Hydrologic Cycle (Water Cycle)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
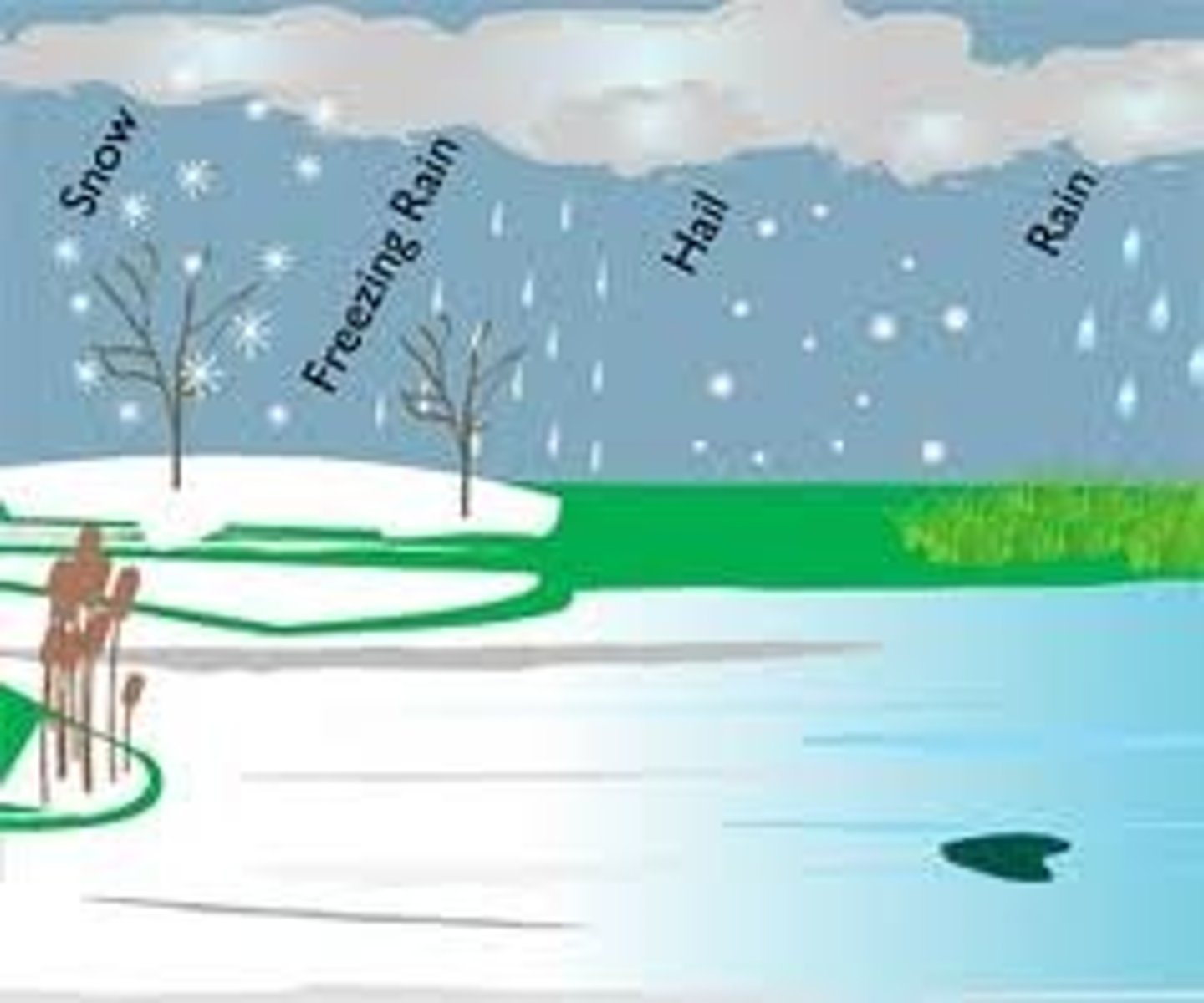
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface like hail, snow, sleet, rain;clouds get heavy and the air cannot hold it anymore
evaporation
The change of a liquid to a gas; the sun heats energy up and turns water into vapor(gas)

condensation
Gas to Liquid; gas gets colder and changes back to liquid , forming clouds

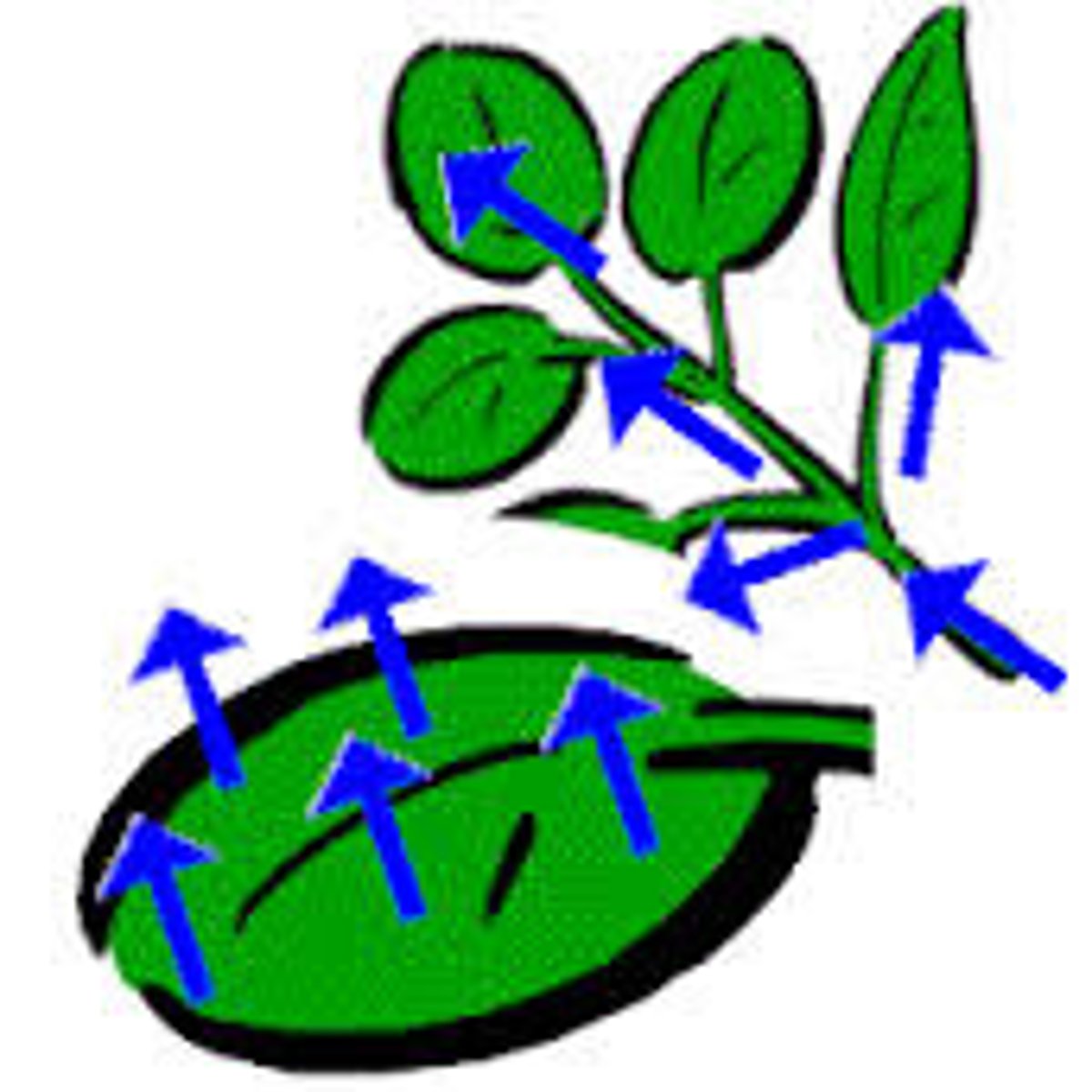
transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant gives of purified water to be evaporated
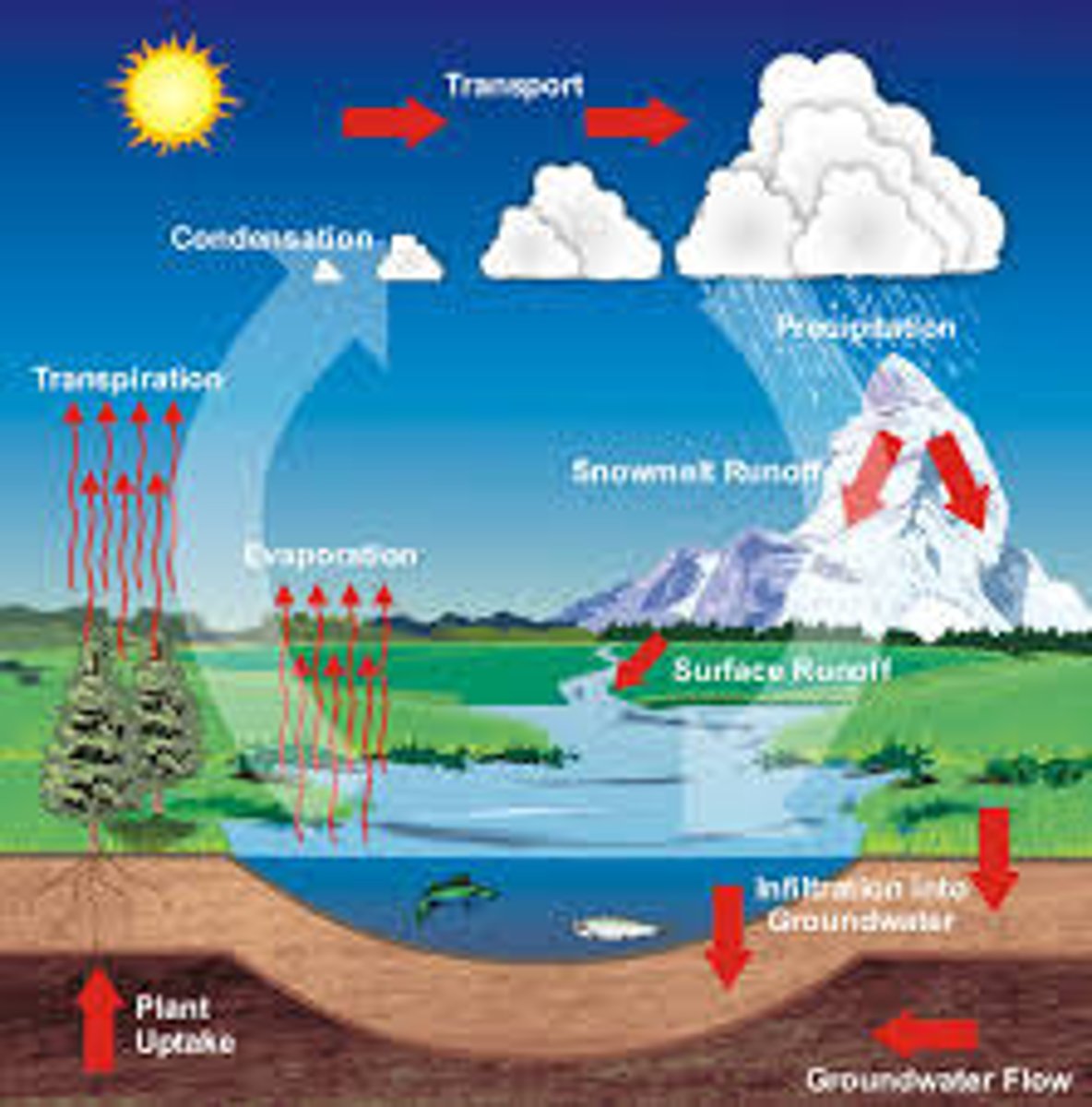
hydrologic cycle (water cycle)
The cycle through which water in the hydrosphere moves; includes such processes as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and surface and groundwater runoff and infiltration
infiltration (seepage)
Flow of water from the land surface into the subsurface; rain water soaks into the ground soil and can get into the groundwater
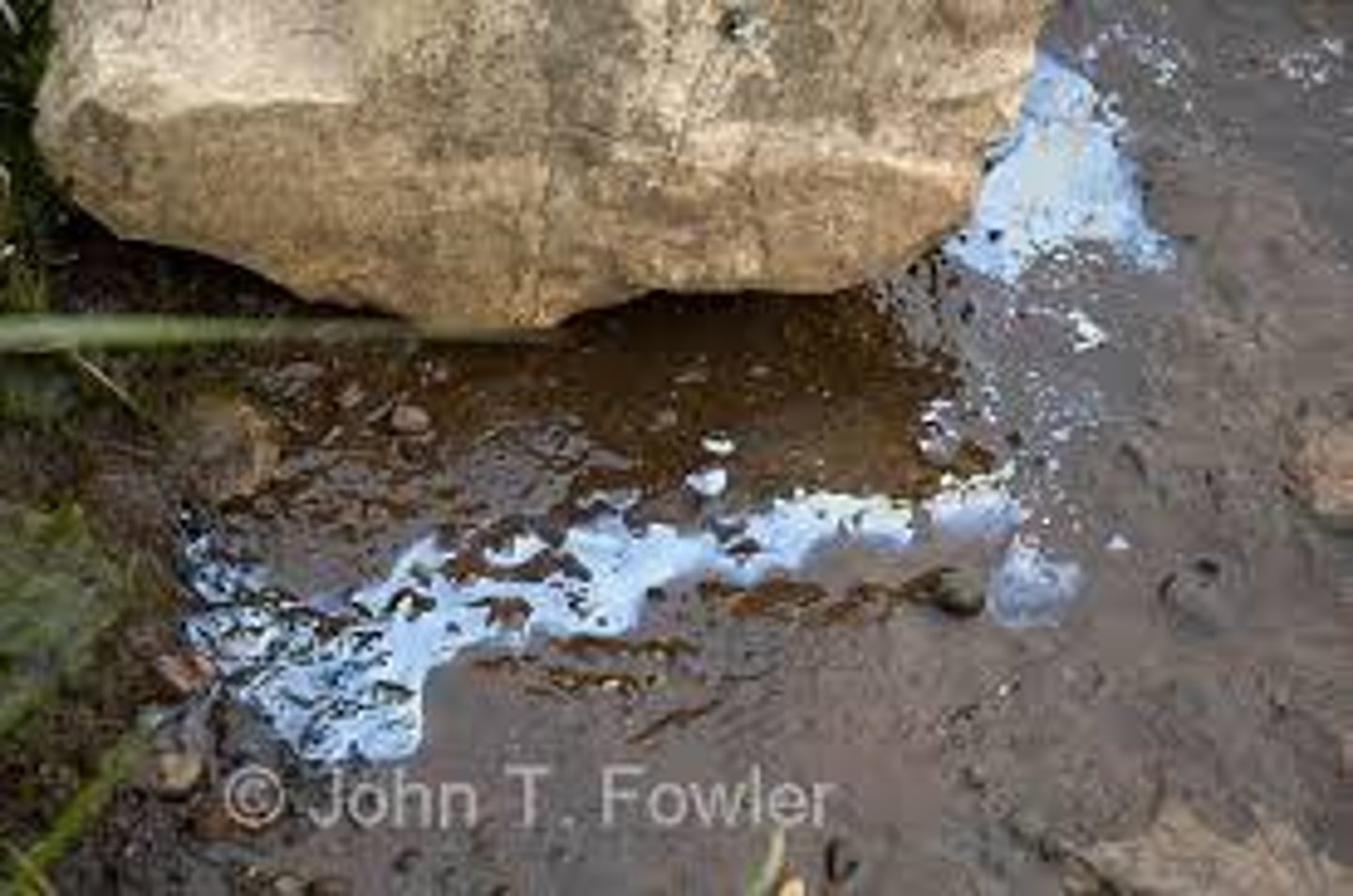

runoff
Part of the water cycle where an excess of water runs down and does not sink into the soil and eventually makes it to the rivers, lakes, and oceans.
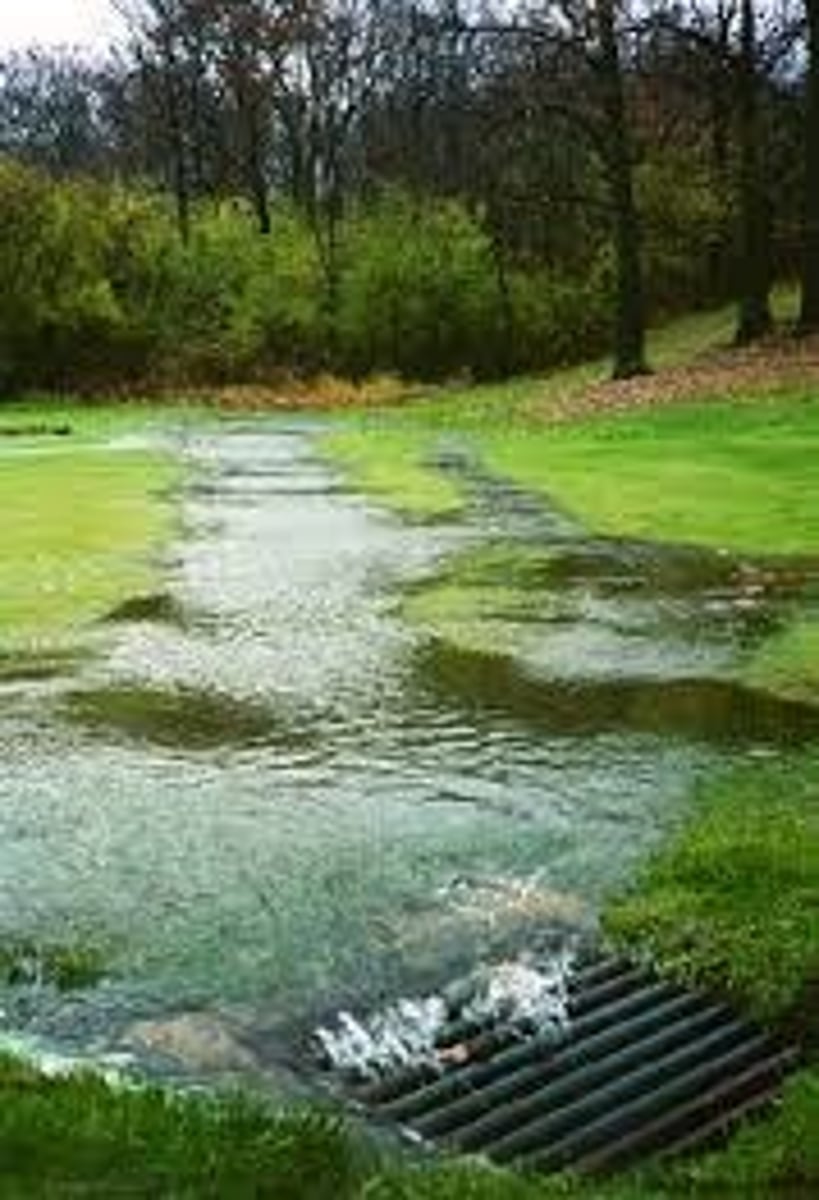

root uptake
Plant roots pull water out of the ground

meaning of the prefix "hydro"
water
Aquitard
Impermeable earth materials that cannot collect/store water.
reservoir
A lake that stores water for human use.
Permeable
When materials allow liquids to flow through it.
Impermeable
When materials do not allow liquids to flow through it.
Aquifer
Permeable earth materials that collect and store water.
infiltration
When water seeps or soaks through soil or sand (or any permeable material)
contaminant
Something that causes impurity or pollutes
atmosphere
A mixture of gases that surrounds a planet or moon.
sun
A typical star that is source of light and heat for plants in the solar system
water vapor
Water in the form of a gas.
groundwater
..., water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers
5 uses of water
1) Drinking 2) Cleaning 3) Livestock 4) Water energy 5) Industrial