sun's energy output, including variations in solar radiation, solar wind, and the magnetic field
How does solar variability change the temperature of earth?
Radiation reaching Earth varies - not just seasons or locations
Every 11 years there are periods of low/high solar activity → solar maximum + minimum (dimming) - difference of 1%
The level of activity is visible as sunspots' - these differ in size, and are associated with changes in magnetic field.
At solar maximums, ozone concentrations are higher, impacting temps and winds.
How do volcanic eruptions heat the Earth?
They release greenhouse gases which contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect
Eruptions produce primarily cO2, but also other gg like: sulphur dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, hydrogen halides
Volcanoes release 180-440 million tonnes of CO2, yearly compared to humans releasing 36.8 billion tonnes of CO 2.
The release of cO2 by volcanoes is important in maintaining Earth's natural greenhouse effect
How do humans heat the earth?
By changing the natural composition of Earth’s atmosphere through emitting greenhouse gases
What is the Earth’s ‘energy budget’?
The balance between how much energy enters and leaves Earth
How does the Earth’s energy budget change?
A constant surface temperature means that the energy coming in is equal to the energy going out → greennouse effect doesn't change this
If the amount of greenhouse gases stays the same the temp will remain constant → equal energy entering + leaving
If the amount of greenhouse gases increases, the temp will increase → energy coming in is greater than energy going out.
Do greenhouse gases alter the energy budget?
Gg don't cause warming, but adding gg to the atmosphere does.
What is the natural greenhouse effect?
Results from the layer of greenhouse gases surrounding Earth that maintains an average temperature suitable for life to exist → water vapour is the main greenhouse gas responsible for this.
Naturally occurring process of warming the Earth's surface, ensuring it remains at a temperature of 15°C
Earths temp is dependant on the balance between the energy inputs: solar radiation from the sun, and outputs: dependant on the level of gases in the trophosphere.
34% (energy reflected back to space)
19% (absorbed by atmosphere)
47% (energy received that reaches planet surface)
What are the advantages of the Greenhouse effect?
Maintains temp
Filters unwanted solar-energy + radiate back ham ful rays
Help in growing offseason crops
Solar powered water heaters use this effect to heat water
Maintains the water level + restricts ice melting
What are the main greenhouse gases?
water rapour (most significant)
Carbon dioxide (second, contributes most to ENHANCED greennouse effect
Methane
Nitrous oxide
chlorofiurocarbons → CFGS, banned now (fridges)
Halons
How much of radiation from the sun is visible?
38% of incoming radiation is visible light to the human eye.
53% is infrared (heat)
9% is the shorter end of spectrum. (Ultraviolet)
What are the atmosphere layers?
Troposphere- (8-15km) - contains 75% of the atmosphere’s total mass - weather occurs here
Stratosphere - (15-50km) - ultraviolet radiation from the sun is absorbed. Upper stratosphere contains the ozone layer
Mesosphere- (50-80km)
Thermosphere - (50-880km)
Exosphere- above/space
What is the ozone layer?
* has nothing to do with the natural greenhouse effect
- Ozone forms when ultraviolet light strikes oxygen forming individual oxygen atoms, these atoms are then able to bind with 02 to form 03
What is the albedo effect?
Is the fraction of solar energy that is reflected from Earth back into space
Albedo can range from a value of 0 (no reflection, light is reflected back) to a value of 1 (100% reflection)
Light surfaces reflect more than dark
Ice + snow have high albedo (0.6-0.9), whereas water is more absorbent, less reflective(0.1), but clouds also, have a high albedo (0.31)
What happens when Earth warms ?
As snow and ice cover decreases, albedo decreases; less energy is reflected back into space and more is absorbed by the ground and water. This warms Earth and causes more ice and snow melt → ice albedo feedback
What is a positive feedback loop?
Where it continues to increase
What is a negative feedback loop?
Where it continues to decrease
How does ocean circulation alter the storage of heat/warmth of the earth?
Oceans play a major role in storage and distribution of heat energy around the globe, with most heat on the surface being stored in oceans.
with circulating ocean currents, both surface and deepwater, distributing heat around to stabilise
gases and delivery of nutrients throughout ecosystems climate patters → impacting local weather, cycling
What are surface currents?
Created and shaped by global wind patterns, rotation of Earth and shape of ocean basins - which move vertically and horizontally
Topography and shape of oceans basins and land masses also influence surface ocean currents
What are global winds caused by?
Global winds are caused by the sun heating different parts of earth, causing the winds to blow in constant directions and surface water to be pushed in the major. wind belts (trade winds, westerlies, polar easterlies)
What is the Corilolis effect?
Earth's rotation deflecting the currents being pushed by wind, increasing circular movement
What are deepwater currents composed of?
Thermoline circulation → oceaninc conveyor belt
What drives deepwater currents?
Currents are driven by the differences in the densities of oceanic waters. Water density is affected by temp (thermo), salinity, and depth
Colder, saltier water is denser than warm, less salty water
The greater the differences in density within layers of the water column, the greater the mixing and circulation
These differences in densities drive the global oceanic conveyor belt which moves nutrients and dissolved CO2 around the globe.
Where are oceanic waterfalls located
In small areas in the North Atlantic and southern ocean
How are ocean waterfalls formed?
From water melting off ice , which is pure (no ice), making it denser than the surrounding highly saline water, causing the water to sink towards the ocean floor creating a waterfall. - This helps drive the ocean conveyor melt
Do oceans heat up faster or slower than landmasses?
Water has higher heat capacity than land, which means that the oceans heat up and cool down more slowly than landmasses do.
How do ocean currents regulate global climate?
By counteracting the uneven distribution of solar radiation hitting the earth’s surface.
List some major currents that affect their local climate
Gulf Stream /North Atlantic Drift → moderates the climate of north-western Europe
Benguela cument → moderates Namibian Desert climate
Humboldt current → moderates the Peru climate
What is carbon sequestration?
Carbon sequestration/storage is a stage of the carbon cycle → where carbon continuously cycles from organisms to the atmosphere, with cO2 being released via respiration and the decomposition of organic material and taken up by plants in photosynthesis
Do oceans store carbon?
Oceans are a major ocean sink, with 40% of Earth’s emissions absorbed due to CO2 dissolving in seawater to form of carbonic acid
Cool oceans = better carbon sinks
- Warmer ocean = less cO2 absorbed
Do forests store carbon?
Yes. Tropical and old growth forests store more. Climatic conditions, natural vegetation, soil texture and drainage aff affect the amount of carbon stored and how long its stored for.
How is carbon released from forests?
Bushfires and deforestation release carbon, but not all carbon is released as some remains in plants which are consumed by animals
Is carbon stored in soil?
In soil, carbon is stored mainly as organic matter where it can be stored for a millennia or be quickly released.
After forest clearing the rate of release of CO2 from soil depends on how rapidly the soil microflora decompose the roots → this is high if the land is cleared for grazing, while on improved pastures the carbon levels don’t drop as much
What is the Enhanced Green house effect?
This is occuring due to human activities increasing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Which leads to more heat energy being absorbed and the gradual warming of the Earth’s surface
This has been occurring since the industrial revolution (1750)
What human activities/factors have contributed to the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Increased combustion of fossil fuels and associated greenhouse gases in response to growth in energy demand in both developed and developing countries
Loss of vegatation cover (forests as carbon sinks) due to the expansion of agricultural activities resulting from population pressures
The manufacture and use of artificial gases like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCS) and hydrofluorocarbons (HCFCS)
Most prevalent greenhouse gases
water vapour
CO2 and Methane - most directly connected to human activities
Nitrous oxide - directly connected to human activity
How does CO2 contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Major contributor due to burning of fossil fuels, clearing and burning of forests
The yearly output of co2 is over 14,000 million tonnes, 50%. is taken up by the atmosphere and the rest is absorbed by the ocean /vegetation.
Its increased from 280 ppmm before the industrial revolution to 422.7 ppm in 2024, highest in history, 50% increase
What is the Keeling Measurement?
The Keeling curve produced the first significant evidence of the increasing CO2 levels
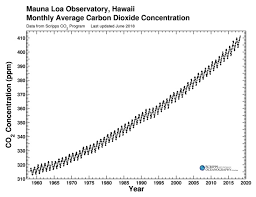
Why does the Keeling Curve fluctuate?
Majority of trees are distributed in the southern hempisphere, which are deciduous. So in summer they leaves grow, absorbing CO2, and in winter the leaves deop and releasing CO2
How is methane produced naturally?
release from wetlands as peat in bogs and tundra decay
Termite activity - account for 40% of emissions
How is methane produced through human activity?
extracting fossil fuels
leaving regetation to rot in rice paddies
disposing of garbage in landfills
treating sewage/farming ruminant animals account for 60% emissions
How much does methane contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Has a low concentration in the atmosphere, but its GWP (Global Warming Potential) is 28 times more than that of CO2 due to its higher capacity to re-radiate →making it the thid most prominent
Does Nitrous Oxide occur naturally?
Yes, but at very low (uncommon) concentrations
Is Nitrous Oxide produced through human activity?
Chemical manufacture, feniliseruse, soil cultivation, catalytic converters in cars, growing leguminous - contributing 40% to N20 emissions.
Do Chloro flurocarbons & Halons occur naturally?
No - Have a greenhouse effect more than 5,000 times that of cO2, and persist in the atmosphere for over 100 years. These have been phased out in accordance with international treaties
What are Perfluorocarbons?
Are artificial gases, that abson 6500 times more infrared radiation than CO2
They are stable and can persist for 50,000 years
Uses:
Largely produced duringthe electrolytic production of acuminium
Used in electronics (fridges), medical and cosmetic purposes ozone
What is ozone, and where is it found?
Is found in the stratosphere and protects Earth by filtering out harmful UV. When closer to the ground the ozone irritates the respiratory system of animals + damages trees.
In the troposphere ozone is a greenhouse gas
How is ozone produced?
Its produced by UV radiation interacting with atmospheric hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides produced from car exhausts and coal-burning plants → photochemical smog. These concentrations of ozone are increasing at an annual rate of 0.5% water vapour
How is water vapour a greenhouse gas?
Greennouse gus unose role in the enhanced greenhouse effect is unclear
Its not usually considered a go due to human activity having little direct the effect on its concentrations.
As temps increase the atmosphere holds more water vapour, increasing its heating capacity. But this also increases cloud cover which reduces temps due to clouds reflecting heat and light
How are aerosols produced?
By burning fossil fuels small aerosol particles are released producing a haze that is often found in urban areas
What role do aerosols play in the greenhouse effect?
Aerosols directly influence the greenhouse effect by scattering and reflecting short-ware radiation, this reflecting of radiation can have a cooling effect.
They also affect cloud formation as clouds formed in polluted air are brighter so they reflect more light (cooling)
What determines whether a gas is a greenhouse gas?
Not all gases in the atmosphere act as greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases are those that get excited by solar radiation at a specific frequency. They absorb energy from incoming radiation and also prevent heat from escaping out to space.
The contribution a gas makes to greenhouse effect depends on:
The capacity of the gas to absorb heat (radiative efficiency)
The length of time it persists in the atmosphere (lifetime)
The concentration in the atmosphere.
What is the ‘Global Warming Potential’?
GWP was developed to compare the impact of different greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
The GWP of a gas is the measure of how much energy can be absorbed by the emission of 1 tonne of gas over its lifetime relative to the emission of 1 tonne of CO2.
The larger the GWP, the more gas can warm Earth compared to CO2 over a 100-year period
CO2 has a GWP of 1
Methane has a GWP of 28-36 over 100 year span, so it will last a decade on average (less than CO2) but absorbs more energy than CO2 → this is reflected in the GWP
What has caused earth’s climate to change over time?
Earth has experienced changes in climate over billions of years due to volcanic eruptions, solar flares, photosynthesis rates (creating oxygen)
Eg: Around 600-700 yrs ago land and oceans were covered in ice, and then volcanic activity increased greenhouse gases and the global temperature higher than today
What recent changes have occurred?
Human-induced climate change in the past 200 years is occurring at a rate of 10-20 times faster than change caused by non-human causes.
- CO2, methane, nitrous oxide are nigher than they have ever been in the last 800,000 years.
Why are multiple methods needed to measure changes in climate?
No method is without error, so multiple methods are used.
How/what are Ice core samples used for?
Cylinders are drilled out of ice sheets/glaciers that reveal info about past temperatures through bubbles. That contain samples of the atmosphere as it was when the ice formed. This can show the CO2 and Methane levels, as well as oxygen 16 to oxygen 18 isotopes in water molecules indicating past temps.
What is paleobotany, and what do they study?
- Paleoclimatologists and palaeobotanists study the plant life of the geological past, and use this to identify the kinds of plants present in the area, which give an indication of the kind of climate that prevailed.
How are plant fossils used to determine past climates?
Scentists use plant fossils or impressions of plant part preserved in sedimentary rocks, coal or other geological deposits
Plants are generaly distributed across the landscape based on temperature and precipitation patterns, plant communities change as these climatic factors change.
By knowing the conditions that these plants preferted, scientists can make general conclusions about aim almate.
How can pollen be studied to determine past climates?
Pollen can be studied as it is often found in lake sediments as wind- pollenating plants that once grew in the lakes vicinity will have released pollen during their lifetime
Why is pollen in lakes ideal to determine the past climates?
Sediment at the bottom of lakes is ideal for determining pollen changes over time because it tends to be laid down in annual layers, with each layer trapping the pollen that sank to the bottom that year
What are some methods for measuring ocean temps?
Direct measurements from weather stations on land and on water
Remotely by thermal and microwave imaging sensors on satellites.
How can past changes in ocean temperatures be determined?
Evidence of past changes include can come tram analysis of long-term temperature records, studies on oceans temperature records, studies using ballon-borne sensors, surface and satellite observations of stratospheric cooling.
What relationships/interactions are involved in the climate
Climate = average weather→ involving interactions between the biosphere, oceans; atmosphere, land surface and weather.
How does climate modelling work?
By dividing the Earth into 200 km2 boxes, they estimate conditions at each corner, it then steps forward in time, creating new conditions, the output for each step becomes the input for the next. Complex mountains or coast lines are divided into 50 km2 boxes for accuracy purposes.
These mathematical representations of the climate stimulate the interactions of important anvers of aimate, allowing it tobe predicted
Do these climate models accomodate for other factors?
Each measurement in isolation only gives a small indication, but these models can focus on different aspects such as interactions between clouds, general warming and the water cycle.
These projections also take into account possible scenarios in terms of how societies around the world will manage climate.
What is the Global Average Temperature used for?
The global average temperature is convenient when detecting and tracking changes in the earths energy budget - how much sunlight Earth absorbs minus how much it radiates to space as heat - overtime.
How is the global average temperature determined?
This is calculated by taking temperature measurements which are then converted from absolute temperatures to temperature anomalies - the differene between the observed temperature and the long-term average temperature for each location date
How is Sea Ice Modelling used?
- This model approximates future Artic sea ice area based on present Artic sea ice area and the sensitivity of sea ice to Artic temperatures → emulating the future evolution of Arctic sea
How does global warming influence sea level rise?
Global warming impacts sea level rise in 2 ways:
Glaciers + ice sheets are melting
warmer water expands
Give examples of climate change across Australia
By 2020 - significant loss of biodiversity in some ecologioally rich sites - QLD Wet Tropics and GBR
By 2030 - water security problems intensify in southern and eastern Australia-increased drought + fire
By 2050- ongoing coastal development and population growth projected to exacerbate risks from sea level rise and increases in severity and frequency of stoms/flooding changes in rainfall and temperature
Why are changes in rainfall difficult to predict?
Due to precipitation patterns being affected by local changes in ocean circulations, sulphate aerosols and changes in behaviour of El Nino and Southern Oscillation
How is rainfall expected to change in Australia?
Rainfall models show a decrease in rainfall over most of mainland Australia in winter and an increase in Tas. But increases in summer rainfall, with spring and autumn being transitional periods.
How is Snow Cover expected to change?
Is expected to be severely reduced, and be more affected by climate change than rainfall pattens will be
with reduced snow cover on plant and animal communities being significant, with reduced snow-met in spring impacting hydro-electric schemes + downstream irrigation
How will climate change impact humans?
Changes in climate may impact insect distribution→ malaria, +> increased risk of insect-borne diseases
Reduced income for those in agriculture - loss of crops
- Requirement of Spillways and drainage systems to cope with more water
Greater chance salination of urban water supplies
Changed power generation requirements - less heating, more cooling
Increased insurance claims due to extreme events
Altered tourism destinations
How will changes in climate harm Biodiversity levels?
Reduction in species' ability to fight diseases and genetic diversity
Altered ecosystem function
Reduced ecosystem resilience
Modification to the 'web of interactions' that cascade as species dependant on climate change- affected species are themselves affected. 6,300 species are in danger this way
Some species will need to adapt/change their range, expanding into areas not previously inhabited
Altered amount and frequency of water availability
increased frequency of extreme events and extinction
What are invasive species?
Invasive species are animals, plants, parasites or disease -causing organisms that establish themselves outside natural range and become pests.
Native species can become pests/invasive if transferred outside their natural range.
Cats, rabbits, goats, cane toads, foxes, feral pigs and escaped or dumped domestic animals are listed as a cause for decline in native species.
How will climate change impact the length of plant growing seasons + animal breeding cycles?
Milder winters and warmer conditions = reduction in frequency of frost damage to crops - good
Enhanced photosynthesis brought by higher levels of CO2 in the atmosphere, known as cO2 fertilisation, increasing growth
Increased CO2 reduces opening of stomata = less water=loss transpiration = thrive in areas of low rainfall:
Plant and animal cycles (migration, breeding) are influenced by climate - the study of such is phenology
How are pollinator interactions impacted by climate change?
The type of interdependence can bet seen in bees and other pollinators of flowering plants. when their previous phenological patterns are disrupted by changes in climate triggers, each misses the vital interaction, and survival is threatened: bees lack food, plants do not get fertilised
What are the coastal consequences of sea level rise?
Increased erosion of low - lying areas and formations
Flooding in low- lying areas
Salt water intrusion into underground water systems
What are the consequences of climate change in agriculture?
Changing temperatures and rainfall may alter the disruption of insect pests → the cattle tick is moving further south.
Concern over water availability
Enhanced growth due to higher CO2 levels
Increased damage to crops due extreme events
increased pests and disease
Reduced income
Reduced frost damage (good thing)
What is climate mitigation?
Is taking steps to reduce or avoid greenhouse gas emissions to minimise the rate and speed of climate change
What is climate change adaptation?
Is taking steps to prepare and respond to the effects of climate change
Provide examples of climate change MITIGATION
Enhancing energy efficiency
Increasing hte uptake of renewable energy
Improving industrial processes to increase energy efficiency and reduce waste and pollution
Increase the uptake of sustainable transport
Enhancing carbon sinks by replanting vegetation
Provide examples of climate change ADAPTATION
Clearing land use to protect buildings and infrastructure from existing and new hazards
Upgrading design of buildings and infrastructure to protect from wind damage and areas expected to see an increase in storms
Adjusting activities/lifestyles to prevent stress on an already stressed environment
Updating emergency/business planning as the economic cost of natural disasters in Aus rises
Increasing community understanding in the community to adapt to change
List examples of stakeholders groups that may be involved in a development/project
Aboriginal + Torres Strait Islander Peoples
A local or regional community
Media
Environmental interest groups
Industry reps
Non-government groups
Government agencies
What role do Aboriginal + Torres Strait Islander Peoples have as a stakeholder?
Have a role in protecting their cultural + intellectual property including sacred sights
What role do teh media have as a stakeholder?
Not only contains informations available from processing by stakeholders but it also records and influences public opinion. It can influence people indirectly through mental representations and communication of content.
What role do non-government groups have as a stakeholder?
Include / present the needs and views of people in the community, which can be streamlined into public policy led by governments/other official organisations.
What role do government agencies have as a stakeholder?
Have important responsibilities regarding implementing government policies, ensuring regulatory frameworks are being met, and advising the government
What do good Environmental Management require?
Planning and Decision making
Monitoring and review
Communication and reporting