MCB 450- Fall 2022 Form A
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What property does a carbonyl have to make it a good target for a nucleophilic attack?
a) A dipole with a partial positive charge on the oxygen and a partial negative charge on the carbon
b) A dipole with a partial positive charge on the carbon and a partial negative charge on the oxygen
c) A quadrupole with a formal positive charge on the carbon
d) The lack of resonance with the neighboring nitrogen of an amide
e) The resonance in a thioester bond
b) A dipole with a partial positive charge on the carbon and a partial negative charge on the oxygen
Which is true about the effect of an enzyme on the activation of a reaction?
a) Increases the transition state so less energy is required to complete the reaction
b) Lowers the transition state so more energy is required to complete the reaction
c) Lowers the transition state so less energy is required to complete the reaction
d) Increases the transition state so more energy is required to complete the reaction
e) Increases the time
c) Lowers the transition state so less energy is required to complete the reaction
The binding pockets of enzymes present amino acid side chains to one another to close the pocket and promote enzymatic activity. Which of the following amino acid interactions is NOT favorable?
a) Lysine and Glutamate
b) Valine and Leucine
c) Arginine and Lysine
d) Serine and Glutamate
e) Phenylalanine and Tryptophan
c) Arginine and Lysine
The binding energy of an Enzyme – Substrate interaction is the sum of which of the following?
a) Strong bonds such as H-bonds, hydrophobic and ionic interactions
b) Strong covalent bonds such as disulfide bonds
c) Lock and key binding
d) Electrostatic van der Waals interactions
e) Weak interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic and hydrophobic interactions
e) Weak interactions such as hydrogen bonds, ionic and hydrophobic interactions
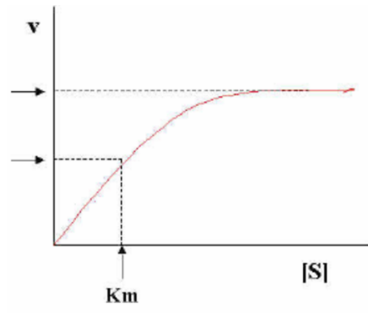
The graph below shows the formation of product versus time in the presence of an enzyme. What does the Km represent?
a) The Km is 1⁄2 of the Vmax and represents the binding affinity of the substrate-enzyme interaction
b) It is the maximum rate of the reaction
c) The entropy of the reaction
d) The reaction has reached equilibrium
e) The DG of the reaction is positive
a) The Km is 1⁄2 of the Vmax and represents the binding affinity of the substrate-enzyme interaction
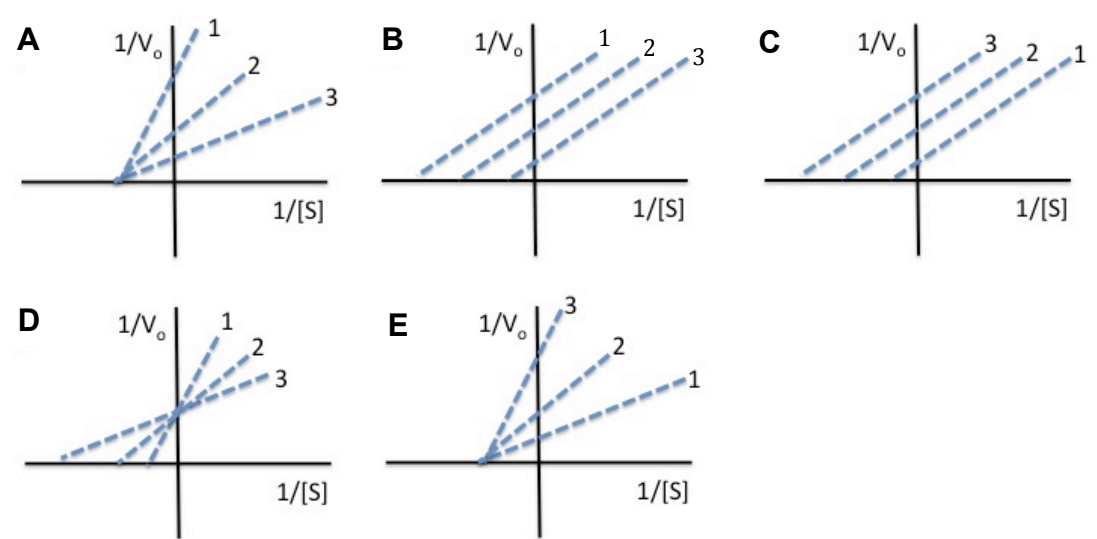
For an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, double-reciprocal plots were determined for three concentrations of a non-competitive inhibitor. Line one represents the highest inhibitor concentration, whereas line three represents the lowest inhibitor concentration. Which of the following sets of curves would you expect to be generated?
Answer A
Aspirin is an irreversible inhibitor. How does it inhibit COX?
a. Aspirin reacts with a Serine in the catalytic pocket of COX to form a covalent bond and inhibit enzyme activity
b. Aspirin electrostatically interacts with the key Serine in COX to block activity
c. Aspirin accumulates in the hydrophobic binding pocket of COX to block substrate access
d. Aspirin mimics the natural substrate and competes for binding COX
e. Aspirin binds the COX substrate to inhibit activity
a. Aspirin reacts with a Serine in the catalytic pocket of COX to form a covalent bond and inhibit enzyme activity
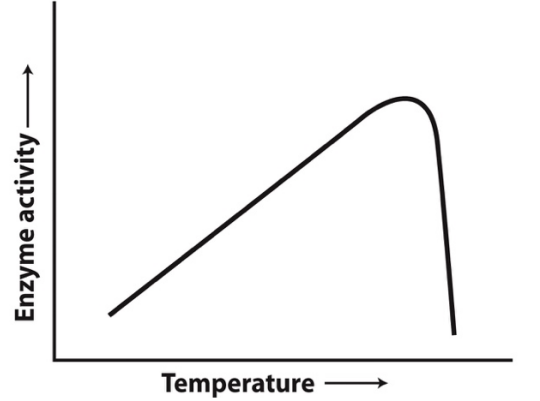
The graph below shows the activity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of temperature. The likeliest reason for the rapid decrease in enzyme activity at higher temperatures is that:
a) a protonated amino acid side chain critical for the enzyme’s activity is rapidly deprotonated.
b) a deprotonated amino acid side chain critical for the enzyme’s activity is rapidly protonated.
c) the enzyme becomes denatured and loses the three-dimensional structure critical for activity.
d) the random thermal motions that result in enzyme-substrate interactions stop.
e) The reaction is endergonic, and all the reactants have been converted to products.
c) the enzyme becomes denatured and loses the three-dimensional structure critical for activity.
Which of the following statements about integral membrane proteins is FALSE?
a) They sometimes consist of beta-sheets that curl up to form a hollow cylinder that serves as a pore in the membrane.
b) Membrane proteins with one or more transmembrane alpha helix/helices may have functional domains on both sides of the membrane.
c) They can be released from membranes by treatments that break hydrogen bonds or interfere with electrostatic interactions.
d) They can be glycosylated.
e) Formation of membrane-spanning alpha helices is favored when the amino acid chain is surrounded by membrane fatty acyl chains and there are no water molecules with which peptide groups can form hydrogen bonds.
c) They can be released from membranes by treatments that break hydrogen bonds or interfere with electrostatic interactions
Which of the following statements about membrane transport is true?
a) Membrane transport proteins make many strong, covalent interactions with their polar substrates, and these replace solute-water interactions.
b) There is no energy barrier to the transport of charged or polar solutes across a cell membrane.
c) If a solute crosses a cell membrane by facilitated diffusion or active transport, the transport process can never be saturated.
d) Solutes that cross a cell membrane by facilitated or passive diffusion will move down a concentration gradient.
e) If a solute crosses a cell membrane through an active transport, it will move across the bilayer using the energy of ATP hydrolysis.
d) Solutes that cross a cell membrane by facilitated or passive diffusion will move down a concentration gradient.
Which of the following does NOT affect membrane fluidity?
a) Acyl chain saturation
b) The charge on the hydrophilic head group
c) Cholesterol content
d) Acyl chain length
e) Double bonds in the lipid hydrocarbons
b) The charge on the hydrophilic head group
Which of the following is not an intracellular mediator (second messenger) of hormone action?
a) cAMP
b) Calmodulin
c) Diacylglycerol (DAG)
d) Inositol trisphosphate (IP3)
e) All of the above are intracellular mediators.
e) All of the above are intracellular mediators.
How does heterotrimeric G-protein (HGP) activation lead to calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
a) GTP bound HGP activates phospholipase C (PLC) which cleaves phosphoinositide 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) to release IP3. IP3 binds to its receptor on the ER leading to calcium release.
b) GDP bound HGP activates phospholipase C (PLC) which cleaves phosphoinositide 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) to release IP3. IP3 binds to its receptor on the Golgi leading to calcium release.
c) GTP bound HGP activates protein kinase A (PKA) which cleaves phosphoinositide 3,4,5 bisphosphate (PIP3) to release IP4. IP4 binds to its receptor on the ER leading to calcium release.
d) ATP bound HGP activates protein kinase C (PKC) which cleaves phosphoinositide 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) to release diacylglycerol (DAG) into the cytoplasm. DAG binds to its receptor on the ER leading to calcium release.
e) GTP bound HGP activates phospholipase A (PLA) which cleaves phosphoinositide 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) to release a lysolipid that binds to its receptor on the ER leading to calcium release.
a) GTP bound HGP activates phospholipase C (PLC) which cleaves phosphoinositide 4,5 bisphosphate (PIP2) to release IP3. IP3 binds to its receptor on the ER leading to calcium release.
What feature is shared by the Kinase Receptor Complexes discussed in class?
a) Transautophosphatase activity
b) De-phosphorylation of ligand
c) Conformational changes occur upon ligand binding
d) Biding Ras
e) Phospholipase activation
c) Conformational changes occur upon ligand binding
Gibbs free energy tells you if a reaction is favorable, unfavorable or near equilibrium. Which of the following represents a very favorable reaction?
a) DG = +1 kcal/mol
b) DG = +50 kcal/mol
c) DG = -50 kcal/mol
d) DG = -1 kcal/mol
e) DG > 0 kcal/mol
c) DG = -50 kcal/mol
What is the effect of mutating the Arg finger to an Asp in the ATP binding pocket of an ATPase?
a) The negative charge of the Asp repels the negative charge of the gamma phosphate.
b) The Asp acts a nucleophile instead of a water.
c) The positive charge of the Asp enhances the polarization of the gamma phosphate.
d) The negative charge of the Asp binds to Ca2+.
e) Polarizes the alpha phosphate.
a) The negative charge of the Asp repels the negative charge of the gamma phosphate
The Walker Box residues in the ATP binding pocket of an ATPase organize a Mg2+. What is the
direct effect of Mg2+ on ATP?
a) Nucleophilic attack of the gamma phosphate.
b) Organize a water to make it the electrophile.
c) Neutralizes phosphate negative charges.
d) Polarizes the alpha phosphate.
e) Repels the Arg finger.
c) Neutralizes phosphate negative charges.
A single carbon can exist in different states of reduction/oxidation. Which of the following correctly shows the molecules going from most oxidized to least oxidized?
a) Methanol < CO2 < Methane
b) CO2 > Methanol > Methane
c) Methane > Methanol > CO2
d) CO2 < Methane < Methanol
e) CO2 < Methanol = Methane
b) CO2 > Methanol > Methane
The full reduction of NAD+ results in which of the following?
a) Gain of 2 protons
b) Loss of 2 electrons and 2 protons
c) Loss of 2 electrons
d) Gain of 2 electrons and 2 protons
e) Gain of 2 electrons and 1 proton
e) Gain of 2 electrons and 1 proton
A Thioester bond is favored over an ester bond for nucleophilic attack due to which of the following?
a) The lack of resonance between the carbonyl oxygen and the sulfur atom
b) The facile protonation of the sulfur atom
c) Sulfur is smaller than oxygen
d) The strong resonance between the ketone oxygen and the sulfur atom
e) The nucleophilic potential of the sulfur atom
a) The lack of resonance between the carbonyl oxygen and the sulfur atom
In a “classic” ATPase enzyme pocket the gamma phosphate of ATP is directly released due to ____.
a) depolarization by magnesium
b) nucleophilic attach by activated water (deprotonated water)
c) repulsion by an Arginine finger
d) All of the above
e) None of the above
b) nucleophilic attach by activated water (deprotonated water)
Why is ATP a good phosphate donor?
a) The gamma-phosphate has a -1 charge
b) ATP is less hydrated than ADP
c) Charge repulsion between gamma and beta phosphate
d) A and B
e) B and C
e) B and C
How can the inhibition of phosphofructokinase (PFK1) by ATP lead to the inhibition of hexokinase?
a) Inhibition of PFK1 results in more Fructose 6-phohsphate, which isomerizes with Glucose 6-phosphate. Hexokinase is inhibited by elevated Glucose 6-phosphate.
b) Inhibition of PFK1 results in more Fructose 1,6-bisphohsphate, which directly inhibits Hexokinase.
c) Inactive PFK1 binds to Hexokinase to prevent Glucose 6-phosphate production.
d) Inactive PFK1 leads to the buildup of glycogen, which inhibits Hexokinase function.
e) None of the above.
a) Inhibition of PFK1 results in more Fructose 6-phohsphate, which isomerizes with Glucose 6-phosphate. Hexokinase is inhibited by elevated Glucose 6-phosphate.
In glycolysis the aldolase step converts one Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to the following product(s):
a) 2 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
b) 2 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
c) 1 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and 1 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
d) 1 dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 1 enediolate
e) Fructose 2,6-phospahte
c) 1 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and 1 dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Pyruvate kinase (PK) is regulated in the liver and other tissues. Which of the following is false?
a) ATP allosterically inactivates PK in the liver
b) PK is phosphorylated by PKA in the liver
c) PK is inactivated by ATP in muscle
d) F1,6BP feeds forward to activate PK in muscle
e) Acetyl-CoA feeds back to inhibit PK in muscle
a) ATP allosterically inactivates PK in the liver
all answers accepted
What happens to phosphofructokinase (PFK1) activity in the presence of Fructose 2,6 bisphosphate (F2,6BP)?
a) F2,6BP decreases the affinity of PFK1 for Fructose 6-phosphate.
b) F2,6BP increases the cooperativity of PFK1.
c) F2,6BP decreases the inhibitory effect of ATP on PFK1.
d) F2,6BP increases the inhibitory effect of ATP on PFK1
e) None of the above
c) F2,6BP decreases the inhibitory effect of ATP on PFK1.
ATP is formed in the glycolytic pathway
a) by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase which also leads to the formation of acetyl CoA.
b) from phosphoenolpyruvate and from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
c) from NADH by the process of substrate level phosphorylation.
d) from fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and from glucose 6-phosphate.
e) using the energy present in the thioester bond of acetyl CoA.
b) from phosphoenolpyruvate and from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
In the first step of glycolysis hexokinase phosphorylates Glucose to make Glucose-6-phosphate. How
does the phosphate get transferred to Glucose?
a) Free orthophosphate diffuses into the active enzyme pocket to attack the hydroxyl on carbon 6 (C6-OH) to make Glucose 6-phosphate
b) The C6-OH is deprotonated by the enzyme to create the C6-O- nucleophile that attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP to make Glucose 6-phosphate
c) An activated water cleaves the gamma phosphate from ATP then the orthophosphate attacks the C6-OH to make Glucose 6-phosphate
d) The C6-OH is deprotonated by the enzyme to create the C6-O- electrophile that attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP to make Glucose 6-phosphate
e) The Mg2+ held by the enzyme cleaves the gamma phosphate after which the orthophosphate attacks the C6-OH to make Glucose 6-phosphate
b) The C6-OH is deprotonated by the enzyme to create the C6-O- nucleophile that attacks the gamma phosphate of ATP to make Glucose 6-phosphate
Consider the following step in Phosphoglucose isomerization: What is the direct role of the glutamate?
a) Donates proton to Carbon 1 to close the sugar ring
b) Donates proton to Carbon 2 to produce enol intermediate
c) Deprotonates Carbon 2 hydroxyl to produce an enol intermediate
d) Takes proton from Carbon 2 to produce an enol intermediate
e) Takes proton from Carbon 1 to close the sugar ring
d) Takes proton from Carbon 2 to produce an enol intermediate
The final step in Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate dehydrogenase is presented below. Which is/are true of the reaction?
a) The orthophosphate attacks the carbonyl due to the negative charged dipole carbon.
b) Upon attack the carbonyl oxygen forms an oxyanion (single bond negatively charged oxygen)
that is stabilized by the protonated base nearby
c) A glycine can act as a potent nucleophilic base (B) in this step of the reaction
d) Upon attack the carbonyl oxygen forms an oxyanion that collapses to sever them thioester bond
e) All of the above
d) Upon attack the carbonyl oxygen forms an oxyanion that collapses to sever them thioester bond
Which is the INCORRECT statement about the regulation of glycogen synthesis and degradation?
a) Glucose 6-phosphate allosterically activates glycogen synthase
b) ATP allosterically inhibits glycogen phosphorylase
c) Glucagon leads to the phosphorylation of both, glycogen synthase and glycogen
phosphorylase
d) Phosphorylated glycogen synthase is active
e) Protein phosphatase 1 can deactivate glycogen phosphorylase by removing phosphate
groups
d) Phosphorylated glycogen synthase is active
What characteristics are found in glycogen and its synthesis/breakdown?
a) The primary linkages between glucose molecules are a-1,4 glycosidic bonds
b) Branch points in glycogen are a-1,6 glycosidic bonds
c) Glycogen breakdown releases Glucose-1-phosphate
d) Released Glucose-1-phosphate is converted to Glucose-6-phosphate through
phosphoglucomutase activity
e) All of the above
e) All of the above
What is the role of Glycogenin?
a) Cleaves alpha-1-4 glycosidic bonds
b) Cleaves alpha-1-6 glycosidic bonds
c) Makes a primer (short glycogen chain) for glycogen extension by glycogen synthase
d) Activates Glucose-1-phosphate
e) Converts Glucose-1-phosphate to Glucose-6-phosphate
c) Makes a primer (short glycogen chain) for glycogen extension by glycogen synthase
Which statement is INCORRECT about Insulin?
a) Insulin is a polypeptide hormone.
b) Insulin is secreted in response to high blood glucose.
c) Insulin promotes synthesis of glycogen.
d) Insulin receptors in target tissues act through c-AMP to promote protein phosphorylation.
e) Insulin binds to a tyrosine kinase receptor.
d) Insulin receptors in target tissues act through c-AMP to promote protein phosphorylation.
In McArdle Disease the glycogen phosphorylase enzyme is defective in muscle. Which of the
following is true?
a) No Glucose 1-P is generated in muscle cells and prevents glucose 6-P from being used as an energy source.
b) Glucose 6-P accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells and prevents glucose from entering the blood stream.
c) Glycogen accumulates in the endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells and prevents glucose from being used as an energy source.
d) Glucose 1-P is accumulated in muscle cells because it cannot be converted to Glucose 6-P preventing its use as an energy source.
e) Glucose 1-P is accumulated in muscle cells because it cannot be converted to Glucose 6-P preventing its release into the blood stream.
a) No Glucose 1-P is generated in muscle cells and prevents glucose 6-P from being used as an energy source.
What is the effect of “Limit dextrin”?
a) A physical barrier that blocks Glycogen phosphorylase from reaching alpha-1-6 branch points
b) The number of dextrins that amylase can cleave at once
c) Helps Glycogen phosphorylase find alpha-1-6 branch points
d) Inhibits protein kinase A phosphorylation of phosphorylase kinase
e) It is the brown color of toasted bread
a) A physical barrier that blocks Glycogen phosphorylase from reaching alpha-1-6 branch points
What is the purpose of rotating glucose in the phosphoglucomutase reaction of glycogen synthesis?
a) It allows for the conversion between glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phospahte.
b) It allows for the attack of UTP by glucose 1-phosphate to make UDP-glucose
c) It permits the exchange between glycogenin and glycogen phosphorylase
d) It facilitates the branching of glycogen
e) There is no rotation of glucose
a) It allows for the conversion between glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phospahte.
Which kinase inactivates glycogen synthase during glycogen breakdown?
a) Protein kinase C
b) Calmodulin dependent kinase
c) Phosphorylase kinase
d) B and C
e) A, B, and C
e) A, B, and C
What is the role of glucose 6-phosphatase during glycogen breakdown?
a) Allows free glucose to exit muscles and enter the blood stream
b) Blocks glucose 6-phosphate from exiting the liver
c) Leads to the release of glucose from the liver to enter the blood stream
d) Makes glucose enter the pentose phosphate pathway
e) Permits glucose 6-phosphate to enter glycogen synthesis in the liver
c) Leads to the release of glucose from the liver to enter the blood stream
The primary role of the pentose phosphate pathway is to produce __________.
a) ATP and Fructose 6-phosphate
b) NADH and ATP
c) Sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and Ribulose 1-phosphate
d) NADP+ and Ribose 5-phosphate
e) NADPH and Ribose 5-phosphate
e) NADPH and Ribose 5-phosphate
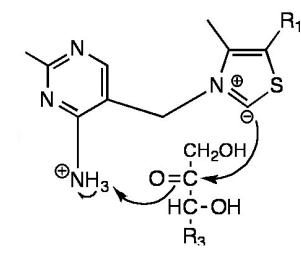
In the first transketolase reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is used as a cofactor. The illustration below shows activated TPP and Xylulose 5-phosphate (X5P). Which of the following is occurring?
a) This reaction occurs in the transaldolase reaction and not the transketolase reaction.
b) The Ylid form of TPP is neutralized by X5P.
c) The TPP carbanion attacks the C2 carbonyl of X5P forming a covalent bond with the substrate.
d) X5P deprotonates the TPP pyrimidine ring amine group and transfers the proton to the TPP carbanion.
e) TPP and X5P interact through hydrogen bonding.
c) The TPP carbanion attacks the C2 carbonyl of X5P forming a covalent bond with the substrate.
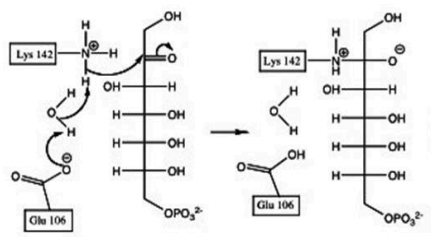
What is the result of the first step of the transaldolase reaction?
a) Deprotonated water (-OH) deprotonates Lys142
b) Formation of intermediate oxyanion
c) Covalent bond to enzyme Lys142
d) Protonation of Glu106
e) All of the above
e) All of the above
In the pentose phosphate pathway, each Glucose 6-Phosphate (G6P) dehydrogenase monomer has two binding sites for NADP+. What are the roles for each NADP+?
a) One is for catalysis and the second is for enzyme dissociation
b) Both are for receiving hydrides from G6P
c) One is for receiving a hydride and the second is for stabilizing enzyme dimerization
d) Both are for oxidizing 6-phosphogluconolactone
e) None of the above
c) One is for receiving a hydride and the second is for stabilizing enzyme dimerization
In the phosphopentose isomerase reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway, Ribulose 5-phosphate
is converted to Ribose 5-phosphate. What happens to the carbonyl?
a) The carbonyl is moved from the carbon-1 position of Ribulose to carbon-2 of Ribose 5-P
b) The carbonyl is moved from the carbon-2 position of Ribulose to carbon-1 of Ribose 5-P
c) The hydroxyl is moved from the carbon-2 position of Ribulose to carbon-1 of Ribose 5-P
d) The hydroxyl is moved from the carbon-1 position of Ribulose to the carbon-2 of Ribose
e) None of the above
b) The carbonyl is moved from the carbon-2 position of Ribulose to carbon-1 of Ribose 5-P
In the Galactose isomerization reaction, what would happen if the 4-ketose intermediate could not rotate?
a) The NAD+ would oxidize the C6-OH
b) The NADH would return the hydride to the Carbon 4 carbonyl and remake galactose
c) The C4-ketone would be reduced to make glucose
d) The NADH would rotate around the galactose instead to make glucose
e) Galactose would react with glucose to reform lactose
b) The NADH would return the hydride to the Carbon 4 carbonyl and remake galactose
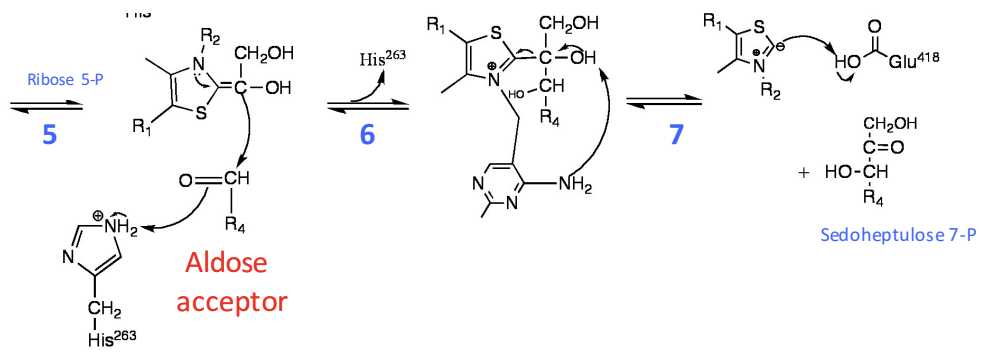
In the transketolase reaction, what leads to the severing of sedoheptulose from TPP?
a) The transaldolase, and not the transketolase reaction, is bound to sedoheptulose
b) The pyrimidine ring of TPP deprotonates the C2-hydroxyl
c) A Glutamate deprotonates the C2-hydroxyl
d) The YLID resonance severs the bond
e) The pyrimidine ring of TPP deprotonates the C3 hydroxyl
b) The pyrimidine ring of TPP deprotonates the C2-hydroxyl
NADPH is used to kill microorganisms that are phagocytosed by white blood cells such as
macrophages and neutrophils. Which of the following is not true?
a) NADPH is used to reduce oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to make glutathione (GSH), which is used in the conversion of H2O2 to water by glutathione peroxidase
b) NADPH oxidase converts O2 to superoxide as part of the respiratory burst
c) NADPH is used by iNOS to generate NO as part of the respiratory burst
d) The NADPH-dependent respiratory burst leads to the formation of HOCl and hydroxyl radicals
that cause cellular damage to the microorganism
e) B and C
a) NADPH is used to reduce oxidized glutathione (GSSG) to make glutathione (GSH), which is used in the conversion of H2O2 to water by glutathione peroxidase
48. In the pentose phosphate pathway, what normally inhibits Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
a) Elevated Glucose 6-phosphate
b) Elevated NADH
c) Elevated NADPH
d) Elevated NADP+
e) Elevated NAD+
c) Elevated NADPH
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in mature erythrocytes can lead to hemolytic anemia. The reason for cellular lysis of erythrocytes in this situation is due to the
a) decreased rate of glycolysis in the erythrocytes.
b) Increased NADPH levels which slows down all reductive biosynthetic pathways in the erythrocytes.
c) increased levels of NADPH leading to low levels of oxidized glutathione as an antioxidant to protect red cells from oxidative damage.
d) Depletion of NADPH leads to low levels of reduced glutathione, which leads to increased reactive oxygen species, the production of Heinz bodies and membrane damage.
e) Enhanced ability to synthesize ribose-5-phosphate through the oxidative phase of the hexose monophosphate shunt.
d) Depletion of NADPH leads to low levels of reduced glutathione, which leads to increased reactive oxygen species, the production of Heinz bodies and membrane damage.
What is true about Hereditary Fructose Intolerance?
a) ATP levels fall
b) Uric acid crystals form
c) Fructose 1-phosphate accumulates
d) Production of glyceraldehyde is blocked
e) All of the above
e) All of the above