Immune System
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is the skin's role as a physical barrier?
A thick, waterproof layer of cells that is difficult for microbes to breach.
What role do secretions like tears and saliva play in defense?
Constant flushing of surfaces, making it harder for bacteria to attach; saliva swallowed goes into stomach acid.
What is the benefit of having a normal microbiome?
Microbial antagonism.
What are the two main goals of the innate immune system?
To eliminate or kill any invading pathogen and to alert the adaptive immune system that it might be needed.
What are two key characteristics of the innate immune system?
They are nonspecific and inducible.
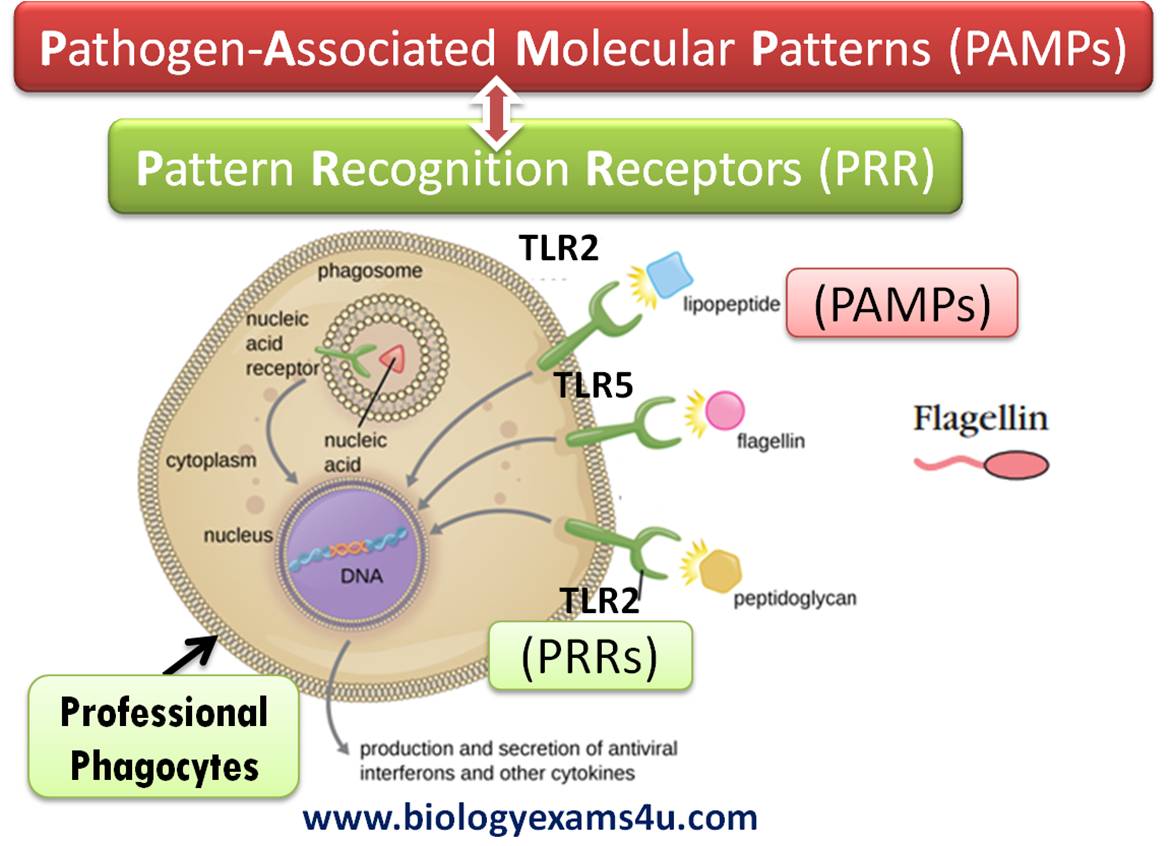
What are PAMPs?
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; common molecules or motifs on classes of microbes, like peptidoglycan.
How do immune cells communicate?
Immune cells release cytokines to communicate with other immune cells.
Why is it critical for phagocytes to differentiate between self and non-self?
They must be able to tell the difference between self and non-self to prevent autoimmunity and damage to the body's own cells.
What characteristics can phagocytes look for to identify pathogens?
Structures or molecules found exclusively on bacterial cells, fungi, or viruses, but not in human cells.
How do innate immune cells recognize PAMPs?
By using Toll-like Receptors (TLRs).
What is the innate immune system meant to do?
To kill any invading pathogen and to alert the adaptive immune system that it might be needed
What patrols for and finds foreign bodies within the body.
The pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as toll-like receptors (TLRs), patrol the interstitial space, sensing any foreign material that may enter the body.
Give three specific characteristics the immune system can look for within a cell.
Peptidoglycan, LPS, and mycolic acid
Name three structures a phagocyte can check for when determining what is self and what is not.
Plasmids, bacterial DNA, double stranded RNA
How does the phagocytosis reaction begin?
Toll-like receptors bind to the PAMP on the surface of a microbe triggering that response.
What does pus consist of.
Neutrophils die at site of infection and that accumulation is pus.
Besides phagocytosis, what power do macrophages and dendritic cells have in addition to it?
An antigen presentation.
What are the two professional antigen presenting cells?
Macrophages and dendritic cells.
Is phagocytosis the goal of a natural killer cell?
Releases poisons.
What results from cellular toll like receptors.
Trigger the production of interferon.
What is the outcome disparity from stimulating intracellular and extracellular toll like receptors triggers?
Extracellular toll like receptors trigger phagocytosis. Cellular toll like receptors trigger the production of these molecules called interferon.
What is the topic of the last homework?
The last homework assignment is about vaccines.
What is the first line of defense in the immune system?
Physical and chemical barriers.
What is the second line of defense that surveys the body for threats?
Innate immune system.
What is the third line of defense that requires full activation and takes 7-10 days?
Adaptive immune system.
How are helper T cells activated?
Binding to antigen on MHC class two.
What confirmation signal do helper T cells make to give b cells the confirmation they need?
CD40L.
What type of infection is used as an example for how helper T cells are activated?
Bacteria in the respiratory tract.
Besides cytotoxic T cells, what is the other main actor in the adaptive immune system?
The B cells.
How many different ways are there to get rid of extracellular pathogens?
Five.
Where are B cells born and where do they mature?
Born and mature in the bone marrow.
How many B cell receptors does each individual B cell have on its surface?
A half million.
When does clonal selection take place?
When a B cell runs into antigen that it can bind with its B cell receptor.
Where do B cells run into antigen?
Secondary lymphoid tissue like lymph node.
Following clonal selection, what is the next step the B cell takes and what type of cell does that make it?
B cells are professional antigen presenting cells.
What happens when the B cell binds to the antigen?
Binds to the antigen, it's gonna trigger phagocytosis.
During partial b cell activation, what protein is made on the surface of the B Cell?
CD40.
What is the first physical connection that needs to be made to fully activate a b cell?
The T cell receptor binds to the antigen and MHC class two on the surface of the B cell.
What is the second physical connection that needs to be made to fully activate a b cell?
CD40L on the TH2 cell binds to the CD40 on the B cell.
After full b cell activation takes place, what process occurs next?
Clonal expansion.
What type of cell do B cells differentiate into?
Plasma cells.
What is the job of a plasma cell?
To make and release antibodies.
What are the five effector functions of antibodies?
Neutralization, opsonization, agglutination, complement activation, and ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity).
What are the long-lived parts of the immunological memory response?
Memory B cells and memory plasma cells.
What region determines which effector functions antibodies can carry out?
Constant region.
What are the three classes of antibodies the lecture focuses on?
IgM, IgG, and IgA.
What effector functions can IgM do?
Agglutination, opsonization and compliment activation.
What effector functions can IgG do?
All five effector functions.
What effector functions can IgA do?
Agglutination and neutralization.
Where can IgG antibodies be found?
In bodily tissues and serum.
Where can IgA antibodies be found?
On mucosal membranes.
What is memory a combination of?
A combination of all of those adaptive cells.
What are the three types of memory cells that the lecture focuses on?
Memory plasma cells, memory B cells, and memory T cells.
What it is the first time that you're exposed to an antigen called?
Primary response.
What is a secondary response?
Second time your immune system is responding
What is a fever caused from when getting a vaccine?
Cytokines being released from cells.
What does an active immune response require?
Requires the activation of your adaptive immune system.
What is passive immunity?
There is some sort of immunity, but you don't have an adaptive immune response, you don't have any of those memory cells