Biology - Chapter 19 - Organisms and their environment
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what is the principal source of energy input to biological systems
The sun
Flow of energy through living organisms
light energy from the sun and chemical energy in organisms
energy is eventually transferred to the environment e.g as heat
Define food chain
shows the transfer of energy from one organism to the next starting with a producer
define food web
a net work of interconnected food chains and interpret food webs
define producer
an organism that makes its organic nutrients, usually using energy from through photosynthesis
define consumer
an organism that gets its energy by feeding on other organisms
what can consumers be classed as
primary, secondary, tertiary and quatemary
example of a simple food chain
grass→mouse→owl
carrot→rabbit→fox→lion
grass→grasshopper→frog→snake→eagle
define herbivore
an animal that gets energy by eating plants
define carnivore
an animal that gets its energy from eating other animals
define primary consumers
herbivores -they feed on producer
define secondary consumers
predators that feed on primary consumers
define tertiary consumers
predators that feed on secondary consumers
define decomposers
bacteria and fungi that get their energy from feeding off dead and decaying organisms and undigested waste (such as faeces) by secreting enzymes to break them down
how population of animals is caused
by humans overharvesting and introducing foreign species to a habitat
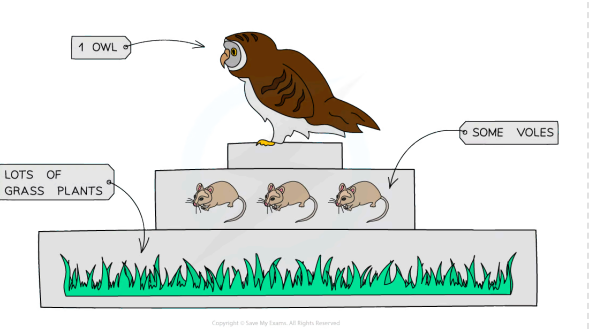
define pyramid of number
diagram that shows how many organisms are there at each level of food chain (the larger an organism the less there are)
example of pyramid of number
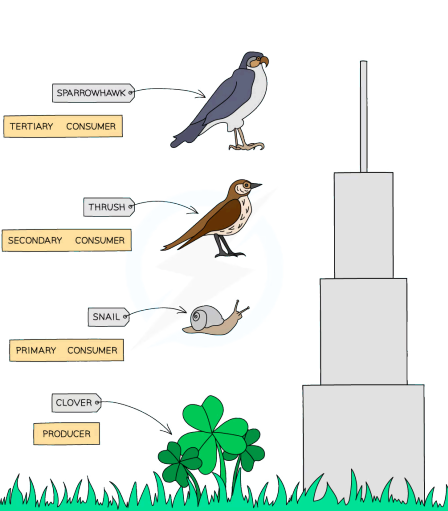
define pyramid of biomass
shows how much mass creatures at level have without including water in body
example of pyramid of biomass
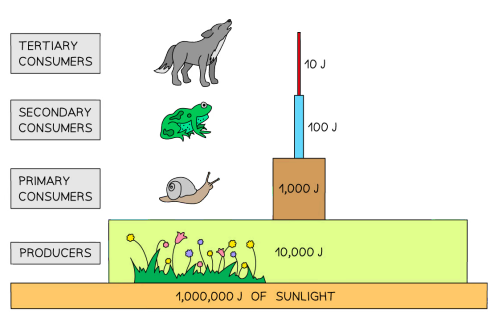
define pyramid of energy
represents energy found in trophic levels
example of pyramid of energy
90% of the energy lost goes up food chain as heat and in digested materials
define trophic level
position of an organism in a food chain, food web or ecological pyramid
advantages of using a pyramid of biomass rather than a pyramid of number to represent a food chain
it is more accurate because it quantifies the actual living matter at each trophic level
advantages of using a pyramid of energy rather than pyramids of numbers or biomass to represent a food chain
Energy pyramids show actual energy flow, account for inefficiencies, standardize units, reflect trophic structure, and highlight the importance of producers.
how a food chain goes
producer→primary→secondary→tertiary→quaternary
why the transfer of energy from one trophic level to another is often not efficient
energy is lost as heat and 10% of productivity of one level ends up as net productivity at next level
why food chains usually have fewer than five trophic levels
energy loss at each trophic level reduces available energy, limiting transfer efficiency and supporting fewer trophic levels
why is it more energy efficient for humans to eat crop plants than eat livestock that have been fed crop plant
energy is lost as it moves up the food chain
describe the carbon cycle
photosynthesis - used
respiration - released
feeding - eaten
decomposition - broken down
formation of fossil fuels - stored
combustion - released
describe nitrogen cycle
decomposition of plant and animal protein to ammonium ions
nitrification
nitrogen fixation by lighting and bacteria
absorption of nitrate ions by plants
production of amino acids and proteins
feeding and digestion of proteins
deamination
denitrification
roles of microorganisms in the nitrogen cycle
decomposition - decomposes nitrogen compounds found in dead organisms into ammonium which releases nitrogen into soil
nitrification - convert ammonium into nitrite and then nitrate so plants can readily absorb them
nitrogen fixation - convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms of nitrogen that plants can use for growth
denitrification - converts nitrate or nitrite back into gaseous nitrogen which returns unto atmosphere
define population
a group of organisms of one species, living in the same area , at the same time
define community
all of the populations of different species in an ecosystem
define ecosystem
a unit containing the community of organisms and their environemtn, interacting together
factors affecting rate of population growth for a population of an organism
food supply
competition
predation
disease
describe The Population Growth Curve
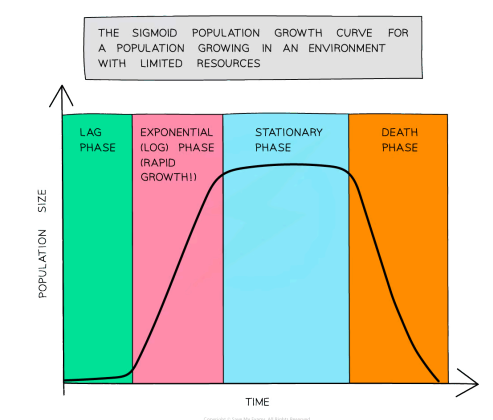
describe lag phase
organisms adapting to environment before they are able to reproduce
describe log phase
food supply is abundant, birth rate is rapid and death rate is low, growth is exponential they are adapted to environment, space is a lot
describe stationary phase
population levels out due to a factor in environment being limited. The birth rate and death rate is equal. space is limited
describe death phase
population decreases as death rate is now greater than birth rate because food supply is short