chapter 8 (incomplete)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Group 2 metals involvement in redox equations
in group 2 metals they all oxidise to form 2+ electrons due to the outer s2 electron configuration and another species will gain these and be reduced.
redox reactions with oxygen involving group 2 elements
all react with oxygen to form a metal oxide gen form MO.
magnesium burns with a white light and forms white magnesium oxide.
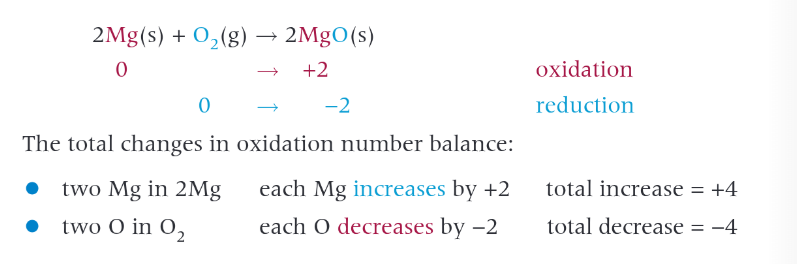
redox reactions with water involving group 2 elements
react to form an alkaline hydroxide with gen formula M(OH)2, and hydrogen gas. water and magnesium react slowly but as you go down the group reactivity increases.
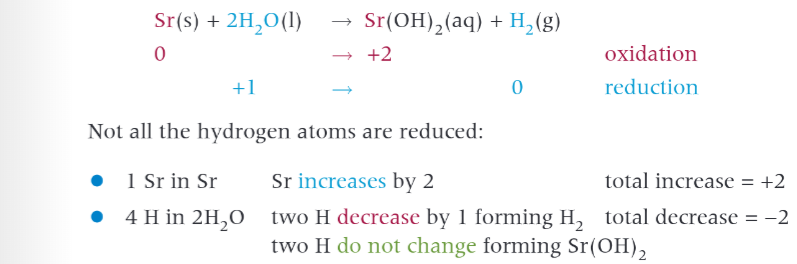
redox reactions with dilute acids involving group 2 elements
react to form a salt and a hydrogen.
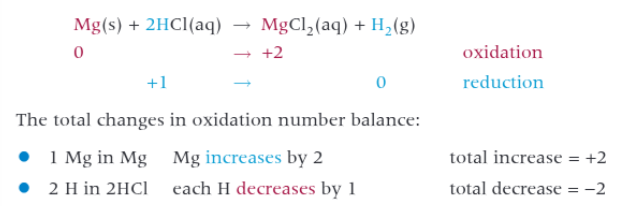
describe the trend of reactivity of group 2 in terms of ionisation energies
the group 2 elements react by loosing there 2 outer electrons and the ionization energy decreases down the group as a result of increasing atomic radius and electron shielding
group 2 oxides reactions with water
release hydroxide ions OH- and form alkoline soltions of the metal hydroxide.
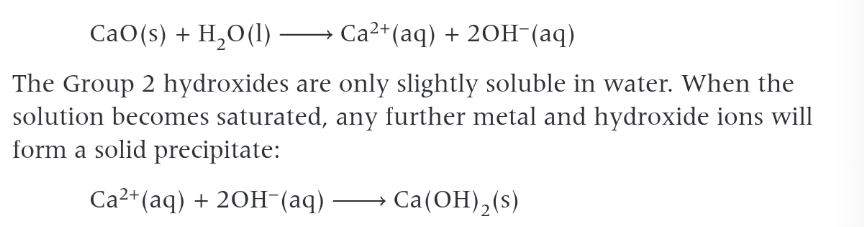
how does the solubility of the hydroxides affect the trends
it increases down the group, so the hydroxides contain more OH- ions and are more alkaline. Mg(OH)2 has a ph about 10 and then Ba(OH)2 has a greater concentration of OH- ions so Ph is about 13

uses of group 2 compounds as bases
medicine-often used as anticids to treat acid indigestion
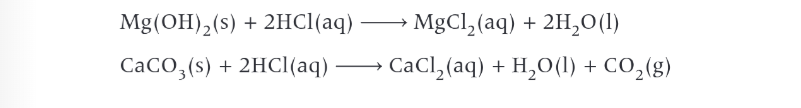
uses of group 2 compounds as bases
agriculture-calcium hydroxide to increase the pH of acidic soils. calcium hydroxide neutralises acid in soil and forms neutral water
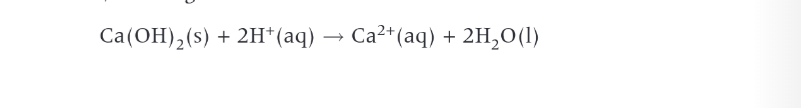
Trends in boiling point in halogens
at RTP all halogens exist as diatomic molecules. group contains elements in all three states moving from gas to solid as you go down the group. in solid state halogens form lattices wt simple molecular structures
redox reactions relative to halogens
electron config- s2p5. In redox reactions, each halogen is reduced gaining one electron to form a 1- halide with the electron config of nearest noble gas
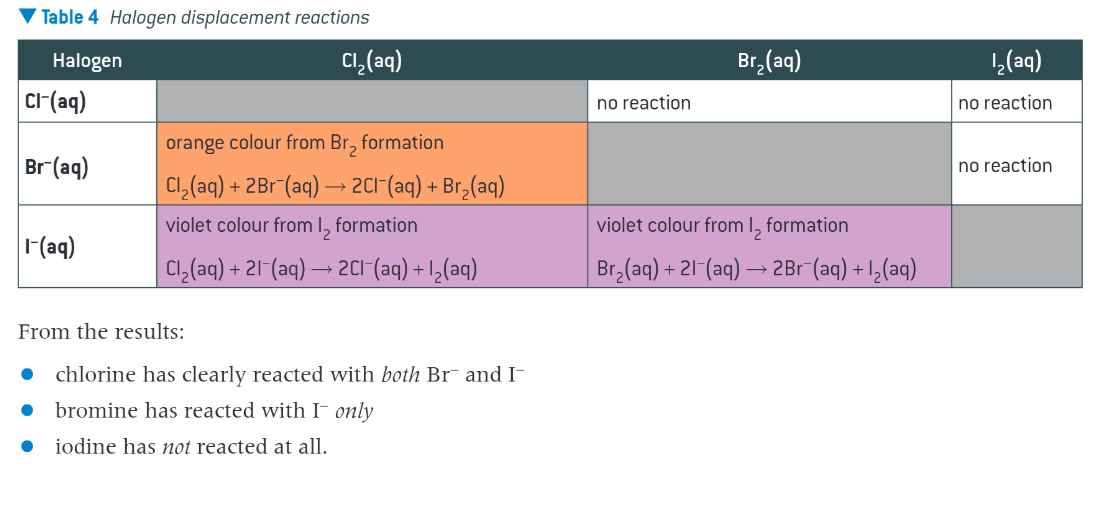
What do halogen-halide displacement rwactions show
results show that the reactivity of halogens decrease down the group. A solution of each halogen is added to an aqueous solution of the other halides. If the halogen added is more reactive than the halide present
a reaction takes place,halogen displaces the halide from solution
solution changes colour
what can you use to distinguish between iodine and bromine in water
organic non-polar solvent such as cyclohexane

reactivity in halogens explained

whats disproportination
redox reaction where the same element is oxidised and reduced
example of a disproportionation reaction
chlorine and water. 2 products are acids chloric acid and hcl. bacterial killed by chloric acid. also acts as a bleach
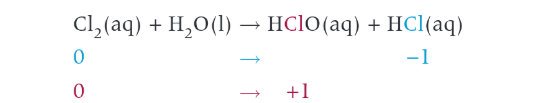
example of a disproportionation reaction
reaction of chlorine with cold, dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide
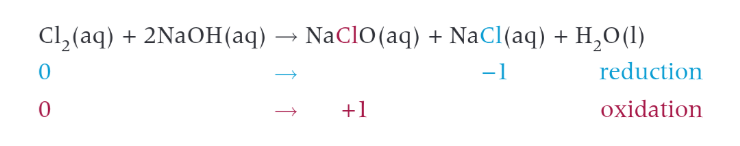
benefits and risks of using chlorine in water treatment
benefits-kills bacteria in water
risks-is a toxic gas, respiratory irritant, if reacted with hydrocarbons can form decayed vegetation which can cause cancer
however the benefit of having clean water outweighs the risk because having unclean water could be more deadly.
another test for halide ions
aqueous halide ions react with aqueous silver ions to form precipitates of silver halides followed by ammonia.
