(cestodes) helminths quiz - microbio II (cls 542)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
cestode general characteristics
Least complex group of helminths
One big gut with one big reproductive system
Most are hermaphrodites--each segment has both male and female reproductive organs
Flat and bilaterally symmetrical, like fettuccini (ok drew)
Absorb nutrients from the host
intestinal cestode/tapeworm/flatworm illness
Few clinical symptoms/psychosomatic
Transmission by ingestion of cysticercus larvae in muscle of intermediate host
Diagnose by finding eggs, gravid proglottids, or scolex in the feces
Treatment:
enema, muscle relaxants (to release scolex), another enema
specific legal/illegal(?) drugs
niclosamide can be used as well
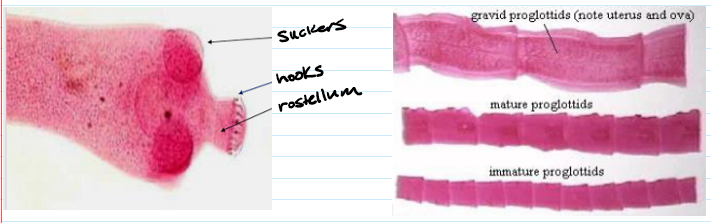
parts of a tapeworm
Scolex: head
Suckers & Hooks
Rostellum (not all have this)
Proglottids: individual segments
Strobila: string of proglottids
1/3 are mature, 1/3 are immature, 1/3 are gravid
Gravid: sexually mature and producing infective eggs
dibrothriocephalus latus / diphyllobothrium latum
AKA fish or broad tapeworm
Single worm infection
Lives in cold, clear, freshwater lakes
Incubation 5-6 weeks
No symptoms, but can lead to:
Diarrhea, abdominal pain
B12 deficiency (competes with host for the vitamin)
Leads to bowel obstruction
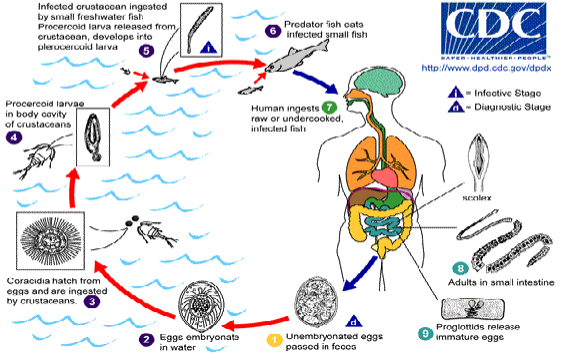
life cycle of dibrothriocephalus latus
unembryonated egg passed in feces
embryonate in water
coracidia hatch & are ingested by crustaceans
develop into procercoid larvae
crustacean ingested by small freshwater fish—larva released and develops into pleocercoid larva
predator fish ingests small fish
human ingests undercooked predator fish
adults live in small intestine & proglottids release immature eggs
key info about d latus / latum life cycle
Larvae live in the muscle of all intermediate hosts
Eggs released from definitive host r unembryonated
Definitive hosts: humans & other carnivores
Matures in water & hatches a coracidium larvae
Larvae eaten by 1st intermediate host--copepod
1st intermediate host eaten by second intermediate host--small fish
Second by the third & etc until a definitive host eats the last intermediate host
Larvae rapidly mature in gut of definitive host
Start laying eggs 2-6 weeks later
Adult can reach 20 meters (65 ft) and can live for decades
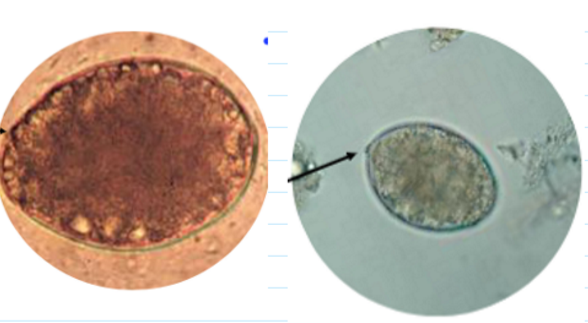
d latus eggs
Abopercular knob
Indistinct, non-shouldered operculum
Chicken shaped egg
55-75 um in length
d latus proglottids
Wider than they are long
Rosette uterus
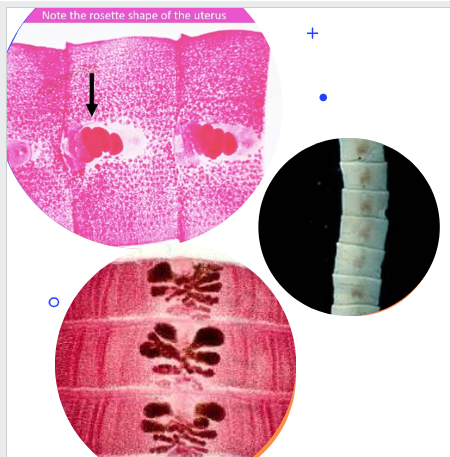
d latus scolex
Length: 3-10 mm wide
Two bothria sucking slits

taenia sp
aka cow and pig tapeworms
Intermediate hosts: Cows/pigs/dogs
Common
Single worm infection
Worldwide distribution
2-3 month incubation period
No symptoms, but may see:
Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, indigestion, occasional intestinal blockage
Can find proglottids in stool
Actively migrate out the anus
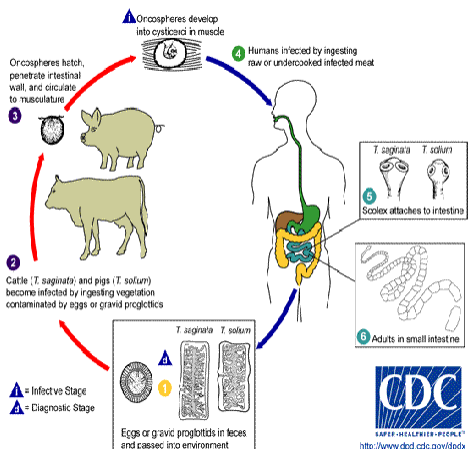
life cycle of taenia sp
eggs/gravid proglottids in feces are passed & end up in environment
cows and pigs become infected by eating vegetation contaminated w proglottids
oncospheres hatch, penetrate intestinal wall & circulate to musculature
oncospheres develop into cysterci in muscle
humans acquire thru ingestion of raw/undercooked meat
scolex attaches to intestine
adults live in small intestine
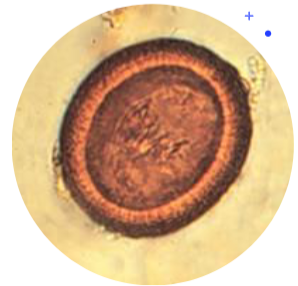
taenia sp eggs
30 x 45 um
Thick, smooth striated shell
Oncosphere has 6 hooks
May not always be visible
Immature larvae
Must find adults to speciate
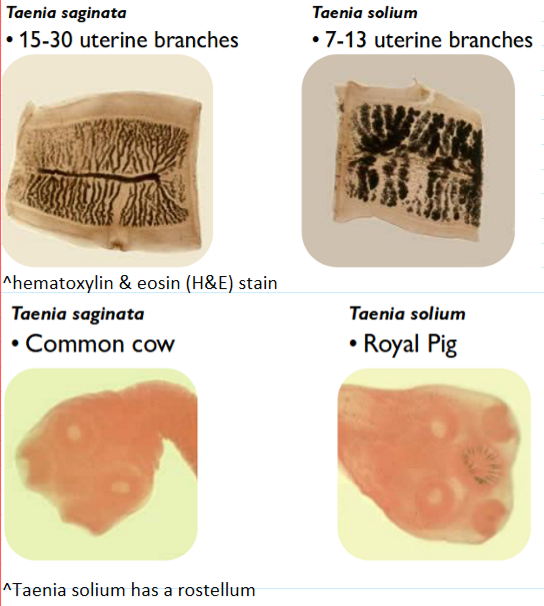
how to differentiate between T solium & saginata
T solium (pigs)
7-13 uterine branches
“royal pig”—crown looking rostellum
T saginata (cow)
15-30 uterine branches
no rostellum—”common cow”
(taenia sp) acid fast staining
Ziehl-Neelsen staining
Not super reproducible study data backing
The embryophore of T saginata is acid fast POS (?)
(taenia sp) cystercercosis
Humans become an accidental intermediate host
Human ingest eggs instead of larvae
Larval form encysts in human muscle, eye, brain etc
hymenolepis nana
AKA dwarf OR bridge club tapeworm
Most common tapeworm infection
Multiple worms present
Worldwide distribution—most common in SE region of US
2-3 weeks incubation
Adults live 4-6 weeks
15-40 mm long
Severe toxicity if worm burden is high
Severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, convulsions, epilepsy, insomnia, behavioral issues
routes of transmission for h nana (3)
through insect intermediate host (beetles and fleas)
human ingested embryonated egg (no intermediate host)
autoinfection (entirely human)
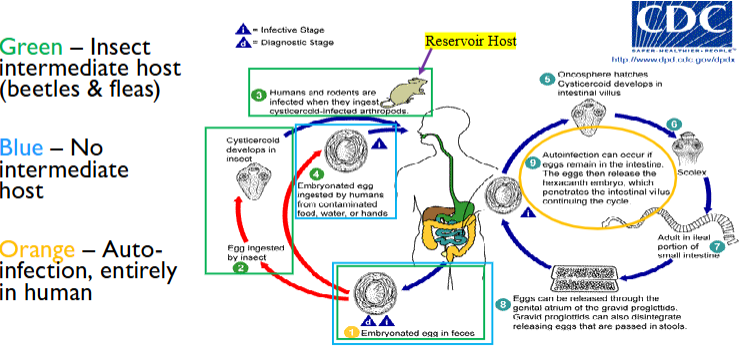
life cycle of h nana
embryonated eggs passed in feces
egg can be ingested by intermediate host or by humans from contaminated food/water/hands
if ingested by beetles, egg develops into cysticercoid
rodents/humans consume insect
autoinfection when eggs remain in intestine
release hexacanth embryo—penetrates intestinal vilus
adults live in ileal portion of small intestine
eggs released by gravid proglottids; proglottids can also disintegrate & release eggs that way
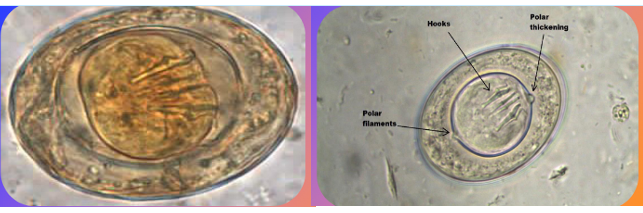
h nana eggs
Polar filaments present
More oval than round
Hooked oncosphere with 6 hooks
Size 47 x 57 um
hymenolepis diminuta
AKA rat tapeworm
Rare infection
Multiple tapeworms
Worldwide distribution
No symptoms
Does not cause hyper infections
Adult size: 20-60 cm
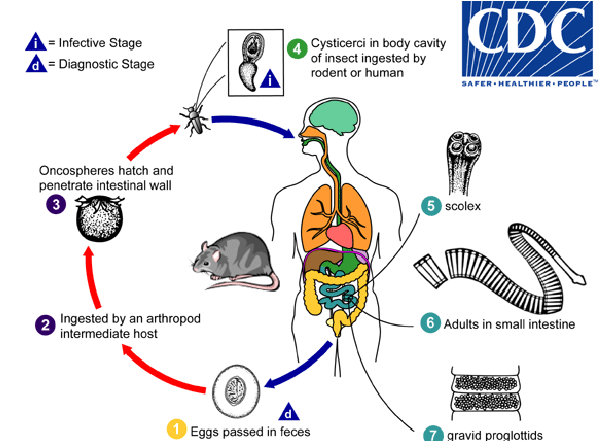
life cycle of h diminuta
embryonated eggs pass in feces
eggs ingested by an arthropod intermediate host
oncospheres hatch and penetrate intestinal wall
cysticerci in body cavity of insect ingested by rodent/human
scolex attaches to small intestine
adults live in small intestine
h diminuta eggs
58 x 85 um
More round than oval
No polar filaments
Shell looks thicker, may appear striated
Hooklets visible

dipylidium caninum
Rare infection ; common in kids
Multiple worms ; adults are 10-70 cm
Worldwide distribution
Acquired by ingested of infected fleas
Known by many names:
Flea tapeworm
Double-pored tapeworm
Cucumber tapeworm
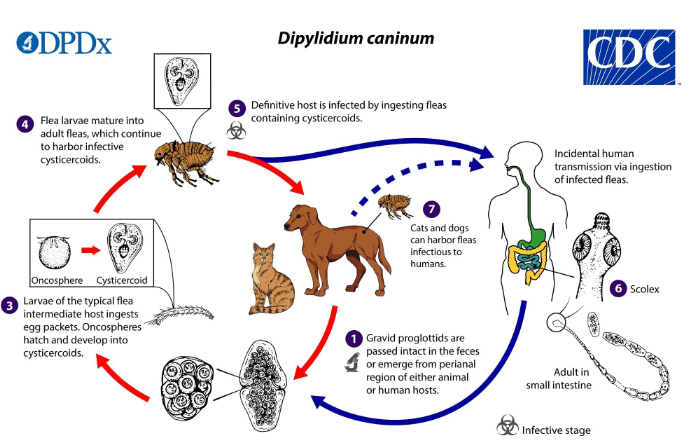
life cycle of d caninum
gravid proglottids are passed intact in the feces or emerge from perianal region of either animal/human hosts
larvae of flea (int host) ingests egg packets
oncospheres hatch and develop into cystercoids
definitive host infected by contaminated fleas
adults live in small intestine
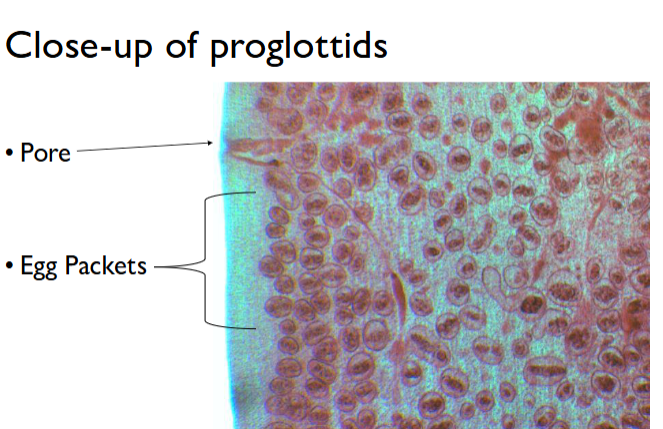
key info for d caninum life cycle
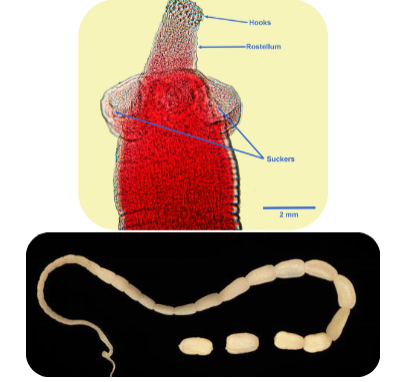
Scolex has suckers and hooks to cling onto the intestinal wall
Proglottids mature, fill with eggs and separate from the tapeworm
Pass out host with feces
Looks like grains of rice
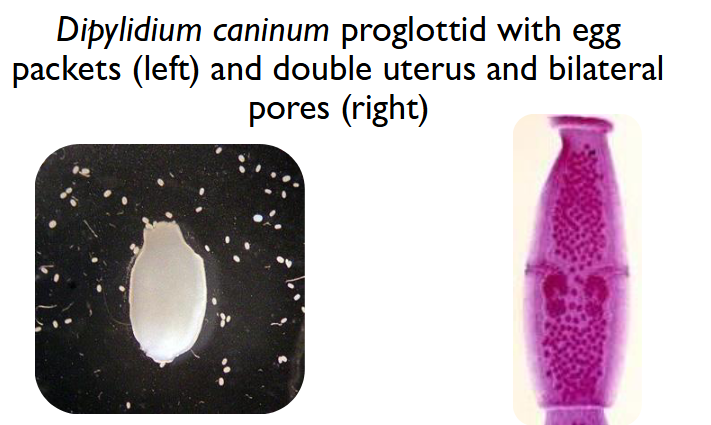
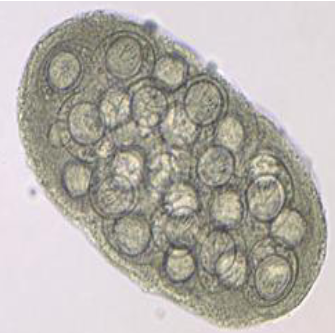
d caninum eggs (packet)
Eggs are 35-40 um
Found in packets usually containing 5-15 eggs
Must see packets to diagnose by eggs alone because they look like Taenia eggs
6 hooked oncosphere
Where the cucumber name comes from
answer the following about d latus:
What form is shed/acquired from the human?
If, an egg, is it embryonated or not?
If it is a larvae, what kind of larvae?
What hatches from the egg?
unembryonated eggs are shed in feces ; no larvae shed
coracidia/coracidium larvae hatch from egg (d latus)
answer the following about d latus:
intermediate host? reservoir host?
What is the infective stage that gets back into the human?
How does the infective stage get back into the human?
General info about what happens once it gets back into the human.
Where do adults live?
intermediate host: crustaceans/small fish; reservoir: predator fish/fish eating mammals
infective stage: pleocercoid larvae
humans ingest raw/undercooked infected fish
attaches to small intestine and release proglottids
adults: small intestine
answer the following about taenia sp:
What form is shed/acquired from the human?
If, an egg, is it embryonated or not?
If it is a larvae, what kind of larvae?
What hatches from the egg?
embryonated eggs/gravid proglottids are shed in feces ; no larvae shed
egg hatches into oncosphere/hexacanth larvae and then develops into cysticerci in muscle of intermediate host
answer the following about taenia sp:
intermediate host? reservoir host?
What is the infective stage that gets back into the human?
How does the infective stage get back into the human?
General info about what happens once it gets back into the human.
Where do adults live?
intermediate & reservoir: pigs/cows
humans can become both hosts when cystercosis develops
infective stage: cystererci
humans ingest raw/undercooked pork/beef
scolex attaches to intestine
adults: small intestine
answer the following abt h nana:
What form is shed/acquired from the human?
If, an egg, is it embryonated or not?
If it is a larvae, what kind of larvae?
What hatches from the egg?
embryonated egg in feces shed from humans ; no larvae shed
if in intermediate host, egg develops into cysticercoid ; if not, oncosphere hatches (autoinfection)
answer the following about h nana:
intermediate host? reservoir host?
What is the infective stage that gets back into the human?
How does the infective stage get back into the human?
General info about what happens once it gets back into the human.
Where do adults live?
intermediate: insects/grain beetles; reservoir: rodents/mice
infective stage: cysticercoid
humans consume cysticercoid infected arthropods or eat embryonated eggs or autoinfection occurs
scolex attaches to intestine & release eggs thru proglottids
adults: ileal portion of small intestine
answer the following about h diminuta:
What form is shed/acquired from the human?
If, an egg, is it embryonated or not?
If it is a larvae, what kind of larvae?
What hatches from the egg?
embryonated eggs passed in feces; no larvae shed
egg hatches into oncosphere & develops into cysticerci in insect ingested by rodent/human
answer the following about h diminuta:
intermediate host? reservoir host?
What is the infective stage that gets back into the human?
How does the infective stage get back into the human?
General info about what happens once it gets back into the human.
Where do adults live?
intermediate: arthopods ; reservoir: rodents
infective stage: cysticerci in insects
humans ingest insect
scolex attaches to small intestines & adults live there
gravid proglottids release eggs
answer the following about d caninum:
What form is shed/acquired from the human?
If, an egg, is it embryonated or not?
If it is a larvae, what kind of larvae?
What hatches from the egg?
gravid proglottids are shed from human/dogs ; no larvae shed
eggs hatch into oncospheres and develop into cysticercoids in fleas
answer the following about d caninum:
intermediate host? reservoir host?
What is the infective stage that gets back into the human?
How does the infective stage get back into the human?
General info about what happens once it gets back into the human.
Where do adults live?
intermediate: fleas/flea larvae ; reservoir: dogs/cats
infective stage: cysticercoids in fleas
humans ingest infected fleas
scolex attaches to small intestine & lives there & releases proglottids