Features of Bones
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Projections
An outward extending part or prominence of a bone that serves a site for tendon and ligament attachment.
Articulations
Where two bones come together. The joint.
Depressions
Recessed area of the bone. Often either fits with a projection or allows attachment.
Openings
Open surfaces of bones. Allows passage of nerves, blood, etc.
Crest
Ridgelike projection. Sites where connective tissue attaches muscle to bone. Ex. Hip bone, median sacral.
Epicondyle
Projection superior to condyle. Attaches muscle and connective tissue to bone, providing support to this musculoskeletal system. Ex. Femur, femoral medial and lateral.

Linea/Line
Projection, narrow slightly raised ridge. Allows a muscle to attach to the bone. Ex. Femur, aspera; pectineal

Process
Projection, bony prominence. Allows for muscle attachment. Ex. Vertebra, spinous; acromial; radial styloid
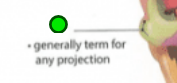
Protuberance
Projection, protruding outgrowth. Attachment for muscles and ligaments. Ex. Skull, external occipital
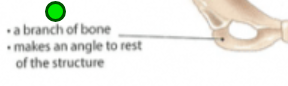
Ramus
Projection, armlike bar, branch of bone, makes an angle to the rest of the structure. Gives structural support to the rest of the bone. Ex. Mandible and Ischium
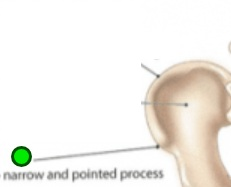
Spine
Projection, thornlike, narrow and pointed. Attachment for muscles and ligaments. Ex. Scapula and Ischium
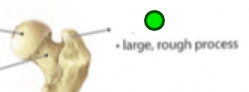
Trochanter
Projection, large rough knob. Attachment for largest muscle groups and most dense connective tissues. Ex. Femur, greater and lesser.
Tubercle
Projection, small knoblike. Connective tissues attach. Ex. Humerous, greater and lesser.
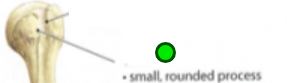
Tuberosity
Projection, small rough elevation. Muscles and connective tissues attach. Ex. Tibial, deltoid, ischial, and radial.
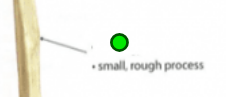
Condyle
Articulation, rounded process. Provides structural support to the
overlying hyaline cartilage. Ex. Femur, Tibia, and Skull.
femoral lateral and medial; tibial lateral and medial; occipital.

Facet
Articulation, nearly flat. Forms a joint with another flat bone or
another facet, together creating a gliding joint. Ex. Vertebra, for flexion and extension of the spine.
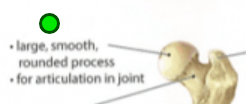
Head
Articulation, expanded end. Prominent extension of bone that forms
part of a joint. Ex. Femur and Radius
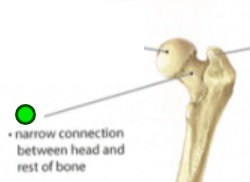
Neck
Narrow connection between head and rest of bone
Fossa
Depression, shallow basin. Receives another articulating bone or act to support brain structures. Ex. Humerous and Cranium. trochlear; posterior, middle, and anterior cranial.
Fovea
Depression, tiny pit. Allows the attachment of a ligament. Ex. Femur, blank capitis of the femur
Fissure
Opening, slit. Houses nerves and blood vessels. Ex. Skull, superior and inferior orbital.
Foramen
Opening, hole. Nerves and blood vessels pass through. Ex. Vertebra, magnum; supraorbital; infraorbital; mental.
Meatus
Opening, tubelike passageway. Provides passage and protection to
nerves, vessels, and even sound. Ex. Skull, external acoustic; internal auditory.

Sinus
Opening, cavity. Open chamber for air and mucus to flow through. Ex. Skull, maxillary; ethmoid; sphenoid; frontal.

Groove/sulcus
Narrow depression
Joints
Synonymous with articulations. Point of contact between: Two bones, cartilage and bone, or teeth and bone. Structure determines strength and flexibility.
Classifications
Either structural or functional.
Functional Classification
Based on the degree of movement permitted, either
• Synarthrosis
• Amphiarthrosis
• Diarthrosis
Synarthrosis
Immovable, ex. sutures of the skull
Amphiarthrosis
Slightly moveable, ex. intervertebral joints
Diarthrosis
Freely movable, ex. hip
Structural Classification
Based on the presence/absence of a synovial cavity and the type of connecting tissue.
• Fibrous
• Cartilaginous
• Synovial
Fibrous Joints
Bones are held together by dense connective tissue containing many collagen fibers; found in bones in close contact. 3 types. Overlaps with two types of function- either synarthrosis or amphiarthrosis.
Suture
Fibrous joint, synarthrotic (immovable). Between flat bones of skull. Thin layer of connective tissue (ligament) connects bones
Syndesmosis
Fibrous joint, amphiarthrotic (flexible, may twist). Bones bound by a sheet of dense connective tissue (interosseous membrane) or a bundle of dense connective tissue (interosseous ligament). Lies between tibia and fibula.
Gomphosis
Fibrous joint, synarthrotic (immovable). Cone-shaped bony process in a socket in jawbone. Tooth in jawbone by periodontal ligament.
Cartilaginous joints
Bones are held together by cartilage. 2 types. Overlaps with two types of function- either synarthrosis or amphiarthrosis.
Synchondrosis
Cartilaginous joints, synarthrotic (immovable). Bands of hyaline cartilage unite bones. Some are temporary, such as epiphyseal plate. Between manubrium and the first rib (costal cartilages, permanent)
Symphysis
Cartilaginous joints, amphiarthrotic (limited movement). Pad of fibrocartilage between bones. Articular surfaces covered by hyaline cartilage. Pubic symphysis. Joint between bodies of adjacent vertebrae (intervertebral discs).
Synovial
Most joints. All are diarthrotic. 6 subtypes.
Synovial joint structure
Fibrous membrane outer layer. Synovial membrane inner layer. Secretes synovial fluid into the synovial cavity it surrounds. Articular cartilage covers articular ends of bones.
Four categories of movement
Gliding, Angular, Rotation, Special.
Gliding movement
Simple movements, associated with plane/planar joints. Back-and-forth or side-to-side. Ex. Carpal joints of the wrist, tarsal joints of the ankle, facet joints of the spine.
Angular movements
Increase or decrease in the angle between articulating bones. Flexion, Extension, Hyperextension, Abduction, Adduction, Circumduction
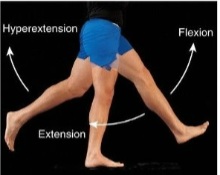
Flexion
Decrease in angle
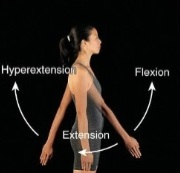
Extension
Increase in angle
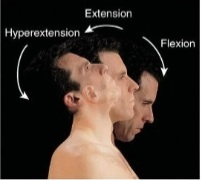
Hyperextension
Extension beyond anatomical position; angular.
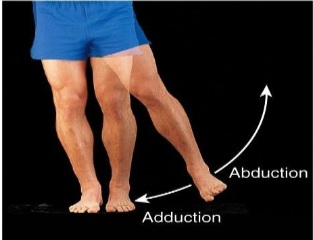
Abduction
Movement of a bone away from the midline. Angular.
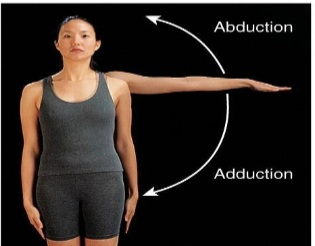
Adduction
Movement of a bone towards the midline. Angular.
Horizontal Abduction
Movement of a bone away from the midline along the transverse plane. Angular.
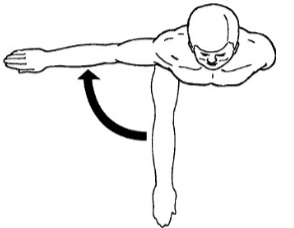
Horizontal Adduction
Movement of a bone towards the midline along the transverse plane. Angular.
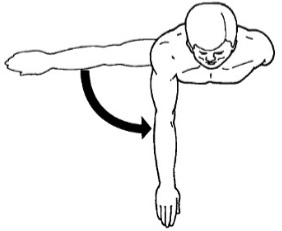
Circumduction
Movement of the distal end of a part of the body in a circle. Angular.
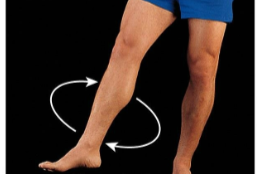
Rotation
Bone revolves around its own longitudinal axis
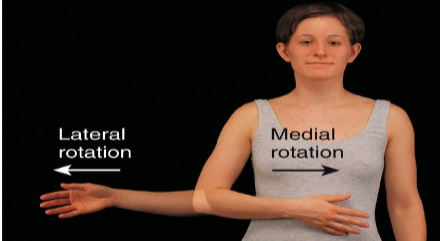
Medial/Internal Rotation
Bone of the limb is turned toward the midline.
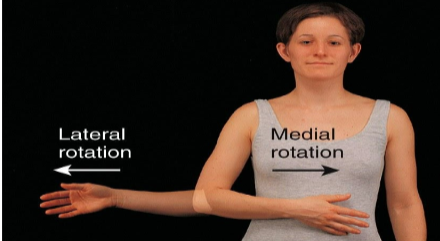
Lateral/External Rotation
Bone of the limb is turned away from the midline.
Special movements
Only occur at certain joints.
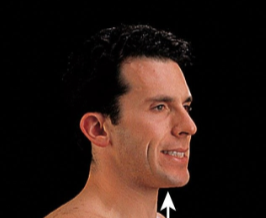
Elevation
Upward special movement
Depression
Downward special movement.

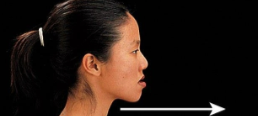
Protraction
Special movement forward.
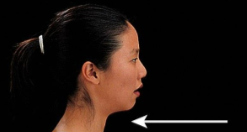
Retraction
Special movement of a protracted back to the anatomical position.
Inversion
Movement of the soles of the feet medially so they face each other.
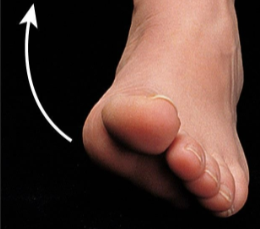
Eversion
Movement of the soles of the feet laterally so they face away from each other.
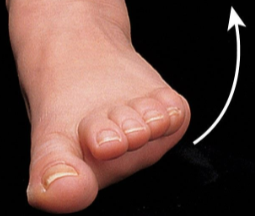
Dorsiflexion
Bending of the foot in the direction of the dorsum (up)
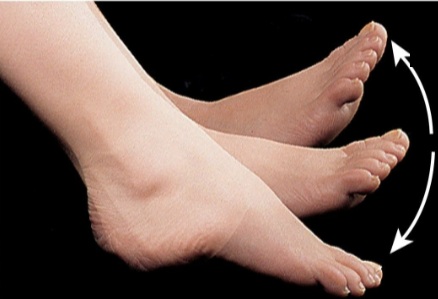
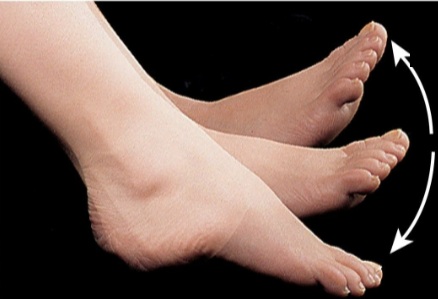
Plantar Flexion
Bending of the foot in the direction of the plantar surface
Supination
Movement of the forearm so that the palm is turned forward
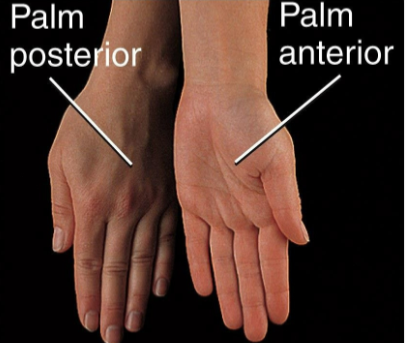
Pronation
Movement of the forearm so that the palm is turned backward
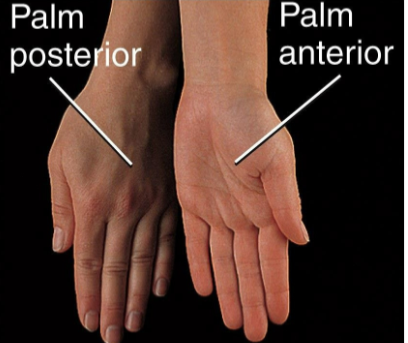
Opposition
Thumb moves across the palm to touch the fingertips on the same hand

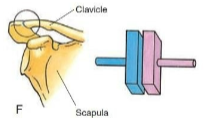
Planar
Type of synovial joint. Joint surfaces are flat. Gliding movement; back-and-forth and side-to-side. Ex. Between tarsals, between carpals.
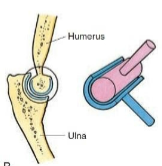
Hinge
Type of synovial joint. Convex surface of one bone fits into the concave surface of another. Flexion/Extension. Ex. Elbow, knee, ankle.
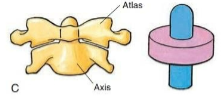
Pivot
Type of synovial joint. Round or pointed surface of one bone fits into a ring formed by another bone and ligament. Rotation. Ex. Atlanto-axial joint of the neck, Radioulnar joint of the forearm at the elbow
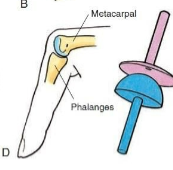
Condyloid
Type of synovial joint. Oval projection of one bone fits into an oval
cavity of another. Flexion/Extension and Ab/Adduction. Ex. Wrist, Metacarpophalangeal joints (2nd-5th)
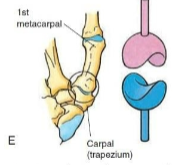
Saddle
Type of synovial joint. Surface of one bone is shaped like a saddle and the other bone fits into the saddle like a rider. Flexion/Extension, Ab/Adduction, and Rotation. Ex. Carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
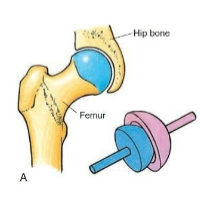
Ball-and-Socket
Type of synovial joint. Ball-shaped surface fits into the cuplike depression of another. Flexion/Extension, Ab/Adduction, and Rotation. Ex. Shoulder, Hip
Sprains
Tearing of connective tissue in joint, without bone dislocation.
Bursitis
Inflammation of a bursa, from overuse or stress.
Arthritis
Inflammation, swelling, and pain in a joint.
Rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease.
Osteoarthritis
degenerative, most common type, occurs with aging.
Lyme arthritis
caused by Lyme disease, passed through tick bite.