C10 - Using Resources
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
What do humans use natural resources for?
energy and fuels for warmth
building materials for shelter
food through farming
fuels for transport
materials for clothing
Why do people argue that we live unsustainably?
Because the human population is growing rapidly, and many humans argue that humans are using up the earths finite resources at rate which is too fast.
What can be done to ensure humans meet their needs?
Chemists try to improve…
Agriculture
Industrial processes
What does sustainable mean?
The future generations of humans must also be able to meet their own needs.
What is a finite resource?
A resource that can only be used once and is limited supply.
Where do finite resources come from?
The Earth’s…
Crust
Oceans
Atmosphere
Why do we use finite resources?
They can be processed to provide energy and useful materials.
What do renewable resources mean?
Resources not right now in the foreseeable future.
Why do renewable resources not run out?
Either because…
The reserves are huge
The current rate of extraction is low
Crude Oil - Key Points (4)
Found in the Earth’s crust
Finite
Processed through fractional distillation and cracking
Produces a wide variety of useful chemicals
Is sea water a renewable of finite resource?
Renewable, as there is such a large amount that humans will not use it all up.
Sometimes, natural products can be supplemented/replaced by ____________ or ________ products.
Give an example.
agricultural or synthetic
e.g. until 1910, all fertilisers were obtained by natural resources such as manure.
What has the Haber Process allowed humans to do?
produce fertilisers from nitrogen in the air
allowed synthetic fertilisers to be produced
What have Synthetic Fertilisers allowed humans to do?
Have allowed intensive farming to become widespread → we can produce enough food to support the growing world population.
Copper is a resource which is commonly ____________.
exploited
How has copper exploitation changed with time?
As time passed, more copper was exploited.
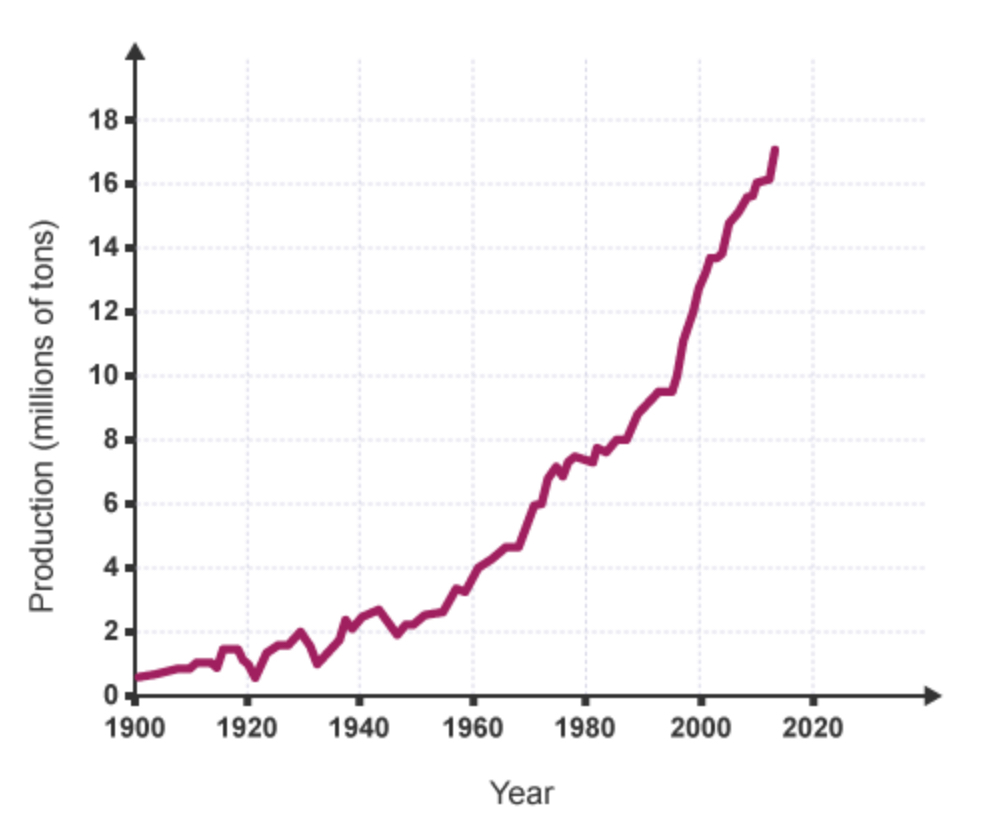
How has the global population changed over time?
The population increased.
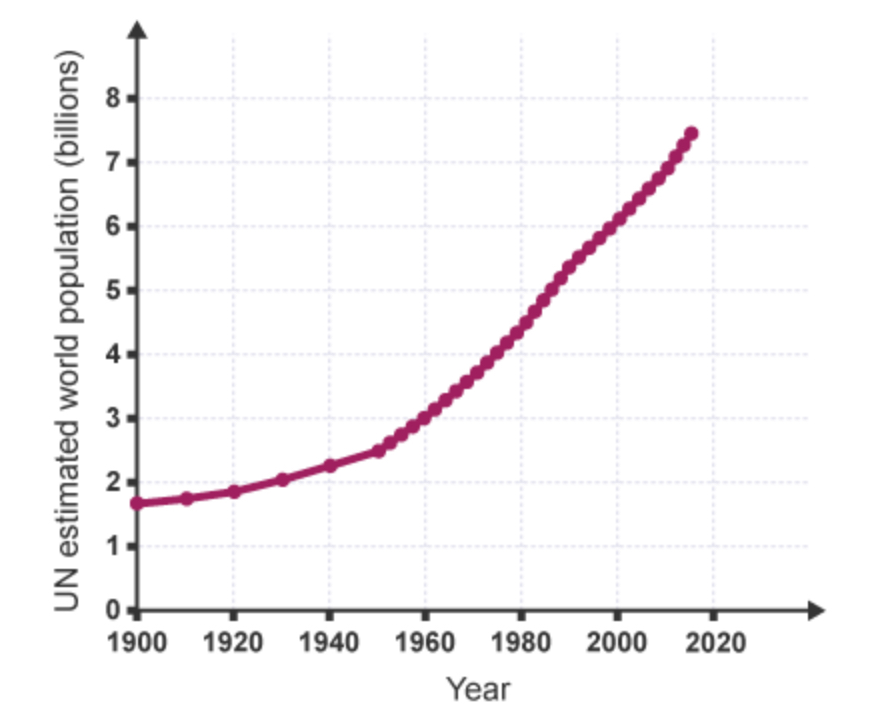
What is the relationship between the increase in global population and the demand for copper?
positive correlation
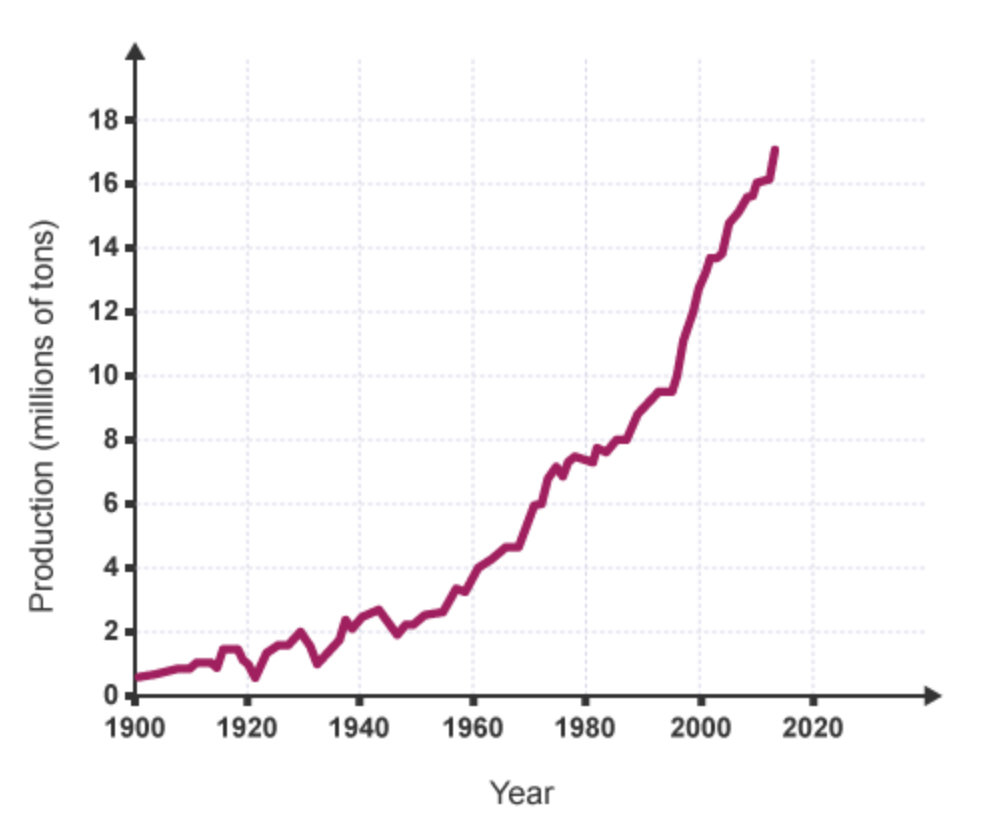
By what factor did the production of copper increase from 1920 and 1995?
By a factor of 10.
(From approx. 1mil → 10mil tonnes per year)
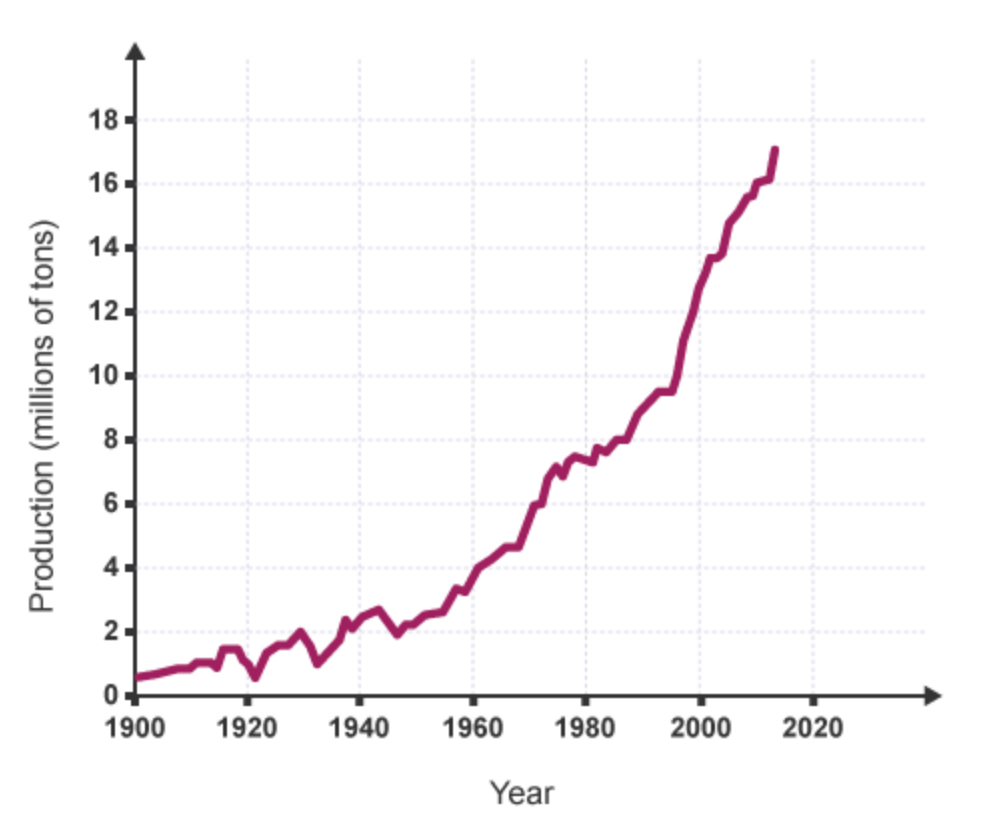
What is potable water?
Water that is safe to drink.
Potable water is pure/impure.
Impure
It almost always contains dissolved impurities.
What are the requirements for water to be potable?
Sufficiently low levels of…
dissolved salts
microbes
Why must potable water have low levels of dissolved salts?
Because they can be harmful for humans.
Why must potable water have low levels of microbes?
They can cause illness.
The methods used to make water potable depend on…
…where you live.
In the UK, ____ provides enough freshwater to meet the needs of the population.
rain
Which is more difficult to start with, fresh water or salt water? Why?
Salt water.
Removing the large amounts of sodium chloride present requires a lot of energy.
When do water reserves sometimes run low in the UK?
In the summer.
How is the summer issue of water reserves running low overcome?
People are encouraged to conserve tap water through hosepipe bans.
Where does rainwater collect? (3)
Rivers
Lakes
In rocks underground
What is most potable water in the UK produced by?
Naturally occurring freshwater
How is the naturally occurring freshwater made safe to drink?
Passing the water through filter beds to remove insoluble particles.
Sterilising the water to kill microbes. (chlorine, ozone or UV light)
What is desalination?
The removal of salt from water. This is an energy-intensive process.
What is desalination also known as?
Desalinisation
What is more difficult, making potable water form freshwater reserves or sea water? Why?
Sea water, because removing the large amount of sodium chloride (35g/kg of sea water) requires a lot of energy.
How can desalination be done? (2)
distillation
reverse osmosis
How can desalination be done by distillation?
Sea water is heated until it boils.
The salt remains in the liquid, and the steam is pure water.
The steam is cooled and condensed to make potable water.
What are the disadvantages of desalination by distillation?
Lots of energy needed to boil the water
Lots of energy needed to cool steam to condense it
Waste water is very salty - difficult to dispose of sustainably, may harm marine ecosystems.
How can desalination be done by reverse osmosis?
Water is put under high pressure and passed through a membrane with tiny pores through it.
The pores allow water molecules through, but prevent most ions and molecules passing through.
What are the disadvantages of desalination by reverse osmosis?
requires expensive membranes
produces a large volume of waste water - low efficiency
Which method of water purification would be best suited to a country in the Middle East which has a large amount of fossil fuel reserves?
Distillation - country would be able to use fossil fuels to provide the energy needed at a relatively low cost.
Where does waste water comes from?
homes
industry
agriculture
What happens to waste water?
It is treated, then released into the environment.
Why must waste water first be treated before being released into the environment?
because pollutants must be present, such as…
human waste contains harmful bacteria and high levels of nitrogen compounds → can harm aquatic ecosystems
industrial waste may contain harmful chemicals, eg. toxic metal compounds
agricultural waste may contai fertilisers or pesticides, which can disrupt ecosystems
What else must be treated?
sewage
Describe the process of sewage treatment. (3)
screening and grit removal to remove larg particles.
sedimentation allows tiny particles to settle out from still water, which produces sewage sludge and effluent (the liquid which remains on top)
the sewage sludge is digested anaerobically by specific bacteria
the effluent is treated with aerobic bacteria to reduce the volume of solid waste
What is the required practical for this topic?
Analysis and purification of water
What is a life-cycle assessment?
A 'cradle-to-grave' analysis of the impact of a manufactured product on the environment.
What is a life-cycle assessment also known as?
a life-cycle analysis or LCA
What are the main stages of an LCA?
extracting and processing the raw materials needed
manufacturing the product and its packaging
using the product during its lifetime
disposing of the product at the end of its useful life
What are the main stages of an LCA - simplified?
raw materials
manufacture
use
disposal
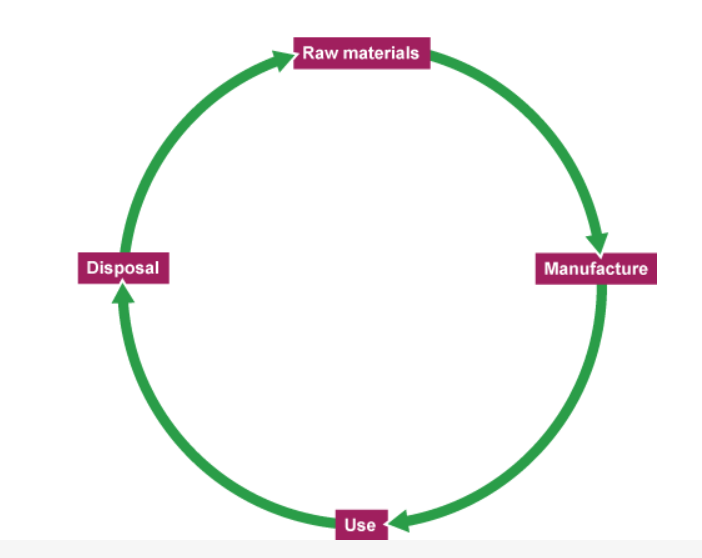
At all stages, an LCA is liely to include information about…
the use of…
energy
transport of materials
the release of waste substances into the environment.
Where do the raw materials come from?
Earth’s crust
Earth’s atmosphere
Earth’s oceans
What impact does obtaining these raw materials have on the environment?
using up limited resources, eg. ores and crude oil
damaging habitats through quarrying, mining or felling trees
What impact does manufacturing have on the environment?
using up land for factories
the use of machines and people
What impact does the use of materials have on the environment?
This depends on the type of product - the impact of a car and a wooden chair will be very different.
What impact does the disposal or materials have on the environment?
using up landfill sites
whether any or all or the product can be recyled or reusedDD
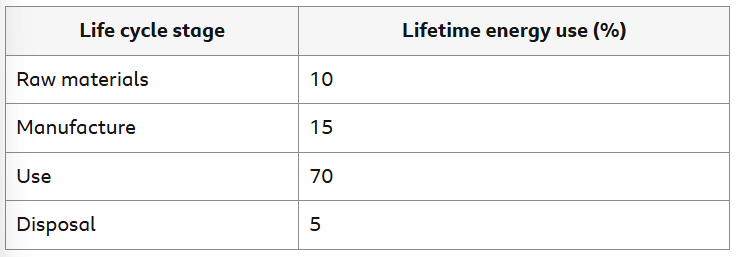
What are the typical percentages of energy used for each LCA stage?
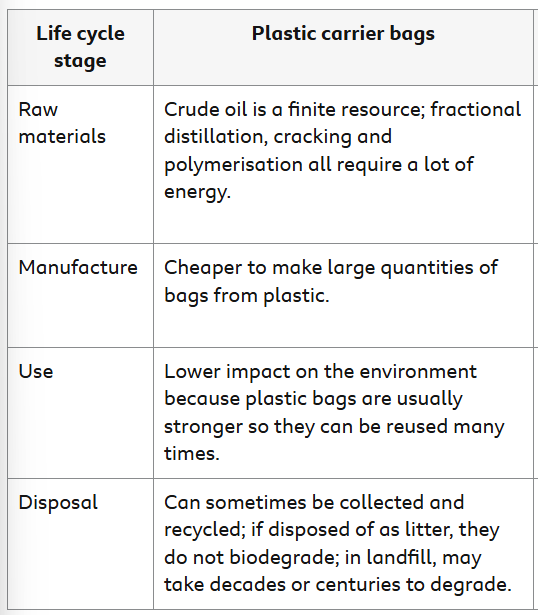
LCA - Plastic Carrier Bags
LCA - Paper Carrier Bags

What are the benefits of LCAs?
easy to work out accurate numerical values, eg. amount of energy needed
What are the disadvantages of LCAs?
some parts require judgements, eg. the effect of pollutant. this means it is a subjective process
there may be bias, eg. only some part of environmental impact
Which materials use mostly limited natural resources to be made? (5)
metals
glass
building materials
clay ceramics
most plastics
Why are reusable items beneficial?
It saves enerrgy and reduces the impact on the environment.
Are glass bottles good for the environment?
Typically, yes - they only need to be washed and sterilised before theu can be filled again.
Other products cannot be reused in this way, but they can be recycled.
What are the advantages of recycling?
fewer quarries and mines needed to extract finite reserves of metal ores
less crude oil needs to be extracted from the crust as a raw material for making plastics
less energy is needed for recycling compared with making a new product from natural resources, so the emission of greenhouse gases is reduced
less waste disposed of in landfill
How much energy is saved when recycling 2 types of metal VS extracting them from their ores?
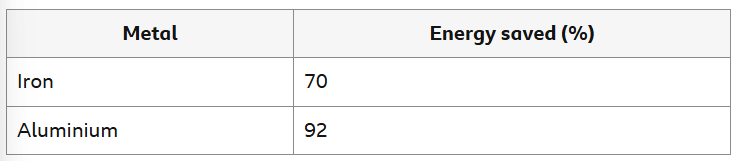
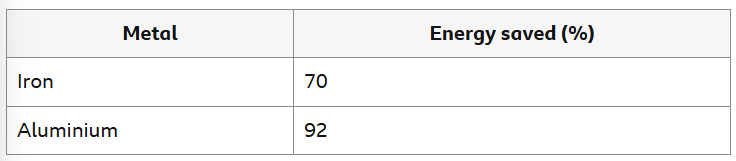
Can you explain the difference between percentages?
Aluminium is extracted from its ore using electrolysis but iron is extracted by heating with carbon. Electrolysis uses more energy, so more energy is used to extract aluminium in the first place. Aluminium has a lower melting point than iron, so less energy is needed to melt it during recycling.
What are the disadvantages of recycling? (3)
the collection and transport of used items needs organisation, workers, vehicles and fuel
it can be difficult to sort different metals from one another
the sorted metal may need to be transported to where it can be turned into ingots
What are ingots?
A block of solid metal, usually rectangular in shape.
The amount of sorting required depends on… (2)
the purity of the mixture of metals
how pure you need the final recycled metal to be
What is copper used for?
Copper can be used for electrical wiring, but this requires a very high purity.
How would you achieve very pure copper through recycling?
The waste copper needs processing before being melted again into copper for wiring.
What is an example of a metal that does not need to be of such high purity?
Steel, when it is being used for construction.
How is steel for construction made through recycling?
Scrap iron can be easily added to the steel furnace when it is being made, reducing the cost of making steel from iron ore.
Describe a simple way to separate aluminium from iron.
A magnet or electromagnet will attract iron but not aluminium.
The Earth's supply of metal ores is _______.
limited
What is an example of a limited metal ore? How has this been overcome?
High-grade copper ores are becoming harder to find and mine.
There are some alternative methods to extract metals from low-grade copper ores that use living organisms.
What are the methods of extracting metals from low-grade metal ores?
phytomining
bioleaching
processing the metal compounds
What is phytomining?
Using plants to absorb metal compounds from the ground through their roots. The plants are then burned to produce an ash containing a high concentration of the metal compounds.
What is phytomining also known as?
phytoextraction
Explain the method used for phytomining.
plants are grown on a low-grade ore
the plants absorb metal ions through their roots and concentrate these ions in their cells
the plants are harvested and burnt
the ash left behind contains metal compounds
What are the advantages of phytomining? (3)
reduces the need to obtain new ore by mining
conserves limited supplies of high-grade ores
reduces the amount of rock waste that must be disposed of after traditional mining
What are the disadvantages of phytomining?
slow process
Suggest reasons why phytomining reduces damage to the environment.
Mining for metal ores involves quarries, which are large holes in the ground. These create noise, dust and traffic. They also destroy natural habitats. Phytomining reduces the need for mining and reduces this damage.
What is bioleaching?
Using bacteria to extract metals from their ores.
Explain in-depth how bioleaching works.
Certain bacteris can break down low-grade ores to produce acidic solution containing copper ions.
The solution is called a leachate.
The metal compounds can then be processed.
What are the advantages of bioleaching?
doesn’t need high temperatures
What are the disadvantages of bioleaching?
produces toxic substances, including sulfuric acid, which damages the environment
How can copper be produced by a copper sulfate leachate?
Iron is more reactive than copper, so it can displace copper from the leachate.
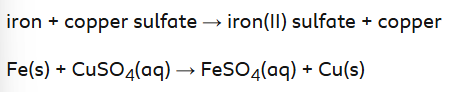
What are the advantages of this displacent method?
Iron is cheaper than copper, so the use of scrap iron is a cost-effective way to produce copper from the leachate.
What is an alternative method for producing copper from this leachate?
The copper compounds ca be dissolved and the solution electrolysted to produce coper metal.
Metals can _______ in air to form _________.
oxidise
metal oxides
What happens to sodium if it is cut or scratched?
I’m It’s freshly exposed shiny surface rapidly turns down as a thin layer of sodium oxide forms.
sodium + oxygen → sodium oxide
Metals oxidised at different ______.
speeds
Some do not oxidise at all (unreactive metals, such as gold).
What does corrosion mean?
When chemicals in the water dissolve minerals in the rocks causing them to break up.
What is another way to say corrosion?
Solution
When does corrosion happen?
When a metal continues to oxidise. The metal becomes weaker overtime and eventually all of it may become metal oxide.
What is a common type of corrosion?
rusting