OSCE 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
3 tooth functions
eating, swallowing, speaking
Determination of tooth position
Forces applied by soft tissues
Impact of size
Forces applied by therapeutic modalities
Missing tooth
Can lead to food impaction → caries
Curve of wilson
curve of spee
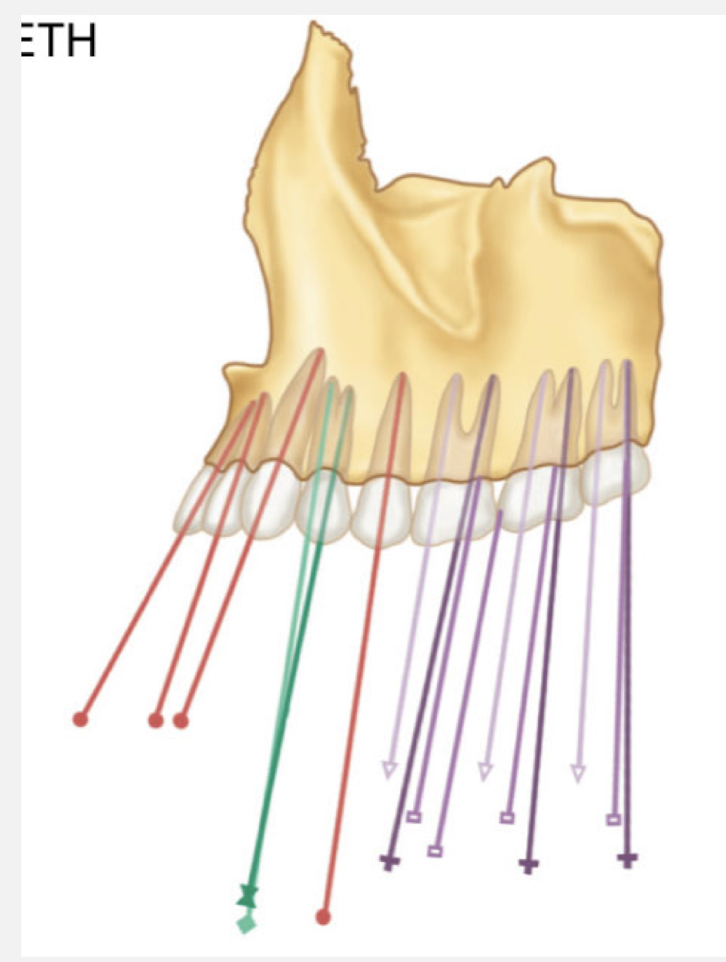
max teeth angulation: Anteriors are mesially inclined, while most posteior teeth become more distally inclined with reference to alveolar bone
angulation of the mandibular: anteriors and posteriors are inclined mesially

all max posteriors are slightly inclined bucally
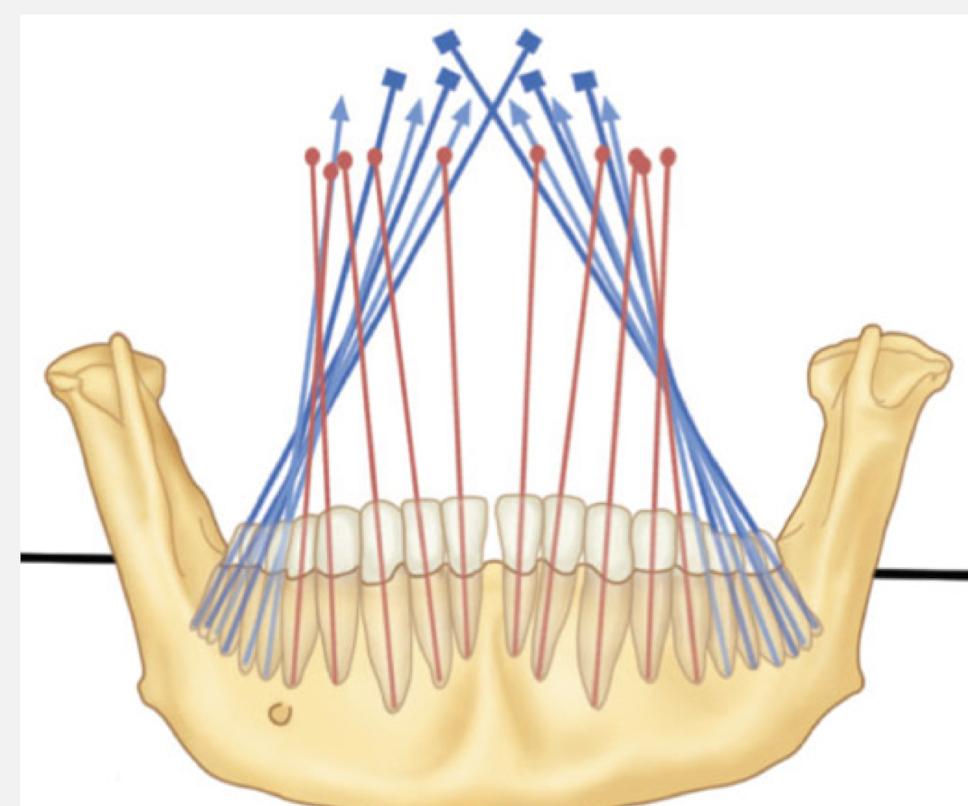
all mandibular posteriors are slightly inclined lingually
With loss of proximal contact…
tooth distal to the extraction site will drift mesially
when a tooth is lost..
distal tooth moves mesially, unopposed tooth erupts seeking occlusal contact
anterior open bite
Lingual force > than labial/buccal
Labial flaring of anteiror teeth
Bite is caused by constant resting of tongue NOT unusual swallowing
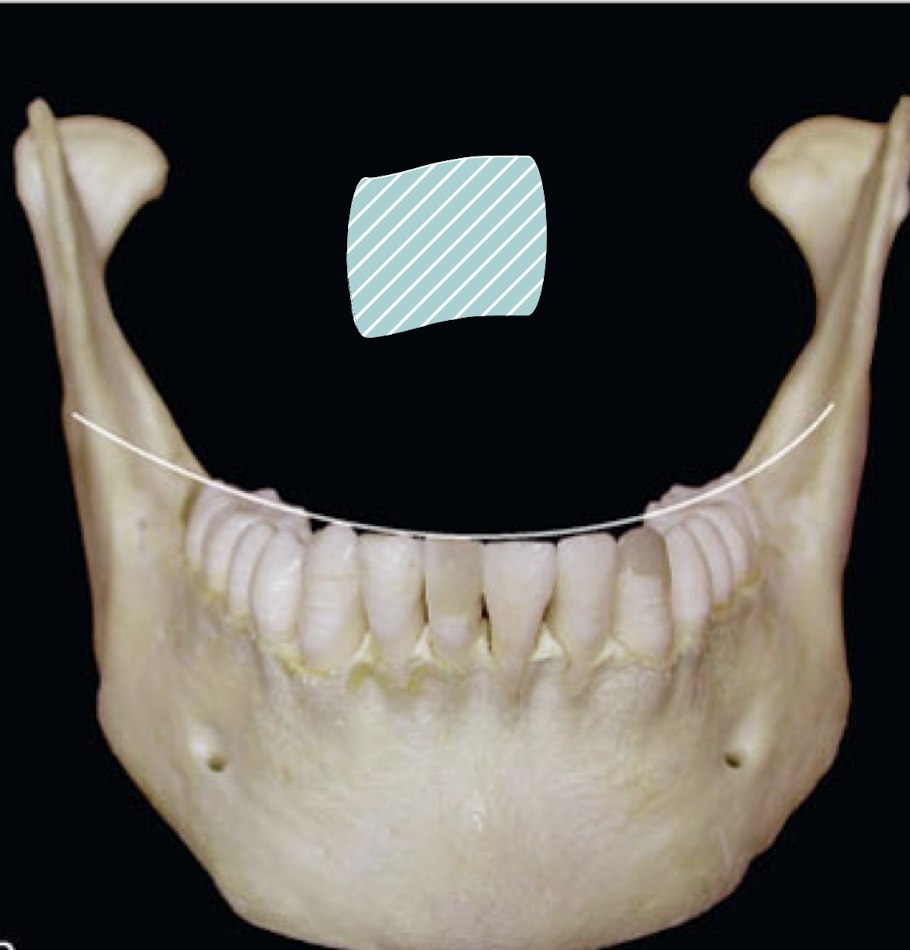
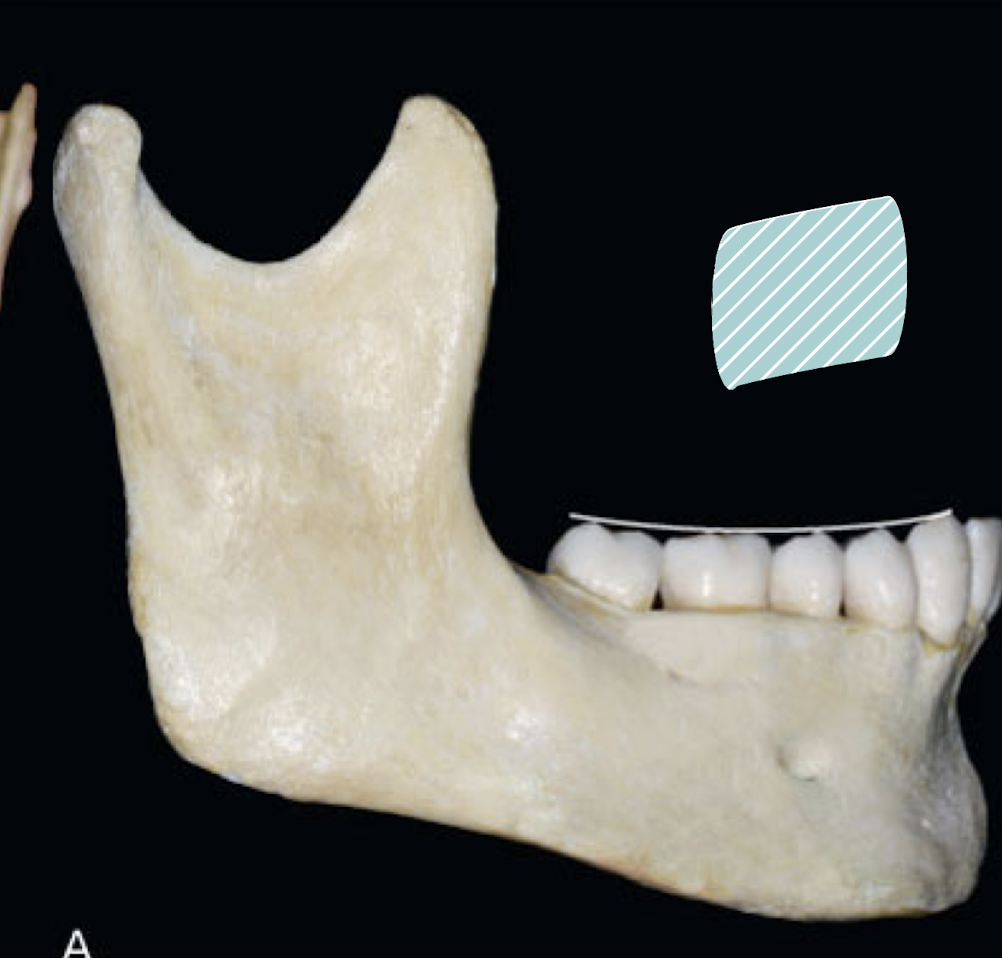
plane of occlusion
plane that would be established if line were drawn through all buccal cusp tips and incisal edges of mandibular teeth and broadened out to included lingual cusp tips and continuing across arch to include buccal and lingual of the opposing arch
Curve of spee: relationships seen where?
Teeth?
Planes of occlusion?
MD axial relationships seen from lateral view
Angulation of teeth w respect to alveolar bone
Max Anteriors: M inclination
Max Post: D inclination of most
Man Ant + Post: M inclination, 2nd and 3rd more inclined than premolars
Maxilla: Convex
Mandible: Concave
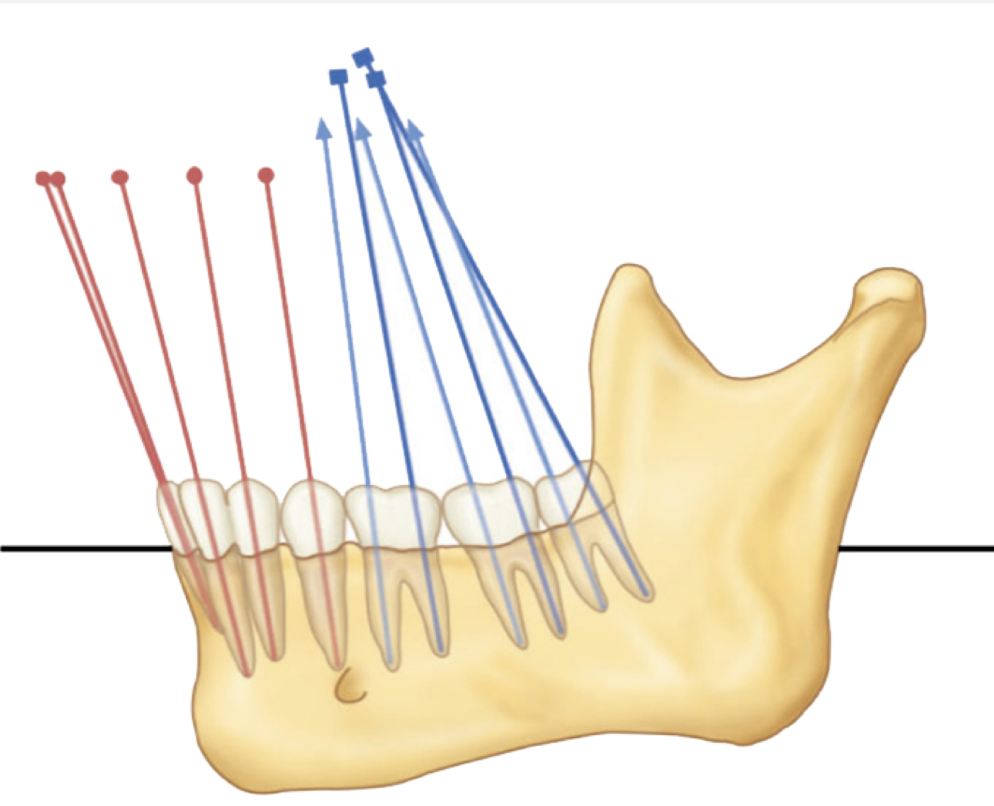
Curve of Wilson: Relationships seen where?
Teeth?
Planes of occlusion?
BL axial relationships seen from frontal
Max Posteriors: slight buccal inclination
Mand Post: slight lingual inclination
Maxilla: Convex
Mandible Concave
Bonwill Triangle
triangle between condyles (mandible) + mesial contact areas of Mandibular central incisors
Condyle - Condyle: 4 inches
Condyle - man cen incisor: 4 inches
Sphere of Monson
Based on bonwill triangle
sphere w 4 inch radius, center equal distance from occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth + center of condyles
Occlusal surfaces divisions
occlusal table, outer aspect
Occlusal table
Area of posterior teeth between B and L cusp tips
Major forces applied here
50-60% total BL dimension of tooth
Positioned over long axis of root structure
Considered inner aspect of tooth
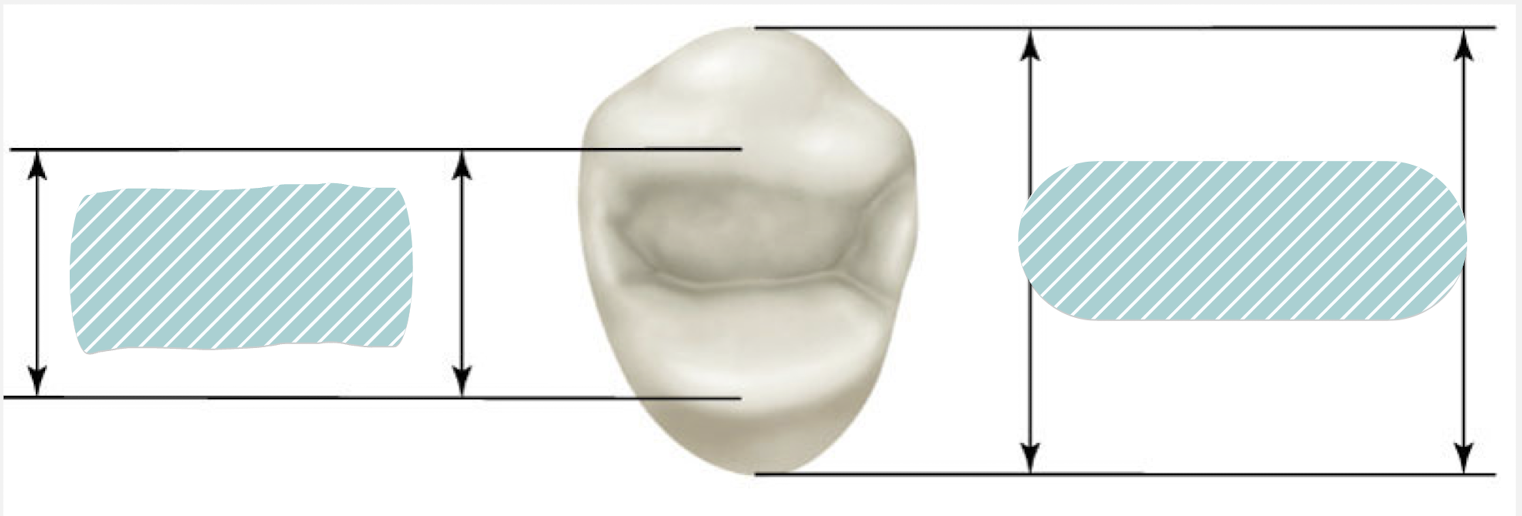
Occlusal table, total BL width
Outer aspect
occlusal area of posterior teeth outside of cusp tips
Occlusal surface divisions are made up of inclines that extend?
outer incline: cusp tips to hight of contour on lingual/labial surface
Inner incline: cusp tips to central fossa area
mesially inclined surfaces face the __ portion of the tooth
mesial
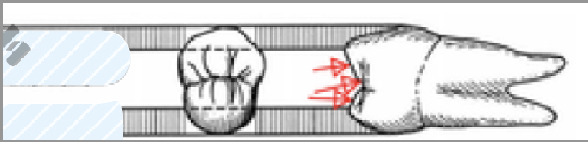
outer incline
inner incline
arch length
line at the distal surface of 3rd molar, extends mesially thru all prox contracts around entire arch ending at distal of opposite 3rd molar
both arches approx same, but max 128 mm, man: 126 mm
the slight difference in arch length is from?
narrow mesialdistal distances of mandibular incisors vs maxillary
arch width
distance across arch
mandibular slightly less than max = each max tooth is more facially positioned than occluding mandibular tooth
since the maxillary teeth are more facially positioned (or facial inclination at leas) the normal occlusal relationship of posterior teeth enables?
mandibular buccal cusps to occlude along central fossa areas of max teeth
max lingual cusps occlude along central fossa of man teeth
protects surrounding soft tissue
cross bite
max buccal cusps contact central fossa of mandibular teeth
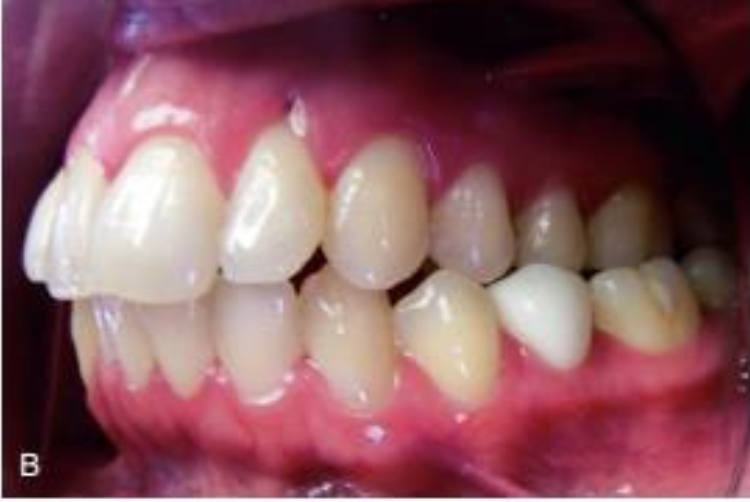
posterior cross bite
supporting/centric cusp: ?
supports what?
buccal cusps of mandibular posterior, lingual cusps of maxillary posterior teeth occlude with opposing central fossa area
these support distance between maxilla and mandible = vertical dimension of occlusion
the centric cusps are ___ and __
when viewed from occlusal, tips are located approx ___ distance into the buccolingual width of tooth
broad and rounded, 1/3
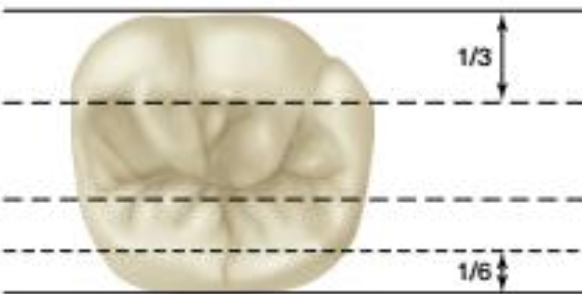
mandibular first molar: 1/3 = centric, 1/6 = guiding/noncentric
guiding, noncentric cusps
buccal cusps of maxillary posterior teeth and lingual cusps of mandibular posterior
guiding cusps are ___
located __ distance into total buccolingual width of the tooth
sharp, 1/6
functional outer aspect
inner incline of guiding cusp near central fossa and either contacts or is close to small portion of outer aspect of opposite centric cusp (1 mm small area)
shearing cusps
noncentric
noncentric cusps major role
minimize tissue impingement, maintain bolus of food on occlusal table, mandible stability, feedback to Neuromuscular system (controls chewing stroke)
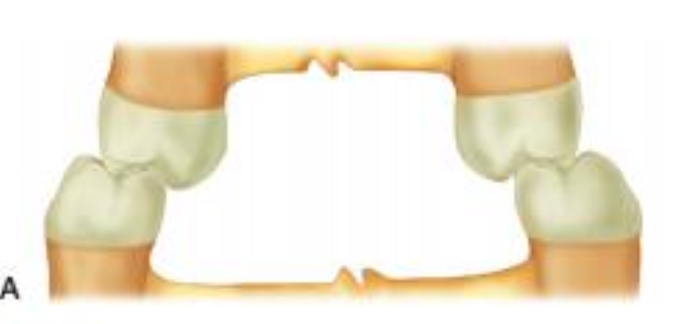
posterior cross bite
If mandible moves laterally from ICP (intracuspsal position)
if mouth is open/closed..
noncentric cusp will contact and guide it
noncentric guides mandible back to ICP
BO line? represents?
occludes with?
buccoocclusal:
line extended thru all buccal cusp tips of mandibular posterior teeth, BO is established: represents demarcation (separation) of inner and outer aspects of buccal teeth
BO line occludes with CF line of maxillary
LO line? represents? occludes with?
lingual occlusal line
line extended thru all lingual cusps of max posterior teeth: demarcation between outer and inner aspects of centric cusps
LO line occludes with Mandibular teeth
LO line (maxillary)

BO line of mandibular
CF line
line thru all central developmental grooves of max and mand posterior teeth: normal arch this is continous
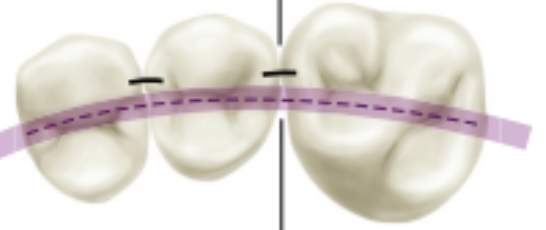
top is buccal embrasure area, bottom is lingual embrasure area
CF line: proximal relationships: ___ lingual embrasure area, __ buccal embrasure area
which acts a major spillway for food being masticated?
larger, smaller
lingual
centric cusps contacting opposing: contact in two areas? (from facial aspect)
CF areas
grinding of pestle in mortar
only certain areas contacting at one time, other areas are spillways
as mandible shifts, new spillways = efficient
Marginal ridges/embrasures
like cusp tip contacting flat surface
Spillways in all directions
circular area around true cusp tip with radius of 5 mm provides contact area with opposite tooth surface
marginal ridge
slightly raised convex areas at mesial and distal borders of occlusal surfaces that join with interproximal surface of teeth
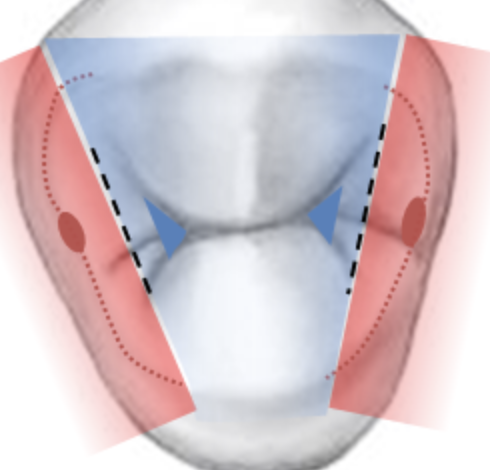
when the normal interach tooth relationship is viewed lateral, each tooth occludes with ?
Two exceptions?
2 teeth
mandibular central incisors and and max 3rd molar
normal relationship, the mandibular teeth are positioned slightly ___ + __
lingual and mesial to counterparts