intro and recap / guest lecture/ and circular economy lecture
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Menu of the day
The Ocean as one economic entity
• An introduction to circular economy and scenarios
• Looking at the power of consumption
• Poster skills
Outcomes of Friday
Global supply chains and related sustainability issue are wicked problems
- Stakeholder power imbalances, local circumstances, and negotiations exclude easy solutions
- Who is ethical responsible for which solutions/contributions
- Is a global company obliged to provide education?
- Still Cocoa is a rather concentrated market (few stakeholders involved in the connecting parts of the supply chains)
few players, those big companies control whole market
- The six biggest companies control ~60% of the market
-Value capture: brand manufacturers 40%, retailers 35%, farmers 3-7% (16% in the 1980ties)
-many parts not transparent
Multiple dimensions involved

guest lecture
sharing one ocean
the ocean covers 70% of our planet
most is salt water
history
often seen as a barrier
HMS challenger expedition : started mapping the ocean depth
there was also a exploitation of the ocean with whale hunting (60s and 70s peak)
the ocean was deemed limitless (anything from dumping, exploitation, to atomic bomb testing)
1910-1997: jacques cousteau: public image on the importance of the ocean
greenpeace
1970s
marine protected areas
the ocean os heterogenic though
fish usually stay around the same place
so you protect static and mobile ones
primary productivity
low nutrients even tho its warm
big productivity is where conveyer belts hit land masses
anything below 100 meters is the europhtic zone does not go through photosynthesis
biomass is captured through thermaclyne but some triggles down to the deep sea
open ocean and coastal water —> color changes because light penetrates at different levels
tropic levels in the sea and on land
aquatic animals have metabolic advantages over terrestrial animals
cold blooded
do not need to fight gravity
do not need the same bone structure
distribution of biomass
plants are the majority on ground
animal biomass
arthropods and in the the ocean its fish
the unnatural history of the sea
the anthropocene ocean
capture has stayed the same but aquaculture HAS increased
example: global fisheries
effective effort has increased and ghg increased - we burn more fuel to catch the same
large pelagic fish has been replaced by small pelagic fish
tragedy of the commons
traditional perspective
resources users are norm free maximizers of immediate gains who will not coop to overcome the commons of the dilemmas they face
designing tules to change incentives of participants is a relatively simple task
often requires central direction
common pool resources management
ex: resulted in us eating fish by moving down the chain
we have change the growth and maturity of fish (cod has becoming smaller because we drive the natural selection)
the cod collapse of the grand banks:
brought back the same amount of fish but only bcuz they had better tech
resilience
mobilization (accessible carbon nutrients and energy) —→ conservation ((climax, consolation, k strategy)—> exploitation (restrategy, pioneer, opportunist) —> creative destruction (fire, storm, etc)
capital value is destroyed when we change from a steady state to a degraded state
organization and connection decreases
we have a steady state and regime changes
a: low intensity production ecosystem —> lots of nutrients and fish
b: local high intensity prod ecosystem —> degraded state —> fossil fuels
a) coral reefs
overfishing
eutrophication (lots of algae)
macroalgae
b) kelp forests
sea otters
hunting
sea urchins
c) small pelagic fish
overfishing
zoo plankton
jellyfish
env threats to the ocean
mangroves and segrass removal
reduced albeado
importance of aquatic foods EAT lancet v1.0
vague
blue food assessment is a follow up of it
all the foods in the ocean
very diverse (2500 species)
demand could double by 2050
we need more aquaculture
blue foods are unequally distributed
countries produce and consume less when wealth formal education and voice and accountability are lacking
aquatic foods are less affordable where gender inequality id greater
policies linked to more just food system outcomes focus son
human rights
inclusive decision making processes
identifying and challenging drivers of injustice
conclusion
the ocean is heterogeneous
blue food is important especially in south
blue food can be more sustainable but differ by species and production
ocean is under stress where they shift to new states that are less productive
Circular economy Concepts & Scenarios
Our lecture’s learning objective
1. Describe the concepts of linear and circular economy
2. Understand different frameworks of circular economy
3. Understand basic types and structure of scenario
resources and reserves
resources are finate
What is the Circular Economy?
we can reuse some materials
some goods can be remanufactures, recycles redistribution, and product life extension
ex: broken washing machine
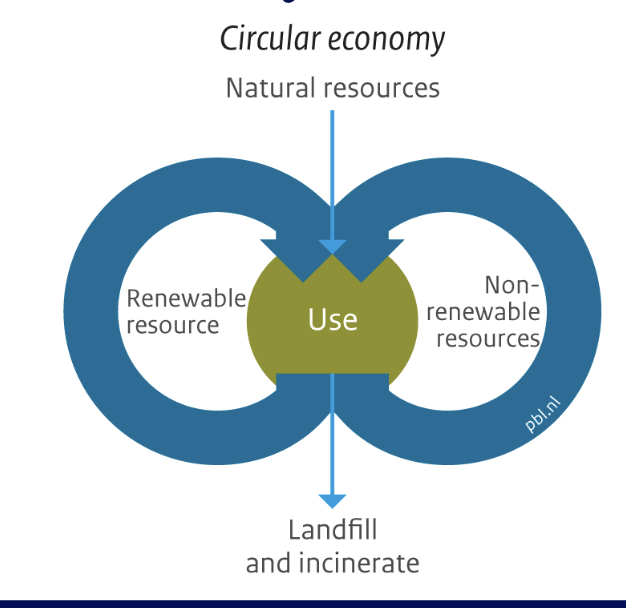
Linear economy
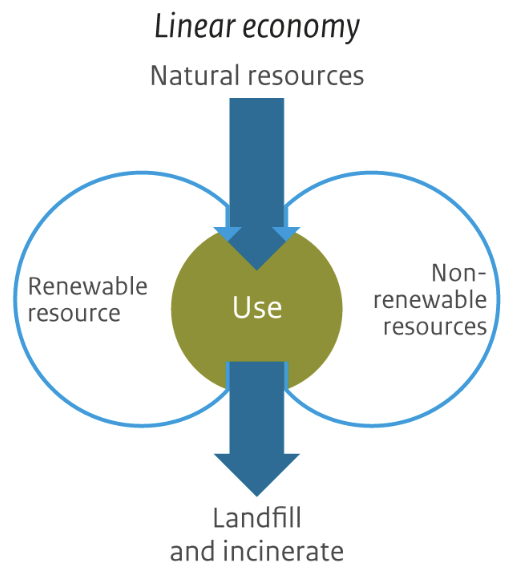
extraction—> production—> consumers —> end of life
take make use dispose
outcomes: waste dumps and incineration dumps
Framework: R strategies
Rs:
- Refuse:
make product redundant
- Reduce:
increase efficiency in
production/use
- Reuse:
use product again
- Repair:
fix broken components
- Refurbish:
fix & “update” old products
- Remanufacture:
use old parts in new products
- Repurpose:
reuse in different function
- Recycle:
material recovery
- Reduce by design:
design products to be circular
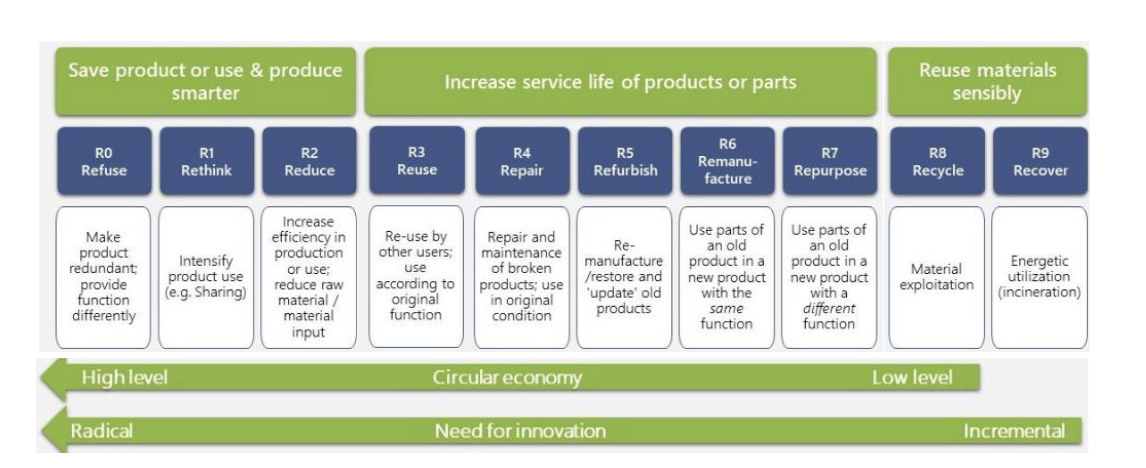
changing vs fixing the system
Discussions
Do you think all R’s are equally important?
How do producers and consumers share responsibility in a circular economy
consumers: decisions with buying (refuse) & recycle
urban mine: resources stored in infrastructure that can be reused
Another Framework – Intended circularity
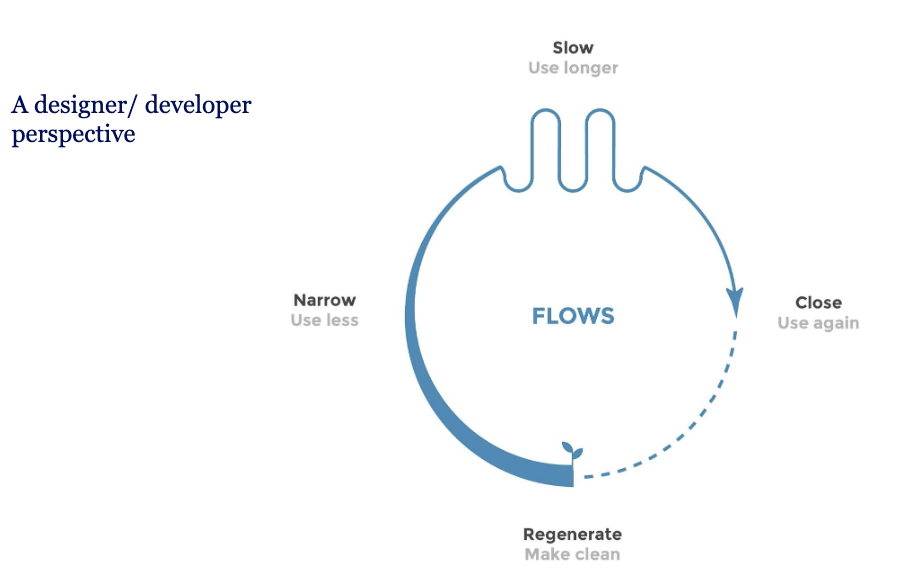
example:
better software to extend cellphone lifespan —> reuse
cloud computing —> rethink or refuse
swap feats: higher utility —> you can repair bikes
Circular economy is only a mean to an end
the big challenges are planetary boundaries
what are scenarios?
A scenario is a description of how the future may
develop, based on a coherent and internally consistent
set of assumptions, about key drivers including
demography, economic processes, technological
innovation, governance, lifestyles, and relationships
among these driving forces. (IPCC, 2021
Features
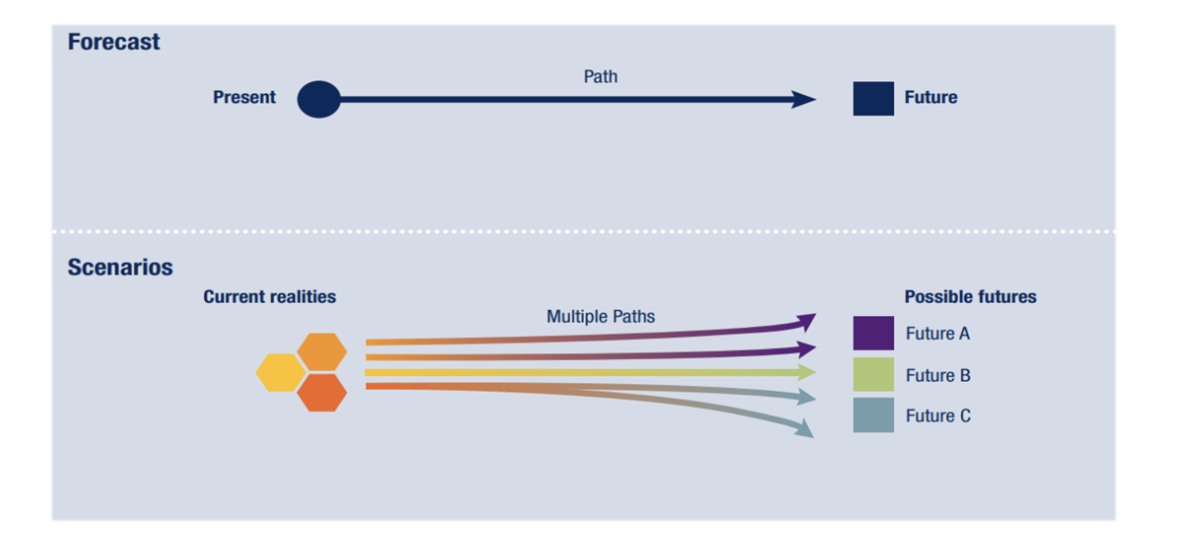
Scenarios are a path, not a simple static snapshot. They
are not a forecast, not a prediction
Types of futures
• Possible – “might” happen (future knowledge)
• Possible – The widest range of scenarios, including all
possibilities
• Plausible – “could” happen (current knowledge)
Plausible – Possibilities that could happen given the bounds of uncertainty
• Probable – “likely to” happen (current trends)
• Probable – The vision we have for possibilities we want to see come true
• Preferred – “want to” happen (value judgement)
• Preferred – The vision we have for possibilities we want to see come true
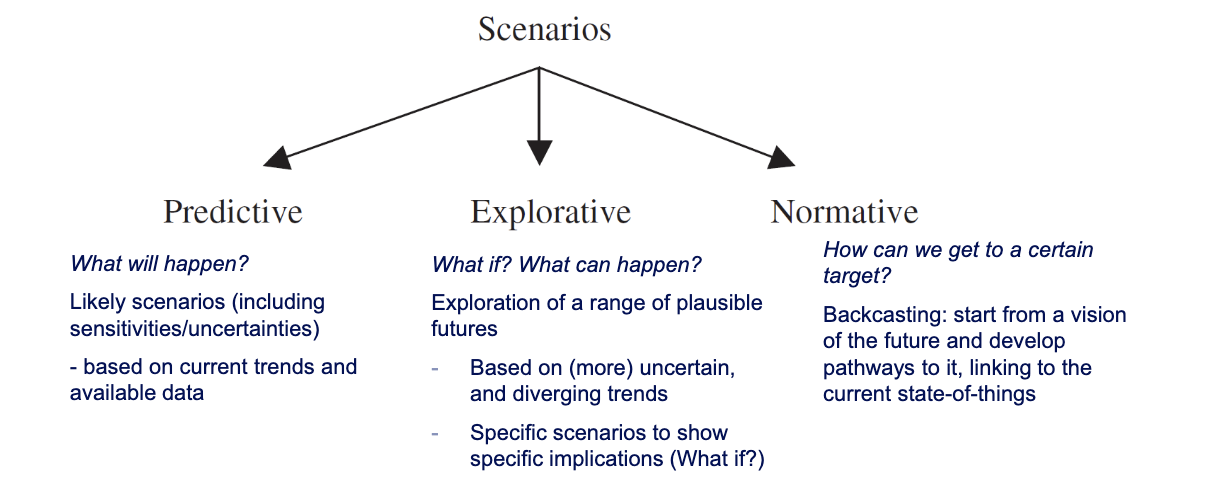
Scenario types
Scenario’s structure
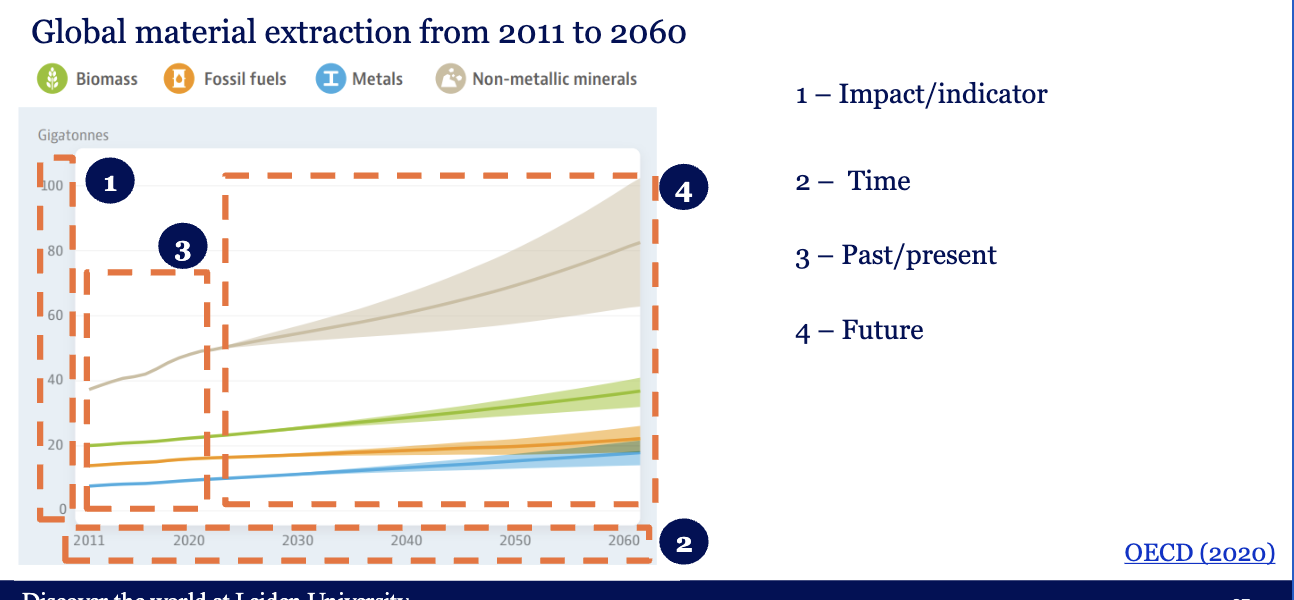
future is further based on indicators
Circular Economy Scenarios
“Consistent and coherent descriptions of possible future developments if circular economy strategies were implemented”
Considerations for Circular Economy Scenarios
The aim is to explore, not to predict (what-if scenarios)
• Assumptions are key for reliable scenarios
- Garbage in = garbage out
- Assumptions cover different areas of influence (technological, economic, political, social,..)
• Supply/demand balance
Simple circular economy scenario
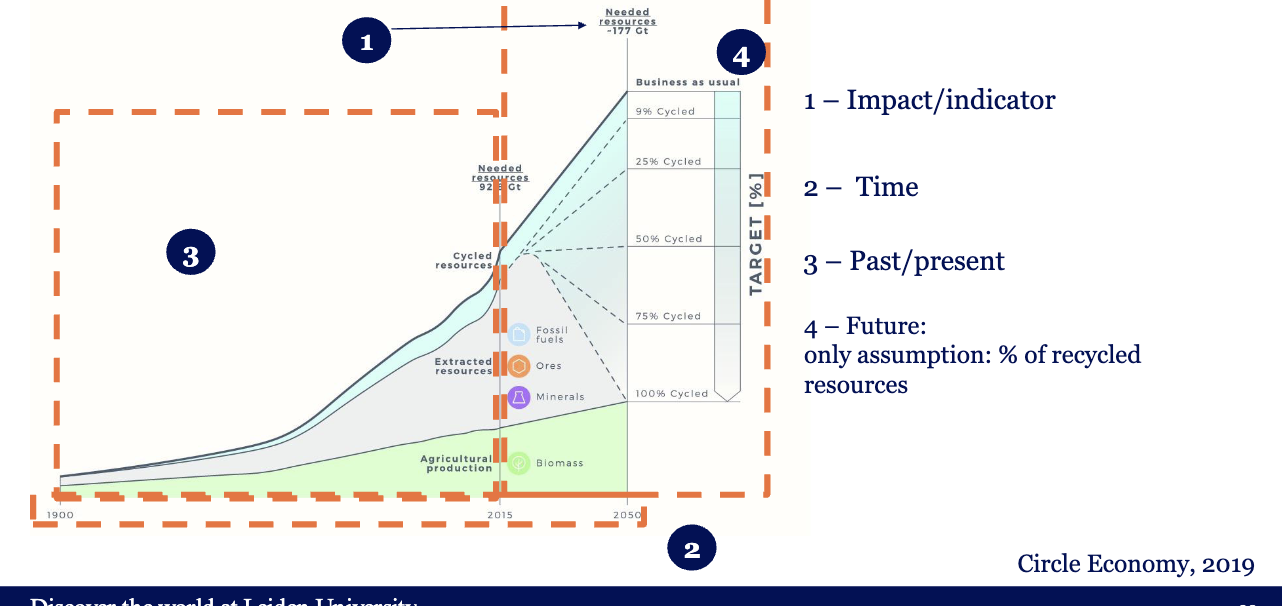
we reuse the most steel
Create your own scenario
What would be the future global material extraction for 2030 in a
business-as-usual scenario?
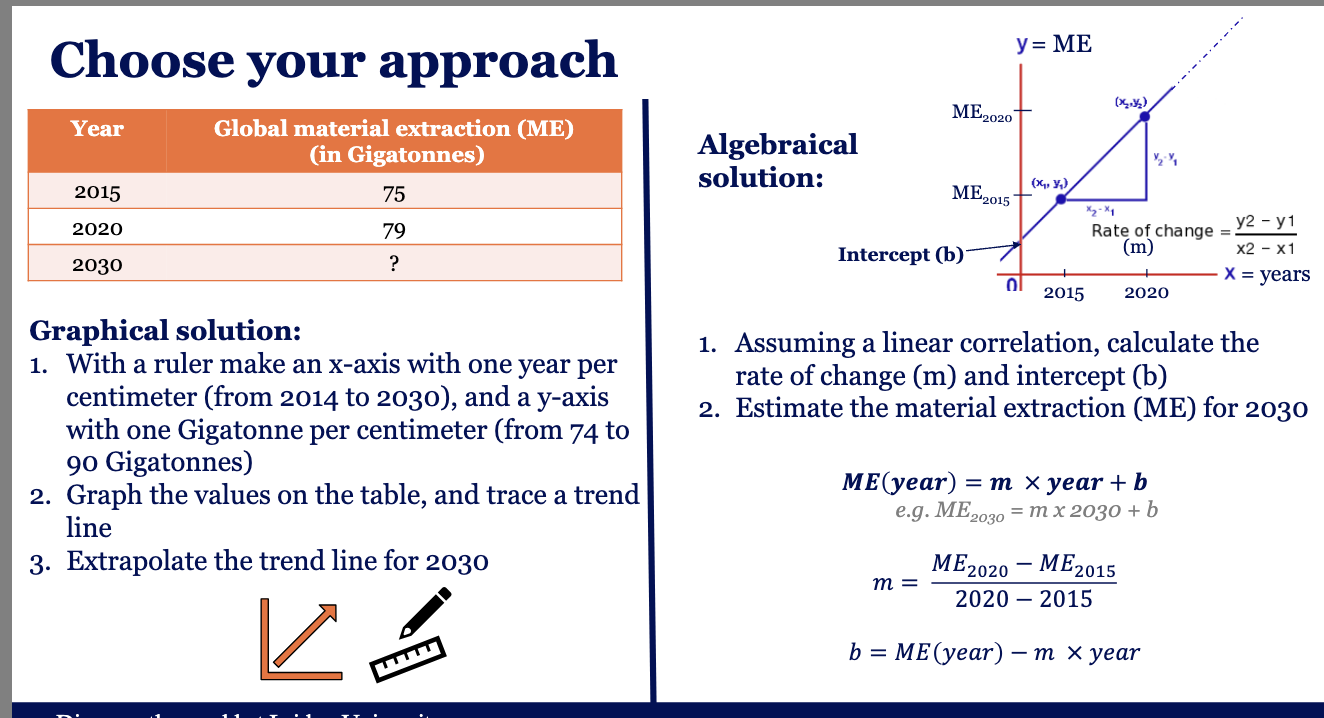
these are prob not linear
Discussion
Do you think a linear trend is suitable for projecting the future global material extraction?
what type of materials are being extracted?
How can circular economy measures influence global material extraction?
circular economy can increase material extraction to set it up
Revisit
• Linear vs. circular economy
• Frameworks for circular economy (R strategies, Slow-narrow-close regenerate)
• Basic structure of scenario