Magma Composition
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
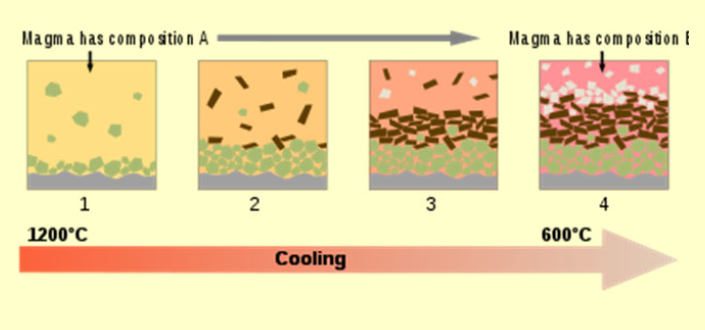
What is fractional crystallization? How does it alter the composition of magma?
Fractional crystallization is the process where, as magma cools, minerals with high freezing points crystallize first and settle out, changing the composition of the remaining melt to become more felsic
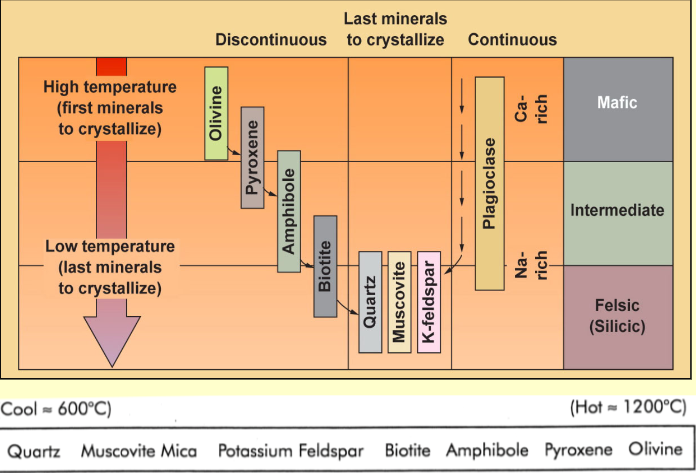
What does Bowen's reaction series illustrate?
Bowen's reaction series describes the order in which different minerals crystallize from a cooling magma. Mafic minerals crystallize first at higher temperatures, and as the magma cools, more felsic minerals begin to form
Will molten material cool faster intrusively or extrusively? Explain why
Molten material will cool faster extrusively because lava at the Earth's surface is exposed to the cooler atmosphere or water, allowing for rapid heat loss compared to magma that is insulated beneath the surface
What does the grain size (texture) of a crystalline igneous rock indicate about its cooling history?
Coarse-grained (phaneritic) textures indicate slow cooling at depth (intrusive), allowing large crystals to grow. Fine-grained (aphanitic) textures indicate rapid cooling at the surface (extrusive), resulting in small crystals

Coarse-grained (phaneritic)
textures indicate slow cooling at depth (intrusive), allowing large crystals to grow.

Fine-grained (aphanitic)
textures indicate rapid cooling at the surface (extrusive), resulting in small crystals

Describe porphyritic texture in igneous rocks. What does it suggest about cooling history?
Porphyritic texture has both large and small crystals. This indicates a two-stage cooling history: slow cooling at depth allowing large crystals to form, followed by rapid cooling at or near the surface resulting in a fine-grained matrix

What are glassy textures in igneous rocks and what do they indicate about cooling rates?
indicates extremely rapid cooling where crystals did not have time to form

What are vesicular textures in igneous rocks and what do they indicate about cooling rates?
Vesicular texture contains holes left by gas bubbles that were trapped during rapid cooling

What is pegmatitic texture?
Very large (> 2.5 cm) crystals Cooling is quick, but form from water-rich melts—large crystals grow rapidly

What are fragmental (pyroclastic) textures in igneous rocks? How do they form?
Fragmental (pyroclastic) textures consist of chunks and shards of volcanic material that have been packed, welded, or cemented together. They form from explosive volcanic eruptions
What are dikes? How do they differ in orientation relative to existing rock layers?
tabular intrusive igneous structures. Dikes cut across existing rock layers (typically vertical or subvertical)
What are sills? How do they differ in orientation relative to existing rock layers?
tabular intrusive igneous structures sills are injected parallel to pre-existing layers (typically horizontal)
Define a pluton
A pluton is an irregular or blob-shaped intrusion of igneous rock
Define a batholith.
A batholith is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock composed of multiple plutons
How do sedimentary rocks form from pre-existing rocks?
Sedimentary rocks form from grains that break off pre-existing rocks through weathering and are then compacted and cemented together